Using Serological Markers for the Surveillance of Plasmodium vivax Malaria: A Scoping Review
Abstract
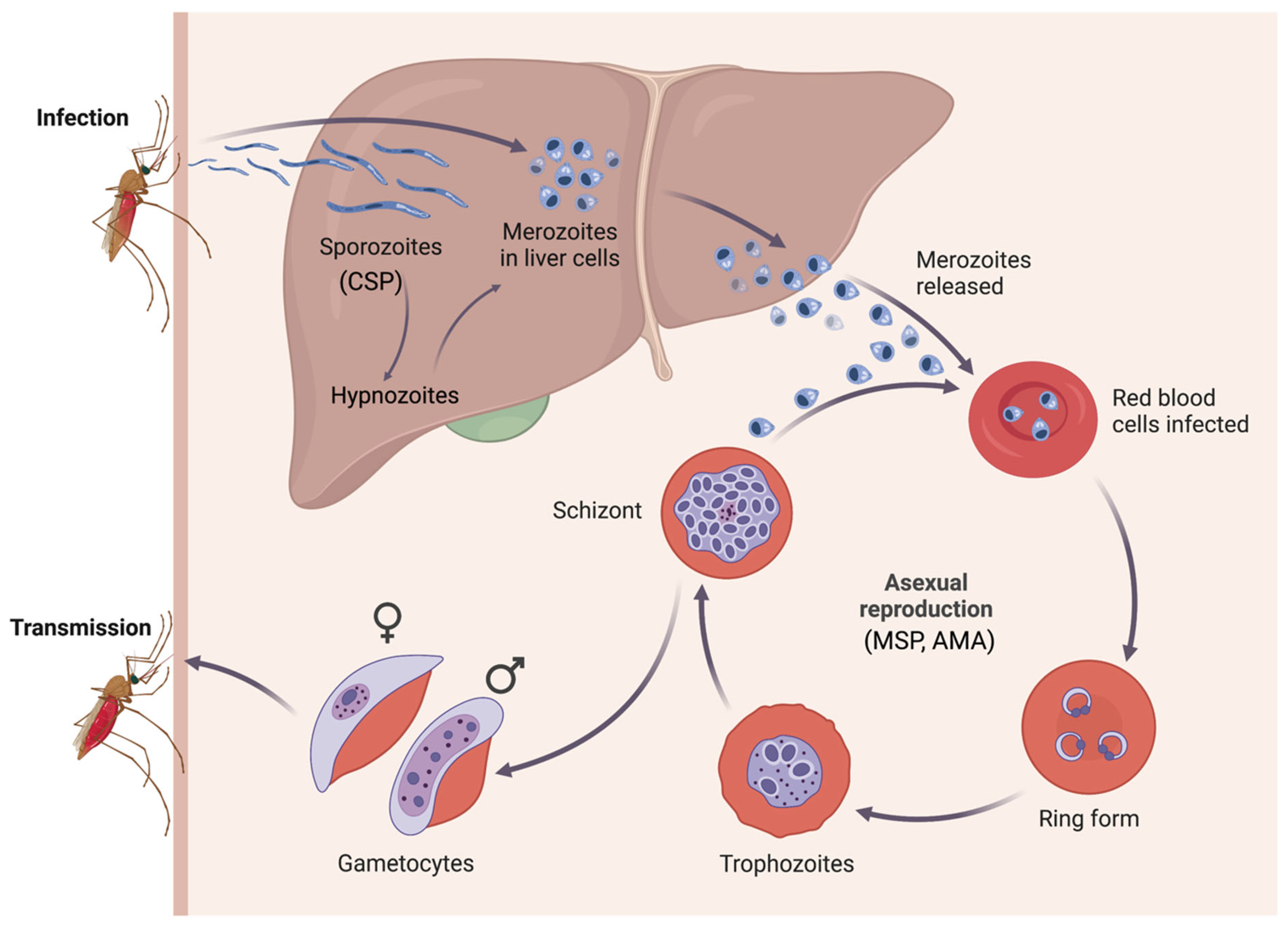
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
3. Results
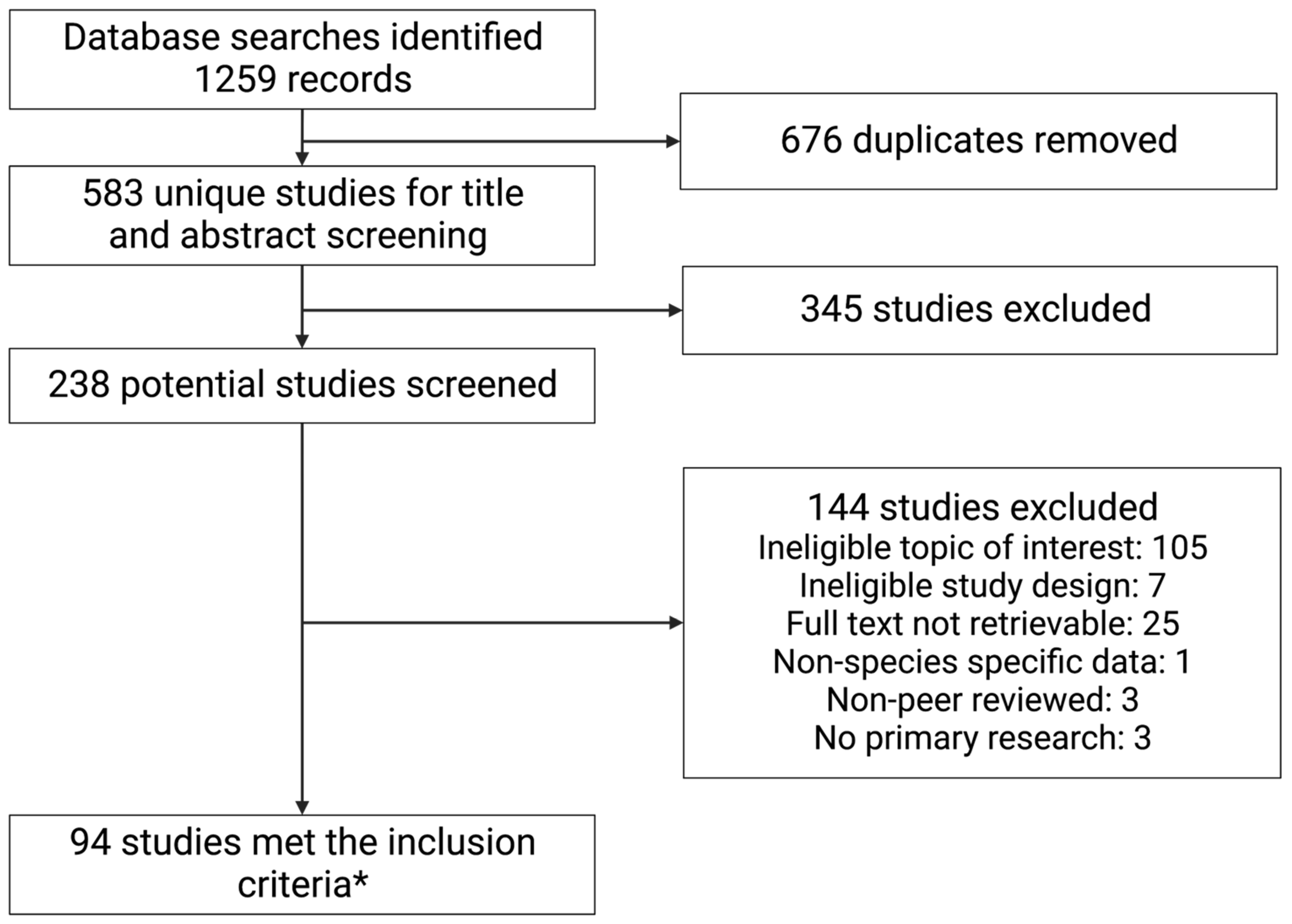
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Seroprevalence
3.4. Emerging Themes on the Advantages and Disadvantages of Serology Implementation
3.5. Advantages
3.6. Disadvantages
4. Discussion
| Study ID | Country of Study | Method | Antigen | Seroprevalence Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Park 2000 [72] | Korea | ELISA | MSP1-19 | 15% |
| Abu-Zeid 2002 [73] | United Arab Emirates | ELISA | MAP4 | 3.30% |
| Volney 2002 [49] | Guinea | ELISA; IFA | ELISA: CSP; IFA: blood stages | ELISA: 0–57.4%; IFA: nd |
| Kim 2003 [90] | Korea | ELISA | CSP1, MSP1, AMA1, SERA, EXP1 | 7.2% reacted to at least one antigen |
| Lee 2003 [101] | Korea | ELISA | CSP | 0.9–9.6% across regions |
| Chang 2004 [70] | East Timor | ELISA | CSP, MSP | CSP: 5.7%; MSP: 3.3% |
| Lim 2005 [48] | Korea | ELISA | CSP | 0–10% across regions |
| Curado 2006 [52] | Brazil | ELISA (IgG); IFA (IgM and IgG) | ELISA: CSP; IFA: blood stages | ELISA: 8.38–34.9% across areas; IFA (IgG): 32.0, 49.0%%, (IgM): 0, 1.93% |
| Arruda 2007 [54] | Brazil | ELISA | CSP | Up to approx. 70% |
| Cerutti Jr 2007 [95] | Brazil | ELISA; IFA | ELISA: CSP; IFA: blood stages | ELISA: 25.4% VK210, 6.3% VK247, 10.7% Pv-like; IFA: 6.2% IgM, 37.7% IgG |
| Ladeia-Andrade 2007 [53] | Brazil | ELISA | MSP1-19 | Dry season: 64.0%; Wet season 69.6% |
| Suárez-Mutis 2007 [113] | Brazil | ELISA | MSP1-19 | 46.90% |
| Gomes 2008 [61] | Brazil | ELISA; IFA | ELISA: CSP; IFA: blood stages | ELISA: up to 38% IFA: 45% |
| Culleton 2009 [87] | Republic of the Congo | ELISA | CSP, MSP1 | CSP: 6%; MSP: 10% |
| Bousema 2010 [65] | Somalia | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | 19.3% reacted to at least one antigen |
| Cook 2010 [91] | Vanuatu | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | MSP1: 6.2, 12.6% AMA1: 10.1, 15.0% |
| Lee 2011 [114] | Korea | IFAT | Whole blood antigen | 2.16% |
| Yildiz Zeyrek 2011 [56] | Turkey | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1-ecto, SERA4, CSP | 79.1% responded to at least one antigen |
| Cook 2012 [81] | Cambodia | ELISA | MSP1-19 | August: 7.9%; November 6.0% |
| Khaireh 2012 [115] | Djibouti | Multiplex bead assay | MSP1 | 17.50% |
| Kim 2012 [116] | Korea | IFAT | Whole blood antigen | 7.24% |
| Zoghi 2012 [55] | Iran | ELISA | MSP1-19 | 0.45–1% across regions and surveys |
| Cho 2013 [66] | Korea | ELISA | CSP | 3.08–50% across regions and years (2010–2011) |
| Rosas-Aguirre 2013 [78] | Peru | ELISA | MSP1-19 | 13.60% |
| Cunha 2014 [117] | Brazil | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | 52.5% to at least one antigen |
| Fru-Cho 2014 [71] | Cameroon | Rapid immunochromatographic card assay | CSP, MSP | 1.1% to at least one antigen |
| Hristov 2014 [64] | Brazil | ELISA, Immunochromatographic test (ICT) | ELISA: MSP1-19; ICT: CSP, MSP | ELISA: 44%; ICT: 38.4% |
| Kim 2014a [68] | Korea | IFAT | blood-stage parasites | 0.94% |
| Kim 2014b [77] | Korea | ELISA | MSP1 | 8.08% |
| Nam 2014 [57] | Korea | Rapid diagnostic test | CSP, MSP1 | CSP: 57.0%; MSP1: 80.2% |
| Ashton 2015 [112] | Ethiopia | ELISA | MSP1, AMA | 11.1% to at least one antigen |
| Lee 2015 [102] | Korea | ELISA | CSP | 6.37% |
| Piperaki 2015 [50] | Greece | ELISA | CSP, MSP1 | 0% local residents; 11.8% immigrants |
| Rosas-Aguirre 2015 [75] | Brazil | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | 33.60% |
| Lopez-Perez 2016 [62] | Colombia | ELISA; IFA | ELISA: CSP, MSP1 IFA: blood stage antigens | ELISA: CSP (32.4%), MSP1, (55.9%); IFA: 47.1% |
| Poirier 2016 [97] | Benin | ELISA | CSP1, MSP1 | MSP1: 28.7%, CSP1: 21.6%, both: 15.2% |
| Priest 2016 [86] | Cambodia | Multiplex bead assay | MSP1-19 | 4.60% |
| Spring 2016 [89] | Cambodia | ELISA | MSP1 | 73% |
| Wahid 2016 [118] | Pakistan | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | 17.6–47.5% across camps |
| Wangroongsarb 2016 [119] | Thailand | ELISA | MSP1-19, MSP2, CSP, AMA | Urban: 3%; Rural: 15% (to at least one antigen) |
| Zakeri 2016 [79] | Iran | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | City: 7%; Village: 13%; (to at least one antigen) |
| Dewasurendra 2017 [80] | Sri Lanka | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | 63.8, 65.1% across regions to at least one antigen |
| Ghinai 2017 [120] | Myanmar | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | 3.10% |
| Idris 2017 [88] | Vanuatu | ELISA | Crude schizont extract, MSP1-19, AMA1 | up to 40% across antigens and years |
| Niang 2017 [92] | Senegal | ELISA | MSP1 | 58% |
| Rogier 2017 [67] | Mali | Multiplex bead assay | MSP1-19 | 17.40% |
| Sáenz 2017 [7] | Ecuador | ELISA; IFAT | ELISA: CSP, MSP1, IFAT: blood stage antigens | ELISA: CSP, 23.08%, MSP1, 27.23%; IFAT: individual Pv results n/a |
| Seol 2017 [121] | Korea | ELISA | GDH | 10.39% |
| Tadesse 2017 [94] | Ethiopia | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | 8.5–36.3% across regions and surveys |
| Yalew 2017 [82] | Ethiopia | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | 21.8% (age-adjusted) |
| Kattenberg 2018 [63] | Vietnam | ELISA | MSP1, AMA1 | Mixed models: 24.9% in the final survey; Classification and regression tree method (CART): 34.9% in the final survey |
| Nyunt 2018 [69] | Myanmar | Protein microarray | MSP1-19, AMA1, DBPII | MSP1-19: 31.5%, AMA1: 24.1%, DBPII: 59.3% |
| Pereira 2018 [74] | Brazil | ELISA | CSP | 62% |
| Assefa 2019 [85] | Ethiopia | Multiplex bead assay | MSP-1, AMA1 | 25.00% |
| Feleke 2019 [59] | Ethiopia | Multiplex bead assay | MSP1-19 | 50% |
| Keffale 2019 [84] | Ethiopia | ELISA | AMA1 | 13.00% |
| Miguel 2019 [122] | Brazil | ELISA | MSP1-19 | 7.70% |
| Surendra 2019 [103] | Indonesia | ELISA | MSP-1, AMA1 | 1.97% to at least one antigen |
| Costa 2020 [51] | Brazil | ELISA | MSP1-19 | 2010: 93.4%, 2012: 78.3%, 2013: 85.1% |
| Labadie-Bracho 2020 [123] | Suriname | Multiplex bead assay | MSP1-19 | Up to approx. 12% across regions |
| Lee 2020 [93] | Korea | Protein array | LSA-N, CSP-VK210, MSP1-19 | 6.7–23.8% (by region and antigen) |
| Lu 2020 [124] | Bangladesh | Multiplex bead assay | MSP1 | 3.10% |
| Seck 2020 [58] | Senegal | Multiplex bead assay | MSP1-19 | 0.7% in the total study population; by age group ranged from 0–1.7% |
| Surendra 2020 [76] | Indonesia | Multiplex bead assay | AMA1, MSP1-19, EB, RBP1a, RBP2b | 38.8–46.3% across surveys |
| Chotirat 2021 [9] | Thailand | Multiplex bead assay | 23 proteins | 2.5–16.8% across proteins |
| Edwards 2021 [105] | Myanmar | ELISA | MSP-1, AMA1 | 3–19.5% |
| Lee 2021 [125] | Korea | ELISA | CSP | 2017: 1.62%, 2018: 1.22% |
| Monteiro 2021 [60] | Brazil | Multiplex bead assay | MSP1 | 52.58% |
| O’Flaherty 2021 [83] | Myanmar | ELISA | AMA1 | 28.40% |
| Leonard 2022 [100] | Ethiopia | Multiplex bead assay | AMA1, MSP1, chimeric MSP1 | 39.90% |
| Oviedo 2022 [30] | Haiti | Multiplex bead assay | MSP1-19 | 0.46% |
| San 2022 [126] | Vietnam | ELISA | AMA1, MSP1-19, CSP allelic variant 210, CSP allelic variant 247 | 31.10% |
| Yao 2022 [15] | China-Myanmar border | ELISA | MSP1-19 | 6.12–12.41% by region |
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Angrisano, F.; Robinson, L.J. Plasmodium vivax—How hidden reservoirs hinder global malaria elimination. Parasitol. Int. 2022, 87, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayipto, Y.; Liu, Z.; Mueller, I.; Longley, R.J. Serology for Plasmodium vivax surveillance: A novel approach to accelerate towards elimination. Parasitol. Int. 2022, 87, 102492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, R.N.; Commons, R.J.; Battle, K.E.; Thriemer, K.; Mendis, K. Plasmodium vivax in the Era of the Shrinking P. Falciparum Map. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Technical Strategy for Malaria 2016–2030, 2021 Update. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240031357 (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Baum, E.; Sattabongkot, J.; Sirichaisinthop, J.; Kiattibutr, K.; Davies, D.H.; Jain, A.; Lo, E.; Lee, M.C.; Randall, A.Z.; Molina, D.M.; et al. Submicroscopic and asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax infections are common in western Thailand—Molecular and serological evidence. Malar J. 2015, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, F.E.; Cortés, A.A.; Valenzuela, G.; Vallejo, A.F.; Castellanos, A.; Loayza, A.C.P.; Gutierrez, J.B.; Alvarez, A.; Yan, Y.H.; Benavides, Y.; et al. Malaria epidemiology in low—Endemicity areas of the northern coast of Ecuador: High prevalence of asymptomatic infections. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, E.; Sattabongkot, J.; Sirichaisinthop, J.; Kiattibutr, K.; Jain, A.; Taghavian, O.; Lee, M.C.; Huw Davies, D.; Cui, L.; Felgner, P.L.; et al. Common asymptomatic and submicroscopic malaria infections in Western Thailand revealed in longitudinal molecular and serological studies: A challenge to malaria elimination. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotirat, S.; Nekkab, N.; Kumpitak, C.; Hietanen, J.; White, M.T.; Kiattibutr, K.; Sa-Angchai, P.; Brewster, J.; Schoffer, K.; Takashima, E.; et al. Application of 23 Novel Serological Markers for Identifying Recent Exposure to Plasmodium vivax Parasites in an Endemic Population of Western Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kho, S.; Qotrunnada, L.; Leonardo, L.; Andries, B.; Wardani, P.A.I.; Fricot, A.; Henry, B.; Hardy, D.; Margyaningsih, N.I.; Apriyanti, D.; et al. Hidden Biomass of Intact Malaria Parasites in the Human Spleen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2067–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; von Seidlein, L.; Nguyen, T.V.; Truong, P.N.; Hung SDo Pham, H.T.; Nguyen, T.U.; Le, T.D.; Dao, V.H.; Mukaka, M.; Day, N.P.; et al. The persistence and oscillations of submicroscopic Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax infections over time in Vietnam: An open cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.J.; Wampfler, R.; Betuela, I.; Karl, S.; White, M.T.; Li Wai Suen, C.S.N.; Hofmann, N.E.; Kinboro, B.; Waltmann, A.; Brewster, J.; et al. Strategies for Understanding and Reducing the Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale Hypnozoite Reservoir in Papua New Guinean Children: A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial and Mathematical Model. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioRender. Available online: https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- The malERA Refresh Consultative Panel on Tools for Malaria Elimination. malERA: An updated research agenda for diagnostics, drugs, vaccines, and vector control in malaria elimination and eradication. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Xiao, L.; Sun, X.; Lin, Z.; Hao, X.; Bai, Q.Q.; Yin, D.H. Surveillance of Plasmodium vivax transmission using serological models in the border areas of China–Myanmar. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, B.F.; Scobie, H.M.; Priest, J.W.; Lammie, P.J. Integrated Serologic Surveillance of Population Immunity and Disease Transmission. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.L.; Saboyà-Díaz, M.I.; Abashawl, A.; Alemayeh, W.; Gwyn, S.; Hooper, P.J.; Keenan, J.; Kalua, K.; Szwarcwald, C.L.; Nash, S.; et al. The use of serology for trachoma surveillance: Current status and priorities for future investigation. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalf, C.J.E.; Farrar, J.; Cutts, F.T.; Basta, N.E.; Graham, A.L.; Lessler, J.; Ferguson, N.M.; Burke, D.S.; Grenfell, B.T. Use of serological surveys to generate key insights into the changing global landscape of infectious disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nale, J.M.; Pharande, R.R.; Majee, S.B.; Gandge, R.S.; Sawane, M.P.; Ingle, S.A. Serosurveillance of rabies antibodies in dogs in Mumbai region by using indirect ELISA. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 76, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murhekar, M.V.; Kamaraj, P.; Kumar, M.S.; Khan, S.A.; Allam, R.R.; Barde, P. Burden of dengue infection in India, 2017: A cross-sectional population based serosurvey. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e1065–e1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salje, H.; Paul, K.K.; Paul, R.; Rodriguez-Barraquer, I.; Rahman, Z.; Alam, M.S.; Rahman, M.; Al-Amin, H.M.; Heffelfinger, J.; Gurley, E. Nationally-representative serostudy of dengue in Bangladesh allows generalizable disease burden estimates. Elife 2019, 8, e42869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Nishimura, M.; Tjan, L.H.; Furukawa, K.; Kurahashi, Y.; Sutandhio, S.; Aoki, K.; Hasegawa, N.; Arii, J.; Uto, K.; et al. Large-scale serosurveillance of COVID-19 in Japan: Acquisition of neutralizing antibodies for Delta but not for Omicron and requirement of booster vaccination to overcome the Omicron’s outbreak. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, J.; White, M.T.; Longley, J.R.; Lacerda, M.; Monteiro, W.; Brewster, J.; Sattabongtot, J.; Guzman-Guzman, M.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; Vinetz, J.M.; et al. Heterogeneity in response to serological exposure markers of recent Plasmodium vivax infections in contrasting epidemiological contexts. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdech, Z.; Mok, S.; Hu, G.; Imwong, M.; Jaidee, A.; Russell, B.; Ginsburg, H.; Nosten, F.; Day, N.P.; White, N.J.; et al. The transcriptome of Plasmodium vivax reveals divergence and diversity of transcriptional regulation in malaria parasites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16290–16295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualdrón-López, M.; Díaz-Varela, M.; Zanghi, G.; Aparici-Herraiz, I.; Steel, R.W.J.; Schäfer, C.; Cuscó, P.; Chuenchob, V.; Kangwangransan, N.; Billman, Z.P.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Identification of Biomarkers in Extracellular Vesicles From Plasmodium vivax Liver Hypnozoite Infections. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2022, 21, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, A.; Patel, S.K.; Ray, S.; Shastri, J.; Chatterjee, G.; Kochar, S.K.; Patankar, S.; Srivastava, S. Proteomics of Plasmodium vivax malaria: New insights, progress and potential. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2016, 13, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covidence—Better Systematic Review Management. Available online: https://www.covidence.org/?_gl=1%2Ak11ap2%2A_ga%2AOTgwMjgzOTQ3LjE2NzA5Nzc2MDY.%2A_ga_HXKEQPTFLR%2AMTY3NTc0Njc5MC4zLjEuMTY3NTc0Njc5MC42MC4wLjA (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- McCaffery, J.N.; Singh, B.; Nace, D.; Moreno, A.; Udhayakumar, V.; Rogier, E. Natural infections with different Plasmodium species induce antibodies reactive to a chimeric Plasmodium vivax recombinant protein. Malar. J. 2021, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, A.; Herman, C.; Knipes, A.; Worrell, C.M.; Fox, L.M.; Desir, L.; Fayette, C.; Javel, A.; Monestime, F.; Mace, K.E.; et al. Spatial cluster analysis of Plasmodium vivax and P. malariae exposure using serological data among Haitian school children sampled between 2014 and 2016. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Chen, S.B.; Wang, Y.; Ju, C.; Zhang, T.; Xu, B.; Shen, H.M.; Mo, X.J.; Molina, D.M.; Eng, M.; et al. An immunomics approach for the analysis of natural antibody responses to Plasmodium vivax infection. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 2354–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Hwang, H.A.; Yun, W.S.; Kim, S.L.; Park, S.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, T.K.; Wongsrichanalai, C.; Sakanari, J.A.; Park, H. efficacy of msp1 of pv as an ag for ELISA to diagnose malaria. Yonsei Med. J. 2004, 45, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Coelho, J.; da Silva Soares, I.; Antunes de Lemos, E.; Carolina Sarti Jimenez, M.; Erikó Kudó, M.; do Lago Moraes, S.; Ferreira, A.W.; Sanchez, M.C. A multianalyte Dot-ELISA for simultaneous detection of malaria, Chagas disease, and syphilis-specific IgG antibodies. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 58, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonaimuthu, P.; Cheong, F.W.; Chin, L.C.; Mahmud, R.; Fong, M.Y.; Lau, Y.L. Detection of human malaria using recombinant Plasmodium knowlesi merozoire surface protein-1 (MSP-119) expressed in Escherichia coli. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 153, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, S.S.; Oh, C.M.; Choi, K.M.; Lin, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Na, B.K.; Han, E.T.; Sohn, Y.; et al. Molecular cloning and expression of the VK247 circumsporozoite protein for serodiagnosis of variant form Plasmodium vivax. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, B.K.; Park, J.W.; Lee, H.W.; Lin, K.; Kim, S.H.; Bae, Y.A.; Sohn, W.M.; Kim, T.S.; Kong, Y. Characterization of Plasmodium vivax heat shock protein 70 and evaluation of its value for serodiagnosis of tertian malaria. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priest, J.W.; Plucinski, M.M.; Huber, C.S.; Rogier, E.; Mao, B.; Gregory, C.J.; Candrinho, B.; Colborn, J.; Barnwell, J.W. Specificity of the IgG antibody response to Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium malariae, and Plasmodium ovale MSP1 19 subunit proteins in multiplexed serologic assays. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhof, K.; Sluydts, V.; Willen, L.; Kim, S.; Canier, L.; Heng, S.; Tsuboi, T.; Sochantha, T.; Sovannaroth, S.; Ménard, D.; et al. Serological markers to measure recent changes in malaria at population level in Cambodia. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhof, K.; Canier, L.; Kim, S.; Heng, S.; Sochantha, T.; Sovannaroth, S.; Vigan-Womas, I.; Coosemans, M.; Sluydts, V.; Ménard, D.; et al. Implementation and application of a multiplex assay to detect malaria-specific antibodies: A promising tool for assessing malaria transmission in Southeast Asian pre-elimination areas. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, C.H.; Han, E.T.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, H.K.; An, S.S.A.; Lim, C.S.; Lee, K.N. Evaluation of Plasmodium vivax ELISA for the blood screen. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2010, 15, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longley, R.J.; White, M.T.; Takashima, E.; Brewster, J.; Morita, M.; Harbers, M.; Obadia, T.; Robinson, L.J.; Matsuura, F.; Liu, Z.S.J.; et al. Development and validation of serological markers for detecting recent Plasmodium vivax infection. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, C.G.; Soares, I.S.; Carvalho, L.H.; Fontes, C.J.F.; Krettli, A.U.; Braga, É.M. IgG isotype to C-terminal 19 kDa of Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein 1 among subjects with different levels of exposure to malaria in Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 95, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longley, R.J.; White, M.T.; Brewster, J.; Liu, Z.S.J.; Bourke, C.; Takashima, E.; Harbers, M.; Tham, W.H.; Healer, J.; Chitnis, C.E.; et al. IgG Antibody Responses Are Preferential Compared with IgM for Use as Serological Markers for Detecting Recent Exposure to Plasmodium vivax Infection. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, C.V.; Alves, J.R.S.; Lima, B.A.S.; Paula, R.B.; Costa, H.L.; Torres, L.M.; Sousa, T.N.; Soares, I.S.; Sanchez, B.A.M.; Fontes, C.J.F.; et al. Blood-stage Plasmodium vivax antibody dynamics in a low transmission setting: A nine year follow-up study in the Amazon region. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, S.S.; Na, B.K.; Lin, K.; Cho, S.H.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, D.K.; Sohn, Y.; Kim, H.; et al. Prevalence of Plasmodium vivax VK210 and VK247 subtype in Myanmar. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister-Tyrrell, M.; Xa, N.X.; Kattenberg, J.H.; van Van, N.; Dung, V.K.A.; Hieu, T.M.; Van Hong, N.; Rovira-Vallbona, E.; Thao, N.T.; Duong, T.T.; et al. Micro-epidemiology of malaria in an elimination setting in Central Vietnam. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkhof, K.; Sluydts, V.; Heng, S.; Kim, S.; Pareyn, M.; Willen, L.; Canier, L.; Sovannaroth, S.; Ménard, D.; Sochantha, T.; et al. Geographical patterns of malaria transmission based on serological markers for falciparum and vivax malaria in Ratanakiri, Cambodia. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.S.; Yoon, J.K.; Chang, E.A.; Suh, I.B.; An, S.S.A.; Lee, K.H.; Chung, J.T.; Tockgo, Y.C. Seroprevalence to the circumsporozoite protein peptide antigen of Plasmodium vivax in Korean children. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 49, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volney, B.; Pouliquen, J.F.; de Thoisy, B.; Fandeur, T. A sero-epidemiological study of malaria in human and monkey populations in French Guiana. Acta Trop. 2002, 82, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piperaki, E.T.; Mavrouli, M.; Tseroni, M.; Routsias, J.; Kallimani, A.; Veneti, L.; Georgitsou, M.; Chania, M.; Georgakopoulou, T.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; et al. Assessment of antibody responses in local and immigrant residents of areas with autochthonous malaria transmission in Greece. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.M.F.; Amador, E.C.C.; Silva, E.S.; Alvarenga, C.O.; Pereira, P.E.; Póvoa, M.M.; Cunha, M.G. Malaria transmission and individual variability of the naturally acquired IgG antibody against the Plasmodium vivax blood-stage antigen in an endemic area in Brazil. Acta Trop. 2020, 209, 105537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curado, I.; dos Santos Malafronte, R.; de Castro Duarte, A.M.R.; Kirchgatter, K.; Branquinho, M.S.; Bianchi Galati, E.A. Malaria epidemiology in low-endemicity areas of the Atlantic Forest in the Vale do Ribeira, São Paulo, Brazil. Acta Trop. 2006, 100, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladeia-Andrade, S.; Ferreira, M.U.; Scopel, K.K.G.; Braga, É.M.; Bastos, M.D.S.; Wunderlich, G.; Coura, J.R. Naturally acquired antibodies to merozoite surface protein (MSP)-1 19 and cumulative exposure to Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax in remote populations of the Amazon Basin of Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2007, 102, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, M.E.; Zimmerman, R.H.; Souza, R.M.C.; Oliveira-Ferreira, J. Prevalence and level of antibodies to the circumsporozoite protein of human malaria parasites in five states of the Amazon region of Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2007, 102, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghi, S.; Mehrizi, A.A.; Raeisi, A.; Haghdoost, A.A.; Turki, H.; Safari, R.; Kahanali, A.A.; Zakeri, S. Survey for asymptomatic malaria cases in low transmission settings of Iran under elimination programme. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeyrek, F.Y.; Palacpac, N.; Yuksel, F.; Yagi, M.; Honjo, K.; Fujita, Y.; Arisue, N.; Takeo, S.; Tanabe, K.; Horii, T.; et al. Serologic markers in relation to parasite exposure history help to estimate transmission dynamics of Plasmodium vivax. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28126. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.W.; Song, K.J.; Ahn, H.J.; Yang, Z.; Chong, C.K.; Cho, P.Y.; Ahn, S.K.; Kim, T.S. Probability of antibody formation against circumsporozoite protein of Plasmodium vivax among Korean malaria patients. Korean J. Parasitol. 2014, 52, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seck, M.C.; Thwing, J.; Badiane, A.S.; Rogier, E.; Fall, F.B.; Ndiaye, P.I.; Diongue, K.; Mbow, M.; Ndiaye, M.; Diallo, M.A.; et al. Analysis of anti-Plasmodium IgG profiles among Fulani nomadic pastoralists in northern Senegal to assess malaria exposure. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feleke, S.M.; Brhane, B.G.; Mamo, H.; Assefa, A.; Woyessa, A.; Ogawa, G.M.; Cama, V. Sero-identification of the aetiologies of human malaria exposure (Plasmodium spp.) in the Limu Kossa District of Jimma Zone, South western Ethiopia. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, E.F.; Fernandez-Becerra, C.; Curado, I.; Wunderlich, G.; Hiyane, M.I.; Kirchgatter, K. Antibody profile comparison against MSP1 antigens of multiple plasmodium species in human serum samples from two different Brazilian populations using a multiplex serological assay. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.D.C.; de Paula, M.B.; Duarte, A.M.R.D.C.; Lima, M.A.; Malafronte, R.D.S.; Mucci, L.F.; Gotlieb, S.L.; Natal, D. Epidemiological and ecological aspects related to malaria in the area of influence of the lake at Porto Primavera dam, in western São Paulo State, Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. 2008, 50, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Perez, M.; Pacheco, M.A.; Buriticá, L.; Escalante, A.A.; Herrera, S.; Arévalo-Herrera, M. Malaria in pregnancy: A passive surveillance study of pregnant women in low transmission areas of Colombia, Latin America. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattenberg, J.H.; Erhart, A.; Truong, M.H.; Rovira-Vallbona, E.; Vu, K.A.D.; Nguyen, T.H.N.; Nguyen, V.H.; Nguyen, V.V.; Bannister-Tyrrell, M.; Thiesen, M.; et al. Characterization of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax recent exposure in an area of significantly decreased transmission intensity in Central Vietnam. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, A.D.; Sanchez, M.C.A.; Ferreira, J.J.B.; de Lima, G.F.M.C.; Inoue, J.; de Costa-Nascimento, M.J.; Sanchez, A.R.; Ramos-Sanchez, E.M.; Di Santi, S.M. Malaria in pregnant women living in areas of low transmission on the southeast Brazilian coast: Molecular diagnosis and humoural immunity profile. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2014, 109, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousema, T.; Youssef, R.M.; Cook, J.; Cox, J.; Alegana, V.A.; Amran, J.; Noor, A.M.; Snow, R.W.; Drakeley, C. Serologic markers for detecting malaria in areas of low endemicity, Somalia, 2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, P.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Ahn, S.K.; Kim, J.S.; Cha, S.H.; Na, B.K.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, W.J.; Nam, H.W.; et al. Evaluation of circumsporozoite protein of Plasmodium vivax to estimate its prevalence in the Republic of Korea: An observational study of incidence. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogier, E.; Moss, D.M.; Chard, A.N.; Trinies, V.; Doumbia, S.; Freeman, M.C.; Lammie, P.J. Evaluation of Immunoglobulin G Responses to Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax in Malian School Children Using Multiplex Bead Assay. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.S.; Kang, Y.J.; Lee, W.J.; Na, B.K.; Moon, S.U.; Cha, S.H.; Lee, S.K.; Park, Y.K.; Pak, J.H.; Cho, P.Y.; et al. Seroprevalence of Plasmodium vivax in the republic of Korea (2003–2005) using indirect fluorescent antibody test. Korean J. Parasitol. 2014, 52, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyunt, M.H.; Soe, T.N.; Shein, T.; Zaw, N.N.; Han, S.S.; Muh, F.; Lee, S.K.; Han, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Ha, K.S.; et al. Estimation on local transmission of malaria by serological approach under low transmission setting in Myanmar. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.A.; Park, I.; Kim, J.Y.; Suh, I.B.; An, S.S.A.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, K.N. Seroprevalence of malaria infections in Korean troops on a peacekeeping mission in East Timor from 2001 to 2002. J. Travel Med. 2004, 11, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fru-Cho, J.; Bumah, V.V.; Safeukui, I.; Nkuo-Akenji, T.; Titanji, V.P.K.; Haldar, K. Molecular typing reveals substantial Plasmodium vivax infection in asymptomatic adults in a rural area of Cameroon. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.G.; Chwae, Y.J.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, J.H.; Hur, G.M.; Jeon, B.H.; Koh, J.S.; Han, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.W.; et al. Serologic responses of Korean soldiers serving in malaria-endemic areas during a recent outbreak of Plasmodium vivax. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 62, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zeid, Y.A.; Alwash, R.; Shaheen, H.M.; Bin-Othman, S.A.; Lukic, M.L.; Amiri, K.M.A. Seroprevalence of antibodies to repetitive domains of Plasmodium vivax circumsporozoite protein in United Arab Emirates children. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 96, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.A.; Sánchez-Arcila, J.C.; Vasconcelos, M.P.A.; Ferreira, A.R.; de Souza Videira, L.; Teva, A.; Perce-da-Silva, D.; Marques, M.T.Q.; de Carvalho, L.H.; Banic, D.M.; et al. Evaluating seroprevalence to circumsporozoite protein to estimate exposure to three species of Plasmodium in the Brazilian Amazon. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Aguirre, A.; Speybroeck, N.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; Rosanas-Urgell, A.; Carrasco-Escobar, G.; Rodriguez, H.; Gamboa, D.; Contreras-Mancilla, J.; Alava, F.; Soares, I.S.; et al. Hotspots of malaria transmission in the Peruvian amazon: Rapid assessment through a parasitological and serological survey. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendra, H.; Supargiyono Ahmad, R.A.; Kusumasari, R.A.; Rahayujati, T.B.; Damayanti, S.Y.; Tetteh, K.K.A.; Chitnis, C.; Stresman, G.; Cook, J.; Drakeley, C. Using health facility-based serological surveillance to predict receptive areas at risk of malaria outbreaks in elimination areas. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.S.; Sohn, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, W.J.; Na, B.K.; Kang, Y.J.; Lee, H.W. Detection of antibodies against the CB9 to ICB10 region of merozoite surface protein-1 of Plasmodium vivax among the inhabitants in epidemic areas. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-aguirre, A.; Llanos-cuentas, A.; Speybroeck, N.; Cook, J.; Contreras-mancilla, J.; Soto, V.; Gamboa, D.; Pozo, E.; Ponce, O.J.; Pereira, M.O.; et al. Assessing malaria transmission in a low endemicity area of north-western Peru. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, S.; Van Den Hoogen, L.L.; Mehrizi, A.A.; Karimi, F.; Raeisi, A.; Drakeley, C. Anti-malarial seroprevalence assessment during an elimination programme in Chabahar District, south-eastern Iran. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewasurendra, R.L.; Dias, J.N.; Sepulveda, N.; Gunawardena, G.S.A.; Chandrasekharan, N.; Drakeley, C.; Karunaweera, N.D. Effectiveness of a serological tool to predict malaria transmission intensity in an elimination setting. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.; Speybroeck, N.; Sochanta, T.; Somony, H.; Sokny, M.; Claes, F.; Lemmens, K.; Theisen, M.; Soares, I.S.; D’Alessandro, U.; et al. Sero-epidemiological evaluation of changes in Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax transmission patterns over the rainy season in Cambodia. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalew, W.G.; Pal, S.; Bansil, P.; Dabbs, R.; Tetteh, K.; Guinovart, C.; Kalnoky, M.; Serda, B.A.; Tesfay, B.H.; Beyene, B.B.; et al. Current and cumulative malaria infections in a setting embarking on elimination: Amhara, Ethiopia. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, K.; Oo, W.H.; Zaloumis, S.G.; Cutts, J.C.; Aung, K.Z.; Thein, M.M.; Drew, D.R.; Razook, Z.; Barry, A.E.; Pasricha, N.; et al. Community-based molecular and serological surveillance of subclinical malaria in Myanmar. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keffale, M.; Shumie, G.; Behaksra, S.W.; Chali, W.; Hoogen LLVDen Hailemeskel, E.; Mekonnen, D.; Chanyalew, M.; Damte, D.; Fanta, T.; Ashine, T.; et al. Serological evidence for a decline in malaria transmission following major scale-up of control efforts in a setting selected for Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum malaria elimination in Babile district, Oromia, Ethiopia. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 113, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, A.; Ali Ahmed, A.; Deressa, W.; Sime, H.; Mohammed, H.; Kebede, A.; Solomon, H.; Teka, H.; Gurrala, K.; Matei, B.; et al. Multiplex serology demonstrate cumulative prevalence and spatial distribution of malaria in Ethiopia. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priest, J.W.; Jenks, M.H.; Moss, D.M.; Mao, B.; Buth, S.; Wannemuehler, K.; Soeung, S.C.; Lucchi, N.W.; Udhayakumar, V.; Gregory, C.J.; et al. Integration of Multiplex Bead Assays for Parasitic Diseases into a National, Population-Based Serosurvey of Women 15–39 Years of Age in Cambodia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culleton, R.; Ndounga, M.; Zeyrek, F.Y.; Coban, C.; Casimiro, P.N.; Takeo, S.; Tsuboi, T.; Yadava, A.; Carter, R.; Tanabe, K. Evidence for the transmission of plasmodium vivax in the Republic of the Congo, West Central Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, Z.M.; Chan, C.W.; Mohammed, M.; Kalkoa, M.; Taleo, G.; Junker, K.; Arcà, B.; Drakeley, C.; Kaneko, A. Serological measures to assess the efficacy of malaria control programme on Ambae Island, Vanuatu. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, M.D.; Pichyangkul, S.; Lon, C.; Gosi, P.; Yongvanichit, K.; Srichairatanakul, U.; Limsalakpeth, A.; Chaisatit, C.; Chann, S.; Sriwichai, S.; et al. Antibody profiles to plasmodium merozoite surface protein-1 in Cambodian adults during an active surveillance cohort with nested treatment study. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ahn, H.J.; Kim, T.S.; Nam, H.W. ELISA detection of vivax malaria with recombinant multiple stage-specific antigens and its application to survey of residents in endemic areas. Korean J. Parasitol. 2003, 41, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.; Reid, H.; Iavro, J.; Kuwahata, M.; Taleo, G.; Clements, A.; McCarthy, J.; Vallely, A.; Drakeley, C. Using serological measures to monitor changes in malaria transmission in Vanuatu. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, M.; Diop, F.; Niang, O.; Sadio, B.D.; Sow, A.; Faye, O.; Diallo, M.; Sall, A.A.; Perraut, R.; Toure-Balde, A. Unexpected high circulation of Plasmodium vivax in asymptomatic children from Kédougou, southeastern Senegal. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Hu, F.; Firdaus, E.R.; Park, J.H.; Han, J.H.; Lee, S.E.; Shin, H.I.; Cho, S.H.; Park, W.S.; Lu, F.; et al. Surveillance on the vivax malaria in endemic areas in the republic of Korea based on molecular and serological analyses. Korean J. Parasitol. 2020, 58, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, F.G.; Van Den Hoogen, L.; Lanke, K.; Schildkraut, J.; Tetteh, K.; Aseffa, A.; Mamo, H.; Sauerwein, R.; Felger, I.; Drakeley, C.; et al. The shape of the iceberg: Quantification of submicroscopic Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax parasitaemia and gametocytaemia in five low endemic settings in Ethiopia. Malar J. 2017, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, C.; Boulos, M.; Coutinho, A.F.; Hatab, M.D.C.L.D.; Falqueto, A.; Rezende, H.R.; Duarte, A.M.; Collins, W.; Malafronte, R.S. Epidemiologic aspects of the malaria transmission cycle in an area of very low incidence in Brazil. Malar. J. 2007, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Bibhu, R.; Das, R.; Dash, A.P.; Supakar, P.C. Genetic diversity in the merozoite surface protein 1 gene of Plasmodium falciparum in different malaria-endemic localities. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 71, 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Poirier, P.; Lang, C.D.; Atchade, P.S.; Lemoine, J.P.; de l’Isle, M.C.; Abou-Bacar, A.; Pfaff, A.W.; Brunet, J.; Arnoux, L.; Haar, E.; et al. The hide and seek of Plasmodium vivax in West Africa: Report from a large—Scale study in Beninese asymptomatic subjects. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, K.I.C.; Kosugi, H.; Thoeun, S.; Araki, H.; Thandar, M.M.; Iwagami, M.; Hongvanthong, B.; Brey, P.T.; Kano, S.; Jimba, M. Systematic review of the clinical manifestations of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in the Greater Mekong Subregion: Implications for malaria elimination and beyond. BMJ Glob. Health 2017, 2, e000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obadia, T.; Nekkab, N.; Robinson, L.J.; Drakeley, C.; Mueller, I.; White, M.T. Developing sero-diagnostic tests to facilitate Plasmodium vivax Serological Test-and-Treat approaches: Modeling the balance between public health impact and overtreatment. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, C.M.; Assefa, A.; Sime, H.; Mohammed, H.; Kebede, A.; Solomon, H.; Drakeley, C.; Murphy, M.; Hwang, J.; Rogier, E. Spatial Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax in Northern Ethiopia by Microscopic, Rapid Diagnostic Test, Laboratory Antibody, and Antigen Data. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.N.; Suh, I.B.; Chang, E.A.; Kim, S.D.; Cho, N.S.; Park, P.W.; An, S.S.; Park, O.; Lim, C. Prevalence of antibodies to the circumsporozite protein of Plasmodium vivax in five different regions of Korea. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2003, 8, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Kang, Y.J.; Cho, S.H.; Na, B.K.; Pak, J.H.; Nam, H.W.; Park, Y.K.; Sohn, Y.; Kim, T.S. Relationship between antibody-positive rate against plasmodium vivax circumsporozoite protein and incidence of malaria. Korean J. Parasitol. 2015, 53, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendra, H.; Wijayanti, M.A.; Murhandarwati, E.H.; Irnawati; Yuniarti, T.; Mardiati; Herdiana; Sumiwi, M.E.; Hawley, W.A.; Lobo, N.F.; et al. Analysis of serological data to investigate heterogeneity of malaria transmission: A community-based cross-sectional study in an area conducting elimination in Indonesia. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.L.; Yao, L.N.; Chen, H.L.; Lu, Q.Y.; Ruan, W. Genetic diversity analysis of PvCSP and its application in tracking of Plasmodium vivax. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 188, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.M.; Dixon, R.; de Beyl, C.Z.; Celhay, O.; Rahman, M.; Oo, M.M.; Lwin, T.; Lin , Z.; San , T.; Han , K.T.; et al. Prevalence and seroprevalence of plasmodium infection in myanmar reveals highly heterogeneous transmission and a large hidden reservoir of infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252957. [Google Scholar]
- Longley, R.J.; Grigg, M.J.; Schoffer, K.; Obadia, T.; Hyslop, S.; Piera, K.A.; Nekkab, N.; Mazhari, R.; Takashima, E.; Tsuboi, T.; et al. Plasmodium vivax malaria serological exposure markers: Assessing the degree and implications of cross-reactivity with P Knowlesi. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruwanpura, V.; Neukom, J.; Grietens, K.P.; Price, R.N.; Thriemer, K.; Lynch, C.A. Opening the policy blackbox: Unravelling the process for changing national diagnostic and treatment guidelines for vivax malaria in seven countries. Malar. J. 2021, 20, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewe, J.A.; Hoinville, L.J.; Cook, A.J.C.; Floyd, T.; Stärk, K.D.C. Evaluation of animal and public health surveillance systems: A systematic review. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrescu, A.I.; Nussbaumer-Streit, B.; Klerings, I.; Wagner, G.; Persad, E.; Sommer, I.; Herkner, H.; Gartlehner, G. Restricting evidence syntheses of interventions to English-language publications is a viable methodological shortcut for most medical topics: A systematic review. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 137, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosselli, D. The language of biomedical sciences. Lancet 2016, 387, 1720–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, J.W.; Bruno, P.; Malik, K.; Connell, G.; Torrance, D.; Ngo, T.; Kirmayr, K.; Avrahami, D.; Riva, J.J.; Ebrahim, S.; et al. An efficient strategy allowed English-speaking reviewers to identify foreign-language articles eligible for a systematic review. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, R.A.; Kefyalew, T.; Rand, A.; Sime, H.; Assefa, A.; Mekasha, A.; Edosa, W.; Tesfaye, G.; Cano, J.; Teka, H.; et al. Geostatistical modeling of malaria endemicity using serological indicators of exposure collected through school surveys. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Mutis, M.C.; Cuervo, P.; Leoratti, F.M.; Moraes-Avila, S.L.; Ferreira, A.W.; Fernandes, O.; Coura, J.R. Cross sectional study reveals a high percentage of asymptomatic Plasmodium vivax infection in the Amazon Rio Negro area, Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo. 2007, 49, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Kim, H.H.; Hwang, S.M.; Park, M.Y.; Kim, N.R.; Cho, S.H.; In, T.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Sattabongkot, J.; Sohn, Y.; et al. Detection of an antibody against Plasmodium vivax in residents of Gimpo-si, South Korea, using an indirect fluorescent antibody test. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaireh, B.A.; Briolant, S.; Pascual, A.; Mokrane, M.; Machault, V.; Travaillé, C.; Khaireh, M.A.; Farah, I.H.; Ali, H.M.; Abdi, A.I.; et al. Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum infections in the Republic of Djibouti: Evaluation of their prevalence and potential determinants. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.H.; Na, B.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Sohn, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, H.W. Estimating the malaria transmission of Plasmodium vivax based on serodiagnosis. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, M.G.; Silva, E.S.; Sepúlveda, N.; Costa, S.P.; Saboia, T.C.; Guerreiro, J.F.; Póvoa, M.M.; Corran, P.H.; Riley, E.; Drakeley, C.J. Serologically defined variations in malaria endemicity in Pará state, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, S.; Stresman, G.H.; Kamal, S.S.; Sepulveda, N.; Kleinschmidt, I.; Bousema, T.; Drakeley, C. Heterogeneous malaria transmission in long-term Afghan refugee populations: A cross-sectional study in five refugee camps in northern Pakistan. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangroongsarb, P.; Hwang, J.; Thwing, J.; Karuchit, S.; Kumpetch, S.; Rand, A.; Drakeley, C.; MacArthur, J.R.; Kachur, S.P.; Satimai, W.; et al. Using Respondent Driven Sampling to Identify Malaria Risks and Occupational Networks among Migrant Workers in Ranong, Thailand. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghinai, I.; Cook, J.; Hla, T.T.; Htet, H.M.; Hall, T.; Lubis, I.N.; Ghinai, R.; Hesketh, T.; Naung, Y.; Lwin, M.M.; et al. Malaria epidemiology in central Myanmar: Identification of a multi-species asymptomatic reservoir of infection. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seol, B.; Shin, H.I.; Kim, J.Y.; Jeon, B.Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Pak, J.H.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, H.W. Sequence conservation of Plasmodium vivax glutamate dehydrogenase among Korean isolates and its application in seroepidemiology. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, R.B.; Albuquerque, H.G.; Sanchez MC, A.; Coura, J.R.; Santos SD, S.; Silva, S.D.; Moreira CJ, C.; Suárez-Mutis, M.C. Asymptomatic Plasmodium infection in a residual malaria transmission area in the Atlantic Forest region: Implications for elimination. Rev. Da Soc. Bras. De Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20180537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labadie-Bracho, M.Y.; van Genderen, F.T.; Adhin, M.R. Malaria serology data from the Guiana shield: First insight in IgG antibody responses to Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium malariae antigens in Suriname. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Cote, O.; Dimitrova, S.D.; Cooley, G.; Alamgir, A.; Uzzaman, M.S.; Flora, M.S.; Widiati, Y.; Akhtar, M.S.; Vandenent, M.; et al. Screening for malaria antigen and anti-malarial IgG antibody in forcibly-displaced Myanmar nationals: Cox’s Bazar district, Bangladesh, 2018. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jin, K.; Ahn, S.K.; Lee, S.K.; Kwon, H.W.; Na, B.K.; Kim, T.S. Seroprevalence of Plasmodium vivax Circumsporozoite Protein Antibody in High-Risk Malaria Areas in Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San, N.N.; Kien, N.X.; Manh, N.D.; Van Thanh, N.; Chavchich, M.; Binh NT, H.; Long, T.K.; Edgel, K.A.; Rovira-Vallbona, E.; Edstein, M.D.; et al. Cross-sectional study of asymptomatic malaria and seroepidemiological surveillance of seven districts in Gia Lai province, Vietnam. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kartal, L.; Mueller, I.; Longley, R.J. Using Serological Markers for the Surveillance of Plasmodium vivax Malaria: A Scoping Review. Pathogens 2023, 12, 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060791
Kartal L, Mueller I, Longley RJ. Using Serological Markers for the Surveillance of Plasmodium vivax Malaria: A Scoping Review. Pathogens. 2023; 12(6):791. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060791
Chicago/Turabian StyleKartal, Lejla, Ivo Mueller, and Rhea J. Longley. 2023. "Using Serological Markers for the Surveillance of Plasmodium vivax Malaria: A Scoping Review" Pathogens 12, no. 6: 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060791
APA StyleKartal, L., Mueller, I., & Longley, R. J. (2023). Using Serological Markers for the Surveillance of Plasmodium vivax Malaria: A Scoping Review. Pathogens, 12(6), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060791






