Ticks and Associated Rickettsiae from Domestic Animals in Bhutan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample Size
2.2. Tick Collection, Storage and Transportation
2.3. Morphological Identification of Ticks
2.4. Processing of Ticks for Rickettsial DNA Testing
2.4.1. Physical Processing
2.4.2. DNA Extraction
2.4.3. Molecular Testing for Rickettsiae
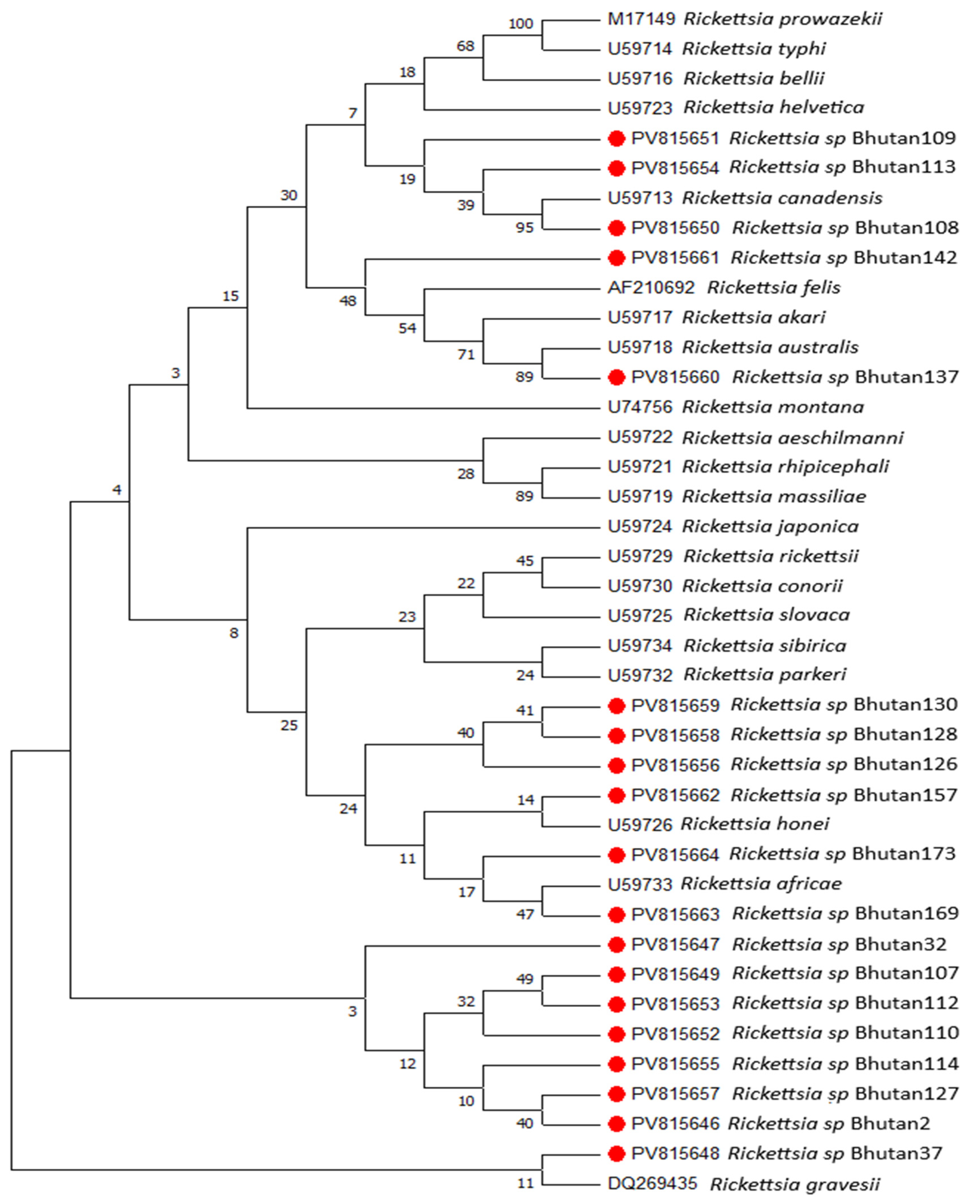
2.5. DNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
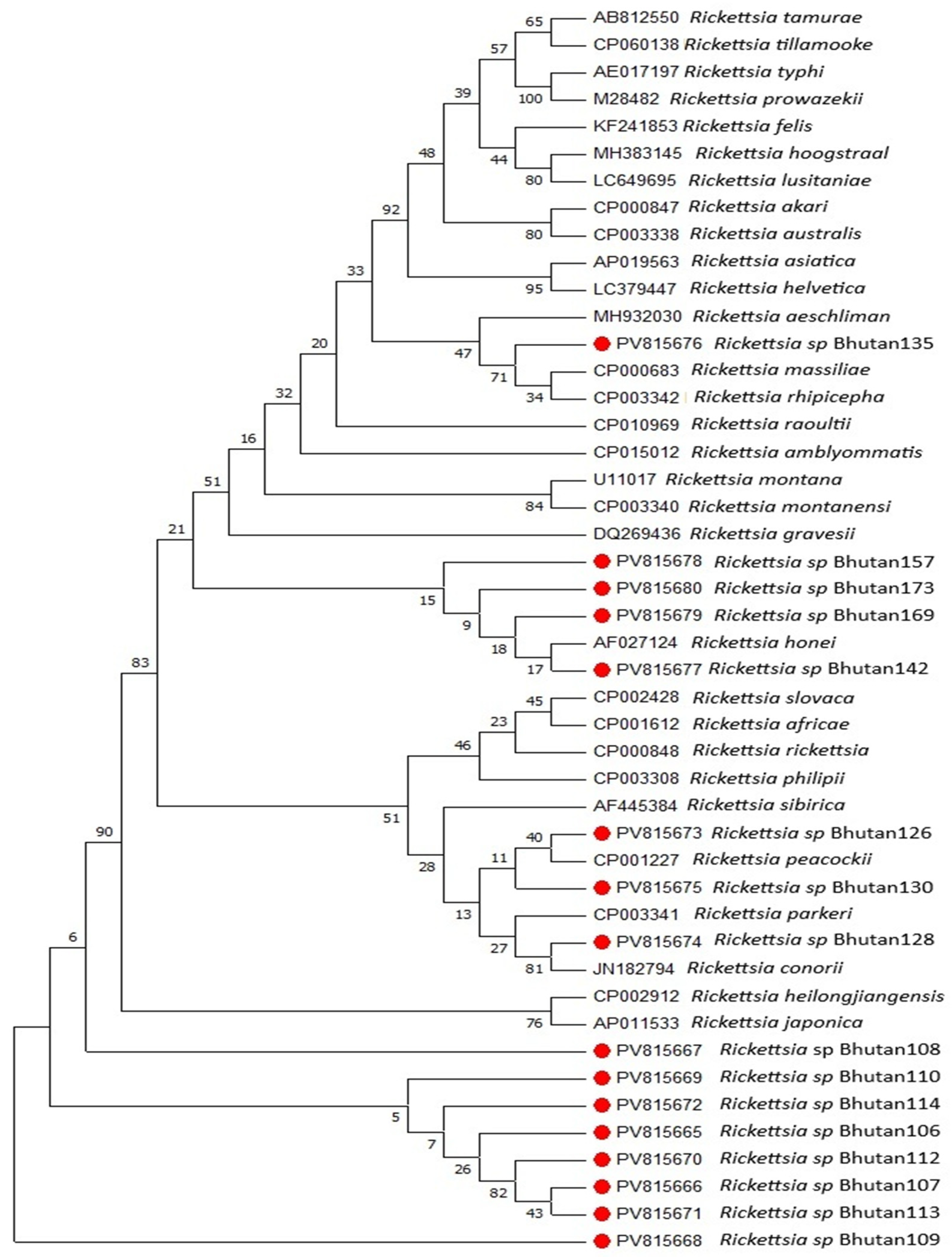
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jongejan, F.; Uilenberg, G. The global importance of ticks. Parasitology 2004, 129, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kho, K.L.; Koh, F.X.; Tay, S.T. Molecular evidence of potential novel spotted fever group rickettsiae, Anaplasma and Ehrlichia species in Amblyomma ticks parasitizing wild snakes. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Robbins, R.G.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Petney, T.N.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Horak, I.G.; Shao, R.; Barker, S.C. The argasidae, Ixodidae and Nuttalliellidae (Acari: Ixodida) of the world: A list of valid species names. Zootaxa 2010, 2528, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Tick Maps. 2023. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/disease-vectors/surveillance-and-disease-data/tick-maps (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Govindarajan, R.; Krishnamoorthi, R.; Venkatesh, A.; Ashwani, K.; Philip Samuel, P. Current status of ticks (Acari: Argasidae, Ixodidae) in India. Halteres 2023, 14, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.J.; Williams, K.; Shukla, M.; Snyder, E.E.; Nordberg, E.K.; Ceraul, S.M.; Dharmanolla, C.; Rainey, D.; Soneja, J.; Shallom, J.M.; et al. Rickettsia Phylogenomics: Unwinding the Intricacies of Obligate Intracellular Life. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- El Karkouri, K.; Ghigo, E.; Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.E. Genomic evolution and adaptation of arthropod-associated Rickettsia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Bruggeman, D.; Meyfroidt, P.; Lambin, E.F. Forest cover changes in Bhutan: Revisiting the forest transition. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 67, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Statistics Bureau, Bhutan. Bhutan Living Standards Survey Report 2017. Available online: https://www.nsb.gov.bt/publications/bhutan-living-standard-survey-report/ (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- National Statistics Bureau, Bhutan. Household Consumption and Expenditure Survey 2025. Available online: https://www.nsb.gov.bt/household-consumption-and-expenditure-survey-hces2025/ (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- National Statistics Bureau, Bhutan. Livestock Statistics of Bhutan. 2016. Available online: https://www.nsb.gov.bt/livestock-statistics-report/ (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- National Statistics Bureau, Bhutan. Integrated Agriculture and Livestock Census of Bhutan. 2023. Available online: https://www.nsb.gov.bt/https-www-nsb-gov-bt-wp-content-uploads-dlm_uploads-2024-07-ialc-2023-report-pdf/ (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Tshokey, T.; Stenos, J.; Tenzin, T.; Drukpa, K.; Gurung, R.B.; Graves, S.R. Serological Evidence of Rickettsia, Orientia, and Coxiella in Domestic Animals from Bhutan: Preliminary Findings. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshokey, T.; Stenos, J.; Durrheim, D.N.; Eastwood, K.; Nguyen, C.; Graves, S.R. Seroprevalence of rickettsial infections and Q fever in Bhutan. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogstraal, H.; Trapido, H. Redescription of the Type Materials of Haemaphysalis (Kaiseriana) bispinosa Neumann (India), H. (K.) neumanni Dönitz (Japan), H. (K.) lagrangei Larrousse (Vietnam), and H. (K.) yeni Toumanoff (Vietnam) (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). J. Parasitol. 1966, 52, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogstraal, H.; Trapido, H.; Kohls, G.M. Studies on southeast Asian Haemaphysalis ticks (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). Speciation in the H. (Kaiseriana) obesa group: H. semermis Neumann, H. obesa Larrousse, H. roubaudi Toumanoff, H. montgomeryi Nuttall, and H. hirsuta sp. n. J. Parasitol. 1966, 52, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apanaskevich, D.A.; Horak, I.G. The genus Hyalomma. XI. Redescription of all parasitic stages of H. (Euhyalomma) asiaticum (Acari: Ixodidae) and notes on its biology. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 52, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, D.H.; Blacksell, S.D.; Stenos, J.; Graves, S.R.; Unsworth, N.B.; Phetsouvanh, R.; Newton, P.N.; Day, N.P. Real-time multiplex PCR assay for detection and differentiation of rickettsiae and orientiae. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenos, J.; Graves, S.; Izzard, L. Rickettsia. In PCR for Clinical Microbiology: An Australian and International Perspective, 1st ed.; Schuller, M., Sloots, T.P., James, G.S., Halliday, C.L., Carter, I.W.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 197–199. Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-90-481-9039-3 (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Stenos, J.; Graves, S.; Lockhart, M. Coxiella burnetiid. In PCR for Clinical Microbiology—An Australian and International Perspective, 1st ed.; Schuller, M., Sloots, T., James, G., Halliday, C., Carter, I., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 145–148. Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-90-481-9039-3 (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Ishikura, M.; Ando, S.; Shinagawa, Y.; Matsuura, K.; Hasegawa, S.; Nakayama, T.; Fujita, H.; Watanabe, M. Phylogenetic Analysis of Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiae Based on gltA, 17-kDa, and rOmpA Genes Amplified by Nested PCR from Ticks in Japan. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 47, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Azhahianambi, P.; De La Fuente, J. Control of ticks of ruminants, with special emphasis on livestock farming systems in India: Present and future possibilities for integrated control—A review. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 40, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Bansal, G.C.; Gupta, S.C.; Ray, D.; Khan, M.Q.; Irshad, H.; Shahiduzzaman; Seitzer, U.; Ahmed, J.S. Status of tick distribution in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Bu, F.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, J. Ticks (Acari: Ixodoidea: Argasidae, Ixodidae) of China. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 51, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswal, M.; Zaman, K.; Suri, V.; Gopi, S.; Kumar, A.; Gopi, T.; Vig, S.; Sharma, N.; Bhalla, A. Molecular confirmation & characterization of Rickettsia conorii in north India: A report of three cases. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 151, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krishnamoorthi, S.; Goel, S.; Kaur, J.; Bisht, K.; Biswal, M. A Review of Rickettsial Diseases Other Than Scrub Typhus in India. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Murphy, H.; Renvoisé, A.; Pandey, P.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Rickettsia honei Infection in Human, Nepal, 2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1865–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-F.; Zhang, M.-Z.; Zhu, D.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Gong, C.-W.; Zhan, L.; Cui, X.-M.; Cao, W.-C. High Diversity and Prevalence of Rickettsial Agents in Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks from Livestock in Karst Landscapes of Southwest China. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target Genes | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|
| Citrate synthase (gltA) gene (2 PCRs) | |
| GACCATGAGCAGAATGCTTCT |
| GGGGGCCTGCTCACGGCGG |
| ATTGCAAAAAGTACAGTGAACA |
| 17 kDa gene (2 PCRs) | |
| TTTACAAAATTCTAAAAACCAT |
| GCTCTTGCAACTTCTATGTT |
| TCAATTCACAACTTGCCATT |
| Scheme | Bhutan Sequence ID | GenBank Seq no. | GenBank Accession no. | Target Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan2 | BankIt2971817 Seq1 | PV815646 | CS (gltA) |
| 2 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan32 | BankIt2971817 Seq2 | PV815647 | CS (gltA) |
| 3 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan37 | BankIt2971817 Seq3 | PV815648 | CS (gltA) |
| 4 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan107 | BankIt2971817 Seq4 | PV815649 | CS (gltA) |
| 5 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan108 | BankIt2971817 Seq5 | PV815650 | CS (gltA) |
| 6 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan109 | BankIt2971817 Seq6 | PV815651 | CS (gltA) |
| 7 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan110 | BankIt2971817 Seq7 | PV815652 | CS (gltA) |
| 8 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan112 | BankIt2971817 Seq8 | PV815653 | CS (gltA) |
| 9 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan113 | BankIt2971817 Seq9 | PV815654 | CS (gltA) |
| 10 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan114 | BankIt2971817 Seq10 | PV815655 | CS (gltA) |
| 11 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan126 | BankIt2971817 Seq11 | PV815656 | CS (gltA) |
| 12 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan127 | BankIt2971817 Seq12 | PV815657 | CS (gltA) |
| 13 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan128 | BankIt2971817 Seq13 | PV815658 | CS (gltA) |
| 14 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan130 | BankIt2971817 Seq14 | PV815659 | CS (gltA) |
| 15 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan137 | BankIt2971817 Seq15 | PV815660 | CS (gltA) |
| 16 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan142 | BankIt2971817 Seq16 | PV815661 | CS (gltA) |
| 17 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan157 | BankIt2971817 Seq17 | PV815662 | CS (gltA) |
| 18 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan169 | BankIt2971817 Seq18 | PV815663 | CS (gltA) |
| 19 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan173 | BankIt2971817 Seq19 | PV815664 | CS (gltA) |
| 20 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan106 | BankIt2972213 Seq1 | PV815665 | 17 kDa |
| 21 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan107 | BankIt2972213 Seq2 | PV815666 | 17 kDa |
| 22 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan108 | BankIt2972213 Seq3 | PV815667 | 17 kDa |
| 23 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan109 | BankIt2972213 Seq4 | PV815668 | 17 kDa |
| 24 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan110 | BankIt2972213 Seq5 | PV815669 | 17 kDa |
| 25 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan112 | BankIt2972213 Seq6 | PV815670 | 17 kDa |
| 26 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan113 | BankIt2972213 Seq7 | PV815671 | 17 kDa |
| 27 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan114 | BankIt2972213 Seq8 | PV815672 | 17 kDa |
| 28 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan126 | BankIt2972213 Seq9 | PV815673 | 17 kDa |
| 29 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan128 | BankIt2972213 Seq10 | PV815674 | 17 kDa |
| 30 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan130 | BankIt2972213 Seq11 | PV815675 | 17 kDa |
| 31 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan135 | BankIt2972213 Seq12 | PV815676 | 17 kDa |
| 32 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan142 | BankIt2972213 Seq13 | PV815677 | 17 kDa |
| 33 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan157 | BankIt2972213 Seq14 | PV815678 | 17 kDa |
| 34 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan169 | BankIt2972213 Seq15 | PV815679 | 17 kDa |
| 35 | Rickettsia sp. Bhutan173 | BankIt2972213 Seq16 | PV815680 | 17 kDa |
| Animals Sampled (n = 155) | No. of Ticks Collected | Tick Species Identified | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhipicephalus microplus | Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides | Haemaphysalis sp. near ramachandrai | Rhipicephalus sanguineus | Haemaphysalis bispinosa | Haemaphysalis sp. near davisi | Haemaphysalis sp. | Haemaphysalis shimoga | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Haemaphysalis tibetensis | Ixodes ovatus | Amblyomma testudinarium | ||
| Cattle (n = 78) | 108 | 79 | 16 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Dogs (n = 47) | 55 | 7 | 39 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Goats (n = 10) | 11 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Horses (n = 10) | 10 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Yaks (n = 5) | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 |
| Sheep (n = 3) | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cats (n = 2) | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 200 | 89 | 63 | 14 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tshokey, T.; Tadepalli, M.; Graves, S.R.; Stenos, J. Ticks and Associated Rickettsiae from Domestic Animals in Bhutan. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101021
Tshokey T, Tadepalli M, Graves SR, Stenos J. Ticks and Associated Rickettsiae from Domestic Animals in Bhutan. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101021
Chicago/Turabian StyleTshokey, Tshokey, Mythili Tadepalli, Stephen R. Graves, and John Stenos. 2025. "Ticks and Associated Rickettsiae from Domestic Animals in Bhutan" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101021
APA StyleTshokey, T., Tadepalli, M., Graves, S. R., & Stenos, J. (2025). Ticks and Associated Rickettsiae from Domestic Animals in Bhutan. Pathogens, 14(10), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101021






