Extrapulmonary and Drug-Resistant Childhood Tuberculosis: Unveiling the Disease to Adopt the Optimal Treatment Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definitions
2.2. Study Design and Population
2.3. Laboratory and Microbiological Investigations
2.4. Treatment
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Clinical Characteristics
3.3. Diagnosis
- Gastric aspirate: collected in 182 cases (67.16%) and associated with positive results in 81 cases (81/182, 44.50%).
- Stool: collected in 81 cases (29.89%) and associated with positive results in 17 cases (17/81, 20.99%).
- Sputum: collected in 70 cases (25.83%) and associated with positive results in 32 cases (32/70, 45.71%).
- Biopsy: collected in 11 cases (4.06%) and associated with positive results in 9 cases (9/11, 81.82%).
- Broncho-alveolar lavage fluid: collected in 11 cases (4.06%) and associated with positive results in 5 cases (5/11, 45.45%).
- Cerebrospinal fluid: collected in 9 cases (3.32%) and associated with positive results in 1 case (1/9, 11.11%).
- Pleural fluid: collected in 7 cases (2.58%) and associated with positive results in 1 case (1/7, 14.29%).
3.4. Treatment
3.5. Outcome
3.6. Factors Associated with Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
3.7. Factors Associated with Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
3.8. Factors Associated with Use of Second-Line Drugs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Characteristics of Children in the Study | Children with PTB 1 N = 227 (%) | Children with EPTB 2 N = 44 (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 115 (50.66) | 27 (61.36) | 0.256 |
| Female | 112 (49.34) | 17 (38.64) | |
| [0–1) years | 5 (2.20) | 1 (1.72) | 1.000 |
| [1–3) years | 23 (10.13) | 6 (13.64) | 0.673 |
| [3–5) years | 69 (30.40) | 14 (31.82) | 0.993 |
| [5–13) years | 91 (40.09) | 14 (31.82) | 0.389 |
| ≥13 years | 39 (17.18) | 10 (22.73) | 0.509 |
| Born in Italy to Italian Parents | 54 (23.79) | 9 (20.45) | 0.776 |
| Born in Italy to Foreign Parents | 84 (37.00) | 14 (31.82) | 0.628 |
| Born Abroad | 89 (39.21) | 21 (47.73) | 0.376 |
| Diagnosis after Contact with a Case | 138 (60.79) | 6 (13.64) | <0.001 |
| Diagnosis during Screening 3 | 23 (10.13) | 2 (4.55) | 0.393 |
| Diagnosis in Children with Symptoms | 63 (27.75) | 36 (81.82) | <0.001 |
| Unknown | 3 (1.32) | 0 (0.00) | - |
| BCG 4 Vaccinated | 36 (15.86) | 7 (15.91) | 0.828 |
| Not BCG Vaccinated | 191 (84.14) | 37 (84.09) | |
| Positive TST 5/QuantiFERON | 209 (92.07) | 40 (90.91) | 0.479 |
| Negative TST/QuantiFERON | 14 (6.17) | 1 (2.27) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 4 (1.76) | 3 (6.82) | - |
| Microbiologically 6 Confirmed | 98 (43.17) | 25 (56.82) | 0.084 |
| Not Microbiologically Confirmed | 90 (39.65) | 11 (25.00) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 39 (17.18) | 8 (18.18) | - |
| Positive PCR 7 | 58 (25.55) | 19 (43.18) | 0.015 |
| Negative PCR | 128 (56.39) | 16 (36.36) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 41 (18.06) | 9 (20.45) | - |
| Positive Microscopy | 28 (12.33) | 8 (18.18) | 0.412 |
| Negative Microscopy | 158 (69.60) | 28 (63.64) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 41 (18.06) | 8 (18.18) | - |
| Positive Culture | 84 (37.00) | 22 (50.00) | 0.104 |
| Negative Culture | 104 (45.81) | 14 (31.82) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 39 (17.18) | 8 (18.18) | - |
| Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis | 6 (2.64) | 3 (6.82) | 0.165 |
| Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis | 42 (18.51) | 16 (36.36) | 0.015 |
| Unknown Drug-Susceptibility Pattern | 179 (78.85) | 25 (56.82) | 0.003 |
| Treated with First-Line Drugs | 182 (80.18) | 22 (50.00) | <0.001 |
| Treated with Second-Line Drugs | 33 (14.54) | 20 (45.45) | |
| Unknown Therapy | 12 (5.28) | 2 (4.55) | - |
| Children Cured | 224 (98.68) | 43 (97.72) | 0.510 |
| Children with Sequelae | 3 (1.32) | 1 (2.28) |
| Characteristics of Children in the Study | Drug-Resistant TB 1 Cases n = 9 (%) | Drug-Susceptible TB Cases n = 58 (%) | Children without DST 2 Results n = 204 (%) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 3 (33.33) | 38 (65.52) | 101 (49.51) | 0.317 |
| Female | 6 (66.67) | 20 (34.48) | 103 (50.49) | |
| [0–1) years | 0 (0.00) | 1 (1.72) | 4 (1.96) | 1.000 |
| [1–3) years | 1 (11.11) | 8 (13.79) | 20 (9.80) | 1.000 |
| [3–5) years | 2 (22.22) | 16 (27.59) | 65 (31.86) | 0.726 |
| [5–13) years | 4 (44.44) | 20 (34.68) | 81 (39.71) | 0.738 |
| ≥13 years | 2 (22.22) | 13 (22.41) | 34 (16.67) | 0.668 |
| Born in Italy to Italian Parents | 1 (11.11) | 14 (24.14) | 48 (23.53) | 0.690 |
| Born in Italy to Foreign Parents | 5 (55.56) | 20 (34.48) | 73 (35.78) | 0.289 |
| Born Abroad | 3 (33.33) | 24 (41.38) | 83 (40.69) | 0.743 |
| Diagnosis after Contact with a Case | 5 (55.56) | 27 (46.55) | 112 (54.90) | 1.000 |
| Diagnosis during Screening 3 | 0 (0.00) | 2 (3.45) | 23 (11.27) | 1.000 |
| Diagnosis in Children with Symptoms | 4 (44.44) | 28 (48.28) | 67 (32.84) | 0.730 |
| Unknown | 0 (0.00) | 1 (1.72) | 2 (0.98) | - |
| BCG 4 Vaccinated | 1 (11.11) | 4 (6.90) | 38 (18.63) | 1.000 |
| Not BCG Vaccinated | 8 (88.89) | 54 (93.10) | 166 (81.37) | |
| Pulmonary Tuberculosis | 6 (66.67) | 42 (72.41) | 179 (87.75) | 0.165 |
| Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis 5 | 3 (33.33) | 16 (25.79) | 25 (12.25) | |
| Positive TST 6/QuantiFERON | 9 (100.00) | 54 (93.10) | 186 (91.18) | 1.000 |
| Negative TST/QuantiFERON | 0 (0.00) | 2 (3.45) | 13 (6.37) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 0 (0.00) | 2 (3.45) | 5 (2.45) | - |
| Microbiologically 7 Confirmed | 9 (100.00) | 58 (100.00) | 56 (27.45) | 0.005 |
| Not Microbiologically Confirmed | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 101 (49.51) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 0 (0.00) | 0(0.00) | 47 (23.04) | - |
| Positive PCR | 5 (55.56) | 46 (79.31) | 26 (12.75) | 0.281 |
| Negative PCR | 4 (44.44) | 12 (20.69) | 128 (62.75) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 50 (24.51) | - |
| Positive Microscopy | 2 (22.22) | 17 (29.31) | 17(8.33) | 0.642 |
| Negative Microscopy | 7 (77.78) | 41 (70.69) | 137 (67.16) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 49 (24.02) | - |
| Positive Culture | 9 (100.00) | 48 (82.76) | 49 (24.02) | 0.001 |
| Negative Culture | 0 (0.00) | 10 (17.24) | 108 (52.94) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 47 (23.04) | - |
| Treated with First-Line Drugs | 2 (22.22) | 45 (77.59) | 157 (76.96) | <0.001 |
| Treated with Second-Line Drugs | 7 (77.78) | 13 (22.41) | 33 (16.18) | |
| Unknown Therapy | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 14 (6.86) | - |
| Children Cured | 8 (88.89) | 56 (96.55) | 203 (99.51) | 0.127 |
| Children with Sequelae | 1 (1.11) | 2 (3.45) | 1 (0.49) |
| Origin of Children in the Study | Drug-Resistant TB 1 Cases n = 9 (%) | Drug-Susceptible TB Cases and Children without DST 2 Results n = 262 (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Italy | 0 (0.00) | 63 (23.75) | 0.123 |
| Western Europe | 0 (0.00) | 2 (0.77) | 1.000 |
| Eastern Europe | 1 (11.11) | 47 (18.01) | 1.000 |
| Africa | 1 (11.11) | 71 (27.20) | 0.453 |
| Asia | 4 (44.44) | 41 (15.71) | 0.045 |
| South-Central America | 3 (33.33) | 33 (12.64) | 0.103 |
| Unknown | 0 (0.00) | 5 (1.92) | 1.000 |
| Second-Line Drugs | Drug-Resistant TB 1 n = 9 (%) | Drug-Susceptible TB n = 58 (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amikacin | 5 (55.56) | 9 (15.52) | 0.015 |
| Cycloserine | 6 (66.67) | 2 (3.45) | 0.000 |
| Linezolid | 5 (55.56) | 2 (3.45) | <0.001 |
| Moxifloxacin | 4 (44.44) | 8 (13.79) | 0.047 |
| Levofloxacin | 2 (22.22) | 3 (5.17) | 0.130 |
| Para-aminosalicylic acid | 2 (22.22) | 0 (0.00) | 0.016 |
References
- Daniel, T.M. The history of tuberculosis. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/global-tuberculosis-report-2022 (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Carvalho, A.C.C.; Cardoso, C.A.A.; Martire, T.M.; Migliori, G.B.; Sant’Anna, C.C. Epidemiological aspects, clinical manifestations, and prevention of pediatric tuberculosis from the perspective of the End TB Strategy. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2018, 44, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Operational Handbook on Tuberculosis: Module 5: Management of Tuberculosis in Children and Adolescents. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240046832 (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Dubois, M.M.; Brooks, M.B.; Malik, A.A.; Siddiqui, S.; Ahmed, J.F.; Jaswal, M.; Amanullah, F.; Becerra, M.C.; Hussain, H. Age-specific Clinical Presentation and Risk Factors for Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis Disease in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2022, 41, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, S.E.; Rustage, K.; Nellums, L.B.; van der Werf, M.J.; Noori, T.; Boccia, D.; Friedland, J.S.; Hargreaves, S. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis among migrants in Europe, 1995 to 2017. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1347.e1–1347.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nuzzo, M.; Trentini, A.; Grilli, A.; Massoli, L.; Biagi, E.; Maritati, M.; Contini, C. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis among immigrants in a low-TB burden and high immigrant receiving city of northern Italy. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ayed, H.; Koubaa, M.; Marrakchi, C.; Rekik, K.; Hammami, F.; Smaoui, F.; Ben, H.; Sourour, Y.; Imed, M.; Damak, J.; et al. Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis: Update on the Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies. Int. J. Trop. Dis. 2018, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, G.S.; Starke, J.R. Tuberculosis in Infants and Children. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 541–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, K.J.; Keshavjee, S.; Rich, M.L. Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis and Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a017863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 5: Management of Tuberculosis in Children and Adolescents. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240046764 (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Pyrazinamide. Tuberculosis 2008, 88, 141–144. [CrossRef]
- Ethambutol. Tuberculosis 2008, 88, 102–105. [CrossRef]
- Isoniazid. Tuberculosis 2008, 88, 112–116. [CrossRef]
- Rifampin. Tuberculosis 2008, 88, 151–154. [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Tuberculosis. In Red Book: 2021 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 32nd ed.; Kimberlin, D.W., Barnett, E.D., Lynfield, R., Sawyer, M.H., Eds.; American Academy of Pediatrics: Itasca, IL, USA, 2021; pp. 786–814. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Operational Handbook on Tuberculosis: Module 4: Treatment: Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Treatment. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240006997 (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Rodríguez-Beltrán, É.; López, G.D.; Anzola, J.M.; Rodríguez-Castillo, J.G.; Carazzone, C.; Murcia, M.I. Heterogeneous fitness landscape cues, pknG low expression, and phthiocerol dimycocerosate low production of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATCC25618 rpoB S450L in enriched broth. Tuberculosis 2022, 132, 102156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregonese, F.; Ahuja, S.D.; Akkerman, O.W.; Arakaki-Sanchez, D.; Ayakaka, I.; Baghaei, P.; Bang, D.; Bastos, M.; Benedetti, A.; Bonnet, M.; et al. Comparison of different treatments for isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis: An individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.S.; Khan, F.A.; Milstein, M.B.; Tolman, A.W.; Benedetti, A.; Starke, J.R.; Becerra, M.C. Treatment outcomes of childhood tuberculous meningitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viney, K.; Linh, N.N.; Gegia, M.; Zignol, M.; Glaziou, P.; Ismail, N.; Kasaeva, T.; Mirzayev, F. New definitions of pre-extensively and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: Update from the World Health Organization. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Definitions and Reporting Framework for Tuberculosis—2013 Revision: Updated December 2014 and January 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241505345 (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Cellestis/Qiagen. QuantiFERON(R)-TB Gold (In-Tube Method) Package Insert. Available online: www.quantiferon.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/English_QFTPlus_ELISA_R04_022016.pdf/ (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Cowger, T.L.; Wortham, J.M.; Burton, D.C. Epidemiology of tuberculosis among children and adolescents in the USA, 2007–2017: An analysis of national surveillance data. Lancet Public Health 2019, 4, e506–e516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducomble, T.; Tolksdorf, K.; Karagiannis, I.; Hauer, B.; Brodhun, B.; Haas, W.; Fiebig, L. The burden of extrapulmonary and meningitis tuberculosis: An investigation of national surveillance data, Germany, 2002 to 2009. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Well, G.T.; Paes, B.F.; Terwee, C.B.; Springer, P.; Roord, J.J.; Donald, P.R.; van Furth, A.M.; Schoeman, J.F. Twenty years of pediatric tuberculous meningitis: A retrospective cohort study in the western cape of South Africa. Pediatrics 2009, 123, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Posey, D.L.; Yang, Q.; Weinberg, M.S.; Maloney, S.A.; Lambert, L.A.; Ortega, L.S.; Marano, N.; Cetron, M.S.; Phares, C.R. Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in U.S.-Bound Immigrants and Refugees. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022, 19, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, Z.; Painter, J.; Douglas, P.; Abubakar, I.; Njoo, H.; Archibald, C.; Halverson, J.; Robson, J.; Posey, D.L. Immigrant Arrival and Tuberculosis among Large Immigrant- and Refugee-Receiving Countries, 2005–2009. Tuberc. Res. Treat. 2017, 2017, 8567893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto, G.; Fornabaio, C.; Prato, R.; Saracino, A.; Tartaglia, A.; Di Tullio, R.; Carbonara, S.; Angarano, G.; Italian Study Group for Infectious Diseases in Immigrants. Tuberculosis and immigrants: A SIMIT (Italian Society of Infectious Diseases) clinical, epidemiological multicentric research investigation. New Microbiol. 2009, 32, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Luque, L.; Rodrigo, T.; Garcia-Garcia, J.M.; Casals, M.; Millet, J.P.; Cayla, J.; Oreau, A. Factors Associated with Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis in Spain and Its Distribution in Immigrant Population. Open Respir. Arch. 2020, 2, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, A.W.; González Fernández, L.; Takwoingi, Y.; Eisenhut, M.; Detjen, A.K.; Steingart, K.R.; Mandalakas, A.M. Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assays for active tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 8, CD013359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, R.; Xing, L.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, C. Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics of Pediatric Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Chongqing, China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, E.; Erdem, E.; Ozlu, N.; Seber, E.; Gencer, S.; Kilicaslan, Z. Demographic and microbial characteristics and drug resistance of childhood tuberculosis in Istanbul: Analysis of 1,541 cases. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.F.; Schraufnagel, D.E.; Hopewell, P.C. Treatment of Tuberculosis. A Historical Perspective. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, 1749–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, D.M.G.C.; Viveiros, M.; Saraiva, M.; Osório, N.S. The Neglected Contribution of Streptomycin to the Tuberculosis Drug Resistance Problem. Genes 2021, 12, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresswell, F.V.; Te Brake, L.; Atherton, R.; Ruslami, R.; Dooley, K.E.; Aarnoutse, R.; Van Crevel, R. Intensified antibiotic treatment of tuberculosis meningitis. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saukkonen, J.J.; Cohn, D.L.; Jasmer, R.M.; Schenker, S.; Jereb, J.A.; Nolan, C.M.; Peloquin, C.A.; Gordin, F.M.; Nunes, D.; Strader, D.B.; et al. An official ATS statement: Hepatotoxicity of antituberculosis therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tostmann, A.; Boeree, M.J.; Aarnoutse, R.E.; de Lange, W.C.; van der Ven, A.J.; Dekhuijzen, R. Antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: Concise up-to-date review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tersigni, C.; Venturini, E.; Cordola, C.; Piccini, P.; Bianchi, L.; Montagnani, C.; Sollai, S.; Chiappini, E.; de Martino, M.; Galli, L. Latent tuberculosis in childhood: Tolerability of two different therapeutic approaches. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2018, 16, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merid, M.W.; Gezie, L.D.; Kassa, G.M.; Muluneh, A.G.; Akalu, T.Y.; Yenit, M.K. Incidence and predictors of major adverse drug events among drug-resistant tuberculosis patients on second-line anti-tuberculosis treatment in Amhara regional state public hospitals; Ethiopia: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, M.W.; Lee, M.; Cai, Y.; Hallahan, C.W.; Shaw, P.A.; Min, J.H.; Goldfeder, L.C.; Alekseyev, V.; Grinkrug, S.; Kang, H.S.; et al. Frequency of adverse reactions to first- and second-line anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy in a Korean cohort. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2012, 16, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecora, F.; Dal Canto, G.; Veronese, P.; Esposito, S. Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Children: The Role of Bedaquiline and Delamanid. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
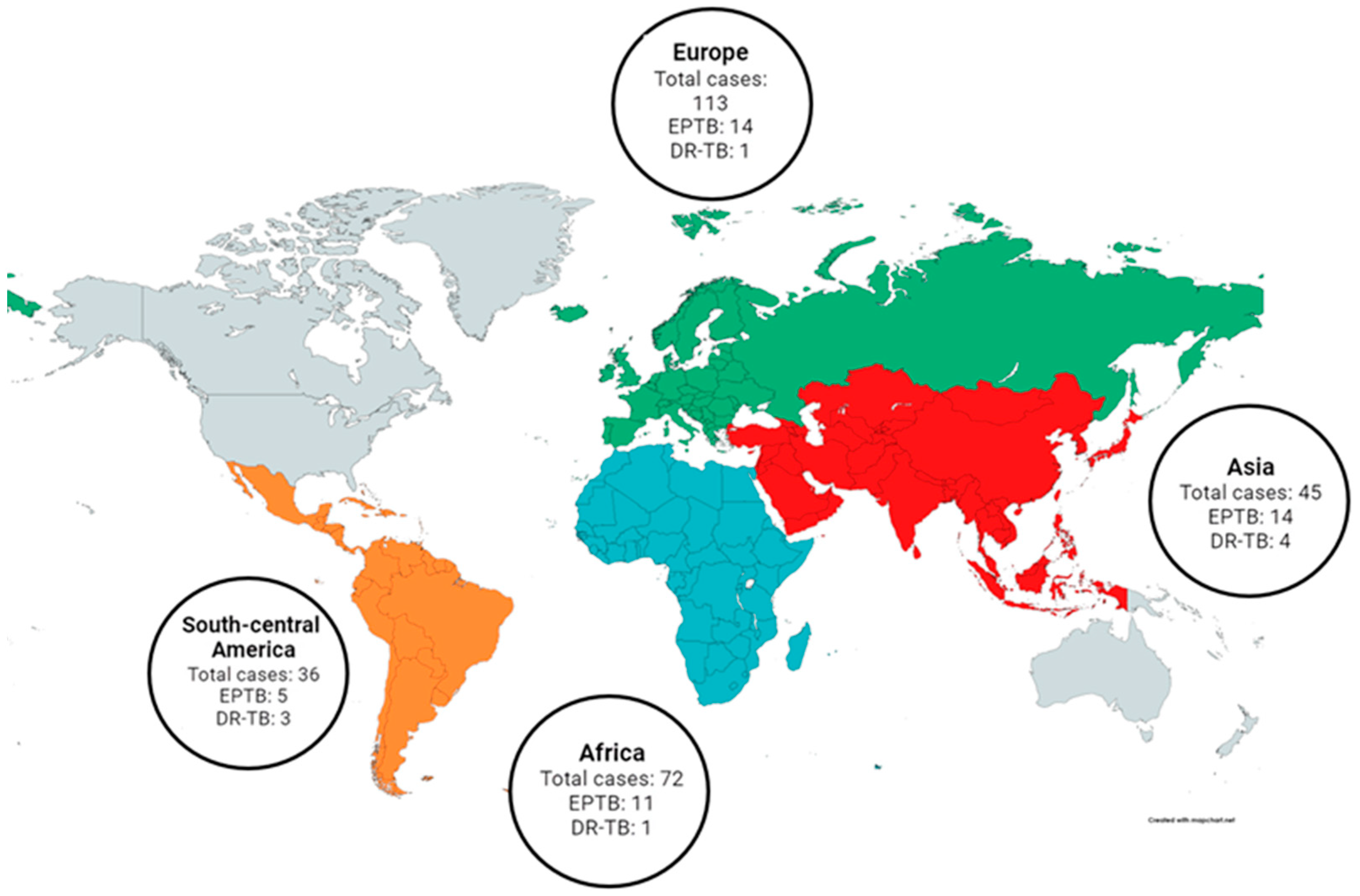



| Characteristics of Children in the Study | Children ≤ 5 Years Old | Children > 5 Years Old | Total | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 131 (%) | n = 140 (%) | n = 271 (%) | ||
| Male | 68 (51.91) | 74 (52.86) | 142 (52.40) | 0.972 |
| Female | 63 (48.09) | 66 (47.14) | 129 (47.60) | |
| Born in Italy to Italian Parents | 37 (28.24) | 26 (18.57) | 63 (23.25) | 0.082 |
| Born in Italy to Foreign Parents | 65 (49.62) | 33 (23.57) | 98 (36.16) | <0.001 |
| Born Abroad | 29 (22.14) | 81 (57.86) | 110 (40.59) | <0.001 |
| Diagnosis after Contact with a Case | 86 (65.65) | 58 (41.43) | 144 (53.14) | <0.001 |
| Diagnosis during Screening 1 | 12 (9.16) | 13 (9.29) | 25 (9.22) | 0.845 |
| Diagnosis in Children with Symptoms | 31 (23.66) | 68 (48.57) | 99 (36.53) | <0.001 |
| Unknown | 2 (1.53) | 1 (0.71) | 3 (1.11) | - |
| BCG 2 Vaccinated | 17 (12.98) | 26 (18.57) | 43 (15.87) | 0.274 |
| Not BCG Vaccinated | 114 (87.02) | 114 (81.43) | 228 (84.13) | |
| Pulmonary Tuberculosis | 111 (84.73) | 116 (82.86) | 227 (83.76) | 0.800 |
| Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis 3 | 20 (15.27) | 24 (17.14) | 44 (16.24) | |
| Positive TST 4/QuantiFERON | 118 (90.08) | 131 (93.57) | 249 (91.88) | 0.494 |
| Negative TST/QuantiFERON | 9 (6.87) | 6 (4.29) | 15 (5.53) | |
| Unknown | 4 (3.05) | 3 (2.14) | 7 (2.59) | - |
| Microbiologically 5 Confirmed | 60 (45.80) | 63 (45.00) | 123 (45.39) | 0.677 |
| Not Microbiologically Confirmed | 53 (40.46) | 48 (34.29) | 101 (37.27) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 18 (13.74) | 29 (20.71) | 47 (17.34) | - |
| Positive PCR 6 | 33 (25.19) | 44 (31.42) | 77 (28.41) | 0.144 |
| Negative PCR | 78 (59.54) | 66 (47.14) | 144 (53.14) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 20 (15.27) | 30 (21.43) | 50 (18.45) | - |
| Positive Microscopy | 13 (9.92) | 23 (16.43) | 36 (13.28) | 0.089 |
| Negative Microscopy | 99 (75.57) | 87 (62.14) | 186 (68.63) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 19 (14.50) | 30 (21.43) | 49 (18.08) | - |
| Positive Culture | 50 (38.17) | 56 (40.00) | 106 (39.11) | 0.426 |
| Negative Culture | 63 (48.09) | 55 (39.29) | 118 (43.54) | |
| Unknown/Absent Result | 18 (38.17) | 29 (28.71) | 47 (17.34) | - |
| Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis | 4 (3.05) | 5 (3.57) | 9 (3.32) | 1.000 |
| Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis | 27 (20.61) | 31 (22.14) | 58 (21.40) | 0.874 |
| Unknown Drug-Susceptibility Pattern | 100 (76.34) | 104 (74.29) | 204 (75.28) | 0.802 |
| Treated with First-Line Drugs | 95 (72.52) | 109 (77.86) | 204 (75.28) | 0.164 |
| Treated with Second-Line Drugs | 31 (23.66) | 22 (15.71) | 53 (19.56) | |
| Unknown Therapy | 5 (3.82) | 9 (6.43) | 14 (5.2) | - |
| Children Cured | 129 (98.47) | 138 (98.57) | 267 (98.52) | 1.000 |
| Children with Sequelae | 2 (1.53) | 2 (1.43) | 4 (1.48) |
| Second-Line Drugs | Drug-Resistant TB 1 n = 9 (%) | Drug-Susceptible TB n = 58 (%) | Children without DST 2 Results n = 204 (%) | p 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amikacin | 5 (55.56) | 9 (15.52) | 19 (9.31) | 0.002 |
| Cycloserine | 6 (66.67) | 2 (3.45) | 11 (5.39) | <0.001 |
| Linezolid | 5 (55.56) | 2 (3.45) | 8 (3.92) | <0.001 |
| Moxifloxacin | 4 (44.44) | 8 (13.79) | 24 (11.76) | 0.020 |
| Levofloxacin | 2 (22.22) | 3 (5.17) | 1 (0.49) | 0.014 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (0.49) | 1.000 |
| Clarithromycin | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (0.49) | 1.000 |
| Streptomycin | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (0.49) | 1.000 |
| Para-aminosalicylic acid | 2 (22.22) | 0 (0.00) | 3 (1.47) | 0.009 |
| Second-Line Drugs | Pulmonary Tuberculosis Cases n = 227 (%) | Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis Cases n = 44 (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amikacin | 25 (11.01) | 8 (18.18) | 0.281 |
| Cycloserine | 11 (4.85) | 8 (18.18) | 0.004 |
| Linezolid | 12 (5.29) | 3 (6.82) | 0.717 |
| Moxifloxacin | 23 (10.13) | 13 (29.55) | 0.001 |
| Levofloxacin | 4 (1.76) | 2 (4.55) | 0.252 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.27) | 1.000 |
| Clarithromycin | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.27) | 1.000 |
| Streptomycin | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.27) | 1.000 |
| Para-aminosalicylic acid | 5 (2.20) | 0 (0.00) | 1.000 |
| Drug Susceptibility | Pulmonary Tuberculosis Cases n = 227 (%) | Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis Cases n = 44 (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug-resistant tuberculosis | 6 (2.65) | 3 (6.82) | 0.165 |
| Drug-susceptible tuberculosis | 42 (18.50) | 16 (36.36) | 0.015 |
| Children without DST 1 results | 179 (78.85) | 25 (56.82) | 0.004 |
| Univariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Population Characteristics | n/N * | OR 1 | 95% CI 2 | p |
| Male | 3/142 | 1.000 | ||
| Female | 6/129 | 2.260 | 0.553–9.230 | 0.256 |
| ≤5 years | 4/131 | 0.850 | 0.223–3.238 | 0.812 |
| >5 years | 5/140 | 1.000 | ||
| Europe | 1/113 | 1.000 | ||
| Africa | 1/72 | 1.577 | 0.097–25.624 | 0.749 |
| Asia | 4/44 | 10.927 | 1.186–100.639 | 0.035 |
| South-Central America | 3/36 | 10.182 | 1.025–101.173 | 0.048 |
| Pulmonary tuberculosis | 6/227 | 0.371 | 0.089–1.543 | 0.173 |
| Extrapulmonary tuberculosis | 3/44 | 1.000 | ||
| Diagnosed in 2006–2015 | 4/178 | 1.000 | ||
| Diagnosed in 2016–2022 | 5/93 | 2.472 | 0.647–9.435 | 0.186 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Population Characteristics | n/N * | OR 1 | 95% CI 2 | p | OR | 95% CI | p |
| Male | 27/142 | 1.000 | |||||
| Female | 17/129 | 0.646 | 0.334–1.251 | 0.195 | |||
| ≤5 years | 20/131 | 0.871 | 0.456–1.665 | 0.676 | |||
| >5 years | 24/140 | 1.000 | |||||
| Italy | 9/63 | 1.000 | |||||
| Eastern Europe | 5/48 | 0.698 | 0.218–2.235 | 0.544 | 0.675 | 0.204–2.231 | 0.520 |
| Africa | 11/72 | 1.082 | 0.417–2.809 | 0.871 | 1.064 | 0.401–2.824 | 0.900 |
| Asia | 14/45 | 2.710 | 1.051–6.983 | 0.039 | 2.758 | 1.041–7.305 | 0.041 |
| South-Central America | 5/36 | 0.968 | 0.298–3.146 | 0.957 | 1.150 | 0.341–3.875 | 0.822 |
| Diagnosis after contact | 6/144 | 1.000 | |||||
| Diagnosis during screening 3 | 2/25 | 2.000 | 0.380–10.519 | 0.413 | |||
| Diagnosed with symptoms | 36/99 | 13.143 | 5.268–32.788 | <0.001 | |||
| DR-TB 4 cases | 3/9 | 2.695 | 0.648–11.211 | 0.173 | |||
| Non DR-TB cases | 41/262 | 1.000 | |||||
| Diagnosed in 2006–2010 | 5/74 | 1.000 | |||||
| Diagnosed in 2011–2015 | 17/104 | 2.697 | 0.947–7.675 | 0.063 | 2.670 | 0.920–7.748 | 0.071 |
| Diagnosed in 2016–2020 | 19/74 | 4.767 | 1.673–13.581 | 0.003 | 5.088 | 1.750–14.795 | 0.003 |
| Diagnosed in 2021–2022 | 3/19 | 2.587 | 0.029–0.180 | 0.224 | 2.438 | 0.510–11.653 | 0.264 |
| Study Population Characteristics | n/N * | OR 1 | 95% CI 2 | p | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 29/142 | 1.000 | |||||
| Female | 24/129 | 0.891 | 0.487–1.627 | 0.706 | |||
| ≤5 years | 31/131 | 1.663 | 0.905–3.054 | 0.101 | |||
| >5 years | 22/140 | 1.000 | |||||
| Italy | 10/63 | 1.000 | |||||
| Eastern Europe | 10/48 | 1.395 | 0.528–3.681 | 0.502 | |||
| Africa | 11/72 | 0.956 | 0.376–2.427 | 0.924 | |||
| Asia | 13/45 | 2.153 | 0.846–5.478 | 0.108 | |||
| South-Central America | 7/36 | 1.279 | 0.440–3.717 | 0.651 | |||
| Diagnosis after contact | 20/144 | 1.000 | |||||
| Diagnosis during screening 3 | 0/25 | ||||||
| Diagnosed with symptoms | 32/99 | 2.961 | 1.573–5.575 | 0.001 | 1.749 | 0.813–3.761 | 0.153 |
| Pulmonary tuberculosis | 33/227 | 1.000 | |||||
| Extrapulmonary tuberculosis 4 | 20/44 | 4.899 | 2.436–9.854 | <0.001 | 4.104 | 1.691–9.962 | 0.002 |
| Microbiologically confirmed 5 | 35/123 | 2.472 | 1.243–4.913 | 0.010 | 2.484 | 1.146–5.384 | 0.021 |
| Not microbiologically confirmed | 14/101 | 1.000 | |||||
| Diagnosed in 2006–2010 | 6/74 | 1.000 | |||||
| Diagnosed in 2011–2015 | 33/104 | 5.268 | 2.076–13.368 | <0.001 | 4.737 | 1.764–12.715 | 0.002 |
| Diagnosed in 2016–2020 | 10/74 | 1.771 | 0.608–5.153 | 0.294 | 0.909 | 0.282–2.931 | 0.874 |
| Diagnosed in 2021–2022 | 4/19 | 3.022 | 0.758–12.051 | 0.117 | 1.717 | 0.387–7.611 | 0.477 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pace, D.; Corvaglia, F.; Lisi, C.; Galli, L.; Chiappini, E. Extrapulmonary and Drug-Resistant Childhood Tuberculosis: Unveiling the Disease to Adopt the Optimal Treatment Strategy. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121439
Pace D, Corvaglia F, Lisi C, Galli L, Chiappini E. Extrapulmonary and Drug-Resistant Childhood Tuberculosis: Unveiling the Disease to Adopt the Optimal Treatment Strategy. Pathogens. 2023; 12(12):1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121439
Chicago/Turabian StylePace, Domenico, Francesca Corvaglia, Catiuscia Lisi, Luisa Galli, and Elena Chiappini. 2023. "Extrapulmonary and Drug-Resistant Childhood Tuberculosis: Unveiling the Disease to Adopt the Optimal Treatment Strategy" Pathogens 12, no. 12: 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121439
APA StylePace, D., Corvaglia, F., Lisi, C., Galli, L., & Chiappini, E. (2023). Extrapulmonary and Drug-Resistant Childhood Tuberculosis: Unveiling the Disease to Adopt the Optimal Treatment Strategy. Pathogens, 12(12), 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121439







