Investigation of the Virome and Characterization of Issyk-Kul Virus from Swedish Myotis brandtii Bats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Bat Saliva Sampling
2.3. RNA Processing, Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Sanger Sequencing of Missing Genomic Regions
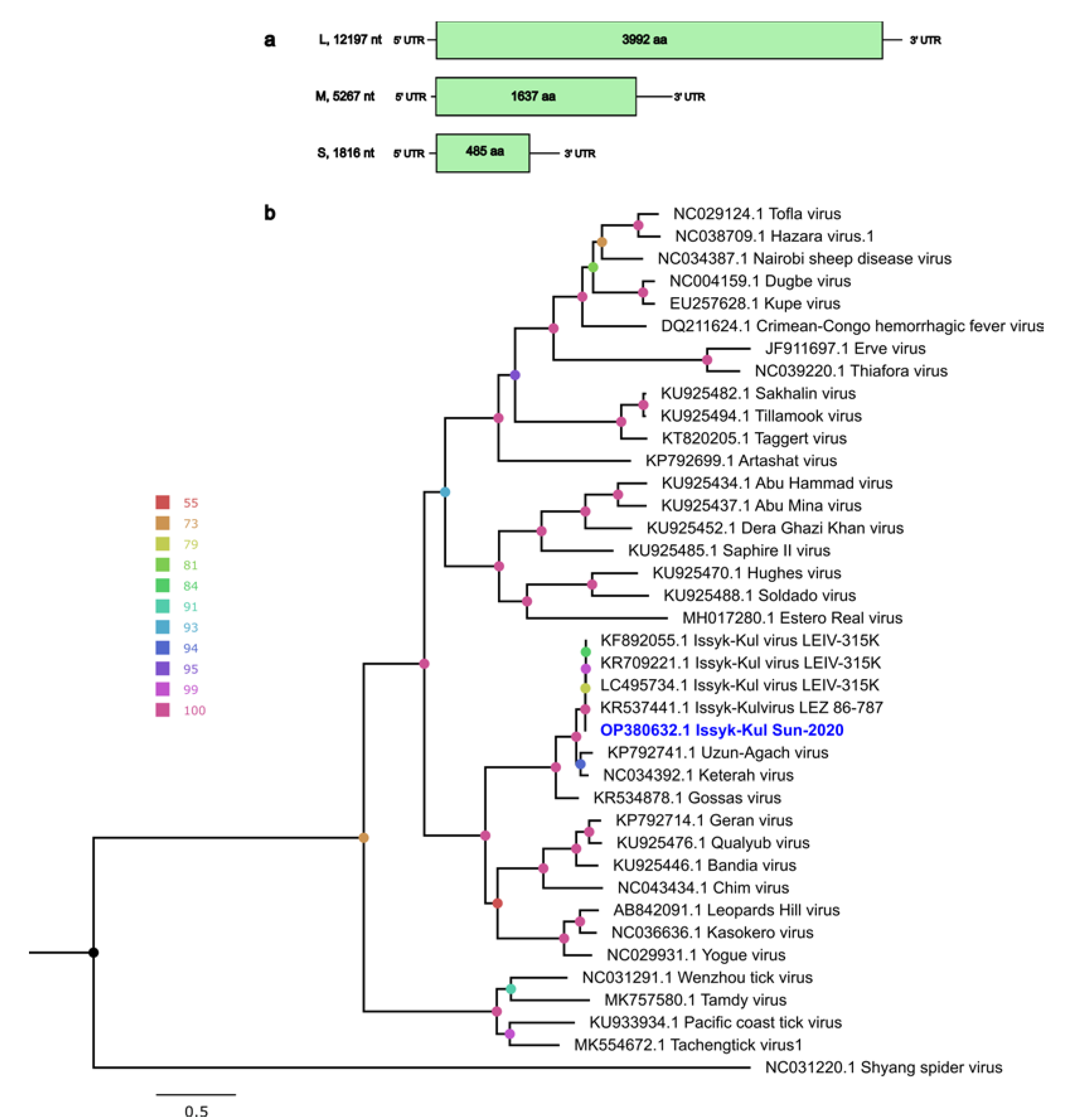
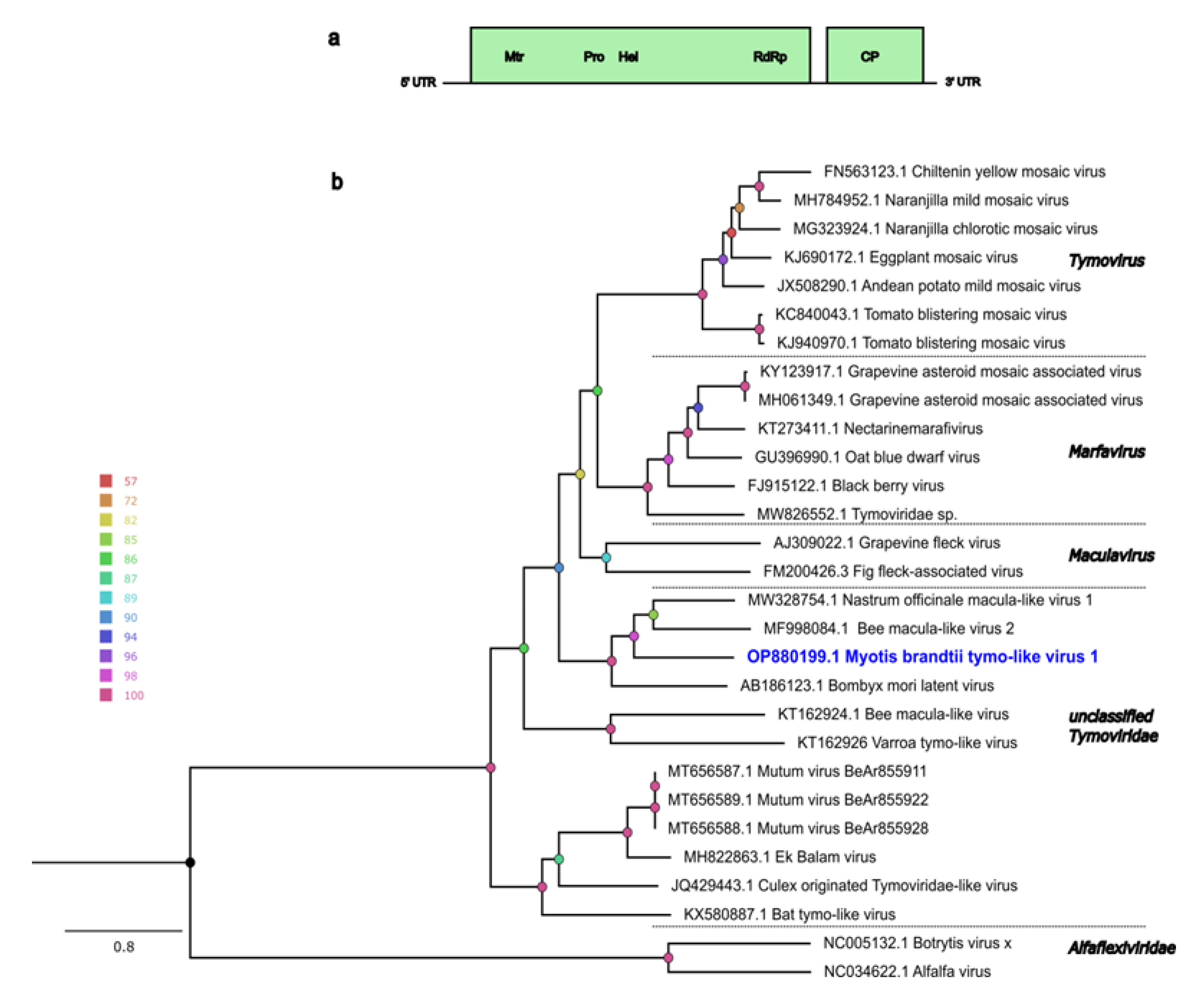
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
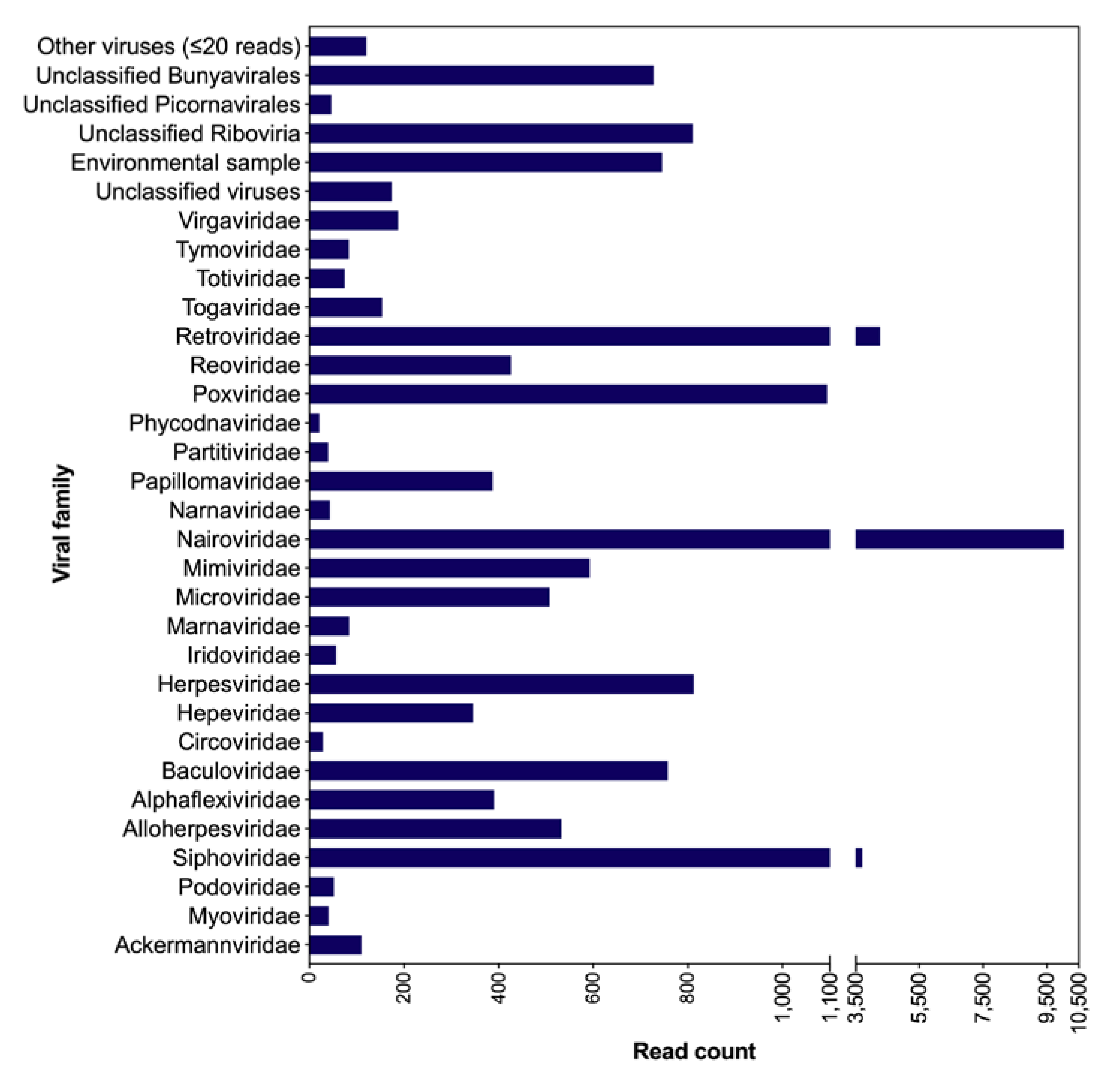
3.1. Taxonomic Classification of Viral Reads from Bat Saliva
3.2. Nairoviridae Family
Genome Characteristics of ISKV
3.3. Other Viral Genomes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, I.; Broos, A.; de Jong, C.; Zeddeman, A.; Smith, C.; Smith, G.; Moore, F.; Barr, J.; Crameri, G.; Marsh, G.; et al. Identifying Hendra virus diversity in pteropid bats. PLoS One 2011, 6, e25275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woon, A.P.; Boyd, V.; Todd, S.; Smith, I.; Klein, R.; Woodhouse, I.B.; Riddell, S.; Crameri, G.; Bingham, J.; Wang, L.F.; et al. Acute experimental infection of bats and ferrets with Hendra virus: Insights into the early host response of the reservoir host and susceptible model species. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, A.; Mbala Kingebeni, P.; Ndimbo Kumugo, S.P.; Lempu, G.; Butel, C.; Serrano, L.; Vidal, N.; Thaurignac, G.; Esteban, A.; Mukadi Bamuleka, D.; et al. Investigating the Circulation of Ebola Viruses in Bats during the Ebola Virus Disease Outbreaks in the Equateur and North Kivu Provinces of the Democratic Republic of Congo from 2018. Pathogens 2021, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, E.M.; Kumulungui, B.; Pourrut, X.; Rouquet, P.; Hassanin, A.; Yaba, P.; Delicat, A.; Paweska, J.T.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Swanepoel, R. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature 2005, 438, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amman, B.R.; Jones, M.E.; Sealy, T.K.; Uebelhoer, L.S.; Schuh, A.J.; Bird, B.H.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Martin, B.E.; Nichol, S.T.; Towner, J.S. Oral shedding of Marburg virus in experimentally infected Egyptian fruit bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacLean, O.A.; Lytras, S.; Weaver, S.; Singer, J.B.; Boni, M.F.; Lemey, P.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Robertson, D.L. Natural selection in the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in bats created a generalist virus and highly capable human pathogen. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelomanantsoa, N.A.F.; Guth, S.; Andrianiaina, A.; Andry, S.; Gentles, A.; Ranaivoson, H.C.; Brook, C.E. The zoonotic potential of bat-borne coronaviruses. Emerg. Top Life Sci. 2020, 4, 353–369. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Aravena, M.; McKee, C.; Gamble, A.; Lunn, T.; Morris, A.; Snedden, C.E.; Yinda, C.K.; Port, J.R.; Buchholz, D.W.; Yeo, Y.Y.; et al. Ecology, evolution and spillover of coronaviruses from bats. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocati, N.; Petrucci, A.G.; Di Giovanni, P.; Masulli, M.; Di Ilio, C.; De Laurenzi, V. Bat-man disease transmission: Zoonotic pathogens from wildlife reservoirs to human populations. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guth, S.; Mollentze, N.; Renault, K.; Streicker, D.G.; Visher, E.; Boots, M.; Brook, C.E. Bats host the most virulent-but not the most dangerous-zoonotic viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113628119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, C.; Brinkmann, A.; Radonic, A.; Dabrowski, P.W.; Muhldorfer, K.; Nitsche, A.; Wibbelt, G.; Kurth, A. The virome of German bats: Comparing virus discovery approaches. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paskey, A.C.; Ng, J.H.J.; Rice, G.K.; Chia, W.N.; Philipson, C.W.; Foo, R.J.H.; Cer, R.Z.; Long, K.A.; Lueder, M.R.; Frey, K.G.; et al. The temporal RNA virome patterns of a lesser dawn bat (Eonycteris spelaea) colony revealed by deep sequencing. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Altan, E.; Reyes, G.; Halstead, B.; Deng, X.; Delwart, E. Virome of Bat Guano from Nine Northern California Roosts. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelli, D.; Moreno, A.; Lavazza, A.; Bresaola, M.; Canelli, E.; Boniotti, M.B.; Cordioli, P. Identification of Mammalian orthoreovirus type 3 in Italian bats. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, C.; Lesnik, R.; Brinkmann, A.; Ebinger, A.; Radonic, A.; Nitsche, A.; Muhldorfer, K.; Wibbelt, G.; Kurth, A. Isolation and characterization of three mammalian orthoreoviruses from European bats. PLoS One 2012, 7, e43106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lumio, J.; Hillbom, M.; Roine, R.; Ketonen, L.; Haltia, M.; Valle, M.; Neuvonen, E.; Lahdevirta, J. Human rabies of bat origin in Europe. Lancet 1986, 1, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, C.; Nitsche, A.; Kurth, A. Update on Potentially Zoonotic Viruses of European Bats. Vaccines 2021, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, A.; Kohl, C.; Radonic, A.; Dabrowski, P.W.; Muhldorfer, K.; Nitsche, A.; Wibbelt, G.; Kurth, A. First detection of bat-borne Issyk-Kul virus in Europe. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Vov D., K.; Kostiukov, M.A.; Daniiarov, O.A.; Tukhtaev, T.M.; Sherikov, B.K. Outbreak of arbovirus infection in the Tadzhik SSR due to the Issyk-Kul virus (Issyk-Kul fever). Vopr. Virusol. 1984, 29, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- de Jong, J.; Gylje Blank, S.; Ebenhard, T.; Ahlén, I. Fladdermusfaunan i Sverige-arternas utbredning och status 2020. Fauna & flora 2020, 2–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hammarin, A.L.; Berndtsson, L.T.; Falk, K.; Nedinge, M.; Olsson, G.; Lundkvist, A. Lyssavirus-reactive antibodies in Swedish bats. Infect Ecol Epidemiol 2016, 6, 31262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lwande, O.W.; Thalin, T.; de Jong, J.; Sjodin, A.; Naslund, J.; Evander, M.; Ecke, F. Alphacoronavirus in a Daubenton’s Myotis Bat (Myotis daubentonii) in Sweden. Viruses 2022, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholleti, H.; de Jong, J.; Blomstrom, A.L.; Berg, M. Characterization of Pipistrellus pygmaeus Bat Virome from Sweden. Viruses 2022, 14, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Beier, S.; Flade, I.; Gorska, A.; El-Hadidi, M.; Mitra, S.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Tappu, R. MEGAN Community Edition - Interactive Exploration and Analysis of Large-Scale Microbiome Sequencing Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soding, J.; Biegert, A.; Lupas, A.N. The HHpred interactive server for protein homology detection and structure prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, (Web Server issue). W244–W248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49,(D1), D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stecher, G.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) for macOS. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; Qin, X.C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.P.; Eden, J.S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, C.; Kurth, A. European bats as carriers of viruses with zoonotic potential. Viruses 2014, 6, 3110–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geldenhuys, M.; Mortlock, M.; Weyer, J.; Bezuidt, O.; Seamark, E.C.J.; Kearney, T.; Gleasner, C.; Erkkila, T.H.; Cui, H.; Markotter, W. A metagenomic viral discovery approach identifies potential zoonotic and novel mammalian viruses in Neoromicia bats within South Africa. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0194527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazov, C.M.; Belsham, G.J.; Botner, A.; Rasmussen, T.B. Full-Genome Sequences of Alphacoronaviruses and Astroviruses from Myotis and Pipistrelle Bats in Denmark. Viruses 2021, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolatti, E.M.; Viarengo, G.; Zorec, T.M.; Cerri, A.; Montani, M.E.; Hosnjak, L.; Casal, P.E.; Bortolotto, E.; Di Domenica, V.; Chouhy, D.; et al. Viral Metagenomic Data Analyses of Five New World Bat Species from Argentina: Identification of 35 Novel DNA Viruses. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, I.; Zorec, T.M.; Lojkic, I.; Kresic, N.; Poljak, M.; Cliquet, F.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Wasniewski, M.; Zrncic, V.; Cukusic, A.; et al. Viral Metagenomic Profiling of Croatian Bat Population Reveals Sample and Habitat Dependent Diversity. Viruses 2020, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Hardmeier, I.; Aeberhard, N.; Qi, W.; Schoenbaechler, K.; Kraettli, H.; Hatt, J.M.; Fraefel, C.; Kubacki, J. Metagenomic analysis of fecal and tissue samples from 18 endemic bat species in Switzerland revealed a diverse virus composition including potentially zoonotic viruses. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0252534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.J.; Wang, J.; Todd, A.K.; Bissielo, A.B.; Yen, S.; Strydom, H.; Moore, N.E.; Ren, X.; Huang, Q.S.; Carter, P.E.; et al. Evaluation of rapid and simple techniques for the enrichment of viruses prior to metagenomic virus discovery. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 195, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose, R.; Constantinides, B.; Tapinos, A.; Robertson, D.L.; Prosperi, M. Challenges in the analysis of viral metagenomes. Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lvov, D.K.; Karas, F.R.; Timofeev, E.M.; Tsyrkin, Y.M.; Vargina, S.G.; Veselovskaya, O.V.; Osipova, N.Z.; Grebenyuk, Y.I.; Gromashevski, V.L.; Steblyanko, S.N.; et al. “Issyk-Kul” virus, a new arbovirus isolated from bats and Argas (Carios) vespertilionis (Latr., 1802) in the Kirghiz S.S.R. Brief report. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch 1973, 42, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, P.J.; Widen, S.G.; Firth, C.; Blasdell, K.R.; Wood, T.G.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.; Guzman, H.; Tesh, R.B.; Vasilakis, N. Genomic Characterization of Yogue, Kasokero, Issyk-Kul, Keterah, Gossas, and Thiafora Viruses: Nairoviruses Naturally Infecting Bats, Shrews, and Ticks. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atkinson, B.; Marston, D.A.; Ellis, R.J.; Fooks, A.R.; Hewson, R. Complete Genomic Sequence of Issyk-Kul Virus. Genome Announc 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostiukov, M.A.; Bulychev, V.P.; Lapina, T.F. Experimental infection of Aedes caspius caspius Pall. mosquitoes on dwarf bats, Vespertilio pipistrellus, infected with the Issyk-Kul virus and its subsequent transmission to susceptible animals. Med Parazitol (Mosk) 1982, 51, 78–79. [Google Scholar]
- Service, M.W. Encyclopedia Of Arthropod-Transmitted Infections Of Man And Domesticated Animals, 1st ed.; CABI: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 231–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hornok, S.; Szoke, K.; Tu, V.T.; Kontschan, J.; Takacs, N.; Sandor, A.D.; Halajian, A.; Foldvari, G.; Estok, P.; Plantard, O.; et al. Mitochondrial gene heterogeneity of the bat soft tick Argas vespertilionis (Ixodida: Argasidae) in the Palaearctic. Parasit Vectors 2017, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandor, A.D.; Corduneanu, A.; Peter, A.; Mihalca, A.D.; Barti, L.; Csosz, I.; Szoke, K.; Hornok, S. Bats and ticks: Host selection and seasonality of bat-specialist ticks in eastern Europe. Parasit Vectors 2019, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandor, A.D.; Mihalca, A.D.; Domsa, C.; Peter, A.; Hornok, S. Argasid Ticks of Palearctic Bats: Distribution, Host Selection, and Zoonotic Importance. Front Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 684737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergonul, O. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006, 6, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, F.J.; Spencer, D.C.; Leman, P.A.; Patterson, B.; Swanepoel, R. Investigation of tick-borne viruses as pathogens of humans in South Africa and evidence of Dugbe virus infection in a patient with prolonged thrombocytopenia. Epidemiol Infect 1996, 116, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasteva, S.; Jara, M.; Frias-De-Diego, A.; Machado, G. Nairobi Sheep Disease Virus: A Historical and Epidemiological Perspective. Front Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woessner, R.; Grauer, M.T.; Langenbach, J.; Dobler, G.; Kroeger, J.; Mielke, H.G.; Mueller, P.; Haass, A.; Treib, J. The Erve virus: Possible mode of transmission and reservoir. Infection 2000, 28, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, S.; Suda, Y.; Nagata, N.; Fukushi, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurosu, T.; Mizutani, T.; Saijo, M.; Shimojima, M. Characterization of Keterah orthonairovirus and evaluation of therapeutic candidates against Keterah orthonairovirus infectious disease. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumagalli, M.J.; de Souza, W.M.; de Araujo, J.; Modha, S.; Queiroz, L.H.; Durigon, E.L.; Murcia, P.R.; Figueiredo, L.T.M. Krykfeie dicistrovirus: A novel dicistrovirus in velvety free-tailed bats from Brazil. Infect Genet Evol. 2019, 75, 104036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmam, S.; Hul, V.; Bigot, T.; Hoem, T.; Gorman, C.; Duong, V.; Dussart, P.; Cappelle, J.; Eloit, M. A Novel Polycipiviridae Virus Identified in Pteropus lylei Stools. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olendraite, I.; Lukhovitskaya, N.I.; Porter, S.D.; Valles, S.M.; Firth, A.E. Polycipiviridae: A proposed new family of polycistronic picorna-like RNA viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lv, X.; Zhai, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, D.; Rayner, S.; Tang, Q.; Liang, G. Genomic characterization of a novel virus of the family Tymoviridae isolated from mosquitoes. PLoS One 2012, 7, e39845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.M.Q.; Adams, M.J.; Carstens, E.B.; Lefkowitz, E.J. Virus Taxonomy: Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 944–952. [Google Scholar]

| Segment | Length, nt | ORF Position | ORF Length, nt/aa | Length of 5’ UTR, nt | Length of 3’ UTR, nt | % of ID, nt Level 1 | % of ID, aa Level 2 | Closest Virus Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 1816 | 45–1502 | 1448/485 | 44 | 314 | 97.91 | 99.59 | Issyk-Kul virus isolate LEZ 86-787 (KR537443) |
| M | 5267 | 15–4828 | 4914/1637 | 14 | 339 | 93.07 | 95.17 | Issyk-Kul virus isolate LEIV-315K (KR709220) |
| L | 12197 | 44–12022 | 11979/3992 | 43 | 175 | 98.61 | 99.62 | Issyk-Kul virus isolate LEZ 86-787 (KR537441) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cholleti, H.; de Jong, J.; Blomström, A.-L.; Berg, M. Investigation of the Virome and Characterization of Issyk-Kul Virus from Swedish Myotis brandtii Bats. Pathogens 2023, 12, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12010012
Cholleti H, de Jong J, Blomström A-L, Berg M. Investigation of the Virome and Characterization of Issyk-Kul Virus from Swedish Myotis brandtii Bats. Pathogens. 2023; 12(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleCholleti, Harindranath, Johnny de Jong, Anne-Lie Blomström, and Mikael Berg. 2023. "Investigation of the Virome and Characterization of Issyk-Kul Virus from Swedish Myotis brandtii Bats" Pathogens 12, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12010012
APA StyleCholleti, H., de Jong, J., Blomström, A.-L., & Berg, M. (2023). Investigation of the Virome and Characterization of Issyk-Kul Virus from Swedish Myotis brandtii Bats. Pathogens, 12(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12010012










