Epidemiology, Clinical Significance, and Diagnosis of Respiratory Viruses and Their Co-Infections in the Post-COVID Era
Abstract
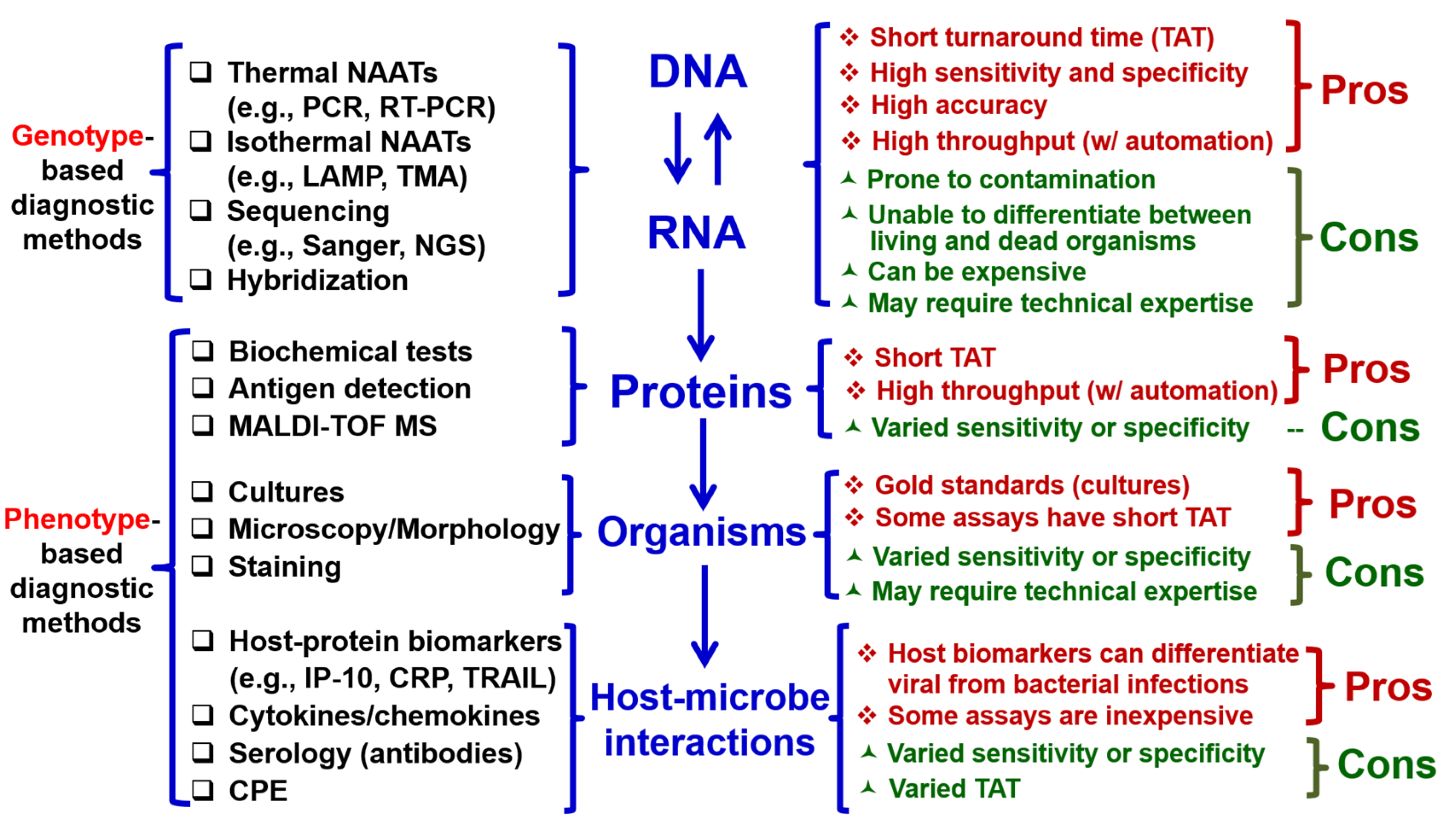
1. Introduction
2. Co-Infection of SARS-CoV-2 with Viral Respiratory Infections
2.1. Influenza Viruses
2.2. RSV
2.3. hMPV
2.4. Enterovirus
2.5. Rhinoviruses
2.6. PIV
2.7. Adenovirus
2.8. Non-SARS-CoV-2 Seasonal HCoVs
3. Multiplex Molecular Testing for Respiratory Viruses and Their Co-Infections
3.1. BioFire Respiratory Panel 2.1
3.2. BioFire Spotfire
3.3. Roche Cobas (GenMark) ePlex Respiratory Pathogen 2 (RP2) Panel
3.4. Qiagen Respiratory Panel
3.5. Luminex NxTAG Respiratory Pathogen Panel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.M.; Hill, H.R. Role of Host Immune and Inflammatory Responses in COVID-19 Cases with Underlying Primary Immunodeficiency: A Review. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2020, 40, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fauci, A.S.; Lane, H.C.; Redfield, R.R. COVID-19—Navigating the Uncharted. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1268–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.M.; Martins, T.B.; Peterson, L.K.; Hill, H.R. Clinical significance of measuring serum cytokine levels as inflammatory biomarkers in adult and pediatric COVID-19 cases: A review. Cytokine 2021, 142, 155478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hebbani, A.V.; Pulakuntla, S.; Pannuru, P.; Aramgam, S.; Badri, K.R.; Reddy, V.D. COVID-19: Comprehensive review on mutations and current vaccines. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 204, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carabelli, A.M.; Peacock, T.P.; Thorne, L.G.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; COVID-19 Genomics UK Consortium; Peacock, S.J.; Barclay, W.S.; de Silva, T.I.; Towers, G.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: Immune escape, transmission and fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.M.; Beck, E.M.; Fisher, M.A. The Brief Case: Ventilator-Associated Corynebacterium accolens Pneumonia in a Patient with Respiratory Failure Due to COVID-19. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0013721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chai, J.; Cai, Y.; Pang, C.; Wang, L.; McSweeney, S.; Shanklin, J.; Liu, Q. Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein recognition of human cell junction protein PALS1. Nat Commun. 2021, 12, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, B.M.; Yao, Q.; Cruz-Cosme, R.; Yarbrough, C.; Draper, K.; Suslovic, W.; Muhammad, I.; Contes, K.M.; Hillyard, D.R.; Teng, S.; et al. Genetic Conservation and Diversity of SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Gene Across Variants of Concern. J. Med. Virol. 2025, 97, e70136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeman, D.; Fielding, B.C. Is there a link between the pathogenic human coronavirus envelope protein and immunopathology? A review of the literature. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, N.L.; Wang, J.; Shi, P.Y.; Wang, T.; Miller, M.A.; Li, K. Overlapping and distinct molecular determinants dictating the antiviral activities of TRIM56 against flaviviruses and coronavirus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13821–13835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagani, I.; Ghezzi, S.; Alberti, S.; Poli, G.; Vicenzi, E. Origin and evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 2023, 138, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/coronavirus-disease-(covid-19) (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Aleem, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19) [Updated 2023 Aug 18]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554776/ (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Eaton, B.T. Bats, civets and the emergence of SARS. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 315, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Health Organization. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome: Global Summary and Assessment of Risk; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-MERS-RA-2022.1 (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Memish, Z.A.; Perlman, S.; Van Kerkhove, M.D.; Zumla, A. Middle East respiratory syndrome. Lancet 2020, 395, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Apostolopoulos, V.; Chavda, V.; Alshahrani, N.Z.; Mehta, R.; Satapathy, P.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Sah, R. MERS outbreak in Riyadh: A current concern in Saudi Arabia. Infez Med. 2024, 32, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Health Organization. Influenza (Seasonal) [Internet]; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal) (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Rezaee, D.; Bakhtiari, S.; Jalilian, F.A.; Doosti-Irani, A.; Asadi, F.T.; Ansari, N. Coinfection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and influenza virus during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jain, S.; Williams, D.J.; Arnold, S.R.; Ampofo, K.; Bramley, A.M.; Reed, C.; Stockmann, C.; Anderson, E.J.; Grijalva, C.G.; Self, W.H.; et al. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Padda, I.S.; Parmar, M. COVID (SARS-CoV-2) Vaccine. [Updated 2023 Jun 3]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567793/ (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Nunziata, F.; Salomone, S.; Catzola, A.; Poeta, M.; Pagano, F.; Punzi, L.; Lo Vecchio, A.; Guarino, A.; Bruzzese, E. Clinical presentation and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to respiratory syncytial virus and other viral respiratory infections in children less than two years of age. Viruses 2023, 15, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Upadhyay, P.; Reddy, J.; Granger, J. SARS-CoV-2 respiratory co-infections: Incidence of viral and bacterial co-pathogens. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipek, O.A.; Stéger, J.; Papp, K.; Visontai, D.; Koopmans, M.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.; Oude Munnink, B.B.; Csabai, I. Systematic detection of co-infection and intra-host recombination in more than 2 million global SARS-CoV-2 samples. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dee, K.; Schultz, V.; Haney, J.; Bissett, L.A.; Magill, C.; Murcia, P.R. Influenza A and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Trigger a Cellular Response That Blocks Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Virus 2 Infection in the Respiratory Tract. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 227, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; He, W.; Sun, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, W.; et al. Influenza and COVID-19 co-infection and vaccine effectiveness against severe cases: A mathematical modeling study. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1347710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, N.L.; Shen, Y.; Bao, X.; Fabrizio, T.; Elbahesh, H.; Webby, R.J.; Li, K. The C-Terminal Tail of TRIM56 Dictates Antiviral Restriction of Influenza A and B Viruses by Impeding Viral RNA Synthesis. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4369–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMessurier, K.S.; Rooney, R.; Ghoneim, H.E.; Liu, B.; Li, K.; Smallwood, H.S.; Samarasinghe, A.E. Influenza A virus directly modulates mouse eosinophil responses. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.M.; Li, N.L.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Li, Z.A.; Marion, T.N.; Li, K. Key roles for phosphorylation and the Coiled-coil domain in TRIM56-mediated positive regulation of TLR3-TRIF-dependent innate immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shen, Y.; Li, N.L.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Lester, S.; Li, K. TRIM56 is an essential component of the TLR3 antiviral signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36404–36413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, B.M.; Rakhmanina, N.Y.; Yang, Z.; Bukrinsky, M.I. Mpox (Monkeypox) Virus and Its Co-Infection with HIV, Sexually Transmitted Infections, or Bacterial Superinfections: Double Whammy or a New Prime Culprit? Viruses 2024, 16, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tang, C.Y.; Boftsi, M.; Staudt, L.; McElroy, J.A.; Li, T.; Duong, S.; Ohler, A.; Ritter, D.; Hammer, R.; Hang, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and influenza co-infection: A cross-sectional study in central Missouri during the 2021-2022 influenza season. Virology 2022, 576, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Morris, D.R.; Qu, Y.; Thomason, K.S.; de Mello, A.H.; Preble, R.; Menachery, V.D.; Casola, A.; Garofalo, R.P. The impact of RSV/SARS-CoV-2 co-infection on clinical disease and viral replication: Insights from a BALB/c mouse model. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mandelia, Y.; Procop, G.W.; Richter, S.S.; Worley, S.; Liu, W.; Esper, F. Dynamics and predisposition of respiratory viral co-infections in children and adults. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 631.e1–631.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.A.; Safamanesh, S.; Ghasemzadeh-Moghaddam, H.; Ghafouri, M.; Mohajerzadeh-Heydari, M.S.; Namdar-Ahmadabad, H.; Azimian, A. Report of death in children with SARS-CoV-2 and human metapneumovirus (hMPV) coinfection: Is hMPV the trigger? J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Touzard-Romo, F.; Tapé, C.; Lonks, J.R. Co-infection with SARS-CoV-2 and Human Metapneumovirus. Rhode Isl. Med. J. 2020, 103, 75–76. [Google Scholar]
- Maltezou, H.C.; Papanikolopoulou, A.; Vassiliu, S.; Theodoridou, K.; Nikolopoulou, G.; Sipsas, N.V. COVID-19 and Respiratory Virus Co-Infections: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Viruses 2023, 15, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sinclair, W.; Omar, M. Enterovirus. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562330/ (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Liu, B. Universal PCR Primers Are Critical for Direct Sequencing-Based Enterovirus Genotyping. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 55, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, B.M.; Mulkey, S.B.; Campos, J.M.; DeBiasi, R.L. Laboratory diagnosis of CNS infections in children due to emerging and re-emerging neurotropic viruses. Pediatr. Res. 2024, 95, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khasawneh, A.I.; Himsawi, N.M.; Abu-Raideh, J.A.; Sammour, A.; Abu Safieh, H.; Obeidat, A.; Azab, M.; Tarifi, A.A.; Al Khawaldeh, A.; Al-Momani, H.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory pathogens among a Jordanian subpopulation during Delta-to-Omicron transition: Winter 2021/2022. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Svyatchenko, V.A.; Legostaev, S.S.; Lutkovskiy, R.Y.; Protopopova, E.V.; Ponomareva, E.P.; Omigov, V.V.; Taranov, O.S.; Ternovoi, V.A.; Agafonov, A.P.; Loktev, V.B. Coxsackievirus A7 and Enterovirus A71 Significantly Reduce SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Cell and Animal Models. Viruses 2024, 16, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, P.; Bahr, N.C.; Snyder, K.; Shoemaker, D.M. Pneumocystis jirovecii Infections Among COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series and Literature Review. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Prieto, A.M.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M. Interferon-stimulated genes and their antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2. mBio 2024, 15, e0210024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Varela, F.H.; Sartor, I.T.S.; Polese-Bonatto, M.; Azevedo, T.R.; Kern, L.B.; Fazolo, T.; de David, C.N.; Zavaglia, G.O.; Fernandes, I.R.; Krauser, J.R.M.; et al. Rhinovirus as the main co-circulating virus during the COVID-19 pandemic in children. J. Pediatr. (Rio J.) 2022, 98, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pereira, M.F.B.; Suguita, P.; Litvinov, N.; Farhat, S.C.L.; Paula, C.S.Y.; Lázari, C.D.S.; Bedê, P.V.; Framil, J.V.S.; Bueno, C.; Branas, P.C.A.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and rhinovirus infections: Are there differences in clinical presentation, laboratory abnormalities, and outcomes in the pediatric population? Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo. 2022, 64, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Westbrook, A.; Wang, T.; Bhakta, K.; Sullivan, J.; Gonzalez, M.D.; Lam, W.; Rostad, C.A. Respiratory Coinfections in Children With SARS-CoV-2. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Adiody, S. Aravind TR.Coinfection with SARS-CoV-2 and parainfluenza virus in an elderly patient: A case report. Int. J. Commun. Med. Public Health 2024, 11, 2056–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svyatchenko, V.A.; Ternovoi, V.A.; Lutkovskiy, R.Y.; Protopopova, E.V.; Gudymo, A.S.; Danilchenko, N.V.; Susloparov, I.M.; Kolosova, N.P.; Ryzhikov, A.B.; Taranov, O.S.; et al. Human Adenovirus and Influenza A Virus Exacerbate SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Animal Models. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Motta, J.C.; Gómez, C.C. Adenovirus and novel coronavirus (SARS-Cov2) coinfection: A case report. IDCases 2020, 22, e00936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wilson, R.; Kovacs, D.; Crosby, M.; Ho, A. Global Epidemiology and Seasonality of Human Seasonal Coronaviruses: A Systematic Review. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sagar, M.; Reifler, K.; Rossi, M.; Miller, N.S.; Sinha, P.; White, L.; Mizgerd, J.P. Recent endemic coronavirus infection is associated with less severe COVID-19. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 143380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.M.; Goodwin, E.C.; Verma, A.; Arevalo, C.P.; Bolton, M.J.; Weirick, M.E.; Gouma, S.; McAllister, C.M.; Christensen, S.R.; Weaver, J.; et al. Seasonal human coronavirus antibodies are boosted upon SARS-CoV-2 infection but not associated with protection. Cell 2021, 184, 1858–1864.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, B.M.; Carlisle, C.P.; Fisher, M.A.; Shakir, S.M. The Brief Case: Capnocytophaga sputigena Bacteremia in a 94-Year-Old Male with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Pancytopenia, and Bronchopneumonia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0247220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Murray, P.R.; Baron, E.J.; Jorgensen, J.H.; Landry, M.L.; Pfaller, M.A. (Eds.) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 9th ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yang, J.X.; Yan, L.; Zhuang, H.; Li, T. Novel HBV Recombinants between Genotypes B and C in 3′-terminal Reverse Transcriptase (RT) Sequences are Associated with Enhanced Viral DNA Load, Higher RT Point Mutation Rates and Place of Birth among Chinese Patients. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 57, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnifro, E.M.; Ashshi, A.M.; Cooper, R.J.; Klapper, P.E. Multiplex PCR: Optimization and application in diagnostic virology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, B.; Totten, M.; Nematollahi, S.; Datta, K.; Memon, W.; Marimuthu, S.; Wolf, L.A.; Carroll, K.C.; Zhang, S.X. Development and Evaluation of a Fully Automated Molecular Assay Targeting the Mitochondrial Small Subunit rRNA Gene for the Detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Specimens. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.M. Epidemiological and clinical overview of the 2024 Oropouche virus disease outbreaks, an emerging/re-emerging neurotropic arboviral disease and global public health threat. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Forman, M.; Valsamakis, A. Optimization and evaluation of a novel real-time RT-PCR test for detection of parechovirus in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Virol. Methods 2019, 272, 113690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.M. History of Food and Nutrition Toxicology; History of global food safety, foodborne illness, and risk assessment; Academic Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; pp. 301–316. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.M. Isothermal nucleic acid amplification technologies and CRISPR-Cas based nucleic acid detection strategies for infectious disease diagnostics. In Manual of Molecular Microbiology; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2026. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.M.; Hayes, A.W. Mechanisms and Assessment of Genotoxicity of Metallic Engineered Nanomaterials in the Human Environment. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lakshmanan, K.; Liu, B.M. Impact of Point-of-Care Testing on Diagnosis, Treatment, and Surveillance of Vaccine-Preventable Viral Infections. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- BioFire Respiratory Panel 2.1. Available online: https://www.biomerieux.com/us/en/our-offer/clinical-products/biofire-respiratory-panels.html (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- BioFire Spotfire. Available online: https://www.biomerieux.com/us/en/our-offer/clinical-products/biofire-spotfire-system.html (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Cobas Eplex RP2 Panel. Available online: https://diagnostics.roche.com/us/en/products/params/eplex-respiratory-pathogen-panel.html (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- QIAstat-Dx Respiratory Panel Plus. Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/us/product-categories/diagnostics-and-clinical-research/infectious-disease/qiastat-dx-syndromic-testing (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Leber, A.L.; Lisby, J.G.; Hansen, G.; Relich, R.F.; Schneider, U.V.; Granato, P.; Young, S.; Pareja, J.; Hannet, I. Multicenter Evaluation of the QIAstat-Dx Respiratory Panel for Detection of Viruses and Bacteria in Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00155-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tyrrell, C.S.; Allen, J.L.Y.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E. Influenza: Epidemiology and hospital management. Medicine 2021, 49, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shang, Z.; Tan, S.; Ma, D. Respiratory syncytial virus: From pathogenesis to potential therapeutic strategies. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4073–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Du, Y.; Yan, R.; Wu, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, G.; Yang, S. Global burden and trends of respiratory syncytial virus infection across different age groups from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 135, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luminex NxTAG Respiratory Pathogen Panel. Available online: https://int.diasorin.com/en/molecular-diagnostics/kits-reagents/nxtag-respiratory-pathogen-panel (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Tang, Y.W.; Gonsalves, S.; Sun, J.Y.; Stiles, J.; Gilhuley, K.A.; Mikhlina, A.; Dunbar, S.A.; Babady, N.E.; Zhang, H. Clinical Evaluation of the Luminex NxTAG Respiratory Pathogen Panel. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1912–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- American Lung Association. Treatment for RSV [Internet]; American Lung Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/rsv/treatment (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) [Internet]; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, Georgia, 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/about/index.html (accessed on 2 March 2025).

| Technology | BioFire FilmArray | GenMark ePlex | Qiagen | Luminex |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA amplification and detection methods | Nested PCR, melt curve analysis | PCR, electrochemical detection | PCR | PCR, liquid phase bead array |
| Turn-around time | 45 min (RP2.1); 15 min (Spotfire RP) | 1.5 h | 67–75 min | 5 h |
| Throughput | 1 test module/instrument; Torch: 2–12 test modules | 3–24 per instrument | 1 test module per instrument | 96-well plate format |
| Sensitivity | 97.1–98.5% | 96–100% | 94–100% | 96–100% |
| Specificity | 99.3–99.4% | 96–100% | 96–100% | 96–100% |
| Example of FDA-approved respiratory panels (number of targets) | RP2 (22); BioFire Spotfire RP (up to 15) | RP (17) | QIAstat-Dx Respiratory Panel Plus (21) | x-TAG RVP (12); x-TAG RVP Fast (8); NxTAG RPP (20) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contes, K.M.; Liu, B.M. Epidemiology, Clinical Significance, and Diagnosis of Respiratory Viruses and Their Co-Infections in the Post-COVID Era. Pathogens 2025, 14, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030262
Contes KM, Liu BM. Epidemiology, Clinical Significance, and Diagnosis of Respiratory Viruses and Their Co-Infections in the Post-COVID Era. Pathogens. 2025; 14(3):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030262
Chicago/Turabian StyleContes, Kaia M., and Benjamin M. Liu. 2025. "Epidemiology, Clinical Significance, and Diagnosis of Respiratory Viruses and Their Co-Infections in the Post-COVID Era" Pathogens 14, no. 3: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030262
APA StyleContes, K. M., & Liu, B. M. (2025). Epidemiology, Clinical Significance, and Diagnosis of Respiratory Viruses and Their Co-Infections in the Post-COVID Era. Pathogens, 14(3), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030262







