The Seroepidemiology of a Neglected Zoonotic and Livestock Pathogen in Free-Ranging Bovids: Leptospirosis in African Buffaloes (Syncerus caffer)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Seroprevalence and Serological Diversity
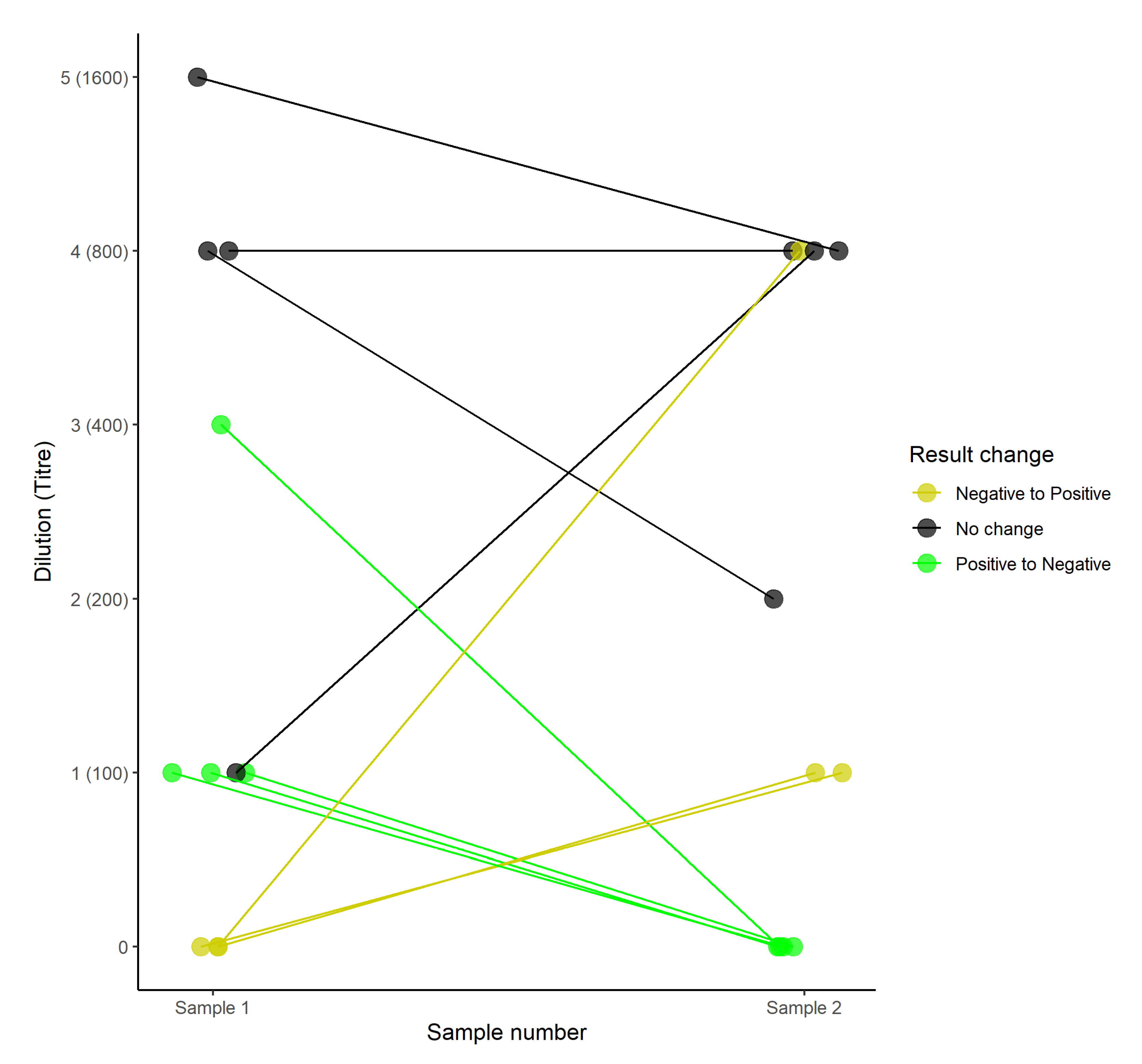
2.2. MAT Titre Dynamics
2.3. Temporal, Age, and Sex Patterns in Exposure Risk
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Viana, M.; Mancy, R.; Biek, R.; Cleaveland, S.; Cross, P.; Lloyd-Smith, J.; Haydon, D. Assembling evidence for identifying reservoirs of infection. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viana, M.; Cleaveland, S.; Matthiopoulos, J.; Halliday, J.; Packer, C.; Craft, M.E.; Hampson, K.; Czupryna, A.; Dobson, A.P.; Dubovi, E.J.; et al. Dynamics of a morbillivirus at the domestic-wildlife interface: Canine distemper virus in domestic dogs and lions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roeder, P.; Mariner, J.; Kock, R. Rinderpest: The veterinary perspective on eradication. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.T.; Schiettekatte, O.; Goarant, C.; Neela, V.K.; Bernet, E.; Thibeaux, R.; Ismail, N.; Khalid, M.K.N.M.; Amran, F.; Masuzawa, T.; et al. Revisiting the taxonomy and evolution of pathogenicity of the genus Leptospira through the prism of genomics. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bulach, D.; Zuerner, R.L.; Wilson, P.; Seemann, T.; McGrath, A.; Cullen, P.A.; Davis, J.; Johnson, M.; Kuczek, E.; Alt, D.; et al. Genome reduction in Leptospira borgpetersenii reflects limited transmission potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14560–14565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allan, K.J.; Halliday, J.; Moseley, M.; Carter, R.W.; Ahmed, A.; Goris, M.G.A.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Keyyu, J.; Kibona, T.; Maro, V.P.; et al. Assessment of animal hosts of pathogenic Leptospira in northern Tanzania. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahelinirina, S.; Moseley, M.H.; Allan, K.J.; Ramanohizakandrainy, E.; Ravaoarinoro, S.; Rajerison, M.; Rakotoharinome, V.; Telfer, S. Leptospira in livestock in Madagascar: Uncultured strains, mixed infections and small mammal-livestock transmission highlight challenges in controlling and diagnosing leptospirosis in the developing world. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterberg, U.W.; Bagnall, R.; Bosch, B.; Perrett, K.; Horner, R.; Gummow, B. A serological prevalence survey of leptospirosis in cattle of rural communities in the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2008, 79, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamond, C.; Martins, G.; Medeiros, M.A.; Lilenbaum, W. Presence of Leptospiral DNA in Semen Suggests Venereal Transmission in Horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2013, 33, 1157–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, G.; Penna, B.; Lilenbaum, W. Maintenance of Leptospira infection in cattle under tropical conditions. Vet. Rec. 2010, 167, 629–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, K.; Moseley, M.; McCarthy, K.; Chingonzoh, R.; Lawrence, C.; Setshedi, G.M.; Frean, J.; Rossouw, J. Fatal Rodentborne Leptospirosis in Prison Inmates, South Africa, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, M.; Naidoo, K.; Bastos, A.; Retief, L.; Frean, J.; Telfer, S.; Rossouw, J. Multi-locus sequence analyses reveal a clonal L. borgpetersenii genotype in a heterogeneous invasive Rattus spp. community across the City of Johannesburg, South Africa. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbizi, V.; Saulez, M.N.; Potts, A.; Lötter, C.; Gummow, B. A study of leptospirosis in South African horses and associated risk factors. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 134, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atherstone, C.; Picozzi, K.; Kalema-Zikusoka, G. Seroprevalence of Leptospira hardjo in cattle and African buffalos in southwestern Uganda. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Myburgh, J.G.; Bengis, R.G.; Bester, C.J.; Chaparro, F. Serological reactions to Leptospira species in buffalo (Syncerus caffer) from the Kruger National Park. Onderstepoort. J. Vet. Res. 1990, 57, 281–282. [Google Scholar]
- Alinaitwe, L.; Kankya, C.; Namanya, D.; Pithua, P.; Dreyfus, A. Leptospira Seroprevalence Among Ugandan Slaughter Cattle: Comparison of Sero-Status With Renal Leptospira Infection. Front. Veter. Sci. 2020, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogonyaro, B.B.; van Heerden, H.; Potts, A.D.; Kolo, B.F.; Lotter, C.; Katsande, C.; Fasina, F.O.; Ko, A.I.; Wunder, E.A.; Adesiyun, A.A. Seroepidemiology of Leptospira infection in slaughtered cattle in Gauteng province, South Africa. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3789–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.; Mannewald, A.; Collins-Emerson, J.; Dreyfus, A.; Sanhueza, J.; Benschop, J.; Verdugo, C.; Emanuelson, U.; Boqvist, S.; Heuer, C. Serological study of Leptospira interrogans serovar Copenhageni and L. borgpetersenii serovars Tarassovi and Ballum in beef cattle, sheep and deer in New Zealand. N. Z. Veter. J. 2021, 69, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yupiana, Y.; Vallee, E.; Wilson, P.; Collins-Emerson, J.; Weston, J.; Benschop, J.; Heuer, C. Emerging Leptospira strain poses public health risk for dairy farmers in New Zealand. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 170, 104727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barasona, J.A.; Vicente, J.; Díez-Delgado, I.; Aznar, J.; Gortázar, C.; Torres, M.J. Environmental Presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex in Aggregation Points at the Wildlife/Livestock Interface. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, E.R.M.; Landman, W.A.; Tadross, M.A.; Malherbe, J.; Weepener, H.; Maluleke, P.; Marumbwa, F.M. Understanding the evolution of the 2014–2016 summer rainfall seasons in southern Africa: Key lessons. Clim. Risk Manag. 2017, 16, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbatha, N.; Xulu, S. Time series analysis of MODIS-Derived NDVI for the Hluhluwe-Imfolozi Park, South Africa: Impact of recent intense drought. Climate 2018, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suwancharoen, D.; Chaisakdanugull, Y.; Thanapongtharm, W.; Yoshida, S. Serological survey of leptospirosis in livestock in Thailand. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 2269–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, W.C.; Jolles, A.E.; Owen-Smith, N. Alternating sexual segregation during the mating season by male African buffalo (Syncerus caffer). J. Zool. 2005, 267, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EKZNW. Annual Report 2018/19. 2019. Available online: http://www.kznwildlife.com/Documents/AnnualReport/EzemveloAR2019.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Goosen, W.; Miller, M.; Chegou, N.N.; Cooper, D.; Warren, R.; van Helden, P.D.; Parsons, S.D. Agreement between assays of cell-mediated immunity utilizing Mycobacterium bovis-specific antigens for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in African buffaloes (Syncerus caffer). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 160, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolles, A.E. Population biology of African buffalo (Syncerus caffer) at Hluhluwe-iMfolozi Park, South Africa. Afr. J. Ecol. 2007, 45, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Calf | Subadult | Adult | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2018 | 2019 | 2016 | 2018 | 2019 | 2016 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| Serovar | Bratislava | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Canicola | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Icterohaemorrhagiae | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pomona | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Tarassovi | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 * | 1 | 1 | 8 † | 6 | 1 | |
| Szwajizak | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Grippotyphosa | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Hardjo | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Prevalence | Annual (npositive/ntested) [95% logit CI] | 0% (0/5) [0–52%] | 0% (0/8) [0–37%] | 0% (0/6) [0–46%] | 43% (3/7) [14–77%] | 25% (1/4) [3–76%] | 20% (1/5) [3–69%] | 38% (8/21) [20–60%] | 33% (7/21) [17–55%] | 5% (1/21) [1–27%] |
| Overall (npositive/ntested) [95% logit CI] | 0% (0/19) [0–18%] | 31% (5/16) [14–57%] | 25% (16/63) [16–38%] | |||||||
| Species | Serogroup | Serovar | Strain |
|---|---|---|---|
| L. interrogans | Australis | Bratislava | Jez Bratislava |
| L. interrogans | Canicola | Canicola | Hond Utrecht IV |
| L. interrogans | Icterohaemorrhagiae | Icterohaemorrhagiae | RGA |
| L. interrogans | Pomona | Pomona | Pomona |
| L. borgpetersenii | Tarrasovi | Tarrasovi | Perepelitsin |
| L. interrogans | Mini | Szwajizak | Szwajizak |
| L. kirschneri | Grippotyphosa | Grippotyphosa | Moskva V |
| L. borgpetersenii | Sejroe | Hardjo | Hardjoprajitno |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goosen, W.; Moseley, M.H.; Kerr, T.J.; Potts, A.; Miller, M. The Seroepidemiology of a Neglected Zoonotic and Livestock Pathogen in Free-Ranging Bovids: Leptospirosis in African Buffaloes (Syncerus caffer). Pathogens 2021, 10, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10091072
Goosen W, Moseley MH, Kerr TJ, Potts A, Miller M. The Seroepidemiology of a Neglected Zoonotic and Livestock Pathogen in Free-Ranging Bovids: Leptospirosis in African Buffaloes (Syncerus caffer). Pathogens. 2021; 10(9):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10091072
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoosen, Wynand, Mark Hamish Moseley, Tanya Jane Kerr, Andrew Potts, and Michele Miller. 2021. "The Seroepidemiology of a Neglected Zoonotic and Livestock Pathogen in Free-Ranging Bovids: Leptospirosis in African Buffaloes (Syncerus caffer)" Pathogens 10, no. 9: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10091072
APA StyleGoosen, W., Moseley, M. H., Kerr, T. J., Potts, A., & Miller, M. (2021). The Seroepidemiology of a Neglected Zoonotic and Livestock Pathogen in Free-Ranging Bovids: Leptospirosis in African Buffaloes (Syncerus caffer). Pathogens, 10(9), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10091072








