Impact of Theaflavins-Enriched Tea Leaf Extract TY-1 against Surrogate Viruses of Human Norovirus: In Vitro Virucidal Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
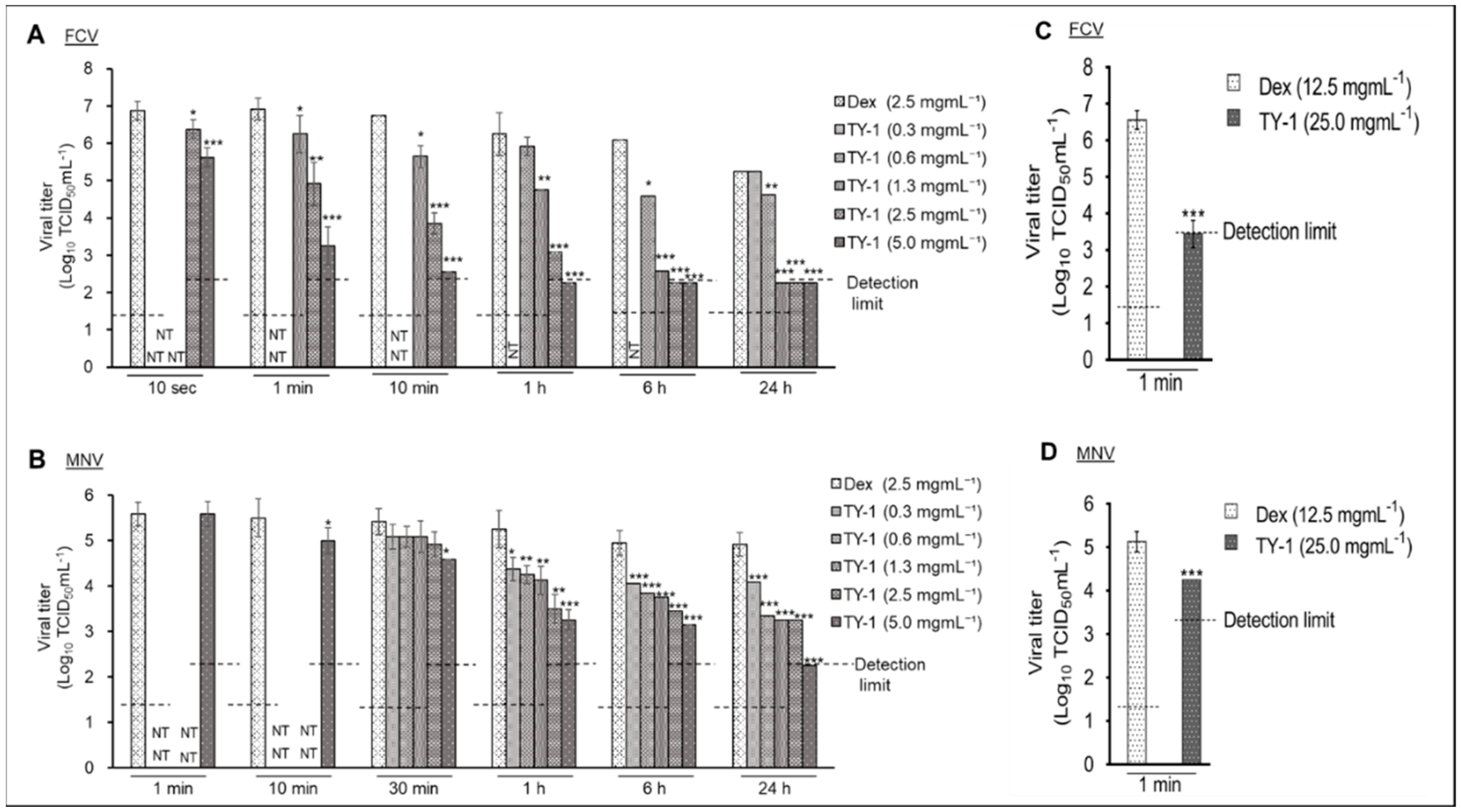
2.1. Virucidal Effects of TY-1 on FCV and MNV
2.2. Virucidal Effect of TY-1 on FCV and MNV on a Dry Surface
2.3. Effect of TY-1 on MNV Structural Protein
2.4. Effect of TY-1 on FCV and MNV Genomes
2.5. Effect of TY-1 on FCV and MNV Viral Particles
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Viruses and Cells
4.2. Preparation of Test Solution Samples
4.3. Evaluation of FCV and MNV Virucidal Effect of TY-1
4.4. Evaluation of FCV and MNV Virucidal Effect of TY-1 on a Dry Surface
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. RT-PCR Analysis
4.7. Observation of Morphology of FCV and MNV Virions by TEM
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bányai, K.; Estes, M.K.; Martella, V.; Parashar, U.D. Viral gastroenteritis. The Lancet 2018, 392, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapikian, A.Z.; Wyatt, R.G.; Dolin, R.; Thornhill, T.S.; Kalica, A.R.; Chanock, R.M. Visualization by immune electron microscopy of a 27-nm particle associated with acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. J. Virol. 1972, 10, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hall, A.J.; Robinson, A.E.; Verhoef, L.; Premkumar, P.; Parashar, U.D.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infec. Dis. 2014, 14, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmar, R.L.; Ramani, S.; Estes, M. Human noroviruses: Recent advances in a 50-year history. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, S.M.; Lopman, B.A.; Ozawa, S.; Hall, A.J.; Lee, B.Y. Global economic burden of norovirus gastroenteritis. PLoS ONE 2018, 11, e0151219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Chien, Y.W.; Papafragkou, E.; Hsiao, H.M.; Jaykus, L.A.; Moe, C. Persistence of human noroviruses on food preparation surfaces and human hands. Food Environ. Virol. 2009, 1, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamhoujeb, S.; Fliss, I.; Ngazoa, S.E.; Jean, J. Molecular study of the persistence of infectious human norovirus on food-contact surfaces. Food Environ. Virol. 2009, 1, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebbi-Simmons, D.; Alhejaili, M.; Janes, M.; King, J.; Xu, W. Survival and inactivation of human norovirus GII. 4 Sydney on commonly touched airplane cabin surfaces. AIMS Public Health 2020, 7, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopman, B.; Gastanaduy, P.; Park, G.W.; Hall, A.J.; Parashar, U.D.; Vinje, J. Environmental transmission of norovirus gastroenteritis. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; Knight, A.; Richards, G.P. Persistence and elimination of human norovirus in food and on food contact surfaces: A critical review. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1273–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magulski, T.; Paulmann, D.; Bischoff, B.; Becker, B.; Steinmann, E.; Steinmann, J.; Goroncy-Bermes, P.; Steinmann, J. Inactivation of murine norovirus by chemical biocides on stainless steel. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, M.; Mattison, K.; Fliss, I.; Jean, J. Efficacy of oxidizing disinfectants at inactivating murine norovirus on ready-to-eat foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 219, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonta, W.; Mauroy, A.; Farnir, F.; Thiry, E. Comparative virucidal efficacy of seven disinfectants against murine norovirus and feline calicivirus, surrogates of human norovirus. Food Environ. Virol. 2016, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duizer, E.; Schwab, K.J.; Neill, F.H.; Atmar, R.L.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Estes, M.K. Laboratory efforts to cultivate noroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettayebi, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Murakami, K.; Broughman, J.R.; Karandikar, U.; Tenge, V.R.; Neill, F.H.; Blutt, S.E.; Zeng, X.-L.; Qu, L.; et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science 2016, 353, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dycke, J.; Ny, A.; Conceição-Neto, N.; Maes, J.; Hosmillo, M.; Cuvry, A. A robust human norovirus replication model in zebrafish larvae. PLoS Path. 2019, 15, e1008009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinjé, J. Advances in laboratory methods for detection and typing of norovirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duizer, E.; Bijkerk, P.; Rockx, B.; De Groot, A.; Twisk, F.; Koopmans, M. Inactivation of caliciviruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4538–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tree, J.A.; Adams, M.R.; Lees, D.N. Disinfection of feline calicivirus (a surrogate for Norovirus) in wastewaters. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wobus, C.E.; Thackray, L.B.; Virgin IV, H.W. Murine norovirus: A model system to study norovirus biology and pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5104–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarasu, P.; Hsu, H.Y.; Moore, M.D. Research progress in viral inactivation utilizing human norovirus surrogates. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Virucidal Effectiveness Testing Using Feline Calicivirus as Surrogate for Norovirus. 2017. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pesticideregistration/virucidal-effectiveness-testing-using-feline-calicivirus-surrogate norovirus (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- Karst, S.M.; Wobus, C.E.; Lay, M.; Davidson, J. STAT1-dependent innate immunity to a Norwalk-like virus. Science 2003, 299, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromeans, T.L.; Kahler, A.M.; Hill, V.R. Inactivation of adenoviruses, enteroviruses, and murine norovirus in water by free chlorine and monochloramine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahler, A.M.; Cromeans, T.L.; Roberts, J.M.; Hill, V.R. Effects of source water quality on chlorine inactivation of adenovirus, coxsackievirus, echovirus, and murine norovirus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5159–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraisse, A.; Temmam, S.; Deboosere, N.; Guillier, L.; Delobel, A.; Maris, P.; Vialette, M.; Morin, T.; Perelle, S. Comparison of chlorine and peroxyacetic-based disinfectant to inactivate Feline calicivirus, Murine norovirus and Hepatitis A virus on lettuce. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, P.; Topping, J.R.; Bellamy, K.; Fotheringham, V.; Gray, J.J.; Golding, J.P.; Wiseman, G.; Knight, A.I. Virolysis of feline calicivirus and human GII. 4 norovirus following chlorine exposure under standardized light soil disinfection conditions. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predmore, A.; Li, J. Enhanced removal of a human norovirus surrogate from fresh vegetables and fruits by a combination of surfactants and sanitizers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4829–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaivani, R.; Bakiyalakshmi, S.V.; Arulmozhi, P. A study on evaluation and effectiveness of herbal hand sanitizer and its anti bacterial activity. Int. J. Trend Sci. Res. Dev. 2018, 2, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Daverey, A.; Dutta, K. COVID-19: Eco-friendly hand hygiene for human and environmental safety. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabadi, R.B.; Kolkar, K.P.; Meti, N.T.; Chalannavar, R.K. Role of plant based hand sanitizers during the recent outbreak of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) disease (Covid-19). Significances Bioeng. Biosci. 2021, 5, 458–468. [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto, M. Manufacturing method for Theafavins using raw tea leaves. Japanese Patent No 4817206, 9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, Y.; Tamura, K.; Jamsransuren, D.; Matsuda, S.; Ogawa, H. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 inactivation activity of the polyphenol-rich tea leaf extract with concentrated theaflavins and other virucidal catechins. Molecules 2021, 26, 4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, I.M.A.; Ogawa, H.; Takeda, Y. In vitro virucidal activity of the theaflavin-concentrated tea extract TY-1 against influenza A virus. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 76, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizaquível, P.; Azizkhani, M.; Aznar, R.; Sánchez, G. The effect of essential oils on norovirus surrogates. Food Control 2013, 32, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, D.H. Phytocompounds for the control of human enteric viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 4, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; D’Souza, D.H. Grape seed extract for control of human enteric viruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3982–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Howell, A.B.; D’Souza, D.H. The effect of cranberry juice and cranberry proanthocyanidins on the infectivity of human enteric viral surrogates. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Sangster, M.Y.; D’Souza, D.H. In vitro effects of pomegranate juice and pomegranate polyphenols on foodborne viral surrogates. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Kawabata, R.; Irie, T.; Nakai, Y.; Tohya, Y.; Sakaguchi, T. Inactivation of pathogenic viruses by plant-derived tannins:Strong effects of extracts from persimmon (Diospyros kaki) on a broad range of viruses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amankwaah, C.; Li, J.; Lee, J.; Pascall, M.A. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan-based films enriched with green tea extracts on murine norovirus, Escherichia coli, and Listeria innocua. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 2, 3941924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randazzo, W.; Falco, I.; Aznar, R.; Sanchez, G. Effect of green tea extract on enteric viruses and its application as natural sanitizer. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, Y.; Murata, T.; Jamsransuren, D.; Suganuma, K.; Kazami, Y.; Batkhuu, J.; Badral, D.; Ogawa, H. Saxifraga spinulosa-derived components rapidly inactivate multiple viruses including SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2020, 12, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliver, D.O. Capsid and infectivity in virus detection. Food Environ. Virol. 2009, 1, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilling, D.H.; Kitajima, M.; Torrey, J.T.; Bright, K.R. Mechanisms of antiviral action of plant antimicrobials against murine norovirus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4898–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.G.; Kim, K.L.; Shin, S.B.; Son, K.T.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Cho, E.J.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, E.W.; et al. Antiviral activity of green tea catechins against feline calicivirus as a surrogate for norovirus. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromeans, T.; Park, G.W.; Costantini, V. Comprehensive comparison of cultivable norovirus surrogates in response to different inactivation and disinfection treatments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5743–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kniel, K.E. The makings of a good human norovirus surrogate. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, G.P. Critical review of norovirus surrogates in food safety research: Rationale for considering volunteer studies. Food Environ. Virol. 2012, 4, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Nakazawa, M.; Ohshima, C.; Sato, M.; Tsuchiya, T.; Takeuchi, A.; Kunou, M.; Kuda, T.; Kimura, B. Heat-denatured lysozyme inactivates murine norovirus as a surrogate human norovirus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, M.E.; Tan, M.T.H.; Li, D. Influence of fucosidaseproducing bifidobacteria on the HBGA antigenicity of oyster digestive tissue and the associated norovirus binding. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 340, 109058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, I.; Díaz-Reolid, A.; Randazzo, W.; Sanchez, G. Green tea extract assisted low-temperature pasteurization to inactivate enteric viruses in juices. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 334, 108809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Ogawa, H.; Bui, V.N.; Inoue, H.; Fukuda, J.; Ohba, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nakamura, K. Inactivation of high and low pathogenic avian influenza virus H5 subtypes by copper ions incorporated in zeolite-textile materials. Antivir. Res. 2012, 93, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, I.M.A.; Jamsransuren, D.; Matsuda, S.; Ogawa, H.; Takeda, Y. Impact of Theaflavins-Enriched Tea Leaf Extract TY-1 against Surrogate Viruses of Human Norovirus: In Vitro Virucidal Study. Pathogens 2022, 11, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11050533
Mohamed IMA, Jamsransuren D, Matsuda S, Ogawa H, Takeda Y. Impact of Theaflavins-Enriched Tea Leaf Extract TY-1 against Surrogate Viruses of Human Norovirus: In Vitro Virucidal Study. Pathogens. 2022; 11(5):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11050533
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Israa M. A., Dulamjav Jamsransuren, Sachiko Matsuda, Haruko Ogawa, and Yohei Takeda. 2022. "Impact of Theaflavins-Enriched Tea Leaf Extract TY-1 against Surrogate Viruses of Human Norovirus: In Vitro Virucidal Study" Pathogens 11, no. 5: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11050533
APA StyleMohamed, I. M. A., Jamsransuren, D., Matsuda, S., Ogawa, H., & Takeda, Y. (2022). Impact of Theaflavins-Enriched Tea Leaf Extract TY-1 against Surrogate Viruses of Human Norovirus: In Vitro Virucidal Study. Pathogens, 11(5), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11050533





