Comparative Patho-Genomics of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Reveal Potential Host-Specific Virulence Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Genome Annotation
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of S. Enteritidis Isolates and Other S. enterica Serovars
2.4. Comparative Genome Analysis
2.5. Predicted Virulence/Fitness Gene Profiling
2.6. Orthologous Gene Clusters and Comparative Genome Matrices
3. Results
3.1. Overview of SEE1 and SEE2 Genomes
3.2. Predicted Virulence/Fitness Gene Profiles of SEE1 and SEE2
3.3. Genetic Relatedness of S. Enteritidis to Other S. enterica Serovars
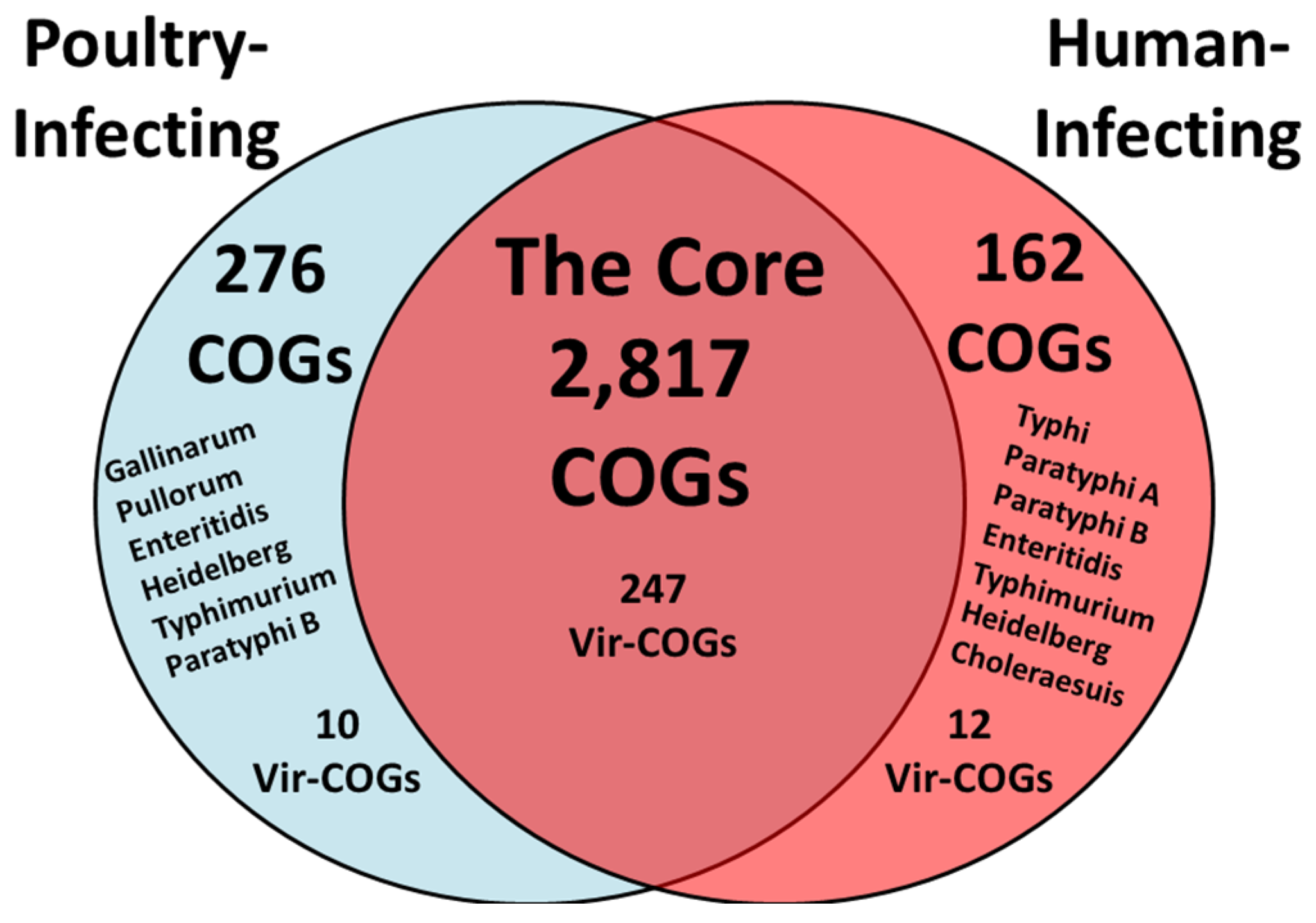
3.4. The Predicted Core and Host-Specific Virulence-Associated COGs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COGs | Clusters of orthologous genes; |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract; |
| WHO | World Health Organization; |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; |
| PFGE | Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis; |
| RAST | Rapid Annotation using Subsystem Technology; |
| ORFs | Open reading frames; |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism; |
| BRIG | Blast Ring Image Generator; |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information; |
| SPIs | Salmonella pathogenicity islands; |
| ANI | Average nucleotide identity; |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide; |
| OMPs | Outer membrane proteins; |
| PAIs | Pathogenicity-associated islands |
References
- Gal-Mor, O.; Boyle, E.C.; Grassl, G.A. Same Species, Different Diseases: How and Why Typhoidal and Non-Typhoidal Salmonella enterica Serovars Differ. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnsen, J.; Perez-Lopez, A.; Nuccio, S.-P.; Raffatellu, M. Exploiting Host Immunity: The Salmonella Paradigm. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenske, G.J.; Pouzou, J.G.; Pouillot, R.; Taylor, D.D.; Costard, S.; Zagmutt, F.J. The Genomic and Epidemiological Virulence Patterns of Salmonella enterica Serovars in the United States. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo-Simón, M.; Hart, R.; Ochman, H. Gene Flow and Species Boundaries of the Genus Salmonella. mSystems 2023, 8, e0029223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.T.; Porwollik, S.; Long, F.; Cheng, P.; Wollam, A.; Clifton, S.W.; Weinstock, G.M. Evolutionary Genomics of Salmonella enterica Subspecies. MBio 2013, 4, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, S.L.; Johnson, T.J.; Ricke, S.C.; Nayak, R.; Danzeisen, J. Salmonella Pathogenicity and Host Adaptation in Chicken-Associated Serovars. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 7, 582–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Calva, E.; Maloy, S. One Health and Food-Borne Disease: Salmonella Transmission between Humans, Animals, and Plants. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelawala, R.N.; Edison, L.K.; Kariyawasam, S. Pre-Harvest Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Control Strategies in Commercial Layer Chickens. Animals 2024, 14, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklemariam, A.D.; Al-Hindi, R.R.; Albiheyri, R.S.; Alharbi, M.G.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Filimban, A.A.R.; Al Mutiri, A.S.; Al-Alyani, A.M.; Alseghayer, M.S.; Almaneea, A.M.; et al. Human Salmonellosis: A Continuous Global Threat in the Farm-to-Fork Food Safety Continuum. Foods 2023, 12, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari Moghadam, M.; Rahimi, E.; Shakerian, A.; Momtaz, H. Prevalence of Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis Isolated from Poultry Meat: Virulence and Antimicrobial-Resistant Genes. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foodborne Illness Source Attribution Estimates—United States, 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ifsac/php/data-research/annual-report-2022.html (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Salmonella Infection (Salmonellosis). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/about/index.html (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Chai, S.J.; White, P.L.; Lathrop, S.L.; Solghan, S.M.; Medus, C.; McGlinchey, B.M.; Tobin-D’Angelo, M.; Marcus, R.; Mahon, B.E. Salmonella enterica Serotype Enteritidis: Increasing Incidence of Domestically Acquired Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, S488–S497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigley, P. Salmonella and the Chicken: Reflections on Salmonellosis and Its Control in the United Kingdom. Poult. Sci. Manag. 2024, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmonella-Information for Healthcare Professionals and Laboratories. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/general/technical.html (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Clinical Overview of Salmonellosis. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/hcp/clinical-overview/index.html (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Symptoms of Salmonella Infection. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/signs-symptoms/index.html (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Ebel, E.; Schlosser, W. Estimating the Annual Fraction of Eggs Contaminated with Salmonella Enteritidis in the United States. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 61, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georganas, A.; Graziosi, G.; Catelli, E.; Lupini, C. Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis in Broiler Chickens: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Animals 2024, 14, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trees, E.; Carleton, H.A.; Folster, J.P.; Gieraltowski, L.; Hise, K.; Leeper, M.; Nguyen, T.A.; Poates, A.; Sabol, A.; Tagg, K.A.; et al. Genetic Diversity in Salmonella enterica in Outbreaks of Foodborne and Zoonotic Origin in the USA in 2006–2017. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Payne, M.; Lan, R. In Silico Identification of Serovar-Specific Genes for Salmonella Serotyping. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.H.; Li, R.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, S.L. Identification of Genes to Differentiate Closely Related Salmonella Lineages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timme, R.E.; Pettengill, J.B.; Allard, M.W.; Strain, E.; Barrangou, R.; Wehnes, C.; Van Kessel, J.S.; Karns, J.S.; Musser, S.M.; Brown, E.W. Phylogenetic Diversity of the Enteric Pathogen Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Inferred from Genome-Wide Reference-Free SNP Characters. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 2109–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrin, S.; Wijnands, L.; Benincà, E.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Delfgou-van Asch, E.H.M.; Villa, L.; Orsini, M.; Losasso, C.; Olsen, J.E.; Barco, L. Assessing Phenotypic Virulence of Salmonella enterica across Serovars and Sources. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1184387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, R.K.; Thakur, Z.; Anand, T.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, B.N. Comparative Genome Analysis of Salmonella enterica Serovar Gallinarum Biovars Pullorum and Gallinarum Decodes Strain Specific Genes. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandt, C.H.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Tewari, D.; Ostroff, S.; Joyce, K.; M’ikanatha, N.M. A Comparison of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella from Humans and Food Animals Using Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, M.R.; Wijetunge, S.; Hewage, E.K.K.; Jayarao, B.M.; Kariyawasam, S. Genome Sequences of Two Strains of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Isolated from Shell Eggs. Am. Soc. Microbiol. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations Using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemis Genome Browser. Available online: https://www.sanger.ac.uk/tool/artemis/ (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Ning, Z.; Cox, A.J.; Mullikin, J.C. SSAHA: A Fast Search Method for Large DNA Databases. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1725–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. The RAxML-VI-HPC Version 2.2.3 Manual. Available online: https://cme.h-its.org/exelixis/resource/download/oldPage/RAxML-Manual.2.2.3.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Alikhan, N.-F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple Prokaryote Genome Comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.; Gish, W.; Miller, W. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Mackey, A.J.; Stoeckert, C.J.; Roos, D.S. OrthoMCL-DB: Querying a Comprehensive Multi-Species Collection of Ortholog Groups. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D363–D368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Call for Experts on the Microbiological Risk Assessment of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella spp. and Campylobacter spp. in Poultry Meat. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/articles-detail/call-for-experts-on-the-microbiological-risk-assessment-of-non-typhoidal-salmonella-spp.-and-campylobacter-spp.-in-poultry-meat (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Estimates of Foodborne Illness in the United States. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodborneburden/index.html (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Li, W.; Ren, Q.; Ni, T.; Zhao, Y.; Sang, Z.; Luo, R.; Li, Z.; Li, S. Strategies Adopted by Salmonella to Survive in Host: A Review. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzzau, S.; Brown, D.J.; Wallis, T.; Rubino, S.; Leori, G.; Bernard, S.; Casadesús, J.; Platt, D.J.; Olsen, J.E. Host Adapted Serotypes of Salmonella enterica. Epidemiol. Infect. 2000, 125, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal-Bayard, J.; Ramos-Morales, F. Salmonella Type III Secretion Effector SlrP Is an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase for Mammalian Thioredoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27587–27595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, M.R.; Saumya, D.; Wijetunge, S.; Bailey, M.L.; Gongati, S.R.; Goodfield, L.L.; Mangala, E.; Hewage, K.K.; Kennett, M.J.; Fedorchuk, C.; et al. Growth in Egg Yolk Enhances Salmonella Enteritidis Colonization and Virulence in a Mouse Model of Human Colitis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, K.; Yang, J.; Xue, J.; Lv, J.; Zhu, P.; Shi, L.; Li, S. A Host E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Regulates Salmonella Virulence by Targeting an SPI-2 Effector Involved in SIF Biogenesis. Mlife 2022, 2, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.K.; Griffiths, M.W. Quorum Sensing and Expression of Virulence in Escherichia coli O157:H7. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 85, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Shin, D.; Kim, M.; Park, J.; Lim, S.; Ryu, S. LsrR-Mediated Quorum Sensing Controls Invasiveness of Salmonella typhimurium by Regulating SPI-1 and Flagella Genes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Shin, D.; Ryu, S. Implication of Quorum Sensing in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Virulence: The LuxS Gene Is Necessary for Expression of Genes in Pathogenicity Island 1. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 4885–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Ding, X.; Bin, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, G. Regulatory Mechanisms between Quorum Sensing and Virulence in Salmonella. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, N.R.; Clayton, D.J.; Windhorst, D.; Vernikos, G.; Davidson, S.; Churcher, C.; Quail, M.A.; Stevens, M.; Jones, M.A.; Watson, M.; et al. Comparative Genome Analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis PT4 and Salmonella Gallinarum 287/91 Provides Insights into Evolutionary and Host Adaptation Pathways. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1624–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledeboer, N.A.; Frye, J.G.; McClelland, M.; Jones, B.D. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Requires the Lpf, Pef, and Tafi Fimbriae for Biofilm Formation on HEp-2 Tissue Culture Cells and Chicken Intestinal Epithelium. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3156–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffatellu, M.; Bäumler, A.J. Salmonella’s Iron Armor for Battling the Host and Its Microbiota. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiga, L.; Fansler, R.T.; Perera, Y.R.; Shealy, N.G.; Munneke, M.J.; David, H.E.; Torres, T.P.; Lemoff, A.; Ran, X.; Richardson, K.L.; et al. Iron Acquisition by a Commensal Bacterium Modifies Host Nutritional Immunity during Salmonella Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 1639–1654.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.B.R.; Gill, N.; Willing, B.P.; Antunes, L.C.M.; Russell, S.L.; Croxen, M.A.; Finlay, B.B. The Intestinal Microbiota Plays a Role in Salmonella-Induced Colitis Independent of Pathogen Colonization. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiennimitr, P.; Winter, S.E.; Winter, M.G.; Xavier, M.N.; Tolstikov, V.; Huseby, D.L.; Sterzenbach, T.; Tsolis, R.M.; Roth, J.R.; Bäumler, A.J. Intestinal Inflammation Allows Salmonella to Use Ethanolamine to Compete with the Microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17480–17485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videnska, P.; Sisak, F.; Havlickova, H.; Faldynova, M.; Rychlik, I. Influence of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Infection on the Composition of Chicken Cecal Microbiota. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.L. Pathobiology of Salmonella, Intestinal Microbiota, and the Host Innate Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Hensel, M. Systematic Analysis of the SsrAB Virulon of Salmonella enterica. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieye, Y.; Ameiss, K.; Mellata, M.; Curtiss, R. The Salmonella Pathogenicity Island (SPI) 1 Contributes More than SPI2 to the Colonization of the Chicken by Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlik, I.; Karasova, D.; Sebkova, A.; Volf, J.; Sisak, F.; Havlickova, H.; Kummer, V.; Imre, A.; Szmolka, A.; Nagy, B. Virulence Potential of Five Major Pathogenicity Islands (SPI-1 to SPI-5) of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis for Chickens. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.A.; Hulme, S.D.; Barrow, P.A.; Wigley, P. The Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 and Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 2 Type III Secretion Systems Play a Major Role in Pathogenesis of Systemic Disease and Gastrointestinal Tract Colonization of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium in the Chicken. Avian Pathol. 2007, 36, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.K.; Winardhi, R.S.; Periasamy, S.; Dykas, M.M.; Jie, Y.; Kenney, L.J. The Horizontally-Acquired Response Regulator SsrB Drives a Salmonella Lifestyle Switch by Relieving Biofilm Silencing. Elife 2016, 5, e10747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandio, V.; Torres, A.G.; Kaper, J.B. Quorum Sensing Escherichia coli Regulators B and C (QseBC): A Novel Two-Component Regulatory System Involved in the Regulation of Flagella and Motility by Quorum Sensing in E. coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 43, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, C.G.; Weinshenker, D.; Sperandio, V. QseC Mediates Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Virulence in Vitro and in Vivo. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 914–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Yeoh, B.S.; Xiao, X.; Kumar, M.; Bachman, M.; Borregaard, N.; Joe, B.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Interplay between Enterobactin, Myeloperoxidase and Lipocalin 2 Regulates E. coli Survival in the Inflamed Gut. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
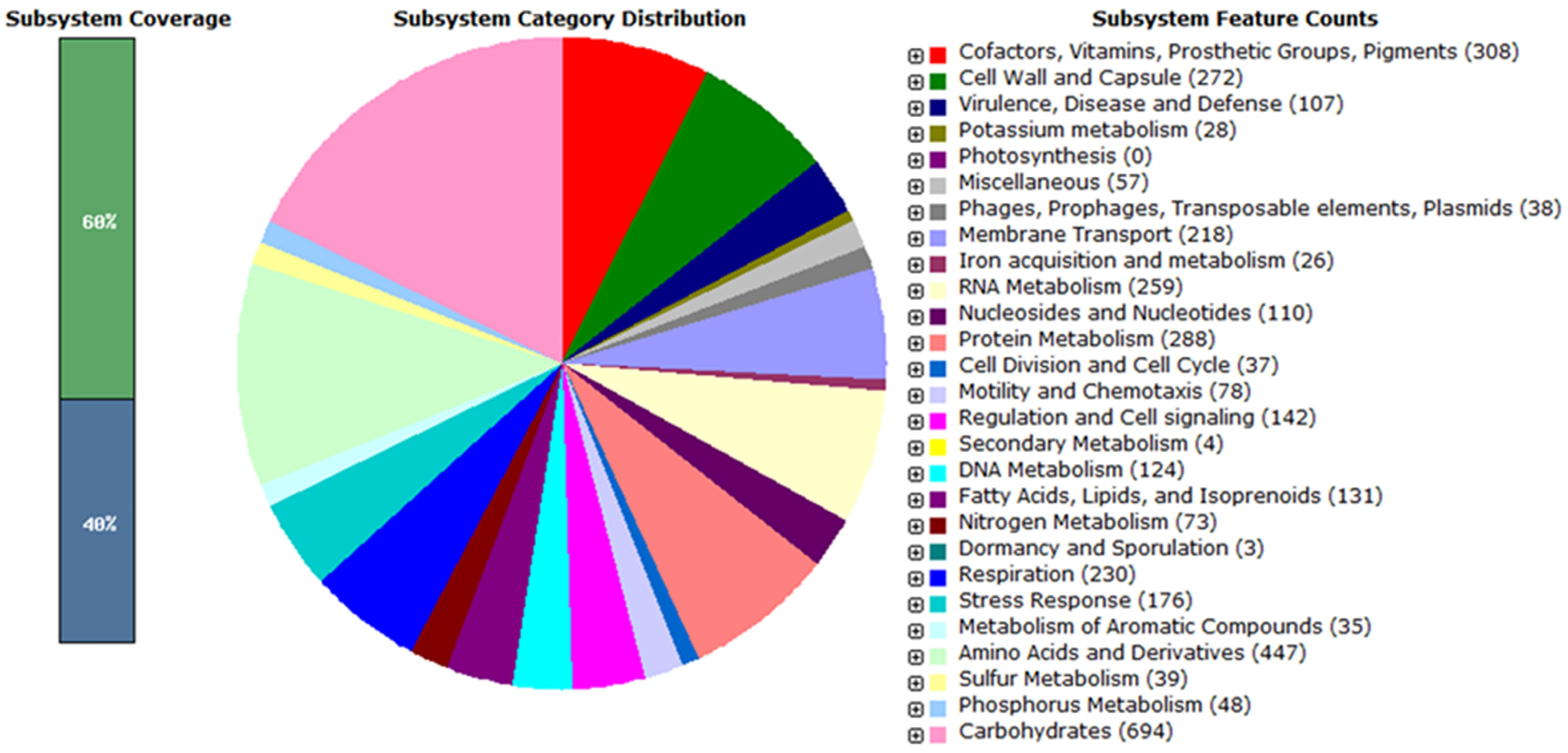

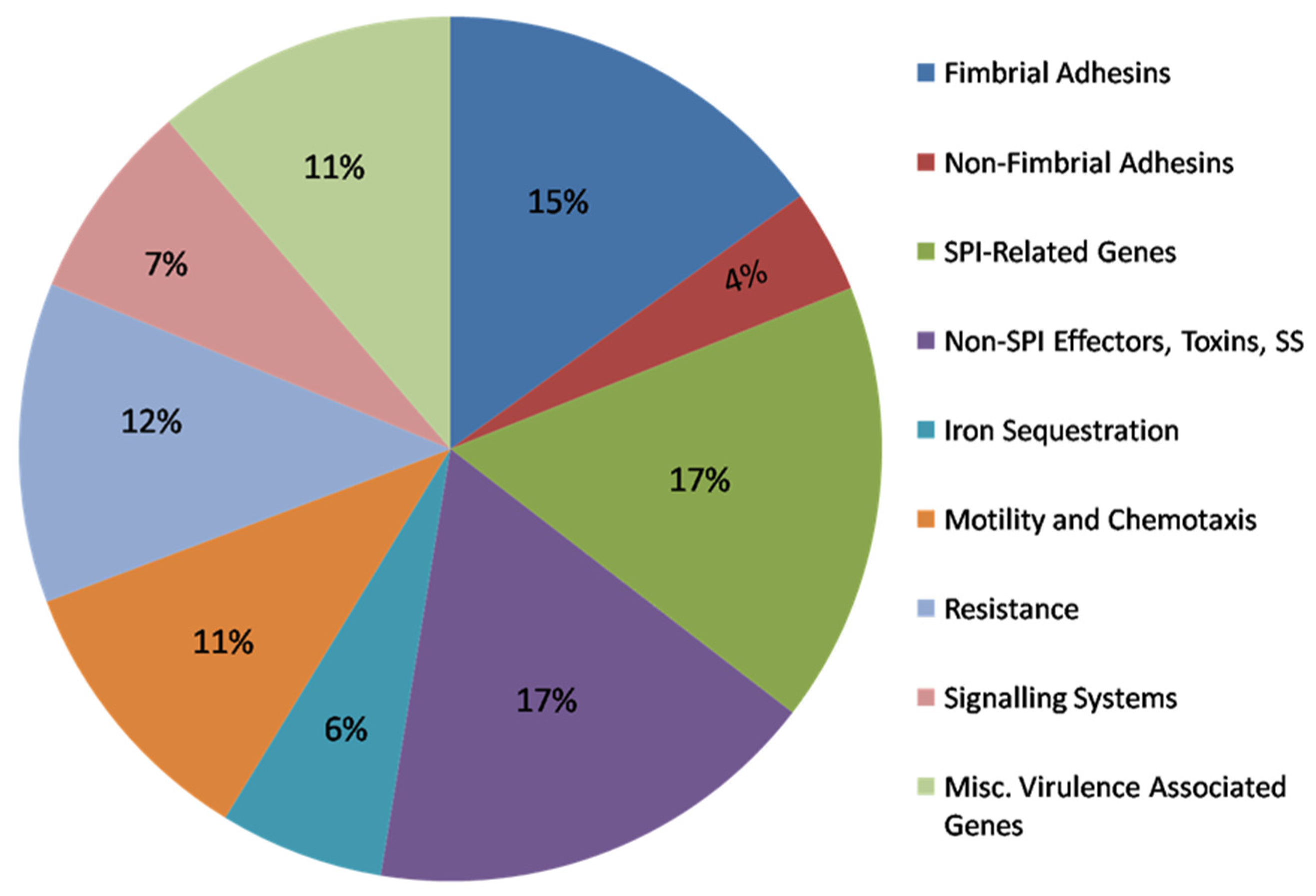
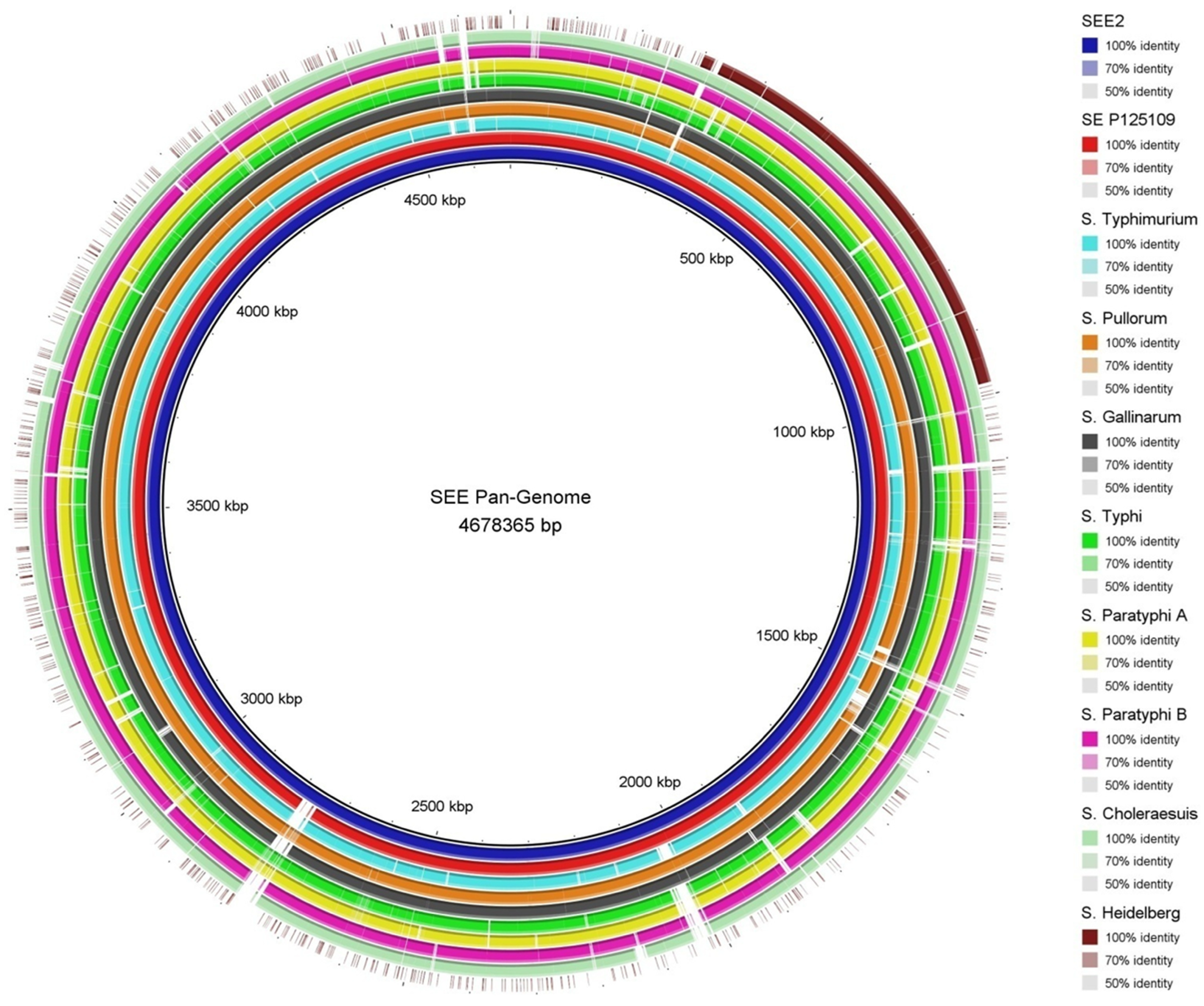
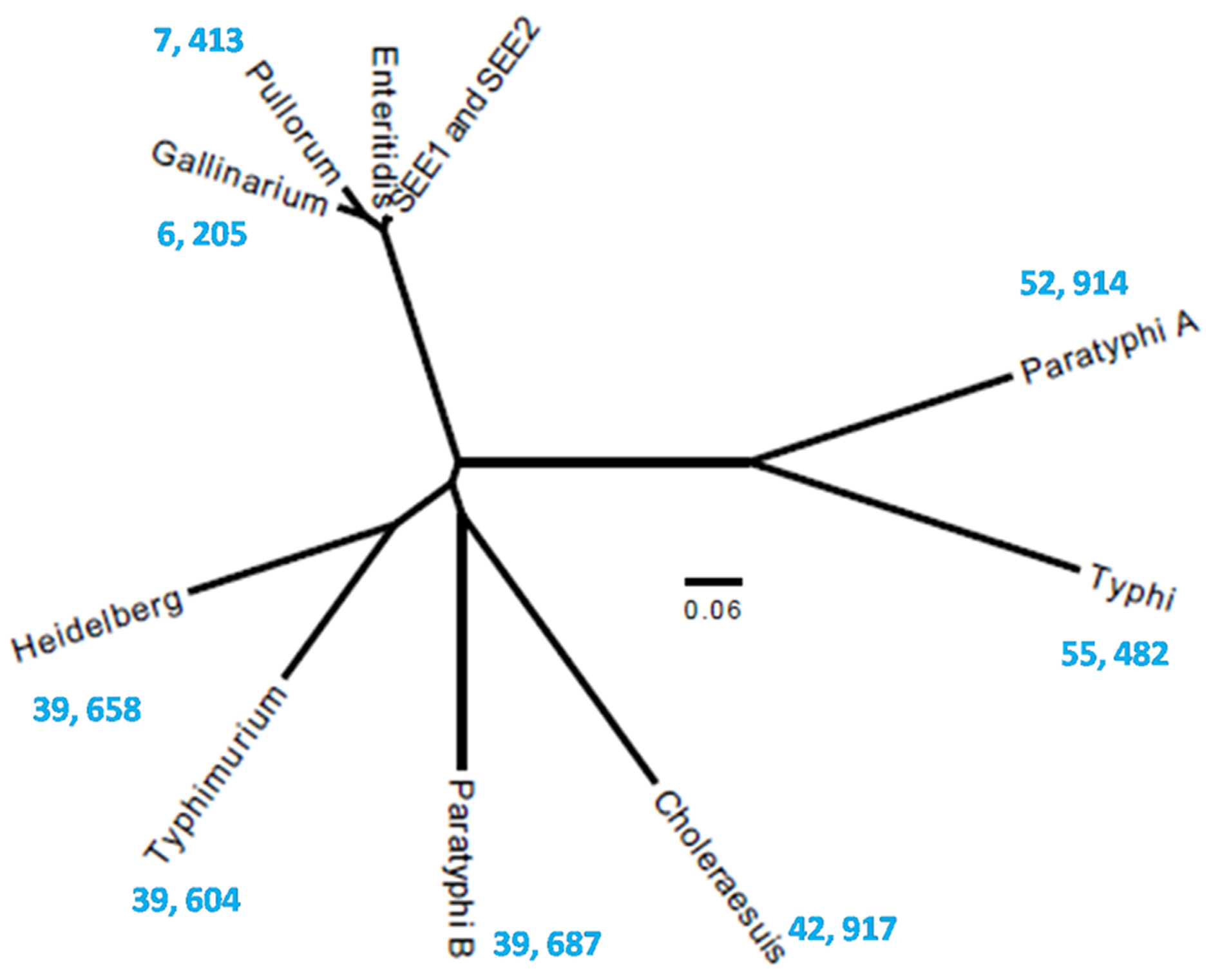
| Strain ID | Serovar | Accession Number | Date of Collection | Collection Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEE1 | Enteritidis | CP011790.1 * | 2010 | Pennsylvania, USA |
| SEE2 | Enteritidis | CP011791.1 * | 2007 | Pennsylvania, USA |
| P125109 | Enteritidis | AM933172.1 | 1991 | England, UK |
| EC20110360 | Enteritidis | CP007258.1 | 2014 | Alberta, Canada |
| EC20110359 | Enteritidis | CP007259.1 | 2013 | Alberta, Canada |
| EC20110358 | Enteritidis | CP007260.1 | 2009 | Alberta, Canada |
| EC20110357 | Enteritidis | CP007261.1 | 2003 | Alberta, Canada |
| EC20110356 | Enteritidis | CP007262.1 | 2009 | Alberta, Canada |
| EC20110361 | Enteritidis | CP007263.1 | 2009 | Alberta, Canada |
| EC20110223 | Enteritidis | CP007266.1 | 2005 | Alberta, Canada |
| Durban | Enteritidis | CP007507.1 | 2013 | Durban, South Africa |
| CDC968 | Enteritidis | CP007528.1 | 2010 | Ohio, USA |
| 77_1427 | Enteritidis | CP007598.1 | 1977 | Unknown, USA |
| SC-B67 | Choleraesuis | AE017220.1 | 2002 | Taiwan |
| C500 | Choleraesuis | CP007639.1 | 2010 | Yangzhou, China |
| ATCC 10708 | Choleraesuis | CP012344.2 | 2018 | Maryland, USA |
| A50 | Choleraesuis | CM001062.1 | 1999 | UK |
| 287/91 | Gallinarum | AM933173.1 | 2008 | Brazil |
| RKS5078 | Gallinarum | CP003047.1 | 2012 | Brazil |
| SL476 | Heidelberg | CP001120.1 | 2003 | Minnesota, USA |
| B182 | Heidelberg | CP003416.1 | 2012 | France |
| CFSAN002069 | Heidelberg | CP005390.2 | 2014 | Washington, USA |
| 41578 | Heidelberg | CP004086.1 | 2011 | Ohio, USA |
| ATCC 9150 | Paratyphi A | CP000026.1 | 2014 | Unknown |
| AKU_12601 | Paratyphi A | FM200053.1 | 2002 | Yemen |
| SPB7 | Paratyphi B | CP000886.1 | 2007 | Unknown |
| RKS4594 | Paratyphi C | CP000857.1 | 1916 | Norway |
| CDC1983-67 | Pullorum | CP003786.1 | 2013 | China |
| S06004 | Pullorum | CP006575.1 | 2014 | China |
| Ty2 | Typhi | AE014613.1 | 1970 | Russia |
| CT18 | Typhi | AL513382.1 | 2001 | Vietnam |
| Ty21a | Typhi | CP002099.1 | 1975 | Egypt |
| P-stx-12 | Typhi | CP003278.1 | 2012 | India |
| LT2 | Typhimurium | AE006468.1 | 1948 | England, UK |
| ST4/74 | Typhimurium | CP002487.1 | 1966 | England, UK |
| UK-1 | Typhimurium | CP002614.1 | 1991 | England, UK |
| 14028S | Typhimurium | CP001363.1 | 1960 | England, UK |
| U288 | Typhimurium | CP003836.1 | 2014 | England, UK |
| Salmonella Serovars | Number of Genomes Available | Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) in % |
|---|---|---|
| S. Gallinarum | 90 | 98.91 |
| S. Pullorum | 166 | 98.91 |
| S. Enteritidis | 40,234 | 98.9 |
| S. Heidelberg | 4750 | 99.14 |
| S. Typhimurium | 34,440 | 99.91 |
| S. Paratyphi A | 2726 | 98.55 |
| S. Paratyphi B | 2101 | 98.97 |
| S. Typhi | 9604 | 98.5 |
| S. Choleraesuis | 287 | 98.85 |
| Gene | Description |
|---|---|
| stiH | fimbriae |
| stiB | fimbrial chaperone |
| stiA | fimbrial subunit |
| SEE1_0554 | outer membrane protein |
| SEE1_0938 | secreted protein SopD-like protein |
| SEE1_1013 | outer membrane protein |
| SEE1_1540 | chemotaxis protein–ribose–galactose sensor receptor |
| lpfD | long polar fimbrial operon protein |
| lpfB | long polar fimbrial chaperone |
| lpfA | long polar fimbria |
| Gene | Description |
|---|---|
| yncD | predicted TonB-dependent iron receptor |
| flgK | flagellar hook-associated protein FlgK |
| ttrC | tetrathionate reductase complex subunit C |
| srfB | ssrAB-activated gene |
| flhA | flagellar biosynthesis protein FlhA |
| flhB | flagellar biosynthesis protein FlhB |
| pegC | outer membrane protein |
| iroD | enterochelin esterase |
| torS | hybrid sensory histidine kinase TorS |
| sthA | fimbrial chaperone protein |
| ttrB | tetrathionate reductase complex subunit B |
| sifB | secreted effector protein |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreau, M.R.; Edison, L.K.; Ivanov, Y.V.; Wijetunge, D.S.S.; Hewage, E.M.K.K.; Linder, J.E.; Kariyawasam, S. Comparative Patho-Genomics of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Reveal Potential Host-Specific Virulence Factors. Pathogens 2025, 14, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020128
Moreau MR, Edison LK, Ivanov YV, Wijetunge DSS, Hewage EMKK, Linder JE, Kariyawasam S. Comparative Patho-Genomics of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Reveal Potential Host-Specific Virulence Factors. Pathogens. 2025; 14(2):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020128
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreau, Matthew R., Lekshmi K. Edison, Yury V. Ivanov, Dona Saumya S. Wijetunge, Eranda Mangala K. Kurundu Hewage, Jessica E. Linder, and Subhashinie Kariyawasam. 2025. "Comparative Patho-Genomics of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Reveal Potential Host-Specific Virulence Factors" Pathogens 14, no. 2: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020128
APA StyleMoreau, M. R., Edison, L. K., Ivanov, Y. V., Wijetunge, D. S. S., Hewage, E. M. K. K., Linder, J. E., & Kariyawasam, S. (2025). Comparative Patho-Genomics of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Reveal Potential Host-Specific Virulence Factors. Pathogens, 14(2), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020128








