Overoxidation and Oligomerization of Trypanosoma cruzi Cytosolic and Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasite Culture and Genetic Manipulation
2.2. Gel Filtration Chromatography
2.3. Expression, Purification, and Treatment of Recombinant Proteins
2.4. Peroxidase Activity Assay
2.5. Molecular Chaperone Activity Assay
2.6. Gel Electrophoresis and Western Blot
2.7. Indirect Immunofluorescence Microscopy
2.8. Detection of Overoxidized TXNPx in Parasites
2.9. Thermotolerance Assay
2.10. In Vitro Infection Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
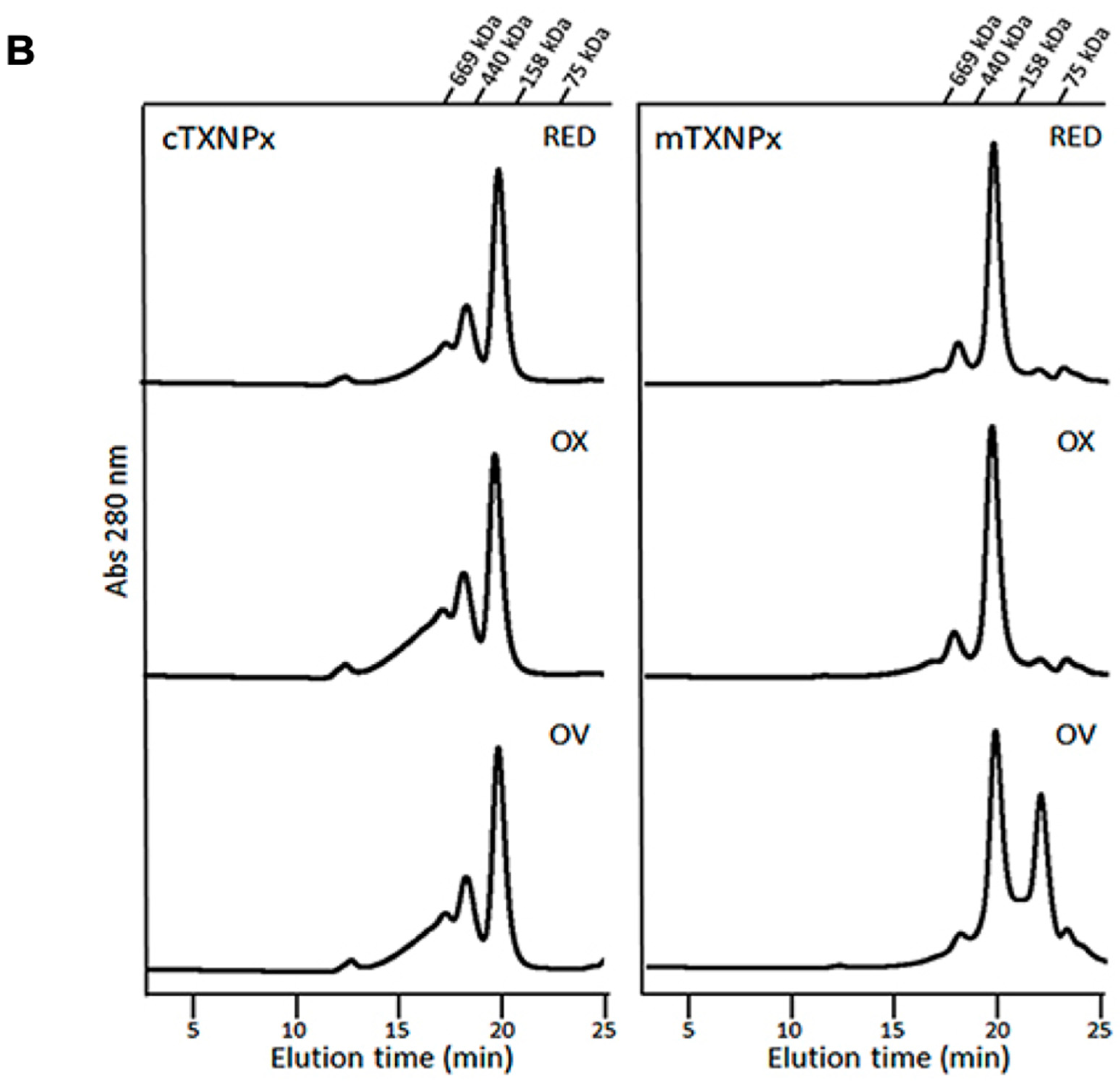
3.1. Recombinant c-TXNPx and m-TXNPx Present Differences in Oligomerization under Oxidative Conditions
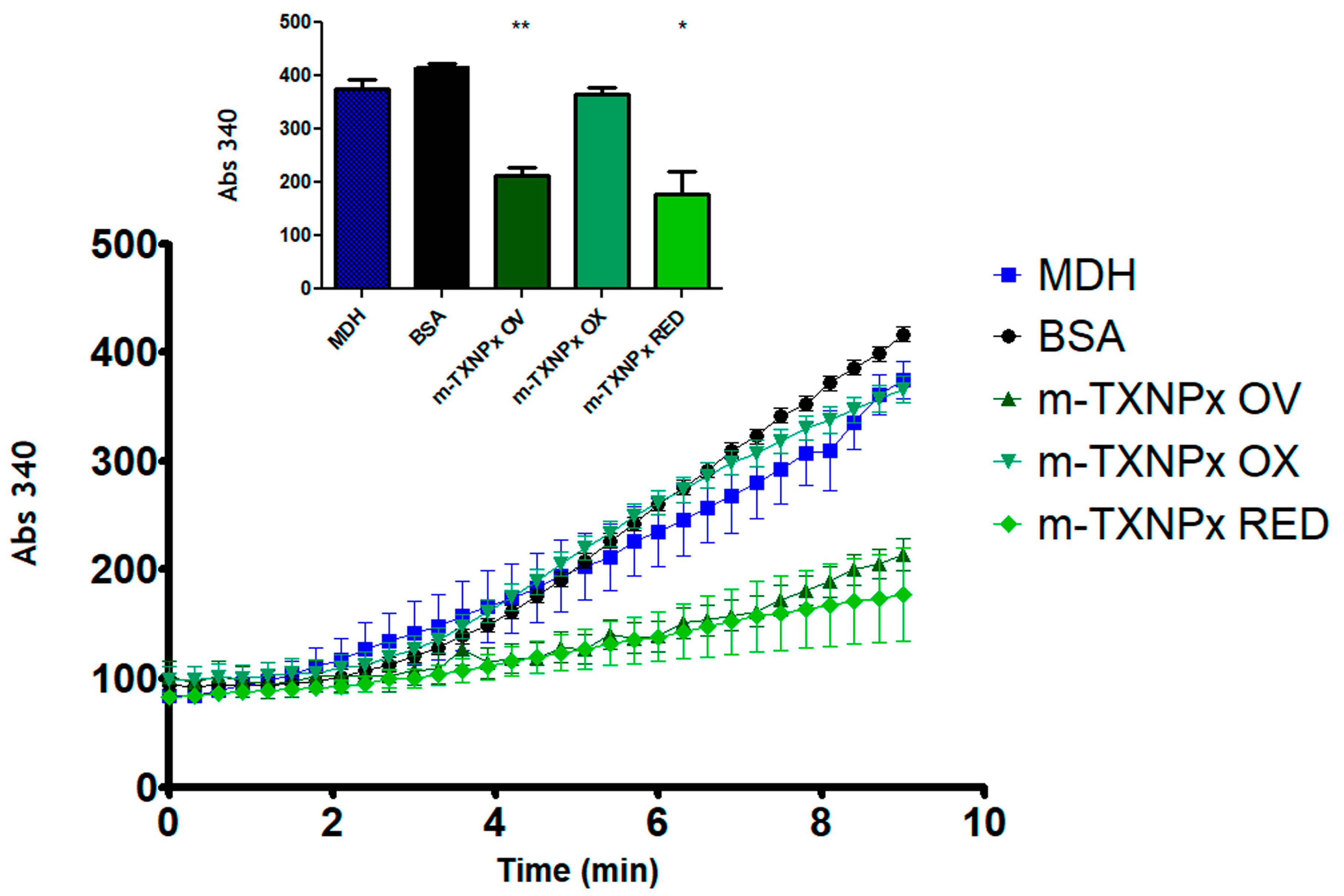
3.2. T. cruzi m-TXNPx Exhibits Molecular Chaperone Activity Dependent on Its Oxidation Status
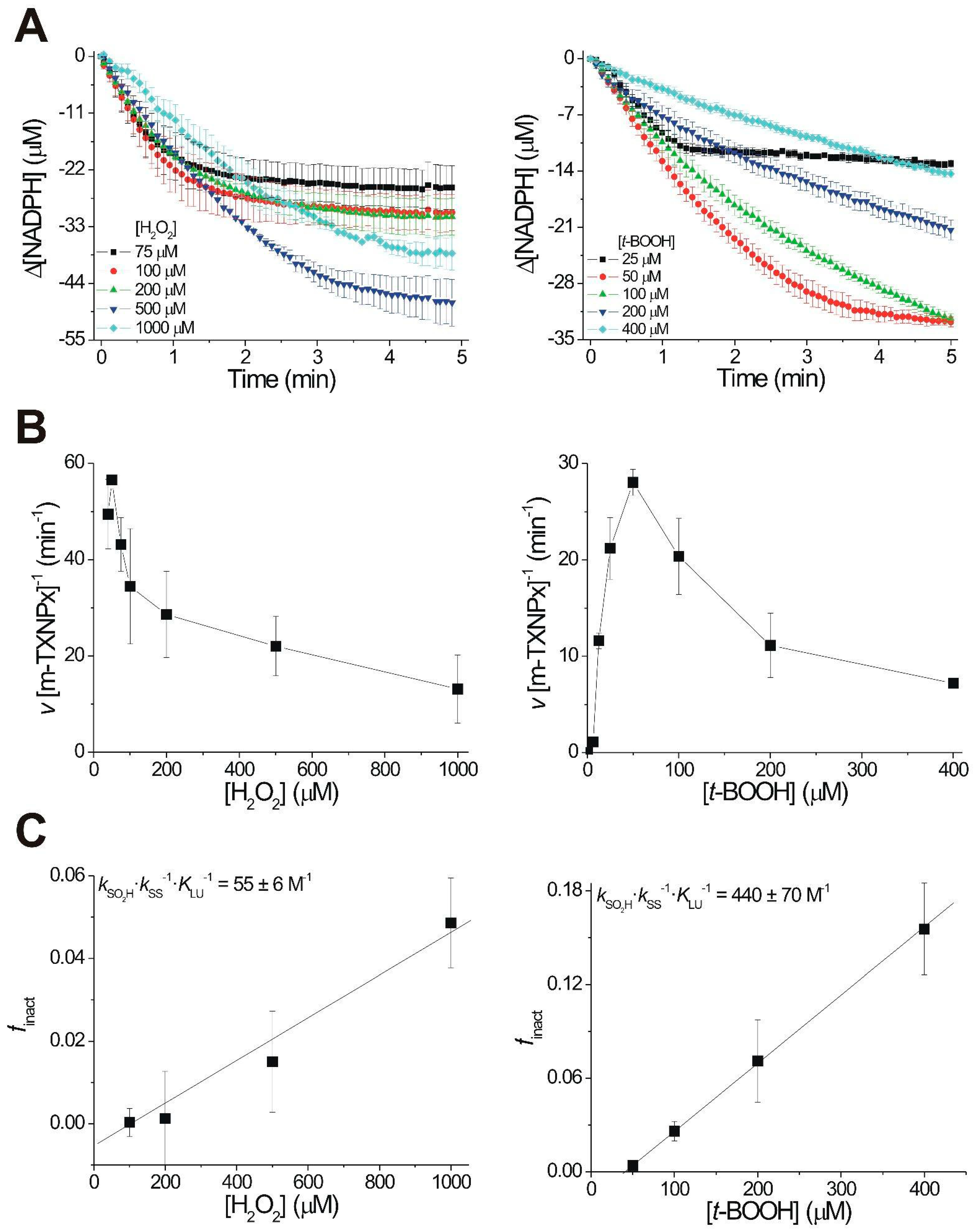
3.3. c-TXNPx and m-TXNPx Show Differences in Susceptibility to Overoxidation during the Catalytic Cycle
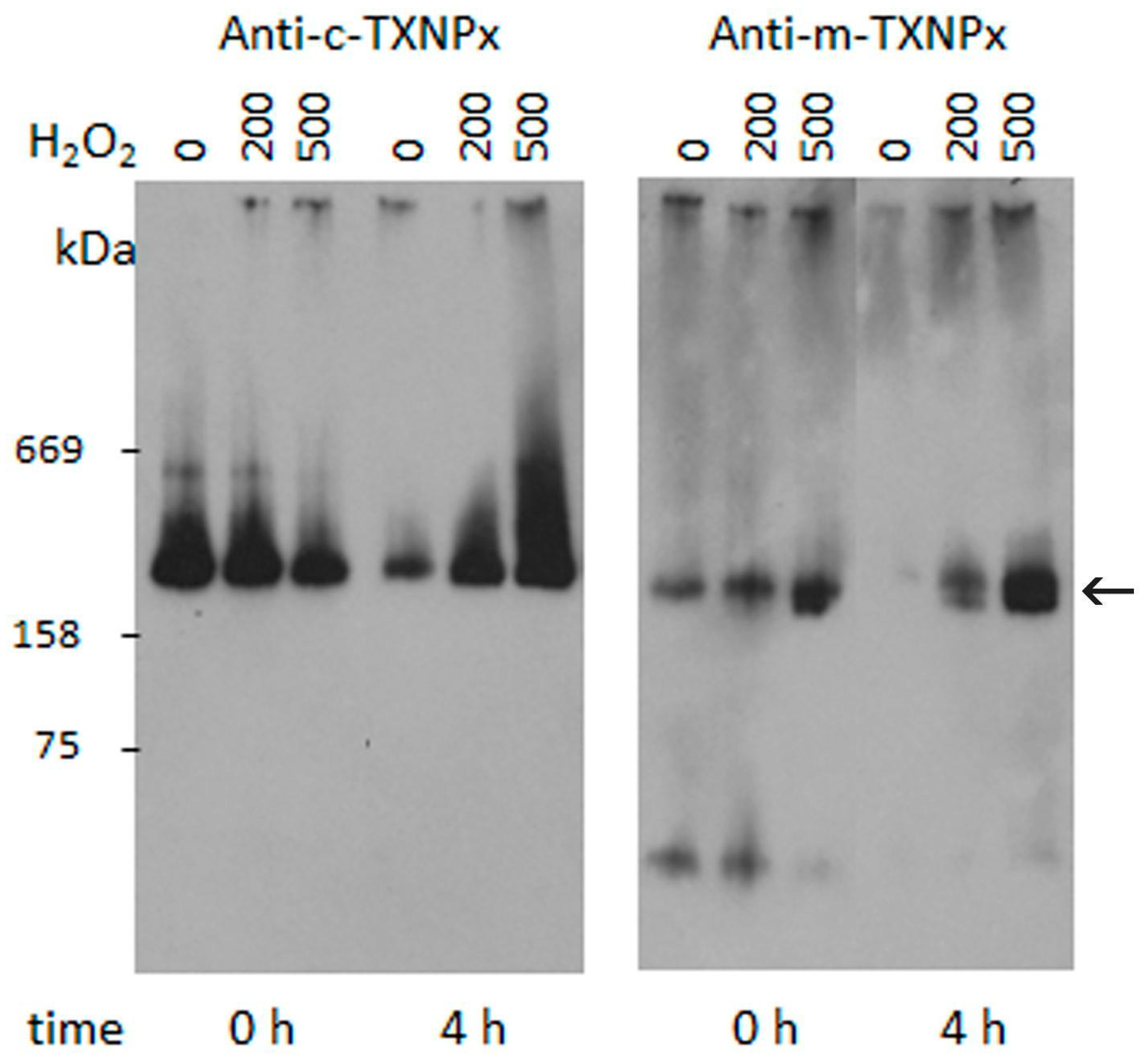
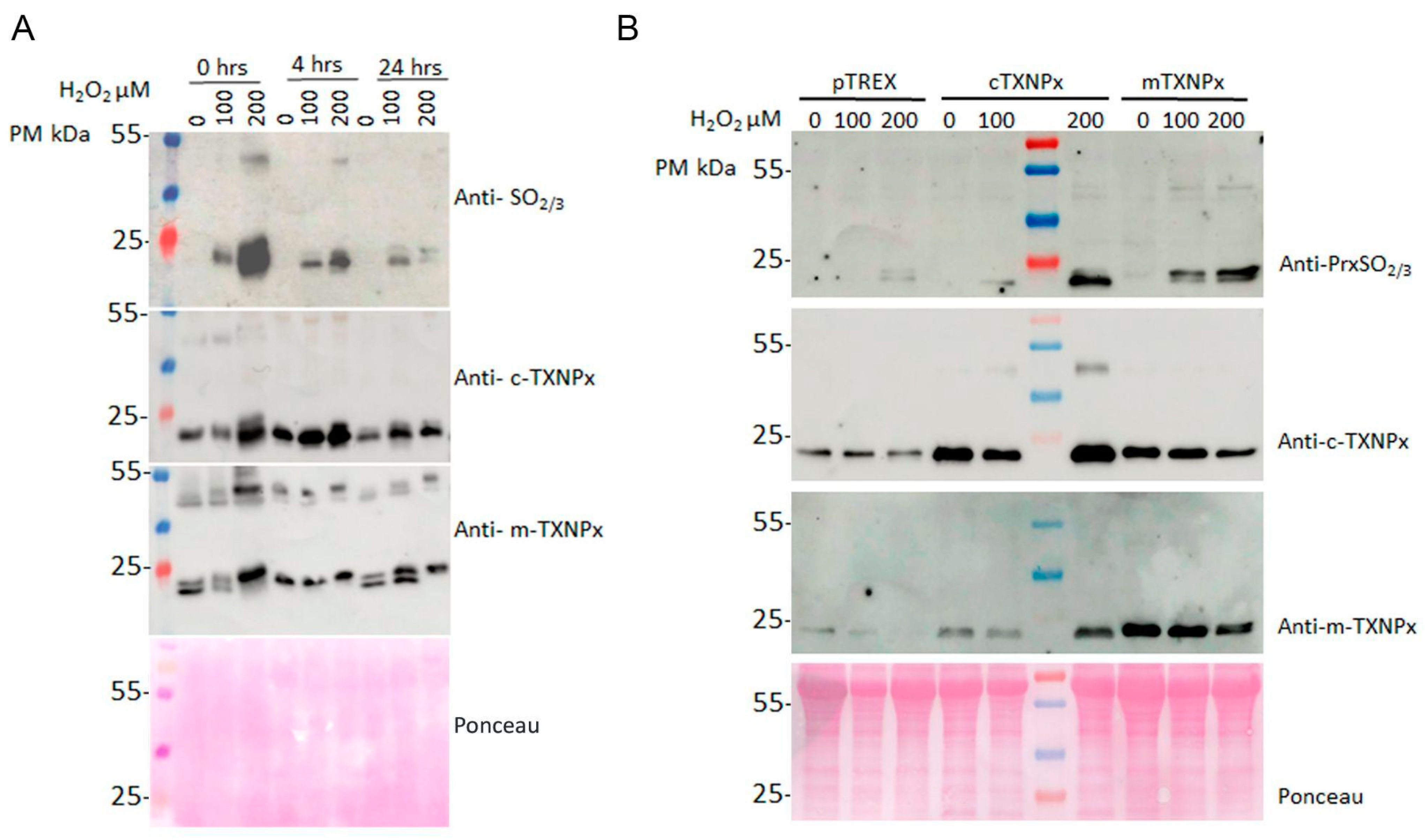
3.4. In Vivo Oligomerization of Prxs in Parasites Treated with Oxidants
3.5. Overoxidized Prx Does Not Actively Reverse in Oxidant-Treated Parasites
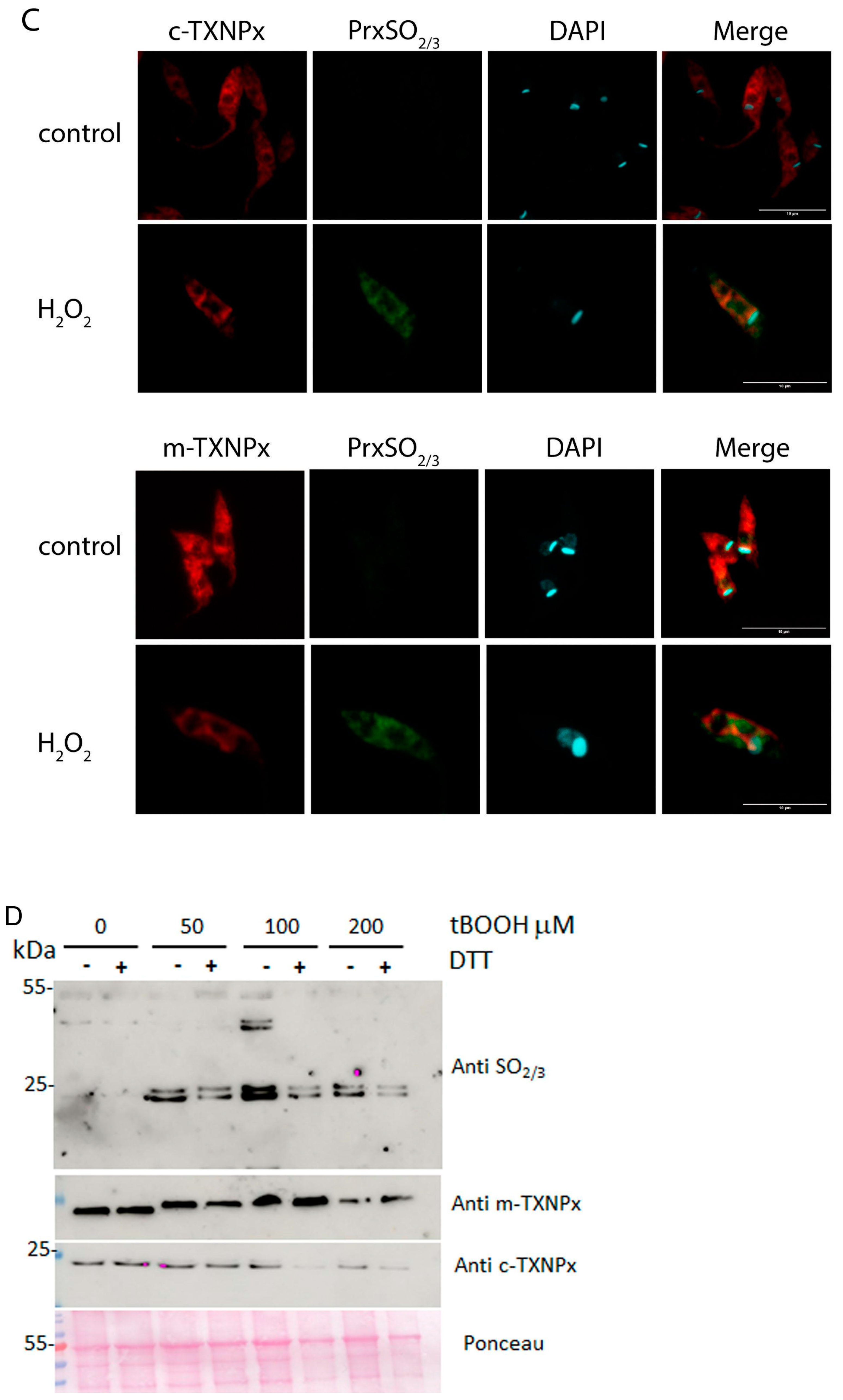
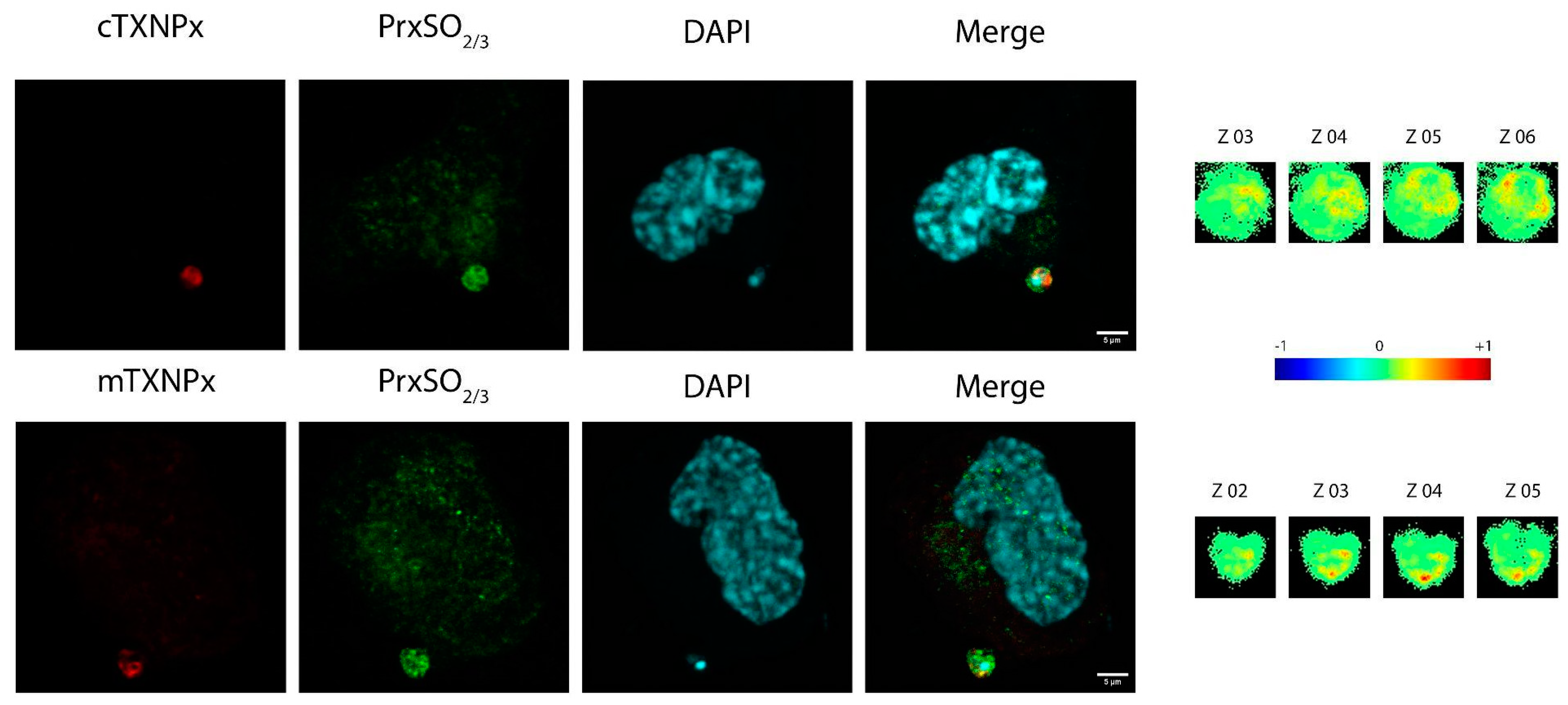
3.6. c-TXNPx and m-TXNPx Are Physiologically Overoxidized in Infection
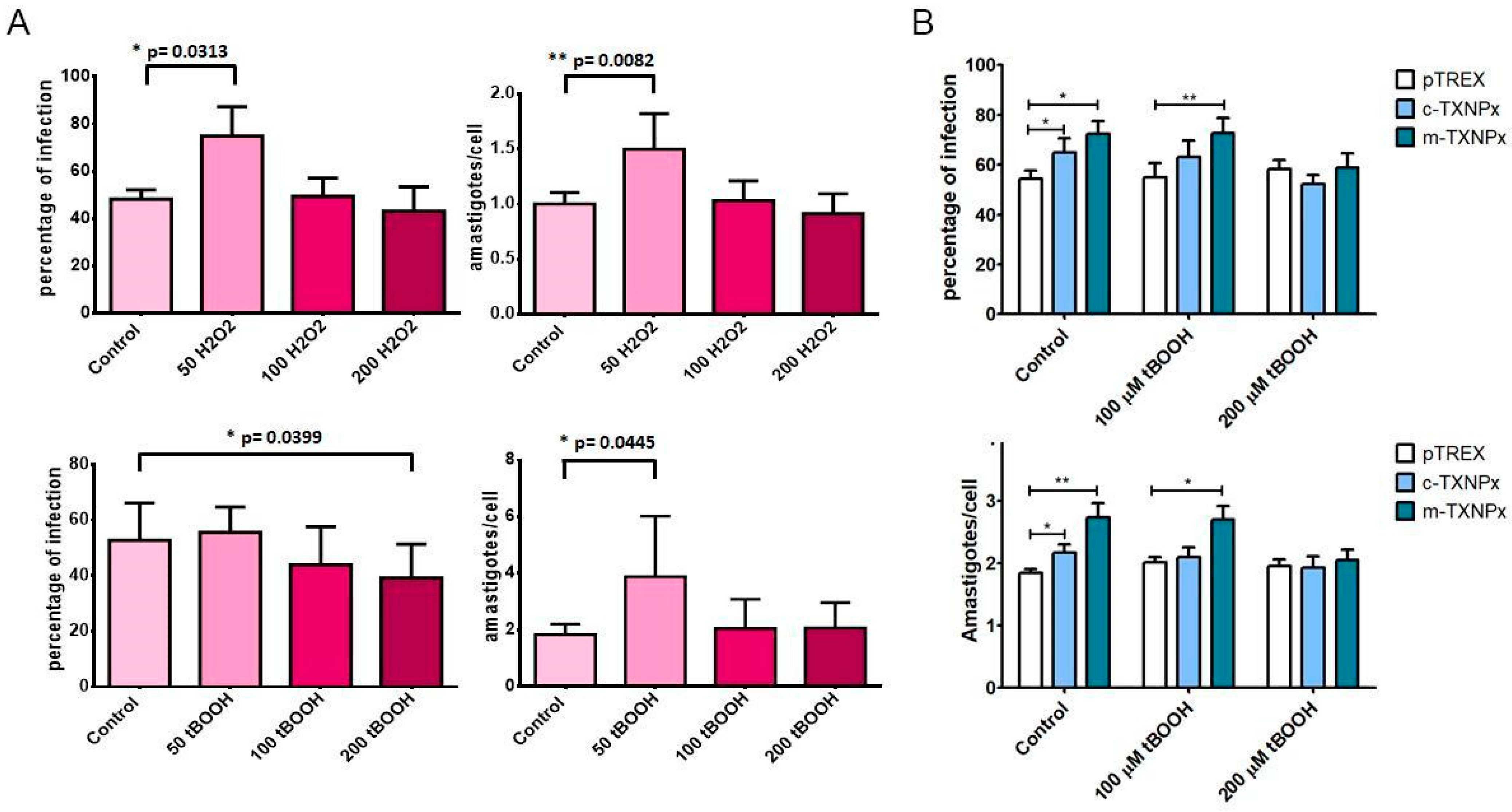
3.7. Oxidant Treatment Alters Parasite Infectivity
3.8. T. cruzi Prxs Contribute to the Acquisition of Cellular Thermotolerance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Molina, J.A.; Molina, I. Chagas Disease. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2018, 391, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, G.; Yoshida, N. Editorial: World Chagas Disease Day 2022. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1209531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeyro, M.D.; Arcari, T.; Robello, C.; Radi, R.; Trujillo, M. Tryparedoxin Peroxidases from Trypanosoma Cruzi: High Efficiency in the Catalytic Elimination of Hydrogen Peroxide and Peroxynitrite. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 507, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, S.R.; Horn, D.; Prathalingam, S.R.; Kelly, J.M. RNA Interference Identifies Two Hydroperoxide Metabolizing Enzymes That Are Essential to the Bloodstream Form of the African Trypanosome. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31640–31646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeyro, M.D.; Parodi-Talice, A.; Arcari, T.; Robello, C. Peroxiredoxins from Trypanosoma Cruzi: Virulence Factors and Drug Targets for Treatment of Chagas Disease? Gene 2008, 408, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, J.P.; Kaprakkaden, A.; Choudhary, M.L.; Shaha, C. Crucial Role of Cytosolic Tryparedoxin Peroxidase in Leishmania Donovani Survival, Drug Response and Virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 372–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacenza, L.; Peluffo, G.; Alvarez, M.N.; Kelly, J.M.; Wilkinson, S.R.; Radi, R. Peroxiredoxins Play a Major Role in Protecting Trypanosoma Cruzi against Macrophage- and Endogenously-Derived Peroxynitrite. Biochem. J. 2008, 410, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallières, C.; Golinelli-Cohen, M.-P.; Guittet, O.; Lepoivre, M.; Huang, M.-E.; Vernis, L. Redox-Based Strategies against Infections by Eukaryotic Pathogens. Genes 2023, 14, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeyro, M.D.; Arias, D.; Ricciardi, A.; Robello, C.; Parodi-Talice, A. Oligomerization Dynamics and Functionality of Trypanosoma Cruzi Cytosolic Tryparedoxin Peroxidase as Peroxidase and Molecular Chaperone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specker, G.; Estrada, D.; Radi, R.; Piacenza, L. Trypanosoma Cruzi Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxin Promotes Infectivity in Macrophages and Attenuates Nifurtimox Toxicity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 749476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.; Teixeira, F.; Romao, S.; Santos, M.; Cruz, T.; Flórido, M.; Appelberg, R.; Oliveira, P.; Ferreira-da-Silva, F.; Tomás, A.M. Leishmania Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxin Plays a Crucial Peroxidase-Unrelated Role during Infection: Insight into Its Novel Chaperone Activity. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.-S.; Kang, S.W.; Woo, H.A.; Hwang, S.C.; Chae, H.Z.; Kim, K.; Rhee, S.G. Inactivation of Human Peroxiredoxin I during Catalysis as the Result of the Oxidation of the Catalytic Site Cysteine to Cysteine-Sulfinic Acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 38029–38036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzi, H.A.; Vazquez, M.P.; Levin, M.J. Integration of Expression Vectors into the Ribosomal Locus of Trypanosoma Cruzi. Gene 2003, 310, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.J.; Parsonage, D.; Karplus, P.A.; Poole, L.B. Evaluating Peroxiredoxin Sensitivity Toward Inactivation by Peroxide Substrates. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 527, pp. 21–40. ISSN 978-0-12-405882-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bolte, S.; Cordelières, F.P. A Guided Tour into Subcellular Colocalization Analysis in Light Microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 224, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolón, M.; Vega, C.; Escario, J.A.; Gómez-Barrio, A. Development of Resazurin Microtiter Assay for Drug Sensibility Testing of Trypanosoma Cruzi Epimastigotes. Parasitol. Res. 2006, 99, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Chaumont, F.; Dallongeville, S.; Chenouard, N.; Hervé, N.; Pop, S.; Provoost, T.; Meas-Yedid, V.; Pankajakshan, P.; Lecomte, T.; Le Montagner, Y.; et al. Icy: An Open Bioimage Informatics Platform for Extended Reproducible Research. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, D.G.; Reinoso, A.; Sasoni, N.; Hartman, M.D.; Iglesias, A.A.; Guerrero, S.A. Kinetic and Structural Characterization of a Typical 2-Cysteine Peroxiredoxin from Leptospira Interrogans Exhibiting Redox Sensitivity. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 77, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, J.A.; Nelson, K.J.; Haynes, A.C.; Lee, J.; Reisz, J.A.; Graff, A.H.; Clodfelter, J.E.; Parsonage, D.; Poole, L.B.; Furdui, C.M.; et al. Novel Hyperoxidation Resistance Motifs in 2-Cys Peroxiredoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 11901–11912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.H.; Lee, K.O.; Chi, Y.H.; Jung, B.G.; Park, S.K.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.R.; Lee, S.S.; Moon, J.C.; Yun, J.W.; et al. Two Enzymes in One; Two Yeast Peroxiredoxins Display Oxidative Stress-Dependent Switching from a Peroxidase to a Molecular Chaperone Function. Cell 2004, 117, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, M.A.B.; Giuseppe, P.O.; Souza, T.A.C.B.; Alegria, T.G.P.; Oliveira, M.A.; Netto, L.E.S.; Murakami, M.T. How pH Modulates the Dimer-Decamer Interconversion of 2-Cys Peroxiredoxins from the Prx1 Subfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 8582–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.; Castro, H.; Cruz, T.; Tse, E.; Koldewey, P.; Southworth, D.R.; Tomás, A.M.; Jakob, U. Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxin Functions as Crucial Chaperone Reservoir in Leishmania Infantum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015, 112, E616–E624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Bhella, D.; Lindsay, J.G. Reconstitution of the Mitochondrial PrxIII Antioxidant Defence Pathway: General Properties and Factors Affecting PrxIII Activity and Oligomeric State. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynton, R.A.; Peskin, A.V.; Haynes, A.C.; Lowther, W.T.; Hampton, M.B.; Winterbourn, C.C. Kinetic Analysis of Structural Influences on the Susceptibility of Peroxiredoxins 2 and 3 to Hyperoxidation. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.; Nelson, K.; Poole, L.B.; Karplus, P.A. Structure-Based Insights into the Catalytic Power and Conformational Dexterity of Peroxiredoxins. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 795–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, K.H.; Lee, S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, E.T.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.; Song, K.; Chae, H.Z. Regulation of Thioredoxin Peroxidase Activity by C-Terminal Truncation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 397, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, A.A.; Williams, D.L. Biochemical Characterization of 2-Cys Peroxiredoxins from Schistosoma Mansoni. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26159–26166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, A.G.; Peskin, A.V.; Paton, L.N.; Winterbourn, C.C.; Hampton, M.B. Redox Potential and Peroxide Reactivity of Human Peroxiredoxin 3. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peskin, A.V.; Dickerhof, N.; Poynton, R.A.; Paton, L.N.; Pace, P.E.; Hampton, M.B.; Winterbourn, C.C. Hyperoxidation of Peroxiredoxins 2 and 3: Rate Constants for the Reactions of the Sulfenic Acid of the Peroxidatic Cysteine. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 14170–14177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogacz, M.; Dirdjaja, N.; Wimmer, B.; Habich, C.; Krauth-Siegel, R.L. The Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxin Displays Distinct Roles in Different Developmental Stages of African Trypanosomes. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biteau, B.; Labarre, J.; Toledano, M.B. ATP-Dependent Reduction of Cysteine-Sulphinic Acid by S. Cerevisiae Sulphiredoxin. Nature 2003, 425, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.A.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, H.K.; Yang, K.-S.; Chae, H.Z.; Rhee, S.G. Reversible Oxidation of the Active Site Cysteine of Peroxiredoxins to Cysteine Sulfinic Acid. Immunoblot Detection with Antibodies Specific for the Hyperoxidized Cysteine-Containing Sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 47361–47364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, W.; Bae, S.H.; Toledano, M.B.; Rhee, S.G. Role of Sulfiredoxin as a Regulator of Peroxiredoxin Function and Regulation of Its Expression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, R.C.N.; Fabrino, D.L.; D’Ávila, H.; Teixeira, H.C.; Ferreira, A.P. Production of Hydrogen Peroxide by Peripheral Blood Monocytes and Specific Macrophages during Experimental Infection with Trypanosoma Cruzi in Vivo. Cell Biol. Int. 2003, 27, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, M.A.B.; Giuseppe, P.O.; Souza, T.A.C.B.; Castro, H.; Honorato, R.V.; Oliveira, P.S.L.; Netto, L.E.S.; Tomas, A.M.; Murakami, M.T. Calcium and Magnesium Ions Modulate the Oligomeric State and Function of Mitochondrial 2-Cys Peroxiredoxins in Leishmania Parasites. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 7023–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, K.; Schwappach, B.; Jakob, U. Thiol-Based Switching Mechanisms of Stress-Sensing Chaperones. Biol. Chem. 2021, 402, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.M.; Lee, S.S.; Tripathi, B.N.; Jung, H.S.; Cao, G.P.; Lee, Y.; Singh, S.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Site-Directed Mutagenesis Substituting Cysteine for Serine in 2-Cys Peroxiredoxin (2-Cys Prx A) of Arabidopsis Thaliana Effectively Improves Its Peroxidase and Chaperone Functions. Ann. Bot. 2015, 116, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, R.; Gadkari, V.V.; Meinen, B.A.; van Mierlo, C.P.M.; Ruotolo, B.T.; Bardwell, J.C.A. Mechanism of the Small ATP-Independent Chaperone Spy Is Substrate Specific. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Li, X.; Xue, H.; Yang, Y.; Mencius, J.; Bai, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Wu, B.; Xue, Y.; et al. Insights into the Client Protein Release Mechanism of the ATP-Independent Chaperone Spy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.G.; Woo, H.A.; Kil, I.S.; Bae, S.H. Peroxiredoxin Functions as a Peroxidase and a Regulator and Sensor of Local Peroxides. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4403–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, Z.A.; Poole, L.B.; Karplus, P.A. Peroxiredoxin Evolution and the Regulation of Hydrogen Peroxide Signaling. Science 2003, 300, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, T.; Okazaki, S.; Murayama, A.; Naganuma, A.; Nomoto, A.; Kuge, S. A Major Peroxiredoxin-Induced Activation of Yap1 Transcription Factor Is Mediated by Reduction-Sensitive Disulfide Bonds and Reveals a Low Level of Transcriptional Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4464–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netto, L.E.S.; Antunes, F. The Roles of Peroxiredoxin and Thioredoxin in Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing and in Signal Transduction. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, A.M.; Brown, J.D.; Taylor, S.R.; Rand, J.D.; Morgan, B.A.; Veal, E.A. Inactivation of a Peroxiredoxin by Hydrogen Peroxide Is Critical for Thioredoxin-Mediated Repair of Oxidized Proteins and Cell Survival. Mol. Cell 2012, 45, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeyro, M.D.; Parodi-Talice, A.; Portela, M.; Arias, D.G.; Guerrero, S.A.; Robello, C. Molecular Characterization and Interactome Analysis of Trypanosoma Cruzi Tryparedoxin 1. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, D.G.; Piñeyro, M.D.; Iglesias, A.A.; Guerrero, S.A.; Robello, C. Molecular Characterization and Interactome Analysis of Trypanosoma Cruzi Tryparedoxin II. J. Proteom. 2015, 120, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, L.; Peloso, E.F.; Leme, A.F.P.; Carnielli, C.M.; Pereira, C.N.; Werneck, C.C.; Guerrero, S.; Gadelha, F.R. Trypanosoma Cruzi Tryparedoxin II Interacts with Different Peroxiredoxins under Physiological and Oxidative Stress Conditions. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 184, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Chávez, Z.; Vázquez, C.; Mejia-Tlachi, M.; Márquez-Dueñas, C.; Manning-Cela, R.; Encalada, R.; Rodríguez-Enríquez, S.; Michels, P.A.M.; Moreno-Sánchez, R.; Saavedra, E. Gamma-Glutamylcysteine Synthetase and Tryparedoxin 1 Exert High Control on the Antioxidant System in Trypanosoma Cruzi Contributing to Drug Resistance and Infectivity. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piñeyro, M.D.; Chiribao, M.L.; Arias, D.G.; Robello, C.; Parodi-Talice, A. Overoxidation and Oligomerization of Trypanosoma cruzi Cytosolic and Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxins. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101273
Piñeyro MD, Chiribao ML, Arias DG, Robello C, Parodi-Talice A. Overoxidation and Oligomerization of Trypanosoma cruzi Cytosolic and Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxins. Pathogens. 2023; 12(10):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101273
Chicago/Turabian StylePiñeyro, María Dolores, María Laura Chiribao, Diego G. Arias, Carlos Robello, and Adriana Parodi-Talice. 2023. "Overoxidation and Oligomerization of Trypanosoma cruzi Cytosolic and Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxins" Pathogens 12, no. 10: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101273
APA StylePiñeyro, M. D., Chiribao, M. L., Arias, D. G., Robello, C., & Parodi-Talice, A. (2023). Overoxidation and Oligomerization of Trypanosoma cruzi Cytosolic and Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxins. Pathogens, 12(10), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101273






