Integrating GPC3 with Other Biomarkers to Improve the Diagnosis of Early-Stage Liver Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
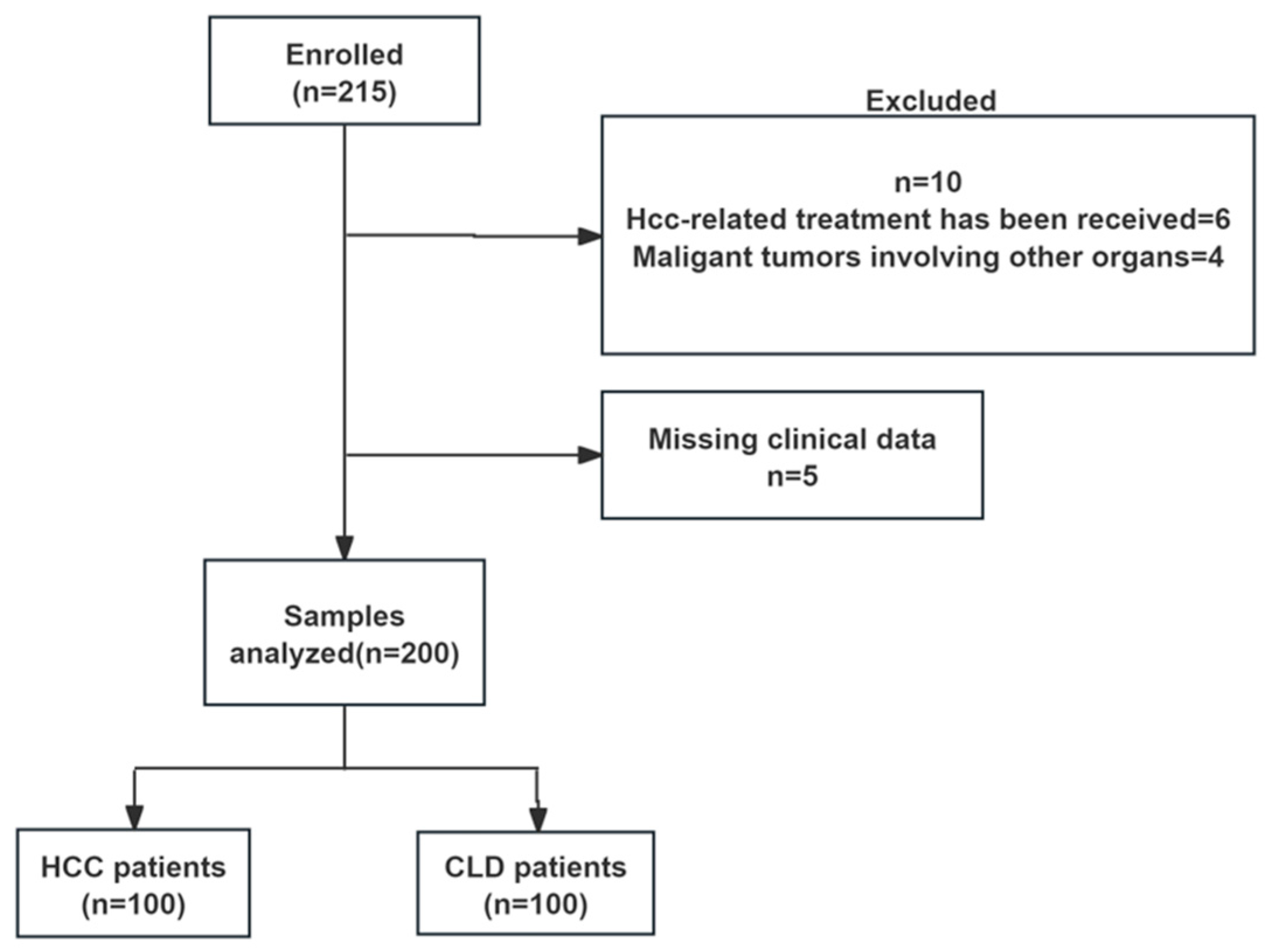
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Biochemical Examination and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
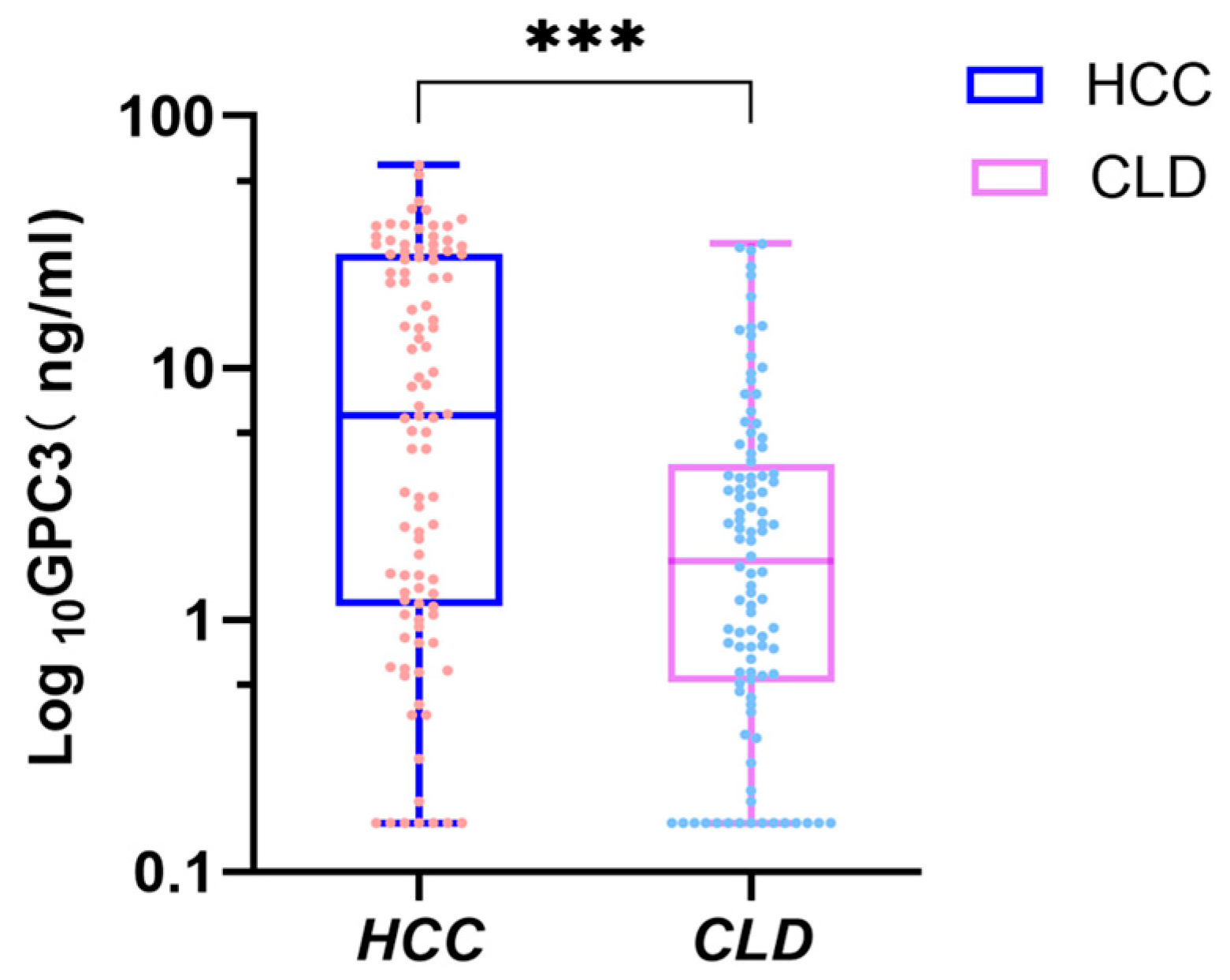
3.2. Analysis of Serum GPC3 Levels and Their Correlation with Clinical Characteristics of HCC
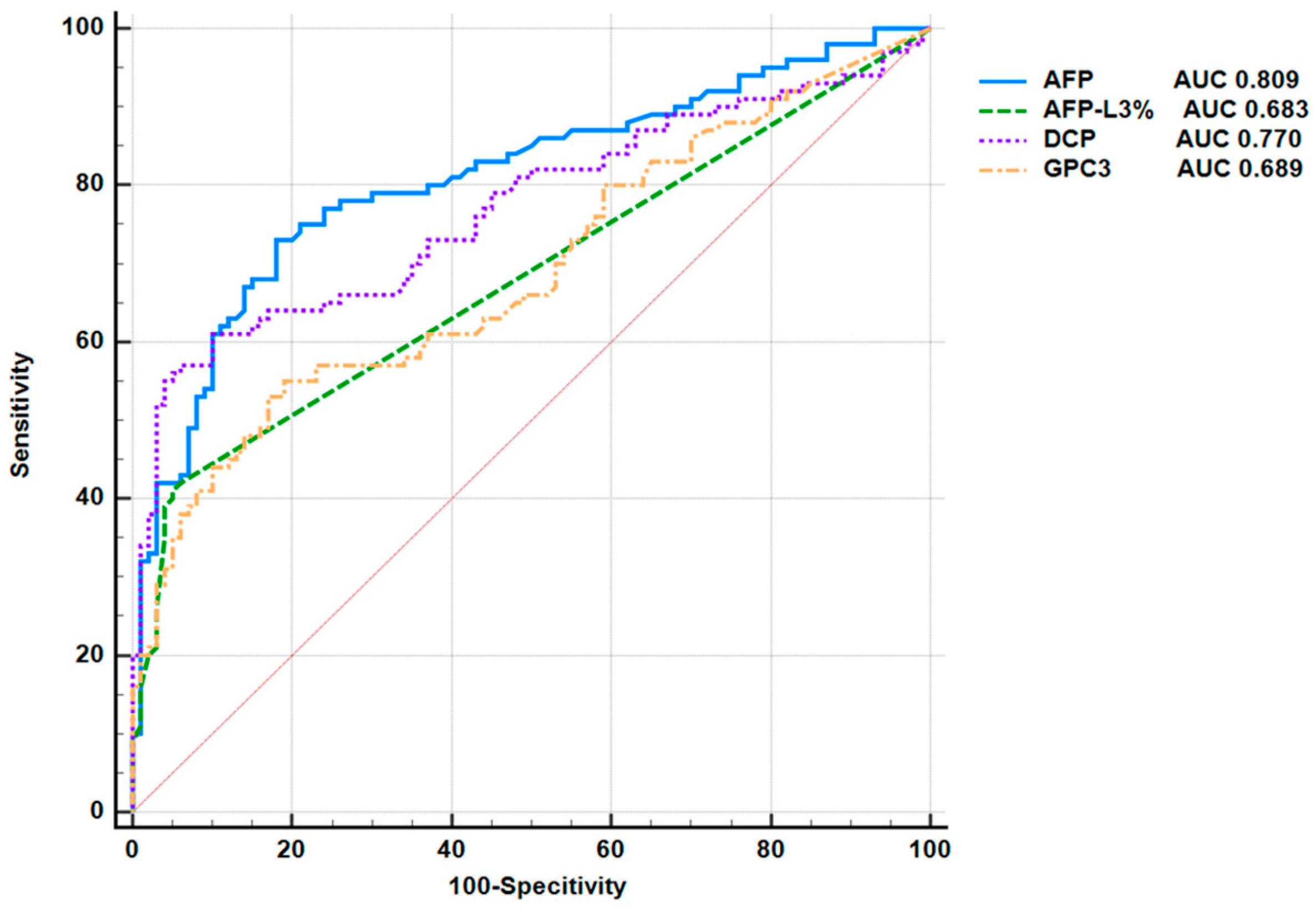
3.3. Application of Serum GPC3 Value in the Diagnosis of Liver Cancer
3.4. Efficacy of Serum GPC3 in Diagnosing AFP-Negative HCC
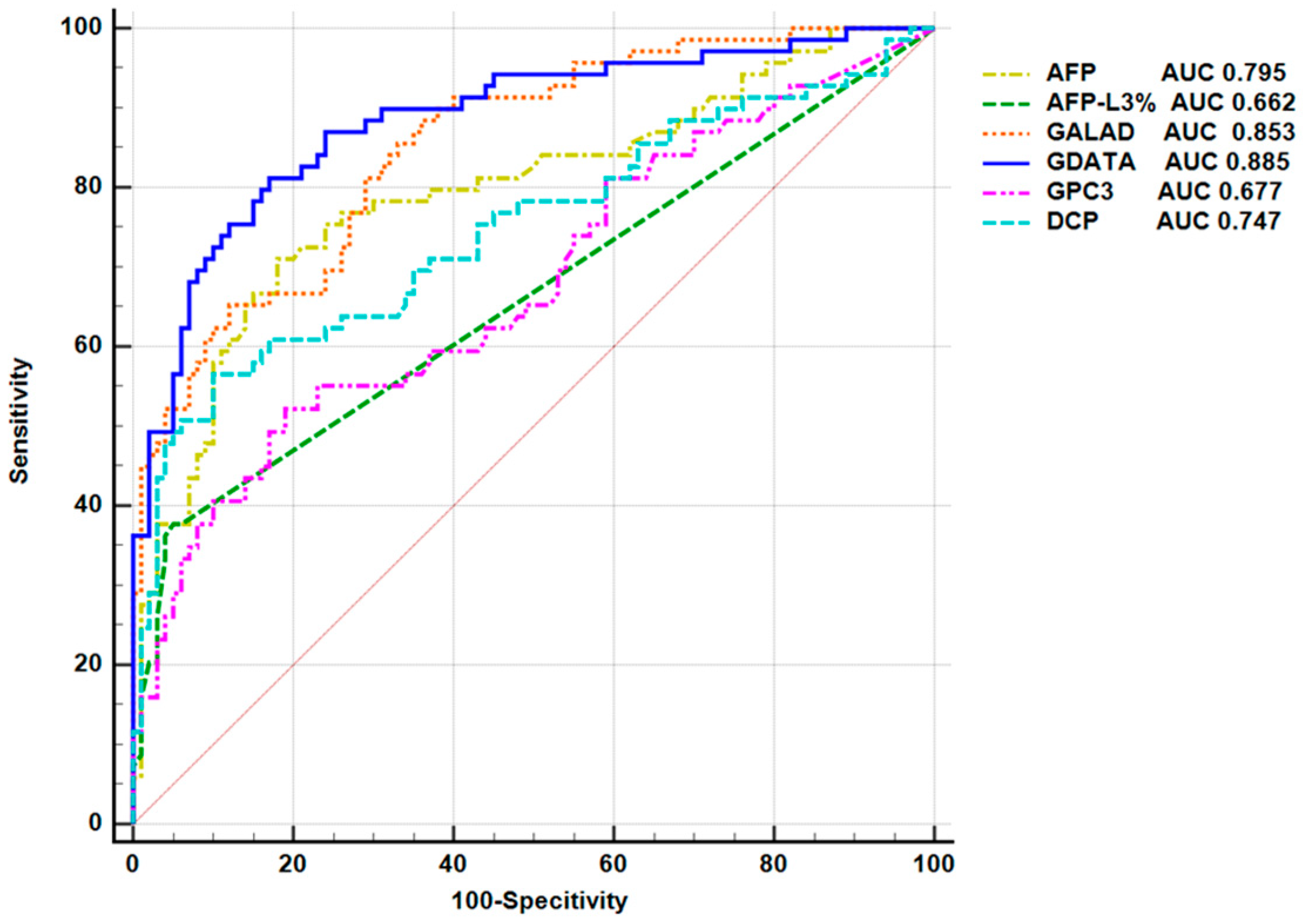
3.5. Efficacy of Serum GPC3 in Diagnosing Early HCC
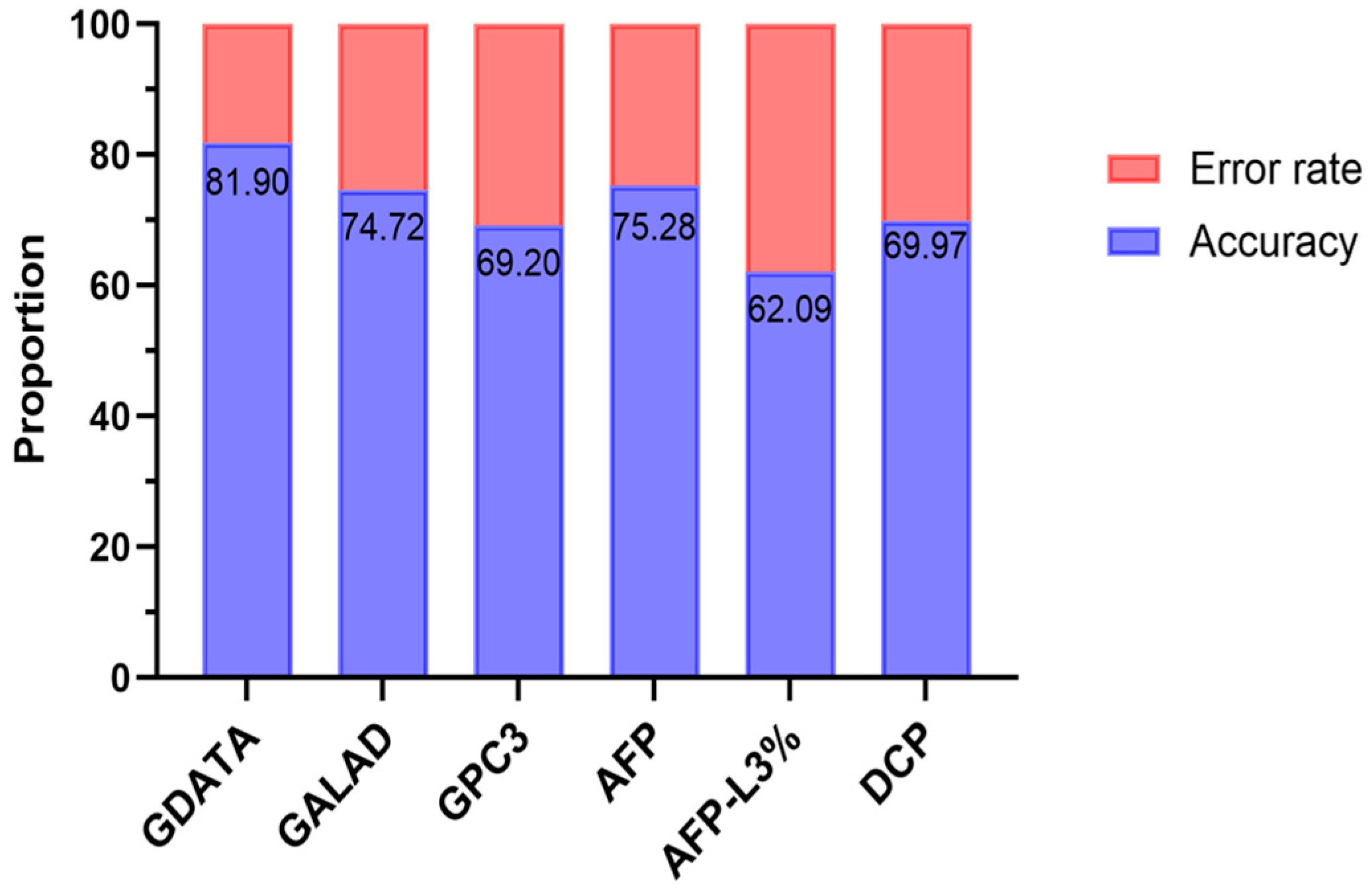
3.6. Construction and Evaluation of an Early HCC Diagnostic Model
0.056 × TBIL + 0.08 × AGE
4. Discussion
Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HBV | Hepatitis B Virus |
| GPC3 | Glypican-3 |
| HCC | Hepatocelllular carcinoma |
| AFP | Alpha-fetoprotein |
| DCP | Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin |
| CHB | Chronic Hepatitis B virus |
| CTC | Circulating tumor cell |
| CLD | Chronic liver disease |
| GPI | Glycophosphatidylinositol |
| AASLD | American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases |
| BCLC | Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer |
| WBC | White blood cells |
| PLT | Platelets |
| PDW | Platelet distribution width |
| ALB | Albumin |
| GLB | Globulin |
| A/G | Albumin/globulin |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| GGT | γ-glutamyl transpeptidase |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| TBIL | Total bilirubin |
| CBC | Complete blood count |
| LFT | Liver function test |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUROC | Area under the receiving operating characteristic curve |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| ALD | Alcohol-related liver disease |
| GALAD | Gender, age, AFP-L3%, AFP, DCP |
| GDATA | GPC3, DCP, AFP-L3%, TBIL, age |
References
- Fung, S.; Choi, H.S.; Gehring, A.; Janssen, H.L. Getting to HBV cure: The promising paths forward. Hepatology 2022, 76, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Fang, M.; Feng, H.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Zhou, L.; et al. N-glycan fingerprint predicts alpha-fetoprotein negative hepatocellular carcinoma: A large-scale multicenter study. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirino, A.; Marascio, N.; Branda, F.; Ciccozzi, A.; Romano, C.; Locci, C.; Azzena, I.; Pascale, N.; Pavia, G.; Matera, G.; et al. Viral Hepatitis: Host Immune Interaction, Pathogenesis and New Therapeutic Strategies. Pathogens 2024, 13, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose-Abrego, A.; Roman, S.; Laguna-Meraz, S.; Panduro, A. Host and HBV Interactions and Their Potential Impact on Clinical Outcomes. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, L.; Wei, W.; Huang, G.; Liu, J. GPC3-targeted immunoPET imaging of hepatocellular carcinomas. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2682–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Li, S.; Holmes, J.A.; Tu, Z.; Li, Y.; Cai, D.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Yang, C.; Jiao, B.; et al. MicroRNA 130a Regulates both Hepatitis C Virus and Hepatitis B Virus Replication through a Central Metabolic Pathway. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02009-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hong, J.; Li, W.; Sheng, Q.; Mezzetti, O.; Xu, M.; Salloum, S.; Chung, R.T.; Lin, W. HBV promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HCC and liver fibrosis through JNK-mediated autophagy. Hepatol. Commun. 2025, 9, e0730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.T.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Lu, P.; Xu, L.; Yuan, H.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Z.S.; Wang, N. Biomarkers for diagnosis and therapeutic options in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danpanichkul, P.; Duangsonk, K.; Chen, V.L.; Saokhieo, P.; Dejvajara, D.; Sukphutanan, B.; Aboona, M.B.; Lopimpisuth, C.; Pang, Y.; Ibrahim, A.F.; et al. Global burden of HBV-related liver disease: Primary liver cancer due to chronic HBV infection increased in over one-third of countries globally from 2000 to 2021. Hepatology 2025, 82, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, R.; Suzuki, H.; Lemaitre, L.; Kubota, N.; Hoshida, Y. Molecular and immune landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma to guide therapeutic decision-making. Hepatology 2025, 81, 1038–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucio-Ortiz, L.; Enriquez-Navarro, K.; Maldonado-Rodriguez, A.; Torres-Flores, J.M.; Cevallos, A.M.; Salcedo, M.; Lira, R. Occult Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Hepatic Diseases and Its Significance for the WHO‘s Elimination Plan of Viral Hepatitis. Pathogens 2024, 13, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwude, V.N.; Lesi, O.A.; Onyekwere, C.; Charpentier, E.; Hubschen, J.M. Clinical Characteristics of Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients in Southwest Nigeria. Pathogens 2025, 14, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderaro, J.; Seraphin, T.P.; Luedde, T.; Simon, T.G. Artificial intelligence for the prevention and clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1348–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Pinyol, R.; Kelley, R.K.; El-Khoueiry, A.; Reeves, H.L.; Wang, X.W.; Gores, G.J.; Villanueva, A. Molecular pathogenesis and systemic therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaranathan-Reghupaty, S.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology, etiology and molecular classification. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 149, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.L.; Huang, L.P.; Lu, W.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zou, D.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.L. Development of a diagnostic nomogram for alpha-fetoprotein-negative hepatocellular carcinoma based on serological biomarkers. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 16, 2463–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Luo, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Zuo, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Xi, Q.; Li, G.; et al. Diagnostic value of 5 serum biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma with different epidemiological backgrounds: A large-scale, retrospective study. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 18, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuc, D.; Preda, C.M.; Sandra, I.; Baicus, C.; Cerban, R.; Constantinescu, I.; Olteanu, A.O.; Ciora, C.A.; Manuc, T.; Chiriac, D.E.; et al. Signification of Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels in Cases of Compensated Cirrhosis and Hepatitis C Virus without Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Med. Life 2020, 13, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Shigeta, K.; Noda, K.; Fukumoto, Y.; Nishimura, H.; Mizuta, M.; Takemoto, T. Clinical implications of alpha-fetoprotein in liver cirrhosis: Five-year follow-up study. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 1980, 27, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, H.; Ali, M.J.; Susheela, A.T.; Khan, I.W.; Luna-Cuadros, M.A.; Khan, M.M.; Lau, D.T.-Y. Update on the applications and limitations of alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, H.A.; Zangi, M.; Fathi, M.; Vakili, K.; Hassan, M.; Rismani, E.; Hossein-Khannazer, N.; Vosough, M. GPC-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma; A novel biomarker and molecular target. Exp. Cell Res. 2025, 444, 114391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wei, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, T.; Jiang, H.; Song, B. Preoperative prediction of glypican-3 positive expression in solitary hepatocellular carcinoma on gadoxetate-disodium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 973153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Gao, F.; Gao, Z.; Ao, L.; Li, N.; Ma, S.; Jia, M.; Li, N.; Lu, P.; Sun, B.; et al. Shed antigen-induced blocking effect on CAR-T cells targeting Glypican-3 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurro, M.; Wanless, I.R.; Sherman, M.; Deboer, G.; Shi, W.; Miyoshi, E.; Filmus, J. Glypican-3: A novel serum and histochemical marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Huang, Z.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y.; Lin, S.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z. Significance of Glypican-3 (GPC3) Expression in Hepatocellular Cancer Diagnosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailemia, M.J.; Park, D.; Lebrilla, C.B. Glycans and glycoproteins as specific biomarkers for cancer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Liang, J.; Wang, W. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic significance of Glypican-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1012418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Shang, W.; Yu, X.; Tian, J. Glypican-3: A promising biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and treatment. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 741–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.J.; Pirrie, S.J.; Cox, T.F.; Berhane, S.; Teng, M.; Palmer, D.; Morse, J.; Hull, D.; Patman, G.; Kagebayashi, C.; et al. The detection of hepatocellular carcinoma using a prospectively developed and validated model based on serological biomarkers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 1, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Xiao, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Gao, C.; Clinical Laboratory Society of Chinese Rehabilitation Medicine Association; Molecular Diagnostics Society of Shanghai Medical Association; Tumor Immunology Branch of Shanghai Society for Immunology. Chinese expert consensus statement on the clinical application of AFP/AFP-L3%/DCP using GALAD and GALAD-like algorithm in HCC. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2023, 37, e24990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Llovet, J.M.; Yarchoan, M.; Mehta, N.; Heimbach, J.K.; Dawson, L.A.; Jou, J.H.; Kulik, L.M.; Agopian, V.G.; Marrero, J.A.; et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1922–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Duan, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, T.; Li, S.; Tan, L.; Shao, T.; Jeyarajan, A.J.; et al. Differentially expressed immune response genes in COVID-19 patients based on disease severity. Aging 2021, 13, 9265–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, P.; Jeyarajan, A.J.; Ma, C.; Zhu, K.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, N.; Li, M.; Shao, T.; Han, M.; et al. Assessment of Non-invasive Markers for the Prediction of Esophageal Variceal Hemorrhage. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 770836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, L.; Shao, T.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Holmes, J.A.; Lin, W.; Han, M. COVID-19 induced liver function abnormality associates with age. Aging 2020, 12, 13895–13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tan, L.; Jiang, N.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Li, S. Assessment of nomogram model for the prediction of esophageal variceal hemorrhage in hepatitis B-induced hepatic cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 36, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X. Evaluation for clinical and prognostic implications of glypican-3 and α-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma: A new subtype? Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 3443–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, L. All of Statistics: A Concise Course in Statistical Inference; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta, S.; Aihara, T.; Nakajima, T.; Yamanaka, N. Alpha-fetoprotein as a prognostic factor in alpha-fetoprotein-negative hepatocellular carcinoma-integration into post-resection prognostic nomograms. Contemp. Oncol. 2025, 29, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, K.; Felden, J.V.; Frundt, T.W.; Krause, J.; Werner, T.; Casar, C.; Jung, C.; Ittrich, H.; Sterneck, M.; Li, J.; et al. Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Since the Introduction of the German Clinical Practice Guideline in 2013. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2021, 118, 540–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-S.; Zhou, W.-L.; Li, H.-S.; Han, Y.-J.; Wang, Q.-S.; Wu, H.-B. Low glucose metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma with GPC3 expression. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangkijvanich, P.; Chanmee, T.; Komtong, S.; Mahachai, V.; Wisedopas, N.; Pothacharoen, P.; Kongtawelert, P. Diagnostic role of serum glypican-3 in differentiating hepatocellular carcinoma from non-malignant chronic liver disease and other liver cancers. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burciu, C.; Șirli, R.; Bende, R.; Popa, A.; Vuletici, D.; Miuțescu, B.; Rațiu, I.; Popescu, A.; Sporea, I.; Dănilă, M. A Statistical Approach to the Diagnosis and Prediction of HCC Using CK19 and Glypican 3 Biomarkers. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jin, R.; Zhang, X.; Lv, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, K.; Li, N.; Chen, D. Oncogenic activation of glypican-3 by c-Myc in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Yeon, J.E.; Suh, S.J.; Lee, S.J.; Yoon, E.L.; Kang, K.; Yoo, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, Y.S.; Yim, H.J.; et al. Clinical utility of plasma glypican-3 and osteopontin as biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yin, X.; Ying, J.; Zhang, B. Golgi protein 73 versus alpha-fetoprotein as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma: A diagnostic meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhai, D.; Liu, J.; Cai, J.; Wang, Y.; Jing, L.; Du, Z. Assessment of the Clinical Utility of Glypican 3 as a Serum Marker for the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto Marques, H.; Gomes Da Silva, S.; De Martin, E.; Agopian, V.G.; Martins, P.N. Emerging biomarkers in HCC patients: Current status. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 82, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, S.; Tümen, D.; Volz, B.; Neumeyer, K.; Egler, N.; Kunst, C.; Tews, H.C.; Schmid, S.; Kandulski, A.; Müller, M.; et al. HCC biomarkers–state of the old and outlook to future promising biomarkers and their potential in everyday clinical practice. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1016952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, T.-C.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.-C.; Wan, Y.-J.Y. Glypican-3: A molecular marker for the detection and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Res. 2020, 4, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowska-Ciemny, J.; Szymański, M.; Kuszerska, A.; Malewski, Z.; von Kaisenberg, C.; Kocyłowski, R. The Role of Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) in Contemporary Oncology: The Path from a Diagnostic Biomarker to an Anticancer Drug. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, H.; Bai, G.; Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Bao, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, H. alpha-1,3-Fucosyltransferase-VII siRNA inhibits the expression of SLex and hepatocarcinoma cell proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhou, X.; Lin, G.; Luo, C.; Meng, W.; Lv, C.; Chen, Y.; Wen, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Deciphering the Oncogenic Landscape of Hepatocytes Through Integrated Single-Nucleus and Bulk RNA-Seq of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2412944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Feng, X.; Inagaki, Y.; Song, T.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Ma, K.; Li, Q.; Kong, D.; et al. Clinical utility of simultaneous measurement of alpha-fetoprotein and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin for diagnosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in China: A multi-center case-controlled study of 1153 subjects. Biosci. Trends 2014, 8, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, W. Alpha-fetoprotein-L3 and Golgi protein 73 may serve as candidate biomarkers for diagnosing alpha-fetoprotein-negative hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Zheng, C.; Zhong, Q.; Shi, Y.; Han, X. Diagnostic value of serum glypican-3 alone and in combination with AFP as an aid in the diagnosis of liver cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 79, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Li, W.; Shang, S.; Qin, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Diagnosis of AFP-negative early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma using Fuc-PON1. Discov. Med. 2017, 23, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.F.; Kroeniger, K.; Wang, C.W.; Jang, T.Y.; Yeh, M.L.; Liang, P.C.; Wei, Y.J.; Hsu, P.Y.; Huang, C.I.; Hsieh, M.Y.; et al. Surveillance Imaging and GAAD/GALAD Scores for Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2024, 12, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.-C.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Ding, Q.; Li, N.; Fu, T.-T.; Zhang, G.-X.; He, Q.-Q.; Shen, F.; Yang, T.; Zhu, H. The Performance of GALAD Score for Diagnosing Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Tayob, N.; Mehta, A.; Marrero, J.A.; El Serag, H.; Jin, Q.; Saenz De Viteri, C.; Fobar, A.; Parikh, N.D. GALAD demonstrates high sensitivity for HCC surveillance in a cohort of patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2022, 75, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, T.L.; Parikh, N.D.; Roberts, L.R.; Schwartz, M.E.; Nguyen, M.H.; Befeler, A.; Page-Lester, S.; Tayob, N.; Srivastava, S.; Rinaudo, J.A.; et al. A Phase 3 Biomarker Validation of GALAD for the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2025, 168, 316–326.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | HCC | CLD | Statistic | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 100) | (n = 100) | |||
| Age (years) | 60.85 ± 11.22 | 48.80 ± 10.87 | t = 7.72 | <0.001 *** |
| Gender [n (%)] | X2 = 1.947 | 0.163 | ||
| Male | 75 (75) | 66 (66) | ||
| Female | 25 (25) | 34 (34) | ||
| Etiology [n (%)] | ||||
| HBV | 69 (69) | 96 (96) | X2 = 25.247 | <0.001 *** |
| HCV | 2 (2) | 0 | - | 0.497 |
| ALD | 2 (2) | 0 | - | 0.497 |
| HBV + ALD | 21 (21) | 4 (4) | X2 = 13.211 | <0.001 *** |
| HCV + ALD | 2 (2) | 0 | - | 0.497 |
| Others | 4 (4) | 0 | - | 0.497 |
| Child-Pugh grade [n (%)] | X2 = 23.464 | <0.001 *** | ||
| A (5–6) | 79 (79) | 100 (100) | ||
| B (7–9) | 21 (21) | 0 | ||
| C (10–15) | 0 | 0 | ||
| ALT (U/L) | 29.00 (21.00~40.75) | 23.00 (16.25~33.00) | Z = −2.705 | 0.07 |
| AST (U/L) | 32.50 (24.25~49.00) | 22.00 (18.00~29.00) | Z = −5.901 | <0.001 *** |
| TBIL (umol/L) | 19.300 (13.700~26.450) | 14.900 (11.200~20.775) | Z = −3.382 | 0.001 ** |
| ALP (U/L) | 101.50 (81.25~137.25) | 79.00 (62.00~98.25) | Z = −4.900 | <0.001 *** |
| GGT(U/L) | 57.00 (30.00~99.50) | 27.50 (19.00~48.00) | Z = −5.734 | <0.001 *** |
| ALB (g/L) | 42.300 (36.300~46.475) | 46.000 (42.825~48.175) | Z = −4.750 | <0.001 *** |
| Characteristics | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Maximum tumor diameter (cm) | |
| ≤2 | 33 (33) |
| >2, ≤3 | 36 (36) |
| >3, ≤5 | 17 (17) |
| >5, ≤10 | 10 (10) |
| >10 | 4 (4) |
| Number of tumors | |
| 1 | 81 (81) |
| 2–3 | 13 (13) |
| ≥4 | 6 (6) |
| Vascular invasion/metastasis | 13 (13) |
| BCLC stage | |
| 0 | 29 (29) |
| A | 40 (40) |
| B | 19 (19) |
| C | 12 (12) |
| D | 0 |
| Variables | GPC3 Level (ng/mL) | Statistical Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | Z = −0.025 | 0.98 | |
| ≤50 | 10.52 (0.77~28.21) | ||
| >50 | 6.49 (1.15~28.45) | ||
| Gender | Z = −0.752 | 0.452 | |
| Male | 5.55 (1.00~28.29) | ||
| Female | 9.63 (3.15~26.38) | ||
| Child–Pugh Classification | Z = −0.351 | 0.752 | |
| Class A (5–6) | 7.04 (1.16~28.25) | ||
| Class B (7–9) | 6.44 (0.82~29.88) | ||
| Tumor Size (cm) | Z = −0.243 | 0.808 | |
| ≤3 | 7.04 (1.27~28.29) | ||
| >3 | 6.30 (1.07~28.58) | ||
| Number of Tumors | Z = −1.955 | 0.051 | |
| Single | 8.51 (1.60~28.91) | ||
| Multiple | 1.47 (0.62~25.90) | ||
| BCLC Staging | Z = −1.174 | 0.24 | |
| 0/A | 5.62 (1.11~23.86) | ||
| B/C | 11.91 (1.13~33.20) | ||
| Metastasis | Z = −1.825 | 0.068 | |
| No Metastasis | 6.30 (1.05~26.76) | ||
| Vascular Invasion/Extra— Hepatic Metastasis | 28.25 (2.66~32.03) |
| Variables | AUC | Cut-Off Value | Sensitivity | Specificity | Youden Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPC3 | 0.689 | >5.53 | 55% | 81% | 0.36 |
| AFP | 0.809 | >3.85 | 73% | 82% | 0.55 |
| AFP-L3% | 0.683 | >6% | 42% | 94% | 0.36 |
| DCP | 0.77 | >18.98 | 61% | 90% | 0.51 |
| GPC3 + AFP | 0.796 | >0.39 | 71% | 81% | 0.52 |
| GPC3 + DCP | 0.803 | >0.40 | 67% | 84% | 0.51 |
| GPC3 + AFP-L3% | 0.792 | >0.46 | 68% | 87% | 0.55 |
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | p Value | Multivariate Analysis | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | |||
| Age (years) | 1.103 | 1.063–1.144 | <0.001 | 1.084 | 1.031–1.139 | 0.002 |
| Sex (male) | 0.635 | 0.319–1.261 | 0.194 | |||
| WBC | 0.786 | 0.649–0.952 | 0.014 | 0.795 | 0.563–1.122 | 0.795 |
| RDW-CV | 0.991 | 0.969–1.014 | 0.456 | |||
| PDW | 0.954 | 0.806–1.130 | 0.586 | |||
| ALB | 0.898 | 0.844–0.954 | 0.001 | 1.011 | 0.916–1.116 | 0.827 |
| ALT | 1.007 | 0.997–1.018 | 0.190 | |||
| AST | 1.015 | 0.999–1.032 | 0.062 | 0.99 | 0.977–1.003 | 0.135 |
| AST/ALT | 2.253 | 1.188–4.270 | 0.013 | 1.88 | 0.848–4.168 | 0.12 |
| GGT | 1.009 | 1.002–1.017 | 0.011 | 1.007 | 0.997–1.016 | 0.175 |
| ALP | 1.012 | 1.003–1.021 | 0.004 | 0.994 | 0.980–1.008 | 0.403 |
| TBIL | 1.057 | 1.021–1.095 | 0.002 | 1.058 | 1.002–1.118 | 0.043 |
| AFP | 1.01 | 1.002–1.018 | 0.013 | 1.004 | 0.995–1.013 | 0.382 |
| LN (AFP-L3%) | 14.99 | 4.465–50.319 | <0.001 | 5.432 | 1.160–25.427 | 0.032 |
| DCP | 1.034 | 1.010–1.085 | 0.005 | 1.021 | 1.003–1.040 | 0.022 |
| GPC3 | 1.081 | 1.043–1.121 | <0.001 | 1.098 | 1.044–1.155 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Tan, L.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Mezzetti, O.; et al. Integrating GPC3 with Other Biomarkers to Improve the Diagnosis of Early-Stage Liver Cancer. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14121189
Xu J, Tan L, Jiang N, Zhang F, Wang J, Li F, Wang J, Li H, Chen L, Mezzetti O, et al. Integrating GPC3 with Other Biomarkers to Improve the Diagnosis of Early-Stage Liver Cancer. Pathogens. 2025; 14(12):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14121189
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jing, Lin Tan, Ning Jiang, Feng Zhang, Jinling Wang, Fengcheng Li, Jin Wang, Heng Li, Lichang Chen, Olivia Mezzetti, and et al. 2025. "Integrating GPC3 with Other Biomarkers to Improve the Diagnosis of Early-Stage Liver Cancer" Pathogens 14, no. 12: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14121189
APA StyleXu, J., Tan, L., Jiang, N., Zhang, F., Wang, J., Li, F., Wang, J., Li, H., Chen, L., Mezzetti, O., Lin, W., Li, S., & Gao, Y. (2025). Integrating GPC3 with Other Biomarkers to Improve the Diagnosis of Early-Stage Liver Cancer. Pathogens, 14(12), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14121189






