Clinical Associations and Coexistence of Polyomavirus DNAemia with EBV and CMV in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Patients, Including HCT Recipients—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
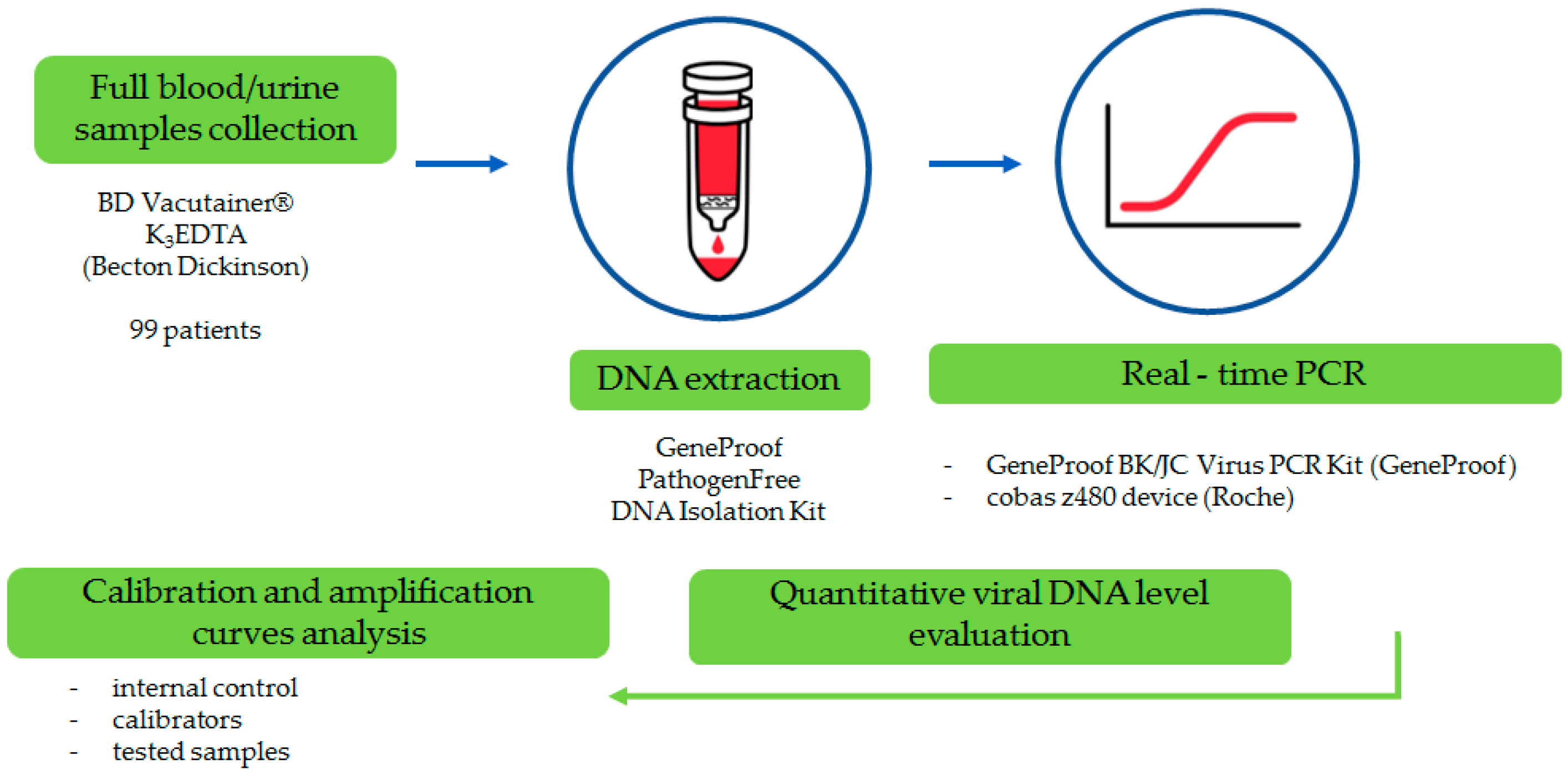
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALAT | alanine aminotransferase |
| ALL | acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| AML | acute myeloid leukemia |
| CMV | cytomegalovirus |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| GvHD | graft-versus-host disease |
| HCT | hematopoietic cell transplantation |
| IU | international unit applied to express the standardized viral DNA level |
| N/A | not applicable |
| PTLD | post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease |
| SAA | severe aplastic anemia. |
References
- Prezioso, C.; Pietropaolo, V. BK Virus and Transplantation. Viruses 2021, 13, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, U.; Prezioso, C.; Pietropaolo, V. Genetic Diversity of the Noncoding Control Region of the Novel Human Polyomaviruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furmaga, J.; Kowalczyk, M.; Zapolski, T.; Furmaga, O.; Krakowski, L.; Rudzki, G.; Jaroszyński, A.; Jakubczak, A. BK Polyomavirus—Biology, Genomic Variation and Diagnosis. Viruses 2021, 13, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assetta, B.; Atwood, W.J. The Biology of JC Polyomavirus. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackard, J.T.; Davies, S.M.; Laskin, B.L. BK Polyomavirus Diversity-Why Viral Variation Matters. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, e2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalianis, T.; Hirsch, H.H. Human Polyomaviruses in Disease and Cancer. Virology 2013, 437, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.J.; Vilchez, R.A.; Randhawa, P.; Shapiro, R.; Butel, J.S.; Kusne, S. Pathogenesis and Management of Polyomavirus Infection in Transplant Recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 35, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.; Dobson, S. BK and JC Virus: A Review. J. Infect. 2014, 68 (Suppl. 1), S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroller, V.; Hamšíková, E.; Ludvíková, V.; Vochozková, P.; Kojzarová, M.; Fraiberk, M.; Saláková, M.; Morávková, A.; Forstová, J.; Němečková, S. Seroprevalence Rates of BKV, JCV, and MCPyV Polyomaviruses in the General Czech Republic Population. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benketira, A.; Tichit, R.; Tenenbaum, J.; Margueritte, G.; Bernard, F. BK virus infection in a child after an hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Arch. Pediatr. 2005, 12 (Suppl. 1), S64–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, M.; Ingrosso, D.; Perna, A.F.; Lombardi, A.; Maggi, P.; Altucci, L.; Caraglia, M. BK Virus Infection and BK-Virus-Associated Nephropathy in Renal Transplant Recipients. Genes 2022, 13, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.; Yazdi, M.K.; Parvin, M.; Zohrehbandian, F.; Azma, R. Haemorrhagic Cystitis Due to BK Virus in a Child with ALL on Standard Chemotherapy without Stem Cell Transplant. Ecancermedicalscience 2013, 7, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefele, J.; Rüssmann, D.; Klein, B.; Weber, L.T.; Führer, M. BK Virus Induced Nephritis in a Boy with Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Undergoing Bone Marrow Transplantation. NDT Plus 2008, 1, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Pinto, L.N.; Laskin, B.L.; Jodele, S.; Hummel, T.R.; Yin, H.J.; Goebel, J. BK Virus Nephropathy in a Pediatric Autologous Stem-Cell Transplant Recipient. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 56, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahye, N.; Bellizzi, A.; May, D.; Wollebo, H.S. The Role of the JC Virus in Central Nervous System Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butic, A.B.; Spencer, S.A.; Shaheen, S.K.; Lukacher, A.E. Polyomavirus Wakes Up and Chooses Neurovirulence. Viruses 2023, 15, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, L.; Khalili, K. Induction of Brain Tumors by the Archetype Strain of Human Neurotropic JCPyV in a Transgenic Mouse Model. Viruses 2021, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Zhang, N.; Jia, M.; Su, M. Association Between Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr Virus Co-Reactivation and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 818167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, C.M.; Kesson, A.; Powys, M.; Wong, M.; Blyth, E. Cytomegalovirus Infections in Children with Primary and Secondary Immune Deficiencies. Viruses 2021, 13, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami Kojidi, M.; Shatizadeh Malekshahi, S.; Jabbari, M.R. The simultaneous presence of active BK, Epstein Barr, and human cytomegalovirus infection and their correlation by host factors in patients suspected of kidney transplant rejection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, S.; Davidovits, M.; Alfandari, H.; Dagan, A.; Borovitz, Y.; Bilavsky, E.; Landau, D.; Haskin, O. EBV, CMV, and BK viral infections in pediatric kidney transplantation: Frequency, risk factors, treatment, and outcomes. Pediatr. Transplant. 2022, 26, e14199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauhiainen, M.K.; Mohanraj, U.; Lehecka, M.; Niemelä, M.; Hirvonen, T.P.; Pratas, D.; Perdomo, M.F.; Söderlund-Venermo, M.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Sinkkonen, S.T. Herpesviruses, polyomaviruses, parvoviruses, papillomaviruses, and anelloviruses in vestibular schwannoma. J. Neurovirol. 2023, 29, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalianis, T.; Eriksson, B.-M.; Felldin, M.; Friman, V.; Hammarin, A.-L.; Herthelius, M.; Ljungman, P.; Mölne, J.; Wennberg, L.; Swartling, L. Management of BK-Virus Infection—Swedish Recommendations. Infect. Dis. 2019, 51, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GeneProof. GeneProof BK/JC Virus (BK/JC) PCR Kit. Available online: https://www.geneproof.com/geneproof-bk-jc-virus-bk-jc-pcr-kit/p1121 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- GeneProof. GeneProof Cytomegalovirus (CMV) PCR Kit (IVDR). Available online: https://www.geneproof.com/geneproof-r-cytomegalovirus-cmv-pcr-kit-ivdr/p6912 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- GeneProof. GeneProof Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) PCR Kit. Available online: https://www.geneproof.com/geneproof-epstein-barr-virus-ebv-pcr-kit/p1083 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Admiraal, R.; de Koning, C.C.H.; Lindemans, C.A.; Bierings, M.B.; Wensing, A.M.J.; Versluys, A.B.; Wolfs, T.F.W.; Nierkens, S.; Boelens, J.J. Viral reactivations and associated outcomes in the context of immune reconstitution after pediatric hematopoietic cell transplantation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1643–1650.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.E.; DiTullio, D.J.; Wilhalme, H.; Bowles, L.; Moore, T.B.; De Oliveira, S.N. Prevalence of Viral Infections and Serious Complications in Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Patients: A Ten-Year Single-Institution Retrospective Study. J. Hematol. 2025, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, G.Z.; Bozkurt, C.; Aksoy, B.A.; Öner, Ö.B.; Aydoğdu, S.; Çipe, F.; Sütçü, M.; Özkaya, O.; Fışgın, T. Evaluation of the Risk Factors for BK Virus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Pediatric Bone Marrow Transplantation Patients: Does Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide Increase the Frequency? Pediatr. Transplant. 2022, 27, e14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-González, R.; León, D.E.A.; Rodríguez-Jurado, R.; Uribe-Uribe, N.O. Systemic BK Virus Infection in a Pediatric Patient With Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2020, 23, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Hill, G.R. Immune control of cytomegalovirus reactivation in stem cell transplantation. Blood 2022, 139, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervevan, J.; Chakrabarti, L.A. Role of CD4+ T Cells in the Control of Viral Infections: Recent Advances and Open Questions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Salazar, C.; Sun, J.C. Coordinated Viral Control by Cytotoxic Lymphocytes Ensures Optimal Adaptive NK Cell Responses. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantanos, T.; Kim, H.T.; Tijaro-Ovalle, N.M.; Li, L.; Cutler, C.; Antin, J.H.; Ballen, K.; Marty, F.M.; Tan, C.S.; Ritz, J.; et al. Reactivation of BK virus after double umbilical cord blood transplantation in adults correlates with impaired reconstitution of CD4+ and CD8+ T effector memory cells and increase of T regulatory cells. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 207, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Jing, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Jia, C.; Luo, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, X.; et al. Analysis of BK Virus Infection in Children After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Retrospective Single-center Study. J. Pediatr. Hematol./Oncol. 2024, 46, e487–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamonowicz-Bodzioch, M.; Frączkiewicz, J.; Czyżewski, K.; Zając-Spychała, O.; Gorczyńska, E.; Panasiuk, A.; Ussowicz, M.; Kałwak, K.; Szmit, Z.; Wróbel, G.; et al. Prospective Analysis of BKV Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Children and Adolescents Undergoing Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, N.N.; Bayram, İ.; Öztürk, G.; Sezgin, G.; Küpeli, S.; Yarkın, F. BK Virus Infections in Pediatric Patients with Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Duzce Med. J. 2020, 22, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, G.; Priftakis, P.; Bogdanovic, G.; Remberger, M.; Dubrulle, M.; Hau, A.; Gutmark, R.; Mattson, J.; Svahn, B.M.; Ringden, O.; et al. BK-viruria and haemorrhagic cystitis are more frequent in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant patients receiving full conditioning and unrelated-HLA-mismatched grafts. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008, 41, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaçar, D.; Guzelcik, Z.; Yozgat, A.K.; Isik, M.; Yarali, N. BK-virus infections in pediatric leukemia patients during leukemia treatment. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2023, 45, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, S.d.S.V.Á.; Monteiro, J.C.; Viegas, A.P.d.V.; de Sá, K.S.G.; da Cruz, S.R.; Lima, S.S.; Vallinoto, I.M.V.C.; Costa, I.B.; Vallinoto, A.C.R. Prevalence of JC and BK Polyomavirus Infection in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease in the State of Pará, Brazil. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi Dehcheshmeh, L.; Makvandi, M.; Timori, A. Prevalence of Human Polyomavirus JC and BK in Normal Population. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 2877–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, K.; Kato, I.; Kawaguchi, K.; Tasaka, K.; Kamitori, T.; Ogata, H.; Mikami, T.; Hiramatsu, H.; Saito, R.; Ogawa, O.; et al. High Incidence of BK Virus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Children after Second or Third Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2018, 22, e13183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, R.T.; Gu, Z.; Liu, W.; Lovins, R.; Kasow, K.; Woodard, P.; Srivastava, K.; Leung, W. Risk Factors for Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Pediatric Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2015, 17, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazquez-Navarro, A.; Dang-Heine, C.; Wittenbrink, N.; Bauer, C.; Wolk, K.; Sabat, R.; Westhoff, T.H.; Sawitzki, B.; Reinke, P.; Thomusch, O.; et al. BKV, CMV, and EBV Interactions and their Effect on Graft Function One Year Post-Renal Transplantation: Results from a Large Multi-Centre Study. EBioMedicine 2018, 34, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Smits, C.; Baker, E.R.; Hirji, I. Coinfection rates and clinical outcome data for cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus in post-transplant patients: A systematic review of the literature. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2020, 22, e13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, S.; Bernal-Maurandi, J.; Cofan, F.; Ventura, P.; Marcos, M.A.; Linares, L.; Cuesta, G.; Diekmann, F.; Moreno, A.; Bodro, M. BK Virus and Cytomegalovirus Coinfections in Kidney Transplantation and Their Impact on Allograft Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubry, A.; Nere, M.L.; Timsit, S.; Calvo, C.; Dalle, J.H.; Gras, J.; Chaix, C.; Gits-Muselli, M.; Delaugerre, C.; LeGoff, J.; et al. Investigating Nosocomial BK Polyomavirus Infections in Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients: Challenges and Prospects. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 232, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rota, S.; Fidan, K.; Bozdayı, G.; Dalgıç, A.; Fidan, I.; Sucak, G.; Müderris, T. Investigation of BK and JC virus DNA positivities by real-time polymerase chain reaction in the clinical samples of patients with high risk. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2011, 45, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahiala, J.; Koskenvuo, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Waris, M.; Vuorinen, T.; Lappalainen, M.; Saarinen-Pihkala, U.; Allander, T.; Söderlund-Venermo, M.; Hedman, K.; et al. Polyomaviruses BK, JC, KI, WU, MC, and TS in Children with Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2016, 20, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybko, J.; Piekarska, A.; Agrawal, S.; Makuch, S.; Urbaniak-Kujda, D.; Biernat, M.; Rybka, B.; Dutka, M.; Sadowska-Klasa, A.; Giebel, S.; et al. BKV Related Hemorrhagic Cystitis—An Insight into Risk Factors and Later Complications—An Analysis on Behalf of Polish Adult Leukemia Group. Cancers 2022, 14, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Hyun, H.S.; Park, E.; Moon, K.C.; Min, S.-I.; Ha, J.; Ha, I.-S.; Cheong, H.I.; Ahn, Y.H.; Kang, H.G. Higher Incidence of BK Virus Nephropathy in Pediatric Kidney Allograft Recipients with Alport Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbue, S.; Franciotta, D.; Giannella, S.; Dolci, M.; Signorini, L.; Ticozzi, R.; D’Alessandro, S.; Campisciano, G.; Comar, M.; Ferrante, P.; et al. Human Polyomaviruses in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Neurological Patients. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, D.M.; Mackay, I.M.; Sloots, T.P. Detection and Differentiation of Human Polyomaviruses JC and BK by LightCycler PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 4357–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, D.M.; Arden, K.E.; Mackay, I.M.; Syrmis, M.W.; Sloots, T.P. Simultaneous Detection and Differentiation of Human Polyomaviruses JC and BK by a Rapid and Sensitive PCR-ELAHA Assay and a Survey of the JCV Subtypes within an Australian Population. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürch, W.; Latour, M.; Barama, A.; Hébert, M.J. Evaluation of a preemptive strategy for BK polyomavirus-associated nephropathy based on prospective monitoring of BK viremia: A kidney transplantation center experience. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 4083–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Diagnosis | Patients (n = 99) | HCT Patients (n = 70) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) | 46 | 46.5 | 38 | 54.3 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | 16 | 16.2 | 15 | 21.4 |
| Aplastic anemia (acquired or congenital, inc. Blackfan-Diamond) | 9 | 9.1 | 7 | 10.0 |
| Inborn errors of immunity (IEI, includingbone marrow failure) | 4 | 4.0 | 3 | 4.3 |
| Immune thrombocytopenia | 4 | 4.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Hemophagocytic syndrome (HLH) | 3 | 3.0 | 1 | 1.4 |
| Myelo dysplastic syndrome (MDS) | 2 | 2.0 | 2 | 2.9 |
| Congenital or acquired CMV infection | 2 | 2.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Non-Hodgkin-lymphoma (NHL) | 1 | 1.0 | 1 | 1.4 |
| Neuroblastoma | 1 | 1.0 | 1 | 1.4 |
| Nejmegen syndrome (NBS) | 1 | 1.0 | 1 | 1.4 |
| Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) | 1 | 1.0 | 1 | 1.4 |
| Cerebellar syndrome | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Splenic abscesses | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Rhabdomyosarcoma (RML) | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Monocytosis | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Wilms’s tumor | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Brain tumor | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Bone marrow donor | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| B-cell lymphoma | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Hydrocephalus, neuroinfection, arachnoid cyst | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Patient No. | Diagnosis | Viral DNA Level [IU/mL] | Age at the Time of BKPyV-Positive Result (Years) | Symptoms at the Samples Collection Time | Age at the Time of Death | Direct Reason of Death | Time Between Initial Diagnosis and BKPyV DNA Presence Confirmation (Years) | Time Between HCT and BKPyV DNA Presence Confirmation (Months) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKPyV | CMV | EBV | ||||||||
| 1 | AML | 1.2 × 103 | 0 | 2.7 × 102 | 9 | fever, dysuria, abdominal pain, lymphoproliferative disease | 9 years | multi-focal stroke | 3.5 | 2.7 |
| 2 | ALL | 1.8 × 103 | 2.3 × 103 | 0 | 7 | bladder infection | N/A | N/A | 3.8 | 1.8 |
| 3 | ALL | 3.2 × 103 | 0 | 2.5 × 103 | 4 | lymph nodes enlargement, EBV PTLD | N/A | N/A | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| 4 | SAA | 9.1 × 103 | 0 | 0 | 14 | fever, dysurical symptoms | N/A | N/A | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| 5 | ALL | 4.9 × 103 | 0 | 0 | 12 | consciousness disturbances, encephalopathy | 12 years | toxic encephalopathy | 0.7 | 1.2 |
| 6 | ALL | 5.2 × 103 | 0 | 0 | 6 | fever | N/A | N/A | 2.2 | 0.9 |
| 7 | AML | 5.3 × 103 | 0 | 0 | 4 | bladder infection, urinemia | 5 years | AML relapse | 0.6 | 1.3 |
| 8 | ALL | 9.1 × 103 | 0 | 0 | 9 | asymptomatic * | N/A | N/A | 0.8 | 1.4 |
| 9 | AML | 9.6 × 103 | 1.9 × 103 | 0 | 10 | gastrointestinal tract bleeding, fever, leukopenia | 10 years | toxic encephalopathy, CMV reactivation | 0.8 | 1.9 |
| 10 | ALL | 1.4 × 104 | 0 | 0 | 12 | asymptomatic * | N/A | N/A | 1.1 | N/A |
| 11 ** | ALL | 2.2 × 104 | 0 | 0 | 5 | hemorrhagic cystitis, mycosis of the left lung | N/A | N/A | 1.5 | 1.0 |
| 12 | ALL | 3.4 × 104 | 0 | 2.5 × 102 | 12 | asymptomatic * | N/A | N/A | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| 13 | ALL | 3.7 × 104 | 0 | 0 | 10 | fever | N/A | N/A | 1.5 | 9.6 |
| 14 | AML | 2.9 × 105 | 0 | 0 | 9 | thrombocytopenia, fever, ALAT level increase | N/A | N/A | 3.1 | 3.3 |
| 15 | ALL | 1.7 × 107 | 7.9 × 104 | 0 | 10 | asymptomatic * | 11 years | multiorgan failure | 1.4 | 6.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bogiel, T.; Rzepka, M.; Depka-Radzikowska, D.; Zalas-Więcek, P.; Czyżewski, K.; Richert-Przygońska, M.; Styczyński, J.; Dębski, R.; Grześk, E.; Grześk, G.; et al. Clinical Associations and Coexistence of Polyomavirus DNAemia with EBV and CMV in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Patients, Including HCT Recipients—A Pilot Study. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111122
Bogiel T, Rzepka M, Depka-Radzikowska D, Zalas-Więcek P, Czyżewski K, Richert-Przygońska M, Styczyński J, Dębski R, Grześk E, Grześk G, et al. Clinical Associations and Coexistence of Polyomavirus DNAemia with EBV and CMV in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Patients, Including HCT Recipients—A Pilot Study. Pathogens. 2025; 14(11):1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111122
Chicago/Turabian StyleBogiel, Tomasz, Mateusz Rzepka, Dagmara Depka-Radzikowska, Patrycja Zalas-Więcek, Krzysztof Czyżewski, Monika Richert-Przygońska, Jan Styczyński, Robert Dębski, Elżbieta Grześk, Grzegorz Grześk, and et al. 2025. "Clinical Associations and Coexistence of Polyomavirus DNAemia with EBV and CMV in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Patients, Including HCT Recipients—A Pilot Study" Pathogens 14, no. 11: 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111122
APA StyleBogiel, T., Rzepka, M., Depka-Radzikowska, D., Zalas-Więcek, P., Czyżewski, K., Richert-Przygońska, M., Styczyński, J., Dębski, R., Grześk, E., Grześk, G., Kanarek, P., & Krawczyk, A. (2025). Clinical Associations and Coexistence of Polyomavirus DNAemia with EBV and CMV in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Patients, Including HCT Recipients—A Pilot Study. Pathogens, 14(11), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111122






