Complement and Coagulation Cascade Activation Regulates the Early Inflammatory Mechanism of Resistance of Suckling Lambs Against Haemonchus contortus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Set Recovery, Data Analysis, and Bioinformatics
2.2. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
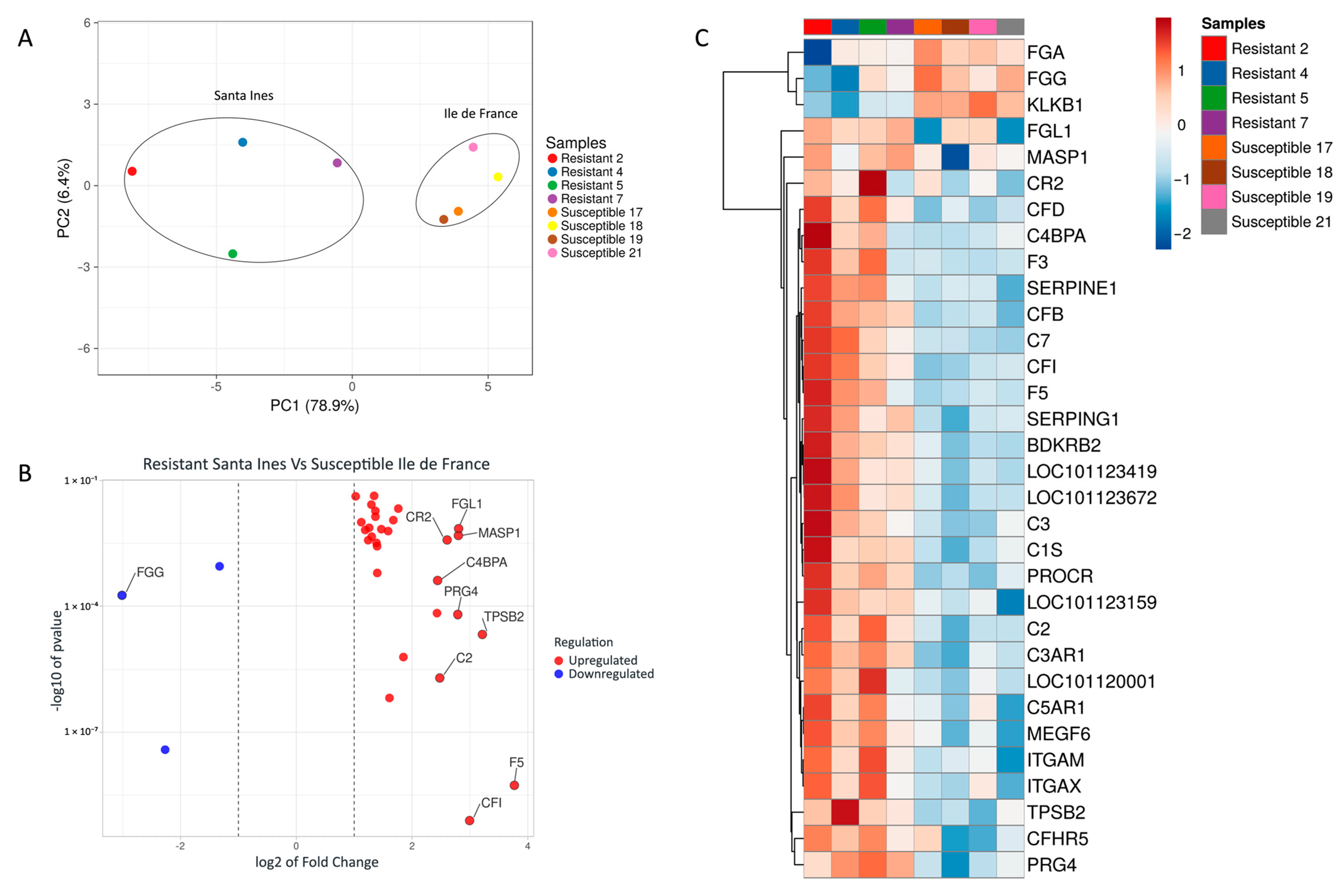
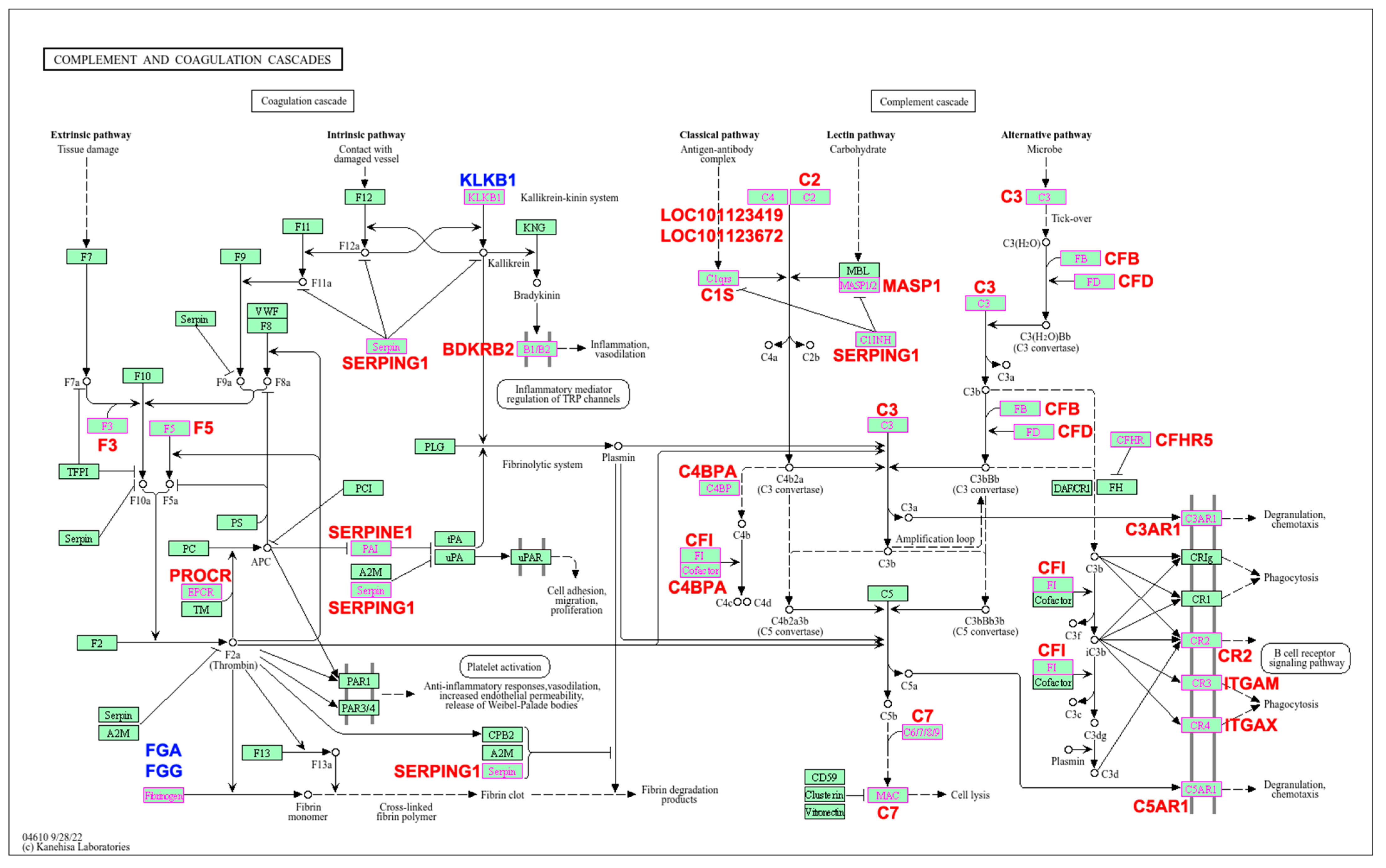
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arsenopoulos, K.V.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Katsarou, E.I.; Papadopoulos, E. Haemonchosis: A Challenging Parasitic Infection of Sheep and Goats. Animals 2021, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lins, J.G.G.; Almeida, F.A.; Albuquerque, A.C.A.; Britton, C.; Amarante, A.F.T. Early-onset immune response to Haemoncus contortus infection in resistant Santa Ines sucking lambs compared with susceptible Ile de France. Vet. Parasitol. 2022, 307–308, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, J.G.G.; Albuquerque, A.C.A.; Almeida, F.A.; Britton, C.; Malossi, C.; Araújo-Júnior, J.P.; Louvandini, H.; Amarante, A.F.T. Abomasal RNA-seq reveals a strong local cell response of suckling lambs with resistance against Haemonchus contortus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2023, 53, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, J.G.G.; Albuquerque, A.C.A.; Britton, C.; Amarante, A.F.T. Dynamics of immune functional mechanisms and their roles in promoting host resistance to Haemonchus contortus infection in suckling lambs. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2025, 164, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambris, J.D.; Ricklin, D.; Geisbrecht, B.V. Complement evasion by human pathogens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkelberger, J.R.; Song, W.C. Complement and its role in innate and adaptive immune responses. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, F.; Hunt, P.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Ingham, A.; Li, R.W. Transcriptome analysis unraveled potential mechanisms of resistance to Haemonchus contortus infection in Merino sheep populations bred for parasite resistance. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, H.I.; Boral, I.; Bevington, A. Complement-coagulation cross-talk: A potential mediator of the physiological activation of complement by low pH. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, P.M.; Commodaro, A.G.; Grigg, M.E. A Protective and Pathogenic Role for Complement During Acute Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 634610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Barros, L.V.; Silva-Moreira, A.L.; Horta, M.F.; Gontijo, N.F.; Castro-Gomes, T. How to get away with murder: The multiple strategies employed by pathogenic protozoa to avoid complement killing. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 149, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Meena, A.S.; Baraiya, T.; Swarnkar, C.P.; Misra, S.S.; Kumar, A. Expression of Toll-like receptors in Haemonchus contortus-resistant sheep: An innate immune parameter for host defense against gastrointestinal nematode infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2024, 275, 110813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, J.; Aimulajiang, K.; Aleem, M.T.; Lu, M.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Yan, R. Excretory/secretory proteins inhibit host immune responses by downregulating the TLR4/NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathway: A possible mechanism of immune evasion in parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1013159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Nakazawa, N.; Iwaki, D.; Takahashi, M.; Matsushita, M.; Fujita, T. Interactions of ficolin and mannose-binding lectin with fibrinogen/fibrin augment the lectin complement pathway. J. Innate Immun. 2010, 2, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology resource: Enriching a GOld mine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D325–D334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG: Integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D545–D551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. ClustVis: A web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using Principal Component Analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedhart, J.; Luijsterburg, M.S. VolcaNoseR is a web app for creating, exploring, labelling and sharing volcano plots. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape, a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenov, Y.; Ramírez, F.; Schelhorn, S.E.; Lengauer, T.; Albrecht, M. Computing topological parameters of biological networks. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, G.D.; Hogue, C.W.V. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, C.L.; Ciufo, S.; Domrachev, M.; Hotton, C.L.; Kannan, S.; Khovanskaya, R.; Leipe, D.; McVeigh, R.; O’Neill, K.; Robbertse, B.; et al. NCBI Taxonomy: A comprehensive update on curation, resources and tools. Database 2020, 2020, baaa062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Cheng, Y.S.; Yu, L.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y. Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed genes and protein-protein interaction networks associated with functional pathways in ulcerative colitis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e927917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, U.; Flierl, M.A.; Rittirsch, D.; Klos, A.; Chen, H.; Acker, B.; Bruckner, U.B.; Nilsson, B.; Gebhard, F.; Lambris, J.D.; et al. Molecular intercommunication between the complement and coagulation systems. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5628–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomopoulou, K.; Ricklin, D.; Ward, P.A.; Lambris, J.D. Interactions between coagulation and complement—Their role in inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balic, A.; Bowles, V.M.; Meeusen, E.N.T. The immunobiology of gastrointestinal nematode infections in ruminants. Adv. Parasitol. 2000, 45, 181–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charleston, W.A.G. Pathogenesis of experimental haemonchosis in sheep, with special reference to the development of resistance. J. Comp. Pathol. 1965, 75, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambell, M.R.; Charleston, W.A.; Tothill, P. Abomasal bleeding caused by immature stages of Haemonchus contortus in sheep showing ‘age resistance’. J. Comp. Pathol. 1964, 74, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H. The interaction between pathogens and the host coagulation system. Physiology 2006, 21, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulshof, A.M.; Hemker, H.C.; Spronk, H.M.H.; Henskens, Y.M.C.; Ten Cate, H. Thrombin-fibrin(ogen) interactions, host defense and risk of thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.; Benz, E., Jr.; Shattil, S.J.; Furie, B.; Cohen, H.J.; Silberstein, L.E.; McGlave, P. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice; Elsevier Churchill Livingstone: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.L.; Bird, R.J. Review article: Coagulation cascade and therapeutics update: Relevance to nephrology. Part 1: Overview of coagulation, thrombophilias and history of anticoagulants. Nephrology 2009, 14, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritten, L.; Gillis-Germitsch, N.; Kockmann, T.; Schnyder, M. Quantitative proteomics analysis of Angiostrongylus vasorum-induced alterations in dog serum sheds light on the pathogenesis of canine angiostrongylosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davalos, D.; Akassoglou, K. Fibrinogen as a key regulator of inflammation in disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease, 5th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sillaber, C.; Baghestanian, M.; Bevec, D.; Willheim, M.; Agis, H.; Kapiotis, S.; Fureder, W.; Bankl, H.C.; Kiener, H.P.; Speiser, W.; et al. The mast cell as site of tissue-type plasminogen activator expression and fibrinolysis. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Munyard, K.; Lee, C.Y.; Wetherall, J.D.; Groth, D.M. Characterization of the sheep complement factor B gene (CFB). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 140, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; González, J.F.; Hernandez, J.N.; McNeilly, T.N.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Frew, D.; Morrison, T.; Yu, P.; Li, R.W. Possible mechanisms of host resistance to Haemonchus contortus infection in sheep breeds native to the Canary Islands. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.; Xu, L.; Yan, R.; Li, X. Haemonchus contortus: Cloning and characterization of serpin. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 125, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobardt, S.D.; Dillman, A.R.; Nair, M.G. The two faces of nematode infection: Virulence and immunomodulatory molecules from nematode parasites of mammals, insects and plants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 577846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchitra, S.; Anbu, K.A.; Rathore, D.K.; Mahawar, M.; Singh, B.P.; Joshi, P. Haemonchus contortus calreticulin binds to C-reactive protein of its host, a novel survival strategy of the parasite. Parasite Immunol. 2008, 30, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Matsushita, M.; Endo, Y. The lectin-complement pathway—Its role in innate immunity and evolution. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Tian, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, W.; Tian, A.L.; Li, C.; Yan, R.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Li, X. Proteomic analysis revealed T cell hyporesponsiveness induced by Haemonchus contortus excretory and secretory proteins. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Chang, W.C.; Takahashi, M.; Pavlov, V.; Ishida, Y.; Bonte, L.L.; Shi, L.; Fujita, T.; Stahl, G.L.; Cott, E.M.V. Mannose-binding lectin and its associated proteases (MASPs) mediate coagulation and its deficiency is a risk factor in developing complications from infection, including disseminated intravascular coagulation. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedamurthy, G.V.; Sahoo, S.; Devi, I.K.; Murugavel, S.; Joshi, P. The N-terminal segment of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase of Haemonchus contortus interacts with complements C1q and C3. Parasite Immunol. 2015, 37, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lins, J.G.G.; Amarante, A.F.T. Complement and Coagulation Cascade Activation Regulates the Early Inflammatory Mechanism of Resistance of Suckling Lambs Against Haemonchus contortus. Pathogens 2025, 14, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050447
Lins JGG, Amarante AFT. Complement and Coagulation Cascade Activation Regulates the Early Inflammatory Mechanism of Resistance of Suckling Lambs Against Haemonchus contortus. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050447
Chicago/Turabian StyleLins, José Gabriel G., and Alessandro F. T. Amarante. 2025. "Complement and Coagulation Cascade Activation Regulates the Early Inflammatory Mechanism of Resistance of Suckling Lambs Against Haemonchus contortus" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050447
APA StyleLins, J. G. G., & Amarante, A. F. T. (2025). Complement and Coagulation Cascade Activation Regulates the Early Inflammatory Mechanism of Resistance of Suckling Lambs Against Haemonchus contortus. Pathogens, 14(5), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050447




