TNF Decoy Receptors Encoded by Poxviruses
Abstract
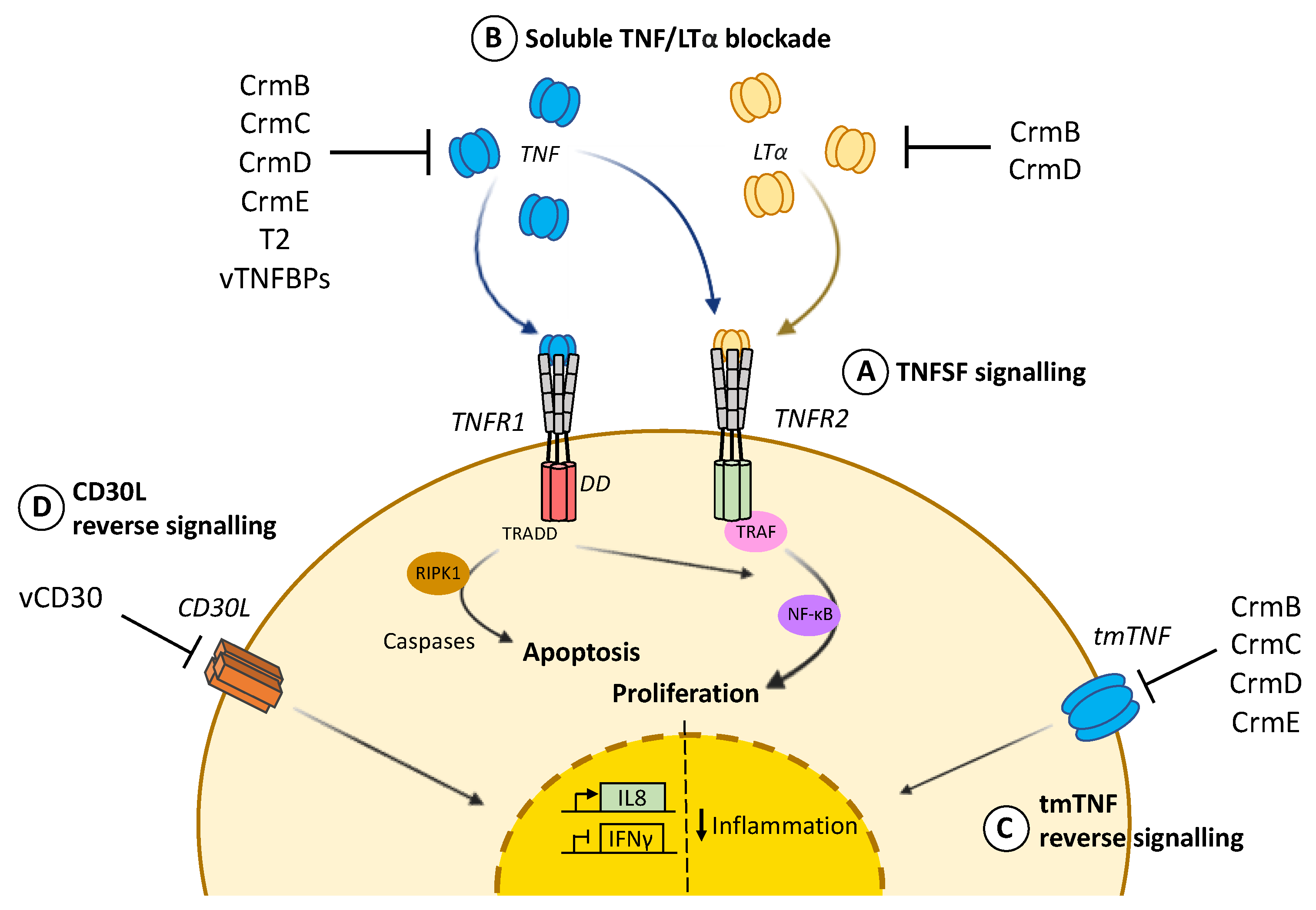
1. TNF Biology
2. Virally Encoded TNFRs and TNFBPs
2.1. Virally Encoded TNFRs
2.1.1. vTNFRs Affinities and Evolution
2.1.2. Modulation of tmTNF
2.1.3. Addition of a Chemokine Binding Domain: SECRET
2.1.4. T2 Protein
2.1.5. vCD30
2.2. vTNFBPs
3. Relevance in Poxvirus Pathogenesis
4. Therapeutic Use of vTNFRs
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watts, A.D.; Hunt, N.H.; Wanigasekara, Y.; Bloomfield, G.; Wallach, D.; Roufogalis, B.D.; Chaudhri, G. A Casein Kinase I Motif Present in the Cytoplasmic Domain of Members of the Tumour Necrosis Factor Ligand Family Is Implicated in “Reverse Signalling”. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelová, H.; Hošek, J. TNF-α Signalling and Inflammation: Interactions between Old Acquaintances. Inflamm. Res. Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. Al 2013, 62, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.; Calvano, S.E.; Lowry, S.F. Inflammatory Cytokines and Cell Response in Surgery. Surgery 2000, 127, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locksley, R.M.; Killeen, N.; Lenardo, M.J. The TNF and TNF Receptor Superfamilies: Integrating Mammalian Biology. Cell 2001, 104, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Signalling Pathways of the TNF Superfamily: A Double-Edged Sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.A.; Rauch, C.T.; Kozlosky, C.J.; Peschon, J.J.; Slack, J.L.; Wolfson, M.F.; Castner, B.J.; Stocking, K.L.; Reddy, P.; Srinivasan, S.; et al. A Metalloproteinase Disintegrin That Releases Tumour-Necrosis Factor-Alpha from Cells. Nature 1997, 385, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Albert, I.; DeFay, K.; Zachariades, N.; Gooding, L.; Kriegler, M. A Nonsecretable Cell Surface Mutant of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Kills by Cell-to-Cell Contact. Cell 1990, 63, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, M.; Douni, E.; Wajant, H.; Löhden, M.; Clauss, M.; Maxeiner, B.; Georgopoulos, S.; Lesslauer, W.; Kollias, G.; Pfizenmaier, K.; et al. The Transmembrane Form of Tumor Necrosis Factor Is the Prime Activating Ligand of the 80 KDa Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor. Cell 1995, 83, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, W.; Vandenabeele, P.; Fiers, W. Dimerization of Chimeric Erythropoietin/75 KDa Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptors Transduces TNF Signals: Necessity for the 75 KDa-TNF Receptor Transmembrane Domain. Cytokine 1995, 7, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S.J. Molecular Mechanisms of Soluble Cytokine Receptor Generation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14177–14181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainez, B.; Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Romero, X.; Esplugues, E.; Cañete, J.D.; Ricart, W.; Engel, P. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Spliced Variant That Encodes Human Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 2. Int. Immunol. 2004, 16, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, G.; O’Rourke, K.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Gentz, R.; Ebner, R.; Ni, J.; Dixit, V.M. The Receptor for the Cytotoxic Ligand TRAIL. Science 1997, 276, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitti, R.M.; Marsters, S.A.; Lawrence, D.A.; Roy, M.; Kischkel, F.C.; Dowd, P.; Huang, A.; Donahue, C.J.; Sherwood, S.W.; Baldwin, D.T.; et al. Genomic Amplification of a Decoy Receptor for Fas Ligand in Lung and Colon Cancer. Nature 1998, 396, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Smolak, P.J.; Walczak, H.; Waugh, J.; Huang, C.P.; DuBose, R.F.; Goodwin, R.G.; Smith, C.A. Cloning and Characterization of TRAIL-R3, a Novel Member of the Emerging TRAIL Receptor Family. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domonkos, A.; Udvardy, A.; László, L.; Nagy, T.; Duda, E. Receptor-like Properties of the 26 KDa Transmembrane Form of TNF. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2001, 12, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eissner, G.; Kolch, W.; Scheurich, P. Ligands Working as Receptors: Reverse Signaling by Members of the TNF Superfamily Enhance the Plasticity of the Immune System. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004, 15, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, J.L.; Ngam-ek, A.; Lawton, P.; DeMarinis, J.; Tizard, R.; Chow, E.P.; Hession, C.; O’Brine-Greco, B.; Foley, S.F.; Ware, C.F. Lymphotoxin Beta, a Novel Member of the TNF Family That Forms a Heteromeric Complex with Lymphotoxin on the Cell Surface. Cell 1993, 72, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.E.; Espevik, T.; Ranges, G.; Sundan, A. Distinct Roles of the Two Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptors in Modulating TNF and Lymphotoxin Alpha Effects. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9778–9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, D.N.; Ebner, R.; Montgomery, R.I.; Kochel, K.D.; Cheung, T.C.; Yu, G.L.; Ruben, S.; Murphy, M.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H.; et al. LIGHT, a New Member of the TNF Superfamily, and Lymphotoxin Alpha Are Ligands for Herpesvirus Entry Mediator. Immunity 1998, 8, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Togni, P.; Goellner, J.; Ruddle, N.H.; Streeter, P.R.; Fick, A.; Mariathasan, S.; Smith, S.C.; Carlson, R.; Shornick, L.P.; Strauss-Schoenberger, J. Abnormal Development of Peripheral Lymphoid Organs in Mice Deficient in Lymphotoxin. Science 1994, 264, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koni, P.A.; Sacca, R.; Lawton, P.; Browning, J.L.; Ruddle, N.H.; Flavell, R.A. Distinct Roles in Lymphoid Organogenesis for Lymphotoxins Alpha and Beta Revealed in Lymphotoxin Beta-Deficient Mice. Immunity 1997, 6, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Mariathasan, S.; Nahm, M.H.; Baranyay, F.; Peschon, J.J.; Chaplin, D.D. Role of Lymphotoxin and the Type I TNF Receptor in the Formation of Germinal Centers. Science 1996, 271, 1289–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ma, X.; Rodriguez, M.; Feng, X.; Zoecklein, L.; Fu, Y.-X.; Roos, R.P. Membrane Lymphotoxin Is Required for Resistance to Theiler’s Virus Infection. Int. Immunol. 2003, 15, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Banks, T.A.; Rickert, S.; Benedict, C.A.; Ma, L.; Ko, M.; Meier, J.; Ha, W.; Schneider, K.; Granger, S.W.; Turovskaya, O.; et al. A Lymphotoxin-IFN-Beta Axis Essential for Lymphocyte Survival Revealed during Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2005, 174, 7217–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Ishikawa, T.; Hobbs, M.V.; Matzke, B.; Schreiber, R.; Chisari, F.V. Intracellular Inactivation of the Hepatitis B Virus by Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes. Immunity 1996, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavić, I.; Polić, B.; Crnković, I.; Lucin, P.; Jonjić, S.; Koszinowski, U.H. Participation of Endogenous Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha in Host Resistance to Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74 (Pt 10), 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ruby, J.; Bluethmann, H.; Peschon, J.J. Antiviral Activity of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Is Mediated via P55 and P75 TNF Receptors. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrasheuskaya, A.V.; Bukin, E.K.; Fredeking, T.M.; Ignatyev, G.M. Protective Effect of Exogenous Recombinant Mouse Interferon-Gamma and Tumour Necrosis Factor-Alpha on Ectromelia Virus Infection in Susceptible BALB/c Mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 136, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.K.-M.; Shisler, J.; Bixby, J.G.; Felices, M.; Zheng, L.; Appel, M.; Orenstein, J.; Moss, B.; Lenardo, M.J. A Role for Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-2 and Receptor-Interacting Protein in Programmed Necrosis and Antiviral Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 51613–51621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidbury, B.A.; Ramshaw, I.A.; Sambhi, S.K. The Role for Host-Immune Factors in the in Vivo Antiviral Effects of Tumour Necrosis Factor. Cytokine 1995, 7, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambhi, S.K.; Kohonen-Corish, M.R.; Ramshaw, I.A. Local Production of Tumor Necrosis Factor Encoded by Recombinant Vaccinia Virus Is Effective in Controlling Viral Replication in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4025–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcami, A. Viral Mimicry of Cytokines, Chemokines and Their Receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejo, A.; Ruiz-Argüello, M.B.; Ho, Y.; Smith, V.P.; Saraiva, M.; Alcami, A. A Chemokine-Binding Domain in the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor from Variola (Smallpox) Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5995–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, G.J.; Buller, R.M.; Glasgow, W.C. Multigenic Evasion of Inflammation by Poxviruses. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Hu, F.Q.; Smith, T.D.; Richards, C.L.; Smolak, P.; Goodwin, R.G.; Pickup, D.J. Cowpox Virus Genome Encodes a Second Soluble Homologue of Cellular TNF Receptors, Distinct from CrmB, That Binds TNF but Not LT Alpha. Virology 1996, 223, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontejo, S.M.; Alejo, A.; Alcami, A. Comparative Biochemical and Functional Analysis of Viral and Human Secreted Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Decoy Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15973–15984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loparev, V.N.; Parsons, J.M.; Knight, J.C.; Panus, J.F.; Ray, C.A.; Buller, R.M.; Pickup, D.J.; Esposito, J.J. A Third Distinct Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor of Orthopoxviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3786–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meusch, U.; Rossol, M.; Baerwald, C.; Hauschildt, S.; Wagner, U. Outside-to-inside Signaling through Transmembrane Tumor Necrosis Factor Reverses Pathologic Interleukin-1beta Production and Deficient Apoptosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Monocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2612–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rumaih, Z.; Tuazon Kels, M.J.; Ng, E.; Pandey, P.; Pontejo, S.M.; Alejo, A.; Alcamí, A.; Chaudhri, G.; Karupiah, G. Poxvirus-Encoded TNF Receptor Homolog Dampens Inflammation and Protects from Uncontrolled Lung Pathology during Respiratory Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26885–26894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhász, K.; Buzás, K.; Duda, E. Importance of Reverse Signaling of the TNF Superfamily in Immune Regulation. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, S.C.; Bahar, M.W.; Abrescia, N.G.A.; Smith, G.L.; Stuart, D.I.; Grimes, J.M. Structure of CrmE, a Virus-Encoded Tumour Necrosis Factor Receptor. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upton, C.; Macen, J.L.; Schreiber, M.; McFadden, G. Myxoma Virus Expresses a Secreted Protein with Homology to the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Gene Family That Contributes to Viral Virulence. Virology 1991, 184, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macen, J.L.; Graham, K.A.; Lee, S.F.; Schreiber, M.; Boshkov, L.K.; McFadden, G. Expression of the Myxoma Virus Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Homologue and M11L Genes Is Required to Prevent Virus-Induced Apoptosis in Infected Rabbit T Lymphocytes. Virology 1996, 218, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedger, L.; McFadden, G. M-T2: A Poxvirus TNF Receptor Homologue with Dual Activities. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1996, 74, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedger, L.M.; Osvath, S.R.; Xu, X.-M.; Li, G.; Chan, F.K.-M.; Barrett, J.W.; McFadden, G. Poxvirus Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor (TNFR)-like T2 Proteins Contain a Conserved Preligand Assembly Domain That Inhibits Cellular TNFR1-Induced Cell Death. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9300–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, M.; Smith, P.; Fallon, P.G.; Alcami, A. Inhibition of Type 1 Cytokine-Mediated Inflammation by a Soluble CD30 Homologue Encoded by Ectromelia (Mousepox) Virus. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Jeng, D.; Singh, R.; Coughlin, J.; Essani, K.; McFadden, G. Interaction of Human TNF and Beta2-Microglobulin with Tanapox Virus-Encoded TNF Inhibitor, TPV-2L. Virology 2009, 386, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Barrett, J.W.; Brouckaert, P.; McFadden, G. Variation in Ligand Binding Specificities of a Novel Class of Poxvirus-Encoded Tumor Necrosis Factor-Binding Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22517–22526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; West, A.P.; Bjorkman, P.J. Crystal Structure of TNFalpha Complexed with a Poxvirus MHC-Related TNF Binding Protein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmer, J.-L.; Schneider, P.; Tschopp, J. The Molecular Architecture of the TNF Superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymowitz, S.G.; Christinger, H.W.; Fuh, G.; Ultsch, M.; O’Connell, M.; Kelley, R.F.; Ashkenazi, A.; de Vos, A.M. Triggering Cell Death: The Crystal Structure of Apo2L/TRAIL in a Complex with Death Receptor 5. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontejo, S.M.; Sanchez, C.; Ruiz-Argüello, B.; Alcami, A. Insights into Ligand Binding by a Viral Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Decoy Receptor Yield a Selective Soluble Human Type 2 TNF Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 5214–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magis, C.; van der Sloot, A.M.; Serrano, L.; Notredame, C. An Improved Understanding of TNFL/TNFR Interactions Using Structure-Based Classifications. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.K.; Chun, H.J.; Zheng, L.; Siegel, R.M.; Bui, K.L.; Lenardo, M.J. A Domain in TNF Receptors That Mediates Ligand-Independent Receptor Assembly and Signaling. Science 2000, 288, 2351–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tsunoda, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Yamagata, Y.; Tsutsumi, Y. Solution of the Structure of the TNF-TNFR2 Complex. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.M.; Frederiksen, J.K.; Zacharias, D.A.; Chan, F.K.; Johnson, M.; Lynch, D.; Tsien, R.Y.; Lenardo, M.J. Fas Preassociation Required for Apoptosis Signaling and Dominant Inhibition by Pathogenic Mutations. Science 2000, 288, 2354–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Q.; Smith, C.A.; Pickup, D.J. Cowpox Virus Contains Two Copies of an Early Gene Encoding a Soluble Secreted Form of the Type II TNF Receptor. Virology 1994, 204, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reading, P.C.; Khanna, A.; Smith, G.L. Vaccinia Virus CrmE Encodes a Soluble and Cell Surface Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor That Contributes to Virus Virulence. Virology 2002, 292, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; Alcami, A. CrmE, a Novel Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Encoded by Poxviruses. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, P.D.; VanArsdale, T.L.; Walter, B.N.; Ware, C.F.; Hession, C.; Ehrenfels, B.; Browning, J.L.; Din, W.S.; Goodwin, R.G.; Smith, C.A. A Lymphotoxin-Beta-Specific Receptor. Science 1994, 264, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, F. Smallpox: Emergence, Global Spread, and Eradication. Hist. Philos. Life Sci. 1993, 15, 397–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mavian, C.; López-Bueno, A.; Bryant, N.A.; Seeger, K.; Quail, M.A.; Harris, D.; Barrell, B.; Alcami, A. The Genome Sequence of Ectromelia Virus Naval and Cornell Isolates from Outbreaks in North America. Virology 2014, 462–463, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, G.; Rivera, J.; Saraiva, M.; Campbell, R.D.; Alcami, A. Genetic Variability of Immunomodulatory Genes in Ectromelia Virus Isolates Detected by Denaturing High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10139–10146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alzhanova, D.; Früh, K. Modulation of the Host Immune Response by Cowpox Virus. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunnion, K.M. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors Encoded by Poxviruses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 1999, 67, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, S.J.; Johnson, G.P.; Perkus, M.E.; Davis, S.W.; Winslow, J.P.; Paoletti, E. The Complete DNA Sequence of Vaccinia Virus. Virology 1990, 179, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.T.; Chan, Y.S.; Smith, G.L. Vaccinia Virus Homologues of the Shope Fibroma Virus Inverted Terminal Repeat Proteins and a Discontinuous ORF Related to the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Family. Virology 1991, 180, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamí, A.; Khanna, A.; Paul, N.L.; Smith, G.L. Vaccinia Virus Strains Lister, USSR and Evans Express Soluble and Cell-Surface Tumour Necrosis Factor Receptors. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80 (Pt 4), 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gileva, I.P.; Nepomnyashchikh, T.S.; Antonets, D.V.; Lebedev, L.R.; Kochneva, G.V.; Grazhdantseva, A.V.; Shchelkunov, S.N. Properties of the Recombinant TNF-Binding Proteins from Variola, Monkeypox, and Cowpox Viruses Are Different. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1764, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossen, C.; Ingold, K.; Tardivel, A.; Bodmer, J.-L.; Gaide, O.; Hertig, S.; Ambrose, C.; Tschopp, J.; Schneider, P. Interactions of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) and TNF Receptor Family Members in the Mouse and Human. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13964–13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontejo, S.M.; Alejo, A.; Alcami, A. Poxvirus-Encoded TNF Decoy Receptors Inhibit the Biological Activity of Transmembrane TNF. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 3118–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, S.; Boldt, S.; Kolch, W.; Haffner, S.; Kazak, S.; Janosch, P.; Holler, E.; Andreesen, R.; Eissner, G. LPS Resistance in Monocytic Cells Caused by Reverse Signaling through Transmembrane TNF (MTNF) Is Mediated by the MAPK/ERK Pathway. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejo, A.; Ruiz-Argüello, M.B.; Pontejo, S.M.; Fernández de Marco, M.D.M.; Saraiva, M.; Hernáez, B.; Alcamí, A. Chemokines Cooperate with TNF to Provide Protective Anti-Viral Immunity and to Enhance Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Lu, Q.; Wei, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, D.; He, G.; Huang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Structural Basis of Chemokine Sequestration by CrmD, a Poxvirus-Encoded Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidarieh, H.; Hernáez, B.; Alcamí, A. Immune Modulation by Virus-Encoded Secreted Chemokine Binding Proteins. Virus Res. 2015, 209, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.L.; Benfield, C.T.O.; Maluquer de Motes, C.; Mazzon, M.; Ember, S.W.J.; Ferguson, B.J.; Sumner, R.P. Vaccinia Virus Immune Evasion: Mechanisms, Virulence and Immunogenicity. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2367–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, J.; Savvides, S.N. Mechanisms of Immunomodulation by Mammalian and Viral Decoy Receptors: Insights from Structures. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.A.; Epperson, M.L.; Singh, S.; Elliott, J.I.; Fremont, D.H. Structural Conservation and Functional Diversity of the Poxvirus Immune Evasion (PIE) Domain Superfamily. Viruses 2015, 7, 4878–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Davis, T.; Anderson, D.; Solam, L.; Beckmann, M.P.; Jerzy, R.; Dower, S.K.; Cosman, D.; Goodwin, R.G. A Receptor for Tumor Necrosis Factor Defines an Unusual Family of Cellular and Viral Proteins. Science 1990, 248, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, M.; McFadden, G. Mutational Analysis of the Ligand-Binding Domain of M-T2 Protein, the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Homologue of Myxoma Virus. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 4486–4495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Davis, T.; Wignall, J.M.; Din, W.S.; Farrah, T.; Upton, C.; McFadden, G.; Goodwin, R.G. T2 Open Reading Frame from the Shope Fibroma Virus Encodes a Soluble Form of the TNF Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 176, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, M.; Sedger, L.; McFadden, G. Distinct Domains of M-T2, the Myxoma Virus Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptor Homolog, Mediate Extracellular TNF Binding and Intracellular Apoptosis Inhibition. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 2171–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, G.; Schreiber, M.; Sedger, L. Myxoma T2 Protein as a Model for Poxvirus TNF Receptor Homologs. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 72, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, R.; Watanabe, T. CD30: Expression and Function in Health and Disease. Semin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panus, J.F.; Smith, C.A.; Ray, C.A.; Smith, T.D.; Patel, D.D.; Pickup, D.J. Cowpox Virus Encodes a Fifth Member of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Family: A Soluble, Secreted CD30 Homologue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8348–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.L.; Delhon, G.; Tulman, E.R.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, A.; Becerra, V.M.; Zsak, L.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. Genome of Deerpox Virus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejo, A.; Saraiva, M.; Ruiz-Argüello, M.B.; Viejo-Borbolla, A.; de Marco, M.F.; Salguero, F.J.; Alcami, A. A Method for the Generation of Ectromelia Virus (ECTV) Recombinants: In Vivo Analysis of ECTV VCD30 Deletion Mutants. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, C.R.; Paulose-Murphy, M.; Singh, R.; Qin, J.; Barrett, J.W.; Tardivel, A.; Schneider, P.; Essani, K.; McFadden, G. A Secreted High-Affinity Inhibitor of Human TNF from Tanapox Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4831–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, T.L.; Bjorkman, P.J. Characterization of a Murine Cytomegalovirus Class I Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Homolog: Comparison to MHC Molecules and to the Human Cytomegalovirus MHC Homolog. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, H.E.; Vally, H.; Lynch, D.M.; Fleming, P.; Shellam, G.R.; Scalzo, A.A.; Davis-Poynter, N.J. Inhibition of Natural Killer Cells by a Cytomegalovirus MHC Class I Homologue in Vivo. Nature 1997, 386, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senkevich, T.G.; Moss, B. Domain Structure, Intracellular Trafficking, and Beta2-Microglobulin Binding of a Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Homolog Encoded by Molluscum Contagiosum Virus. Virology 1998, 250, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Afonso, C.L.; Tulman, E.R.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Osorio, F.A.; Balinsky, C.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. The Genome of Swinepox Virus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.; Ziring, D.; Korin, Y.; Desai, S.; Kim, S.; Lin, J.; Gjertson, D.; Braun, J.; Reed, E.; Singh, R.R. TNFalpha Blockade in Human Diseases: Mechanisms and Future Directions. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Kalden, J.R. Advances in Rheumatology: New Targeted Therapeutics. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13 (Suppl. 1), S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitoma, H.; Horiuchi, T.; Tsukamoto, H.; Ueda, N. Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Anti-TNF-α Agents - Comparison among Therapeutic TNF-α Antagonists. Cytokine 2018, 101, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiodras, S.; Samonis, G.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Fungal Infections Complicating Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Blockade Therapy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-M.; Uhm, W.-S.; Bae, S.-C.; Yoo, D.-H.; Kim, T.-H. Incidence of Tuberculosis among Korean Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis Who Are Taking Tumor Necrosis Factor Blockers. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2218–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaron, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Q.; Burgin, M.; Schutz, L.N.; Awo, E.; Wise, L.; Krause, K.L.; Ildefonso, C.J.; Kwiecien, J.M.; et al. Deriving Immune Modulating Drugs from Viruses—A New Class of Biologics. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gileva, I.P.; Viazovaia, E.A.; Toporkova, L.B.; Tsyrendorzhiev, D.D.; Shchelkunov, S.N.; Orlovskaya, I.A. TNF Binding Protein of Variola Virus Acts as a TNF Antagonist at Epicutaneous Application. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viazovaia, E.A.; Gileva, I.P.; Toporkova, L.B.; Shchelkunov, S.N.; Orlovskaya, I.A. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Variola Virus TNF Decoy Receptor in an Experimental Model of Contact Dermatitis. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2018, 19, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchelkunov, S.N.; Taranov, O.S.; Tregubchak, T.V.; Maksyutov, R.A.; Silkov, A.N.; Nesterov, A.E.; Sennikov, S.V. The Gene Therapy of Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats by Intramuscular Administration of the Plasmid Encoding TNF-Binding Domain of Variola Virus CrmB Protein. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 469, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkin, S.J.; Lewis, J.W.; Krautter, F.; Chimen, M.; McGettrick, H.M. Triggering the Resolution of Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases: Can Targeting Leukocyte Migration Be the Answer? Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejo, A.; Sánchez, C.; Amu, S.; Fallon, P.G.; Alcamí, A. Addition of a Viral Immunomodulatory Domain to Etanercept Generates a Bifunctional Chemokine and TNF Inhibitor. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruglov, A.A.; Grivennikov, S.I.; Kuprash, D.V.; Winsauer, C.; Prepens, S.; Seleznik, G.M.; Eberl, G.; Littman, D.R.; Heikenwalder, M.; Tumanov, A.V.; et al. Nonredundant Function of Soluble LTα3 Produced by Innate Lymphoid Cells in Intestinal Homeostasis. Science 2013, 342, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, V.; Fu, Y.-X. Lymphotoxin Signalling in Immune Homeostasis and the Control of Microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.-H.; Cohen, M.; Tang, Y.; Lazear, E.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H.; Sigal, L.J. The Orthopoxvirus Type I IFN Binding Protein Is Essential for Virulence and an Effective Target for Vaccination. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoine, G.; Scheiflinger, F.; Dorner, F.; Falkner, F.G. The Complete Genomic Sequence of the Modified Vaccinia Ankara Strain: Comparison with Other Orthopoxviruses. Virology 1998, 244, 365–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, T.J.; Alcami, A.; Andrea, P.; Smith, G.L. Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara Undergoes Limited Replication in Human Cells and Lacks Several Immunomodulatory Proteins: Implications for Use as a Human Vaccine. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79 (Pt 5), 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamí, A.; Symons, J.A.; Smith, G.L. The Vaccinia Virus Soluble Alpha/Beta Interferon (IFN) Receptor Binds to the Cell Surface and Protects Cells from the Antiviral Effects of IFN. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 11230–11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Protein | Key Refs. | Virus | Virulence Factor | Known Ligands | Cellular Homology | kDa | Special Traits | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vTNFRs | CrmB | [33,34] | CMPXV, CPXV, MPXV, VARV | Unclear (~50-fold LD50 reduction after intracranial inoculation) | hTNF, mTNF, hLTα, mLTα | TNFR2 | 48 | SECRET domain-mediated chemokine inhibition; Reverse signalling |
| CrmC | [35,36] | CPXV, VACV | Minor effect (difference in weight loss) | hTNF, mTNF | TNFR2 | 25 | Reverse signalling | |
| CrmD | [37,38,39,40] | CPXV, ECTV | Yes (reduced LD50 in 6 orders of magnitude) | hTNF, mTNF, hLTα, mLTα | TNFR2 | 46 | SECRET domain-mediated chemokine inhibition; Reverse signalling | |
| CrmE | [41] | CPXV, VACV | Minor effect (difference in weight loss) | hTNF, mTNF | TNFR2 | 18 | Mouse tmTNF inhibition w/o sTNF; Reverse signalling | |
| T2 | [42,43,44,45] | MYXV | Yes (reduce mortality) | rabbit TNF | TNFR2 | M-T2: 40.5 | PLAD mediated antiapoptotic activity | |
| SFV | hTNF, rabbit TNF | TNFR2 | S-T2: 58 | |||||
| vCD30 | [46] | DPXV, CPXV, ECTV | No | CD30L | CD30 | 12 | Reverse signalling through CD30L; inhibition of IFNγ production in splenocytes | |
| vTNFBPs | 2L | [47,48,49] | TPXV | ND | rabbit, human, monkey, canine TNF | MHC I heavy chain | 47 | Can associate with β2 microglobulin to inhibit MHC-I |
| YMTV | rabbit, human, monkey TNF | |||||||
| SPV003 | [48] | SPXV | ND | porcine TNF | MHC I heavy chain | 47 | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez-de Miranda, F.J.; Alonso-Sánchez, I.; Alcamí, A.; Hernaez, B. TNF Decoy Receptors Encoded by Poxviruses. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081065
Alvarez-de Miranda FJ, Alonso-Sánchez I, Alcamí A, Hernaez B. TNF Decoy Receptors Encoded by Poxviruses. Pathogens. 2021; 10(8):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081065
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez-de Miranda, Francisco Javier, Isabel Alonso-Sánchez, Antonio Alcamí, and Bruno Hernaez. 2021. "TNF Decoy Receptors Encoded by Poxviruses" Pathogens 10, no. 8: 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081065
APA StyleAlvarez-de Miranda, F. J., Alonso-Sánchez, I., Alcamí, A., & Hernaez, B. (2021). TNF Decoy Receptors Encoded by Poxviruses. Pathogens, 10(8), 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081065






