Research Progress on Hepatitis E Virus Culture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Virological Characteristics of HEV
2.1. HEV Virion Morphology
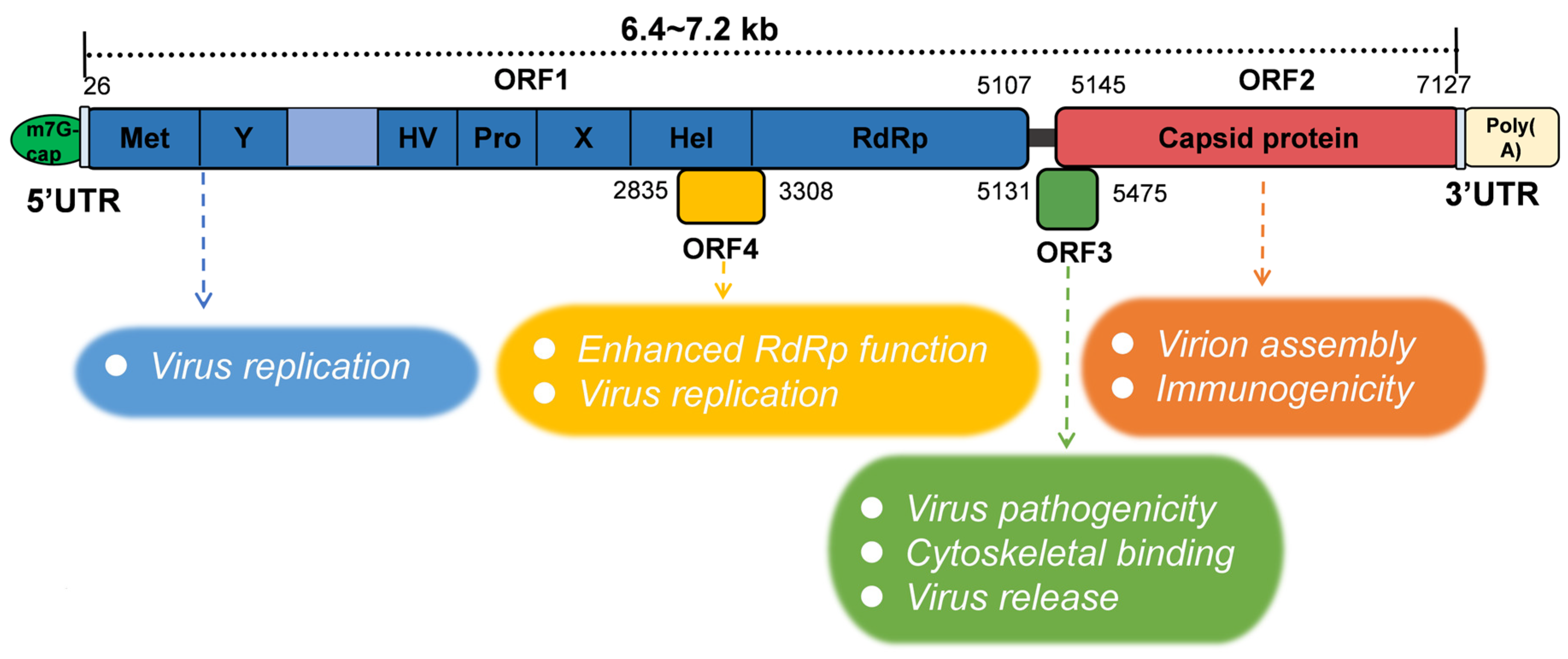
2.2. Genomic Structure and Viral Markers of HEV
2.3. Hosts and Transmission Routes of HEV
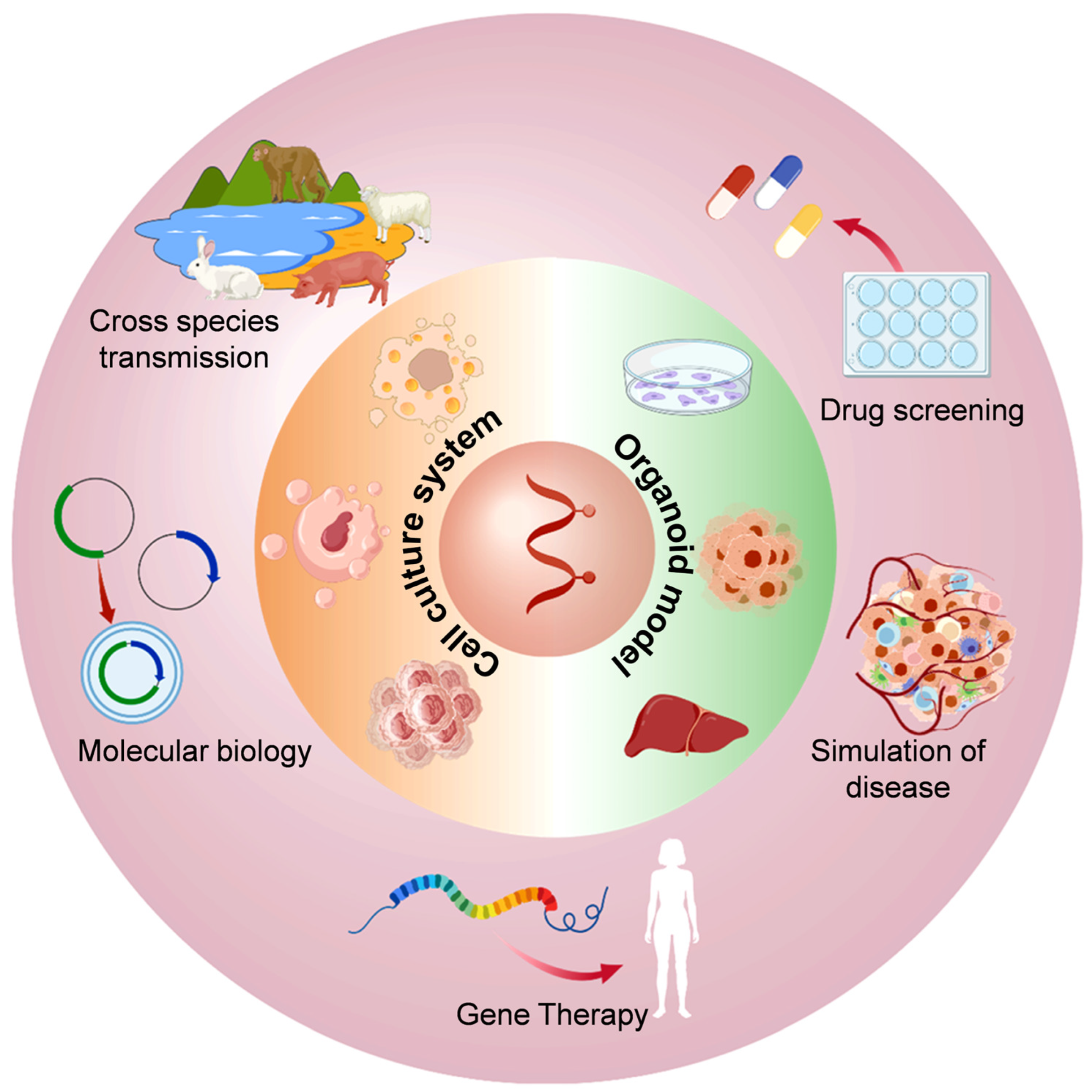
3. In Vitro Culture Models of HEV Infection
3.1. HEV Cell Culture Models
3.1.1. Cell Culture Systems for Natural Virus Isolation
3.1.2. HEV Infectious Clonal Culture System
| HEV Genera | HEV Genotype | Strain | Year of Publication | Susceptible Cell Lines | cDNA Cloned or Not | Mode of Transformation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | HEV-1 | 87A | 1995 |
| No | [97] | |
| A | HEV-1 | 87A | 1999 |
| No | [98] | |
| A | HEV-1 | Sar55 | 2003 |
| No | [86] | |
| A | HEV-1 | Sar55 | 2010 |
| No | [99] | |
| A | HEV-1 | Sar55 | 2018 |
| No | [100] | |
| A | HEV-1 | Sar55/S17 | 2016 |
| No | Introduced the S17 fragment from Kernow-C1/P6 | [68,101] |
| A | HEV-1 | JE04-1601S | 2023 |
| pJE04-1601S_p12 | [95] | |
| A | HEV-2 | MEX-14 | 2018 |
| No | [102] | |
| A | HEV-3 | JE03-1760F | 2007 |
| pJE03-1760F/wt | [93] | |
| A | HEV-3 | Kernow-C1 | 2011 |
| No | F2 subclone was isolated from the HepG2/C3A cell line and used in a polarized monolayer culture to achieve highly efficient HEV culture | [58,71] |
| A | HEV-3 | Kernow-C1 | 2016 |
| Kernow-C1-p6 | All tested cell lines supported the replication of HEV RNA and demonstrated HEV entry into the oligodendrocyte line M03.13 | [68] |
| A | HEV-3 | Kernow-C1 | 2021 |
| No | Remained infectious to pigs after 6 generations | [22] |
| A | HEV-3 | SwJB-P5 SwJB-E10 SwJB-M8 | 2014 |
| No | [102] | |
| A | HEV-3 | SAAS-JDY5 | 2014 |
| pGEM4z-SAAS-JDY5 | [87] | |
| A | HEV-3ra | LR | 2023 |
| LR_Y1320H LR_K1383N LR_K1634G LR_K1634R | [84] | |
| A | HEV-3ra | ME-2016-rab52 | 2022 |
| rab52LucA26 rab81LucA26 | [103] | |
| A | HEV-3ra | rbIM223LR | 2021 |
| pUC57-T7RHEV-LR | [104] | |
| A | HEV-4 | HE-JF5/15F | 2009 |
| HE-JF5/15F_p6 | [94] | |
| A | HEV-4 | HB-3 | 2011 |
| No | [54] | |
| A | HEV-4 | TW6196E | 2012 |
| pHEV-4TW | [74] | |
| A | HEV-4 | KM01 | 2024 |
| No | [20] | |
| A | HEV-1 + HEV-4 chimeric virus | IND-SW-00-01 | 2016 |
| pSK-HEV2 | All 12 chimeric vectors could replicate in S10-3 cells, but only 2 could replicate in PK15 | [96] |
| A | HEV-5 | JBOAR135-Shiz09 | 2018 |
| G5 HEV | [75,105,106] | |
| A | HEV-6 | wbJHG_23 | 2024 |
| pwbJHG_23_P1 pwbJHG_23_P1-GAA | [59] | |
| A | HEV-7 | DcHEV-180c | 2021 |
| No | [75,106] | |
| A | HEV-7 | DcHEV-180c | 2016 |
| pUC57-T7DcHEV | [107] | |
| A | HEV-8 | M2 | 2021 |
| pVL1393-G8n111ORF2 | [75,106,108] | |
| B | HEV_Avian | avian HEV-prototype | 2005 |
| pT7-aHEV-5 pTG-aHEV-10 pT7G-aHEV-6 | [87] | |
| B | HEV_Avian | avian HEV-VA | 2011 |
| pT7-aHEV-K | [89] | |
| B | HEV_Avian | HH-F9 | 2015 |
| pT11-aHEV-K | [88] | |
| C | HEV-C1 | R63 | 2015 |
| pUC19-R63 | [91] | |
| C | HEV-C1 | LA-B350 | 2016 |
| pLA-B350 pLA-B350/luc | [92] | |
| C | HEV-C1 | ratELOMB-131 | 2018 |
| pUC-ratELOMB-131L_wt | [47] |
3.2. In Vitro Organoid HEV Infection Model
3.2.1. Current Status of HEV Organoid Infection Models
3.2.2. Novel Organoid Models for HEV Infection
4. Application of In Vitro Cell Culture Models of HEV Infection
4.1. Molecular Biology Research on HEV
4.2. HEV Disease Simulation Studies
4.3. Research on the Cross-Species Transmission of HEV
4.4. HEV Gene Therapy Research
4.5. Anti-HEV Drug Screening
5. Advantages, Disadvantages, and Prospects of In Vitro Culture Models of HEV Infection
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Su, J.; Ma, Z.; Bramer, W.M.; Cao, W.; de Man, R.A.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. The global epidemiology of hepatitis E virus infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1516–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Harrison, T.J.; Huang, W.; Zhao, C.; Kong, W.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y. Hepatitis E Virus Produced from Cell Culture Has a Lipid Envelope. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, E.M. Zoonotic Hepatitis E Virus: An Ignored Risk for Public Health. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, M.A.; Drexler, J.F.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; de Souza, W.M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Smith, D.B. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Izopet, J.; Nicot, F.; Simmonds, P.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; et al. Update: Proposed reference sequences for subtypes of hepatitis E virus (species Orthohepevirus A). J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abravanel, F.; Lhomme, S. Hecolin vaccine: Long-term efficacy against HEV for a three-dose regimen. Lancet 2024, 403, 782–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; de Man, R.A.; Kamar, N.; Pan, Q. Chronic hepatitis E: Advancing research and patient care. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Mallet, V.; Izopet, J. Ribavirin for chronic hepatitis E virus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2447–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Izopet, J.; Tripon, S.; Bismuth, M.; Hillaire, S.; Dumortier, J.; Radenne, S.; Coilly, A.; Garrigue, V.; D’Alteroche, L.; et al. Ribavirin for chronic hepatitis E virus infection in transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.; Ratho, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Saxena, S.K.; Bora, I.; Thakur, P. Viral Hepatitis E and Chronicity: A Growing Public Health Concern. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 577339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, I.M.; Karam-Allah Ramadan, H.; Hafez, M.H.R.; Elkhawaga, A.A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) open reading frame 2: Role in pathogenesis and diagnosis in HEV infections. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Halbur, P.G.; Lehman, J.R.; Webb, D.M.; Tsareva, T.S.; Haynes, J.S.; Thacker, B.J.; Emerson, S.U. A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9860–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Nagashima, S.; Jirintai, S.; Kawakami, M.; Sonoda, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Shigemoto, K.; Ashida, K.; et al. Molecular characterization of a novel hepatitis E virus (HEV) strain obtained from a wild boar in Japan that is highly divergent from the previously recognized HEV strains. Virus Res. 2014, 180, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ma, Z.; Harrison, T.J.; Feng, R.; Zhang, C.; Qiao, Z.; Fan, J.; Ma, H.; Li, M.; Song, A.; et al. A novel genotype of hepatitis E virus prevalent among farmed rabbits in China. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Teng, J.L.L.; Cao, K.-Y.; Wernery, U.; Schountz, T.; Chiu, T.H.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Wong, P.-C.; Wong, E.Y.M.; et al. New Hepatitis E Virus Genotype in Bactrian Camels, Xinjiang, China, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2219–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.H.; Tan, B.H.; Teo, E.C.; Lim, S.G.; Dan, Y.Y.; Wee, A.; Aw, P.P.; Zhu, Y.; Hibberd, M.L.; Tan, C.K.; et al. Chronic Infection With Camelid Hepatitis E Virus in a Liver Transplant Recipient Who Regularly Consumes Camel Meat and Milk. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 355–357.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, A.K.; Joseph, M.; Wong, E.Y.; Tang, Y.; Sivakumar, S.; Xie, J.; Bai, R.; et al. New hepatitis E virus genotype in camels, the Middle East. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Kataoka, M.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Kishida, N.; Shirakura, M.; Imai, M.; Asanuma, H.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T.; et al. Characterization of self-assembled virus-like particles of ferret hepatitis E virus generated by recombinant baculoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tei, S.; Kitajima, N.; Takahashi, K.; Mishiro, S. Zoonotic transmission of hepatitis E virus from deer to human beings. Lancet 2003, 362, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xia, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, H.; Zhong, G.; Chen, D.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, F. Hepatitis E virus infection upregulates ING5 expression in vitro and in vivo. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2024, 56, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Ferreira, N.; Zhang, X.; Van Dycke, J.; Neyts, J.; Kaptein, S.; Rocha-Pereira, J. Hepatitis E virus replication is facilitated by epithelial cell turnover and targets enteroendocrine cells in human intestinal organoids. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, M.; Hirchaud, E.; Blanchard, Y.; Pavio, N.; Doceul, V. Characterization of a Cell Culture System of Persistent Hepatitis E Virus Infection in the Human HepaRG Hepatic Cell Line. Viruses 2021, 13, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lavrijsen, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Verstegen, M.M.A.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.-C.; et al. Recapitulating hepatitis E virus–host interactions and facilitating antiviral drug discovery in human liver–derived organoids. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabj5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Nishiyama, T.; Primadharsini, P.P.; Okamoto, H. Characterization of the Quasi-Enveloped Hepatitis E Virus Particles Released by the Cellular Exosomal Pathway. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00822-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Ambardekar, C.; Lu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Ou, J.H.J. Distinct Entry Mechanisms for Nonenveloped and Quasi-Enveloped Hepatitis E Viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4232–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balayart, M.S.; Andjaparidze, A.G.; Savinskaya, S.S.; Ketiladze, E.S.; Braginsky, D.M.; Savinov, A.P.; Poleschuk, V.F. Evidence for a Virus in Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis Transmitted via the Fecal-Oral Route. Intervirology 1983, 20, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Hu, F.; Madden, V.; Ping, L.; Jeong, S.H.; Walker, C.; Lanford, R.E.; Lemon, S.M. A pathogenic picornavirus acquires an envelope by hijacking cellular membranes. Nature 2013, 496, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, H.; Hoshino, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Jirintai; Mizuo, H.; Yazaki, Y.; Takagi, T.; Azuma, M.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) strains in serum samples can replicate efficiently in cultured cells despite the coexistence of HEV antibodies: Characterization of HEV virions in blood circulation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, A.W.; Smith, M.M.; Guerra, M.E.; Huang, C.-C.; Bradley, D.W.; Fry, K.E.; Reyes, G.R. Hepatitis E virus (HEV): Molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome. Virology 1991, 185, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabrane-Lazizi, Y.; Meng, X.-J.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Evidence that the Genomic RNA of Hepatitis E Virus Is Capped. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8848–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.; Torian, U.; Nguyen, H.; Emerson, S.U. A Bicistronic Subgenomic mRNA Encodes both the ORF2 and ORF3 Proteins of Hepatitis E Virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5919–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazaki, Y.; Mizuo, H.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Sasaki, N.; Gotanda, Y.; Okamoto, H. Sporadic acute or fulminant hepatitis E in Hokkaido, Japan, may be food-borne, as suggested by the presence of hepatitis E virus in pig liver as food. J. General Virol. 2003, 84, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, S.U.; Zhang, M.; Meng, X.J.; Nguyen, H.; St Claire, M.; Govindarajan, S.; Huang, Y.K.; Purcell, R.H. Recombinant hepatitis E virus genomes infectious for primates: Importance of capping and discovery of a cis-reactive element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15270–15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Purdy, M.A.; Rozanov, M.N.; Reyes, G.R.; Bradley, D.W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: Delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8259–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieulaine, S.; Tubiana, T.; Bressanelli, S. De novo modelling of HEV replication polyprotein: Five-domain breakdown and involvement of flexibility in functional regulation. Virology 2023, 578, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahola, T.; Karlin, D.G. Sequence analysis reveals a conserved extension in the capping enzyme of the alphavirus supergroup, and a homologous domain in nodaviruses. Biol. Direct 2015, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magden, J.; Takeda, N.; Li, T.; Auvinen, P.; Ahola, T.; Miyamura, T.; Merits, A.; Kääriäinen, L. Virus-specific mRNA capping enzyme encoded by hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6249–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpe, Y.A.; Lole, K.S. NTPase and 5′ to 3′ RNA duplex-unwinding activities of the hepatitis E virus helicase domain. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3595–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tian, Y.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y. Characteristics and Functions of HEV Proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1417, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montpellier, C.; Wychowski, C.; Sayed, I.M.; Meunier, J.C.; Saliou, J.M.; Ankavay, M.; Bull, A.; Pillez, A.; Abravanel, F.; Helle, F.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus Lifecycle and Identification of 3 Forms of the ORF2 Capsid Protein. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 211–223.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Ying, D.; Lhomme, S.; Tang, Z.; Walker, C.M.; Xia, N.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Z. Origin, antigenicity, and function of a secreted form of ORF2 in hepatitis E virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardanova, E.S.; Takova, K.H.; Toneva, V.T.; Zahmanova, G.G.; Tsybalova, L.M.; Ravin, N.V. A plant-based transient expression system for the rapid production of highly immunogenic Hepatitis E virus-like particles. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 2441–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ling, R.; Li, H.; Harrison, T.J. The complete sequence of hepatitis E virus genotype 4 reveals an alternative strategy for translation of open reading frames 2 and 3. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.; Nguyen, H.; Kasorndorkbua, C.; Halbur, P.G.; St Claire, M.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. In vitro and in vivo mutational analysis of the 3′-terminal regions of hepatitis e virus genomes and replicons. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafrullah, M.; Ozdener, M.H.; Kumar, R.; Panda, S.K.; Jameel, S. Mutational Analysis of Glycosylation, Membrane Translocation, and Cell Surface Expression of the Hepatitis E Virus ORF2 Protein. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 4074–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.W.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.M.; Ou, S.H.; Huang, G.Y.; He, Z.Q.; Ge, S.X.; Xian, Y.L.; Pang, S.Q.; Ng, M.H.; et al. A bacterially expressed particulate hepatitis E vaccine: Antigenicity, immunogenicity and protectivity on primates. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2893–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanggis; Kobayashi, T.; Takahashi, M.; Jirintai, S.; Nishizawa, T.; Nagashima, S.; Nishiyama, T.; Kunita, S.; Hayama, E.; Tanaka, T.; et al. An analysis of two open reading frames (ORF3 and ORF4) of rat hepatitis E virus genome using its infectious cDNA clones with mutations in ORF3 or ORF4. Virus Res. 2018, 249, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Yamada, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. Monoclonal antibodies raised against the ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus (HEV) can capture HEV particles in culture supernatant and serum but not those in feces. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Shao, Z.; Xiong, X.; Qi, S.; Guan, J.; Wang, M.; Tang, Y.D.; Feng, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Palmitoylation-dependent association with Annexin II directs hepatitis E virus ORF3 sorting into vesicles and quasi-enveloped virions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2418751122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.P.; Anang, S.; Subramani, C.; Madhvi, A.; Bakshi, K.; Srivastava, A.; Shalimar; Nayak, B.; Ct, R.K.; Surjit, M. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induced Synthesis of a Novel Viral Factor Mediates Efficient Replication of Genotype-1 Hepatitis E Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wißing, M.H.; Brüggemann, Y.; Steinmann, E.; Todt, D. Virus–Host Cell Interplay during Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, G.R.; Purdy, M.A.; Kim, J.; Luk, K.-C.; Young, L.M.; Fry, K.E.; Bradley, D.W. Isolation of a cDNA from the Virus Responsible for Enterically Transmitted Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis. Science 1990, 247, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.J.; Halbur, P.G.; Shapiro, M.S.; Govindarajan, S.; Bruna, J.D.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Genetic and experimental evidence for cross-species infection by swine hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9714–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, D.S.; Wu, Y.Q.; He, Q.G.; Chen, H.C.; Liu, Z.F. Both swine and human cells are capable to support the replication of swine hepatitis E virus type 4 in vitro. Virus Res. 2011, 158, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arankalle, V.A.; Goverdhan, M.K.; Banerjee, K. Antibodies against hepatitis E virus in Old World monkeys. J. Viral Hepat. 1994, 1, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Tian, J.; Teng, X.; Liu, T. Vital role of autophagy flux inhibition of placental trophoblast cells in pregnancy disorders induced by HEV infection. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2276336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sabato, L.; Domanico, M.; De Santis, P.; Cecca, D.; Bonella, G.; Mastrandrea, G.; Onorati, R.; Sorbara, L.; Varcasia, B.M.; Franzetti, B.; et al. Longitudinal serological and virological survey of hepatitis E virus in wild boar (Sus scrofa majori, Maremman wild boar) and fallow deer (Dama dama) populations in a protected area of Central Italy. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1511823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Engle, R.E.; Faulk, K.; Dalton, H.R.; Bendall, R.P.; Keane, F.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Cross-species infections of cultured cells by hepatitis E virus and discovery of an infectious virus-host recombinant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Murata, K.; Okamoto, H. The Full-Genome Analysis and Generation of an Infectious cDNA Clone of a Genotype 6 Hepatitis E Virus Variant Obtained from a Japanese Wild Boar: In Vitro Cultivation in Human Cell Lines. Viruses 2024, 16, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Teng, J.L.L.; Chiu, T.H.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Hepatitis E Virus Genotypes and Evolution: Emergence of Camel Hepatitis E Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ling, R.; Erker, J.C.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Desai, S.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Harrison, T.J. A divergent genotype of hepatitis E virus in Chinese patients with acute hepatitis. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80 Pt 1, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Izopet, J.; Pavio, N.; Aggarwal, R.; Labrique, A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Sato, H.; Sato, Y.; Jirintai; Nagashima, S.; Okamoto, H. Analysis of the full-length genome of a hepatitis E virus isolate obtained from a wild boar in Japan that is classifiable into a novel genotype. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Tsatsralt-Od, B.; Nyamdavaa, K.; Dulmaa, N.; Osorjin, B.; Tseren-Ochir, E.O.; Sharav, T.; Bayasgalan, C.; Sukhbaatar, B.; et al. Identification and a full genome analysis of novel camel hepatitis E virus strains obtained from Bactrian camels in Mongolia. Virus Res. 2021, 299, 198355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johne, R.; Heckel, G.; Plenge-Bönig, A.; Kindler, E.; Maresch, C.; Reetz, J.; Schielke, A.; Ulrich, R.G. Novel Hepatitis E Virus Genotype in Norway Rats, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero-Gómez, J.; Rivero-Juarez, A.; Jurado-Tarifa, E.; Jiménez-Martín, D.; Jiménez-Ruiz, E.; Castro-Scholten, S.; Ulrich, R.G.; López-López, P.; Rivero, A.; García-Bocanegra, I. Serological and molecular survey of hepatitis E virus in cats and dogs in Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios-Muñoz, L.; Gonzálvez, M.; Caballero-Gomez, J.; Castro-Scholten, S.; Casares-Jimenez, M.; Agulló-Ros, I.; Corona-Mata, D.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Lopez-Lopez, P.; Fajardo, T.; et al. Detection of Rat Hepatitis E Virus in Pigs, Spain, 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drave, S.A.; Debing, Y.; Walter, S.; Todt, D.; Engelmann, M.; Friesland, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Neyts, J.; Behrendt, P.; Steinmann, E. Extra-hepatic replication and infection of hepatitis E virus in neuronal-derived cells. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, A.W.; White, R.; Reed, E.; Short, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fuerst, T.R.; Lanford, R.E. In vitro propagation and production of hepatitis E virus from in vivo-infected primary macaque hepatocytes. Virology 1996, 215, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kusano, E.; Okamoto, H. Development and evaluation of an efficient cell-culture system for Hepatitis E virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, N.; Marion, O.; Dubois, M.; Allart, S.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Lhomme, S.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Chapuy-Regaud, S. Vectorial Release of Hepatitis E Virus in Polarized Human Hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01207-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capelli, N.; Dubois, M.; Pucelle, M.; Da Silva, I.; Lhomme, S.; Abravanel, F.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Izopet, J. Optimized Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Culture and its Application to Measurements of HEV Infectivity. Viruses 2020, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Qi, Y.; Harrison, T.J.; Luo, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Song, A.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y. Hepatitis E genotype 4 virus from feces of monkeys infected experimentally can be cultured in PLC/PRF/5 cells and upregulate host interferon-inducible genes. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdoba, L.; Feagins, A.R.; Opriessnig, T.; Cossaboom, C.M.; Dryman, B.A.; Huang, Y.W.; Meng, X.J. Rescue of a genotype 4 human hepatitis E virus from cloned cDNA and characterization of intergenotypic chimeric viruses in cultured human liver cells and in pigs. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Muramatsu, M.; Li, T.C. Mongolia Gerbils Are Broadly Susceptible to Hepatitis E Virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Yamakawa, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tatsumi, M.; Razak, M.A.; Uchida, T.; Takeda, N.; Miyamura, T. Expression and self-assembly of empty virus-like particles of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 7207–7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Rong, L.; Rong, D.; Yang, Y.; Hao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, L.; Rao, G.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Development of cell culture infectious clones for hepatitis C virus genotype 1b and transcription analysis of 1b-infected hepatoma cells. Antivir. Res. 2021, 193, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripon, P.; Rumin, S.; Urban, S.; Le Seyec, J.; Glaise, D.; Cannie, I.; Guyomard, C.; Lucas, J.; Trepo, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johne, R.; Reetz, J.; Ulrich, R.G.; Machnowska, P.; Sachsenröder, J.; Nickel, P.; Hofmann, J. An ORF1-rearranged hepatitis E virus derived from a chronically infected patient efficiently replicates in cell culture. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schemmerer, M.; Johne, R.; Erl, M.; Jilg, W.; Wenzel, J.J. Isolation of Subtype 3c, 3e and 3f-Like Hepatitis E Virus Strains Stably Replicating to High Viral Loads in an Optimized Cell Culture System. Viruses 2019, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, J.; Dallner, M.; Nasheri, N. Optimization of the replication of hepatitis E virus genotype 3 in vitro. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 135, lxae137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, X.; Yu, Y.; Ren, W.; Dong, L.; Meng, X.; Deng, H.; Nan, Y.; Ding, Q. The PRMT5/WDR77 complex restricts hepatitis E virus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Mahsoub, H.M.; Li, W.; Heffron, C.L.; Tian, D.; Hassebroek, A.M.; LeRoith, T.; Meng, X.J. Ribavirin Treatment Failure-Associated Mutation, Y1320H, in the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase of Genotype 3 Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Enhances Virus Replication in a Rabbit HEV Infection Model. mBio 2023, 14, e0337222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, S. Construction of hybrid viruses containing SV40 and λ phage DNA segments and their propagation in cultured monkey cells. Cell 1976, 9, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, S.U.; Nguyen, H.; Graff, J.; Stephany, D.A.; Brockington, A.; Purcell, R.H. In vitro replication of hepatitis E virus (HEV) genomes and of an HEV replicon expressing green fluorescent protein. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4838–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, F.; Shi, B.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, Z. Construction of an Infectious cDNA Clone of a Swine Genotype 3 HEV Strain Isolated in Shanghai, China. Intervirology 2014, 57, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.F.; Pierson, F.W.; Toth, T.E.; Meng, X.J. Construction and characterization of infectious cDNA clones of a chicken strain of hepatitis E virus (HEV), avian HEV. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2585–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, B.W.; Moon, H.W.; Sung, H.W.; Yoon, B.I.; Meng, X.J.; Kwon, H.M. Construction of an infectious cDNA clone of genotype 1 avian hepatitis E virus: Characterization of its pathogenicity in broiler breeders and demonstration of its utility in studying the role of the hypervariable region in virus replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.M.; LeRoith, T.; Pudupakam, R.S.; Pierson, F.W.; Huang, Y.-W.; Dryman, B.A.; Meng, X.-J. Construction of an infectious cDNA clone of avian hepatitis E virus (avian HEV) recovered from a clinically healthy chicken in the United States and characterization of its pathogenicity in specific-pathogen-free chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 147, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.F.; Larsen, C.T.; Huang, F.F.; Billam, P.; Pierson, F.W.; Toth, T.E.; Meng, X.J. Generation and infectivity titration of an infectious stock of avian hepatitis E virus (HEV) in chickens and cross-species infection of turkeys with avian HEV. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2658–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Yang, T.; Yoshizaki, S.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Ishii, K.; Haga, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ochiai, S.; Takaji, W.; et al. Construction and characterization of an infectious cDNA clone of rat hepatitis E virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debing, Y.; Mishra, N.; Verbeken, E.; Ramaekers, K.; Dallmeier, K.; Neyts, J. A rat model for hepatitis E virus. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. Construction of an infectious cDNA clone of hepatitis E virus strain JE03-1760F that can propagate efficiently in cultured cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Mizuo, H.; Okamoto, H. Development and Characterization of a Genotype 4 Hepatitis E Virus Cell Culture System Using a HE-JF5/15F Strain Recovered from a Fulminant Hepatitis Patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1906–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Tanaka, T.; Jirintai, S.; Takahashi, M.; Murata, K.; Okamoto, H. Development and Characterization of Efficient Cell Culture Systems for Genotype 1 Hepatitis E Virus and Its Infectious cDNA Clone. Viruses 2023, 15, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.N.; Devhare, P.B.; Pingle, S.Y.; Paingankar, M.S.; Arankalle, V.A.; Lole, K.S. Hepatitis E virus (HEV)-1 harbouring HEV-4 non-structural protein (ORF1) replicates in transfected porcine kidney cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Nakazono, N.; Ishii, K.; Li, D.; Kawamata, O.; Kawaguchi, R.; Tsukada, Y. Hepatitis E virus (87A strain) propagated in A549 cells. J. Med. Virol. 1995, 47, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, D.; Wei, S.; Li, Q.; Yuan, X.; Geng, L.; Li, X.; Liu, M. Cell culture of sporadic hepatitis E virus in China. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1999, 6, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, S.U.; Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Burke, D.; Engle, R.; Purcell, R.H. Release of genotype 1 hepatitis E virus from cultured hepatoma and polarized intestinal cells depends on open reading frame 3 protein and requires an intact PXXP motif. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 9059–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Liu, P.; Takacs, C.N.; Xiang, K.; Andrus, L.; Gouttenoire, J.; Moradpour, D.; Rice, C.M. Pan-Genotype Hepatitis E Virus Replication in Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocellular Systems. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 663–674.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knegendorf, L.; Drave, S.A.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Debing, Y.; Brown, R.J.P.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Resner, K.; Friesland, M.; Khera, T.; Engelmann, M.; et al. Hepatitis E virus replication and interferon responses in human placental cells. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, Y.; Yasue, H.; Takahashi, K.; Hattori, S.; Ideno, S.; Urayama, T.; Chiba, M.; Osari, S.; Naito, T.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. Mode of swine hepatitis E virus infection and replication in primary human hepatocytes. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2677–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierniak, F.; Ulrich, R.G.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. A Modular Hepatitis E Virus Replicon System for Studies on the Role of ORF1-Encoded Polyprotein Domains. Pathogens 2022, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Jirintai, S.; Takahashi, M.; Okamoto, H.; Takeda, N.; Muramatsu, M.; Li, T.C. Persistent infection with a rabbit hepatitis E virus created by a reverse genetics system. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Bai, H.; Yoshizaki, S.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Takahashi, K.; Mishiro, S.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T. Genotype 5 Hepatitis E Virus Produced by a Reverse Genetics System Has the Potential for Zoonotic Infection. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Kataoka, M.; Takeda, N.; Muramatsu, M.; Li, T. A Cross-Species Transmission of a Camel-Derived Genotype 8 Hepatitis E Virus to Rabbits. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.-C.; Zhou, X.; Yoshizaki, S.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T. Production of infectious dromedary camel hepatitis E virus by a reverse genetic system: Potential for zoonotic infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Takeda, N.; Muramatsu, M.; Li, T.C. Generation of a Bactrian camel hepatitis E virus by a reverse genetics system. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, V.L.D.; Dill, M.; Prallet, S.; Mehnert, A.-K.; Schweiggert, S. Human stem cell-derived hepatic and intestinal culture systems to study HEV transmission along the gut-liver axis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, S262–S263. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, S.; Kakinuma, S.; Asahina, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Miyoshi, M.; Tsunoda, T.; Nitta, S.; Asano, Y.; Nagata, H.; Otani, S.; et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatic cell lines as a new model for host interaction with hepatitis B virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, K.W.; Catá, E.M.; Crawford, C.M.; Sinagoga, K.L.; Schumacher, M.; Rockich, B.E.; Tsai, Y.H.; Mayhew, C.N.; Spence, J.R.; Zavros, Y.; et al. Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids. Nature 2014, 516, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, O.; Lhomme, S.; Nayrac, M.; Dubois, M.; Pucelle, M.; Requena, M.; Migueres, M.; Abravanel, F.; Peron, J.M.; Carrere, N.; et al. Hepatitis E virus replication in human intestinal cells. Gut 2020, 69, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Renner, M.; Martin, C.A.; Wenzel, D.; Bicknell, L.S.; Hurles, M.E.; Homfray, T.; Penninger, J.M.; Jackson, A.P.; Knoblich, J.A. Cerebral organoids model human brain development and microcephaly. Nature 2013, 501, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Wetzel, I.; Dréau, D.; Cho, H. 3D Miniaturization of Human Organs for Drug Discovery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Gehart, H.; Artegiani, B.; LÖpez-Iglesias, C.; Dekkers, F.; Basak, O.; van Es, J.; Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S.M.; Begthel, H.; Korving, J.; et al. Long-Term Expansion of Functional Mouse and Human Hepatocytes as 3D Organoids. Cell 2018, 175, 1591–1606.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuijk, E.W.; Rasmussen, S.; Blokzijl, F.; Huch, M.; Gehart, H.; Toonen, P.; Begthel, H.; Clevers, H.; Geurts, A.M.; Cuppen, E. Generation and characterization of rat liver stem cell lines and their engraftment in a rat model of liver failure. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruitwagen, H.S.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; Vernooij, I.; Schrall, I.M.; van Wolferen, M.E.; Bannink, F.; Roesch, C.; van Uden, L.; Molenaar, M.R.; Helms, J.B.; et al. Long-Term Adult Feline Liver Organoid Cultures for Disease Modeling of Hepatic Steatosis. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantasanti, S.; Spee, B.; Kruitwagen, H.S.; Chen, C.; Geijsen, N.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; van Wolferen, M.E.; Pelaez, N.; Fieten, H.; Wubbolts, R.W.; et al. Disease Modeling and Gene Therapy of Copper Storage Disease in Canine Hepatic Organoids. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, N.; Inacio, P.; Huch, M. Liver organoids: From basic research to therapeutic applications. Gut 2019, 68, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, T.; Stuart, H.T.; Gromberg, E.; Ishihara, K.; Cislo, D.; Melchionda, M.; Becerril Perez, F.; Wang, J.; Costantini, E.; Lehr, S.; et al. Mouse neural tube organoids self-organize floorplate through BMP-mediated cluster competition. Dev. Cell 2024, 59, 1940–1953.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagst, M.; Gömer, A.; Augustyniak, S.; Klöhn, M.; Rehm, A.; Ulrich, R.G.; Bader, V.; Winklhofer, K.F.; Brüggemann, Y.; Gold, R.; et al. Modeling extrahepatic hepatitis E virus infection in induced human primary neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2411434121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwokoye, P.N.; Abilez, O.J. Bioengineering methods for vascularizing organoids. Cell Rep. Methods 2024, 4, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cao, Y.; Weng, J.; Gao, S.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xia, C.; Yin, X.; et al. Hepatitis E virus infects human testicular tissue and Sertoli cells. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2332657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvatits, T.; Wißmann, J.E.; Johne, R.; Groschup, M.H.; Gadicherla, A.K.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; Eiden, M.; Todt, D.; Reimer, R.; Dähnert, L.; et al. Hepatitis E virus persists in the ejaculate of chronically infected men. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossaboom, C.M.; Córdoba, L.; Sanford, B.J.; Piñeyro, P.; Kenney, S.P.; Dryman, B.A.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.J. Cross-species infection of pigs with a novel rabbit, but not rat, strain of hepatitis E virus isolated in the United States. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Freistaedter, A.; Schmelas, C.; Gunkel, M.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Grimm, D. An RNA Interference/Adeno-Associated Virus Vector-Based Combinatorial Gene Therapy Approach Against Hepatitis E Virus. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Liang, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Nie, J. Research Progress on Hepatitis E Virus Culture. Pathogens 2025, 14, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050456
Zhang J, Liang Z, Liu F, Wang Y, Huang W, Nie J. Research Progress on Hepatitis E Virus Culture. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050456
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jie, Ziteng Liang, Fan Liu, Youchun Wang, Weijin Huang, and Jianhui Nie. 2025. "Research Progress on Hepatitis E Virus Culture" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050456
APA StyleZhang, J., Liang, Z., Liu, F., Wang, Y., Huang, W., & Nie, J. (2025). Research Progress on Hepatitis E Virus Culture. Pathogens, 14(5), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050456






