Comparison of Serological and Molecular Assays for Bartonella Species in Dogs with Hemangiosarcoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Study Design and Sample Sources
4.2. Bartonella Detection Methods
4.3. Study Size and Statistical Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Kordick, D.L.; Malarkey, D.E.; Keene, B.; Hadfield, T.L.; Wilson, K. Endocarditis in a Dog Due to Infection with a Novel Bartonella Subspecies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.S.; Worthington, M.G.; Brenner, D.O.N.J.; Moss, C.W.; Hollis, D.G.; Weyant, R.S.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Weaver, R.E.; Daneshvar, M.I.; Connor, S.P.O. Rochalimaea Elizabethae Sp. Nov. Isolated from a Patient with Endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, T.L.; Warren, R.; Kass, M.; Brun, E.; Levy, C. Endocarditis Caused by Rochalimaea Henselae. Hum. Pathol. 1993, 24, 1140–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodino, K.G.; Stone, E.; Saleh, O.A.; Theel, E.S. The Brief Case: Bartonella Henselae Endocarditis—A Case of Delayed Diagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00114-19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golly, E.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Balakrishnan, N.; Moore, D.; Bizikova, P. Bartonella Henselae, Bartonella Koehlerae, and Rickettsia Rickettsii Seroconversion and Seroreversion in a Dog with Acute-Onset Fever, Lameness, and Lymphadenopathy Followed by a Protracted Disease Course. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2016, 7, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheslock, M.A.; Embers, M.E. Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Fernández, A.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Solano-Gallego, L. Bartonella Infections in Cats and Dogs Including Zoonotic Aspects. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.A.; McCurley, T.L.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Hager, C.; McCoy, J.A.; Anderson, B.; Collins, R.D.; Edwards, K.M. Cat Scratch Disease: Detection of Bartonella Henselae DNA in Archival Biopsies from Patients with Clinically, Serologically, and Histologically Defined Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 149, 2161–2167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Regnery, R.L.; Olson, J.G.; Perkins, B.A.; Bibb, W. Serological Response to “Rochalimaea Henselae” Antigen in Suspected Cat-Scratch Disease. Lancet 1992, 339, 1443–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Sims, K.; Regnery, R.; Robinson, L.; Schmidt, M.J.; Goral, S.; Hager, C.; Edwards, K. Detection of Rochalimaea Henselae DNA in Specimens from Cat Scratch Disease Patients by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, L.; Rao, K.; McGough, C.; Becker, A. A Rare Case of Bartonella Encephalitis With Hemiplegia. Child Neurol. Open 2019, 6, 2329048X19826480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Greenberg, R.; Maggi, R.; Mozayeni, B.R.; Lewis, A.; Bradley, J. Bartonella Henselae Blood Stream Infection in a Boy with Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome (PANS). J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2019, 11, 1179573519832014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, J.C.; Fonseca, K.; Pabbaraju, K.; Meatherall, B.L. Case Report: Bartonella Quintana Endocarditis Outside of the Europe–African Gradient: Comprehensive Review of Cases within North America. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edouard, S.; Nabet, C.; Lepidi, H.; Fournier, P.-E.; Raoult, D. Bartonella, a Common Cause of Endocarditis: A Report on 106 Cases and Review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Scola, B.; Raoult, D. Culture of Bartonella Quintana and Bartonella Henselae from Human Samples: A 5-Year Experience (1993 to 1998). J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1899–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theonest, N.O.; Carter, R.W.; Amani, N.; Doherty, S.L.; Hugho, E.; Keyyu, J.D.; Mable, B.K.; Shirima, G.M.; Tarimo, R.; Thomas, K.M.; et al. Molecular Detection and Genetic Characterization of Bartonella Species from Rodents and Their Associated Ectoparasites from Northern Tanzania. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, M.H.; Bai, Y.; Malania, L.; Winchell, J.M.; Kosoy, M. Development of a Novel Genus-Specific Real-Time PCR Assay for Detection and Differentiation of Bartonella Species and Genotypes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1645–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allizond, V.; Costa, C.; Sidoti, F.; Scutera, S.; Bianco, G.; Sparti, R.; Banche, G.; Dalmasso, P.; Cuffini, A.M.; Cavallo, R.; et al. Serological and Molecular Detection of Bartonella Henselae in Specimens from Patients with Suspected Cat Scratch Disease in Italy: A Comparative Study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, M.J.; Verbakel, H.; Notermans, D.W.; Reimerink, J.H.J.; Peeters, M.F. Evaluation of Sensitivity, Specificity and Cross-Reactivity in Bartonella Henselae Serology. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, M.J.; Herremans, M.; Verbakel, H.; Bergmans, A.M.C.; Roord, J.J.; van Dijken, P.J.; Peeters, M.F. Serological Testing for Bartonella Henselae Infections in The Netherlands: Clinical Evaluation of Immunofluorescence Assay and ELISA. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmans, A.M.C.; Peeters, M.F.; Schellekens, J.F.P.; Vos, M.C.; Sabbe, L.J.M.; Ossewaarde, J.M.; Verbakel, H.; Hooft, H.J.; Schouls, L.M. Pitfalls and Fallacies of Cat Scratch Disease Serology: Evaluation of Bartonella Henselae-Based Indirect Fluorescence Assay and Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupon, M.; Savin De Larclause, A.M.; Brouqui, P.; Drancourt, M.; Raoult, D.; De Mascarel, A.; Lacut, J.Y. Evaluation of Serological Response to Bartonella Henselae, Bartonella Quintana and Afipia Felis Antigens in 64 Patients with Suspected Cat-Scratch Disease. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 28, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, A.; Posselt, M.; Oberle, K.; Bredt, W. Seroprevalence of Antibodies to Bartonella Henselae in Patients with Cat Scratch Disease and in Healthy Controls: Evaluation and Comparison of Two Commercial Serological Tests. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1998, 5, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, M.R.; dos Santos, L.S.; Silva, M.N.D.; Almeida, A.R.D.; Diniz, P.P.V.D.P.; Angerami, R.; Velho, P.E.N.F. False Negative Results in Bartonellosis Diagnosis. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzitelli, M.; Lamberti, A.G.; Quirino, A.; Marascio, N.; Barreca, G.S.; Costa, C.; Pisani, V.; Strazzulla, A.; Greco, G.; Liberto, M.C.; et al. Utility of Molecular Identification and Quantitation of Bartonella Species with Species-Specific Real-Time PCR for Monitoring Treatment Response: A Case Series. Open Microbiol. J. 2018, 12, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G. Bartonella Quintana and Bartonella Vinsonii Subsp. Vinsonii Bloodstream Co-Infection in a Girl from North Carolina, USA. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, M.; Tsuneoka, H.; Tanimoto, A.; Otsuyama, K.I.; Nishikawa, J.; Matsui, T.; Nojima, J.; Ichihara, K. Bartonella Henselae DNA in Seronegative Patients with Cat-Scratch Disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Bradley, J.M.; Maggi, R.G.; Lashnits, E.; Reicherter, P. Bartonella Associated Cutaneous Lesions (BACL) in People with Neuropsychiatric Symptoms. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Pang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Vayssier-Taussat, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Bartonella and Mammalian Erythrocyte Interactions: A Review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, H.L.; Calzada, J.; Saldaña, A.; Santamaria, A.M.; Pineda, V.; Gonzalez, K.; Chaves, L.F.; Garner, B.; Gottdenker, N. Domestic Dog Health Worsens with Socio-Economic Deprivation of Their Home Communities. Acta Trop. 2014, 135, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, J.E.; Saldaña, A.; González, K.; Rigg, C.; Pineda, V.; Santamaría, A.M.; Rodríguez, I.; Gottdenker, N.L.; Laurenti, M.D.; Chaves, L.F. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Dogs: Is High Seroprevalence Indicative of a Reservoir Role? Parasitology 2015, 142, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosford, K.L. Brucella Canis: An Update on Research and Clinical Management. Can. Vet. J. 2018, 59, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gunstra, A.; Steurer, J.A.; Seibert, R.L.; Dixon, B.C.; Russell, D.S. Sensitivity of Serologic Testing for Dogs Diagnosed with Coccidioidomycosis on Histology: 52 Cases (2012–2013). J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2019, 55, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosypal, A.C.; Troy, G.C.; Duncan, R.B.; Zajac, A.M.; Lindsay, D.S. Utility of Diagnostic Tests Used in Diagnosis of Infection in Dogs Experimentally Inoculated with a North American Isolate of Leishmania Infantum Infantum. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2005, 19, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, I.L.D.; Batista, J.F.; Schallig, H.; Alonso, D.P.; Ribolla, P.E.M.; Costa, D.L.; Costa, C.H.N. The Performance of Serological Tests for Leishmania Infantum Infection Screening in Dogs Depends on the Prevalence of the Disease. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2017, 59, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Portillo, A.; Maggi, R.; Oteo, J.A.; Bradley, J.; García-Álvarez, L.; San-Martín, M.; Roura, X.; Breitschwerdt, E. Bartonella Spp. Prevalence (Serology, Culture, and PCR) in Sanitary Workers in La Rioja Spain. Pathogens 2020, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitassi, L.H.U.; de Paiva Diniz, P.P.V.; Scorpio, D.G.; Drummond, M.R.; Lania, B.G.; Barjas-Castro, M.L.; Gilioli, R.; Colombo, S.; Sowy, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; et al. Bartonella Spp. Bacteremia in Blood Donors from Campinas, Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.G.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Pultorak, E.L.; Hegarty, B.C.; Bradley, J.M.; Mozayeni, B.R.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella Spp. Bacteremia in High-Risk Immunocompetent Patients. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 71, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashnits, E.; Correa, M.; Hegarty, B.C.; Birkenheuer, A.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella Seroepidemiology in Dogs from North America, 2008–2014. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 222–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E. Bartonellosis: One Health Perspectives for an Emerging Infectious Disease. ILAR J. 2014, 55, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowser, N.; Anderson, N.; Bowser, N.H.; Anderson, N.E. Dogs (Canis Familiaris) as Sentinels for Human Infectious Disease and Application to Canadian Populations: A Systematic Review. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Williams, C.; Wey, A.C.; Henn, J.B.; Maggi, R.; Carrasco, S.; Mazet, J.; Boulouis, H.J.; Maillard, R.; et al. Bartonella Endocarditis: A Pathology Shared by Animal Reservoirs and Patients. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1166, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E. Bartonellosis, one Health and All Creatures Great and Small. Vet. Dermatol. 2017, 28, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, P.; Hegarty, B.C.; Marr, H.S.; Maggi, R.G.; Birkenheuer, A.J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Evaluation of Cell Culture-Grown Bartonella Antigens in Immunofluorescent Antibody Assays for the Serological Diagnosis of Bartonellosis in Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1958–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, A.W.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. A Combined Approach for the Enhanced Detection and Isolation of Bartonella Species in Dog Blood Samples: Pre-Enrichment Liquid Culture Followed by PCR and Subculture onto Agar Plates. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 69, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Maggi, R.G.; Diniz, P.P.V.P.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Molecular and Serological Diagnosis of Bartonella Infection in 61 Dogs from the United States. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashnits, E.; Neupane, P.; Bradley, J.M.; Richardson, T.; Thomas, R.; Linder, K.E.; Breen, M.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Molecular Prevalence of Bartonella, Babesia, and Hemotropic Mycoplasma Species in Dogs with Hemangiosarcoma from across the United States. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, R.A.; Grego, E.; Battaia, S.; Gianella, P.; Tursi, M.; Di Girolamo, N.; Biasato, I.; Perego, M. Prevalence of Selected Cardiotropic Pathogens in the Myocardium of Adult Dogs with Unexplained Myocardial and Rhythm Disorders or with Congenital Heart Disease. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2019, 255, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashnits, E.; Neupane, P.; Maggi, R.G.; Linder, K.E.; Bradley, J.M.; Balakrishnan, N.; Southern, B.L.; McKeon, G.P.; Chandrashekar, R.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Detection of Bartonella Spp. in Dogs after Infection with Rickettsia Rickettsii. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, B.C.; Bradley, J.M.; Lappin, M.R.; Balakrishnan, N.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Analysis of Seroreactivity against Cell Culture-Derived Bartonella Spp. Antigens in Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Cherry, N.; Linder, K.E.; Pierce, E.; Sontakke, N.; Hegarty, B.C.; Bradley, J.M.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Experimental Infection of Dogs with Bartonella Henselae and Bartonella Vinsonii Subsp. Berkhoffii. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 156, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, W.A.; Fall, M.Z.; Rooney, J.; Kordick, D.L.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Rapid Identification and Differentiation of Bartonella Species Using a Single-Step PCR Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Duncan, A.W.; Nicholson, W.L.; Hegarty, B.C.; Woods, C.W. Bartonella Species in Blood of Immunocompetent Persons with Animal and Arthropod Contact. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.G.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Havenga, L.N.; Naidoo, V.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Co-Infection with Anaplasma Platys, Bartonella Henselae and Candidatus Mycoplasma Haematoparvum in a Veterinarian. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Potential Limitations of the 16S-23S RRNA Intergenic Region for Molecular Detection of Bartonella Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, P.; Sevala, S.; Balakrishnan, N.; Marr, H.; Wilson, J.; Maggi, R.; Birkenheuer, A.; Lappin, M.; Chomel, B.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Validation of Bartonella Henselae Western Immunoblotting for Serodiagnosis of Bartonelloses in Dogs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01335-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Suksawat, J.; Chomel, B.; Hegarty, B.C. The Immunologic Response of Dogs to Bartonella Vinsonii Subspecies Berkhoffii Antigens: As Assessed by Western Immunoblot Analysis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2003, 15, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, R.G.; Richardson, T.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Miller, J.C. Development and Validation of a Droplet Digital PCR Assay for the Detection and Quanti Fi Cation of Bartonella Species within Human Clinical Samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 176, 106022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.; Albert, P.S. Estimating Diagnostic Accuracy without a Gold Standard: A Continued Controversy. J. Biopharm. Stat. 2016, 26, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, S.L.; Zhou, X.H. Evaluation of Diagnostic Tests without Gold Standards. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1998, 7, 354–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, W.O.; Gastwirth, J.L.; Pearson, L.M. Screening without a ‘Gold Standard’; The Hui-Walter Paradigm Revisited. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 153, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlin, J.; Laughlin, L.; Gordon, S.; Romero, S.; Solórzano, N.; Regnery, R.L. Serodiagnosis of Bartonella Bacilliformis Infection by Indirect Fluorescence Antibody Assay: Test Development and Application to a Population in an Area of Bartonellosis Endemicity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4269–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angkasekwinai, N.; Atkins, E.H.; Romero, S.; Grieco, J.; Chao, C.C.; Ching, W.M. An Evaluation Study of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Using Recombinant Protein Pap31 for Detection of Antibody against Bartonella Bacilliformis Infection among the Peruvian Population. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilson, I.G. MINIREVIEW Inhibition and Facilitation of Nucleic Acid Amplification. Appl Env Micro. 1997, 63, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southern, B.L.; Neupane, P.; Ericson, M.E.; Dencklau, J.C.; Linder, K.E.; Bradley, J.M.; McKeon, G.P.; Long, C.T.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella Henselae in a Dog with Ear Tip Vasculitis. Vet. Dermatol. 2018, 29, 537-e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pultorak, E.L.; Maggi, R.G.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Serial Testing from a 3-Day Collection Period by Use of the Bartonella Alphaproteobacteria Growth Medium Platform May Enhance the Sensitivity of Bartonella Species Detection in Bacteremic Human Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Musulin, S.; Varanat, M.; Bradley, J.M.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Serological and Molecular Prevalence of Selected Canine Vector Borne Pathogens in Blood Donor Candidates, Clinically Healthy Volunteers, and Stray Dogs in North Carolina. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, R.K.; Langohr, I.M.; Wise, A.G.; Smedley, R.C.; Thaiwong, T.; Kiupel, M. Beyond H&E: Integration of Nucleic Acid-Based Analyses Into Diagnostic Pathology. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 238–256. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Wu, W.; Wei, H.; Gao, C.; Zhang, L.; Wu, C.; Hou, L. Using Droplet Digital PCR in the Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis DNA in FFPE Samples. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, K.; Shinzawa, N.; Kawai, A.; Suzuki, M.; Kidoya, H.; Takakura, N.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kameyama, T.; Inagaki, H.; Kurahashi, H.; et al. The Bartonella Autotransporter BafA Activates the Host VEGF Pathway to Drive Angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, S.C.; Dehio, C. Bartonella Entry Mechanisms into Mammalian Host Cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez Vera, C.; Diniz, P.P.V.P.P.; Pultorak, E.L.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. An Unmatched Case Controlled Study of Clinicopathologic Abnormalities in Dogs with Bartonella Infection. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 36, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.E.; Westropp, J.L.; Kasten, R.W.; Chomel, B.B. Association between Bartonella Species Infection and Disease in Pet Cats as Determined Using Serology and Culture. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2010, 12, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, E.C.; Chomel, B.B.; Singhasivanon, O.-U.; Namekata, D.Y.; Kasten, R.W.; Kass, P.H.; Cortés-Vecino, J.; Gennari, S.M.; Rajapakse, R.P.; Huong, L.T.; et al. Bartonella Infection in Urban and Rural Dogs from the Tropics: Brazil, Colombia, Sri Lanka and Vietnam. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 141, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cherry, N.; Diniz, P.; Maggi, R.; Hummel, J.; Hardie, E.; Behrend, E.; Rozanski, E.; DeFrancesco, T.; Cadenas, M.; Breitschwerdt, E. Isolation or Molecular Detection of Bartonella Henselae and Bartonella Vinsonii Subsp. Berkhoffii from Dogs with Idiopathic Cavitary Effusions. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2009, 23, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flor, M.; Weiß, M.; Selhorst, T.; Müller-Graf, C.; Greiner, M. Comparison of Bayesian and Frequentist Methods for Prevalence Estimation under Misclassification. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McV Messam, L.L.; Branscum, A.J.; Collins, M.T.; Gardner, I.A. Frequentist and Bayesian Approaches to Prevalence Estimation Using Examples from Johne’s Disease. Anim. Health Res. Rev. Conf. Res. Work. Anim. Dis. 2008, 9, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostoulas, P.; Nielsen, S.S.; Branscum, A.J.; Johnson, W.O.; Dendukuri, N.; Dhand, N.K.; Toft, N.; Gardner, I.A. STARD-BLCM: Standards for the Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies That Use Bayesian Latent Class Models. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 138, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, K.L.; Gerba, C.P.; Pepper, I.L. Polymerase Chain Reaction Detection of Nonviable Bacterial Pathogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 3513–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, R.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Buffet, J.-P.; Harrus, S. Guidelines for the Isolation, Molecular Detection, and Characterization of Bartonella Species. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazcko, C.; Thomas, R. The Establishment of the Pfizer-Canine Comparative Oncology and Genomics Consortium Biospecimen Repository. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Quach, C.; Bradley, J.M. Bartonella Spp. Bloodstream Infection in a Canadian Family. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varanat, M.; Maggi, R.G.; Linder, K.E.; Horton, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Cross-Contamination in the Molecular Detection of Bartonella from Paraffin-Embedded Tissues. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beath, K.J. Randomlca: An r Package for Latent Class with Random Effects Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 81, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, I.S.; Dhooria, S.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Behera, D.; Agarwal, R. Diagnostic Performance of Xpert MTB/RIF in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonfrate, D.; Marrone, R.; Silva, R.; Mirisola, C.; Ragusa, A.; Mistretta, M.; Perandin, F.; Bisoffi, Z. Prevalence of Strongyloidiasis in a Cohort of Migrants in Italy and Accuracy of a Novel Elisa Assay for s. Stercoralis Infection, a Cross-Sectional Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater Reliability: The Kappa Statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
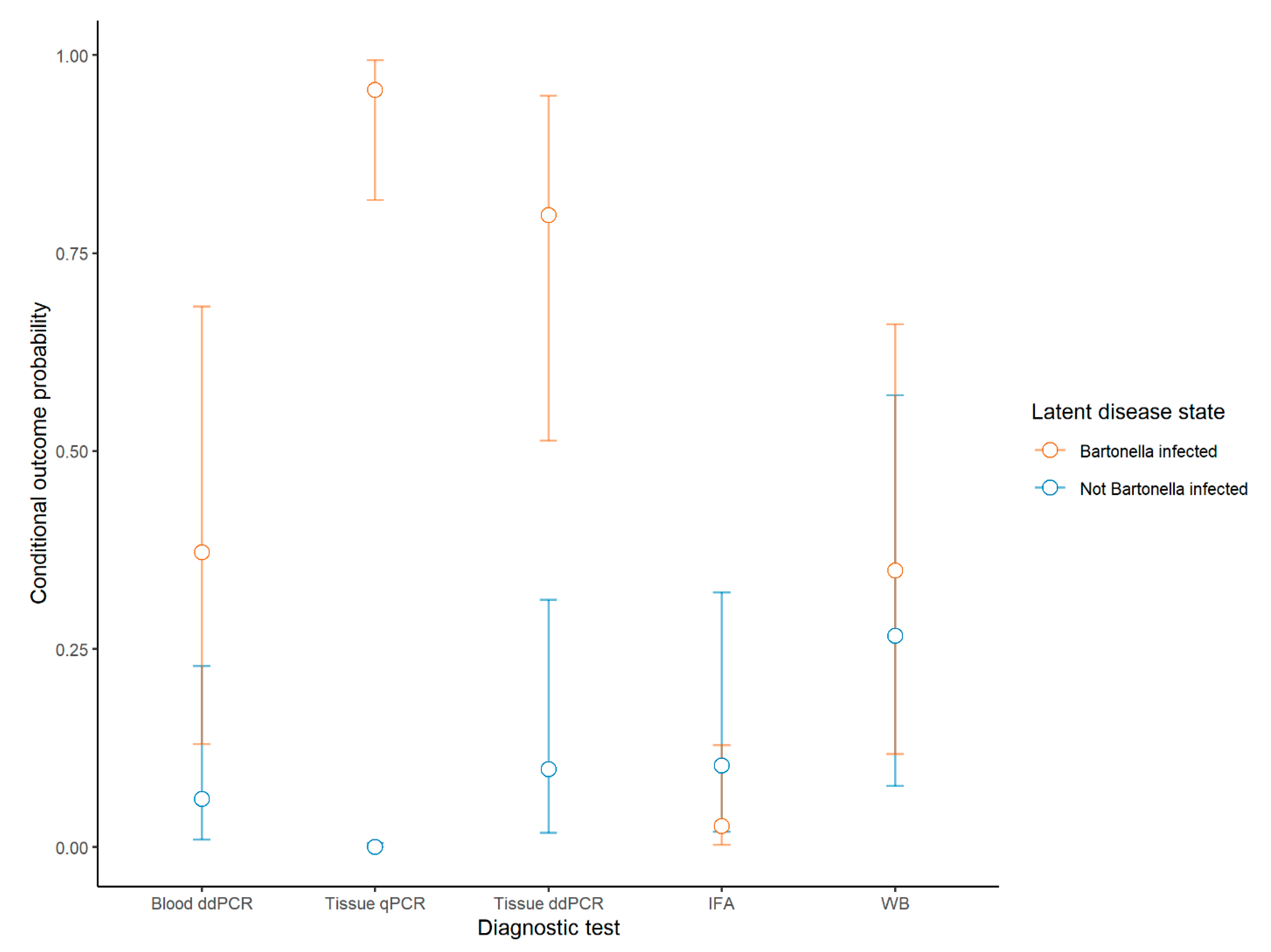
| Positive Dogs (n = 90) | % Sensitivity (95% CI) | % Specificity (95% CI) | Dogs Positive Solely by This Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE-LCA | CRS | RE-LCA | CRS | |||
| Individual molecular tests | ||||||
| Blood qPCR | 0 | -- | 0 (0–5.2) | -- | NA | 0 |
| Blood ddPCR | 25 | 38 (25–54) | 36 (26–47) | 92 (80–100) | 100 (89–100) | 0 |
| Tissue ddPCR | 50 | 78 (65–98) | 71 (60–81) | 88 (70–100) | 94 (79–98) | 2 |
| Tissue qPCR | 56 | 94 (79–100) | 80 (69–88) | 100 (71–100) | 87 (71–95) | 4 |
| Individual serology tests | ||||||
| IFA | 6 | 4 (0–9) | 8.6 (4.0–18) | 88 (72–100) | 100 (89–100) | 0 |
| WB | 30 | 36 (23–49) | 43 (32–55) | 72 (50–89) | 84 (67–93) | 5 |
| Combinations of tests | ||||||
| Any serology test | 32 | -- | 46 (35–57) | -- | 84 (67–93) | -- |
| Any molecular test | 64 | -- | 91 (83–96) | -- | 81 (64–91) | -- |
| Tissue qPCR + IFA (in parallel) | 60 | -- | 86 (76–92) | -- | 87 (71–95) | -- |
| Any of the six assays (CRS sensitivity) | 70 | -- | reference | -- | 65 (47–79) | -- |
| 2 or more of the six assays (CRS specificity) | 59 | -- | 84 (74–91) | -- | reference | -- |
| Assay Result | Number of Dogs | Probability of Classification | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Result summary | Blood ddPCR | Tissue qPCR | Tissue ddPCR | IFA | WB | Observed | Expected | Infected | Not infected |
| Blood ddPCR + Tissue qPCR + Tissue ddPCR only positive | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 9.7 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| All positive except IFA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 7.3 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| Tissue qPCR + Tissue ddPCR only positive | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 16.4 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| Tissue qPCR + Tissue ddPCR + WB only positive | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 8.8 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| Blood ddPCR + Tissue qPCR only positive | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| Blood ddPCR + Tissue qPCR + WB only positive | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1.3 | 0.999 | 0.001 |
| Tissue qPCR + Tissue ddPCR + IFA only positive | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.999 | 0.001 |
| Tissue qPCR only positive | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5.9 | 0.999 | 0.001 |
| All positive except blood ddPCR | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.998 | 0.002 |
| Tissue qPCR + WB only positive | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2.2 | 0.998 | 0.002 |
| Blood ddPCR + Tissue ddPCR only positive | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.720 | 0.280 |
| Tissue ddPCR only positive | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2.9 | 0.410 | 0.590 |
| Blood ddPCR + WB only positive | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.099 | 0.901 |
| Tissue ddPCR + IFA only positive | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.059 | 0.941 |
| Tissue ddPCR + IFA + WB only positive | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.044 | 0.956 |
| All assays negative | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 17.4 | 0.037 | 0.963 |
| WB only positive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 5.9 | 0.027 | 0.973 |
| Blood ddPCR + IFA + WB only positive | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.010 | 0.990 |
| IFA + WB only positive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.003 | 0.997 |
| Tissue qPCR Result | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| Tissue ddPCR result | Positive | 44 (49%) | 6 (6.7%) |
| Negative | 12 (13%) | 28 (31%) | |
| IFA Result | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| WB result | Positive | 4 (4.4%) | 26 (29%) |
| Negative | 2 (2.2%) | 58 (64%) | |
| Molecular Result | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| Serology result | Positive | 26 (29%) | 6 (6.7%) |
| Negative | 38 (42%) | 20 (22%) | |
| Tissue Molecular Result | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| Blood molecular result | Positive | 23 | 2 |
| Negative | 39 | 26 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lashnits, E.; Neupane, P.; Bradley, J.M.; Richardson, T.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Comparison of Serological and Molecular Assays for Bartonella Species in Dogs with Hemangiosarcoma. Pathogens 2021, 10, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070794
Lashnits E, Neupane P, Bradley JM, Richardson T, Maggi RG, Breitschwerdt EB. Comparison of Serological and Molecular Assays for Bartonella Species in Dogs with Hemangiosarcoma. Pathogens. 2021; 10(7):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070794
Chicago/Turabian StyleLashnits, Erin, Pradeep Neupane, Julie M. Bradley, Toni Richardson, Ricardo G. Maggi, and Edward B. Breitschwerdt. 2021. "Comparison of Serological and Molecular Assays for Bartonella Species in Dogs with Hemangiosarcoma" Pathogens 10, no. 7: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070794
APA StyleLashnits, E., Neupane, P., Bradley, J. M., Richardson, T., Maggi, R. G., & Breitschwerdt, E. B. (2021). Comparison of Serological and Molecular Assays for Bartonella Species in Dogs with Hemangiosarcoma. Pathogens, 10(7), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070794







