Transovarial Transmission of Anaplasma marginale in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Ticks Results in a Bottleneck for Strain Diversity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Tick Dissection and Hemolymph Collection
2.4. DNA Extraction from Different Samples
2.5. Anaplasma marginale Detection
2.6. Amplification, Cloning, and Sequencing of the msp1α Gene
3. Results
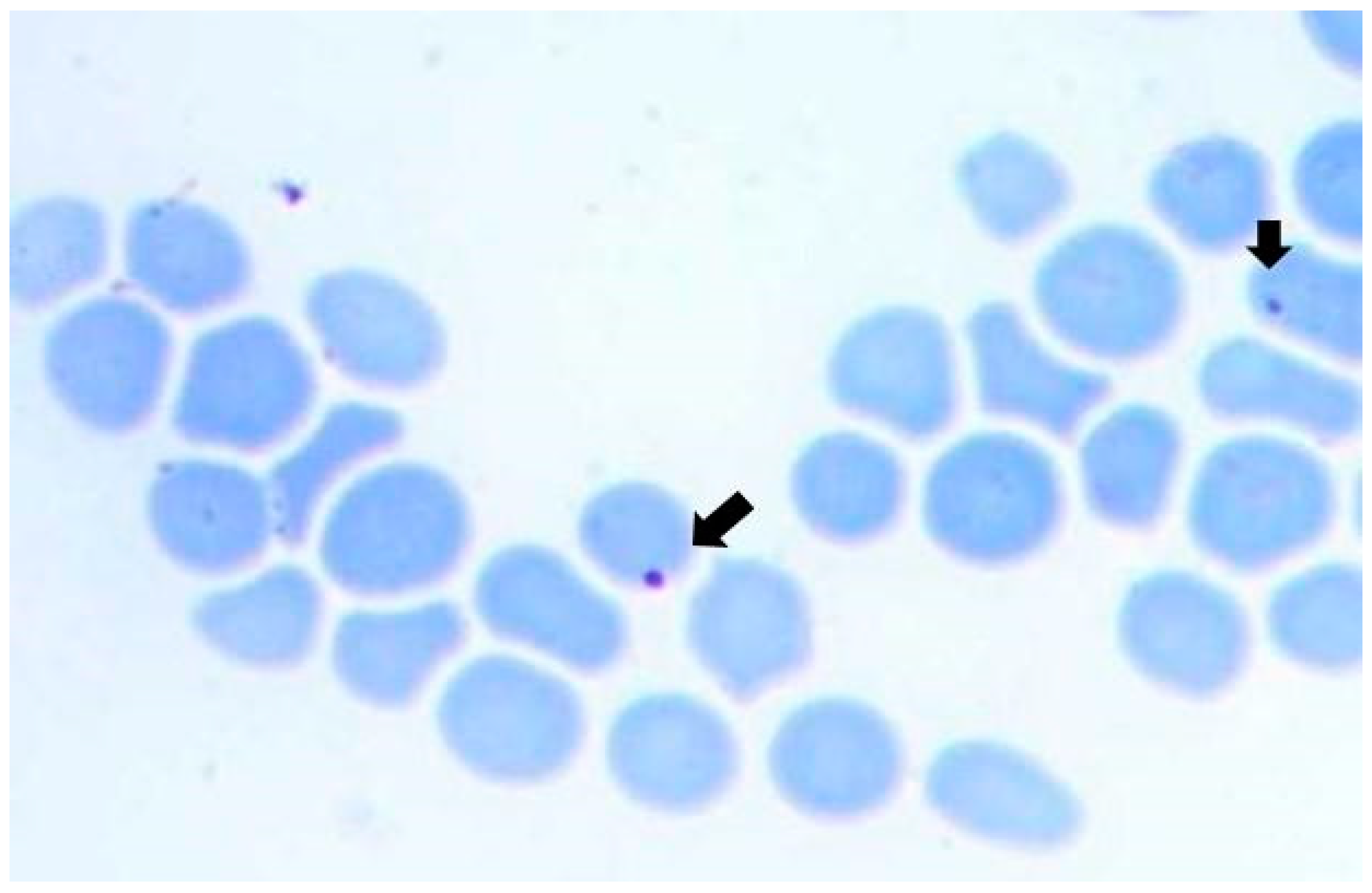
3.1. Natural Infection of Bovines and R. microplus Ticks with A. marginale
3.2. Experimental A. marginale Transmission from Newly Hatched Naturally Infected Larvae to Splenectomized Bovine
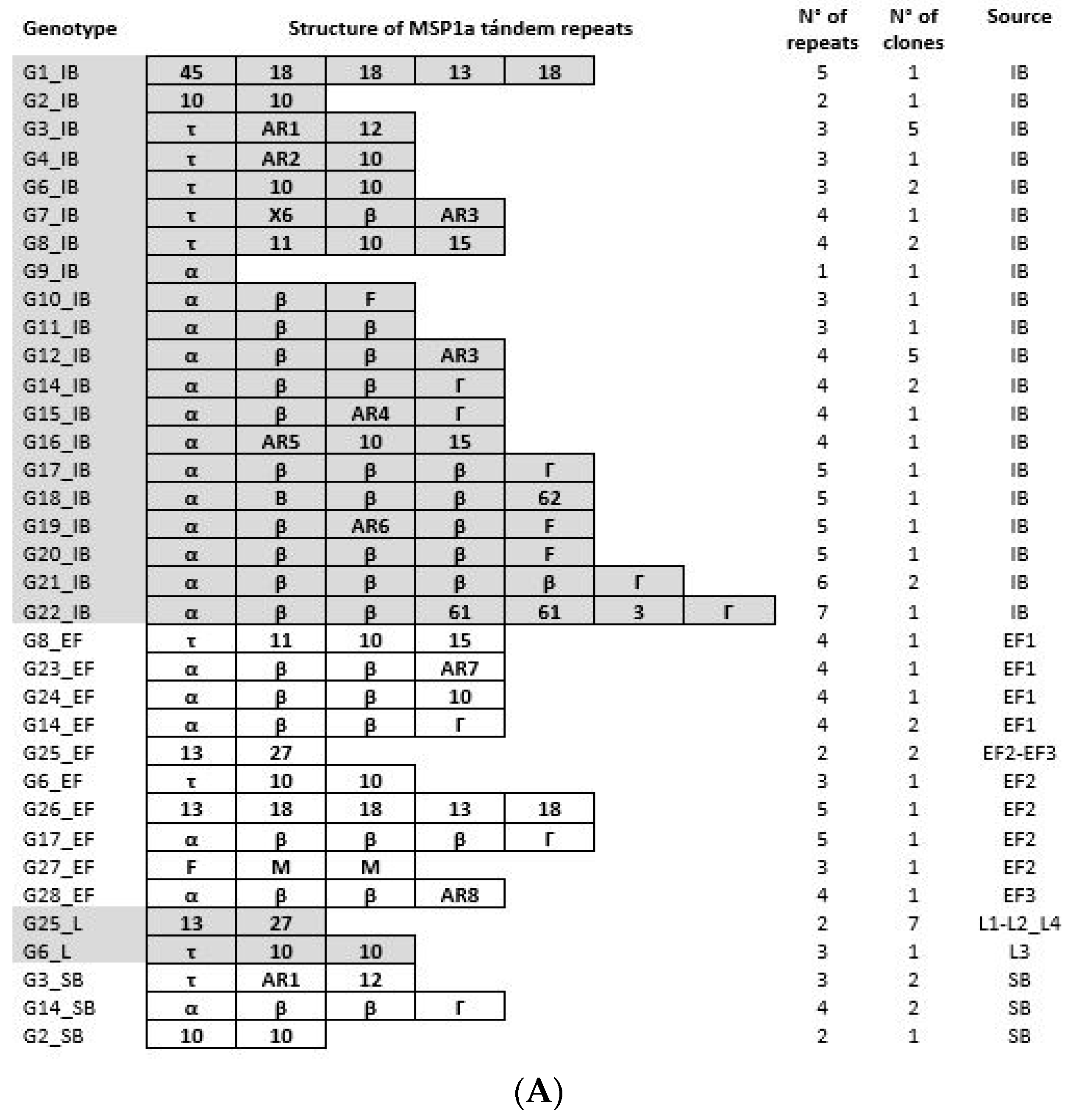
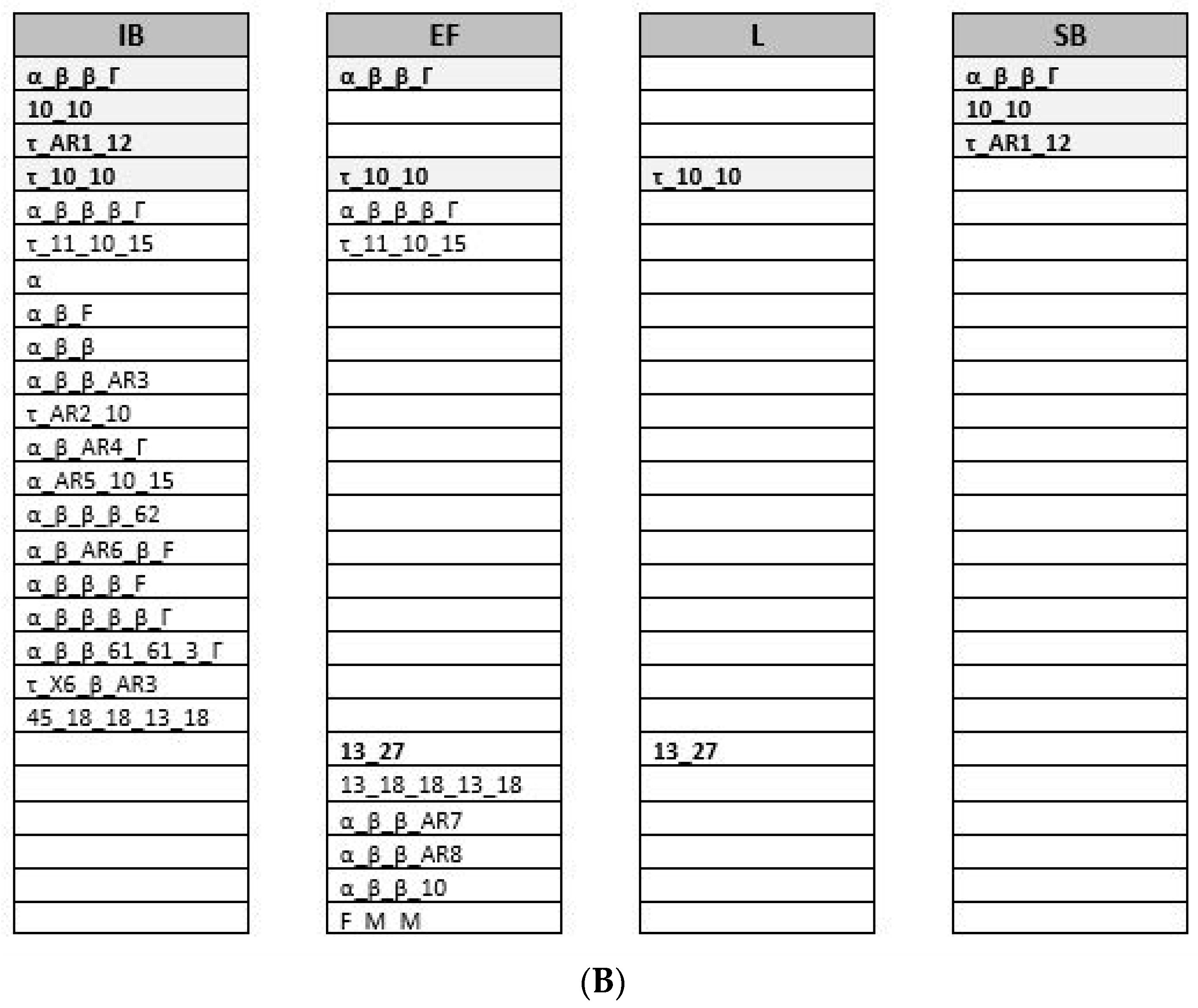
3.3. Anaplasma Marginale Strain Genotyping during the Transmission Cycle
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aubry, P.; Geale, D.W. A review of bovine anaplasmosis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eygelaar, D.; Jori, F.; Mokopasetso, M.; Sibeko, K.P.; Collins, N.E.; Vorster, I.; Troskie, M.; Oosthuizen, M.C. Tick-borne haemoparasites in African buffalo (Syncerus caffer) from two wildlife areas in Northern Botswana. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, Q.U.A.; Khan, A.U.; Khattak, R.M.; Ali, M.; Shaikh, R.S.; Ali, M.; Iqbal, F. A report on the high prevalence of Anaplasma sp. in buffaloes from two provinces in Pakistan. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, J.A.G.G.; Rabelo, E.M.L.L.; Ribeiro, M.F.B.B. Molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens of the family Anaplasmataceae in brazilian brown brocket deer (Mazama gouazoubira, Fischer, 1814) and marsh deer (Blastocerus dichotomus, Illiger, 1815). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudan, V.; Sharma, R.L.; Borah, M.K. Subclinical anaplasmosis in camel (Camelus dromedarius) and its successful therapeutic management. J. Parasit. Dis. 2014, 38, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemi, E.C.; de La Fourniere, S.; Orozco, M.; Peña Martinez, J.; Correa, E.; Fernandez, J.; Lopez Arias, L.; Paoletta, M.; Corona, B.; Pinarello, V.; et al. Molecular identification of Anaplasma marginale in two autochthonous south american wild species revealed an identical new genotype and its phylogenetic relationship with those of bovines. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hornok, S.; Horváth, G.; Takács, N.; Farkas, R.; Szőke, K.; Kontschán, J. Molecular evidence of a badger-associated Ehrlichia sp., a Candidatus Neoehrlichia lotoris-like genotype and Anaplasma marginale in dogs. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Parveen, A.; Ashraf, S.; Hussain, M.; Aktas, M.; Ozubek, S.; Shaikh, R.S.; Iqbal, F. First report regarding the simultaneous molecular detection of Anaplasma marginale and Theileria annulata in equine blood samples collected from southern Punjab in Pakistan. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocan, K.M.; De la Fuente, J.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Meléndez, R.D. Antigens and alternatives for control of Anaplasma marginale infection in cattle. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocan, K.M.; De La Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Garcia-Garcia, J.C. Anaplasma marginale (Rickettsiales: Anaplasmataceae): Recent advances in defining host-pathogen adaptations of a tick-borne rickettsia. Parasitology 2004, 129, S285–S300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruybal, P.; Moretta, R.; Perez, A.; Petrigh, R.; Zimmer, P.; Alcaraz, E.; Echaide, I.; Torioni de Echaide, S.; Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; et al. Genetic diversity of Anaplasma marginale in Argentina. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 162, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayton, K.A. Transmisión de Anaplasma marginale por garrapatas. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2012, 3, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, S.A. Transmission of Anaplasma marginale by arthropods. In Proceedings of the 7th National Anaplasmosis Conference, Starkville, MS, USA, 21–23 October 1981; pp. 395–423. [Google Scholar]
- Hornok, S.; Földvári, G.; Elek, V.; Naranjo, V.; Farkas, R.; de la Fuente, J. Molecular identification of Anaplasma marginale and rickettsial endosymbionts in blood-sucking flies (Diptera: Tabanidae, Muscidae) and hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 154, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Deng, Y.P.; Yang, T.; Li, L.Y.; Cheng, T.Y.; Liu, G.H.; Duan, D.Y. Metagenomics of the midgut microbiome of Rhipicephalus microplus from China. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Coetzee, J.F.; Ewing, S.A. The natural history of Anaplasma marginale. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, D.H.; Gaido, A.B.; Vinabal, A.E.; De Echaide, S.T.; Guglielmone, A.A. Transmission of Anaplasma marginale with adult Boophilus microplus ticks fed as nymphs on calves with different levels of rickettsaemia. Parasite 1994, 1, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, M.K.; Yamamura, M.H.; Kawasaki, P.M.; Tamekuni, K.; Igarashi, M.; Vidotto, O.; Vidotto, M.C. Detection of Anaplasma marginale DNA in larvae of Boophilus microplus ticks by Polymerase Chain Reaction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1026, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocan, K.M.; De La Fuente, J.; Cabezas-Cruz, A. The genus Anaplasma: New challenges after reclassification. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz 2015, 34, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leatch, G. Preliminary studies on the transmission of Anaplasma marginale by Boophilus microplus. Aust. Vet. J. 1973, 49, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, M.; Hall, W.T.K. Transmission of Anaplasma marginale by the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Aust. Vet. J. 1972, 48, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves Ruiz, P.M.; Friche Passos, L.M.; Barbosa Ribeiro, M.F. Lack of infectivity of a brazilian Anaplasma marginale isolate for Boophilus microplus ticks. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 128, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, E.; Pohl, P.C.; Klafke, G.M.; Reck, J.; Fogaça, A.C.; Martins, J.R.; Daffre, S. Low temperature affects cattle tick reproduction but does not lead to transovarial transmission of Anaplasma marginale. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 214, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Disease Control Malaria Glossary of Terms. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/glossary.html (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Dumler, J.S.; Barbet, A.F.; Bekker, C.P.J.; Dasch, G.A.; Palmer, G.H.; Ray, S.C.; Rikihisa, Y.; Rurangirwa, F.R. Reorganization of genera in the families Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae in the order Rickettsiales: Unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia and Ehrlichia with Neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 2145–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snellgrove, A.N.; Krapiunaya, I.; Ford, S.L.; Stanley, H.M.; Wickson, A.G.; Hartzer, K.L.; Levin, M.L. Vector competence of Rhipicephalus canguineus Sensu stricto for Anaplasma platys. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, Y.; Inokuma, H. Molecular detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum from larvae of Haemaphysalis longicornis in Ibaraki, Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 72, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, K.; Matsuyama, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Sakamoto, L.; Matsumoto, K.; Yokoyama, N.; Inokuma, H. Detection of Anaplasma bovis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum DNA from Haemaphysalis megaspinosa in Hokkaido, Japan. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 168, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauck, D.; Jordan, D.; Springer, A.; Schunack, B.; Pachnicke, S.; Fingerle, V.; Strube, C. Transovarial transmission of Borrelia spp., Rickettsia spp. and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Ixodes ricinus under field conditions extrapolated from DNA detection in questing larvae. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemi, E.C.; Ruybal, P.; Lia, V.; Gonzalez, S.; Lew, S.; Zimmer, P.; Lopez Arias, L.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Rodriguez, S.Y.; Frutos, R.; et al. Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for the study of Anaplasma marginale population structure over space and time. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 30, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Venzal, J.; González Acuña, D.; Martins, T.M.; Guglielmone, A.A. Ticks of the Southern Cone of America: Diagnosis, Distribution, and Hosts with Taxonomy, Ecology and Sanitary Importance, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 9780128110768. [Google Scholar]
- Pipano, E. Vaccines against hemoparasitic diseases in Israel with special reference to quality assurance. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1997, 29, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J. Behavior of larvae of the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Canestrini), on cattle of differing degrees of resistance. J. Parasitol. 1971, 57, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.T.; Goddard, J.; Varela-Stokes, A.S. Examination of the internal morphology of the ixodid tick, Amblyomma maculatum Koch, (Acari: Ixodidae); a “How-to” pictorial dissection guide. Midsouth Entomol. 2009, 2, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, T.G.; Dietrich, G.; Brandt, K.; Dolan, M.C.; Piesman, J.; Gilmore, R.D. Saliva, salivary gland, and hemolymph collection from Ixodes scapularis ticks. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 60, e3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halos, L.; Jamal, T.; Vial, L.; Maillard, R.; Suau, A.; Le Menach, A.; Boulouis, H.; Vayssier-Taussat, M. determination of an efficient and reliable method for DNA extraction from ticks. Vet. Res. 2004, 35, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparagano, O.A.E.; Allsopp, M.T.E.P.; Mank, R.A.; Rijpkema, S.G.T.; Figueroa, J.V.; Jongejan, F. Molecular detection of pathogen DNA in ticks (Acari: Ixodidae): A Review. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1999, 23, 929–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torioni De Echaide, S.; Knowles, D.P.; McGuire, T.C.; Palmer, G.H.; Suarez, C.E.; McElwain, T.F. Detection of cattle naturally infected with Anaplasma marginale in a region of endemicity by Nested PCR and a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant Major Surface Protein 5. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilgiç, H.B.; Karagenç, T.; Simuunza, M.; Shiels, B.; Tait, A.; Eren, H.; Weir, W. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Theileria annulata, Babesia bovis and Anaplasma marginale in cattle. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 133, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente, J.; Van Den Bussche, R.A.; Kocan, K.M. Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of north american isolates of Anaplasma marginale (Rickettsiaceae: Ehrlichieae). Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 97, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanese, H.N.; Brayton, K.A.; Gebremedhin, A.H. RepeatAnalyzer: A tool for analysing and managing short-sequence repeat data. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, M.; Ozubek, S. Molecular evidence for trans-stadial transmission of Anaplasma platys by Rhipicephalus sanguineus Sensu Lato under field conditions. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2018, 32, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atif, F.A. Anaplasma marginale and Anaplasma phagocytophilum: Rickettsiales pathogens of veterinary and public health significance. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 3941–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletta, M.S.; López Arias, L.; de la Fournière, S.; Guillemi, E.C.; Luciani, C.; Sarmiento, N.F.; Mosqueda, J.; Farber, M.D.; Wilkowsky, S.E. Epidemiology of Babesia, Anaplasma and Trypanosoma species using a new expanded reverse line blot hybridization assay. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemi, E.C.; Imbert, M.; de la Fournière, S.; Orozco, M.M.; Martinez, J.P.; Rosas, A.C.; Montenegro, V.N.; Farber, M.D. Closing the gaps to understand the tick transmission of Anaplasma marginale among giant anteaters (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) in Argentina. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, I.A.; García-Ortiz, M.A.; Preciado de la Torre, J.F.; Rojas-Ramírez, E.E.; Hernández-Ortiz, R.; Alpírez-Mendoza, F.; Rodríguez Camarillo, S.D. Transmission of Anaplasma marginale by unfed Rhipicephalus microplus tick larvae under experimental conditions. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2020, 11, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.D.; Levy, M.G.; Kuhlenschmidt, M.S.; Adams, J.H.; Rzechula, D.L.; Hardt, T.A.; Kocan, K.M. Isolate of Anaplasma marginale not transmitted by ticks. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1986, 47, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wickwire, K.B.; Kocan, K.M.; Barron, S.J.; Ewing, S.A.; Smith, R.D.; Hair, J.A. Infectivity of three Anaplasma marginale isolates for Dermacentor andersoni. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1987, 48, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente, J.; Garcia-Garcia, J.C.; Blouin, E.F.; Kocan, K.M. Characterization of the functional domain of Major Surface Protein 1a involved in adhesion of the rickettsia Anaplasma marginale to host cells. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 91, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hove, P.; Chaisi, M.E.; Brayton, K.A.; Ganesan, H.; Catanese, H.N.; Mtshali, M.S.; Mutshembele, A.M.; Oosthuizen, M.C.; Collins, N.E. Co-infections with multiple genotypes of Anaplasma marginale in cattle indicate pathogen diversity. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primo, M.E.; Sarli, M.; Thompson, C.S.; Torioni, S.M.; Echaide, I.E. Sensitivity of Anaplasma marginale genotypes to oxytetracycline assessed by analyzing the msp1α gene in experimentally infected cattle. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquerra, E.V.; Herndon, D.R.; Mendoza, F.A.; Mosqueda, J.; Palmer, G.H. Anaplasma marginale superinfection attributable to pathogen strains with distinct genomic backgrounds. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 5286–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Koku, R.; Herndon, D.R.; Avillan, J.; Morrison, J.; Futse, J.E.; Palmer, G.H.; Brayton, K.A.; Noh, S.M. Both coinfection and superinfection drive complex Anaplasma marginale strain structure in a natural transmission setting. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00166-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, K.E.; Palmer, G.H.; Crowder, D.W.; Ueti, M.W.; Noh, S.M. Restriction of Francisella novicida genetic diversity during infection of the vector midgut. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, S.M.; Dark, M.J.; Reif, K.E.; Ueti, M.W.; Kappmeyer, L.S.; Scoles, G.A.; Palmer, G.H.; Brayton, K.A. Superinfection exclusion of the ruminant pathogen Anaplasma marginale in its tick vector is dependent on the time between exposures to the strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3217–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Scherman, K.; Råberg, L. Multiple-strain infections of Borrelia afzelii: A role for within-host interactions in the maintenance of antigenic diversity? Am. Nat. 2013, 181, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanese, H.N.; Brayton, K.A.; Gebremedhin, A.H. A nearest-neighbors network model for sequence data reveals new insight into genotype distribution of a pathogen. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | msp1β | msp5 | msp1α |
|---|---|---|---|
| IB | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
| EF | |||
| Hemolymph | |||
| EF 1 | POSITIVE | ND | ND |
| EF 2 | NEGATIVE | ND | ND |
| EF 3 | NEGATIVE | ND | ND |
| EF 4 | NEGATIVE | ND | ND |
| Bodies after oviposition | |||
| EF 1 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
| EF 2 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
| EF 3 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
| EF 4 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | NA |
| Salivary glands | |||
| EF 5 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 6 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 7 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 8 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 9 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 10 | NEGATIVE | NEGATIVE | ND |
| Ovaries | |||
| EF 5 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 6 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 7 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 8 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 9 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | ND |
| EF 10 | NEGATIVE | NEGATIVE | ND |
| Larvae | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
| L1 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
| L2 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
| L3 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
| L4 | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
| SB | POSITIVE | POSITIVE | POSITIVE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Fournière, S.; Guillemi, E.C.; Paoletta, M.S.; Pérez, A.; Obregón, D.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Sarmiento, N.F.; Farber, M.D. Transovarial Transmission of Anaplasma marginale in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Ticks Results in a Bottleneck for Strain Diversity. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081010
de la Fournière S, Guillemi EC, Paoletta MS, Pérez A, Obregón D, Cabezas-Cruz A, Sarmiento NF, Farber MD. Transovarial Transmission of Anaplasma marginale in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Ticks Results in a Bottleneck for Strain Diversity. Pathogens. 2023; 12(8):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081010
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Fournière, Sofía, Eliana Carolina Guillemi, Martina Soledad Paoletta, Agustina Pérez, Dasiel Obregón, Alejandro Cabezas-Cruz, Néstor Fabián Sarmiento, and Marisa Diana Farber. 2023. "Transovarial Transmission of Anaplasma marginale in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Ticks Results in a Bottleneck for Strain Diversity" Pathogens 12, no. 8: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081010
APA Stylede la Fournière, S., Guillemi, E. C., Paoletta, M. S., Pérez, A., Obregón, D., Cabezas-Cruz, A., Sarmiento, N. F., & Farber, M. D. (2023). Transovarial Transmission of Anaplasma marginale in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Ticks Results in a Bottleneck for Strain Diversity. Pathogens, 12(8), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081010












