Recent Developments in Lateral Flow Assays for Salmonella Detection in Food Products: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Salmonella
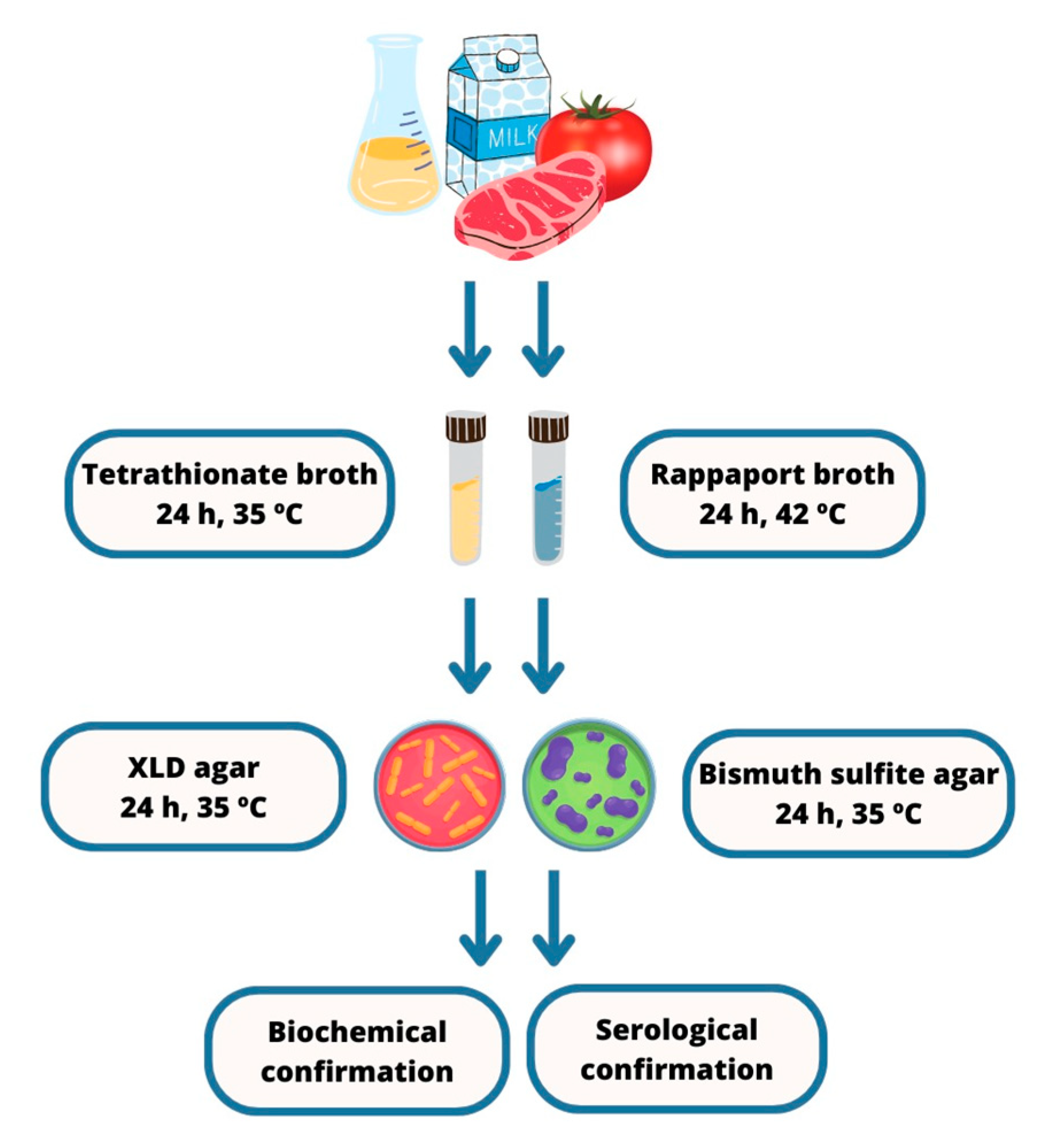
3. Salmonella Detection Methods
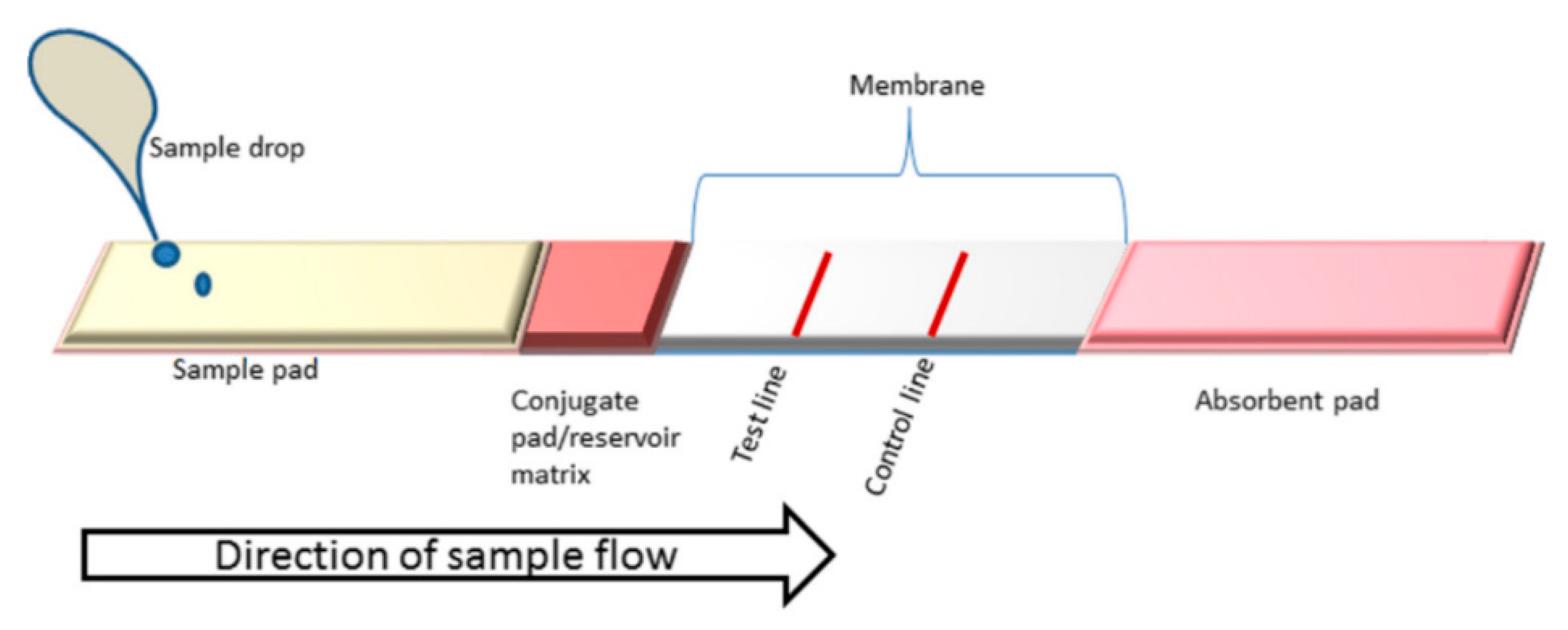
4. Lateral Flow Assays (LFAs)
4.1. Bioreceptors
4.2. Labels
4.2.1. Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs)
4.2.2. Magnetic Nanoparticle (MNPs)
4.2.3. Quantum Dots (QDs)
5. Future Prospects of LFA as a Method for Salmonella Detection
6. Challenges Related to LFAs in Salmonella Detection
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). World Health Statistics 2018: Monitoring Health for the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, L.; Wu, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Kan, B.; Klena, J.D.; Lo Fo Wong, D.M.A.; Angulo, F.J.; et al. Laboratory-Based Surveillance of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Infections in China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiken, T.; Leighton, F.A.; Fouchier, R.A.; LeDuc, J.W.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Schudel, A. Pathogen surveillance in animals. Science 2005, 309, 1680–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwat, A.A. Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Listeria monocytogenes 376 and Salmonella strains by real-time PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 84, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, C.; Cerqueira, L.; Azevedo, N.F.; Vieira, M.J. Detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis using real time PCR, immunocapture assay, PNA FISH and standard culture methods in different types of food samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 161, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagkli, D.M.; Weber, T.P.; Van den Bulcke, M.; Folloni, S.; Tozzoli, R.; Morabito, S. Application of the modular approach to an in-house validation study of real-time PCR methods for the detection and serogroup determination of verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6954–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Kubota, J.; Fujihara, K.; Honjoh, K.; Lio, M. Simultaneous Enrichment of Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli O157: H7, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, and Listeria monocytogenes by Single Broth and Screening of the Pathogens by Multiplex Real-time PCR. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2009, 15, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. Dual FITC lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 15, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Huang, H.; Zhu, P. Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick for equipment-free detection of Salmonella in shellfish. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Song, S. Identification and quantification of eight Listeria monocytogene serotypes from Listeria spp. using a gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow assay. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, L.; Xing, K.; Lu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lai, W.; Chen, T. Nanozyme-based lateral flow assay for the sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 5770–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasbasi, B.; Guner, B.; Sudagidan, M.; Ucak, S.; Kavruk, M.; Ozalp Veli, C. Label-free lateral flow assay for Listeria monocytogenes by aptamer-gated release of signal molecules. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 587, 113449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Mohamed, M.; Zagorovsky, K.; Chan, W. State of diagnosing infectious pathogens using colloidal nanomaterials. Biomaterials 2017, 146, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad Nor, N.; Abdul Razak, K.; Tan, S.C.; Noordin, R. Properties of surface functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles (ferrofluid) conjugated antibody for lateral flow immunoassay application. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 538, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Roggentin, P.; Mikoleit, M.; Guibourdenche, M.; de Pinna, E.; Nair, S.; Fields, P.I.; Weill, F.-X. Supplement 2008–2010 (no. 48) to the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health. Technical Manual of Laboratory Diagnosis of Salmonella spp.; Ministry of Health: Brasilia, Brazil, 2011; p. 64.
- Hirsh, D.C. Salmonella. In Veterinary Microbiology; Hirsh, D.C., Zee, Y.C., Eds.; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012; pp. 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, N.K.S.; de Barros, V.B.; Jimenez, S.M.C.; Machado, E.D.L.; Dutra, R.A.F.; de Lima Filho, J.L. Salmonella spp., an important pathogenic agent transmitted in food. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2008, 13, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jasim, I.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, L.; Dweik, M.; Zhang, S.; Almasri, M. A microfluidic based biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella in food products. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 6579:2002; International Standard. Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella. Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Yang, X.; Bai, X.N.; Yang, J.Y.J.; Xu, F.; Xu, H.Y. Magnetic nano-beads based separation combined with propidium monoazide treatment and multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of viable Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Listeria monocytogenes in food products. Food Microbiol. 2013, 34, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.F.D.; Magalhães, J.M.C.S.; Freire, C.; Delerue-Matos, C. Electrochemical biosensors for Salmonella: State of the art and challenges in food safety assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, B.D.G.M. Métodos alternativos de análise microbiológica de alimentos: Uma revisão. Bol. Da SBCTA 1999, 33, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, A.M.A.; de Fatima Borges, M.; Ferro Furtado, R.; Alves, C.R.; Teixeira de Figueiredo, E.A. Métodos Alternativos para Detecção de Salmonella em Alimentos; Embrapa Agroindústria Tropical: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2018; Available online: https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/item/189768/1/DOC18005.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Blivet, D.; Soumet, C.; Ermel, G.; Colin, P. Rapid detection methods for pathogens. In Proceedings of the 3rd Karlsruhe Nutrition Symposium European Research towards Safer and Better Food, Review and Transfer, Karlsruhe, Germany, 18–20 October 1998; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Di Febo, T.; Schirone, M.; Visciano, P.; Portanti, O.; Armillotta, G.; Persiani, T.; Di Giannatale, E.; Tittarelli, M.; Luciani, M. Development of a capture ELISA for rapid detection of Salmonella enterica in food samples. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-O.; Kim, S.-S. Bacterial pathogen detection by conventional culture-based and recent alternative (polymerase chain reaction, isothermal amplification, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, bacteriophage amplification, and gold nanoparticle aggregation) methods in food samples: A review. J. Food Saf. 2021, 41, e12870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Olson, N.A.; You, W.; Haugland, R.P. A sensitive competitive ELISA for 2, 4-dinitrophenol using 3, 6-fluorescein diphosphate as a fluorogenic substrate. J. Immunol. Methods 1992, 149, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sue, M.J.; Yeap, S.K.; Omar, A.R.; Tan, S.W. Application of PCR-ELISA in Molecular Diagnosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 653014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Huang, Z.; Wu, W.; Liu, M.; Huang, K.; Yang, Y.; Deng, H.; Xia, X.; Chen, W. Versatile High-Performance Electrochemiluminescence ELISA Platform Based on a Gold Nanocluster Probe. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 24812–24819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Rica, R.; Stevens, M.M. Plasmonic ELISA for the ultrasensitive detection of disease biomarkers with the naked eye. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.-H.; Irudayaraj, J. In-situ immuno-gold nanoparticle network ELISA biosensors for pathogen detection. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 164, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chunglok, W.; Wuragil, D.K.; Oaew, S.; Somasundrum, M.; Surareungchai, W. Immunoassay based on carbon nanotubesenhanced ELISA for Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3584–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, J.; Yuk, H.-G.; Guo, L. Immuno-and nucleic acid-based current technique for Salmonella detection in food. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, M.-G. Advancements in DNA-assisted Immunosensors. BioChip J. 2020, 14, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenollar, F.; Raoult, D. Molecular genetic methods for the diagnosis of fastidious microorganisms. APMIS 2004, 112, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamin, O.; Kuuranne, T.; Saugy, M.; Leuenberger, N. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) as an alternative to PCR: A rapid on-site detection of gene doping. Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 9, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, J.; Yu, S.; Yu, D.; Huang, Y. Establishment of a duplex real-time qPCR method for detection of Salmonella spp. and Serratia fonticola in fishmeal. AMB Express 2020, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossu, A.; Levin, R.E. Rapid conventional PCR and real-time-qPCR detection of low numbers of Salmonella enterica from ground beef without enrichment. Food Biotechnol. 2014, 28, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zou, D.; Dong, D.; Yang, Z.; Ao, D.; Liu, W.; Huang, L. Development of a multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella spp. and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.P.; Chen, S.H.; Levin, R.E. Application of ethidium bromide monoazide for quantification of viable and dead cells of Salmonella enterica by real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 117, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hønsvall, B.K.; Robertson, L.J. From research lab to standard environmental analysis tool: Will NASBA make the leap? Water Res. 2017, 109, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakruddin, M.D.; Mazumdar, R.M.; Chowdhury, A.; Mannan, K.S.B. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA)-prospects and applications. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2012, 2, 106–121. [Google Scholar]
- Mollasalehi, H.; Yazdanparast, R. An improved non-crosslinking gold nanoprobe-NASBA based on 16S rRNA for rapid discriminative bio-sensing of major salmonellosis pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Yan, Q.; Yang, P.; Li, R. Development of a rapid test method for Salmonella enterica detection based on fluorescence probe-based recombinase polymerase amplification. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Surendran, P.K.; Thampuran, N. Evaluation of culture, ELISA and PCR assays for the detection of Salmonella in seafood. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada-González, D.; Merkoçi, A. Nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xu, H.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y. Membrane-based lateral flow immunochromatographic strip with nanoparticles as reporters for detection: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.M.; Bu, T.; Zhang, M. Metal-polydopamine framework based lateral flow assay for highly sensitive detection of tetracycline in food samples. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, L.; de La Escosura-Muniz, A.; Pons, J.; Merkoci, A. Lateral flow biosensors based on gold nanoparticles. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, 66th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 569–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Climent, E.; Ast, S.; Weller, M.G.; Canning, J.; Rurack, K. Development of a lateral flow test for rapid pyrethroid detection using antibody-gated indicator-releasing hybrid materials. Analyst 2020, 145, 3490–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkinson, J.L.; Stillman, B.A. Nitrocellulose: A tried-and-true polymer finds utility as a post-genomic substrate. Front. Biosci. 2002, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Yang, S. Replacing antibodies with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Sharma, S.; Nara, S. Evaluation of gold nanoparticle based lateral flow assays for diagnosis of enterobacteriaceae members in food and water. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, W.C.; Beni, V.; Turner, A.P. Lateral-flow technology: From visual to instrumental. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Fu, S.; Qin, X.; Chen, Q.; Man, C.; Jiang, Y. An Enhanced Lateral Flow Assay Based on Aptamer–Magnetic Separation and Multifold AuNPs for Ultrasensitive Detection of Salmonella typhimurium in Milk. Foods 2021, 10, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Miao, X.; Mae, T.; Leng, Y.; Hao, L.; Duan, H.; Yuan, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Gold nanobeads with enhanced absorbance for improved sensitivity in competitive lateral flow immunoassays. Foods 2021, 10, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazin, I.; Tria, S.A.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.-L. New biorecognition molecules in biosensors for the detection of toxins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, Y. Biosensors for rapid detection of Salmonella in food: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 149–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, A.L.; Francis, M.B. Impedance-based detection of bacteria. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 700–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukman, Y.M.; Dyana, Z.N.; Rahmah, N.; Khairunisak, A.R. Development and Evaluation of Colloidal Gold Lateral Flow Immunoassays for Detection of Escherichia coli O157 and Salmonella Typhi. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1082, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Kwon, D.; Lee, S.; Jeon, S. Detection of Salmonella bacteria in milk using gold-coated magnetic nanoparticle clusters and lateral flow filters. J. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 48445–48448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Fan, C. Aptamer-based biosensors. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, T.; Yao, X.; Huang, L.; Dou, L.; Zhao, B.; Yang, B.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Dual recognition strategy and magnetic enrichment based lateral flow assay toward Salmonella enteritidis detection. Talanta 2020, 206, 120204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; He, Y.; Fan, E.; Wang, L.; Lu, S.; Fu, Z. Label-free electrochemiluminescent biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa using phage as highly specific recognition agent. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.; Martins, V.C.; Nóbrega, C.; Carvalho, C.M.; Cardoso, F.A.; Cardoso, S.; Azeredo, J. A bacteriophage detection tool for viability assessment of Salmonella cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayan, H.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.W. Recent development in rapid detection techniques for microorganism activities in food matrices using bio-recognition: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templier, V.; Roux, A.; Roupioz, Y.; Livache, T. Ligands for label-free detection of whole bacteria on biosensors: A review. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
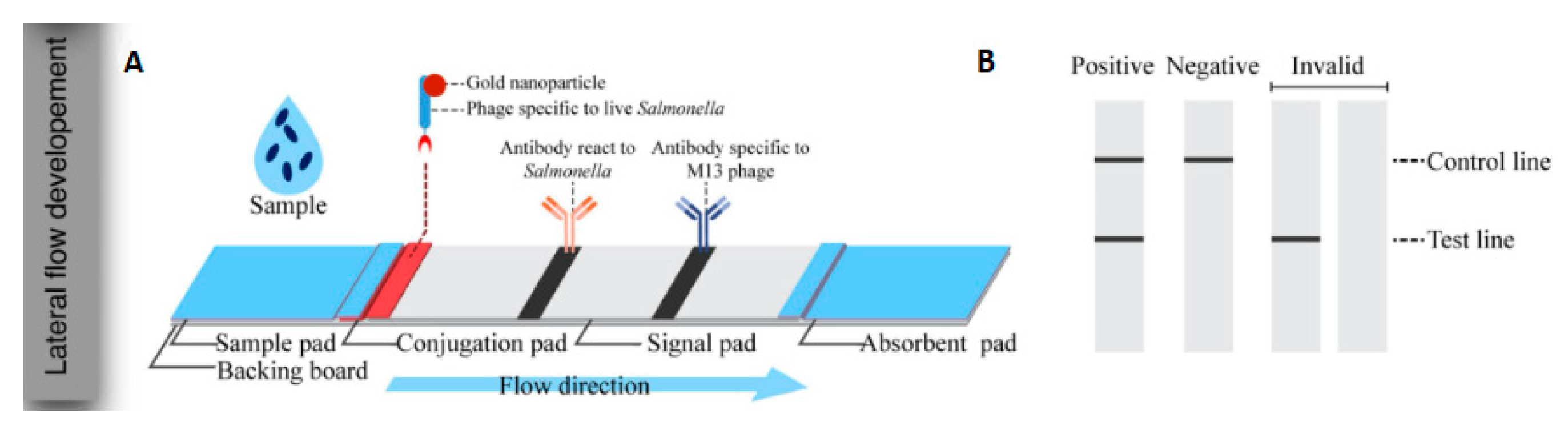
- Charlermroj, R.; Makornwattana, M.; Phuengwas, S.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. A rapid colorimetric lateral flow test strip for detection of live Salmonella enteritidis using whole phage as a specific binder. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1008817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Akhtar, N. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): The quintessential ‘offense and defense’ molecules are more than antimicrobials. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.; Fu, Y.; Lei, C.; Li, Y. Advances in antimicrobial peptides-based biosensing methods for detection of foodborne pathogens: A review. Food Control 2020, 112, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulagina, N.V.; Lassman, M.E.; Ligler, F.S.; Taitt, C.R. Antimicrobial peptides for detection of bacteria in biosensor assays. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6504–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyun, A.; Ahlatcioglu, E.; Ipek, Y.K. Biosensors and Their Principles; Intech Open: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Kawde, A.; Daud, M. Designs, formats and applications of lateral flow assay: A literature review. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2015, 19, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.L.; Coronado, E.; Zhao, L.L.; Schatz, G.C. The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: The influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrica-González, P.; Zamora-Justo, J.A.; Chavez-Sandoval, B.E.; Vázquez-Martínez, G.R.; Balderas-López, J.A. Measurement of the Optical Properties of Gold Colloids by Photoacoustic Spectroscopy. Int. J. Thermophys. 2018, 39, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wu, A.; Xu, L.; Xu, C.; Liu, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, X. Recent progress on lateral flow immunoassays in foodborne pathogen detection. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Fang, S.; Yang, H.; Li, B.; Liu, Q. Development and comparison of immunochromatographic strips with four nanomaterial labels: Colloidal gold, new colloidal gold, multi-branched gold nanoflowers and Luminol-reduced Au nanoparticles for visual detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood. Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Gao, P.; Song, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, T.; Chen, S.; Fu, S.; Qin, X.; Shao, M.; Man, C.; et al. An aptamer-exonuclease III (Exo III)–assisted amplification-based lateral flow assay for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8517–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, T.; Huang, Q.; Yan, L.; Huang, L.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Q.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Ultra-technically-simple and sensitive detection for Salmonella enteritidis by immunochromatographic assay based on gold growth. Food Control 2018, 84, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Xu, C.; Kuang, H. Nanoparticle-based sensors for food contaminants. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ramos, J.V.; Sánchez-Cortés, S. Espectroscopía vibracional sobre nanoestructuras metálicas (SERS y SEIR): Nuevos sustratos y aplicaciones. Opt. Pura Apl. 2006, 39, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
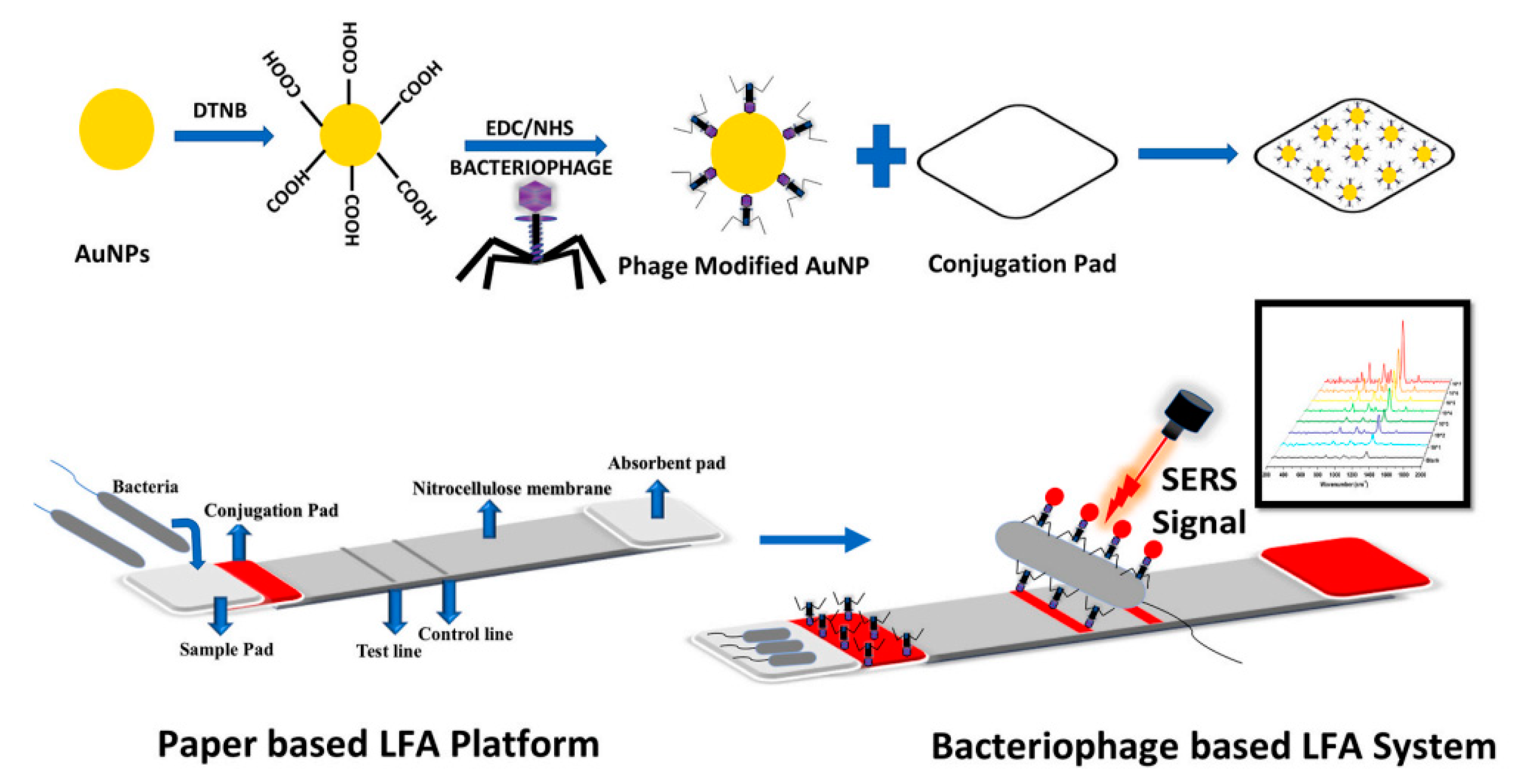
- Ilhan, H.; Tayyarcan, E.K.; Caglayan, M.G.; Boyaci, İ.H.; Saglam, N.; Tamer, U. Replacement of antibodies with bacteriophages in lateral flow assay of Salmonella enteritidis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquina, C.; Teresa, J.M.; Cardoso, F.A.; Saurel, D.; Cardoso, S.; Freitas, P.P.; Ibarra, M.R. GMR sensors and magnetic nanoparticles for Immuno-chromatographic assays. J. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3495–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.S.; Rutka, J.T.; Chan, W.C.W. Nanomedicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2434–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Zi, M.; Zeng, J. Colorimetric and photothermal dual-mode lateral flow immunoassay based on Au-Fe3O4 multifunctional nanoparticles for detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Huang, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, G.; Wang, S.; Chen, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, D.; Liu, C.; Lai, W. Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella enteritidis by a pre-concentrated immunochromatographic assay in a large-volume sample system. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 55141–55147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Tang, M.; Wu, L.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, D. Colorimetric-fluorescent-magnetic nanosphere-based multimodal assay platform for Salmonella detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kairdolf, B.A.; Smith, A.M.; Stokes, T.H.; Wang, M.D.; Young, A.N.; Nie, S. Semiconductor quantum dots for bioimaging and biodiagnostic applications. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 6, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Hildebrandt, N. Semiconductor quantum dots for in vitro diagnostics and cellular imaging. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.C.; Maxwell, D.J.; Gao, X.; Bailey, R.E.; Han, M.; Nie, S. Luminescent quantum dots for multiplexed biological detection and imaging. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso Dos Santos, M.; Algar, W.R.; Medintz, I.L.; Hildebrandt, N. Quantum Dots for Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET). TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 125, 115819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhang, H.; Qin, L.; Zhang, S.; Cao, J.; Jiang, H. Magnetic Fluorescent Quantum Dots Nanocomposites in Food Contaminants Analysis: Current Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Wu, W. Quantum Dot Biosensor Combined with Antibody and Aptamer for Tracing Food-Borne Pathogens. Food Qual. Saf. 2021, 5, fyab019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Cai, S.; Ye, Q.; Wu, Q.; Shao, Y.; Qu, X.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, B.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M.; et al. Quantum dot nanobeads-labelled lateral flow immunoassay strip for rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on strand displacement loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Engineering 2022, 19, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Tang, F.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Liu, C. Rapid screening and quantitative detection of Salmonella using a quantum dot nanobead-based biosensor. Analyst 2020, 145, 2184–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-M.; Runyon, M.; Hermann, T.J.; Phillips, R.; Hsieh, J. Review of Salmonella detection and identification methods: Aspects of rapid emergency response and food safety. Food Control 2015, 47, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Kim, K.E.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. An Improved Particle Filter with a Novel Hybrid Proposal Distribution for Quantitative Analysis of Gold Immunochromatographic Strips. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2019, 18, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, G.B.L.; Campos, F.V.; Guimarães, M.C.C.; Oliveira, J.P. Recent Developments in Lateral Flow Assays for Salmonella Detection in Food Products: A Review. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121441
Silva GBL, Campos FV, Guimarães MCC, Oliveira JP. Recent Developments in Lateral Flow Assays for Salmonella Detection in Food Products: A Review. Pathogens. 2023; 12(12):1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121441
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Gabrielle B. L., Fabiana V. Campos, Marco C. C. Guimarães, and Jairo P. Oliveira. 2023. "Recent Developments in Lateral Flow Assays for Salmonella Detection in Food Products: A Review" Pathogens 12, no. 12: 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121441
APA StyleSilva, G. B. L., Campos, F. V., Guimarães, M. C. C., & Oliveira, J. P. (2023). Recent Developments in Lateral Flow Assays for Salmonella Detection in Food Products: A Review. Pathogens, 12(12), 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121441






