Prevalence of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) in Farmed Procambarus clarkii of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Identification of IHHNV
2.3. Acquisition of IHHNV CP Gene
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis of CP Genes
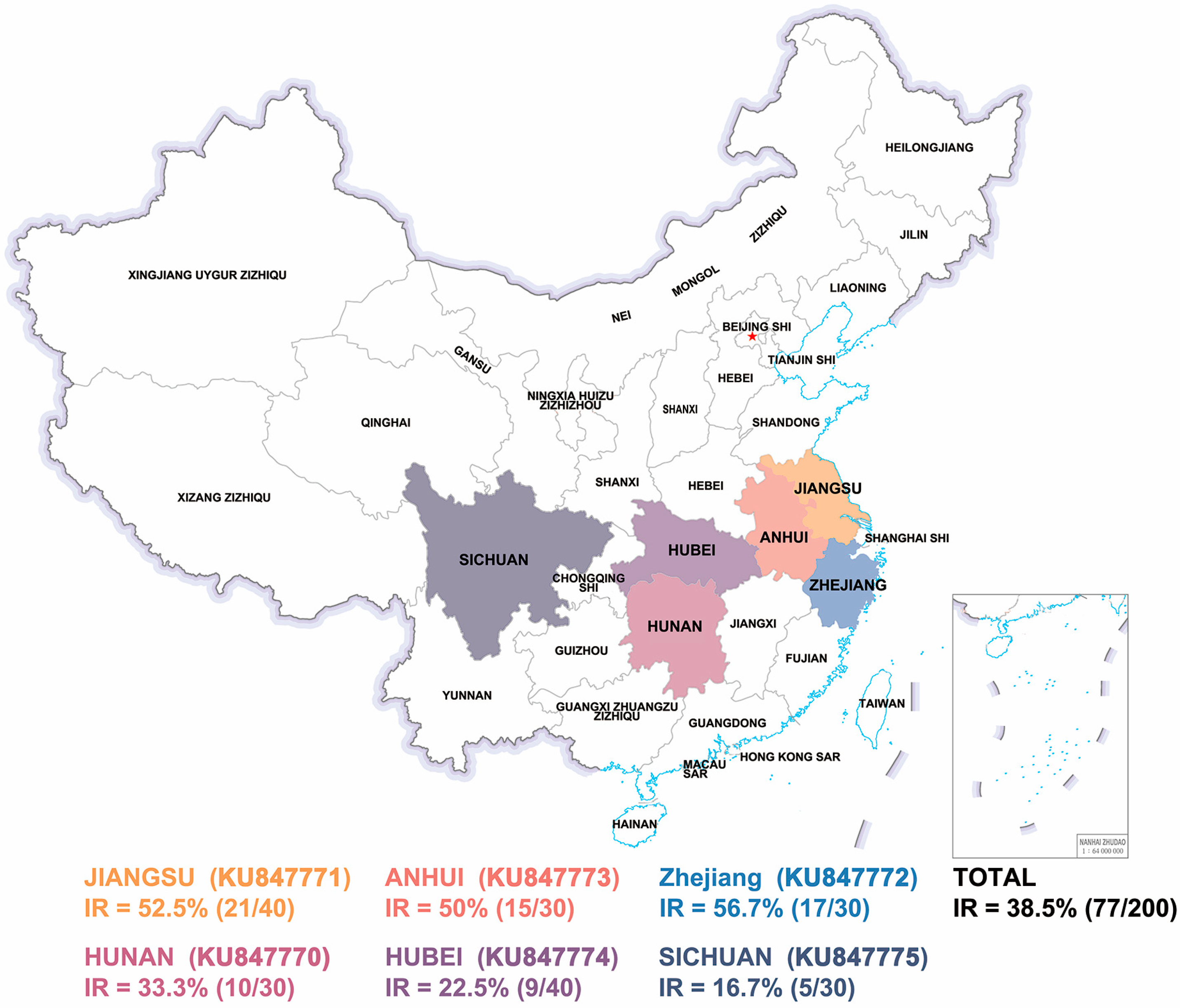
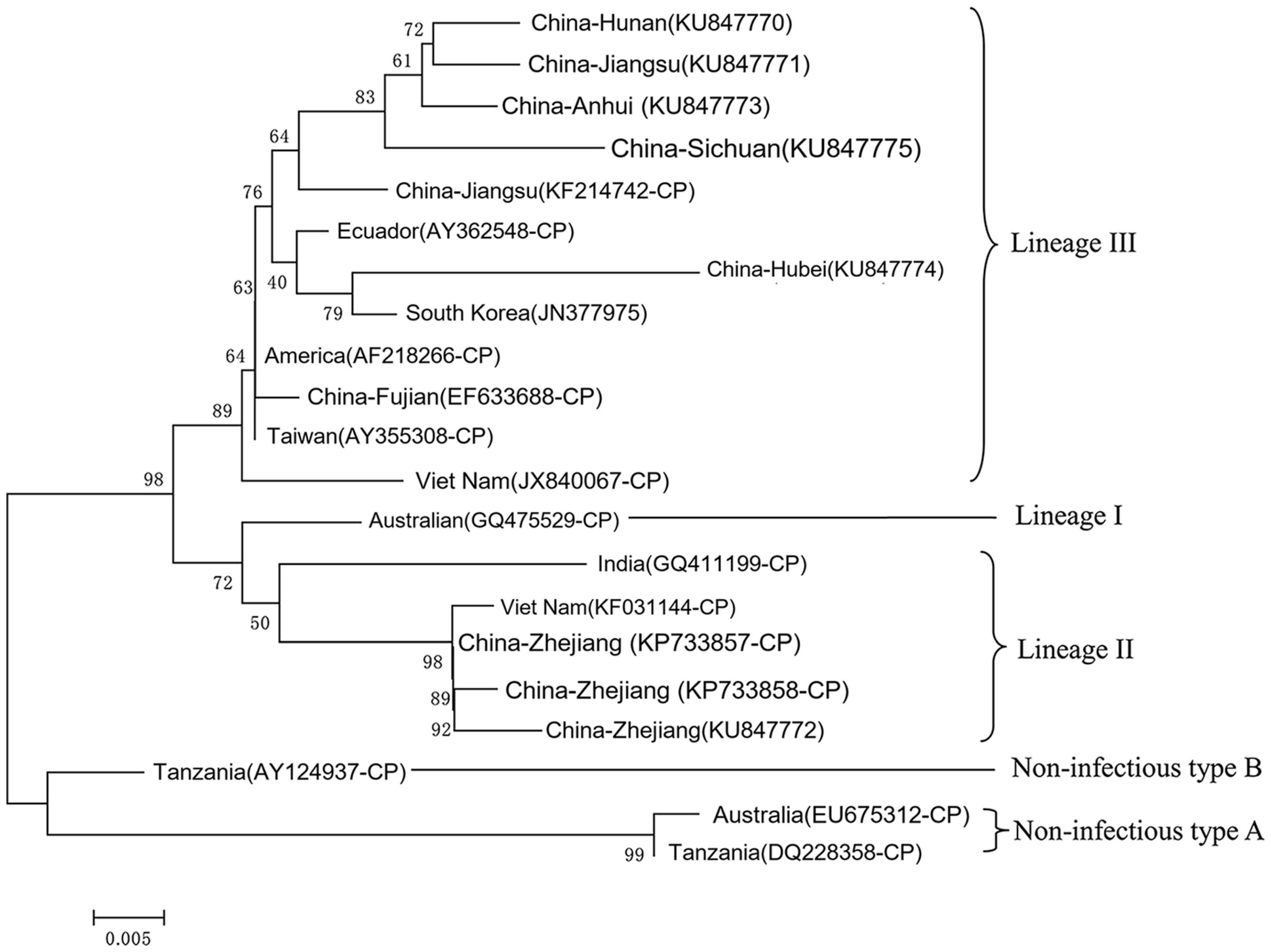
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Bell, T.A. Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis, a newly recognized virus disease of penaeid shrimp. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1983, 42, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.Y.; Yang, N.; Hou, Z.H.; Wang, J.J.; Li, T.; Chang, L.R.; Fang, Y.; Yan, D.C. Research progress on hosts and carriers, prevalence, virulence of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 183, 107556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cotmore, S.F.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Canuti, M.; Chiorini, J.A.; Eis-Hubinger, A.M.; Hughes, J.; Mietzsch, M.; Modha, S.; Ogliastro, M.; Pénzes, J.J.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Parvoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rai, P.; Safeena, M.P.; Krabsetsve, K.; La Fauce, K.; Owens, L.; Karunasagar, I. Genomics, molecular epidemiology and diagnostics of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus. Indian J. Virol. 2012, 23, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Dhar, A.K.; Cruz-Flores, R.; Warg, J.; Killian, M.L.; Orry, A.; Ramos, J.; Garfias, M.; Lyons, G. Genetic relatedness of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus isolates, United States, 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 373–381. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Choi, S.K.; Jeon, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, S.; Park, J.K.; Han, S.H.; Bae, S.; Kim, J.H. Detection of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV, Decapod Penstylhamaparvovirus 1) in commodity red claw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) imported into South Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 856. [Google Scholar]
- Pantoja, C.R.; Lightner, D.V.; Holtschmit, K.H. Prevalence and geographic distribution of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in wild blue shrimp Penaeus stylirostris from the Gulf of California, Mexico. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1999, 11, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Lightner, D.V. Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV)-related sequences in the genome of the black tiger prawn Penaeus monodon from Africa and Australia. Virus. Res. 2006, 118, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.W.; Fan, D.D.; Chen, J. The mussel Mytilus edulis L. as an important reservoir of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 758–759. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Song, X.L.; Huang, J.; Shi, C.Y.; Liu, L. Evidence of existence of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus in penaeid shrimp cultured in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 120, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranguren Caro, L.F.; Gomez-Sanchez, M.M.; Piedrahita, Y.; Mai, H.N.; Cruz-Flores, R.; Alenton, R.R.R.; Dhar, A.K. Current status of infection with infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in the Peruvian and Ecuadorian shrimp industry. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272456. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Chuang, P.C.; Chen, L.C.; Tu, C.; Chien, M.S.; Huang, K.C.; Kao, H.F.; Tung, M.C.; Tsai, S.S. Infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) infections in giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván-Alvarez, D.; Mendoza-Cano, F.; Hernández-López, J.; Sánchez-Paz, A. Experimental evidence of metabolic disturbance in the white shrimp Penaeus vannamei induced by the infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 111, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, G.H.; Li, J.; Bai, Z.; Wang, C.M.; Feng, F. Genetic diversity and population structure of the invasive alien red swamp crayfish. Biol. Invasions. 2010, 12, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.F.; Huang, Y.; Dai, Y.G.; Bi, C.W.; Hu, C.Y. Genetic diversity among red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) populations in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River based on AFLP markers. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 791–800. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.-K.; Dong, Z.; Liu, D.P.; Yan, Y.B.; Pang, N.Y.; Nian, Y.Y.; Yan, D.C. Iinfectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) infection in freshwater crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Aquaculture 2017, 477, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Liu, Y.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y. Prevalence and genomic analysis of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp farmed in Shanghai, China. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 3189–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Sikisaka, R.; Bohonak, A.J.; McClenaghan, L.R., Jr.; Dhar, A.K. Genetic signature of rapid IHHNV (infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus) expansion in wild Penaeus shrimp populations. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.K.; Nguyen, V.G.; Park, B.K.; Choresca, C.H.; Shin, S.P.; Han, J.E.; Jun, J.W.; Park, S.C. Genomic sequence of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) KLV-2010-01 originating from the first Korean outbreak in cultured Litopenaeus vannamei. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.K.; Robles-Sikisaka, R.; Saksmerprome, V.; Lakshman, D.K. Biology, Genome organization, and evolution of parvoviruses in marine shrimp. Adv. Virus Res. 2014, 89, 85–139. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.M.; Wei, Y.W.; Fan, D.D.; Li, C.H.; Miao, L.; Chen, J. Application of the infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) to bivalve shellfish. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2018, 49, 883–888. [Google Scholar]
- Sellars, M.J.; Cowley, J.A.; Musson, D.; Rao, M.; Menzies, M.L.; Coman, G.J.; Murphy, B.S. Reduced growth performance of Black Tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) infected with infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus. Aquaculture 2018, 499, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagayan, H.; Godin, D.M.; Kanna, R.; Brock, J. IHHN virus as an etiological factor in runt-deformity syndrome (RDS) of juvenile Penaeus vannamei cultured in Hawaii. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 1991, 22, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | ||
| GQ475529 | 1 | 93.7 | 95.4 | 95.1 | 95.1 | 94.5 | 94.3 | 94.5 | 94.3 | 94.3 | 94.9 | 95.3 | 94.2 | 95.2 | 95.6 | 95.4 | 95.5 | 95.2 | 87.2 | 87.1 | 91.4 | |
| GQ411199 | 2 | 6.6 | 92.9 | 93.1 | 92.8 | 92.7 | 92.6 | 92.8 | 92.6 | 92.5 | 93.0 | 93.3 | 92.2 | 93.2 | 93.6 | 93.6 | 93.7 | 93.2 | 86.6 | 86.5 | 90.3 | |
| KF031144 | 3 | 4.8 | 7.5 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.2 | 94.2 | 94.4 | 94.0 | 94.4 | 94.6 | 94.9 | 94.3 | 94.8 | 95.3 | 95.1 | 95.2 | 94.8 | 97.3 | 87.2 | 91.3 | |
| KP733857 | 4 | 5.1 | 7.2 | 0.3 | 99.6 | 99.5 | 94.1 | 94.3 | 93.9 | 94.3 | 94.5 | 94.8 | 94.2 | 94.7 | 95.2 | 94.9 | 95.1 | 94.7 | 87.2 | 87.1 | 91.2 | |
| KP733858 | 5 | 5.1 | 7.6 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 99.1 | 94.1 | 94.3 | 93.9 | 94.3 | 94.5 | 94.8 | 94.2 | 94.7 | 95.2 | 94.9 | 95.1 | 94.7 | 97.3 | 87.2 | 91.3 | |
| 6 | 5.7 | 7.7 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 93.6 | 93.8 | 93.4 | 93.8 | 94.0 | 94.3 | 93.7 | 94.2 | 94.6 | 94.4 | 94.5 | 94.2 | 87.1 | 87.0 | 90.8 | ||
| 7 | 5.9 | 7.8 | 6.0 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 99.4 | 99.2 | 98.6 | 98.6 | 98.5 | 97.2 | 98.2 | 98.6 | 98.4 | 98.5 | 98.2 | 86.6 | 86.5 | 90.6 | ||
| KU847771 | 8 | 5.7 | 7.5 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 5.9 | 6.5 | 0.6 | 99.2 | 98.8 | 98.6 | 98.7 | 97.4 | 98.4 | 98.8 | 98.6 | 98.7 | 98.4 | 86.8 | 86.7 | 90.8 | |
| KU847773 | 9 | 5.9 | 7.8 | 6.2 | 6.3 | 6.3 | 6.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 98.6 | 98.4 | 98.3 | 97.0 | 98.0 | 98.4 | 98.2 | 98.3 | 98.0 | 86.5 | 86.4 | 90.4 | |
| KU847775 | 10 | 5.9 | 7.9 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 5.9 | 6.5 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 98.2 | 98.3 | 97.2 | 98.0 | 98.4 | 98.2 | 98.3 | 98.0 | 86.4 | 86.3 | 90.4 | |
| KF214742 | 11 | 5.2 | 7.3 | 5.6 | 5.7 | 5.7 | 6.2 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 99.1 | 97.8 | 98.8 | 99.2 | 99.0 | 99.1 | 98.8 | 86.8 | 86.7 | 90.6 | |
| AY362548 | 12 | 4.9 | 7.0 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 98.5 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 99.0 | 87.1 | 87.0 | 90.9 | |
| KU847774 | 13 | 6.0 | 8.2 | 5.9 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.6 | 2.9 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 1.5 | 98.8 | 98.4 | 98.2 | 98.3 | 97.9 | 86.3 | 86.2 | 90.1 | |
| JN377975 | 14 | 5.0 | 7.1 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 99.4 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 98.9 | 87.1 | 87.0 | 90.8 | |
| AF218266 | 15 | 4.6 | 6.7 | 4.9 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.6 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.5 | 87.6 | 87.5 | 91.2 | |
| EF633688 | 16 | 4.8 | 6.7 | 5.1 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 5.8 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 99.9 | 99.3 | 97.4 | 87.3 | 91.0 | |
| AY355308 | 17 | 4.7 | 6.5 | 5.0 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.7 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 1.7 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 99.4 | 87.5 | 87.4 | 91.1 | |
| JX840067 | 18 | 5.0 | 7.1 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 87.1 | 87.0 | 90.7 | |
| DQ228358 | 19 | 14.1 | 14.8 | 14.0 | 14.1 | 14.0 | 14.2 | 14.9 | 14.6 | 15.0 | 15.1 | 14.6 | 14.2 | 15.2 | 14.2 | 13.6 | 13.9 | 13.7 | 14.2 | 99.7 | 89.1 | |
| EU675312 | 20 | 14.3 | 15.0 | 14.1 | 14.2 | 14.1 | 14.4 | 15.0 | 14.7 | 15.1 | 15.2 | 14.7 | 14.4 | 15.4 | 14.4 | 13.7 | 14.0 | 13.9 | 14.4 | 0.3 | 89.0 | |
| AY124937 | 21 | 9.1 | 10.4 | 9.2 | 9.4 | 9.2 | 9.8 | 10.1 | 9.8 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 9.8 | 9.4 | 9.6 | 9.5 | 9.9 | 11.8 | 12.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Wei, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, J. Prevalence of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) in Farmed Procambarus clarkii of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in China. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081038
Xu F, Wei Y, Lu J, Chen J. Prevalence of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) in Farmed Procambarus clarkii of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in China. Pathogens. 2023; 12(8):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081038
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Feng, Yongwei Wei, Jianfei Lu, and Jiong Chen. 2023. "Prevalence of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) in Farmed Procambarus clarkii of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in China" Pathogens 12, no. 8: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081038
APA StyleXu, F., Wei, Y., Lu, J., & Chen, J. (2023). Prevalence of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) in Farmed Procambarus clarkii of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in China. Pathogens, 12(8), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081038












