Pathogenic Biofilm Removal Potential of Wild-Type Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbial Strains
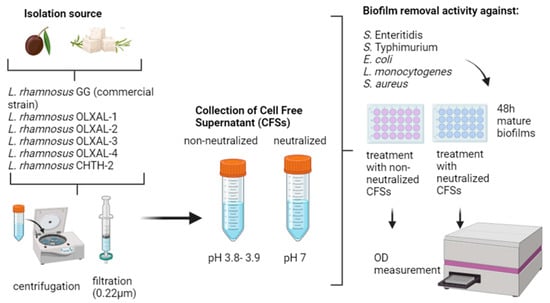
2.2. Preparation of LAB CFS (Cell-Free Supernatants)
2.3. Biofilm Removal Activity
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šušković, J.; Kos, B.; Beganović, J.; Pavunc, A.; Habjanič, K.; Matošić, S. Antimicrobial Activity—The Most Important Property of Probiotic and Starter Lactic Acid Bacteria. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 296–307. [Google Scholar]
- Júnior, W.; Ferrari, Í.; Viana de Souza, J.; Silva, C.; Costa, M.; Dias, F. Characterization and Evaluation of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Goat Milk. Food Control 2015, 53, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero-Sariñena, S.; Barlow, J.; Costabile, A.; Gibson, G.R.; Rowland, I. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of a Range of Probiotics against Pathogens: Evidence for the Effects of Organic Acids. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Ouali, F.; Al Kassaa, I.; Cudennec, B.; Abdallah, M.; Bendali, F.; Sadoun, D.; Chihib, N.-E.; Drider, D. Identification of Lactobacilli with Inhibitory Effect on Biofilm Formation by Pathogenic Bacteria on Stainless Steel Surfaces. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 191, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminnezhad, S.; Kasra-Kermanshahi, R. Antibiofilm Activity of Cell-Free Supernatant from Lactobacillus Casei in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Feyz 2014, 81, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Khiralla, G.M.; Mohamed, E.A.H.; Farag, A.G.; Elhariry, H. Antibiofilm Effect of Lactobacillus pentosus and Lactobacillus plantarum Cell-Free Supernatants against Some Bacterial Pathogens. J. Biotech. Res. 2015, 6, 86–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgasem, B.Y.; Lani, M.N.; Hassan, Z.; Wan Yusoff, W.M.; Fnaish, S.G. Antifungal Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains Isolated from Natural Honey against Pathogenic Candida Species. Mycobiology 2016, 44, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Stitt, G.; Son, L.; Enioutina, E.Y. Probiotics and Their Bioproducts: A Promising Approach for Targeting Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.-G.; Li, X.-D.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Li, X.; Liu, W.-X.; Lin, L.-B.; Wang, F. Isolation, Antibacterial Characterization, and ATF-Based Preparation of Viable Cells of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei XLK 401 and Its Potential Application in Milk Preservation. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Qin, G. New Strategies for Biocontrol of Bacterial Toxins and Virulence: Focusing on Quorum-Sensing Interference and Biofilm Inhibition. Toxins 2023, 15, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanafari, A.; Porgham, S.H. Investigation of Probiotic Chocolate Effect on Streptococcus Mutans Growth Inhibition. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2012, 5, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R.M. Biofilms: Microbial Life on Surfaces. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegari, A.; Kheyrolahzadeh, K.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S.M.; Sharifi, S.; Memar, M.Y.; Zununi Vahed, S. The Battle of Probiotics and Their Derivatives Against Biofilms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srey, S.; Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.-D. Biofilm Formation in Food Industries: A Food Safety Concern. Food Control 2013, 31, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhu, X. Biofilm Formation and Food Safety in Food Industries. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelios, G.; Santarmaki, V.; Pavlatou, C.; Dimitrellou, D.; Kourkoutas, Y. New Wild-Type Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strains as Candidates to Manage Type 1 Diabetes. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeer, S.; De Keersmaecker, S.C.J.; Verhoeven, T.L.A.; Fadda, A.A.; Marchal, K.; Vanderleyden, J. Functional Analysis of luxS in the Probiotic Strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Reveals a Central Metabolic Role Important for Growth and Biofilm Formation. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohestani, M.; Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Badali, A. Effects of Cell-Free Supernatant of Lactobacillus acidophilus LA5 and Lactobacillus casei 431 against Planktonic Form and Biofilm of Staphylococcus aureus. Vet. Res. Forum 2018, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Calderón, M.C.; Hernández-González, L.; Gómez-Navia, C.; Blanco-Blanco, M.T.; Sánchez-Silos, R.; Lucio, L.; Pérez-Giraldo, C. Antifungal and Anti-Biofilm Activity of a New Spanish Extract of Propolis against Candida Glabrata. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Ladero, M.A.; Blanco-Blanco, M.T.; Hurtado, C.; Pérez-Giraldo, C.; Blanco, M.T.; Gómez-García, A.C. Determination of Biofilm Production by Candida Tropicalis Isolated from Hospitalized Patients and Its Relation to Cellular Surface Hydrophobicity, Plastic Adherence and Filamentation Ability. Yeast 2013, 30, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Slama, R.; Kouidhi, B.; Zmantar, T.; Chaieb, K.; Bakhrouf, A. Anti-listerial and Anti-biofilm Activities of Potential Probiotic Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Tunisian Traditional Fermented Food. J. Food Saf. 2013, 33, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelyuntha, W.; Chaiyasut, C.; Kantachote, D.; Sirilun, S. Cell-Free Supernatants from Cultures of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Grape as Biocontrol against Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Typhimurium Virulence via Autoinducer-2 and Biofilm Interference. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divyashree, S.; Anjali, P.G.; Somashekaraiah, R.; Sreenivasa, M.Y. Probiotic Properties of Lactobacillus casei-MYSRD 108 and Lactobacillus plantarum-MYSRD 71 with Potential Antimicrobial Activity against Salmonella paratyphi. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 32, e00672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazehabadi, M.H.; Algburi, A.; Popov, I.V.; Ermakov, A.M.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Weeks, R.; Chikindas, M.L. Probiotic Bacilli Inhibit Salmonella Biofilm Formation Without Killing Planktonic Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 615328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, A.G.; Esaam, A.; Hazaa, M.M. Cell Free Preparations of Probiotics Exerted Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities against Multidrug Resistant E. coli. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apiwatsiri, P.; Pupa, P.; Yindee, J.; Niyomtham, W.; Sirichokchatchawan, W.; Lugsomya, K.; Shah, A.A.; Prapasarakul, N. Anticonjugation and Antibiofilm Evaluation of Probiotic Strains Lactobacillus plantarum 22F, 25F, and Pediococcus acidilactici 72N Against Escherichia Coli Harboring Mcr-1 Gene. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 614439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Fang, K.; Medina, D.; Wan, J.; Lee, J.; Hong, S.H. The probiotic, Leuconostoc mesenteroides, inhibits Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, M.E. Bacteriocins Produced by Leuconostoc Species. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Mardani, K.; Tajik, H. Characterization and Application of Postbiotics of Lactobacillus Spp. on Listeria Monocytogenes in Vitro and in Food Models. LWT 2019, 111, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahasneh, A.M.; Hamdan, S.; Mahasneh, S.A. Probiotic Properties of Lactobacillus Species Isolated from Local Traditional Fermented Products. JJBS 2015, 8, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Isolate Code | Bacterial Species | Source of Isolation |
|---|---|---|
| GG (ATCC 53103) | Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus | Human intestines |
| OLXAL-1 | Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus | Olive (fruit) |
| OLXAL-2 | Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus | Olive (fruit) |
| OLXAL-3 | Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus | Olive (fruit) |
| OLXAL-4 | Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus | Olive (fruit) |
| CHTH-2 | Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus | Feta-type cheese |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitropoulou, G.; Kompoura, V.; Nelios, G.; Kourkoutas, Y. Pathogenic Biofilm Removal Potential of Wild-Type Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strains. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121449
Mitropoulou G, Kompoura V, Nelios G, Kourkoutas Y. Pathogenic Biofilm Removal Potential of Wild-Type Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strains. Pathogens. 2023; 12(12):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121449
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitropoulou, Gregoria, Vasiliki Kompoura, Grigorios Nelios, and Yiannis Kourkoutas. 2023. "Pathogenic Biofilm Removal Potential of Wild-Type Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strains" Pathogens 12, no. 12: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121449
APA StyleMitropoulou, G., Kompoura, V., Nelios, G., & Kourkoutas, Y. (2023). Pathogenic Biofilm Removal Potential of Wild-Type Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strains. Pathogens, 12(12), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121449