First Report of Trypanosoma vivax (Duttonella), Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina DNA in Cattle from the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador, and Its Relationship with Anaplasma marginale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
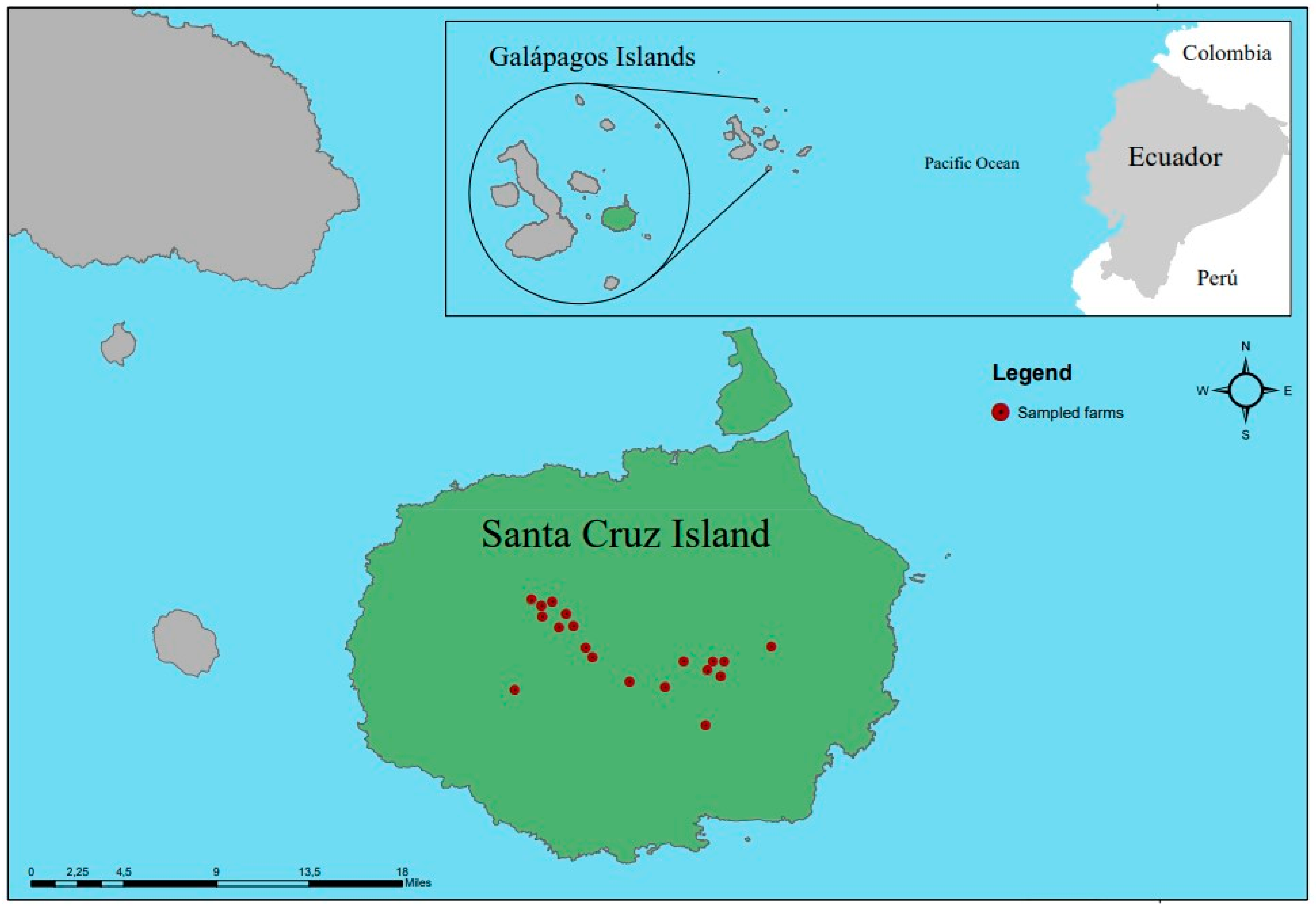
2.1. Study Area and Collection of Blood Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Diagnostic of Haemotropic Agents by PCR
2.4. CatL-PCR to Detect T. vivax
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
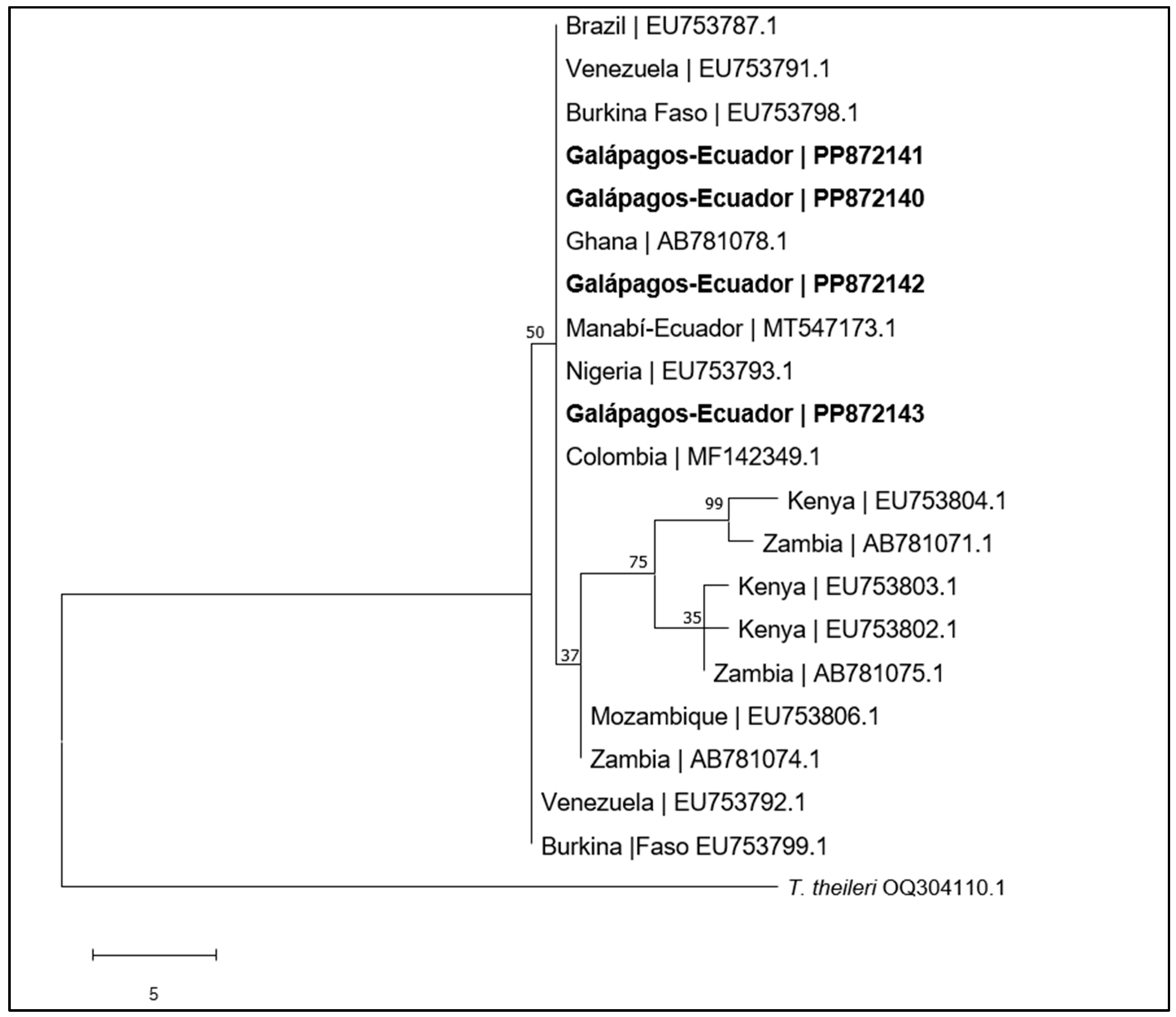
4.1. Trypanosoma vivax
4.2. Anaplasma marginale
4.3. Babesia spp.
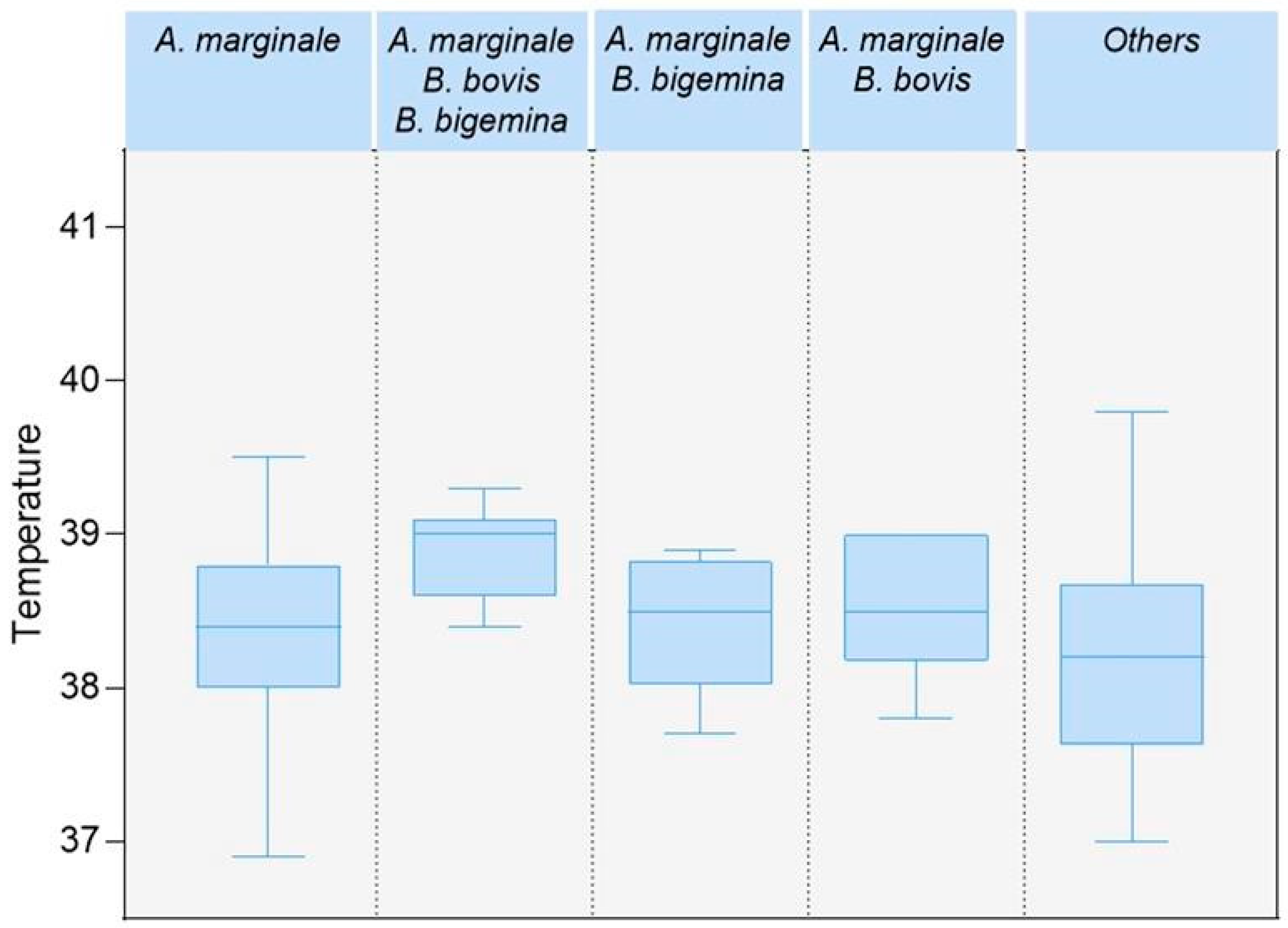
4.4. Coinfections
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fetene, E.; Leta, S.; Regassa, F.; Büscher, P. Global Distribution, Host Range and Prevalence of Trypanosoma Vivax: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florentin, A.; Garcia Perez, H.A.; Rodrigues, C.M.F.; Dubois, E.F.; Monzón, C.M.; Teixeira, M.M.G. Molecular Epidemiological Insights into Trypanosoma vivax in Argentina: From the Endemic Gran Chaco to Outbreaks in the Pampas. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, T.S.A.; Faria, A.M.; Madrid, D.M.D.C.; Bessa, L.C.D.; Linhares, G.F.C.; Fidelis Junior, O.L.; Sampaio, P.H.; Cruz, B.C.; Cruvinel, L.B.; Nicaretta, J.E.; et al. First Outbreak and Subsequent Cases of Trypanosoma Vivax in the State of Goiás, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Veterinária 2017, 26, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, O.L.E.; Macedo, L.O.D.; Santos, M.A.B.; Silva, J.A.B.A.; Mendonça, C.L.D.; Faustino, M.A.D.G.; Ramos, C.A.D.N.; Alves, L.C.; Ramos, R.A.N.; Carvalho, G.A.D. Detection and Molecular Characterization of Trypanosoma (Duttonella) Vivax in Dairy Cattle in the State of Sergipe, Northeastern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Veterinária 2017, 26, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzatti, M.I.; González-Baradat, B.; Aso, P.M.; Reyna-Bello, A. Trypanosoma (Duttonella) Vivax and Typanosomosis in Latin America: Secadera/Huequera/Cacho Hueco. In Trypanosomes and Trypanosomiasis; Magez, S., Radwanska, M., Eds.; Springer: Wien, Austria, 2014; pp. 261–285. ISBN 978-3-7091-1556-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jaimes-Dueñez, J.; Triana-Chávez, O.; Mejía-Jaramillo, A.M. Parasitological and Molecular Surveys Reveal High Rates of Infection with Vector-Borne Pathogens and Clinical Anemia Signs Associated with Infection in Cattle from Two Important Livestock Areas in Colombia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aregawi, W.G.; Agga, G.E.; Abdi, R.D.; Büscher, P. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Global Distribution, Host Range, and Prevalence of Trypanosoma Evansi. Parasites. Vectors 2019, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Iglesias, J.R.; Eleizalde, M.C.; Reyna-Bello, A.; Mendoza, M. Molecular diagnosis of cattle trypanosomes in Venezuela: Evidences of Trypanosoma Evansi and Trypanosoma Vivax infections. J. Parasites Dis. 2017, 41, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Larrea, M.A.; Cholota-Iza, C.; Cueva-Villavicencio, J.; Yugcha-Díaz, M.; Ron-Román, J.W.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, A.; Saegerman, C.; Reyna-Bello, A. Molecular Identification of Trypanosoma Theileri (Laveran, 1902) in Cattle from Two Slaughterhouses in Ecuador and Its Relation with Other Haemotropic Agents. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1153069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocan, K.M.; De La Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Coetzee, J.F.; Ewing, S.A. The Natural History of Anaplasma Marginale. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, R.; Jackson, L.; De Vos, A.; Jorgensen, W. Babesiosis of Cattle. Parasitology 2004, 129, S247–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rar, V.; Tkachev, S.; Tikunova, N. Genetic Diversity of Anaplasma Bacteria: Twenty Years Later. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 91, 104833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdala, A.A.; Larriestra, A.J.; Signorini, M. Estimación de pérdidas económicas causadas por Trypanosoma vivax en un rodeo lechero de Argentina. Rev. Vet. 2021, 31, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, A.; Dávila, A.M.; Silva, R.A. Estimated Financial Impact of Trypanosoma Vivax on the Brazilian Pantanal and Bolivian Lowlands. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1999, 94, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osório, A.L.A.R.; Madruga, C.R.; Desquesnes, M.; Soares, C.O.; Ribeiro, L.R.R.; Costa, S.C.G.D. Trypanosoma (Duttonella) Vivax: Its Biology, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Introduction in the New World—A Review. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2008, 103, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magri, A.; Galuppi, R.; Fioravanti, M. Autochthonous Trypanosoma spp. in European Mammals: A Brief Journey amongst the Neglected Trypanosomes. Pathogens 2021, 10, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cadena, E.; Camacho, M.; Vaca, F.; Enríquez, S.; Eleizalde, M.C.; Arrivillaga-Henríquez, J.; Mendoza, M.; Navarro, J.C.; Ramírez-Iglesias, J.R. Molecular Identification of Trypanosoma Theileri in Cattle from the Ecuadorian Amazon. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2023, 37, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Naranjo, V.L.; Reyna-Bello, A.; Tavares-Marques, L.M.; Campos, A.M.; Ron-Román, J.W.; Moyano, J.C.; Jarrín-Porras, E.C.; Sandoval-Morejón, E.D.; Chávez-Larrea, M.A. Diagnosis of hemotropics Anaplasma marginale, Trypanosoma spp. and Babesia spp. by ELISAi and PCR techniques in three livestock farms of Pastaza Province, Ecuador. Rev. Cient. Fac. Vet. 2017, 27, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, E.A.; Betancourt, A.; Ramirez, L.E. Serological Evidence for the Geographical Distribution of Trypanosoma Vivax in the New World. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1977, 71, 448–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Larrea, M.A.; Medina-Pozo, M.L.; Cholota-Iza, C.E.; Jumbo-Moreira, J.R.; Saegerman, C.; Proaño-Pérez, F.; Ron-Román, J.; Reyna-Bello, A. First Report and Molecular Identification of Trypanosoma (Duttonella) Vivax Outbreak in Cattle Population from Ecuador. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2422–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plan Galápagos Plan de Desarrollo Sustentable y Ordenamiento Territorial del Régimen Especial de Galápagos; Plan Galápagos: Puerto Baquerizo Moreno, Ecuador, 2016.
- Instituto Nacional de Estadisticas y Censos Ecuador INEC Censo Nacional Agropecuario 2000. Available online: https://www.ecuadorencifras.gob.ec/censo-nacional-agropecuario (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Rhea, S.; Camacho, B.E.; Amoriello, C.W.; Correa, M.; Lewbart, G.A.; Cruz, M.; Vélez, A.; Castillo, P.; Pairis-Garcia, M. Assessing Livestock Production Practices on Small-Scale Multi-Species Farms Located on Floreana Island, Galápagos Islands. Animals 2023, 13, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, V.; Escudero, L.; Valverde, M.; Allauca, J. Productividad y Sostenibilidad de Los Sistemas de Producción Agropecuaria de Las Islas Galápagos-Ecuador; Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Agropecuarias (INIAP): Quito, Ecuador, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gioia, G.V.; Vinueza, R.L.; Marsot, M.; Devillers, E.; Cruz, M.; Petit, E.; Boulouis, H.J.; Moutailler, S.; Monroy, F.; Coello, M.A.; et al. Bovine Anaplasmosis and Tick-Borne Pathogens in Cattle of the Galapagos Islands. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.J.; Rosenberg, D.E.; Yirui, H. Prevalence of Vector-Borne Diseases in a Sample of Client-Owned Dogs on Santa Cruz in the Galápagos Islands: A Pilot Study. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2016, 6, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheibel, J.; Garcia-Porta, J.; Quezada, G.; Ibáñez, A. Phylogeography and Prevalence of Hemoparasites (Apicomplexa: Eucoccidiorida) in Galápagos Marine Iguanas, Amblyrhynchus Cristatus (Reptilia: Iguanidae). Animals 2022, 12, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleizalde, M.C.; Gómez-Piñeres, E.; Ramírez-Iglesias, J.R.; Mendoza, M. Evaluation of Five Primer Sets for Molecular Detection of Trypanosoma Vivax by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Their Implementation for Diagnosis in Naturally Infected Ruminants from Venezuela. Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Reports 2021, 25, 100594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masake, R.A.; Majiwa, P.A.; Moloo, S.K.; Makau, J.M.; Njuguna, J.T.; Maina, M.; Kabata, J.; Nantulya, V.M. Sensitive and Specific Detection of Trypanosoma vivax Using the Polymerase Chain Reaction. Exp. Parasitol. 1997, 85, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, A.P.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Garcia, H.A.; Neves, L.; Batista, J.S.; Bengaly, Z.; Paiva, F.; Teixeira, M.M.G. Cathepsin L-Like Genes of Trypanosoma Vivax from Africa and South America—Characterization, Relationships and Diagnostic Implications. Mol. Cell. Probes 2009, 23, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, W.G.; Claes, F.; My, L.N.; Thanh, N.G.; Tam, P.T.; Verloo, D.; Büscher, P.; Goddeeris, B.; Vercruysse, J. A comparative evaluation of parasitological tests and a PCR for Trypanosoma evansi diagnosis in experimentally infected water buffaloes. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 97, 23–33. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0304401701003818 (accessed on 1 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Braem, C. Evaluation of DNA Extraction Methods and Primersets for Diagnosis of Sleeping Sickness. Doctoral Dissertation, UIA, Antwerp, Belgium, 1999; 50p. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, N.; Sivakumar, T.; Fukushi, S.; Tattiyapong, M.; Tuvshintulga, B.; Kothalawala, H.; Silva, S.S.P.; Igarashi, I.; Inoue, N. Genetic diversity in Trypanosoma theileri from Sri Lankan cattle and water buffaloes. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.C.; Garcia, H.A.; Ortiz, P.A.; Cortez, A.P.; Martinkovic, F.; Paiva, F.; Batista, J.S.; Minervino, A.H.; Campaner, M.; Pral, E.M.; et al. Cysteine proteases of Trypanosoma (Megatrypanum) theileri: Cathepsin L-like gene sequences as targets for phylogenetic analysis, genotyping diagnosis. Parasitol. Int. 2010. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1383576910000553 (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Olmeda, A.S.; Armstrong, P.M.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Valladares, B.; Del Castillo, A.; De Armas, F.; Miguelez, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Rodrıguez, J.R.; Spielman, A.; et al. A subtropical case of human babesiosis. Acta Tropica 1997, 67, 229–234. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0001706X97000454 (accessed on 1 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.V.; Chieves, L.P.; Johnson, G.S.; Buening, G.M. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction based assay for the detection of Babesia bigemina, Babesia bovis and Anaplasma marginale DNA in bovine blood. Vet. Parasitol. 1993, 50, 69–81. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/030440179390008B (accessed on 1 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.E.; Palmer, G.H.; Jasmer, D.P.; Hines, S.A.; Perryman, L.E.; McElwain, T.F. Characterization of the gene encoding a 60-kilodalton Babesia bovis merozoite protein with conserved and surface exposed epitopes. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1991, 46, 45–52. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/016668519190197E (accessed on 1 October 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa-Millán, J.V.; Lira-Amaya, J.J.; Castañeda-Arriola, R.; Álvarez-Martínez, J.A.; Takata, C.; Bautista-Garfias, C.R. Optimización de una prueba de PCR-RFLP para detección y diferenciación de Babesia sp en garrapatas Rhipicephalus microplus. Entomol. Mex. 2014, 1, 978–983. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, J.V.; Chieves, L.P.; Johnson, G.S.; Buening, G.M. Detection of Babesia bigemina-infected carriers by polymerase chain reaction amplification. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 2576–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tana-Hernández, L.; Navarrete-Arroyo, K.; Ron-Román, J.; Reyna-Bello, A.; Chávez-Larrea, M.A. PCR-Diagnosis of Anaplasma Marginale in Cattle Populations of Ecuador and Its Molecular Identification through Sequencing of Ribosomal 16S Fragments. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna-Bello, A.; Cloeckaert, A.; Vizcaíno, N.; Gonzatti, M.I.; Aso, P.M.; Dubray, G.; Zygmunt, M.S. Evaluation of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Using Recombinant Major Surface Protein 5 for Serological Diagnosis of Bovine Anaplasmosis in Venezuela. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1998, 5, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desquesnes, M.; Gonzatti, M.; Sazmand, A.; Thévenon, S.; Bossard, G.; Boulangé, A.; Gimonneau, G.; Truc, P.; Herder, S.; Ravel, S.; et al. A Review on the Diagnosis of Animal Trypanosomoses. Parasites. Vectors 2022, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Pérez, H.A.; Rodrigues, C.M.F.; Pivat, I.H.V.; Fuzato, A.C.R.; Camargo, E.P.; Minervino, A.H.H.; Teixeira, M.M.G. High Trypanosoma Vivax Infection Rates in Water Buffalo and Cattle in the Brazilian Lower Amazon. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 79, 102162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, T.S.A.; Faria, A.M.; Couto, L.F.M.; Nicaretta, J.E.; Cavalcante, A.S.D.A.; Zapa, D.M.B.; Ferreira, L.L.; Heller, L.M.; Madrid, D.M.D.C.; Cruvinel, L.B.; et al. Epidemiological and Molecular Identification of Trypanosoma Vivax Diagnosed in Cattle during Outbreaks in Central Brazil. Parasitology 2020, 147, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes-Dueñez, J.; Triana-Chávez, O.; Mejía-Jaramillo, A.M. Spatial-Temporal and Phylogeographic Characterization of Trypanosoma spp. in Cattle (Bos Taurus) and Buffaloes (Bubalus Bubalis) Reveals Transmission Dynamics of These Parasites in Colombia. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 249, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.B.; Wiedenfeld, D.A.; Snell, H.L. Current Status of Alien Vertebrates in the Galápagos Islands: Invasion History, Distribution, and Potential Impacts. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desquesnes, M. Livestock Trypanosomoses and Their Vectors in Latin America; OIE: Paris, France, 2004; ISBN 978-92-9044-634-7. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnizo, T.R.M.; Alvarez, D.O.; Díaz-Sánchez, A.A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Gutiérrez, L.Z.; Marrero, S.M.; Corona-González, B. Epidemiology and Genetic Diversity of Anaplasma Marginale in Zamora-Chinchipe, Ecuador. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, J.D.M.; Blanco, Y.A.C.; Bruhn, F.R.P.; Guimarães, A.M. Seroprevalence of Trypanosoma Vivax, Anaplasma Marginale, and Babesia Bovis in Dairy Cattle. Ciênc. Anim. Bras. 2016, 17, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.V.C.; Abreu, A.P.M.; Thomé, S.M.G.; Massard, C.L.; Santos, H.A.; Ubiali, D.G.; Brito, M.F. Parasitological and Clinical-Pathological Findings in Twelve Outbreaks of Acute Trypanosomiasis in Dairy Cattle in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 22, 100466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, C.E.; Alzan, H.F.; Silva, M.G.; Rathinasamy, V.; Poole, W.A.; Cooke, B.M. Unravelling the Cellular and Molecular Pathogenesis of Bovine Babesiosis: Is the Sky the Limit? Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, A.; Moreau, E.; Bonnet, S.; Plantard, O.; Malandrin, L. Babesia and Its Hosts: Adaptation to Long-Lasting Interactions as a Way to Achieve Efficient Transmission. Vet. Res. 2009, 40, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya-Delgado, A.; Madder, M.; Benítez-Ortíz, W.; Saegerman, C.; Berkvens, D.; Ron-Garrido, L. Molecular Screening of Cattle Ticks, Tick-Borne Pathogens and Amitraz Resistance in Ticks of Santo Domingo de Los Tsáchilas Province in Ecuador. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buestán, J.; Navarrete, R. Lista actualizada de Tabanos (Diptera: Tabanidae) del Ecuador. Rev. Ecuat. Hig. Med. Trop. 2007, 44, 23–78. [Google Scholar]
- Reinbold, J.B.; Coetzee, J.F.; Hollis, L.C.; Nickell, J.S.; Riegel, C.M.; Christopher, J.A.; Ganta, R.R. Comparison of Iatrogenic Transmission of Anaplasma Marginale in Holstein Steers via Needle and Needle-Free Injection Techniques. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2010, 71, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, E.; Vourc’h, G.; Vial, L.; Chevillon, C.; McCoy, K.D. Changing Distributions of Ticks: Causes and Consequences. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 59, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, C.L.; Lincango, M.P.; Causton, C.E.; Parker, P.G. Trypanosomatids Detected in the Invasive Avian Parasite Philornis downsi (Diptera: Muscidae) in the Galapagos Islands. Insects 2020, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, R.; De Vos, A.; Kingston, T.; Mclellan, D. Effect of Breed of Cattle on Innate Resistance to Infection with Babesia Bovis, B Bigemina and Anaplasma Marginale. Aust. Vet. J. 1997, 75, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavides, M.V.; Sacco, A.M.S. Differential Bos Taurus Cattle Response to Babesia Bovis Infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 150, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmone, A.A. Epidemiology of Babesiosis and Anaplasmosis in South and Central America. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 57, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Salas, D.; Mira, A.; Mosqueda, J.; García-Vázquez, Z.; Hidalgo-Ruiz, M.; Vela, N.A.O.; De León, A.A.P.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Schnittger, L. Molecular and Serological Detection of Babesia Bovis and Babesia Bigemina Infection in Bovines and Water Buffaloes Raised Jointly in an Endemic Field. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 217, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Organism | Target Gen | Primers (Sequence 5′-3′) | Size (bp) | Thermocycler Conditions | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Cycle | 35 Cycles | 1 Cycle | |||||||
| ID | D | H | E | FE | |||||
| T. vivax | Diagnostic antigen (Da) | ILO 1264 (CAGCTCGGCGAAGGCCACTTGGCTGGG) ILO 1265 (TCGCTACCACAGTCGCAATCGTCGTCTCAAGG) | ~400 | 5′ to 95 °C | 30″ to 95 °C | 30″ to 60 °C | 1′ to 72 °C | 10′ to 72 °C | [28,29] |
| Catl | TviCatL1 (CGTCTCTGGCTCCGGTCAAAC) DTO155 (TTAAAGCTTCCACGAGTTCTTGATGATCCAGTA) | ~177 | 5′ to 94 °C | 30″ to 94 °C * | 30″ to 65 °C | 30″ to 72 °C | 10′ to 72 °C | [20,30] | |
| T. evansi | ESAG | ESAG 6/7F (ACATTCCAGCAGGAGTTGGAG) ESAG 6/7R (CACGTGAATCCTCAATTTTGT) | ~237 | 4′ to 94 °C | 1′ to 94 °C | 1′ to 65 °C | 30″ to 72 °C | 5′ to 72 °C | [31,32] |
| T. theileri | Catl | TthCatL1 (CGTCTCTGGCTCCGGTCAAAC) DTO155 (TTAAAGCTTCCACGAGTTCTTGATGATCCAGTA) | ~273 | 5′ to 95 °C | 30″ to 95 °C * | 30″ to 63 °C * | 30″ to 72 °C * | 10′ to 72 °C | [33,34] |
| Babesia sp. | 18S rRNA | PIRO A (AATACCCAATCCTGACACAGGG) PIRO B (TTAAATACACGAATGCCCCCCCAAC) | ~400 | 5′ to 94 °C | 1′ to 94 °C | 1′ to 61 °C | 30″ to 72 °C | 5′ to 72 °C | [18,35] |
| B. bovis | rap-1 | BoF (CACGAGGAAGGAACTACCGATGTTGA) BoR (CCAAGGAGCTTCAACGTACGAGGTCA) | ~356 | 5′ to 95 °C | 1′ to 95 °C | 1′ to 63 °C | 30″ to 72 °C | 7′ to 72 °C | [36,37] |
| B. bigemina | hyp | BilA (CATCTAATTTCTCTCCTACCCCTCC) BilB (CCTCGGCTTCAACTCTGATGCCAAAG) | ~278 | 5′ to 95 °C | 1′ to 95 °C | 1′ to 60 °C | 30″ to 72 °C | 7′ to 72 °C | [38,39] |
| A. marginale | msp5 | 19A (GTTGTTCCTGGGGTACTCCTA) 19B (TGATCTGGTCAGCCCCAGCT) | ~715 | 5′ to 94 °C | 45″ to 94 °C | 30″ to 64 °C | 1′ to 72 °C | 10′ to 72 °C | [40,41] |
| Infections | Bella Vista | Puerto Ayora | Santa Rosa | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm (n = 4) | Cattle (n = 40) | Farm (n = 2) | Cattle (n = 14) | Farm (n = 13) | Cattle (n = 116) | Farm (n = 19) | Cattle (n = 170) | |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| T. vivax | 3 (75) | 7 (17.5) | 0 | 0 | 5 (38.5) | 18 (15.5) | 8 (42.1) | 25 (14.7) |
| B. bovis | 1 (25) | 4 (10) | 0 | 0 | 8 (61.5) | 15 (12.9) | 9 (47.4) | 19 (11.2) |
| B. bigemina | 3 (75) | 4 (10) | 2 (100) | 2 (14.3) | 10 (76.9) | 19 (16.4) | 15 (78.9) | 25 (14.7) |
| A. marginale | 4 (100) | 23 (57.5) | 2 (100) | 10 (71.4) | 13 (100) | 81 (69.8) | 19 (100) | 114 (67.1) |
| T. vivax Da-PCR | B. bovis rap-1-PCR | B. bigemina hyp-PCR | A. marginale msp5-PCR | Total (No. %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - | 42 (24.7) |
| - | - | - | + | 75 (44.1) |
| - | - | + | - | 3 (1.8) |
| - | - | + | + | 11 (6.5) |
| - | + | - | - | 3 (1.8) |
| - | + | - | + | 3 (1.8) |
| - | + | + | - | 1 (0.6) |
| - | + | + | + | 7 (4.1) |
| + | - | - | - | 7 (4.1) |
| + | - | - | + | 12 (7.1) |
| + | - | + | + | 1 (0.6) |
| + | + | - | + | 3 (1.8) |
| + | + | + | + | 2 (1.2) |
| n = 170 |
| T. vivax Da-PCR | B. bovis rap-1-PCR | B. bigemina hyp-PCR | A. marginale msp5-PCR | Total (No. %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | + | 2 (10.5) |
| - | - | + | + | 5 (26.3) |
| - | + | - | + | 1 (5.3) |
| - | + | + | + | 3 (15.8) |
| + | - | - | + | 1 (5.3) |
| + | - | + | + | 2 (10.5) |
| + | + | + | + | 5 (26.3) |
| n = 19 | ||||
| Explanatory Variable | Modalities | Nº Animals Sampled (%) | T. vivax Da-PCR | Babesia spp. 18S rRNA-PCR | B. bovis rap-1-PCR | B. bigemina hyp-PCR | A. marginale msp5-PCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Sex | Male | 12 (7.1) | 1 (8.3) | 6 (50) | 3 (25) | 6 (50) | 9 (75) |
| Female | 158 (92.9) | 24 (15.2) | 28 (17.7) | 16 (10.1) | 19 (12) | 105 (66.5) | |
| Age | 0–9 months | 5 (3) | 0 | 3 (60) | 1 (20) | 2 (40) | 5 (100) |
| 10–18 months | 16 (9.4) | 4 (25) | 10 (62.5) | 8 (50) | 9 (56.3) | 15 (93.8) | |
| 19–36 months | 39 (22.9) | 6 (15.4) | 9 (23.1) | 4 (10.3) | 6 (15.4) | 33 (84.6) | |
| >36 months | 107 (62.9) | 15 (14) | 12 (11.2) | 6 (5.6) | 8 (7.5) | 59 (55.1) | |
| ND | 3 (1.8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (66.7) | |
| Breed | Crossbreed | 30 (17.6) | 3 (10) | 10 (33.3) | 5 (16.7) | 8 (26.7) | 28 (93.3) |
| Holstein | 28 (16.5) | 3 (10.7) | 2 (7.1) | 0 | 2 (7.1) | 16 (57.1) | |
| Brown Swiss | 30 (17.6) | 7 (23.3) | 6 (20) | 4 (13.3) | 5 (16.7) | 17 (56.7) | |
| Simmental | 78 (45.9) | 12 (15.4) | 15 (19.2) | 10 (12.8) | 9 (11.5) | 50 (64.1) | |
| ND | 4 (2.4) | 0 | 1 (25) | 0 | 1 (25) | 3 (75) |
| Explanatory Variable | Modalities | Total Farms (%) | T. vivax Da-PCR | Babesia spp. 18S rRNA-PCR | B. bovis rap-1-PCR | B. bigemina hyp-PCR | A. marginale msp5-PCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Production system | Meat | 3 (15.8) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | 3 (100) |
| Mixed | 16 (84.2) | 7 (43.8) | 14 (87.5) | 8 (50) | 13 (81.3) | 16 (100) | |
| Livestock movement | No | 8 (42.1) | 5 (62.5) | 7 (87.5) | 6 (75) | 7 (87.5) | 8 (100) |
| Yes | 11 (57.9) | 3 (27.3) | 9 (81.8) | 3 (27.3) | 8 (72.7) | 11 (100) | |
| Separate sick cattle | No | 5 (26.3) | 2 (40) | 4 (80) | 2 (40) | 4 (80) | 5 (100) |
| Yes | 14 (84.2) | 6 (42.9) | 12 (85.7) | 7 (50) | 11 (78.6) | 14 (100) | |
| Change needles | No | 9 (47.4) | 4 (44.4) | 8 (88.9) | 3 (33.3) | 7 (77.8) | 9 (100) |
| Yes | 10 (57.9) | 4 (40) | 8 (80) | 6 (60) | 8 (80) | 10 (100) | |
| Pasture rotation | No | 4 (21.1) | 2 (50) | 3 (75) | 3 (75) | 3 (75) | 4 (100) |
| Yes | 15 (73.7) | 6 (40) | 13 (86.7) | 6 (40) | 12 (80) | 15 (100) | |
| Presence of vectors | Ticks | 13 (76.5) | 7 (53.8) | 12 (92.3) | 6 (46.2) | 12 (92.3) | 13(100) |
| Ticks and flies | 4 (23.5) | 0 | 3 (75) | 2 (50) | 2 (50) | 4 (100) | |
| Presence of other domestic animals | No | 6 (31.6) | 1 (16.7) | 5 (83.3) | 2 (33.3) | 5 (83.3) | 6 (100) |
| Yes | 13 (68.4) | 7 (53.9) | 11 (84.6) | 7 (53.8) | 10 (76.9) | 13 (100) | |
| Presence of dead animals last year | No | 12 (63.2) | 5 (41.7) | 11 (91.7) | 7 (58.3) | 10 (83.3) | 12 (100) |
| Yes | 6 (31.6) | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 1 (16.7) | 4 (66.7) | 6 (100) | |
| Presence of urine with blood | No | 17 (89.5) | 7 (41.2) | 14 (82.4) | 7 (41.2) | 13 (76.5) | 17 (100) |
| Yes | 2 (10.5) | 1 (50) | 2 (100) | 2 (100) | 2 (100) | 2 (100) | |
| Muscle tremors | No | 18 (94.7) | 8 (44.4) | 15 (83.3) | 8 (44.4) | 14 (77.8) | 18 (100) |
| Yes | 1 (5.3) | 0 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | 1 (100) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chávez-Larrea, M.A.; Cholota-Iza, C.; Yugcha-Diaz, M.; Ron-Román, J.; Proaño-Pérez, F.; Maya-Delgado, A.; Jumbo-Moreira, J.; Reyna-Bello, A.; Saegerman, C. First Report of Trypanosoma vivax (Duttonella), Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina DNA in Cattle from the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador, and Its Relationship with Anaplasma marginale. Pathogens 2024, 13, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100910
Chávez-Larrea MA, Cholota-Iza C, Yugcha-Diaz M, Ron-Román J, Proaño-Pérez F, Maya-Delgado A, Jumbo-Moreira J, Reyna-Bello A, Saegerman C. First Report of Trypanosoma vivax (Duttonella), Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina DNA in Cattle from the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador, and Its Relationship with Anaplasma marginale. Pathogens. 2024; 13(10):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100910
Chicago/Turabian StyleChávez-Larrea, María Augusta, Cristina Cholota-Iza, Michelle Yugcha-Diaz, Jorge Ron-Román, Freddy Proaño-Pérez, Alicia Maya-Delgado, Jimmy Jumbo-Moreira, Armando Reyna-Bello, and Claude Saegerman. 2024. "First Report of Trypanosoma vivax (Duttonella), Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina DNA in Cattle from the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador, and Its Relationship with Anaplasma marginale" Pathogens 13, no. 10: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100910
APA StyleChávez-Larrea, M. A., Cholota-Iza, C., Yugcha-Diaz, M., Ron-Román, J., Proaño-Pérez, F., Maya-Delgado, A., Jumbo-Moreira, J., Reyna-Bello, A., & Saegerman, C. (2024). First Report of Trypanosoma vivax (Duttonella), Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina DNA in Cattle from the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador, and Its Relationship with Anaplasma marginale. Pathogens, 13(10), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100910








