Nutritional Stress Leads to Persistence and Persister-like Growth in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
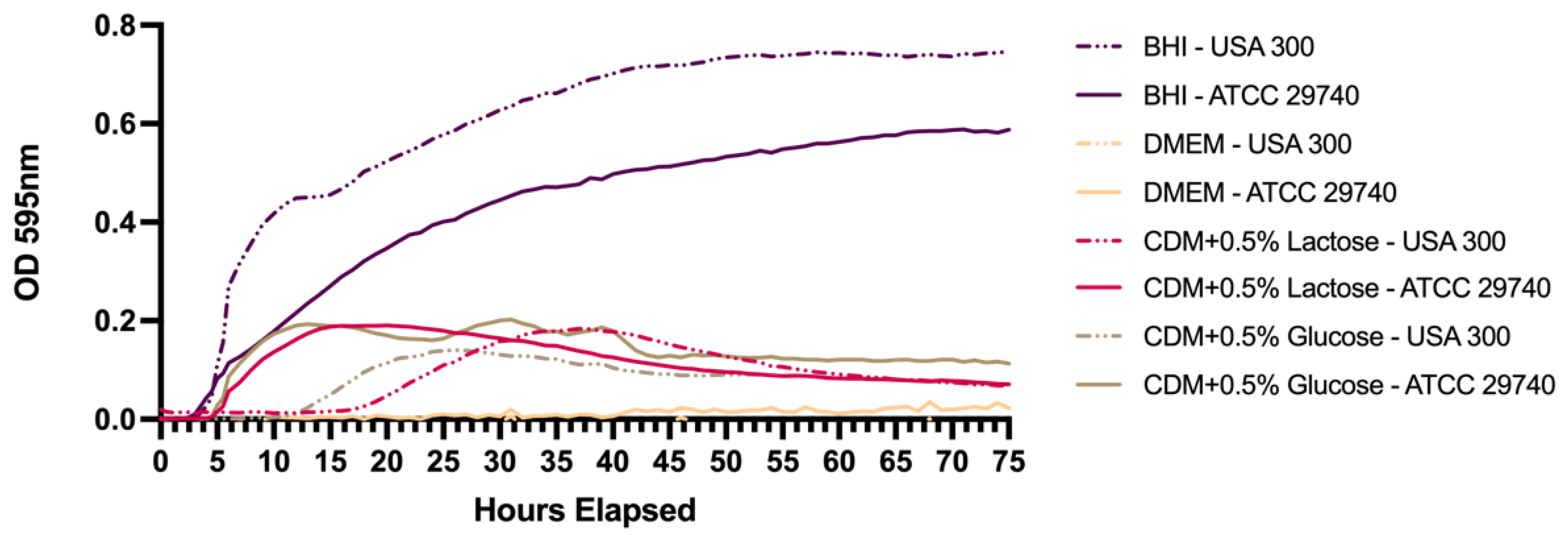
2.2. Growth Curves in Different Media
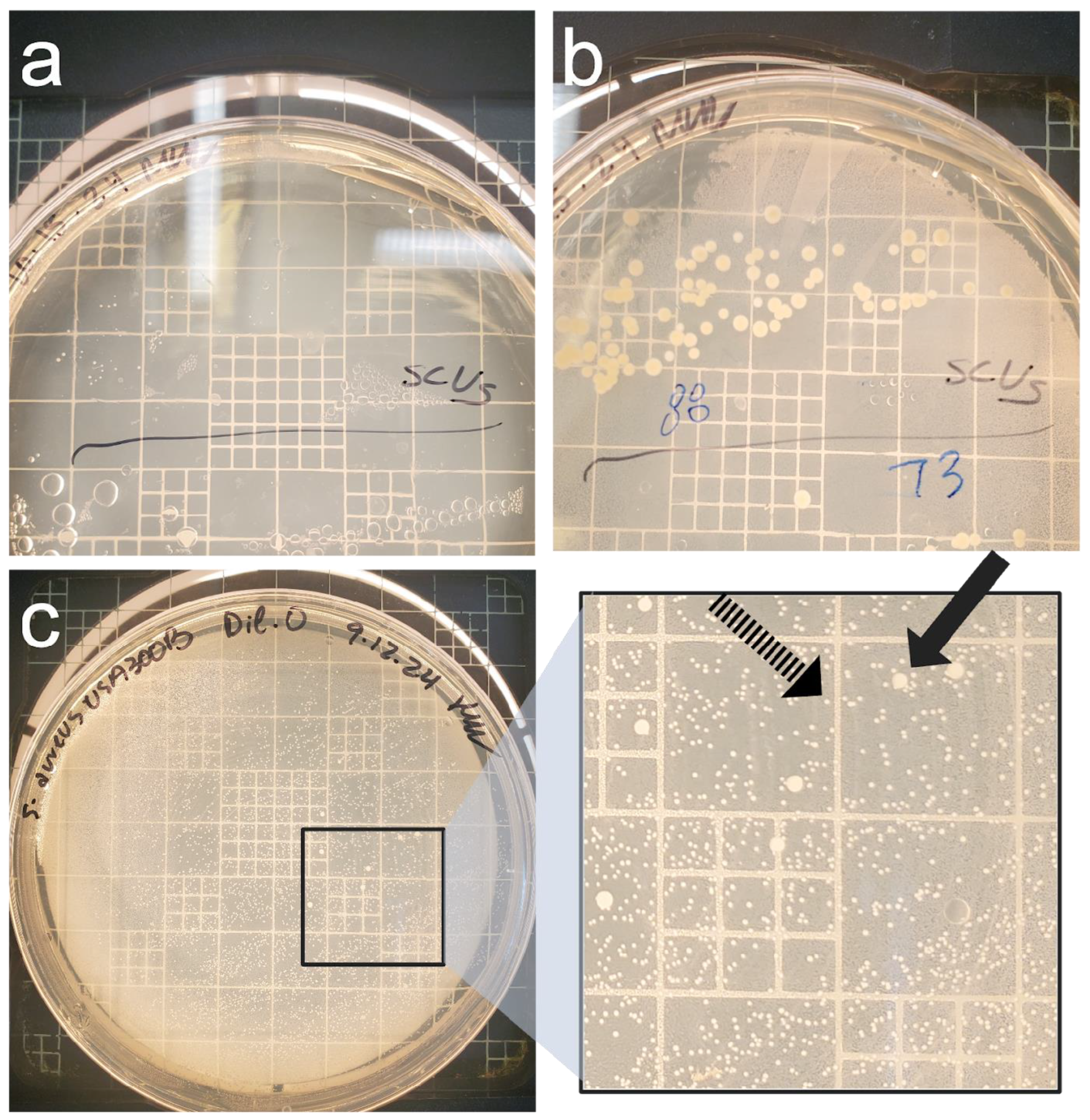
2.3. Nutritional Deprivation and Cell Enumeration
2.4. Quantitative PCR and ATP Assays
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Persistence Establishes Within 72 h in Nutrient Deficient Conditions
3.2. Persistence Continues for over 120 Days When Challenged with Nutritional Stress and Induces Persister-like Growth Patterns
3.3. Culture-Based Methods of Detection Do Not Accurately Reflect Viability
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| SCV | Small Colony Variant |
Appendix A
| Between Strain | Lactose | 0.14370278 | |||
| Glucose | 0.684679703 | ||||
| DMEM | 0.902200382 | ||||
| BHI | 0.396304143 | ||||
| USA300 | Lactose | Glucose | DMEM | BHI | |
| Lactose | NA | ||||
| Glucose | 0.474397606 | NA | |||
| DMEM | 0.459986984 | 0.404311317 | NA | ||
| BHI | 0.275856074 | 0.171969557 | 0.648222506 | NA | |
| ATCC 29740 | Lactose | Glucose | DMEM | BHI | |
| Lactose | NA | ||||
| Glucose | 0.686956269 | NA | |||
| DMEM | 0.284479808 | 0.07761123 | NA | ||
| BHI | 0.07761123 | 0.158564251 | 0.372151583 | NA |
| USA300 Lactose | USA300 Lactose | USA300 Lactose | ATCC 29740 Lactose | ATCC 29740 Lactose | ATCC 29740 Lactose | USA300 Glucose | USA300 Glucose | USA300 Glucose | ATCC 29740 Glucose | ATCC 29740 Glucose | ATCC 29740 Glucose | USA300 DMEM | USA300 DMEM | USA300 DMEM | ATCC 29740 DMEM | ATCC 29740 DMEM | ATCC 29740 DMEM | USA300 BHI | USA300 BHI | USA300 BHI | ATCC 29740 BHI | ATCC 29740 BHI | ATCC 29740 BHI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polynomial: Third Order (Y = A + B × X + C × X2 + D × X3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Best-fit values | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | −0.02955 | −0.02211 | −0.04404 | −0.03076 | −0.00408 | −0.00111 | −0.02581 | −0.03726 | −0.03781 | −0.03469 | 0.01471 | 0.005401 | −0.003383 | −0.01499 | −0.00909 | 0.0002317 | −0.01088 | −0.01937 | −0.008495 | −0.06706 | 0.006125 | −0.03296 | −0.03929 | −0.01938 |
| B | 0.01028 | 0.00604 | 0.01091 | 0.01756 | 0.01414 | 0.01442 | 0.0096 | 0.008371 | 0.01159 | 0.01882 | 0.01215 | 0.0143 | −0.0008398 | −0.0001539 | 0.0008184 | −0.0004362 | 0.0002157 | 0.002274 | 0.03717 | 0.04576 | 0.03491 | 0.02802 | 0.02734 | 0.01746 |
| C | −0.0001998 | −4.69 × 10−05 | −0.0001984 | −0.0004227 | −0.0003586 | −0.0003699 | −0.0001915 | −0.000144 | −0.0002658 | −0.0004149 | −0.0003274 | −0.000327 | 1.92 × 10−05 | 9.57 × 10−06 | −1.52 × 10−05 | 3.05 × 10−05 | 1.19 × 10−05 | −4.55 × 10−05 | −0.0005777 | −0.0008184 | −0.0006166 | −0.0003767 | −0.0004096 | −0.0002194 |
| D | 1.03 × 10−06 | −1.35 × 10−07 | 9.69 × 10−07 | 2.71 × 10−06 | 2.41 × 10−06 | 2.49 × 10−06 | 1.13 × 10−06 | 6.76 × 10−07 | 1.65 × 10−06 | 2.56 × 10−06 | 2.28 × 10−06 | 2.08 × 10−06 | −1.53 × 10−07 | −1.01 × 10−07 | 8.03 × 10−08 | −2.34 × 10−07 | −1.28 × 10−07 | 2.62 × 10−07 | 3.05 × 10−06 | 4.67 × 10−06 | 3.58 × 10−06 | 1.65 × 10−06 | 2.23 × 10−06 | 8.96 × 10−07 |
| 95% CI (profile likelihood) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | −0.04944 to −0.009659 | −0.04571 to 0.001492 | −0.06369 to −0.02439 | −0.04600 to −0.01553 | −0.02068 to 0.01252 | −0.01817 to 0.01595 | −0.03908 to −0.01253 | −0.05263 to −0.02188 | −0.05377 to −0.02186 | −0.05573 to −0.01365 | −0.006418 to 0.03584 | −0.01603 to 0.02684 | −0.006616 to −0.0001501 | −0.01899 to −0.01099 | −0.01359 to −0.004586 | −0.004664 to 0.005127 | −0.01424 to −0.007522 | −0.02343 to −0.01530 | −0.03834 to 0.02135 | −0.08336 to −0.05076 | −0.03117 to 0.04342 | −0.06039 to −0.005528 | −0.05340 to −0.02518 | −0.03421 to −0.004551 |
| B | 0.008121 to 0.01244 | 0.003478 to 0.008601 | 0.008783 to 0.01305 | 0.01591 to 0.01921 | 0.01234 to 0.01594 | 0.01256 to 0.01627 | 0.008159 to 0.01104 | 0.006703 to 0.01004 | 0.009857 to 0.01332 | 0.01654 to 0.02110 | 0.009854 to 0.01444 | 0.01197 to 0.01663 | −0.001191 to −0.0004890 | −0.0005882 to 0.0002803 | 0.0003297 to 0.001307 | −0.0009674 to 9.499 × 10−05 | −0.0001486 to 0.0005799 | 0.001833 to 0.002716 | 0.03393 to 0.04040 | 0.04399 to 0.04753 | 0.03086 to 0.03896 | 0.02504 to 0.03100 | 0.02581 to 0.02887 | 0.01585 to 0.01907 |
| C | −0.0002590 to −0.0001406 | −0.0001171 to 2.342 × 10−05 | −0.0002569 to −0.0001399 | −0.0004681 to −0.0003773 | −0.0004081 to −0.0003092 | −0.0004207 to −0.0003191 | −0.0002311 to −0.0001520 | −0.0001897 to −9.819 × 10−05 | −0.0003133 to −0.0002183 | −0.0004776 to −0.0003523 | −0.0003903 to −0.0002645 | −0.0003908 to −0.0002631 | 9.538 × 10−06 to 2.879 × 10−05 | −2.350 × 10−06 to 2.148 × 10−05 | −2.860 × 10−05 to −1.776 × 10−06 | 1.588 × 10−05 to 4.504 × 10−05 | 1.940 × 10−06 to 2.193 × 10−05 | −5.765 × 10−05 to −3.343 × 10−05 | −0.0006666 to −0.0004888 | −0.0008669 to −0.0007698 | −0.0007277 to −0.0005056 | −0.0004584 to −0.0002950 | −0.0004516 to −0.0003676 | −0.0002636 to −0.0001753 |
| D | 5.783 × 10−07 to 1.473 × 10−06 | −6.660 × 10−07 to 3.955 × 10−07 | 5.275 × 10−07 to 1.411 × 10−06 | 2.364 × 10−06 to 3.049 × 10−06 | 2.032 × 10−06 to 2.778 × 10−06 | 2.108 × 10−06 to 2.876 × 10−06 | 8.323 × 10−07 to 1.429 × 10−06 | 3.305 × 10−07 to 1.022 × 10−06 | 1.292 × 10−06 to 2.010 × 10−06 | 2.090 × 10−06 to 3.036 × 10−06 | 1.802 × 10−06 to 2.753 × 10−06 | 1.593 × 10−06 to 2.557 × 10−06 | −2.258 × 10−07 to −8.040 × 10−08 | −1.914 × 10−07 to −1.143 × 10−08 | −2.094 × 10−08 to 1.816 × 10−07 | −3.443 × 10−07 to −1.241 × 10−07 | −2.037 × 10−07 to −5.273 × 10−08 | 1.709 × 10−07 to 3.538 × 10−07 | 2.378 × 10−06 to 3.720 × 10−06 | 4.299 × 10−06 to 5.032 × 10−06 | 2.740 × 10−06 to 4.417 × 10−06 | 1.034 × 10−06 to 2.268 × 10−06 | 1.916 × 10−06 to 2.550 × 10−06 | 5.627 × 10−07 to 1.230 × 10−06 |
| Goodness of Fit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Degrees of Freedom | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 |
| R squared | 0.6769 | 0.6625 | 0.7278 | 0.8629 | 0.7557 | 0.7563 | 0.7914 | 0.7442 | 0.7214 | 0.8016 | 0.595 | 0.6719 | 0.6505 | 0.1705 | 0.2138 | 0.8226 | 0.809 | 0.6781 | 0.9693 | 0.9899 | 0.9265 | 0.9633 | 0.9901 | 0.9758 |
| Sum of Squares | 0.0896 | 0.1262 | 0.08741 | 0.05256 | 0.06238 | 0.06593 | 0.03992 | 0.05353 | 0.05765 | 0.1003 | 0.1011 | 0.1041 | 0.002367 | 0.003627 | 0.004594 | 0.005427 | 0.002552 | 0.003744 | 0.2017 | 0.06016 | 0.315 | 0.1704 | 0.0451 | 0.04981 |
| Sy.x | 0.03121 | 0.03703 | 0.03082 | 0.0239 | 0.02604 | 0.02677 | 0.02083 | 0.02412 | 0.02503 | 0.03302 | 0.03315 | 0.03363 | 0.005072 | 0.006279 | 0.007066 | 0.007681 | 0.005266 | 0.006379 | 0.04683 | 0.02557 | 0.05851 | 0.04304 | 0.02214 | 0.02327 |
References
- Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peton, V.; Le Loir, Y. Staphylococcus aureus in veterinary medicine. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, A.G.; Madrenas, J. The broad landscape of immune interactions with Staphylococcus aureus: From commensalism to lethal infections. Burns 2013, 39, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanamani, A.; Hariharan, P.; Paul-Satyaseela, M. Staphylococcus aureus: Overview of Bacteriology, Clinical Diseases, Epidemiology, Antibiotic Resistance and Therapeutic Approach. In Frontiers in Staphylococcus aureus; InTech Open: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.L. Epidemiology of Nosocomial Infections Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann. Intern. Med. 1982, 97, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.K. Nosocomial Infections and Drug Susceptibility Patterns in Methicillin Sensitive and Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 2178–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Wozniak, D.J.; Stoodley, P.; Hall-Stoodley, L. Prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Expert. Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 1499–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.; Pickering, A.C.; Rocha, L.S.; Aguilar, A.P.; Fabres-Klein, M.H.; de Oliveira Mendes, T.A.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; de Oliveira Barros Ribon, A. Diversity and pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus from bovine mastitis: Current understanding and future perspectives. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haag, A.F.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Penadés, J.R. Staphylococcus aureus in Animals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangra, S.; Khunger, S.; Chattopadhya, D. Antimicrobial Resistance in Staphylococci Special Emphasis on Methicillin Resistance among Companion Livestock and Its Impact on Human Health in Rural India. In Bovine Science-Challenges and Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Ronholm, J. Staphylococcus aureus in Agriculture: Lessons in Evolution from a Multispecies Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, F.C.; Markey, B.K. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in animals: A review. Vet. J. 2008, 175, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, L.A.; Alreshidi, M.M. Adaptive Metabolism in Staphylococci: Survival and Persistence in Environmental and Clinical Settings. J. Pathog. 2018, 2018, 1092632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassat, J.E.; Skaar, E.P. Metal ion acquisition in Staphylococcus aureus: Overcoming nutritional immunity. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grim, K.P.; Francisco, B.S.; Radin, J.N.; Brazel, E.B.; Kelliher, J.L.; Párraga Solórzano, P.K.; Kim, P.C.; McDevitt, C.A.; Kehl-Fie, T.E. The Metallophore Staphylopine Enables Staphylococcus aureus To Compete with the Host for Zinc and Overcome Nutritional Immunity. mBio 2017, 8, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantosti, A.; Sanchini, A.; Monaco, M. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus Aureus. Future Microbiol. 2007, 2, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, P.C. Microbiology of Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, S165–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, H.F.; Deleo, F.R. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinges, M.M.; Orwin, P.M.; Schlievert, P.M. Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, B.P. Staphylococcus aureus chronic and relapsing infections: Evidence of a role for persister cells: An investigation of persister cells, their formation and their role in S. aureus disease. BioEssays 2014, 36, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Lee, R.-E.; Lee, W. A pursuit of Staphylococcus aureus continues: A role of persister cells. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2020, 43, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K. Persister Cells: Molecular Mechanisms Related to Antibiotic Tolerance. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 211, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Proctor, R.A.; von Eiff, C.; Kahl, B.C.; Becker, K.; McNamara, P.; Herrmann, M.; Peters, G. Small colony variants: A pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, R.A.; Kriegeskorte, A.; Kahl, B.C.; Becker, K.; Löffler, B.; Peters, G. Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variants (SCVs): A road map for the metabolic pathways involved in persistent infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Heitmann, V.; Hussain, M.; Viemann, D.; Roth, J.; von Eiff, C.; Peters, G.; Becker, K.; Löffler, B. Staphylococcus aureus Small-Colony Variants Are Adapted Phenotypes for Intracellular Persistence. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Medina, E.; Hussain, M.; Völker, W.; Heitmann, V.; Niemann, S.; Holzinger, D.; Roth, J.; Proctor, R.A.; Becker, K.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus phenotype switching: An effective bacterial strategy to escape host immune response and establish a chronic infection. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K. Detection, Identification and Diagnostic Characterization of the Staphylococcal Small Colony-Variant (SCV) Phenotype. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, S.E.; Beam, J.E.; Conlon, B.P. Recalcitrant Staphylococcus aureus Infections: Obstacles and Solutions. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaatout, N.; Ayachi, A.; Kecha, M. Staphylococcus aureus persistence properties associated with bovine mastitis and alternative therapeutic modalities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1102–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.-Q.; Liu, Z.-Z.; Zhou, C.-K.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Luo, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.-G.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.-J. Trained immunity in recurrent Staphylococcus aureus infection promotes bacterial persistence. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1011918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Oh, D.H.; Broadbent, D.R.; Johnson, M.E.; Weimer, B.C.; Steele, J.L. Aromatic amino acid catabolism by lactococci. Le. Lait. 1997, 77, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.; Weimer, B.C.; Gann, R.; Desai, P.T.; Shah, J.D. The Yin and Yang of pathogens and probiotics: Interplay between Salmonella enterica sv. Typhimurium and Bifidobacterium infantis during co-infection. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1387498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabyan, N.; Park, D.; Foutouhi, S.; Weis, A.M.; Huang, B.C.; Williams, C.C.; Desai, P.; Shah, J.; Jeannotte, R.; Kong, N.; et al. Salmonella Degrades the Host Glycocalyx Leading to Altered Infection and Glycan Remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smug, B.J.; Opalek, M.; Necki, M.; Wloch-Salamon, D. Microbial lag calculator: A shiny-based application and an R package for calculating the duration of microbial lag phase. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2024, 15, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrusson, F.; Nguygen, T.K.; Najdovski, T.; Van Bambeke, F. Host Cell Oxidative Stress Induces Dormant Staphylococcus aureus Persisters. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0231321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrapetyan, M.; Williams, T.C.; Baxter, R.; Oliver, J.D. Viable but Nonculturable and Persister Cells Coexist Stochastically and Are Induced by Human Serum. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 4194–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, M.; Shambat, S.M.; Bergada-Pijuan, J.; Söderholm, S.; Boumasmoud, M.; Vulin, C.; Gómez-Mejia, A.; Antelo Varela, M.; Tripathi, V.; Götschi, S.; et al. Molecular reprogramming and phenotype switching in Staphylococcus aureus lead to high antibiotic persistence and affect therapy success. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2014920118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, E.J.; Bacigalupe, R.; Harrison, E.M.; Weinert, L.A.; Lycett, S.; Vrieling, M.; Robb, K.; Hoskisson, P.A.; Holden, M.T.G.; Feil, E.J.; et al. Gene exchange drives the ecological success of a multi-host bacterial pathogen. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stülke, J.; Hillen, W. Carbon. catabolite repression in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1999, 2, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrapetyan, M.; Williams, T.; Oliver, J.D. Relationship between the Viable but Nonculturable State and Antibiotic Persister Cells. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.P.; Clements, M.O.; Foster, S.J. Characterization of the Starvation-Survival Response of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, J.; Hobbs, G.; Nakouti, I. Persister cells: Formation, resuscitation and combative therapies. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 5899–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Eiff, C. Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants: A challenge to microbiologists and clinicians. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Zilm, P.S.; Kidd, S.P. Novel Research Models for Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variants (SCV) Development: Co-pathogenesis and Growth Rate. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foddai, A.C.G.; Grant, I.R. Methods for detection of viable foodborne pathogens: Current state-of-art and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4281–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Cell Viability Assays. Assay Guidance Manual; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Risoen, K.R.; Shaw, C.A.; Weimer, B.C. Nutritional Stress Leads to Persistence and Persister-like Growth in Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens 2025, 14, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030251
Risoen KR, Shaw CA, Weimer BC. Nutritional Stress Leads to Persistence and Persister-like Growth in Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens. 2025; 14(3):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030251
Chicago/Turabian StyleRisoen, Katie R., Claire A. Shaw, and Bart C. Weimer. 2025. "Nutritional Stress Leads to Persistence and Persister-like Growth in Staphylococcus aureus" Pathogens 14, no. 3: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030251
APA StyleRisoen, K. R., Shaw, C. A., & Weimer, B. C. (2025). Nutritional Stress Leads to Persistence and Persister-like Growth in Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens, 14(3), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030251







