Suppressive Effect of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris YRC3780 on a Murine Model of Japanese Cedar Pollinosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of YRC3780
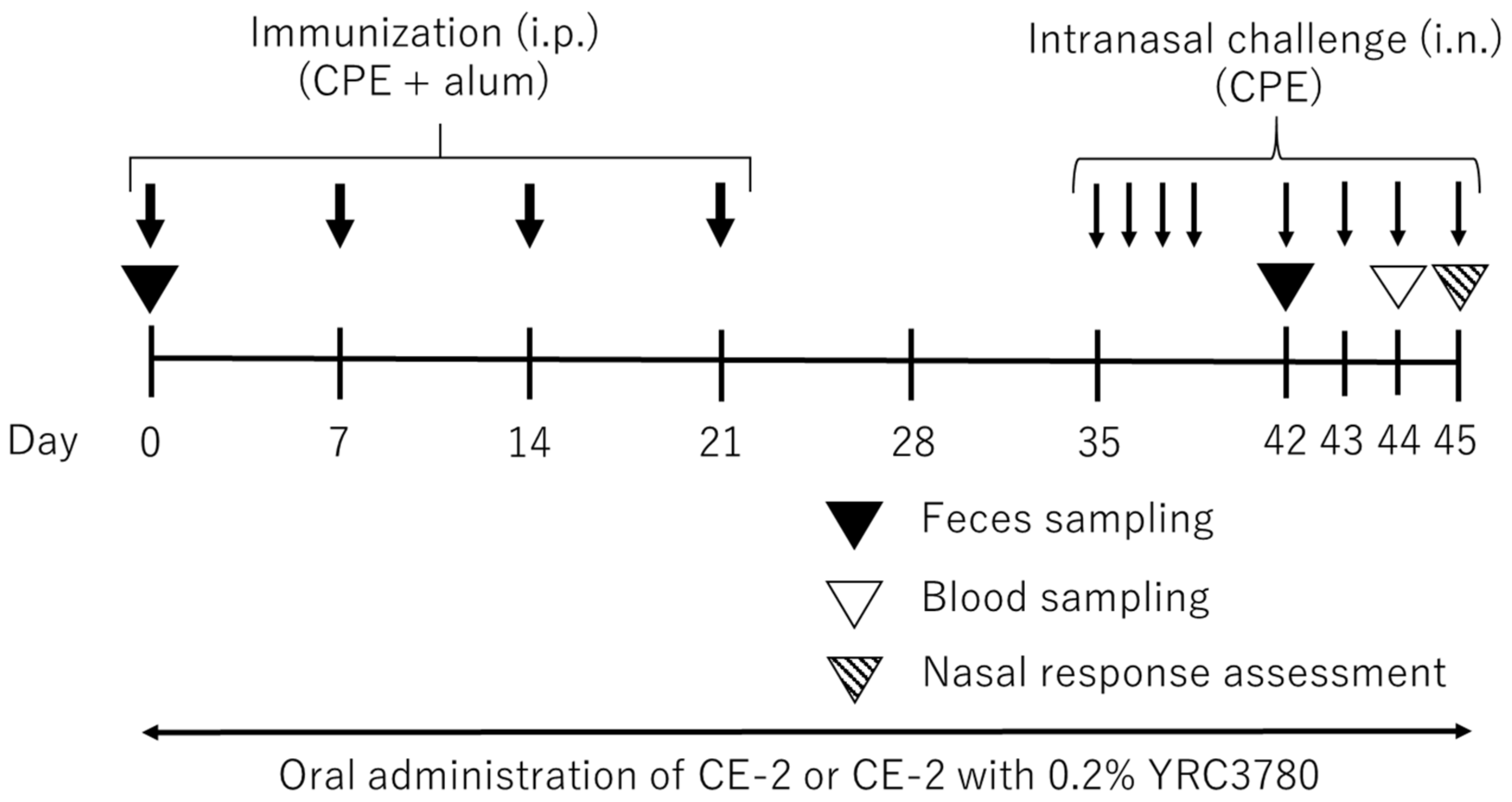
2.2. Administration of YRC3780 to Mice
2.3. Mouse JCP Model
2.4. Measurement of Serum IgE Level
2.5. Microbiota Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
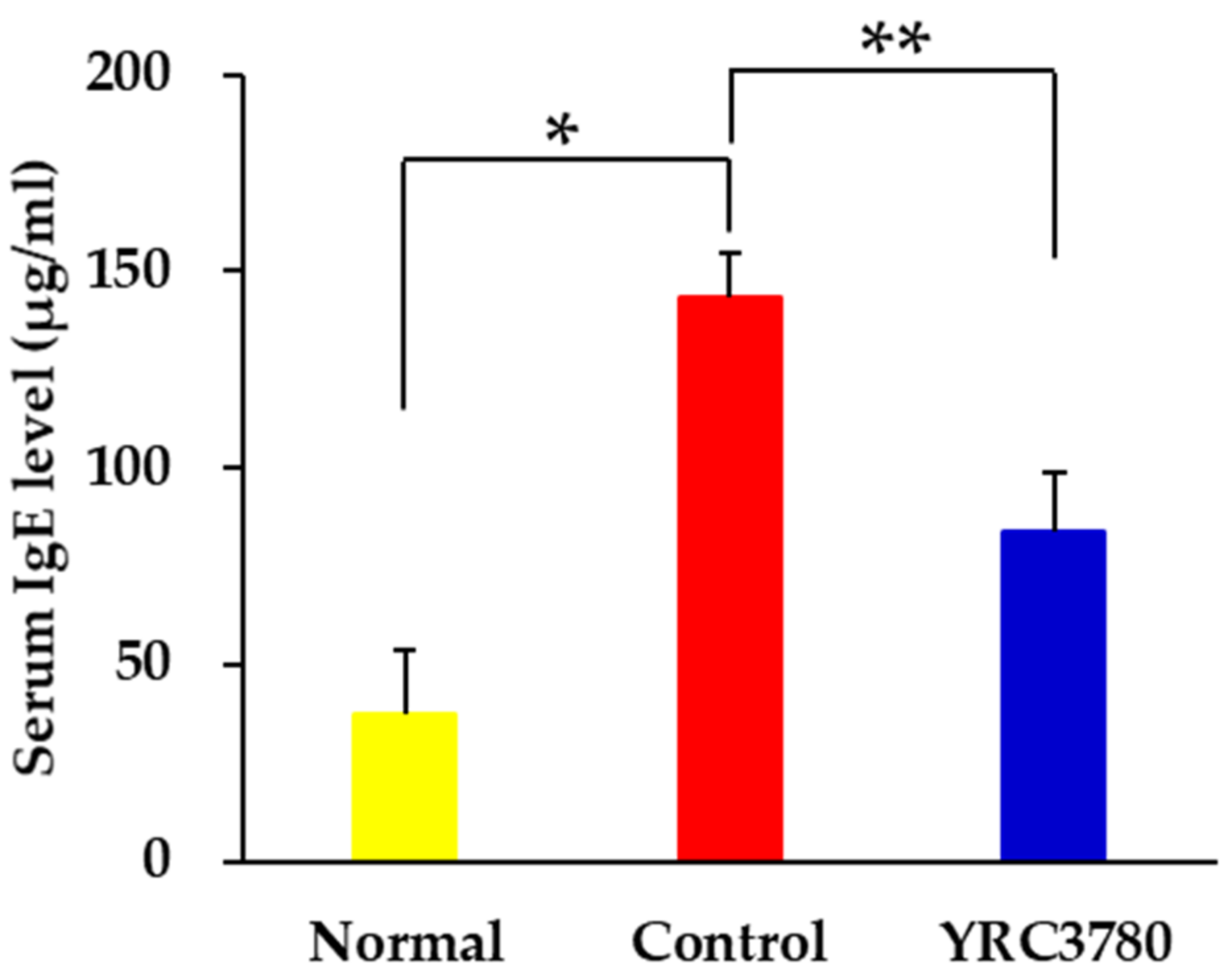
3.1. Effect of YRC3780 on Serum IgE Response
3.2. Effect on Nasal Responses
3.3. Effect on Eosinophil Accumulation in the Nasal Mucosa
3.4. Influence on Fecal Microbiota
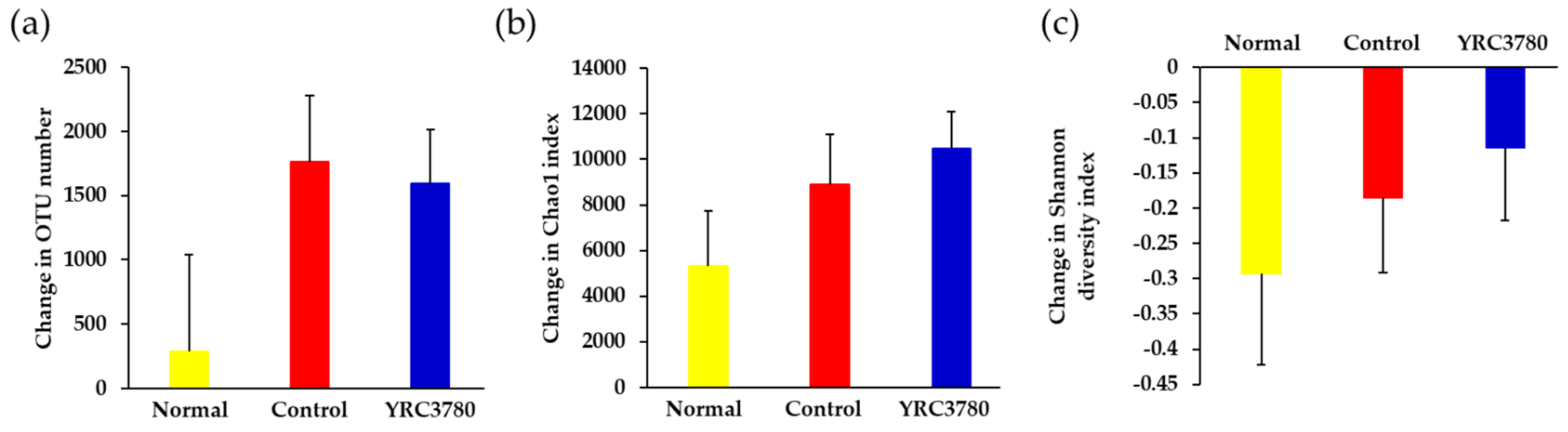
3.4.1. Diversity of Microbiota
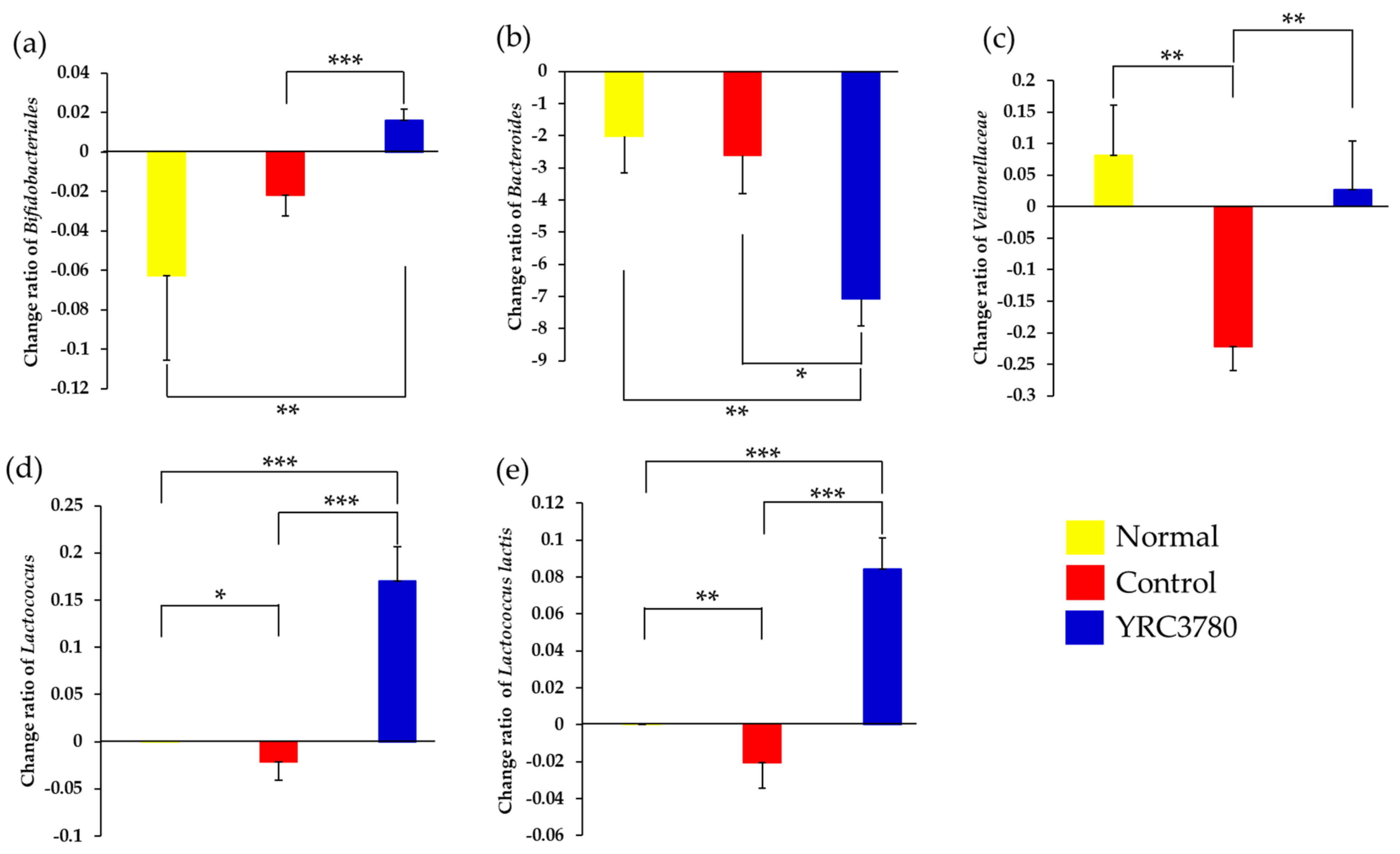
3.4.2. Bacterial Species
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsubara, A.; Sakashita, M.; Gotoh, M.; Kawashima, K.; Matsuoka, T.; Kondo, S.; Yamada, T.; Takeno, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Urashima, M.; et al. Epidemiological Survey of Allergic Rhinitis in Japan 2019. J. Otolaryngol. Japan. 2020, 123, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, M. Practical guideline for the management of allergic rhinitis in Japan (2020 version). Arerugi 2021, 70, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda-Yamamoto, M.; Nagai, H.; Ema, K.; Kanda, E.; Okada, N.; Yasue, M. Effects and safety of consecutive intake of Benifuuki green tea and enhancement of the effect by ginger extract in subjects with Japanese cedar-pollinosis. J. Japan. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubota, N.; Suzuki, S.; Kakiyama, S.; Shiinoki, J.; Nakamori, K.; Igarashi, T.; Shida, K.; Mizusawa, N. Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Parallel Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of a Citrus Juice Fermented with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum YIT 0132 for Japanese Cedar Pollinosis. Japan. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 49, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, D.; Wakabayashi, H.; Watanabe, H.; Nishida, S.; Iino, H. A double-blind trial of Lactobacillus paracasei strain KW3110 administration for immunomodulation in patients with pollen allergy. Allergol. Int. 2005, 54, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishida, Y.; Nakamura, F.; Kanzato, H.; Sawada, D.; Yamamoto, N.; Kagata, H.; Oh-Ida, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Fujiwara, S. Effect of Milk fermented with Lactobacillus acidophilus strain L-92 on symptoms of Japanese cedar pollen allergy: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.-Z.; Kondo, S.; Yanagisawa, N.; Takahashi, N.; Odamaki, T.; Iwabuchi, N.; Miyaji, K.; Iwatsuki, K.; Togashi, H.; Enomoto, K. Probiotics in the treatment of Japanese cedar pollinosis: A double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2006, 36, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.-Z.; Kondo, S.; Yanagisawa, N.; Miyaji, K.; Enomoto, K.; Sakoda, T.; Iwatsuki, K.; Enomoto, T. Clinical efficacy of probiotic Bifidobacterium longum for the treatment of symptoms of Japanese cedar pollen allergy in subjects evaluated in an environmental exposure unit. Allergol. Int. 2007, 56, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, M.; Shikina, T.; Morihana, T.; Hayama, M.; Kajimoto, O.; Sakamoto, A.; Kajimoto, Y.; Watanabe, O.; Nonaka, C.; Shida, K.; et al. Effects of probiotics on allergic rhinitis induced by Japanese cedar pollen: Randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 143, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, G.; Akagi, H.; Okada, C.; Hirano, A.; Amano, Y.; Ohmura, E.; Nakashige, Y.; Sunada, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Clinical effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus strain L-55-contained yogurt on symptoms of Japanese cedar pollen allergy. Japan. J. Allergol. 2012, 61, 628–641. [Google Scholar]
- Niino, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Sagesaka, Y.; Sakoda, T.; Enomoto, M. Palliative efficacy of a drink containing Enterococcus faecalis EC-12 for alleviating symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis triggered by cedar pollen. Japan. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 40, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, K.; Arai, S.; Iwabuchi, N.; Xiao, J.G.; Abe, F.; Enomoto, M. Effect of Dairy Products Containing Bifidobacterium longum BB536 on Symptoms of Perennial Allergic Rhinitis―A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study. Japan. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 48, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, K.; Hirota, T.; Onodera, T.; Nagayama, K.; Yasue, M.; Nakamura, Y. Efficacy of Heat-killed Lactobacillus acidophilus L-92 on Perennial Allergic Rhinitis in Subjects with Mild to Moderate Symptoms-A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Parallel Group Comparison Study. Japan. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 46, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, M.; Kobatake, E.; Obuchi, S.; Iwai, M.; Ichikawa, K.; Kabuki, T.; Enomoto, T. Intake safety of Lactobacillus helveticus SBT2171 and its effects on nasal and ocular symptoms associated with mites and house dust: An open-label study and a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2019, 9, 52–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, S.; Oe, M.; Kamijyo, F.; Shimada, K.; Okuyama, Y.; Nishiyama, H.; Matsuoka, R.; Masuda, Y.; Kanemitsu, T.; Enomoto, T. Acetic Acid Bacteria (Gluconacetobacter hansenii GK-1) Relieves Nasal Discomfort—A Randomized Double-blind Placebo-controlled Study. Japan. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 47, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Motoshima, H.; Uchida, K.; Watanabe, T.; Tsukasaki, F. Immunopotentiating effects of kefir and kefir isolates in mice. In Proceedings of the 26th International Dairy Congress, Paris, France, 24–27 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Nakajima-Adachi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, W.; Hiraide, E.; Morinaga, M.; Nakagawa, R.; Nakamura, S.; Takano, T.; et al. Regulation of Th2 responses by Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris YRC3780 alleviates DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis in the mouse model. J. Funct. Foods. 2022, 94, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K.; Motoshima, H.; Katano, N.; Hachimura, S.; Tanaka, A.; Nishihira, J. Effect of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris YRC3780 on birch pollinosis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Funct. Foods. 2018, 43, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K.; Fujioka, I.; Kato, T.; Oda, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Motoshima, H.; Katano, N.; Hachimura, S.; Enomoto, T. Effect of drinkable yogurt containing Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris YRC3780 on symptoms of perennial allergic rhinitis—A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group comparison study. Japan. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 49, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Wakasa, Y.; Takagi, H.; Hirose, S.; Yang, L.; Saeki, M.; Nishimura, T.; Kaminuma, O.; Hiroi, T.; Takaiwa, F. Oral immunotherapy with transgenic rice seed containing destructed Japanese cedar pollen allergens, Cryj1 and cryj2, against Japanese cedar pollinosis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2013, 11, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wijk, R.G.; Dieges, P.H. Comparison of nasal responsiveness to histamine, methacholine and phentolamine in allergic rhinitis patients and controls. Clin. Allergy 1987, 17, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Kaminuma, O.; Saeki, M.; Kitamura, N.; Gotoh, M.; Mori, A.; Hiroi, T. Effects of anti-allergic drugs on T cell-mediated nasal hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of allergic rhinitis. Allergol. Int. 2018, 67, S25–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminuma, O.; Suzuki, K.; Mori, A. Effect of sublingual immunotherapy on antigen-induced bronchial and nasal inflammation in mice. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 152, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Kaminuma, O.; Saeki, M.; Kitamura, N.; Matsuoka, K.; Yonekawa, H.; Mori, A.; Hiroi, T. Essential Contribution of CD4+ T Cells to Antigen-Induced Nasal Hyperresponsiveness in Experimental Allergic Rhinitis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima1, Y.; Osaki, T.; Shimada, A.; Kamiya, S.; Hasegawa-Ishii, S. Sex-dependent differences in the gut microbiota following chronic nasal inflammation in adult mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Kobatake, E.; Kabuki, T. Anti-allergic effect of Lactobacillus helveticus SBT2171 on pollen allergen-induced allergy model. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2019, 9, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repa, A.; Grangette, C.; Daniel, C.; Hochreiter, R.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Thalhamer, J.; Kraft, D.; Breiteneder, H.; Mercenier, A.; Widermann, U. Mucosal co-application of lactic acid bacteria and allergen induces counter-regulatory immune responses in a murine model of birch pollen allergy. Vaccine 2003, 22, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashihara, T.; Ikegami, S.; Sueki, N.; Yamaji, T.; Kino, K.; Taketomo, N.; Gotoh, M.; Okubo, K. Oral administration of heat-killed Lactobacillus gasseri OLL2809 reduces cedar pollen antigen-induced peritoneal eosinophilia in mice. Allergol. Int. 2008, 57, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminuma, O.; Mori, A.; Ogawa, K.; Nakata, A.; Kikkawa, H.; Naito, K.; Suko, M.; Okudaira, H. Successful transfer of late phase eosinophil infiltration in the lung by infusion of helper T cell clones. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 16, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabussova, I.; Hufnag, K.; Tang, M.L.K.; Hoflehner, E.; Wagner, A.; Loupal, G.; Nutten, S.; Zuercher, A.; Mercenier, A.; Wiedermann, U. Perinatal Maternal Administration of Lactobacillus paracasei NCC 2461 Prevents Allergic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Birch Pollen Allergy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Mihara, T.; Oki, M.; Kumagai, T. Effects of heat-killed Lactobacillus casei subsp. casei 327 intake on defecation in healthy volunteers: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health. 2018, 37, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugawara, T.; Sawada, D.; Ishida, Y.; Aihara, K.; Aoki, Y.; Takehara, I.; Takano, K.; Fujiwara, S. Regulatory effect of paraprobiotic Lactobacillus gasseri CP2305 on gut environment and function. Biosci. Microbial. Ecol. Health Dis. 2016, 27, 30259. [Google Scholar]
- Thorakkattu, P.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Shah, K.; Babu, K.S.; Mundanat, A.S.; Deliephan, A.; Deokar, G.S.; Santivarangkna, C.; Nirmal, N.P. Postbiotics: Current trends in food and Pharmaceutical industry. Foods 2018, 11, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.H.; Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Sordillo, J.; Bunyavanich, S.; Zhou, Y.; O’Connor, G.; Sandel, M.; Bacharier, L.B.; Zeiger, R.; Sodergren, E.; et al. A prospective microbiome-wide association study of food sensitization and food allergy in early childhood. Allergy 2018, 73, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, K.; Lou, W.; Tun, H.M.; Konya, T.B.; Morales-Lizcano, N.; Chari, R.S.; Field, C.J.; Guttman, D.S.; Mandal, R.; Wishart, D.S.; et al. From Birth to Overweight and Atopic Disease: Multiple and Common Pathways of the Infant Gut Microbiome. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.V.; Wood, R.A.; Boushey, H.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bloomber, G.R.; Kattan, M.; O’Connor, G.T.; Sandel, M.T.; Calatroni, A.; Matsui, E.; et al. Effects of early-life exposure to allergens and bacteria on recurrent wheeze and atopy in urban children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uchida, K.; Iida, K.; Fujioka, I.; Hachimura, S.; Kaminuma, O. Suppressive Effect of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris YRC3780 on a Murine Model of Japanese Cedar Pollinosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111347
Uchida K, Iida K, Fujioka I, Hachimura S, Kaminuma O. Suppressive Effect of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris YRC3780 on a Murine Model of Japanese Cedar Pollinosis. Pathogens. 2022; 11(11):1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111347
Chicago/Turabian StyleUchida, Kenji, Kenichi Iida, Ikumi Fujioka, Satoshi Hachimura, and Osamu Kaminuma. 2022. "Suppressive Effect of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris YRC3780 on a Murine Model of Japanese Cedar Pollinosis" Pathogens 11, no. 11: 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111347
APA StyleUchida, K., Iida, K., Fujioka, I., Hachimura, S., & Kaminuma, O. (2022). Suppressive Effect of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris YRC3780 on a Murine Model of Japanese Cedar Pollinosis. Pathogens, 11(11), 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111347





