Progress towards Sustainable Control of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca in Olive Groves of Salento (Apulia, Italy)
Abstract
1. The Phytosanitary Emergencies
2. The Concept of Pathogen Control in Plant Pathology and Xylella Fastidiosa
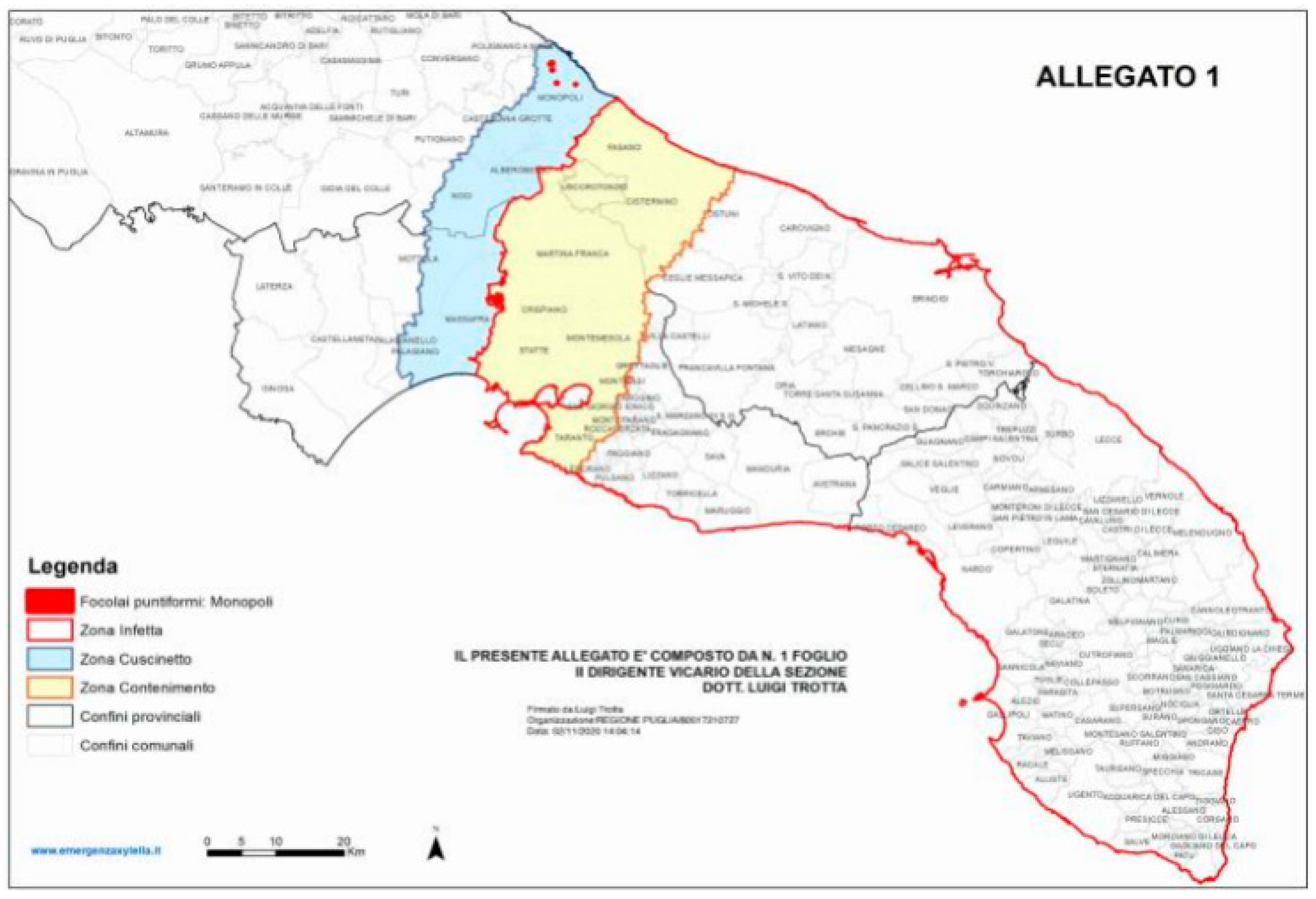
3. Xylella Fastidiosa subsp. Pauca in Apulia, Italy
4. A Control Strategy to Preserve a Multi-millennial Agroecosystem
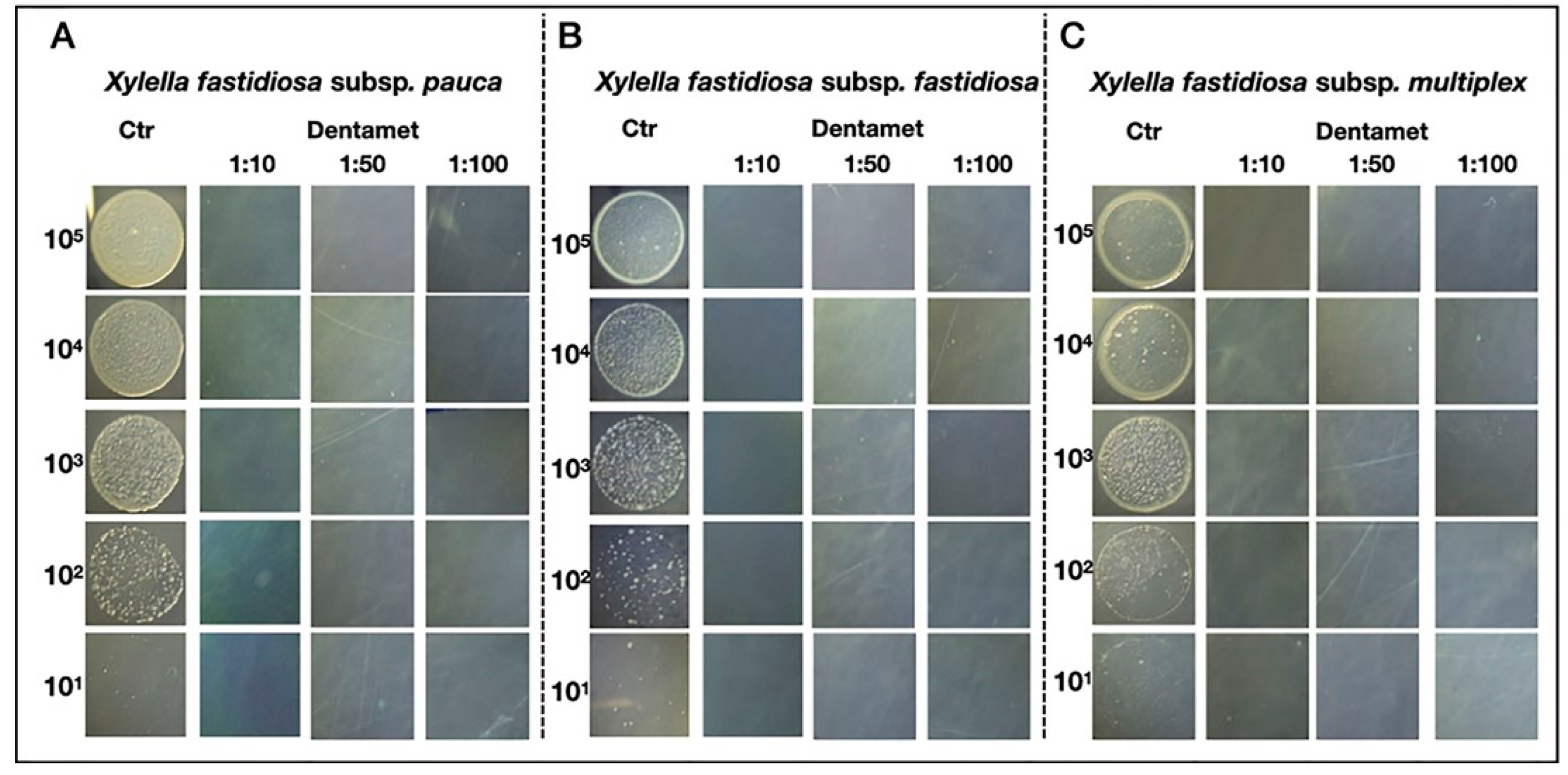
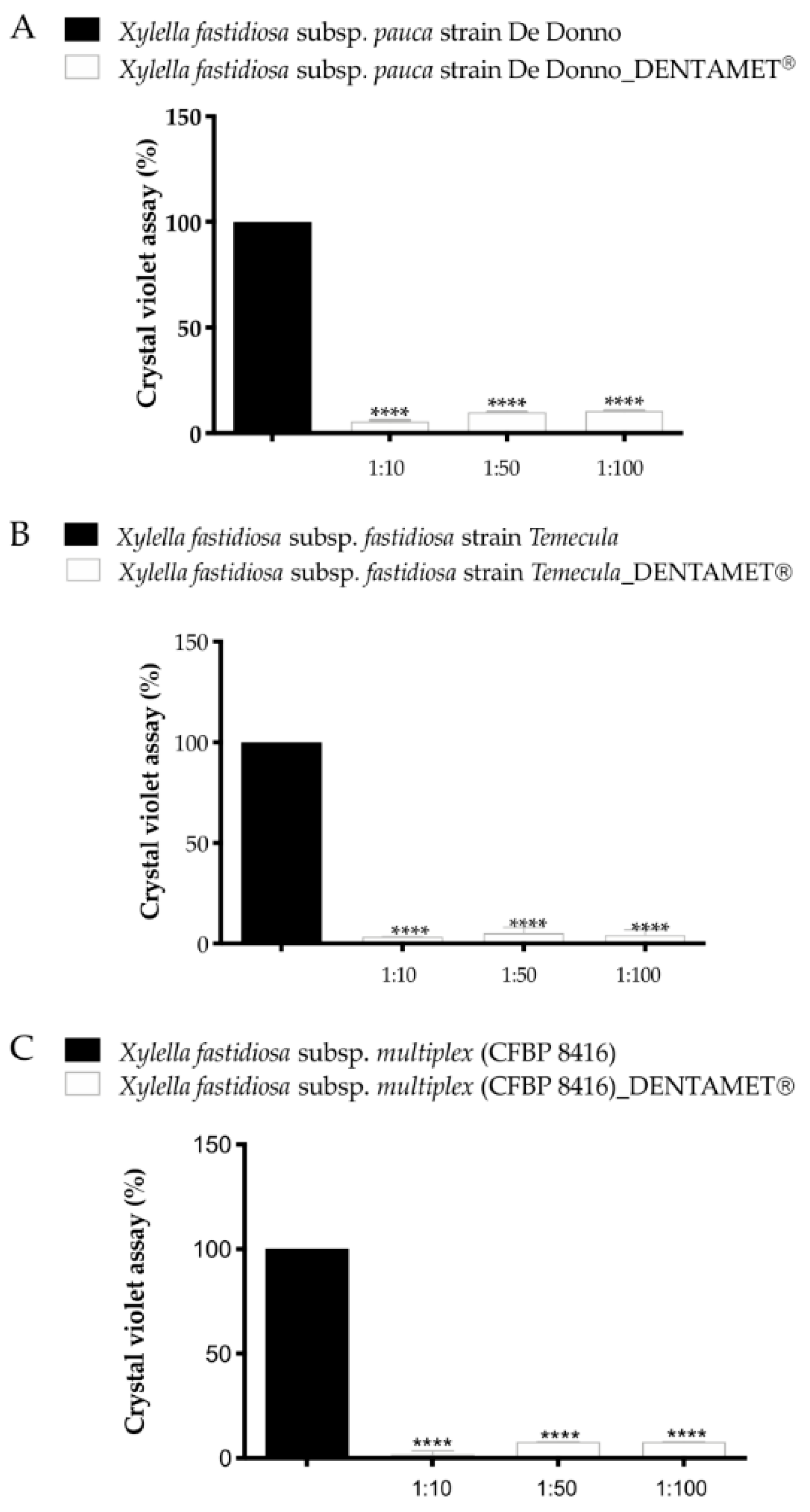
5. The Basic Knowledge and Criteria for Choosing an Effective Compound
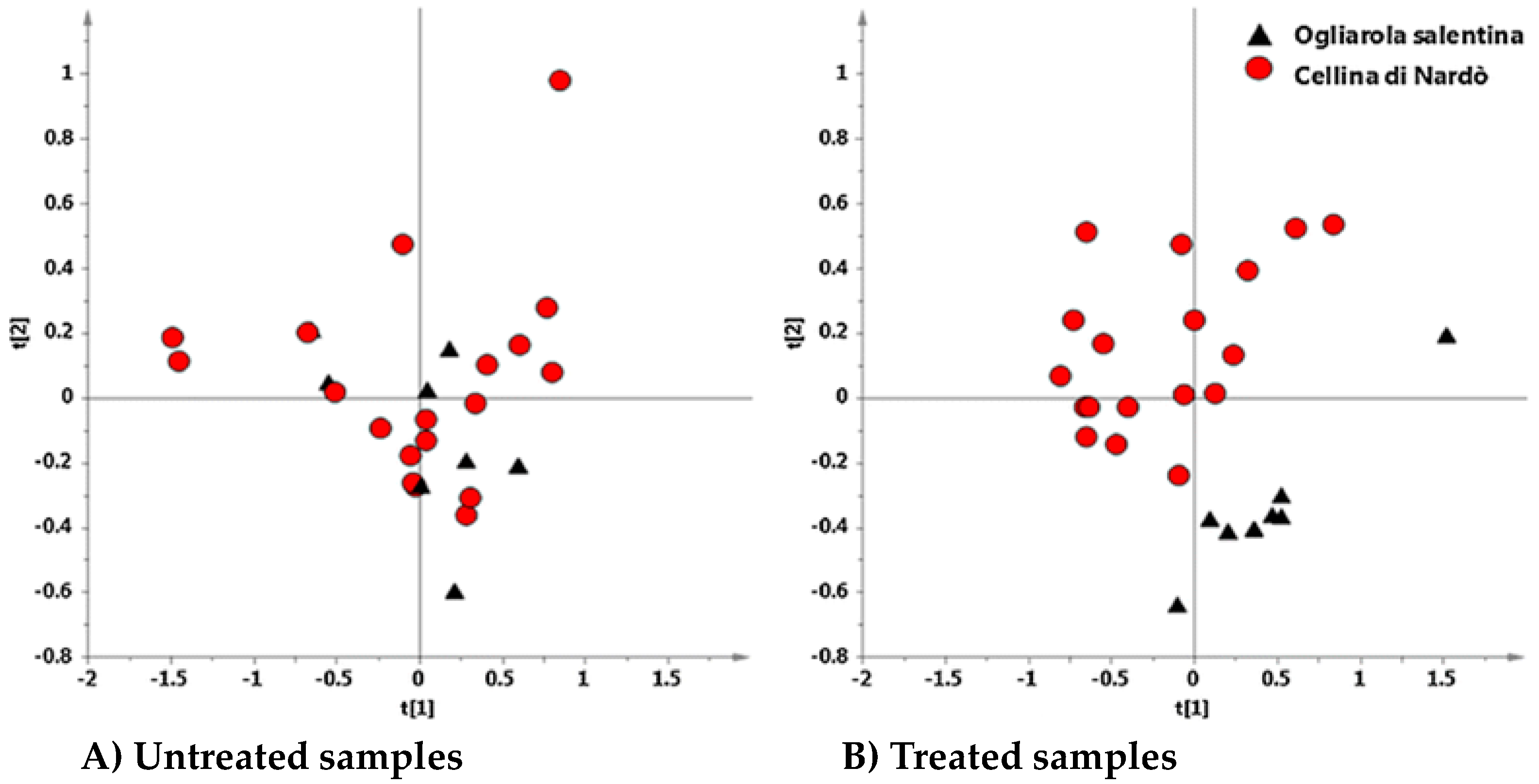
6. Interdisciplinary Studies to Set Up a Sustainable Control Strategy
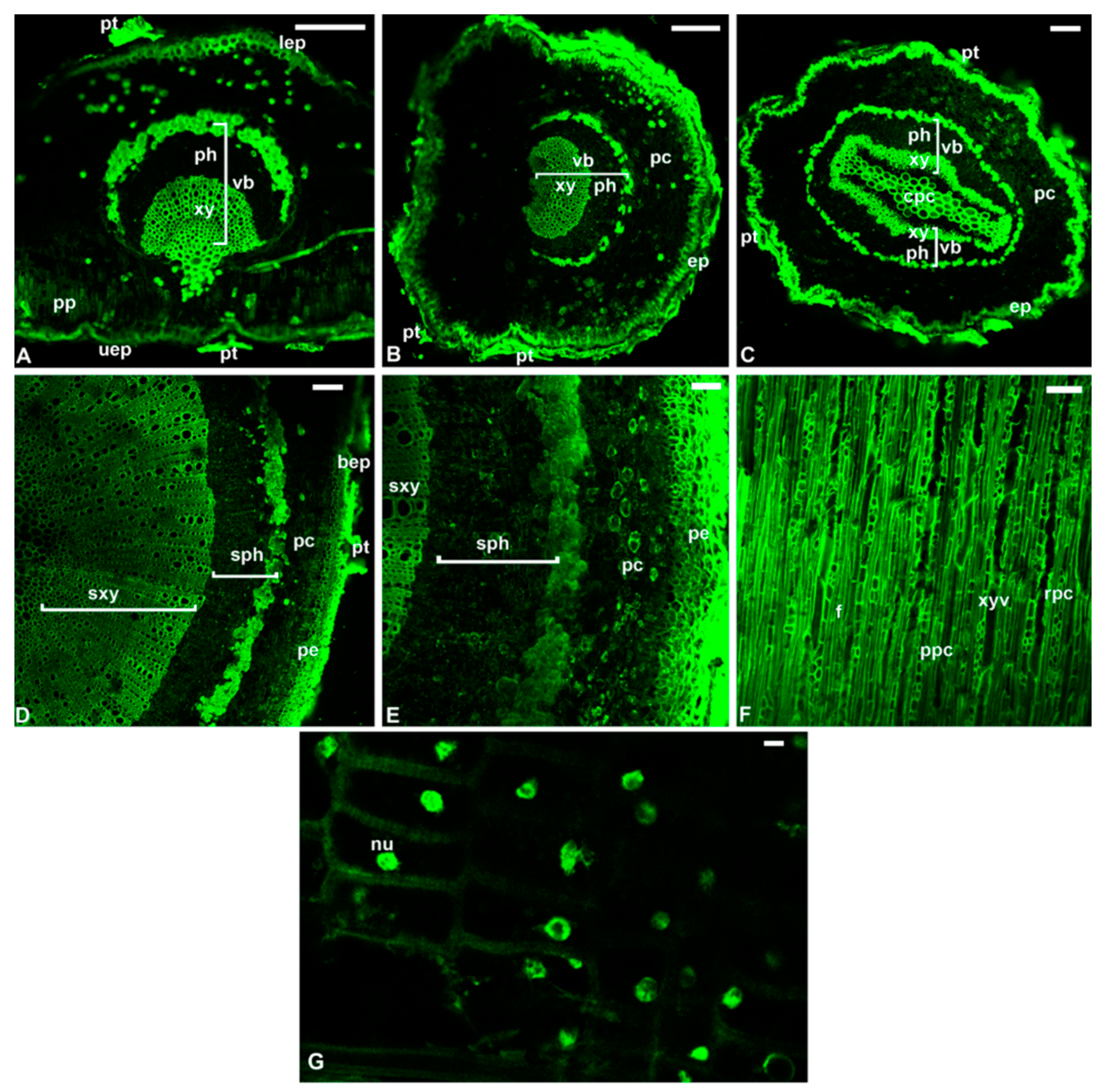
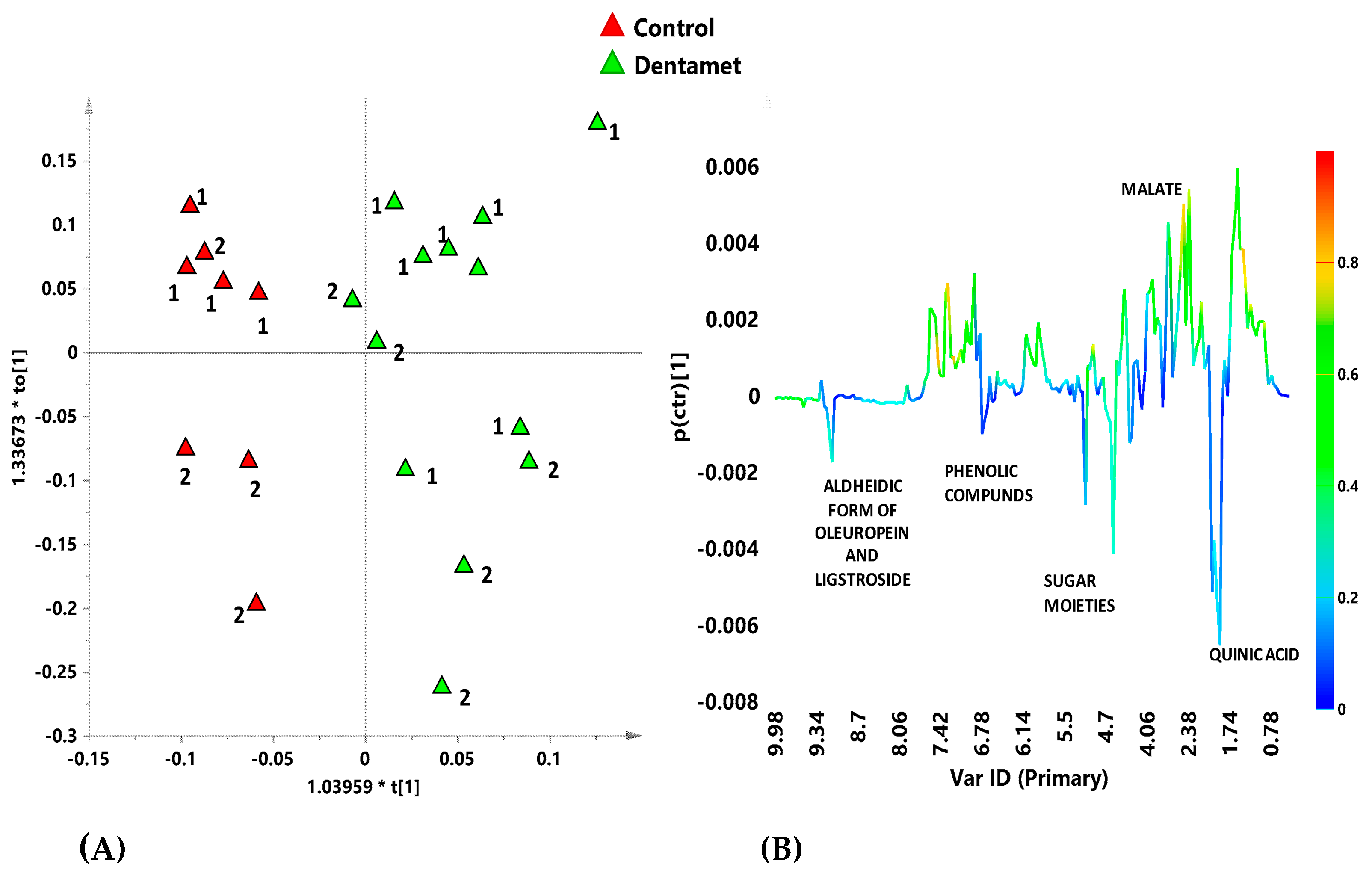
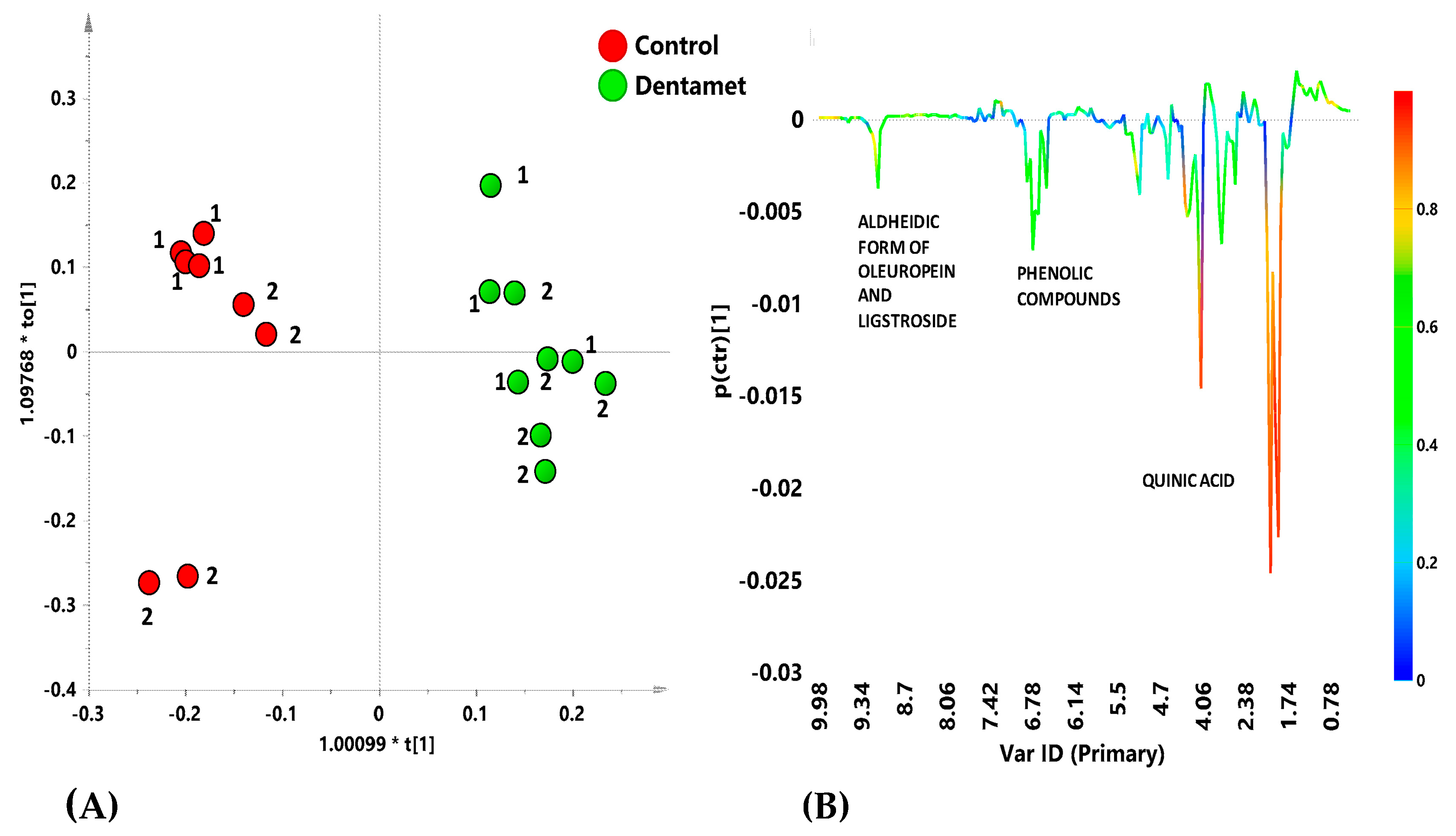
7. The Reprogramming of Metabolic Pathways in the Treated Trees
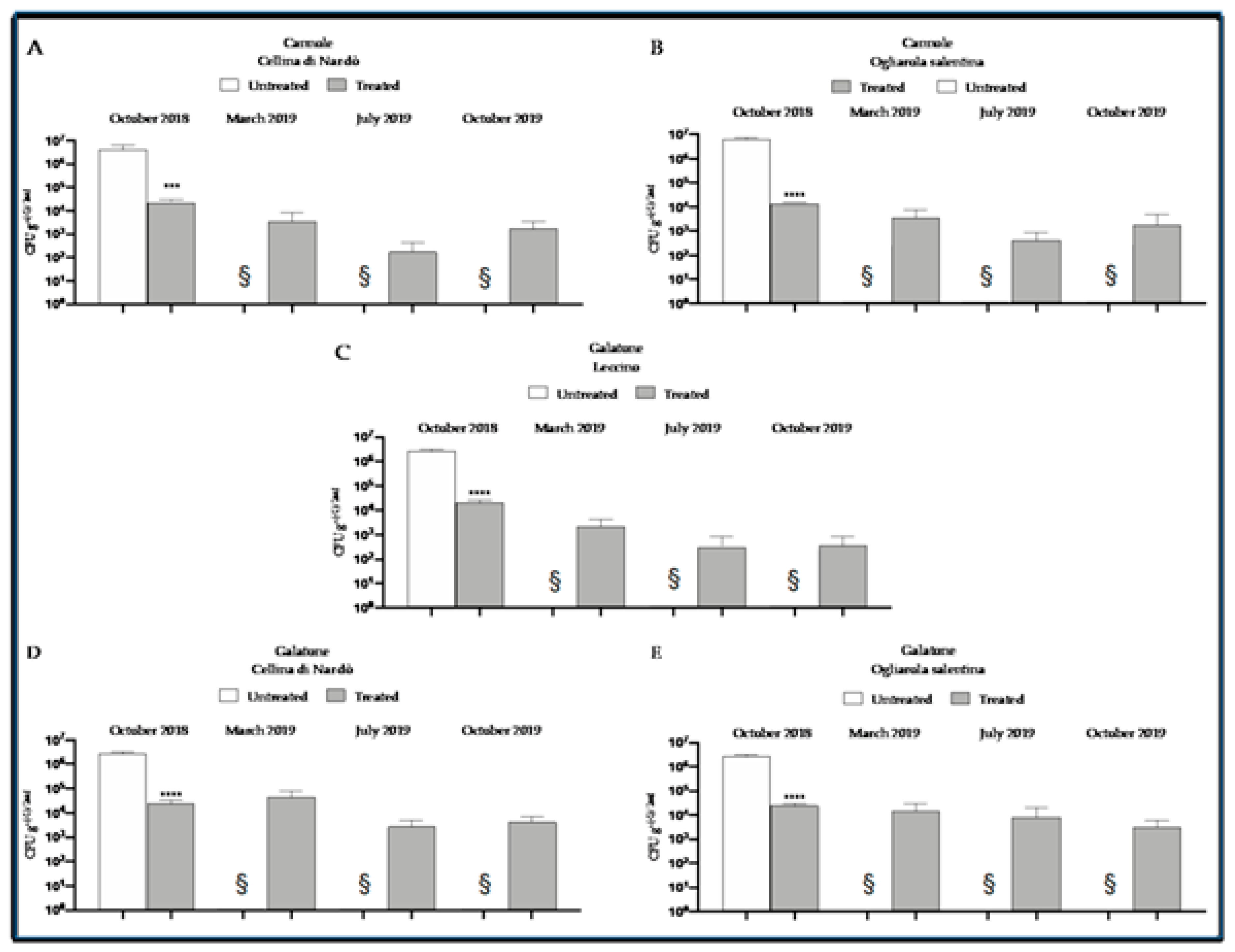
8. The Control Strategy at Work
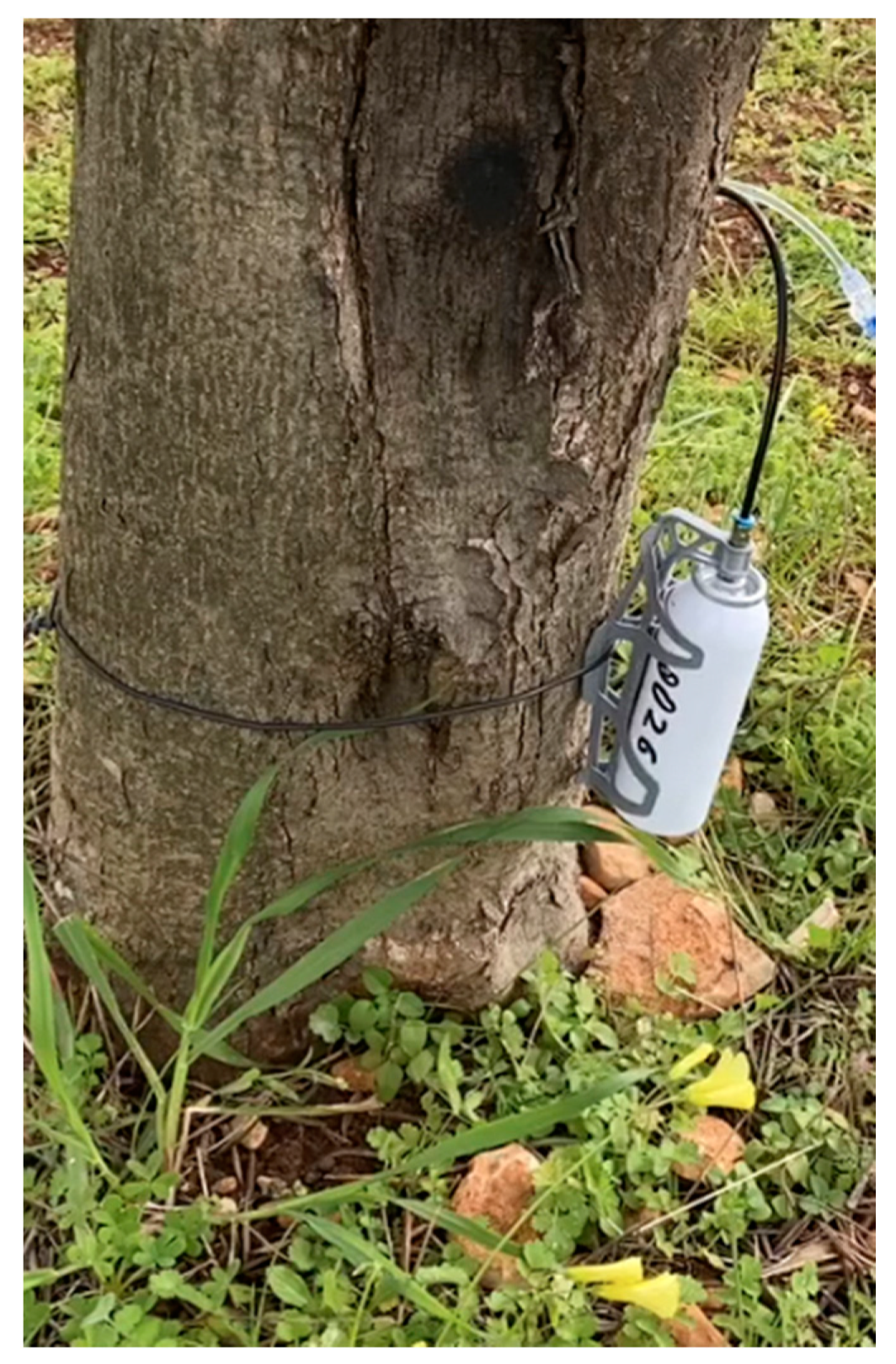
9. A Novel Endotherapy to Fine-Tune the Tree Recovery
10. Considerations and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hulme, P.E. Trade, transport and trouble: Managing invasive species pathways in an era of globalization. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Gladieux, P.; Rahman, H.; Saqib, M.S.; Fiaz, M.; Ahmad, H.; Leconte, M.; Gautier, A.; Justesen, A.F.; Hovmøller, M.S.; et al. Inferring the contribution of sexual reproduction, migration and off-season survival to the temporal maintenance of microbial populations: A case study on the wheat fungal pathogen Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebber, D.P.; Holmes, T.; Gurr, S.J. The global spread of crop pests and pathogens. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgroom, M.G.; Sotirovski, K.; Spica, D.; Davis, J.E.; Brewer, M.T.; Milev, M.; Cortesi, P. Clonal population structure of the chestnut blight fungus in expanding ranges in southeastern Europe. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 4446–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasier, C.; Webber, J. Plant Pathology: Sudden larch death. Nature 2010, 466, 824–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, A.; Ghelardini, L.; De Pace, C.; Desprez-Loustau, M.L.; Capretti, P.; Chandelier, A.; Cech, T.; Chira, D.; Diamandis, S.; Gaitniekis, T.; et al. Biogeographical patterns and determinants of invasion by forest pathogens in Europe. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, H.C.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Pan, H.; Zhong, C.; Rikkerink, E.H.; Templeton, M.D.; Straub, C.; Colombi, E.; et al. Origin and evolution of the kiwifruit canker pandemic. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcelletti, S.; Scortichini, M. Genome-wide comparison and taxonomic relatedness of multiple Xylella fastidiosa strains reveal the occurrence of three subspecies and a new Xylella species. Arch. Microbiol. 2016, 198, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampetruzzi, A.; Saponari, M. Genome-wide analysis provides evidence on the genetic relatedness of the mergent Xylella fastidiosa genotype in Italy to isolates from Central America. Phytopathology 2017, 107, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numminem, E.; Laine, A.-L. The spread of a wild plant pathogen is driven by the road network. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gippet, J.M.W.; Liebhold, A.M.; Fenn-Moltu, G.; Bertelsmeier, C. Human-mediated dispersal in insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 35, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbelotto, M.; Pautasso, M. Impacts of exotic forest pathogens on Mediterranean ecosystem: Four cases studies. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundin, G.W.; Castiblanco, L.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, C.-H. Bacterial diseases management: Challenges, experiences, innovation and future prospects. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2016, 17, 1506–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloy, O.C.; Baudoin, A. Disease control principles. In Enclyclopedia of Plant Pathology; Maloy, O.C., Murray, T.D., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 330–332. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.-C.; Zhan, J.-S.; Xie, L.-H. Problems, challenges and future of plant disease management: From an ecological point of view. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Security Authority (EFSA), Panel of Plant Health. Update of the scientific opinion on the risks to plant health posed by Xylella fastidiosa in the EU territory. EFSA J. 2019, 17, 5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampetruzzi, A.; Morelli, M.; Saponari, M.; Loconsole, G.; Chiumenti, M.; Boscia, D.; Savino, V.N.; Martelli, G.P.; Saldarelli, P. Transcriptome profiling of two olive cultivars in response to infection by the CoDiRO strain of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, D.L. Biological control of Pierce’s disease in the vineyard with strains of Xylella fastidiosa benign to grapevine. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccari, C.; Antonova, E.; Lindow, S. Biological control of Pierce’s disease of grape by an endophytic bacterium. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponari, M.; Boscia, D.; Nigro, F.; Martelli, G.P. Identification of DNA sequences related to Xylella fastidiosa in oleander, almond and olive trees exhibiting leaf scorch symptoms in Apulia (southern Italy). J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 95, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariddi, C.; Saponari, M.; Boscia, D.; De Stradis, A.; Loconsole, G.; Nigro, F.; Porcelli, F.; Potere, O.; Martelli, G.P. Isolation of a Xylella fastidiosa strain infecting olive and oleander in Apulia, Italy. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 96, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, G.P. The current status of quick decline syndrome of olive in southern Italy. Phytoparasitica 2016, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Security Authority (EFSA), Panel of Plant Health. Scientific opinion on the risk to plant health posed by Xylella fastidiosa in the EU territory, with the identification and evaluation of risk reduction options. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scortichini, M.; Cesari, G. An evaluation of monitoring surveys of the quarantine bacterium Xylella fastidiosa performed in containment and buffer areas of Apulia, southern Italy. Appl. Biosaf. 2019, 24, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, R.; Martinez Sanchez, L. Monitoring the impact of Xylella on Apulia’s olive orchards using MODIS satellite data supported by weather data. In Proceedings of the 2nd European Conference on Xylella fastidiosa, Ajaccio, France, 29–30 October 2019; Available online: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/event/191029-xylella/S6.P1_BECK.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Scortichini, M. The multi-millenial olive agroecosystem of Salento (Apulia, Italy) threatened by Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca: A working possibility of restoration. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, L.; De Pascali, S.A.; Fanizzi, F.P. NMR-metabolomic study on monovarietal and blend Salento EVOOs including some from secular olive trees. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, C.; Aprile, A.; Luvisi, A.; Nicolì, F.; Nutricati, E.; Vergine, M.; Miceli, A.; Blando, F.; Sabella, E.; De Bellis, L. Phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of Italian monovarietal extravirgin olive oil. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobine, P.A.; Cruz, L.F.; Navarrete, F.; Duncan, D.; Tygart, M.; De La Fuente, L. Xylella fastidiosa differentially accumulates mineral elements in biofilm and planktonic cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, F.; De La Fuente, L. Response of Xylella fastidiosa to zinc: Decreased culturability, increased exopolysaccharide production, and formation of resilient biofilms under flow conditions. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, F.; De La Fuente, L. Zinc detoxification Is required for full virulence and modification of the host leaf ionome by Xylella fastidiosa. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2015, 28, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, B.; Meyer, M. Identification of mechanisms mediating cold therapy of Xylella fastidiosa-infected grapevine. In Proceedings of the Pierce’s Disease Research Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–14 December 2007; California Department of Food and Agriculture: Sacramento, CA, USA; pp. 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Scortichini, M.; Chen, J. A zinc, copper and citric acid biocomplex shows promise for control of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca in olive trees in Apulia region (southern Italy). Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2018, 57, 48–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatulli, G.; Modesti, V.; Pucci, N.; Scala, V.; L’Aurora, A.; Lucchesi, S.; Salustri, M.; Scortichini, M.; Loreti, S. Further in vitro assessment and mid-term evaluation of control strategy of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca in olive groves of Salento (Apulia, Italy). Pathogens 2021, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haworth, M.; Marino, G.; Brunetti, C.; Killi, D.; De Carlo, A.; Centritto, M. The impact of heat stress and water deficit on the photosynthetic and stomatal physiology of olive (Olea europaea L.)—A case study of the 2017 heat wave. Plants 2018, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deborde, C.; Moing, A.; Roch, L.; Jacob, D.; Rolin, D.; Giraudeau, P. Plant metabolism as studied by NMR spectroscopy. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2017, 102, 61–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiss, K.A.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R.; Klinkhamer, P.G. An overview of NMR-based metabolomics to identify secondary plant compounds involved in host plant resistance. Phytochem. Rev. 2011, 10, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Freitas, D.; Carlos, E.F.; de Souza Gil, M.C.S.; Vieira, L.G.E.; Alcantara, G.B. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of Huanglongbing-asymptomatic and-symptomatic citrus trees. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7582–7588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Coco, L.; Scortichini, M.; Petriccione, M.; Zampella, L.; Mastrobuoni, F.; Cesari, G.; Bertaccini, A.; D’Amico, G.; Contaldo, N.; et al. Xylella fastidiosa and olive quick decline syndrome (CoDiRO) in Salento (southern Italy): A chemometric 1H NMR-based preliminary study on Ogliarola salentina and Cellina di Nardò cultivars. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, C.R.; Angilè, F.; Del Coco, L.; Migoni, D.; Zampella, L.; Marcelletti, S.; Cristella, N.; Marangi, P.; Scortichini, M.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H-NMR metabolite fingerprinting analysis reveals a disease biomarker and a field treatment response in Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca-infected olive trees. Plants 2019, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvisi, A.; Aprile, A.; Sabella, E.; Vergine, M.; Nicoli, F.; Nutricati, E.; Miceli, A.; Negro, C.; De Bellis, L. Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca (CoDiRO) strain infection in four olive (Olea europea L.) cultivars: Profile of phenolic compounds in leaves and progression of leaf scorch symptoms. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2017, 66, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabella, E.; Luvisi, A.; Aprile, A.; Negro, C.; Vergine, M.; Nicoli, F.; Miceli, A.; De Bellis, L. Xylella fastidiosa induces differential expression of lignification related genes and lignin accumulation in tolerant olive trees cv. Leccino. J. Plant. Physiol. 2018, 220, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, C.M.; Wallingford, A.K.; Chen, J. Effect of cultivar phenology, and Xylrella fastidiosa infection on grapevine xylem sap and tissue phenolic content. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 84, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnersley, A.M.; Turano, F.J. Gamma-aminobutis acid (GABA) and plant response to stress. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2000, 19, 479–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bown, A.W.; Shelp, B.J. Plant GABA: Not just a metabolite. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Coco, L.; Angilè, F.; Scortichini, M.; Fanizzi, F.P. Olive cultivars susceptible or tolerant to Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca exhibit mid-term different metabolomes upon natural infection or a curative treatment. Plants 2021, 10, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dichio, B.; Margiotta, G.; Xiloyannis, C.; Bufo, S.A.; Sofo, A.; Cataldi, T.R. Changes in water status and osmolyte contents in leaves and roots of olive plants (Olea europaea L.) subjected to water deficit. Trees 2009, 23, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechri, B.; Tekaya, M.; Hammami, M.; Chehab, H. Effects of drought stress on phenolic accumulation in greenhouse-grown olive trees (Olea europaea). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2020, 92, 104112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekaya, M.; El-Gharbi, S.; Mechri, B.; Chehab, H.; Bchir, A.; Chraief, I.; Ayachi, M.; Boujnah, D.; Attia, F.; Hammami, M. Improving performance of olive trees by the enhancement of key physiological parameters of olive leaves in response to foliar fertilization. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlilat, A.; Ragone, R.; Gualano, S.; Santoro, F.; Gallo, V.; Varvaro, L.; Mastrorilli, P.; Saponari, M.; Nigro, F.; D’Onghia, A.M. Anon-targeted metabolomics study on Xylella fastidiosa infected olive plants grown under controlled conditions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, C.; Cavalieri, V.; Bodino, N.; Tauro, D.; Di Carolo, M.; Fumarola, G.; Altamura, G.; Lasorella, C.; Bosco, D. Plant selection and population trend of spittlebug immatures (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae) in olive groves of the Apulia region of Italy. J. Econ. Èntomol. 2018, 112, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodino, N.; Cavalieri, V.; Dongiovanni, C.; Plazio, E.; Saladini, M.A.; Volani, S.; Simonetto, A.; Fumarola, G.; Di Carolo, M.; Porcelli, F.; et al. Phenology, seasonal abundance and stage-structure of spittlebug (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae) populations inolive groves in Italy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbett, G.S. Pruning mature bearing olive trees. In Olive Production Manual, 2nd ed.; Sibbett, G.S., Ferguson, L., Eds.; University of California, Division of Agriculture and Natural Resource: Oakland, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, M.A.; Lopes, J.I.; Ferreira, I.Q.; Arrobas, M. Olive tree response to the severity of pruning. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2018, 42, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombesi, A. Advances in harvesting and pruning of olive trees. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 42, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Scortichini, M. Predisposing factors for “olive quick decline syndrome” in Salento (Apulia, Italy). Agronomy 2020, 10, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Coletta-Filho, H.; Castillo, A.I.; Ferraz Laranjeira, F.; Chumbinho de Andrade, E.; Teixeira Silva, N.; Alves de Souza, A.; Esteves Bossi, M.; Almeida, R.P.P.; Lopes, J.R.S. Citrus variegated chlorosis: An overview of 30 years of research and disease management. Trop. Plant Pathol 2020, 45, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendson, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant. Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scortichini, M.; Migoni, D.; Angilè, F.; Del Coco, L.; Girelli, C.R.; Zampella, L.; Mastrobuoni, F.; Fanizzi, F.P. Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca on olive in Salento (Southern Italy): Infected trees have low in planta micronutrient content. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2019, 58, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, L.; Migoni, D.; Girelli, C.R.; Angilè, F.; Scortichini, M.; Fanizzi, F.P. Soil and leaf ionome heterogeneity in Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca-infected, non-infected and treated olive groves in Apulia, Italy. Plants 2020, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poschenrieder, C.; Toirà, R.; Barcelo, J. Can metal defend plants against biotic stress? Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabot, C.; Martos, S.; Llugany, M.; Gallego, B.; Toirà, R.; Poschenrieder, C. A role for zinc in plant defense 3389/fpls.2019.01171.against pathogens and herbivores. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behlau, F.; Amorim, L.; Belasque, J.; Bergamin, A.; Leite, R.P.; Graham, J.H.; Gottwald, T.R. Annual and polyetic progression of citrus canker on trees protected with copper sprays. Plant Pathol. 2010, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behlau, F.; Canteros, B.I.; Minsavage, G.V.; Jones, J.B.; Graham, J.H. Molecular characterization of copper resistance genes from Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri and Xanthomonas alfalfae subsp. citrumelonis. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4089–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Security Authority (EFSA), Panel of Plant Health. Treatment solutions to cure Xylella fastidiosa diseased plants. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
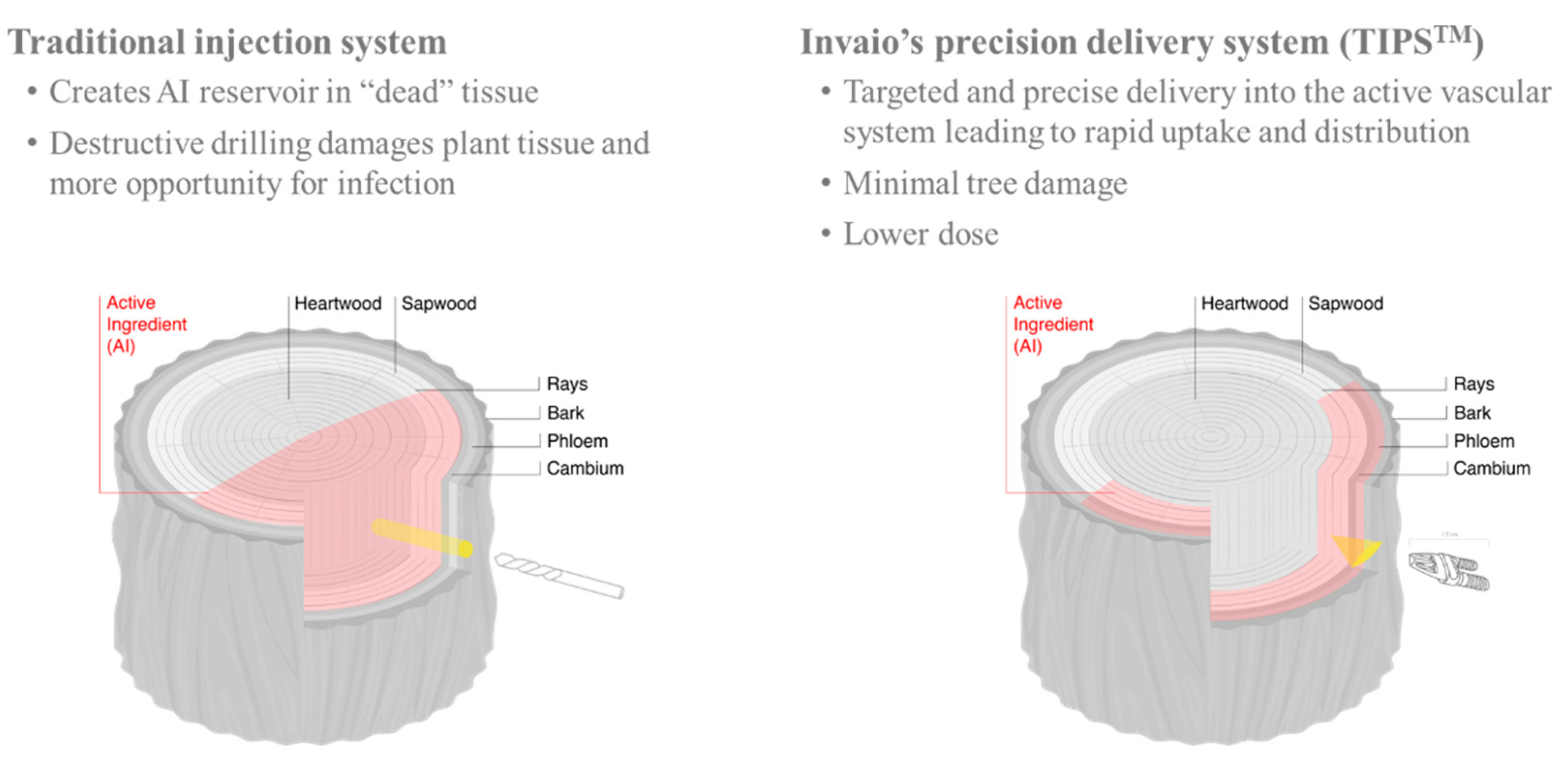
- Berger, C.; Laurent, F. Trunk injection of plant protection products to protect trees from pests and diseases. Crop Prot. 2019, 124, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J.C. Enhancing resistance management and performance of biorational insecticides with novel delivery systems in tree fruit IPM. In Insect Control and Resistance Management; Horowitz, A., Ishaaya, I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.T.; Lewis, P.A. Potential concerns for tree wound response from stem injection. In Proceedings of the Third Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Conference, Asheville, NC, USA, 1–3 February 2005; pp. 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Shortle, W.C.; Dudzik, K.R.; Smith, K.T. Development of wood decay in wound-initiated discolored wood of eastern red cedar. Holzforschung 2010, 64, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doccola, J.J.; Smitley, D.R.; Davis, T.W.; Alken, J.J.; Wild, P.M. Tree wound responses following systemic insecticide trunk injection treatments in green ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica Marsh.) as determined by destructive autopsy. Arboric. Urban For. 2011, 37, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pallardy, S.G. Physiology of Woody Plants, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; p. 464. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp, K.; Mencuccini, M.; Perks, M.; Gardiner, B. The regulation of sapwood area: Water transport and heartwood formation in Sitka spruce. Plant Ecol. Divers. 2013, 6, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2018/1981. Renewing the Approval of the Active Substances Copper Compounds, as Candidates for Substitution, in Accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning the Placing of Plant Protection Products on the Market, and Amending the Annex to Commission Implementing Regulation (EU); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]


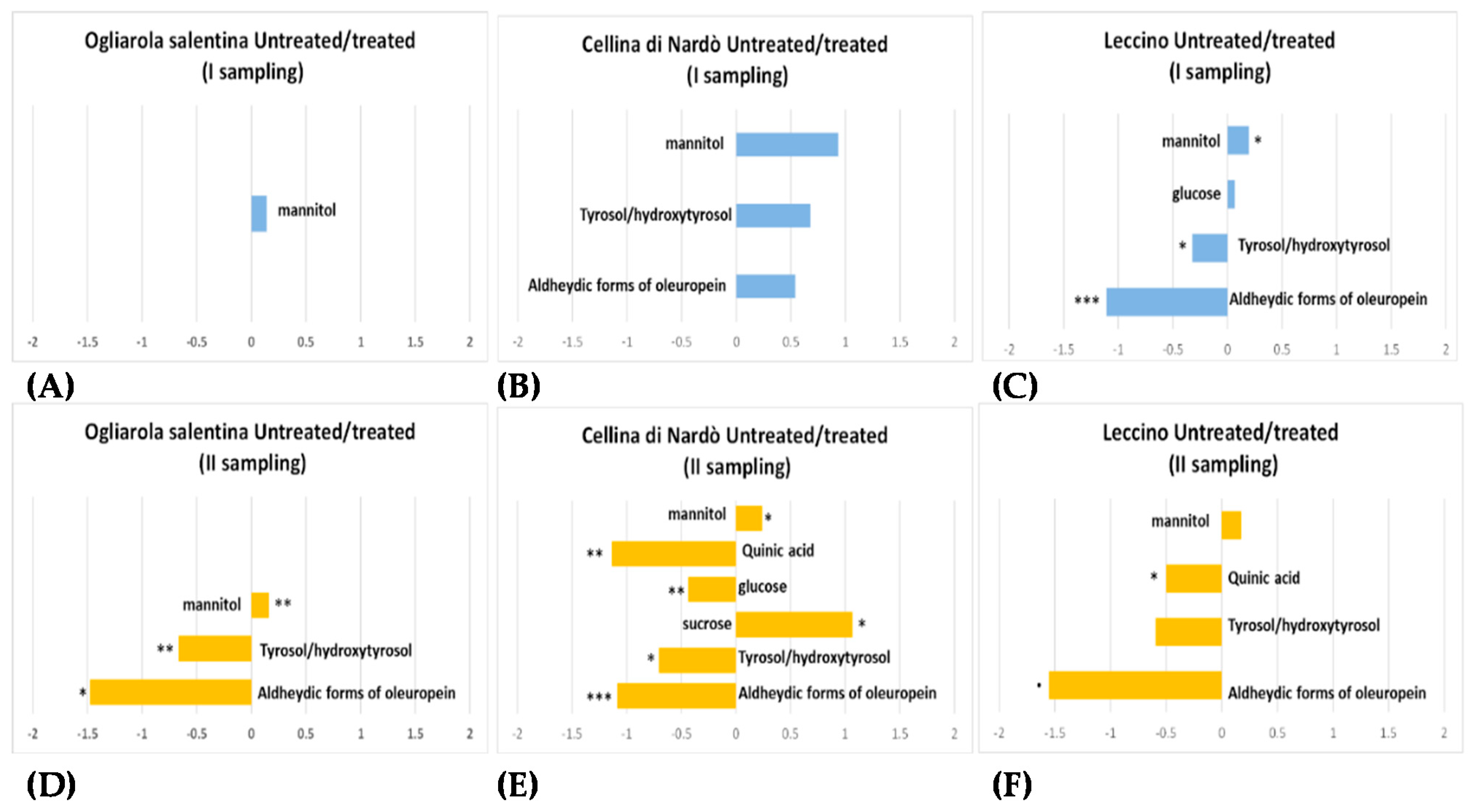



| Infected | Healthy | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ogliarola | Cellina | Leccino | Ogliarola | Cellina | Leccino | ||||
| Untreated | Treated | Untreated | Treated | Untreated | Treated | Untreated | Untreated | Untreated | |
| Oleuropein derivatives | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Glucose | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| Sucrose | ✓ | ||||||||
| Flavonoids | ✓ | ||||||||
| Mannitol | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Malate | ✓ | ||||||||
| Quinic acid | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scortichini, M.; Loreti, S.; Pucci, N.; Scala, V.; Tatulli, G.; Verweire, D.; Oehl, M.; Widmer, U.; Codina, J.M.; Hertl, P.; et al. Progress towards Sustainable Control of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca in Olive Groves of Salento (Apulia, Italy). Pathogens 2021, 10, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060668
Scortichini M, Loreti S, Pucci N, Scala V, Tatulli G, Verweire D, Oehl M, Widmer U, Codina JM, Hertl P, et al. Progress towards Sustainable Control of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca in Olive Groves of Salento (Apulia, Italy). Pathogens. 2021; 10(6):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060668
Chicago/Turabian StyleScortichini, Marco, Stefania Loreti, Nicoletta Pucci, Valeria Scala, Giuseppe Tatulli, Dimitri Verweire, Michael Oehl, Urs Widmer, Josep Massana Codina, Peter Hertl, and et al. 2021. "Progress towards Sustainable Control of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca in Olive Groves of Salento (Apulia, Italy)" Pathogens 10, no. 6: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060668
APA StyleScortichini, M., Loreti, S., Pucci, N., Scala, V., Tatulli, G., Verweire, D., Oehl, M., Widmer, U., Codina, J. M., Hertl, P., Cesari, G., De Caroli, M., Angilè, F., Migoni, D., Del Coco, L., Girelli, C. R., Dalessandro, G., & Fanizzi, F. P. (2021). Progress towards Sustainable Control of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca in Olive Groves of Salento (Apulia, Italy). Pathogens, 10(6), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060668










