Further Characterization of Glycoform-Selective Prions of Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
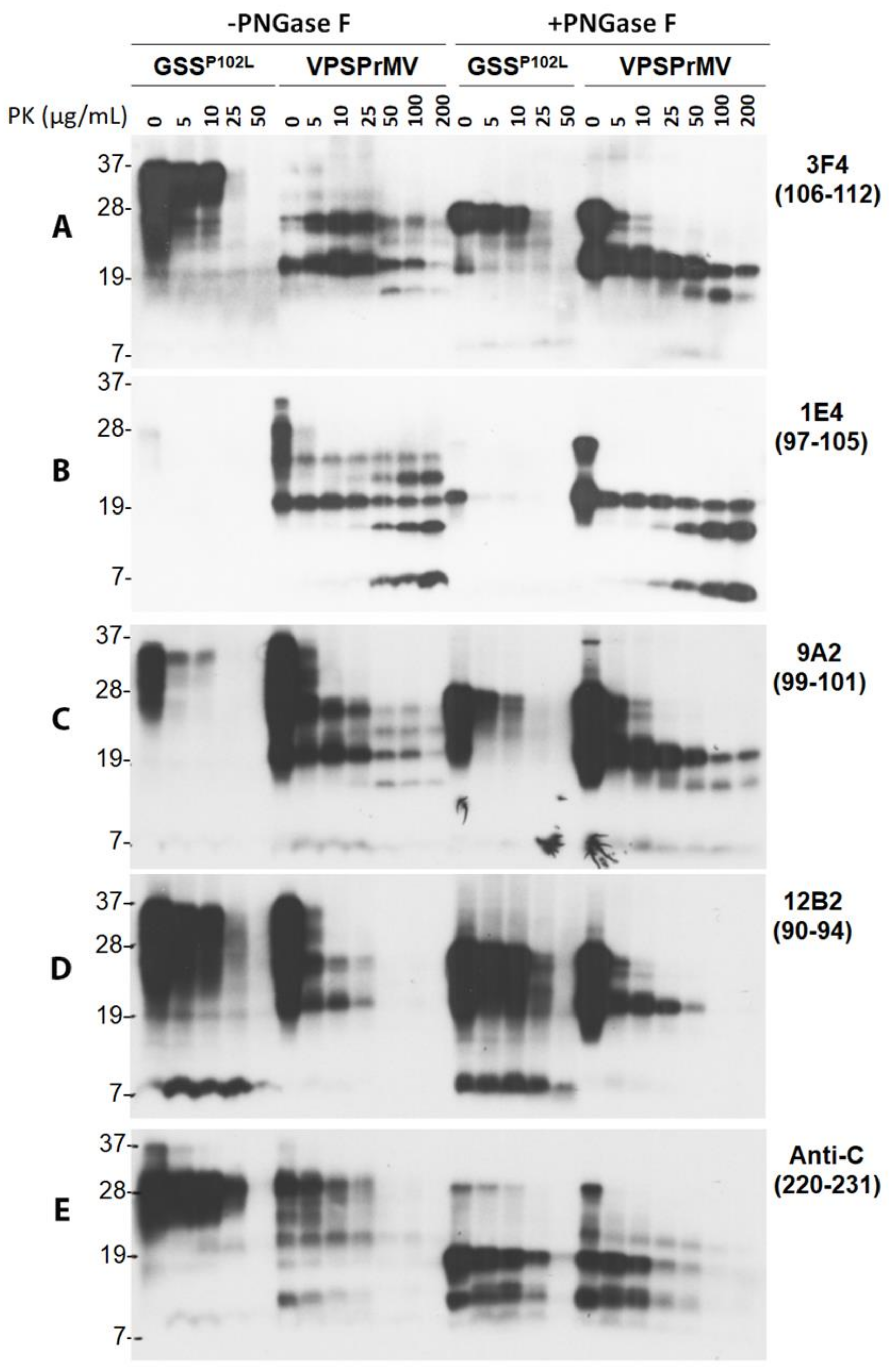
2.1. Ladder-Like PrPres Electrophoretic Profile Results from PK Dose-Dependent Two-Step Truncation of PrPSc
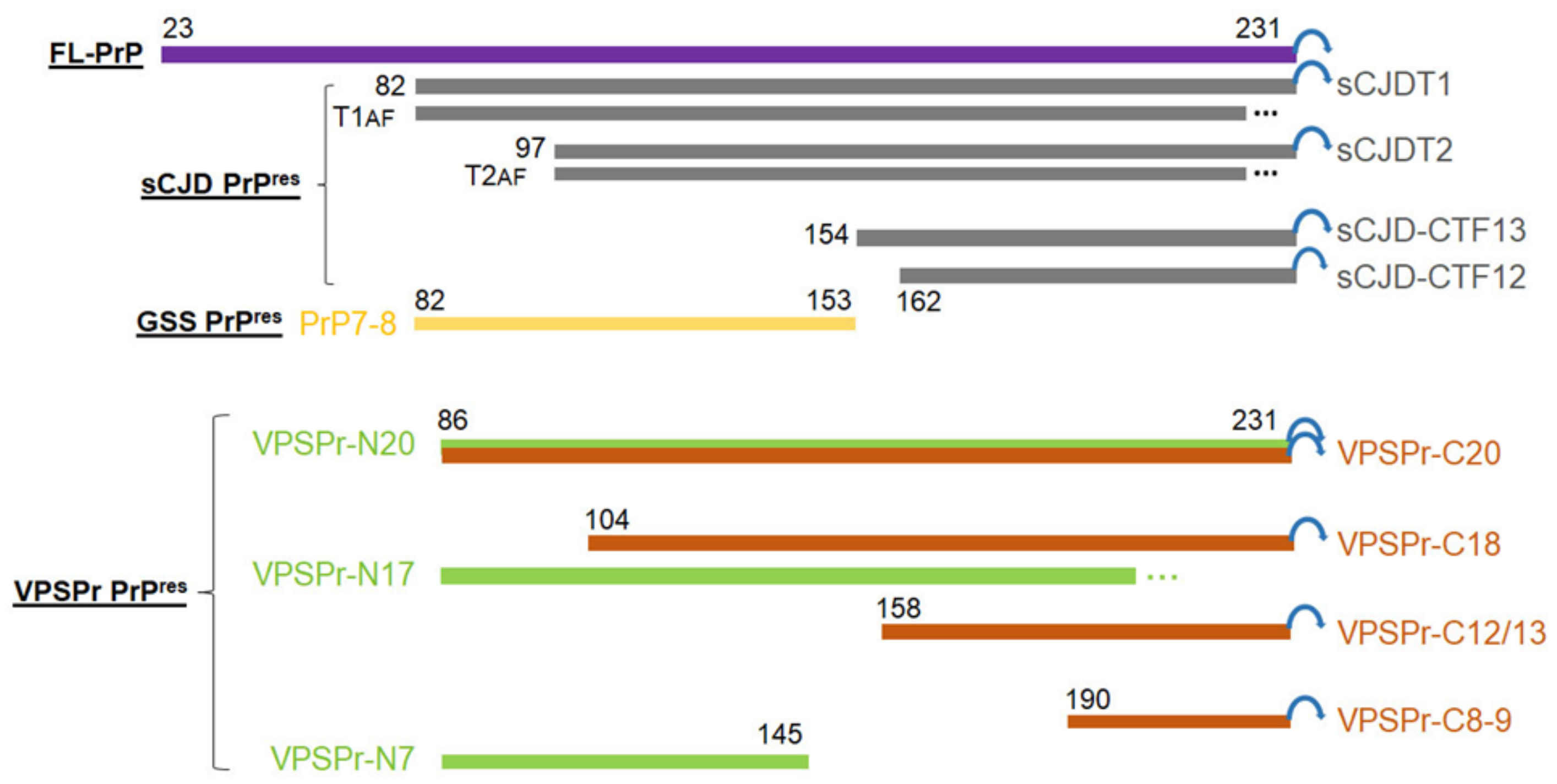
2.2. Two Groups of PrPres Fragments Are Generated upon PK-Treatment of PrPSc
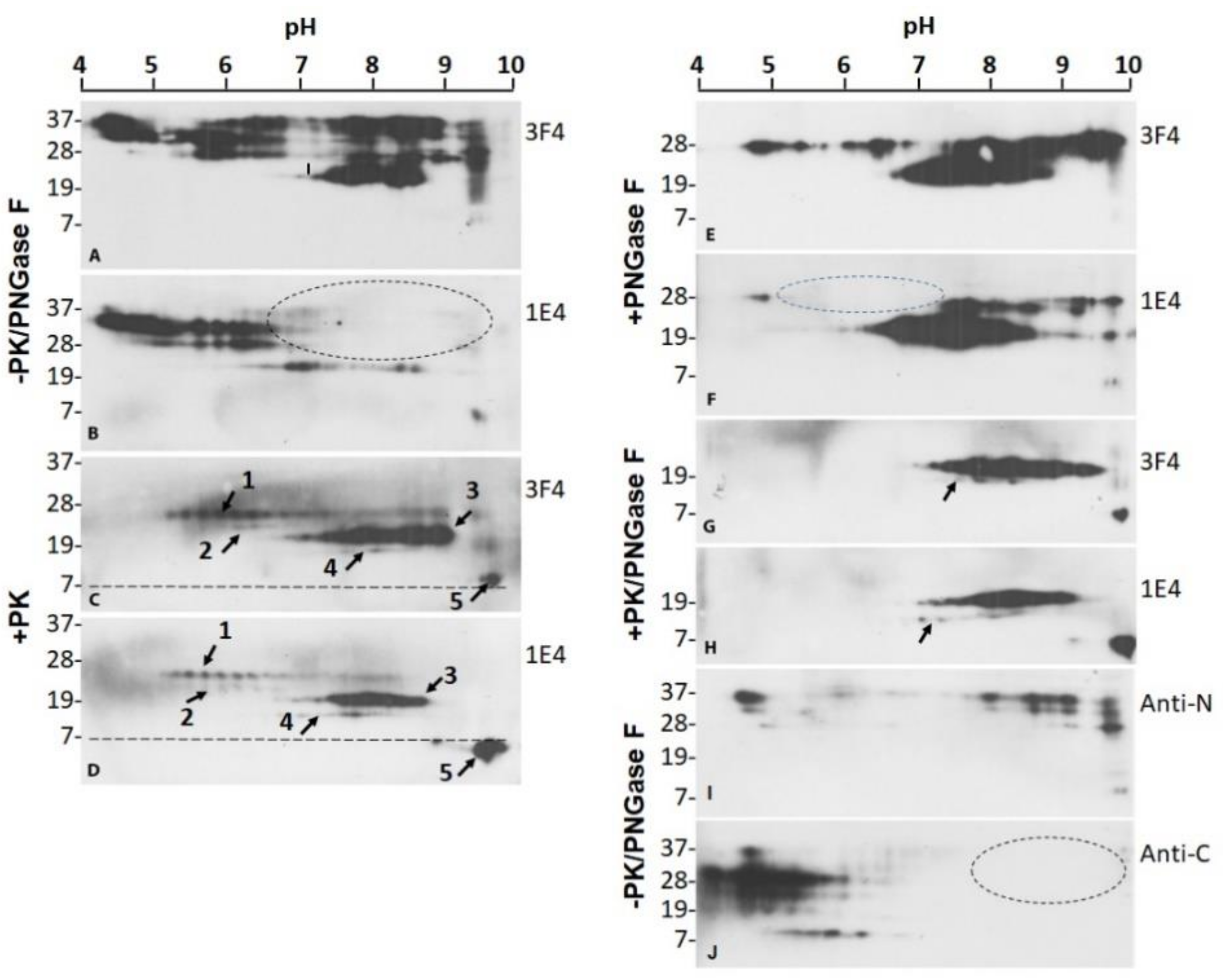
2.3. 1E4 Has a Poorer Affinity to the Full-Length but a Better Affinity to Truncated PrP Compared to 3F4
2.4. Mono181 and Mono197 PrP Glycoforms May Contain Less or Smaller Glycans in VPSPr Compared to Those in sCJD
2.5. VPSPr7 Is Different from GSS PrP7–8 and PrPP102L Mutation Inhibits Binding of 1E4 to the Mutant PrP
2.6. PrPSc-Seeding Activity Is Lower in VPSPr Than in sCJD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Preparation of Brain Samples
4.3. RT-QuIC Assay
4.4. Two-Dimensional Western Blotting
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughey, B.; Raymond, G.J.; Callahan, M.A.; Wong, C.; Baron, G.S.; Xiong, L.W. Interactions and conversions of prion protein isoforms. Adv. Protein Chem. 2001, 57, 139–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, G.S.; Wehrly, K.; Dorward, D.W.; Chesebro, B.; Caughey, B. Conversion of raft associated prion protein to the protease-resistant state requires insertion of PrP-res (PrP(Sc)) into contiguous membranes. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliavini, F.; Prelli, F.; Porro, M.; Rossi, G.; Giaccone, G.; Farlow, M.R.; Dlouhy, S.R.; Ghetti, B.; Bugiani, O.; Frangione, B. Amyloid fibrils in Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease (Indiana and Swedish kindreds) express only PrP peptides encoded by the mutant allele. Cell 1994, 79, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, J.; Sidle, K.C.; Meads, J.; Ironside, J.; Hill, A.F. Molecular analysis of prion strain variation and the aetiology of ‘new variant’ CJD. Nature 1996, 383, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.; Castellani, R.; Capellari, S.; Ghetti, B.; Young, K.; Chen, S.G.; Farlow, M.; Dickson, D.W.; Sima, A.A.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Molecular basis of phenotypic variability in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.; Giese, A.; Capellari, S.; Brown, P.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Windl, O.; Zerr, I.; Budka, H.; Kopp, N.; Piccardo, P.; et al. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliavini, F.; Lievens, P.M.; Tranchant, C.; Warter, J.M.; Mohr, M.; Giaccone, G.; Perini, F.; Rossi, G.; Salmona, M.; Piccardo, P.; et al. A 7-kDa prion protein (PrP) fragment, an integral component of the PrP region required for infectivity, is the major amyloid protein in Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease A117V. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6009–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q.; Capellari, S.; Parchi, P.; Sy, M.S.; Gambetti, P.; Chen, S.G. Identification of novel proteinase K-resistant C-terminal fragments of PrP in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40429–40436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambetti, P.; Kong, Q.; Zou, W.; Parchi, P.; Chen, S.G. Sporadic and familial CJD: Classification and characterisation. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 66, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanusso, G.; Polo, A.; Farinazzo, A.; Nonno, R.; Cardone, F.; Di Bari, M.; Ferrari, S.; Principe, S.; Gelati, M.; Fasoli, E.; et al. Novel prion protein conformation and glycotype in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccone, G.; Di Fede, G.; Mangieri, M.; Limido, L.; Capobianco, R.; Suardi, S.; Grisoli, M.; Binelli, S.; Fociani, P.; Bugiani, O.; et al. A novel phenotype of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2007, 78, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambetti, P.; Dong, Z.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, M.; Alshekhlee, A.; Castellani, R.; Cohen, M.; Barria, M.A.; Gonzalez-Romero, D.; et al. A novel human disease with abnormal prion protein sensitive to protease. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q.; Puoti, G.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, J.; Qing, L.; Cali, I.; Shimoji, M.; Langeveld, J.P.; Castellani, R.; Notari, S.; et al. Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy: A new sporadic disease of the prion protein. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q.; Langeveld, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, S.; McGeer, P.L.; Yuan, J.; Payne, M.C.; Kang, H.E.; McGeehan, J.; Sy, M.S.; et al. PrP conformational transitions alter species preference of a PrP-specific antibody. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13874–13884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Dong, Z.; Guo, J.P.; McGeehan, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J.; Cali, I.; McGeer, P.L.; Cashman, N.R.; Bessen, R.; et al. Accessibility of a critical prion protein region involved in strain recognition and its implications for the early detection of prions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.S.; Zou, W.Q. Prions: Beyond a Single Protein. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 633–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, M.W.; Knight, R.; Zeidler, M.; Yull, H.; Barlow, A.; Ironside, J.W. A case of protease sensitive prionopathy in a patient in the UK. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2009, 35, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, C.; Head, M.W.; van Gool, W.A.; Baas, F.; Yull, H.; Ironside, J.W.; Rozemuller, A.J. The first case of protease-sensitive prionopathy (PSPr) in The Netherlands: A patient with an unusual GSS-like clinical phenotype. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, M.W.; Lowrie, S.; Chohan, G.; Knight, R.; Scoones, D.J.; Ironside, J.W. Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy in a PRNP codon 129 heterozygous UK patient with co-existing tau, alpha synuclein and Abeta pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.; Parchi, P.; Capellari, S.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Schuur, M.; Strammiello, R.; Corrado, P.; Bishop, M.T.; van Gool, W.A.; Verbeek, M.M.; et al. Human prion diseases in the Netherlands (1998–2009): Clinical, genetic and molecular aspects. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Martinez, A.B.; Lopez de Munain, A.; Ferrer, I.; Zarranz, J.J.; Atares, B.; Villagra, N.T.; Arteagoitia, J.M.; Garrido, J.M.; Juste, R.A. Coexistence of protease sensitive and resistant prion protein in 129VV homozygous sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2012, 6, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, M.W.; Yull, H.M.; Ritchie, D.L.; Langeveld, J.P.; Fletcher, N.A.; Knight, R.S.; Ironside, J.W. Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy in the UK: A retrospective review 1991–2008. Brain 2013, 136, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peden, A.H.; Sarode, D.P.; Mulholland, C.R.; Barria, M.A.; Ritchie, D.L.; Ironside, J.W.; Head, M.W. The prion protein protease sensitivity, stability and seeding activity in variably protease sensitive prionopathy brain tissue suggests molecular overlaps with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, A.; Bieniek, K.F.; Lin, W.L.; Notari, S.; Zou, W.Q.; Gambetti, P.; Pedraza, O.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Ferman, T.J.; Dickson, D.W. Concurrent variably protease-sensitive prionopathy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, N.; Perry, A.; McKeel, D.; Schmidt, R.E.; Carter, D.; Norton, J.; Zou, W.Q.; Xiao, X.; Puoti, G.; Notari, S.; et al. Variably Protease-sensitive Prionopathy in an Apparent Cognitively Normal 93-Year-Old. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2015, 29, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Yuan, J.; Haik, S.; Cali, I.; Zhan, Y.; Moudjou, M.; Li, B.; Laplanche, J.L.; Laude, H.; Langeveld, J.; et al. Glycoform-selective prion formation in sporadic and familial forms of prion disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q.; Gambetti, P.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, J.; Langeveld, J.; Pirisinu, L. Prions in variably protease-sensitive prionopathy: An update. Pathogens 2013, 2, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notari, S.; Xiao, X.; Espinosa, J.C.; Cohen, Y.; Qing, L.; Aguilar-Calvo, P.; Kofskey, D.; Cali, I.; Cracco, L.; Kong, Q.; et al. Transmission characteristics of variably protease-sensitive prionopathy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 2006–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diack, A.B.; Ritchie, D.L.; Peden, A.H.; Brown, D.; Boyle, A.; Morabito, L.; Maclennan, D.; Burgoyne, P.; Jansen, C.; Knight, R.S.; et al. Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy, a unique prion variant with inefficient transmission properties. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonno, R.; Notari, S.; Di Bari, M.A.; Cali, I.; Pirisinu, L.; d’Agostino, C.; Cracco, L.; Kofskey, D.; Vanni, I.; Lavrich, J.; et al. Variable Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy Transmission to Bank Voles. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambetti, P.; Cali, I.; Notari, S.; Kong, Q.; Zou, W.Q.; Surewicz, W.K. Molecular biology and pathology of prion strains in sporadic human prion diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambetti, P.; Puoti, G.; Zou, W.Q. Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy: A novel disease of the prion protein. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 45, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.-Q. Insoluble Cellular Prion Protein. In Prions and Diseases, 1st ed.; Zou, W.Q., Gambetti, P., Eds.; Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Notari, S.; Capellari, S.; Giese, A.; Westner, I.; Baruzzi, A.; Ghetti, B.; Gambetti, P.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Parchi, P. Effects of different experimental conditions on the PrPSc core generated by protease digestion: Implications for strain typing and molecular classification of CJD. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16797–16804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cali, I.; Castellani, R.; Yuan, J.; Al-Shekhlee, A.; Cohen, M.L.; Xiao, X.; Moleres, F.J.; Parchi, P.; Zou, W.Q.; Gambetti, P. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease revisited. Brain 2006, 129, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Sakuma, N.; Matsuura, Y.; Mohri, S.; Aguzzi, A.; Kitamoto, T. Experimental verification of a traceback phenomenon in prion infection. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3230–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolan, K.M.; Colby, D.W. Conformation-dependent epitopes recognized by prion protein antibodies probed using mutational scanning and deep sequencing. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kascsak, R.J.; Rubenstein, R.; Merz, P.A.; Tonna-DeMasi, M.; Fersko, R.; Carp, R.I.; Wisniewski, H.M.; Diringer, H. Mouse polyclonal and monoclonal antibody to scrapie-associated fibril proteins. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 3688–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeveld, J.P.; Jacobs, J.G.; Erkens, J.H.; Bossers, A.; van Zijderveld, F.G.; van Keulen, L.J. Rapid and discriminatory diagnosis of scrapie and BSE in retro-pharyngeal lymph nodes of sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 2006, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Cali, I.; Dong, Z.; Puoti, G.; Yuan, J.; Qing, L.; Wang, H.; Kong, Q.; Gambetti, P.; Zou, W.Q. Protease-sensitive prions with 144-bp insertion mutations. Aging 2013, 5, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudjou, M.; Treguer, E.; Rezaei, H.; Sabuncu, E.; Neuendorf, E.; Groschup, M.H.; Grosclaude, J.; Laude, H. Glycan-controlled epitopes of prion protein include a major determinant of susceptibility to sheep scrapie. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9270–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.; Chen, S.G.; Brown, P.; Zou, W.; Capellari, S.; Budka, H.; Hainfellner, J.; Reyes, P.F.; Golden, G.T.; Hauw, J.J.; et al. Different patterns of truncated prion protein fragments correlate with distinct phenotypes in P102L Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8322–8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Shen, P.; Abskharon, R.; Lang, Y.; Dang, J.; Adornato, A.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Feng, J.; et al. In Vitro Seeding Activity of Glycoform-Deficient Prions from Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy and Familial CJD Associated with PrP(V180I) Mutation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5456–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.; Zou, W.; Wang, W.; Brown, P.; Capellari, S.; Ghetti, B.; Kopp, N.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Head, M.W.; et al. Genetic influence on the structural variations of the abnormal prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10168–10172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notari, S.; Strammiello, R.; Capellari, S.; Giese, A.; Cescatti, M.; Grassi, J.; Ghetti, B.; Langeveld, J.P.; Zou, W.Q.; Gambetti, P.; et al. Characterization of truncated forms of abnormal prion protein in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30557–30565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xiao, X.; McGeehan, J.; Dong, Z.; Cali, I.; Fujioka, H.; Kong, Q.; Kneale, G.; Gambetti, P.; Zou, W.Q. Insoluble aggregates and protease-resistant conformers of prion protein in uninfected human brains. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34848–34858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.S.; Fujioka, H.; Guo, J.P.; Xiao, X.; Shimoji, M.; Kong, C.; Chen, C.; Tasnadi, M.; Voma, C.; Yuan, J.; et al. Characterization of spontaneously generated prion-like conformers in cultured cells. Aging 2011, 3, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Bongarzone, S.; Giachin, G.; Rossetti, G.; Carloni, P.; Legname, G. Dominant-negative effects in prion diseases: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations on mouse prion protein chimeras. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 31, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamat, M.K.; Dron, M.; Chapuis, J.; Langevin, C.; Laude, H. Prion propagation in cells expressing PrP glycosylation mutants. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzi, N.L.; Cancellotti, E.; Baybutt, H.; Blackford, L.; Bradford, B.; Plinston, C.; Coghill, A.; Hart, P.; Piccardo, P.; Barron, R.M.; et al. Host PrP glycosylation: A major factor determining the outcome of prion infection. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, K.A.; Deleault, N.R.; Mahal, S.P.; Baskakov, I.; Luhrs, T.; Riek, R.; Supattapone, S. The stoichiometry of host PrPC glycoforms modulates the efficiency of PrPSc formation in vitro. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 14129–14139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghiaian, F.; Grosclaude, J.; Lesceu, S.; Debey, P.; Doublet, B.; Treguer, E.; Rezaei, H.; Knossow, M. Insight into the PrPC-->PrPSc conversion from the structures of antibody-bound ovine prion scrapie-susceptibility variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10254–10259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraudet, C.; Morel, N.; Simon, S.; Volland, H.; Frobert, Y.; Creminon, C.; Vilette, D.; Lehmann, S.; Grassi, J. Screening of 145 anti-PrP monoclonal antibodies for their capacity to inhibit PrPSc replication in infected cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11247–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orru, C.D.; Yuan, J.; Appleby, B.S.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Winner, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhan, Y.A.; Rodgers, M.; Rarick, J.; et al. Prion seeding activity and infectivity in skin samples from patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Manca, M.; Foutz, A.; Camacho, M.V.; Raymond, G.J.; Race, B.; Orru, C.D.; Yuan, J.; Shen, P.; Li, B.; et al. Early preclinical detection of prions in the skin of prion-infected animals. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Xiao, X.; Ding, M.; Yuan, J.; Foutz, A.; Moudjou, M.; Kitamoto, T.; Langeveld, J.P.M.; Cui, L.; Zou, W.-Q. Further Characterization of Glycoform-Selective Prions of Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy. Pathogens 2021, 10, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050513
Zhang W, Xiao X, Ding M, Yuan J, Foutz A, Moudjou M, Kitamoto T, Langeveld JPM, Cui L, Zou W-Q. Further Characterization of Glycoform-Selective Prions of Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy. Pathogens. 2021; 10(5):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050513
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Weiguanliu, Xiangzhu Xiao, Mingxuan Ding, Jue Yuan, Aaron Foutz, Mohammed Moudjou, Tetsuyuki Kitamoto, Jan P. M. Langeveld, Li Cui, and Wen-Quan Zou. 2021. "Further Characterization of Glycoform-Selective Prions of Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy" Pathogens 10, no. 5: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050513
APA StyleZhang, W., Xiao, X., Ding, M., Yuan, J., Foutz, A., Moudjou, M., Kitamoto, T., Langeveld, J. P. M., Cui, L., & Zou, W.-Q. (2021). Further Characterization of Glycoform-Selective Prions of Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy. Pathogens, 10(5), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050513





