Detection and Molecular Diversity of Brucella melitensis in Pastoral Livestock in North-Eastern Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
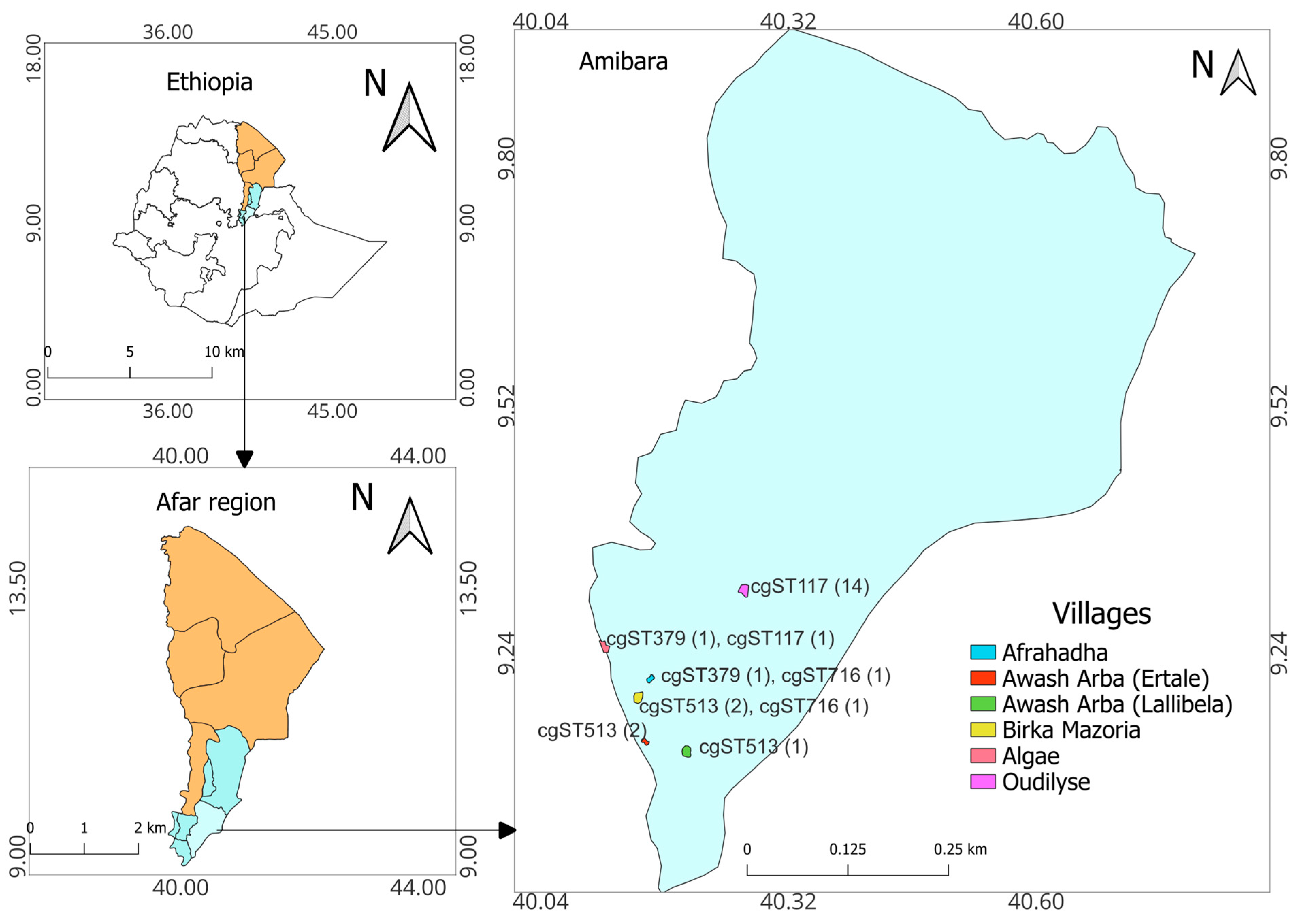
2.1. Study Area
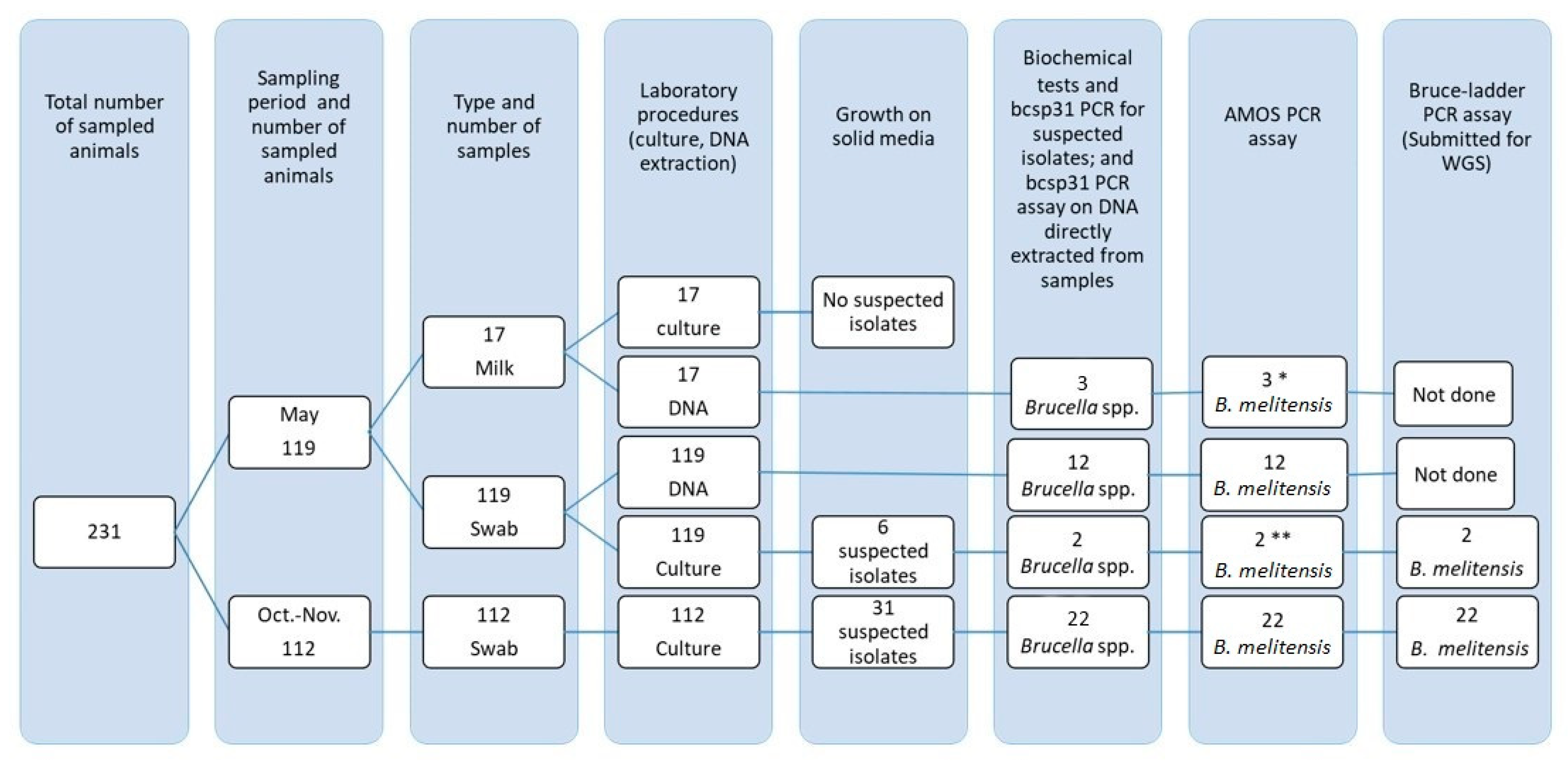
2.2. Study Animals and Sampling
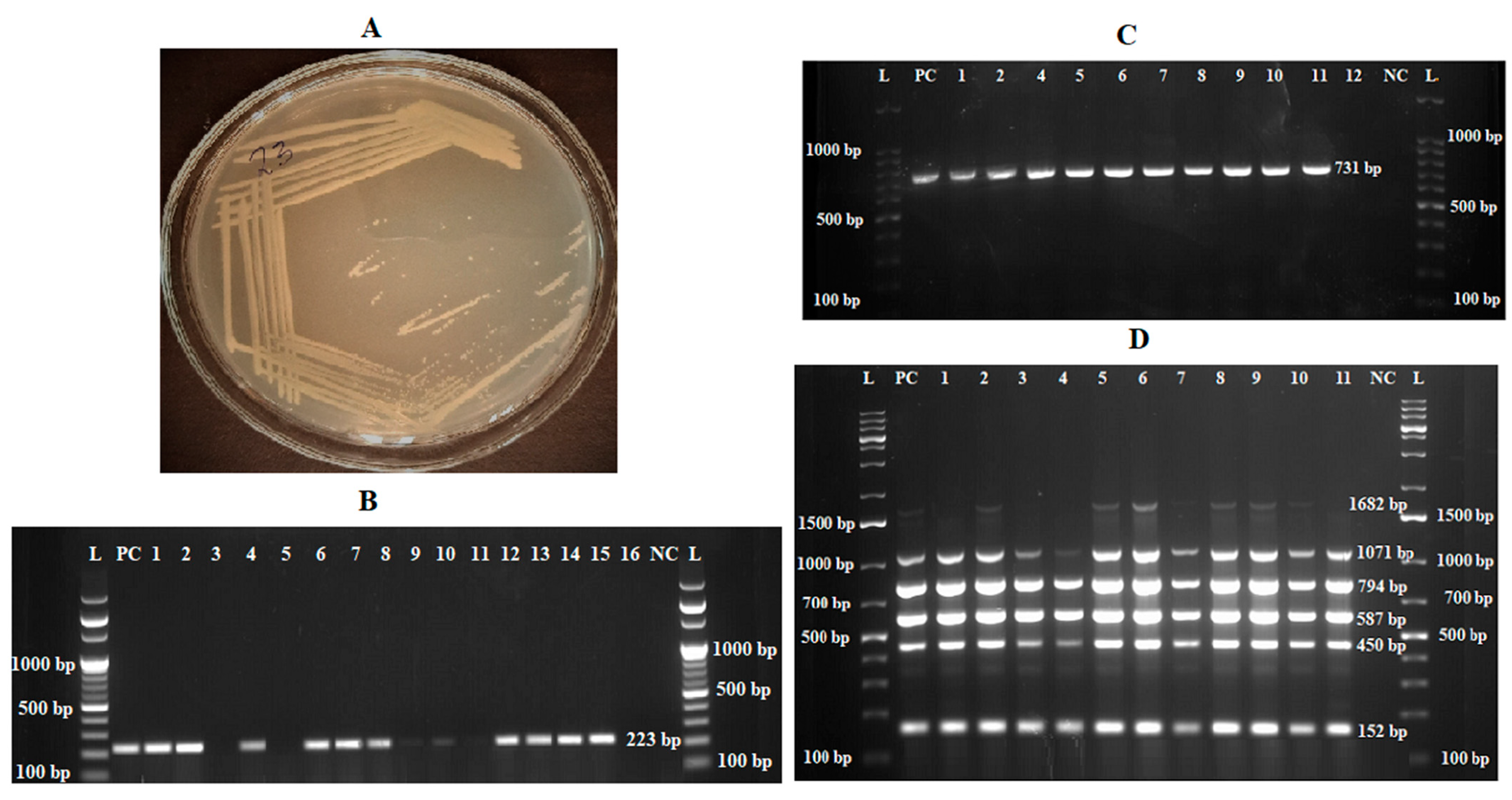
2.3. Brucella Isolation and Characterization
2.4. Molecular Assays
2.4.1. DNA Extraction
2.4.2. PCR Assays
2.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing, Assembly, and Bioinformatic Analyses
2.5.1. DNA Library Preparation and Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.5.2. Retrieval of Regional/International Short-Reads from Public Databases
2.5.3. Quality Assessment of Short Reads
2.5.4. Genome Assembly
2.5.5. Genome Assembly Quality Assessment
2.5.6. Pan-Genome Analysis
2.5.7. Whole-Genome SNP (wgSNP) Calling and Phylogenetic Tree Construction
2.5.8. In Silico MLST Analyses
2.5.9. Predictions of Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
3. Results
3.1. Abortions and Occurrence of Brucella melitensis
3.2. Brucella spp. Detection and Isolation
3.3. Genome Assembly
3.4. Pan-Genome Analysis
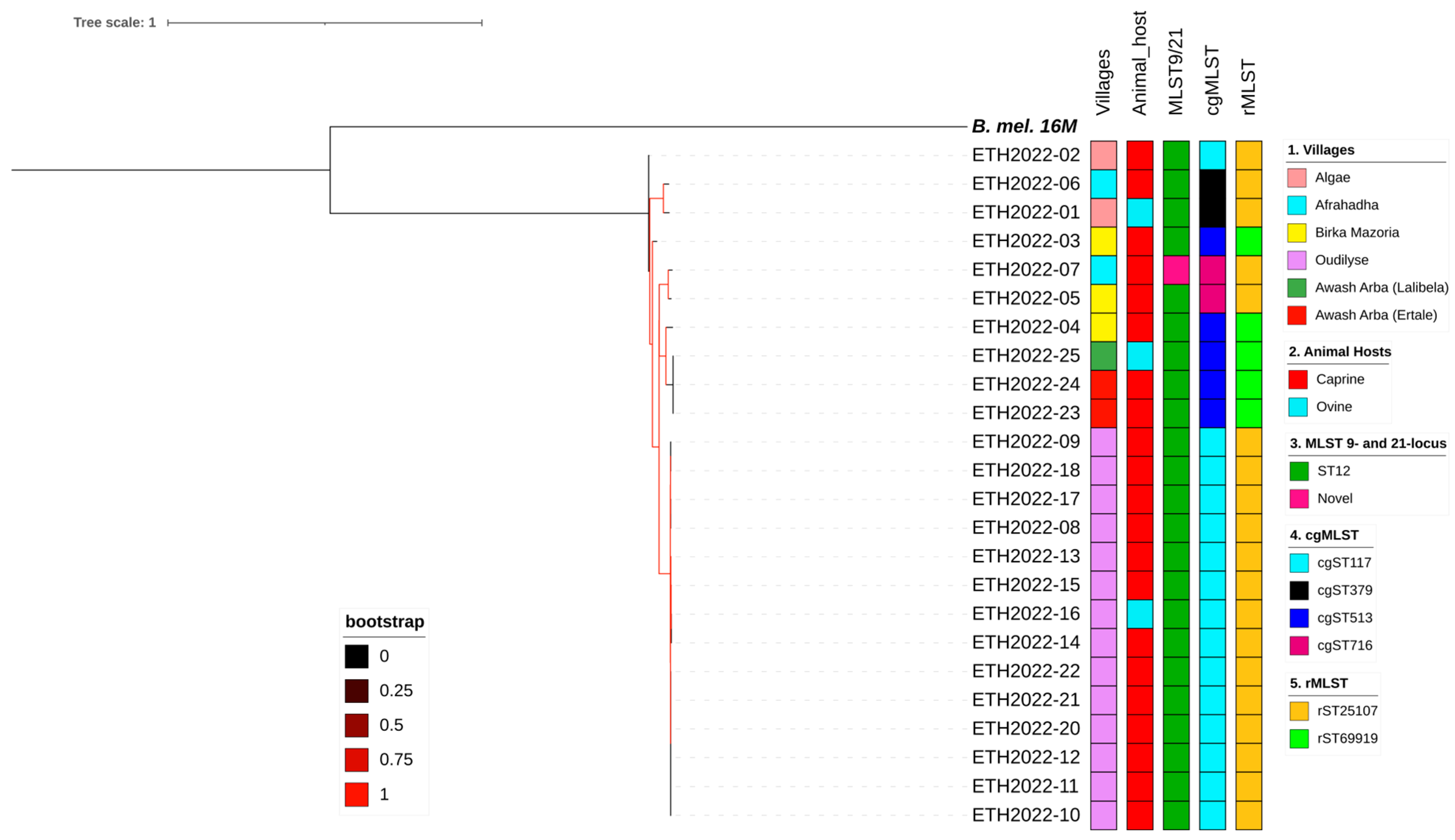
3.5. Whole-Genome SNP (wgSNP) Analysis of Ethiopian Isolates
3.6. Regional and Global Comparisons
In Silico MLST9, MLST21, cgMLST, and rMLST
3.7. Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dean, A.S.; Crump, L.; Greter, H.; Hattendorf, J.; Schelling, E.; Zinsstag, J. Clinical Manifestations of Human Brucellosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilnejad-Ganji, S.M.; Esmaeilnejad-Ganji, S.M.R. Osteoarticular Manifestations of Human Brucellosis: A Review. World J. Orthop. 2019, 10, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, M.P.; Mulder, M.; Gilman, R.H.; Smits, H.L. Human Brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, C.G.; Johnson, V.E.; Scott, H.M.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Global Estimate of Human Brucellosis Incidence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadar, M.; Shahali, Y.; Whatmore, A.M. Human Brucellosis Caused by Raw Dairy Products: A Review on the Occurrence, Major Risk Factors and Prevention. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 292, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, M.J.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization; World Organisation for Animal Health. Brucellosis in Humans and Animals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; pp. 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Spickler, A.R. Brucellosis: Brucella melitensis. Factsheet, Center for Food, Security and Public Health: Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA. 2018. Available online: https://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/Factsheets/pdfs/brucellosis_melitensis.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Godfroid, J. Brucella spp. at the Wildlife-Livestock Interface: An Evolutionary Trajectory through a Livestock-to-Wildlife “Host Jump”? Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, M.N.; Paixão, T.A.; Poester, F.P.; Lage, A.P.; Santos, R.L. Pathological, Immunohistochemical and Bacteriological Study of Tissues and Milk of Cows and Fetuses Experimentally Infected with Brucella abortus. J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 140, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byndloss, M.X.; Tsolis, R.M. Brucella spp. Virulence Factors and Immunity. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2016, 4, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, M.N.; Costa, É.A.; Paixão, T.A.; Santos, R.L. The Genus Brucella and Clinical Manifestations of Brucellosis. Ciência Rural 2009, 39, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.L.; Gonzalez-Juarrero, M.; Bowen, R.A. Evaluation of Shedding, Tissue Burdens, and Humoral Immune Response in Goats after Experimental Challenge with the Virulent Brucella melitensis Strain 16M and the Reduced Virulence Vaccine Strain Rev. 1. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwida, M.; El-Gohary, A.; Melzer, F.; Khan, I.; Rösler, U.; Neubauer, H. Brucellosis in Camels. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 92, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieracci, E.G.; Hall, A.J.; Gharpure, R.; Haile, A.; Walelign, E.; Deressa, A.; Bahiru, G.; Kibebe, M.; Walke, H.; Belay, E. Prioritizing Zoonotic Diseases in Ethiopia Using a One Health Approach. One Health 2016, 2, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkyihun, G.A.; Gari, F.R.; Edao, B.M.; Kassa, G.M. A Review on One Health Approach in Ethiopia. One Health Outlook 2022, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibhat, B.; Tessema, T.S.; Nile, E.; Asmare, K. Brucellosis in Ethiopia: A Comprehensive Review of Literature from the Year 2000–2020 and the Way Forward. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e1231–e1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, G. Brucellosis Seropositivity in Animals and Humans in Ethiopia: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negassa, A.; Rashid, S.; Gebremedhin, B.; Kennedy, A. Livestock Production and Marketing. Food Agric. Ethiop. Prog. Policy Chall. 2013, 9780812208, 159–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Mayberry, D.; Jemberu, W.; Schrobback, P.; Herrero, M.; Chaters, G.; Knight-Jones, T.; Rushton, J. Characterizing Ethiopian Cattle Production Systems for Disease Burden Analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1233474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njeru, J.; Nthiwa, D.; Akoko, J.; Oyas, H.; Bett, B. Incidence of Brucella Infection in Various Livestock Species Raised under the Pastoral Production System in Isiolo County, Kenya. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoko, J.M.; Pelle, R.; Lukambagire, A.H.S.; Machuka, E.M.; Nthiwa, D.; Mathew, C.; Fèvre, E.M.; Bett, B.; Cook, E.A.J.; Othero, D.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Brucella Species in Mixed Livestock-Human Ecosystems in Kenya. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfroid, J.; De bolle, X.; Roop, R.M.; O’Callaghan, D.; Tsolis, R.M.; Baldwin, C.; Santos, R.L.; McGiven, J.; Olsen, S.; Nymo, I.H.; et al. The Quest for a True One Health Perspective of Brucellosis. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2014, 33, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfroid, J. Brucellosis in Livestock and Wildlife: Zoonotic Diseases without Pandemic Potential in Need of Innovative One Health Approaches. Arch. Public Health 2017, 75, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacchini, L.; Wahab, T.; Di Giannatale, E.; Zilli, K.; Abass, A.; Garofolo, G.; Janowicz, A. Whole Genome Sequencing for Tracing Geographical Origin of Imported Cases of Human Brucellosis in Sweden. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgi, E.; Walter, M.C.; Pfalzgraf, M.T.; Northoff, B.H.; Holdt, L.M.; Scholz, H.C.; Zoeller, L.; Zange, S.; Antwerpen, M.H. Whole Genome Sequencing of Brucella melitensis Isolated from 57 Patients in Germany Reveals High Diversity in Strains from Middle East. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, T.B.; Scheffer, L.; Jensen, V.K.; Bohlin, J.; Feruglio, S.L. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Antimicrobial Resistance in Brucella melitensis from a Norwegian Perspective. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledwaba, M.B.; Glover, B.A.; Matle, I.; Profiti, G.; Martelli, P.L.; Casadio, R.; Zilli, K.; Janowicz, A.; Marotta, F.; Garofolo, G.; et al. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Brucella abortus Isolates from Various Regions of South Africa. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edao, B.M.; Ameni, G.; Berg, S.; Tekle, M.; Whatmore, A.M.; Wood, J.L.N.; Van Tonder, A.J.; Ashford, R.T.; Ashford, R.T. Whole Genome Sequencing of Ethiopian Brucella abortus Isolates Expands the Known Diversity of an Early Branching Sub-Saharan African Lineage. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1128966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintayehu, G.; Melesse, B.; Abayneh, D.; Sintayehu, A.; Melaku, S.; Alehegne, W.; Mesfin, S.; De Blas, I.; Casal, J.; Allepuz, A.; et al. Epidemiological Survey of Brucellosis in Sheep and Goats in Selected Pastoral and Agro-Pastoral Lowlands of Ethiopia. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 881–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekle, M.; Legesse, M.; Edao, B.M.; Ameni, G.; Mamo, G. Isolation and Identification of Brucella melitensis Using Bacteriological and Molecular Tools from Aborted Goats in the Afar Region of North-Eastern Ethiopia. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakjira, B.S.; Jorga, E.; Lakew, M.; Olani, A.; Tadesse, B.; Tuli, G.; Belaineh, R.; Abera, S.; Kinfe, G.; Gebre, S. Animal Brucellosis: Seropositivity Rates, Isolation and Molecular Detection in Southern and Central Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2022, 13, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESS Housing and Population Census 2007—Affar. Ethiopian Statistical Service, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia 2007. Available online: http://www.statsethiopia.gov.et/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Population-and-Housing-Census-2007-Affar_Statistical.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Yosef, T.; Mengistu, U.; Solomon, A.; Mohammed, Y.K.; Kefelegn, K. Camel and Cattle Population Dynamics and Livelihood Diversification as a Response to Climate Change in Pastoral Areas of Ethiopia. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2013, 25, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, J. Dairy Goat Body Condition Scoring; American Dairy Goat Association, Spindale, NC, USA: 1996. Available online: https://adga.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/adga-dairy-goat-body-condition-scoring.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- Ghosh, C.P.; Datta, S.; Mandal, D.; Das, A.K.; Roy, D.C.; Roy, A.; Tudu, N.K. Body Condition Scoring in Goat: Impact and Significance. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2019, 7, 554–560. [Google Scholar]
- WOAH Brucellosis (Infection with Brucella abortus, B. melitensis and B. suis); World Organization for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2022; pp. 1–48. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/disease/brucellosis/ (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Adamowicz, M.S.; Stasulli, D.M.; Sobestanovich, E.M.; Bille, T.W. Evaluation of Methods to Improve the Extraction and Recovery of DNA from Cotton Swabs for Forensic Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e116351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, C. Improved Method for Purification of Bacterial DNA from Bovine Milk for Detection of Brucella Spp. by PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3735–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baily, G.G.; Krahn, J.B.; Drasar, B.S.; Stoker, N.G. Detection of Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus by DNA Amplification. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1992, 95, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Bricker, B.J.; Halling, S.M. Differentiation of Brucella abortus Bv. 1, 2, and 4, Brucella melitensis, Brucella ovis, and Brucella suis Bv. 1 by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Goñi, I.; García-Yoldi, D.; Marín, C.M.; De Miguel, M.J.; Muñoz, P.M.; Blasco, J.M.; Jacques, I.; Grayon, M.; Cloeckaert, A.; Ferreira, A.C.; et al. Evaluation of a Multiplex PCR Assay (Bruce-Ladder) for Molecular Typing of All Brucella Species, Including the Vaccine Strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3484–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Leung, H.C.M.; Yiu, S.M.; Chin, F.Y.L. IDBA-UD: A de Novo Assembler for Single-Cell and Metagenomic Sequencing Data with Highly Uneven Depth. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, M.; Berkeley, M.R.; Seppey, M.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing Genomic Data Quality and Beyond. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk v2: Memory Friendly Classification with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 5315–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Rinke, C.; Mussig, A.J.; Chaumeil, P.A.; Hugenholtz, P. GTDB: An Ongoing Census of Bacterial and Archaeal Diversity through a Phylogenetically Consistent, Rank Normalized and Complete Genome-Based Taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D785–D794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the Genomic Gold Standard for the Prokaryotic Species Definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid Large-Scale Prokaryote Pan Genome Analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the Problem of Comparing Whole Bacterial Genomes across Different Sequencing Platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v6: Recent Updates to the Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation Tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatmore, A.M.; Perrett, L.L.; MacMillan, A.P. Characterisation of the Genetic Diversity of Brucella by Multilocus Sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatmore, A.M.; Koylass, M.S.; Muchowski, J.; Edwards-Smallbone, J.; Gopaul, K.K.; Perrett, L.L. Extended Multilocus Sequence Analysis to Describe the Global Population Structure of the Genus Brucella: Phylogeography and Relationship to Biovars. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: BIGSdb Software, the PubMLST.Org Website and Their Applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.F.; Sergeant, M.J.; Luhmann, N.; Vaz, C.; Francisco, A.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Achtman, M. Grapetree: Visualization of Core Genomic Relationships among 100,000 Bacterial Pathogens. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florensa, A.F.; Kaas, R.S.; Clausen, P.T.L.C.; Aytan-Aktug, D.; Aarestrup, F.M. ResFinder—An Open Online Resource for Identification of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Next-Generation Sequencing Data and Prediction of Phenotypes from Genotypes. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legesse, A.; Mekuriaw, A.; Gelaye, E.; Abayneh, T.; Getachew, B.; Weldemedhin, W.; Tesgera, T.; Deresse, G.; Birhanu, K. Comparative Evaluation of RBPT, I-ELISA, and CFT for the Diagnosis of Brucellosis and PCR Detection of Brucella Species from Ethiopian Sheep, Goats, and Cattle Sera. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittarelli, M.; Di Ventura, M.; De Massis, F.; Scacchia, M.; Giovannini, A.; Nannini, D.; Caporale, V. The Persistence of Brucella melitensis in Experimentally Infected Ewes Through Three Reproductive Cycles. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2005, 52, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschopp, R.; GebreGiorgis, A.; Abdulkadir, O.; Molla, W.; Hamid, M.; Tassachew, Y.; Andualem, H.; Osman, M.; Waqjira, M.W.; Mohammed, A.; et al. Risk Factors for Brucellosis and Knowledge-Attitude Practice among Pastoralists in Afar and Somali Regions of Ethiopia. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 199, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakew, A.; Hiko, A.; Abraha, A.; Hailu, S.M. Sero-Prevalence and Community Awareness on the Risks Associated with Livestock and Human Brucellosis in Selected Districts of Fafan Zone of Ethiopian-Somali National Regional State. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2019, 7, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legesse, M.; Medhin, G.; Bayissa, M.; Mamo, G. Knowledge and Perception of Pastoral Community Members about Brucellosis as a Cause of Abortion in Animals and Its Zoonotic Importance in Amibara District, Afar Region, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulahi, M. The Legal Status of the Communal Land Holding System in Ethiopia: The Case of Pastoral Communities. Int. J. Minor. Gr. Rights 2007, 14, 85–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.; Schnurrenberger, P.R.; Brown, R.R. Numbers of Brucella abortus in the Placenta, Umbilicus and Fetal Fluid of Two Naturally Infected Cows. Vet. Rec. 1981, 108, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, C.M.; Alabart, J.L.; Blasco, J.M. Effect of Antibiotics Contained in Two Brucella Selective Media on Growth of Brucella abortus, B. melitensis, and B. ovis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Glil, M.Y.; Thomas, P.; Brandt, C.; Melzer, F.; Subbaiyan, A.; Chaudhuri, P.; Harmsen, D.; Jolley, K.A.; Janowicz, A.; Garofolo, G.; et al. Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Improved Characterization and Epidemiological Surveillance of Pathogenic Brucella. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0031122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfroid, J.; Käsbohrer, A. Brucellosis in the European Union and Norway at the Turn of the Twenty-First Century. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 90, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, H.A. Briefing Paper Livestock Trade in the Kenyan, Somali and Ethiopian Borderlands; Chatham House: London, UK, 2010; Available online: https://www.chathamhouse.org/sites/default/files/public/Research/Africa/0910mahmoud.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Intergovernmental Authority for Development. Identification and Mapping of Key CrossBorder Livestock Routes and Markets, Services and Priority Transboundary Animal Diseases Including Zoonotics for Regional and International Trade; Intergovernmental Authority for Development, IGAD Center for Pastoral Areas and Livestock Development (ICPALD): Nairobi, Kenya, 2013; pp. 9–39. Available online: https://icpald.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/Cross-border-livestock-routes-and-markets-TADs-and-zoonoses-study-7.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Khan, A.U.; Melzer, F.; Sayour, A.E.; Shell, W.S.; Linde, J.; Abdel-glil, M.; El-soally, S.A.G.E.; Elschner, M.C.; Sayour, H.E.M.; Ramadan, E.S.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing for Tracing the Genetic Diversity of Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis Isolated from Livestock in Egypt. Pathogens 2021, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadar, M.; Alamian, S.; Brangsch, H.; Elbadawy, M.; Elkharsawi, A.R.; Neubauer, H.; Wareth, G. Determination of Virulence-Associated Genes and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Brucella Isolates Recovered from Humans and Animals in Iran Using NGS Technology. Pathogens 2023, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, Z.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Hashemi, S.H.; Kamarehei, F.; Arabestani, M.R. Prevalence of the Most Common Virulence- Associated Genes among Brucella melitensis Isolates from Human Blood Cultures in Hamadan Province, West of Iran. Iran J. Med. Sci. 2016, 41, 422–429. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemifar, I.; Yadegar, A.; Jazi, F.M.; Amirmozafari, N. Molecular Prevalence of Putative Virulence-Associated Genes in Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus Isolates from Human and Livestock Specimens in Iran. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnejad, R.; Jazi, F.M.; Mostafaei, S.; Sedighi, M. Molecular Investigation of Virulence Factors of Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus Strains Isolated from Clinical and Non-Clinical Samples. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, J.M.; Molina-Flores, B. Control and Eradication of Brucella melitensis Infection in Sheep and Goats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2011, 27, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, J.M. A Review of the Use of B. melitensis Rev 1 Vaccine in Adult Sheep and Goats. Prev. Vet. Med. 1997, 31, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Month (2022) | No. Villages Visited § | No. HHs Visited | No. HHs with Recent * Abortion (%) | No. HHs Positive for B. melitensis (%) | No. Animals Positive for B. melitensis (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May | 2 | 312 | 89/312 (28.5) | 13/89 (14.6) | 13/119 (10.9) |
| Oct–Nov | 5 | 419 | 54/419 (12.9) | 17/54 (31.5) | 22/112 (19.6) |
| Total | 6 | 731 | 143/731 (19.6) | 29/143 (20.3) | 35/231 (15.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sibhat, B.; Adamu, H.; Asmare, K.; Lindahl, J.F.; Magnusson, U.; Sisay Tessema, T. Detection and Molecular Diversity of Brucella melitensis in Pastoral Livestock in North-Eastern Ethiopia. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121063
Sibhat B, Adamu H, Asmare K, Lindahl JF, Magnusson U, Sisay Tessema T. Detection and Molecular Diversity of Brucella melitensis in Pastoral Livestock in North-Eastern Ethiopia. Pathogens. 2024; 13(12):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121063
Chicago/Turabian StyleSibhat, Berhanu, Haileeyesus Adamu, Kassahun Asmare, Johanna F. Lindahl, Ulf Magnusson, and Tesfaye Sisay Tessema. 2024. "Detection and Molecular Diversity of Brucella melitensis in Pastoral Livestock in North-Eastern Ethiopia" Pathogens 13, no. 12: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121063
APA StyleSibhat, B., Adamu, H., Asmare, K., Lindahl, J. F., Magnusson, U., & Sisay Tessema, T. (2024). Detection and Molecular Diversity of Brucella melitensis in Pastoral Livestock in North-Eastern Ethiopia. Pathogens, 13(12), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121063








