Iliopsoas Muscle Weakness as a Key Diagnostic Marker in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis (HAM/TSP)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
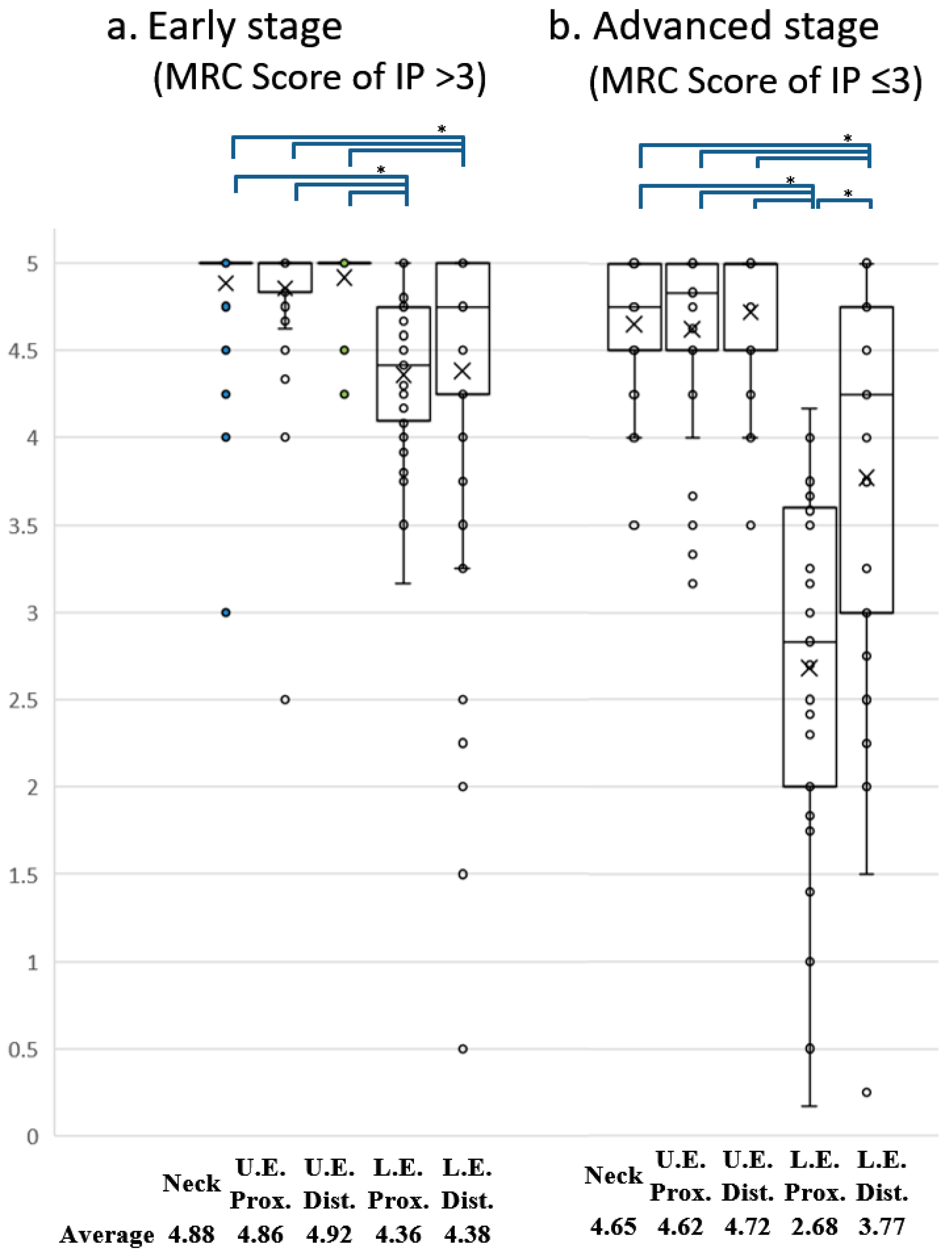
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gessain, A.; Barin, F.; Vernant, J.C.; Gout, O.; Maurs, L.; Calender, A.; de Thé, G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet 1985, 2, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osame, M.; Usuku, K.; Izumo, S.; Ijichi, N.; Amitani, H.; Igata, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Tara, M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet 1986, 1, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Izumo, S.; Ijichi, S.; Kubota, H.; Arimura, K.; Kawabata, M.; Osame, M. HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: Analysis of 213 patients based on clinical features and laboratory findings. J. Neurovirol. 1995, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, Y.; Matsuura, E.; Sagara, Y.; Nozuma, S.; Kodama, D.; Tanaka, M.; Koriyama, C.; Kubota, R.; Takashima, H. High Prevalence of HTLV-1 Carriers Among the Elderly Population in Kagoshima, a Highly Endemic Area in Japan. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2022, 38, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsiedel, L.; Woodman, R.J.; Flynn, M.; Wilson, K.; Cassar, O.; Gessain, A. Human T-Lymphotropic Virus type 1 infection in an Indigenous Australian population: Epidemiological insights from a hospital-based cohort study. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, E.; Nozuma, S.; Tashiro, Y.; Kubota, R.; Izumo, S.; Takashima, H. HTLV-1 associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP): A comparative study to identify factors that influence disease progression. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 371, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, A.; Maloney, E.M.; Morgan, O.S.; Rodgers-Johnson, P.; Manns, A.; Murphy, E.L.; Larsen, S.; Cranston, B.; Murphy, J.; Benichou, J.; et al. Risk factors and cofactors for human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I)-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) in Jamaica. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 142, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuji, Y.; Sugai, F.; Watanabe, S.; Kaido, M.; Koguchi, K.; Abe, K.; Sakoda, S. HTLV-I-associated myelopathy manifested after renal transplantation. J. Neurol. Sci. 2000, 177, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, Y. Pathology of chronic myelopathy associated with HTLV-I infection (HAM/TSP). J. Neurol. Sci. 1990, 96, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumo, S.; Ijichi, T.; Higuchi, I.; Tashiro, A.; Takahashi, K.; Osame, M. Neuropathology of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy–A report of two autopsy cases. Acta Paediatr. Jpn. Overseas Ed. 1992, 34, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, A.; Rafatpanah, H.; Azarpazhooh, A.; Mokhber, N.; Hedayati-Moghaddam, M.R.; Amiri, A.; Hashemi, P.; Foroghipour, M.; Hoseini, R.F.; Bazarbachi, A.; et al. Clinical features of HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) in northeast Iran. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2013, 113, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, G.A.; Yoshikawa, G.T.; Koyama, R.V.; Fujihara, S.; Martins, L.C.; Medeiros, R.; Quaresma, J.A.; Fuzii, H.T. Neurological manifestations in individuals with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis in the Amazon. Spinal Cord 2016, 54, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, M.; de Almeida Scaldaferri, G.B.; Barbosa Dos Santos, J.I.; Melo, A.; da Silva Ribeiro, N.M. Spasticity distribution and severity in individuals with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. J. Neurovirol. 2021, 27, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimura, K.; Arimura, Y.; Moritoyo, H.; Tokimura, Y.; Takenaga, S.; Sonoda, Y.; Yamanaka, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Izumo, S.; Osame, M. How helpful is thoracic paraspinal EMG in HAM/TSP? Muscle Nerve 1995, 18, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osame, M. Review of WHO Kagoshima meeting and diagnostic guidelines for HAM/TSP. In Human Retrovirology: HTLV; Blattner, W.A., Ed.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Nozuma, S.; Matsuura, E.; Matsuzaki, T.; Watanabe, O.; Kubota, R.; Izumo, S.; Takashima, H. Familial clusters of HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thijs, R.D.; Notermans, N.C.; Wokke, J.H.; van der Graaf, Y.; van Gijn, J. Distribution of muscle weakness of central and peripheral origin. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 65, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, O.S.; Rodgers-Johnson, P.; Mora, C.; Char, G. HTLV-1 and polymyositis in Jamaica. Lancet 1989, 2, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inose, M.; Higuchi, I.; Yoshimine, K.; Suehara, M.; Izumo, S.; Arimura, K.; Osame, M. Pathological changes in skeletal muscle in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 1992, 110, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbai, A.A.; Wiley, C.A.; Oliveira, A.S.; Smith, R.; Schmidt, B.; Nobrega, J.A.; Bordin, J.O.; Roman, G.C. Skeletal muscle involvement in tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-1-associated myelopathy. Muscle Nerve 1994, 17, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, D.T.; Morgan, O.; Smikle, M.F.; Simeon, D.; Barton, E.N. HTLV-1 associated polymyositis in Jamaica. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2001, 104, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, H.M.; Higuchi, I.; Kubota, R.; Matsuura, E.; Hashiguchi, A.; Abdelbary, N.H.; Inamori, Y.; Takashima, H.; Izumo, S. Histopathological differences between human T-lymphotropic virus type 1-positive and human T-lymphotropic virus type 1-negative polymyositis. Clin. Exp. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 2, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozden, S.; Gessain, A.; Gout, O.; Mikol, J. Sporadic inclusion body myositis in a patient with human T cell leukemia virus type 1-associated myelopathy. Clin. Infect Dis. 2001, 32, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, E.; Umehara, F.; Nose, H.; Higuchi, I.; Matsuoka, E.; Izumi, K.; Kubota, R.; Saito, M.; Izumo, S.; Arimura, K.; et al. Inclusion body myositis associated with human T-lymphotropic virus-type I infection: Eleven patients from an endemic area in Japan. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzoi, A.C.; Araújo, A.Q. Disability and determinants of gait performance in tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP). Spinal Cord 2007, 45, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, N.; Kudo, Y.; Nakagawa, M. Efficacy of Rehabilitation for patients with HAM (HTLV-1 associated myelopathy). Jpn. J. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 47, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamano, T.; Fujiyama, J.; Kawamura, Y.; Hirayama, M.; Ito, K.; Inagaki, T.; Kumano, T.; Mutoh, T.; Kuriyama, M. Muscle MRI findings of HTLV-1-associated myelopathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 199, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüle, R.; Wiethoff, S.; Martus, P.; Karle, K.N.; Otto, S.; Klebe, S.; Klimpe, S.; Gallenmüller, C.; Kurzwelly, D.; Henkel, D.; et al. Hereditary spastic paraplegia: Clinicogenetic lessons from 608 patients. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsuta, N.; Watanabe, H.; Ito, M.; Banno, H.; Suzuki, K.; Katsuno, M.; Tanaka, F.; Tamakoshi, A.; Sobue, G. Natural history of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA): A study of 223 Japanese patients. Brain 2006, 129, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisaki, N.; Suwazono, S.; Suehara, M.; Nakachi, R.; Kido, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Oshiro, S.; Tokashiki, T.; Takashima, H.; Nakagawa, M. The natural history of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with proximal dominant involvement (HMSN-P) in 97 Japanese patients. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2018, 7, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, I.R.; Franzoi, A.C.; Araújo, A.Q. Low-back pain in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: Nociceptive or neuropathic? Spinal Cord 2010, 48, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, E.; Yoshimura, A.; Nozuma, S.; Higuchi, I.; Kubota, R.; Takashima, H. Clinical presentation of axial myopathy in two siblings with HTLV-1 associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| a. Patient Characteristics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, Years | 61.4 (14–83) | |||
| Sex, male/female | 30/71 | |||
| Age at disease onset, years | 50.4 (13–76) | |||
| Duration of disease, years | 10.9 (0.3–49) | |||
| Rapid progression | 23 (23%) | |||
| Data are presented as average (range), n, or n (%). | ||||
| b. Muscles susceptible to injury from HAM/TSP (%) | ||||
| Patients presenting with no muscle weakness but with spastic gait: 3/101 patients (3.0%) | ||||
| Manual muscle testing | Name of muscles | Segment level in spinal cord | Average MRC score (0–5) | Percentage of impairment (%) |
| Knee flexion | Hamstrings | L5S1 | 3.50 | 91.2 |
| Hip flexion | Iliopsoas | L3L4 | 3.46 | 91.1 |
| Hip abduction | Gluteus medius + | L5S1 | 3.74 | 73.2 |
| Knee extension | Quadriceps | L3L4 | 4.11 | 63.3 |
| Hip extension | Gluteus maximus | L5S1 | 3.92 | 63.2 |
| Ankle dorsiflexion | Tibialis anterior | L5 | 4.06 | 59.0 |
| Hip adduction | Leg adductors | L234 | 4.13 | 57.1 |
| Ankle plantar flexion | Gastrocnemius + | S1 | 4.32 | 47.4 |
| Neck flexion | Neck flexors | C1-5 | 4.74 | 28.4 |
| Shoulder abduction | Deltoid | C5 | 4.76 | 26.0 |
| Shoulder adduction | Pectoralis major | C5-Th1 | 4.78 | 23.5 |
| Elbow flexion | Biceps brachii | C5 | 4.83 | 22.8 |
| Elbow extension | Triceps brachii | C7 | 4.83 | 21.6 |
| Wrist flexion | Wrist flexors | C7-8 | 4.84 | 21.4 |
| Wrist extension | Wrist extensors | C678 | 4.86 | 18.6 |
| Neck extension | Neck extensors | C1-8 | 4.90 | 13.2 |
| c. Affected part of the body (%) | ||||
| Neck | Upper extremities | Lower extremities | ||
| U.E. Prox. | U.E. Dist. | L.E. Prox. | L.E. Dist. | |
| 28.4% (27/95) | 43.6% (44/101) | 96.0% (97/101) | ||
| 40.6% (41/101) | 22.4% (22/98) | 95.0% (96/101) | 62.0% (62/100) | |
| Neck only | U.E.Prox. only | U.E.Dist. Only | L.E.Prox. Only | L.E.Dost. Only |
| 0 | 1.0% (1/101) | 0 | 15.8% (16/101) | 1% (1/100) |
| Manual Muscle Testing | Name of Muscles | Segment Level in Spinal Cord | Average of MRC Score (0–5) | Percentage of Impairment (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip flexion | Iliopsoas | L3L4 | 2.08 | 100.0 |
| Knee flexion | Hamstrings | L5S1 | 2.55 | 100.0 |
| Hip abduction | Gluteus medius + | L5S1 | 2.61 | 100.0 |
| Hip extension | Gluteus maximus | L5S1 | 3.03 | 93.3 |
| Hip adduction | Leg adductors | L234 | 3.16 | 86.4 |
| Knee extension | Quadriceps | L34 | 3.28 | 87.5 |
| Ankle dorsiflexion | Tibialis anterior | L5 | 3.55 | 75.8 |
| Ankle plantar flexion | Gastrocnemius + | S1 | 4.00 | 63.6 |
| Neck flexion | Neck flexors | C1-5 | 4.55 | 51.6 |
| Shoulder abduction | Deltoid | C5 | 4.59 | 43.8 |
| Shoulder adduction | Pectoralis major | C5-Th1 | 4.65 | 39.1 |
| Wrist extension | Wrist extensors | C678 | 4.69 | 34.4 |
| Elbow flexion | Biceps brachii | C5 | 4.70 | 33.3 |
| Elbow extension | Triceps brachii | C7 | 4.74 | 33.3 |
| Wrist flexion | Wrist flexors | C78 | 4.76 | 33.3 |
| Neck extension | Neck extensors | C1-8 | 4.79 | 32.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsuura, E.; Nozuma, S.; Dozono, M.; Kodama, D.; Tanaka, M.; Kubota, R.; Takashima, H. Iliopsoas Muscle Weakness as a Key Diagnostic Marker in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis (HAM/TSP). Pathogens 2023, 12, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12040592
Matsuura E, Nozuma S, Dozono M, Kodama D, Tanaka M, Kubota R, Takashima H. Iliopsoas Muscle Weakness as a Key Diagnostic Marker in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis (HAM/TSP). Pathogens. 2023; 12(4):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12040592
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsuura, Eiji, Satoshi Nozuma, Mika Dozono, Daisuke Kodama, Masakazu Tanaka, Ryuji Kubota, and Hiroshi Takashima. 2023. "Iliopsoas Muscle Weakness as a Key Diagnostic Marker in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis (HAM/TSP)" Pathogens 12, no. 4: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12040592
APA StyleMatsuura, E., Nozuma, S., Dozono, M., Kodama, D., Tanaka, M., Kubota, R., & Takashima, H. (2023). Iliopsoas Muscle Weakness as a Key Diagnostic Marker in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis (HAM/TSP). Pathogens, 12(4), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12040592





