Interferon-λ Activates a Differential Response in Peripheral Neurons That Is Effective against Alpha Herpesvirus Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus Strains
2.2. Primary Neuronal Culture
2.3. Viral Infection and Drug Treatment in Compartment Neuronal Cultures
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
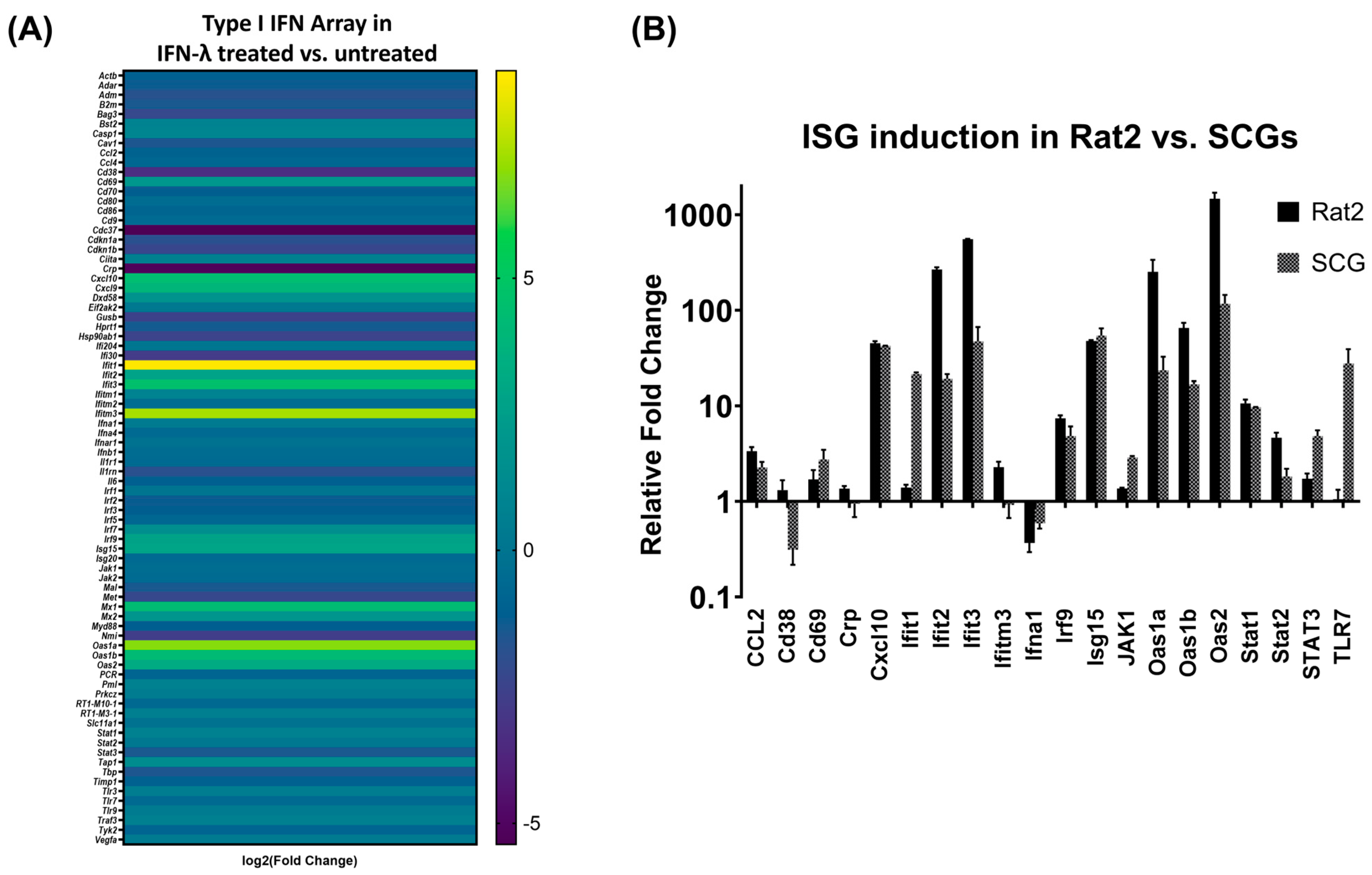
3.1. IFN-λ Treatment Activates a Differential Response in Rat2 Cells versus Primary Neurons
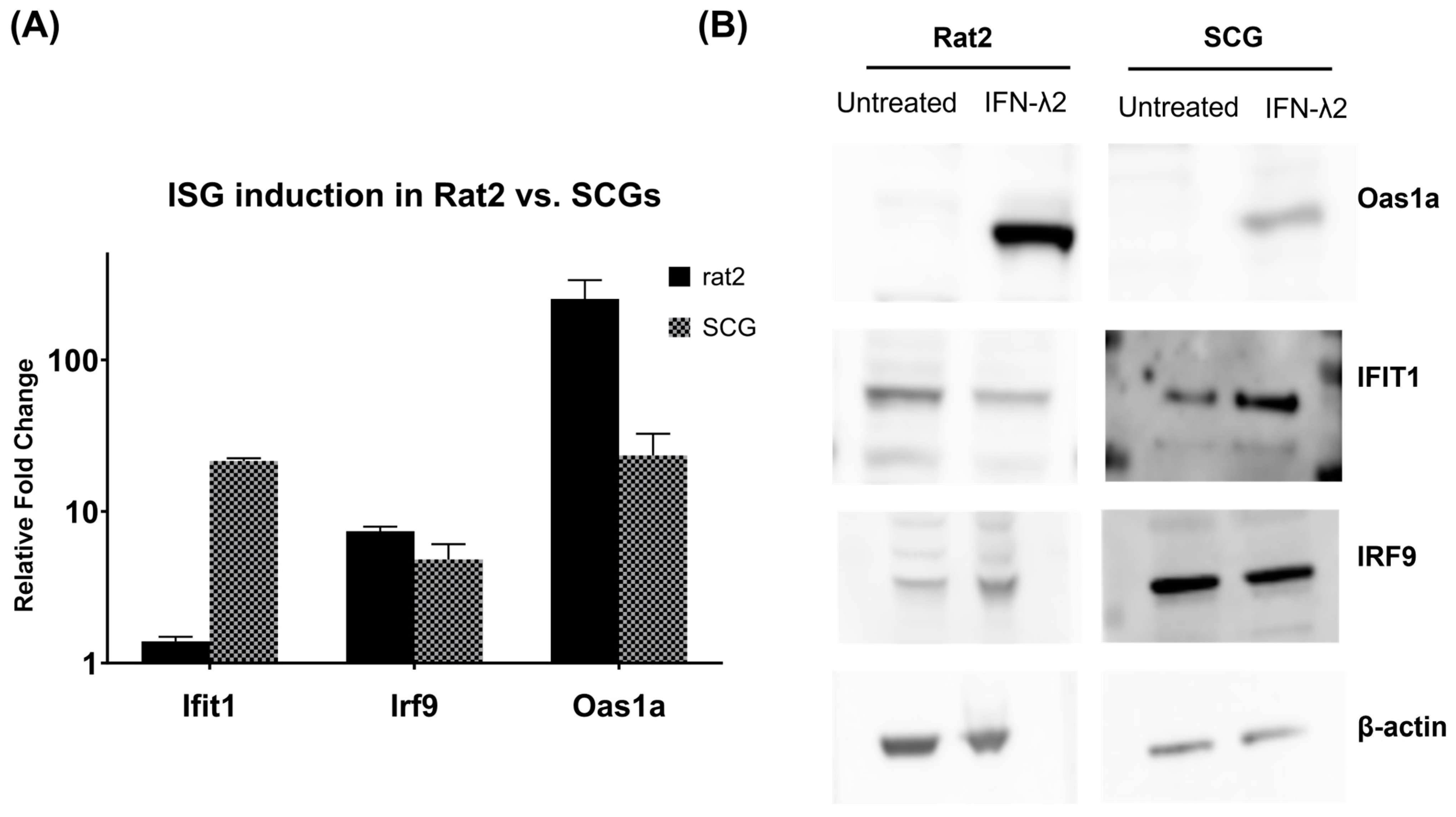
3.2. IFN-λ Induces Differential Expression of Interferon Stimulated Genes (ISG) in Primary Neurons
3.3. Verification of Target ISG Induction in Rat2 Cells vs. Primary Neurons upon IFN-λ Treatment
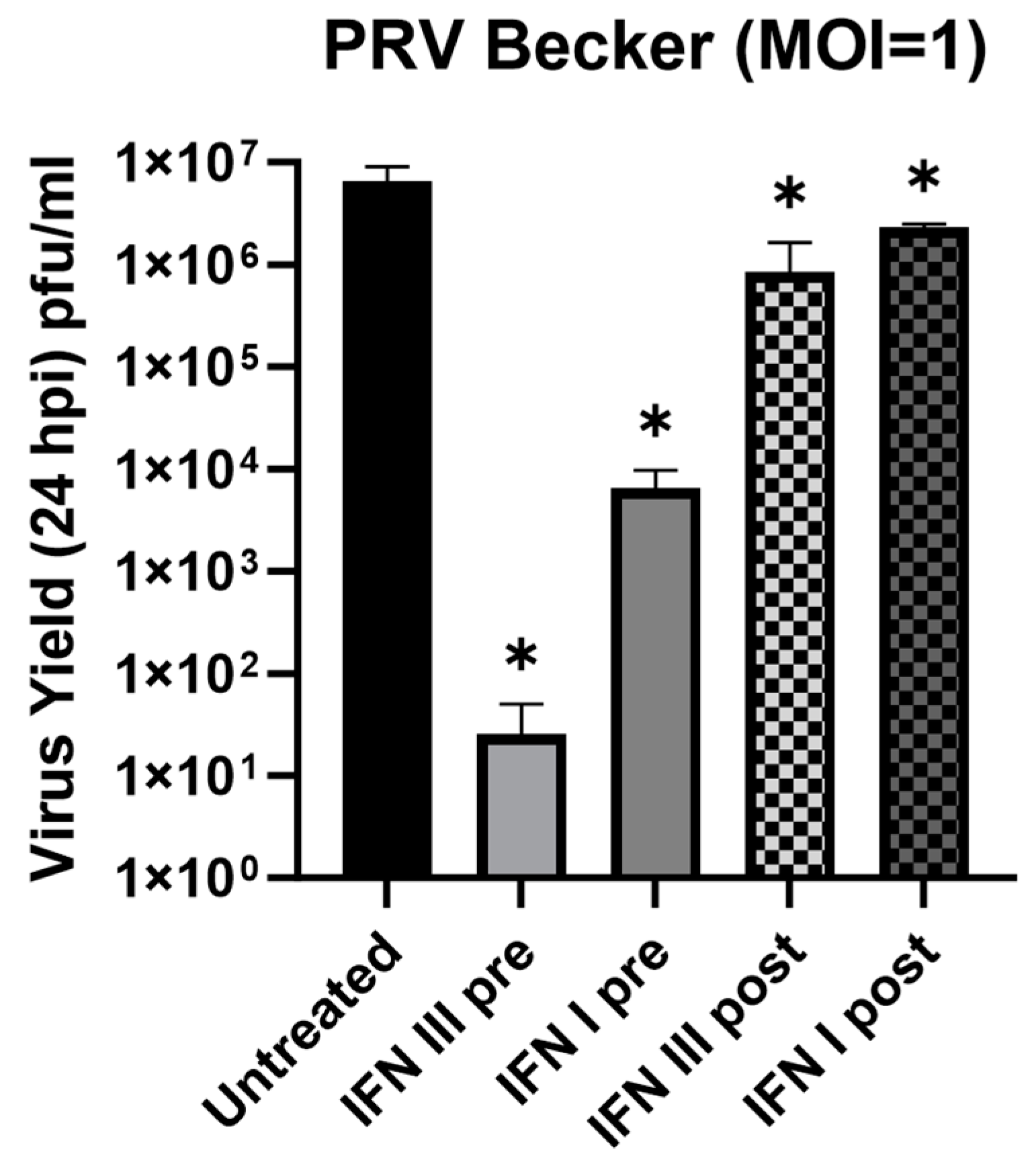
3.4. Antiviral Effect of IFN-λ in Rat2 Cells against Pseudorabies Virus (PRV)
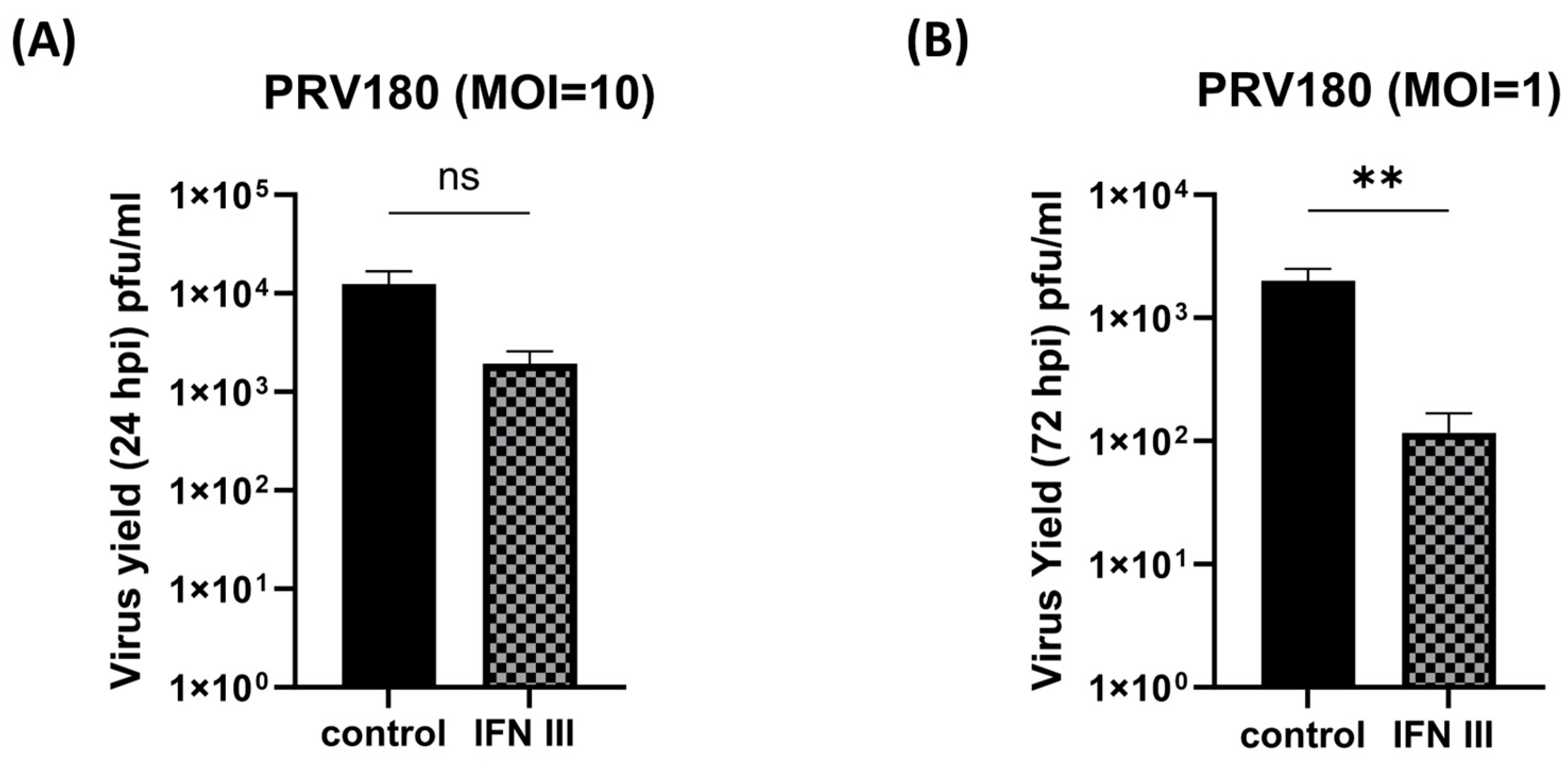
3.5. Antiviral Effect of IFN-λ in Primary SCG Neurons against Pseudorabies Virus (PRV)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broggi, A.; Granucci, F.; Zanoni, I. Type III interferons: Balancing tissue tolerance and resistance to pathogen invasion. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 217, e20190295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, C.M.; Carr, D.J. Defining nervous system susceptibility during acute and latent herpes simplex virus-1 infection. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 308, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.C.; Webb, M.; Wisner, T.W.; Brunetti, C. Herpes simplex virus gE/gI sorts nascent virions to epithelial cell junctions, promoting virus spread. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Zhu, J.; Phasouk, K.; Koelle, D.M.; Wald, A.; Corey, L. An effector phenotype of CD8+ T cells at the junction epithelium during clinical quiescence of herpes simplex virus 2 infection. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10587–10596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sufiawati, I.; Tugizov, S.M. HIV-associated disruption of tight and adherens junctions of oral epithelial cells facilitates HSV-1 infection and spread. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyuncu, O.O.; Hogue, I.B.; Enquist, L.W. Virus infections in the nervous system. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, F.C.; Sridhar, P.R.; Baldridge, M.T. Differential roles of interferons in innate responses to mucosal viral infections. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNab, F.; Mayer-Barber, K.; Sher, A.; Wack, A.; O’Garra, A. Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotenko, S.V.; Gallagher, G.; Baurin, V.V.; Lewis-Antes, A.; Shen, M.; Shah, N.K.; Langer, J.A.; Sheikh, F.; Dickensheets, H.; Donnelly, R.P. IFN-λs mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wack, A.; Terczyńska-Dyla, E.; Hartmann, R. Guarding the frontiers: The biology of type III interferons. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Hamming, O.J.; Ank, N.; Paludan, S.R.; Nielsen, A.L.; Hartmann, R. Type III interferon (IFN) induces a type I IFN-like response in a restricted subset of cells through signaling pathways involving both the Jak-STAT pathway and the mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7749–7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellgren, C.; Gad, H.H.; Hamming, O.J.; Melchjorsen, J.; Hartmann, R. Human interferon-lambda3 is a potent member of the type III interferon family. Genes. Immun. 2009, 10, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlakoiv, T.; Hernandez, P.; Gronke, K.; Diefenbach, A.; Staeheli, P. Leukocyte-derived IFN-α/β and epithelial IFN-λ constitute a compartmentalized mucosal defense system that restricts enteric virus infections. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Wane, X.D.; Nauwynck, H.; Holtappels, G.; Zhang, L.; Johnston, S.L.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Bachert, C.; Zhang, N. Th2 biased upper airway inflammation is associated with an impaired response to viral infection with Herpes simplex virus 1. Rhinology 2016, 54, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Hernandez, C.J.; Sokoloski, K.J.; Stocke, K.S.; Dukka, H.; Jin, S.; Metzler, M.A.; Zaitsev, K.; Shpak, B.; Shen, D.; Miller, D.P.; et al. Microbiome-mediated incapacitation of interferon lambda production in the oral mucosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2105170118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, S.T.; Kennedy, E.A.; Brigleb, P.H.; Taylor, G.M.; Urbanek, K.; Bricker, T.L.; Lee, S.; Shin, H.; Dermody, T.S.; Boon, A.C.M.; et al. Disruption of type III interferon (IFN) genes Ifnl2 and Ifnl3 recapitulates loss of the type III IFN receptor in the mucosal antiviral response. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01073-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggi, A.; Ghosh, S.; Sposito, B.; Spreafico, R.; Balzarini, F.; Lo Cascio, A.; Clementi, N.; De Santis, M.; Mancini, N.; Granucci, F.; et al. Type III interferons disrupt the lung epithelial barrier upon viral recognition. Science 2020, 369, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ank, N.; West, H.; Bartholdy, C.; Eriksson, K.; Thomsen, A.R.; Paludan, S.R. Lambda interferon (IFN-λ), a type III IFN, is induced by viruses and IFNs and displays potent antiviral activity against select virus infections in vivo. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4501–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Zhu, J.; Klock, A.; Phasouk, K.; Huang, M.L.; Koelle, D.M.; Wald, A.; Corey, L. Evasion of the mucosal innate immune system by herpes simplex virus type 2. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12559–12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, P.C.; Leib, D.A. Neuronal interferon signaling is required for protection against herpes simplex virus replication and pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hu, S.; Zhou, L.; Ye, L.; Wang, X.; Ho, J.; Ho, W. Interferon lambda inhibits herpes simplex virus type I infection of human astrocytes and neurons. Glia 2011, 59, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.; Koyuncu, O.O.; Greco, T.M.; Diner, B.A.; Cristea, I.M.; Enquist, L.W. Two Modes of the Axonal Interferon Response Limit Alphaherpesvirus Neuroinvasion. mBio 2016, 7, e02145-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, K.B.; Mare, C.J.; Hinz, P.N. Differentiation of vaccine strains and field isolates of pseudorabies (Aujeszky’s disease) virus: Thermal sensitivity and rabbit virulence markers. Arch. Virol. 1979, 60, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio, T.; Ch’ng, T.H.; Flood, E.A.; Gross, S.P.; Enquist, L.W. Heterogeneity of a fluorescent tegument component in single pseudorabies virus virions and enveloped axonal assemblies. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3903–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curanović, D.; Ch’ng, T.H.; Szpara, M.; Enquist, L. Compartmented neuron cultures for directional infection by alpha herpesviruses. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2009, 43, 26.4.1–26.4.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hean Ch’ng, T.; Flood, E.A.; Enquist, L.W. Culturing primary and transformed neuronal cells for studying pseudorabies virus infection. DNA Viruses Methods Protoc. 2005, 292, 299–315. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, A.K. Detection of pseudorabies virus transcripts in trigeminal ganglia of latently infected swine. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 2908–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, S.; Wavreil, F.; Schepens, B.; Gad, H.H.; Hartmann, R.; Rocha-Pereira, J.; Neyts, J.; Saelens, X.; Michiels, T. Species specificity of type III interferon activity and development of a sensitive luciferase-based bioassay for quantitation of mouse interferon-λ. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2018, 38, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmans, J.; Clitherow, K.; Murdoch, C.; Hatton, P.; Spain, S.; Colley, H. Mucoadhesive Electrospun Fibre-Based Technologies for Oral Medicine. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolen, C.R.; Ding, S.; Robek, M.D.; Kleinstein, S.H. Dynamic expression profiling of type I and type III interferon-stimulated hepatocytes reveals a stable hierarchy of gene expression. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1262–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.A.; Enquist, L.W. A self-recombining bacterial artificial chromosome and its application for analysis of herpesvirus pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4873–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstrand, M.I.; Enquist, L.W.; Pomeranz, L.E. The alpha-herpesviruses: Molecular pathfinders in nervous system circuits. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paladino, P.; Mossman, K.L. Mechanisms employed by herpes simplex virus 1 to inhibit the interferon response. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frade, J.M.; Ovejero-Benito, M.C. Neuronal cell cycle: The neuron itself and its circumstances. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R. Neuroimmune Interactions: From the Brain to the Immune System and Vice Versa. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 477–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Romero, N.; Favoreel, H.W. Pseudorabies virus inhibits type I and type III interferon-induced signaling via proteasomal degradation of Janus kinases. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00793-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au-Yeung, N.; Mandhana, R.; Horvath, C.M. Transcriptional regulation by STAT1 and STAT2 in the interferon JAK-STAT pathway. Jak-Stat 2013, 2, e23931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Li, S.; Cha, E.; Schindler, C. Immune response in Stat2 knockout mice. Immunity 2000, 13, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.T.; Buck, M.D.; Lada, S.M.; Schindler, C.; Shresta, S. STAT2 mediates innate immunity to Dengue virus in the absence of STAT1 via the type I interferon receptor. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, H.; Holvey-Bates, E.G.; Schoggins, J.W.; Forster, S.; Hertzog, P.; Imanaka, N.; Rice, C.M.; Jackson, M.W.; Junk, D.J.; Stark, G.R. IFNβ-dependent increases in STAT1, STAT2, and IRF9 mediate resistance to viruses and DNA damage. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2751–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, M.B.; Ank, N.; Melchjorsen, J.; Paludan, S.R. Expression of type III interferon (IFN) in the vaginal mucosa is mediated primarily by dendritic cells and displays stronger dependence on NF-κB than type I IFNs. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4579–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumar, T.A.; Bhushal, S.; Kalinke, U.; Wirth, D.; Hauser, H.; Köster, M.; Hornef, M.W. Identification of a predominantly interferon-λ-induced transcriptional profile in murine intestinal epithelial cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabayashi, T.; Kojima, T.; Masaki, T.; Yokota, S.; Imaizumi, T.; Tsutsumi, H.; Himi, T.; Fujii, N.; Sawada, N. Type-III interferon, not type-I, is the predominant interferon induced by respiratory viruses in nasal epithelial cells. Virus Res. 2011, 160, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Schnepf, D.; Staeheli, P. Interferon-λ orchestrates innate and adaptive mucosal immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziennis, S.; Alkayed, N. Role of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 in Neuronal Survival and Regeneration. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 19, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S.M.; Krüger, C.; Park, B.; Derkow, K.; Rosenberger, K.; Baumgart, J.; Trimbuch, T.; Eom, G.; Hinz, M.; Kaul, D.; et al. An unconventional role for miRNA: Let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, Z.Z.; Park, C.K.; Berta, T.; Ji, R.R. Toll-like receptor 7 mediates pruritus. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1460–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, J.L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.B.; Zhuang, K.; Gao, J.F.; Liu, S.; Sang, M.; Wu, J.G.; Ho, W.Z. Induction of interferon-λ contributes to TLR3 and RIG-I activation-mediated inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 2 replication in human cervical epithelial cells. MHR Basic Sci. Reprod. Med. 2015, 21, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyuncu, O.O.; Song, R.; Greco, T.M.; Cristea, I.M.; Enquist, L.W. The number of alphaherpesvirus particles infecting axons and the axonal protein repertoire determines the outcome of neuronal infection. MBio 2015, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Actb | CGTCCACCCGCGAGTACAACC | CGACGACGAGCGCAGCGATATCG |
| CCL2 | GCTAATGCATCCACTCTC | GTTTAACATTACTTAAGGC |
| Cd38 | GCGTAGTCTTCATTGGTGATG | CGCTGACATCATCTTGGGACGC |
| Cd69 | CGCAGTCTACAGAAGCAAC | GACTGAAACACTGGATTGGGC |
| Crp | GGGGCAGGAGCAGGACTCG | CATAGACTGCATTGATCTG |
| Cxcl10 | GGCTTCCCAATTCTCTAAGAGC | GAGCAGGCTGGGGCATGGC |
| Gapdh | GCAACAATGTCCACTTTGTC | GCCTGGTTACCAGGGCTGC |
| Ifit1 | CGCTACGCAGCCAAGTATTTCC | CTGTTGCTTGTAACAGAGCCC |
| Ifit2 | GCTGAGTGCTTTGACACAGC | GCTCTCCAATGATTCCTTAC |
| Ifit3 | GCAACTGCAGAATACAGG | CTTATTCATGTACTCCATAG |
| Ifitm3 | CCCCCAGTGGCAGCGTTCACG | GAACAGTCCGACAGAGCC |
| Ifna1 | GCCAGTAGGGAGTCTTCCTGG | GCTTGGGATGCAACCCTCC |
| Irf9 | CCAACCTGCCACTCTCGC | CCTTGCACTTTCTCTTGGCC |
| Isg15 | GGTCCCCTGAAACTAAGG | GCTGACCCAGTGAGTCTCTC |
| Jak1 | CGAAGGCAGAAACTCCATG | CGGAACCTCTACCACGAGAAC |
| Oas1a | CGAATGTATCTCCCTGGGG | GCATAGACCGTGAGCAGC |
| Oas1b | GCGCCAATTCAGGAAGTACAGC | CCCAACCCACAATTCTACG |
| Oas2 | GGTGATGATCGATGTGCTG | CTGGTCTTGGAACTGTTTG |
| Stat1 | GCATTTAAAGTCATATTCATC | CCGTGATGTTAGATAAAC |
| Stat2 | GGAGTGGGTGGGAAACGGG | GCAACATCTCCCACTGCGCC |
| Stat3 | GCAGGAATCGGCTATACTGC | CCTGGCGCCTTGGATTGAGAGC |
| Tlr7 | GGACTTCTTCAAGAATCTGC | GGCTAAGGAGAGAGTCGTTAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salazar, S.; Luong, K.T.Y.; Nua, T.; Koyuncu, O.O. Interferon-λ Activates a Differential Response in Peripheral Neurons That Is Effective against Alpha Herpesvirus Infections. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091142
Salazar S, Luong KTY, Nua T, Koyuncu OO. Interferon-λ Activates a Differential Response in Peripheral Neurons That Is Effective against Alpha Herpesvirus Infections. Pathogens. 2023; 12(9):1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091142
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalazar, Stephanie, Khanh T. Y. Luong, Taulima Nua, and Orkide O. Koyuncu. 2023. "Interferon-λ Activates a Differential Response in Peripheral Neurons That Is Effective against Alpha Herpesvirus Infections" Pathogens 12, no. 9: 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091142
APA StyleSalazar, S., Luong, K. T. Y., Nua, T., & Koyuncu, O. O. (2023). Interferon-λ Activates a Differential Response in Peripheral Neurons That Is Effective against Alpha Herpesvirus Infections. Pathogens, 12(9), 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091142







