Prediction of Selected Biosynthetic Pathways for the Lipopolysaccharide Components in Porphyromonas gingivalis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pathway/Genome Database Building
2.2. LPS Biosynthetic Pathway Modeling
2.2.1. O-Type Antigen Biosynthetic Pathway
2.2.2. Lipid A Biosynthetic Pathway
2.2.3. K-Type Antigen Biosynthetic Pathway
2.2.4. A-Type Antigen Biosynthetic Pathway
2.3. Analysis of LPS Biosynthetic Pathways in Other P. gingivalis Strains
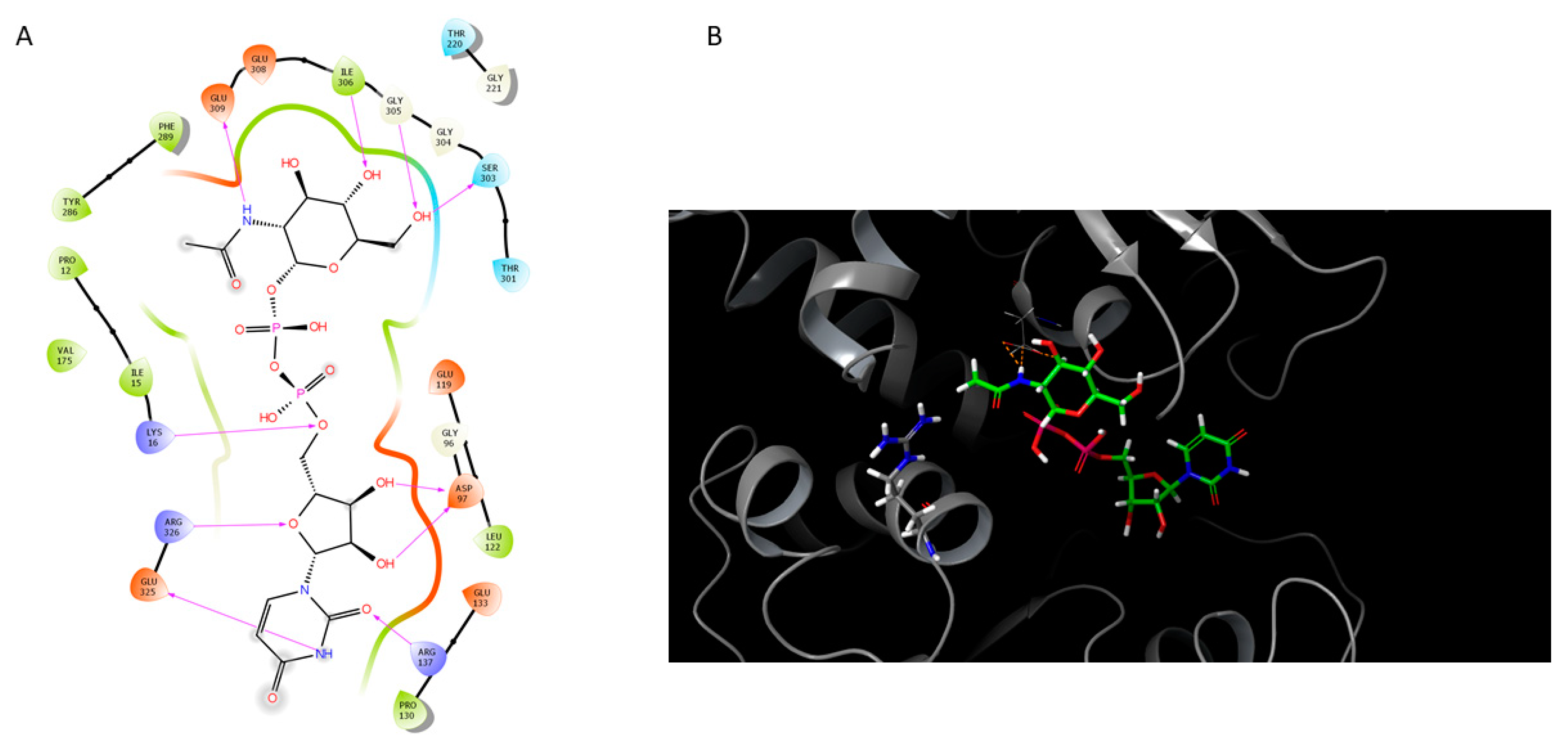
2.4. Homology Modeling of Selected Components from the LPS Biosynthetic Pathway
2.4.1. O-Antigen Biosynthetic Pathway
2.4.2. K Antigen Biosynthetic Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genomes
4.2. LPS Biosynthetic Pathways Reconstruction
4.3. Ortholog Computation
4.4. Homology Modeling of WbaQ Enzyme
4.5. Homology Modeling of the UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine 2-Epimerase
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rangarajan, M.; Aduse-Opoku, J.; Paramonov, N.A.; Hashim, A.; Curtis, M.A. Hemin binding by Porphyromonas gingivalis strains is dependent on the presence of A-LPS. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2017, 32, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasica, A.M.; Goulas, T.; Mizgalska, D.; Zhou, X.; de Diego, I.; Ksiazek, M.; Madej, M.; Guo, Y.; Guevara, T.; Nowak, M.; et al. Structural and functional probing of PorZ, an essential bacterial surface component of the type-IX secretion system of human oral-microbiomic Porphyromonas gingivalis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, C.; Williams, D.M.; Kelly, S.D. Lipopolysaccharide O-antigens-bacterial glycans made to measure. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 10593–10609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramonov, N.; Bailey, D.; Rangarajan, M.; Hashim, A.; Kelly, G.; Curtis, M.A.; Hounsell, E.F. Structural analysis of the polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Porphyromonas gingivalis strain W50. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 4698–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, M.; Yukitake, H.; Sato, K.; Shibata, Y.; Naito, M.; Aduse-Opoku, J.; Abiko, Y.; Curtis, M.A.; Nakayama, K. Identification of an O-antigen chain length regulator, WzzP, in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Microbiologyopen 2013, 2, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, M.; Sato, K.; Yukitake, H.; Kamaguchi, A.; Sasaki, Y.; Naito, M.; Nakayama, K. Identification of genes encoding glycosyltransferases involved in lipopolysaccharide synthesis in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2018, 33, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramonov, N.; Aduse-Opoku, J.; Hashim, A.; Rangarajan, M.; Curtis, M.A. Identification of the linkage between A-polysaccharide and the core in the A-lipopolysaccharide of Porphyromonas gingivalis W50. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, H.; Moxon, E.R.; Martin, A.; Krajcarski, D.; Richards, J.C. Structure of the variable and conserved lipopolysaccharide oligosaccharide epitopes expressed by Haemophilus influenzae serotype b strain Eagan. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 2091–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Pither, M.D.; Martufi, M.; Scarinci, I.; Guzman-Caldentey, J.; Lakomiec, E.; Jachymek, W.; Bruijns, S.C.M.; Santamaria, S.M.; Frick, J.S.; et al. Pairing Bacteroides vulgatus LPS Structure with Its Immunomodulatory Effects on Human Cellular Models. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1602–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, H.; Kondo, S.; Umemoto, T.; Hisatsune, K. Chemical structure of the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharide isolated from Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1993, 108, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bainbridge, B.W.; Coats, S.R.; Pham, T.T.; Reife, R.A.; Darveau, R.P. Expression of a Porphyromonas gingivalis lipid A palmitylacyltransferase in Escherichia coli yields a chimeric lipid A with altered ability to stimulate interleukin-8 secretion. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenobia, C.; Hajishengallis, G. Porphyromonas gingivalis virulence factors involved in subversion of leukocytes and microbial dysbiosis. Virulence 2015, 6, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T. Chemical structure of lipid A from Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis lipopolysaccharide. FEBS Lett. 1993, 332, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, N.; Ogawa, T.; Asai, Y.; Makimura, Y.; Sugiyama, A. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent recognition of structurally different forms of chemically synthesized lipid As of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 148, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coats, S.R.; Jones, J.W.; Do, C.T.; Braham, P.H.; Bainbridge, B.W.; To, T.T.; Goodlett, D.R.; Ernst, R.K.; Darveau, R.P. Human Toll-like receptor 4 responses to P. gingivalis are regulated by lipid A 1- and 4’-phosphatase activities. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, M.A.; Percival, R.S.; Devine, D.; Darveau, R.P.; Coats, S.R.; Rangarajan, M.; Tarelli, E.; Marsh, P.D. Temperature-dependent modulation of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipid A structure and interaction with the innate host defenses. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangarajan, M.; Aduse-Opoku, J.; Hashim, A.; McPhail, G.; Luklinska, Z.; Haurat, M.F.; Feldman, M.F.; Curtis, M.A. LptO (PG0027) Is Required for Lipid A 1-Phosphatase Activity in Porphyromonas gingivalis W50. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Chang, A.M.; Singh, M.; McLean, J.S.; Coats, S.R.; Kramer, R.W.; Darveau, R.P. Identification of PGN_1123 as the Gene Encoding Lipid A Deacylase, an Enzyme Required for Toll-Like Receptor 4 Evasion, in Porphyromonas gingivalis. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, I.; Singhrao, S.K. Importance of heterogeneity in Porhyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide lipid A in tissue specific inflammatory signalling. J. Oral Microbiol. 2018, 10, 1440128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainbridge, B.W.; Karimi-Naser, L.; Reife, R.; Blethen, F.; Ernst, R.K.; Darveau, R.P. Acyl chain specificity of the acyltransferases LpxA and LpxD and substrate availability contribute to lipid A fatty acid heterogeneity in Porphyromonas gingivalis. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 4549–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qutub, M.N.; Braham, P.H.; Karimi-Naser, L.M.; Liu, X.; Genco, C.A.; Darveau, R.P. Hemin-dependent modulation of the lipid A structure of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4474–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reife, R.A.; Coats, S.R.; Al-Qutub, M.; Dixon, D.M.; Braham, P.A.; Billharz, R.J.; Howald, W.N.; Darveau, R.P. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide lipid A heterogeneity: Differential activities of tetra- and penta-acylated lipid A structures on E-selectin expression and TLR4 recognition. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangarajan, M.; Aduse-Opoku, J.; Paramonov, N.; Hashim, A.; Bostanci, N.; Fraser, O.P.; Tarelli, E.; Curtis, M.A. Identification of a second lipopolysaccharide in Porphyromonas gingivalis W50. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 2920–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aduse-Opoku, J.; Slaney, J.M.; Hashim, A.; Gallagher, A.; Gallagher, R.P.; Rangarajan, M.; Boutaga, K.; Laine, M.L.; Van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Curtis, M.A. Identification and characterization of the capsular polysaccharide (K-antigen) locus of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, P.D.; Shoji, M.; O’Hair, R.A.J.; Leeming, M.G.; Nie, S.; Glew, M.D.; Reid, G.E.; Nakayama, K.; Reynolds, E.C. Type IX Secretion System Cargo Proteins Are Glycosylated at the C Terminus with a Novel Linking Sugar of the Wbp/Vim Pathway. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanterpool, E.; Roy, F.; Fletcher, H.M. Inactivation of vimF, a putative glycosyltransferase gene downstream of vimE, alters glycosylation and activation of the gingipains in Porphyromonas gingivalis W83. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 3971–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, I.; Feldman, M.F. Analogies and homologies in lipopolysaccharide and glycoprotein biosynthesis in bacteria. Glycobiology 2011, 21, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldias, M.S.; Patel, K.; Marolda, C.L.; Bittner, M.; Contreras, I.; Valvano, M.A. Distinct functional domains of the Salmonella enterica WbaP transferase that is involved in the initiation reaction for synthesis of the O antigen subunit. Microbiology 2008, 154, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.B.; Ciepichal, E.; Swiezewska, E.; Valvano, M.A. The C-terminal domain of the Salmonella enterica WbaP (UDP-galactose:Und-P galactose-1-phosphate transferase) is sufficient for catalytic activity and specificity for undecaprenyl monophosphate. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukose, V.; Luo, L.; Kozakov, D.; Vajda, S.; Allen, K.N.; Imperiali, B. Conservation and Covariance in Small Bacterial Phosphoglycosyltransferases Identify the Functional Catalytic Core. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 7326–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, L.C.; Das, D.; Entova, S.; Lukose, V.; Lynch, A.J.; Imperiali, B.; Allen, K.N. Membrane association of monotopic phosphoglycosyl transferase underpins function. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.E.; Mosimann, S.C.; Tanner, M.E.; Strynadka, N.C. The structure of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase reveals homology to phosphoglycosyl transferases. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 14993–15001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.M.; Sala, R.F.; Tanner, M.E. Eliminations in the reactions catalyzed by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10269–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, R.F.; Morgan, P.M.; Tanner, M.E. Enzymatic formation and release of a stable glycal intermediate: The mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 3033–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, P.D.; Latendresse, M.; Caspi, R. The pathway tools pathway prediction algorithm. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2011, 5, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, A.G.; Boyce, S.; Tipton, K.F. ExplorEnz: The primary source of the IUBMB enzyme list. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D593–D597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenobia, C.; Hasturk, H.; Nguyen, D.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Kantarci, A.; Darveau, R.P. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipid A phosphatase activity is critical for colonization and increasing the commensal load in the rabbit ligature model. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, P.D.; Riley, M.; Paley, S.M.; Pellegrini-Toole, A.; Krummenacker, M. EcoCyc: Enyclopedia of Escherichia coli Genes and Metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, P.D.; Billington, R.; Holland, T.A.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Weaver, D.; Latendresse, M.; Paley, S. Computational Metabolomics Operations at BioCyc.org. Metabolites 2015, 5, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, P.D.; Midford, P.E.; Billington, R.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Latendresse, M.; Ong, W.K.; Subhraveti, P.; Caspi, R.; Fulcher, C.; et al. Pathway Tools version 23.0 update: Software for pathway/genome informatics and systems biology. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, P.D.; Billington, R.; Caspi, R.; Fulcher, C.A.; Latendresse, M.; Kothari, A.; Keseler, I.M.; Krummenacker, M.; Midford, P.E.; Ong, Q.; et al. The BioCyc collection of microbial genomes and metabolic pathways. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, R.; Billington, R.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Midford, P.E.; Ong, W.K.; Paley, S.; Subhraveti, P.; Karp, P.D. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes—A 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D445–D453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.L.; Karp, P.D. A Bayesian method for identifying missing enzymes in predicted metabolic pathway databases. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, M.; Sato, K.; Yukitake, H.; Naito, M.; Nakayama, K. Involvement of the Wbp pathway in the biosynthesis of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide with anionic polysaccharide. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B.A.; Cornacchione, L.P.; Collins, M.; Malamy, M.H.; Duncan, M.J.; Hu, L.T. Using Tn-seq To Identify Pigmentation-Related Genes of Porphyromonas gingivalis: Characterization of the Role of a Putative Glycosyltransferase. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
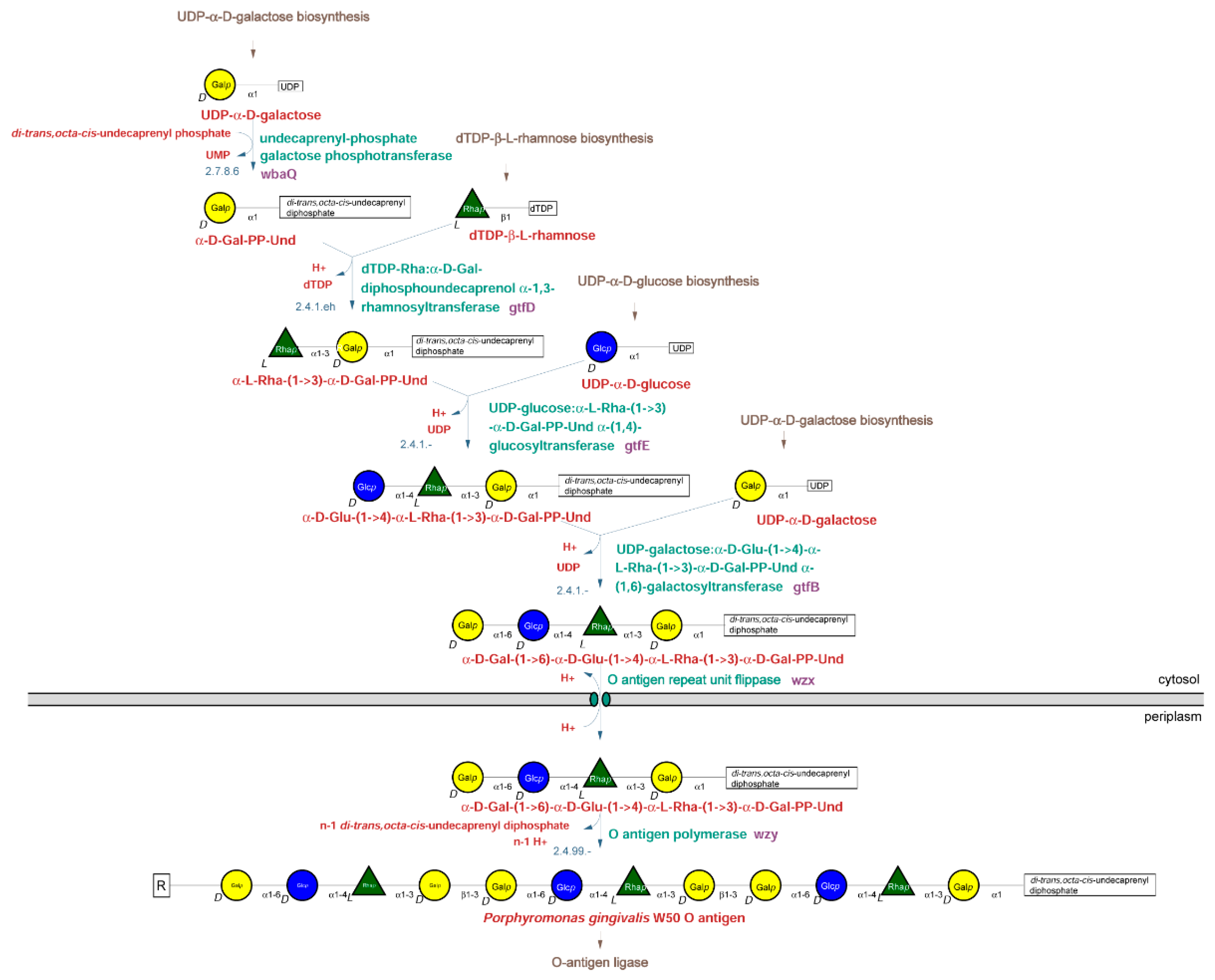
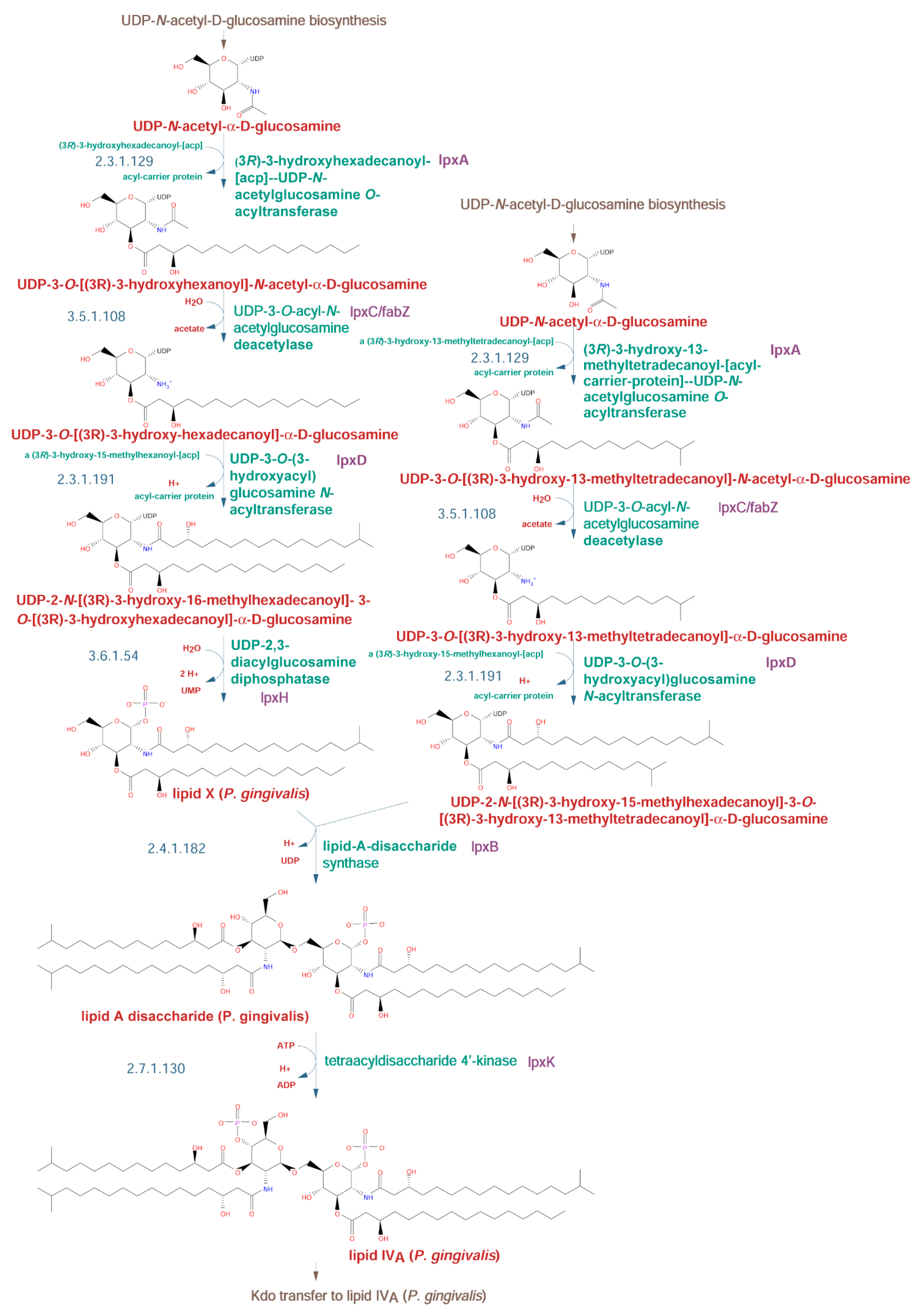
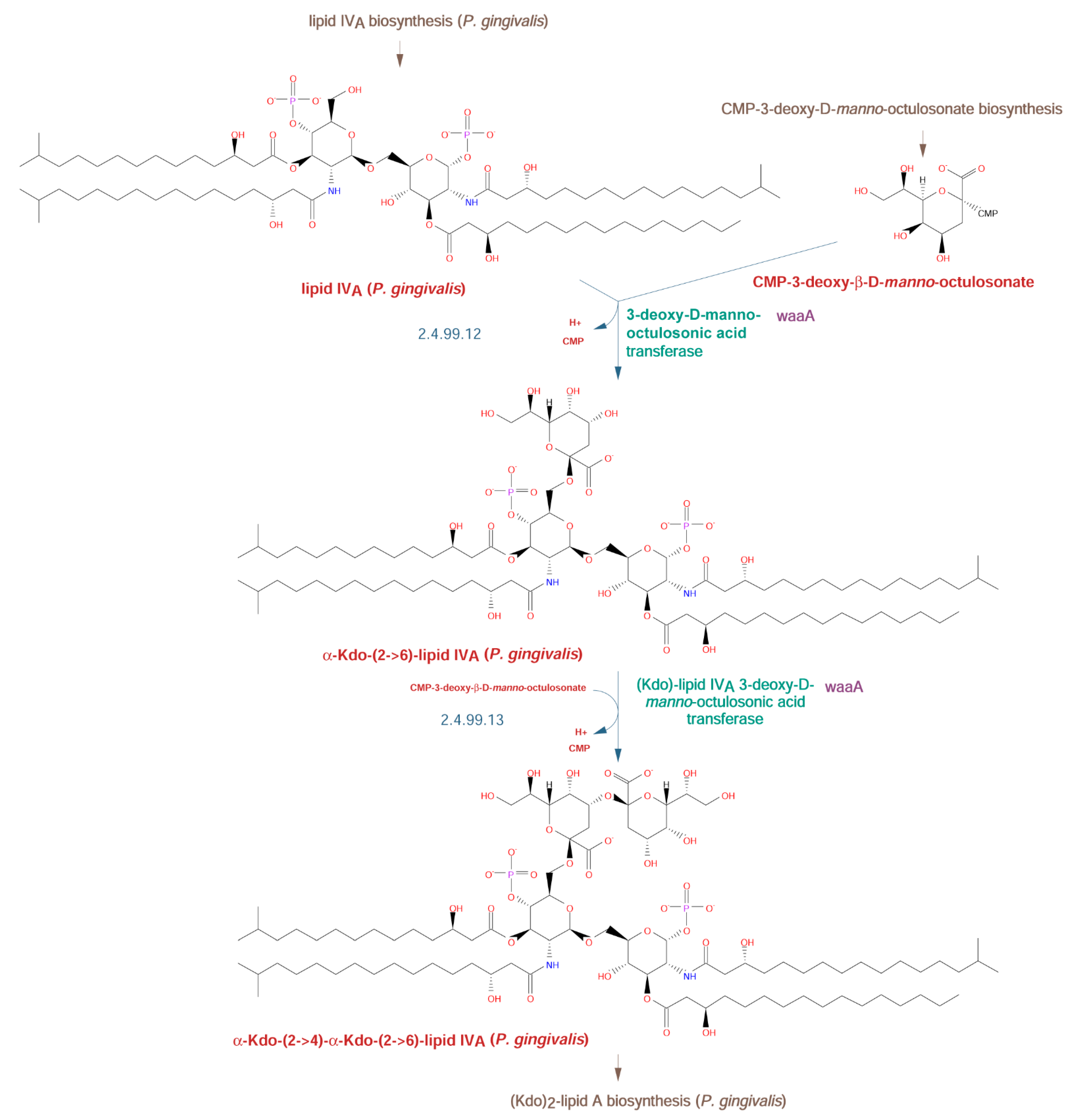



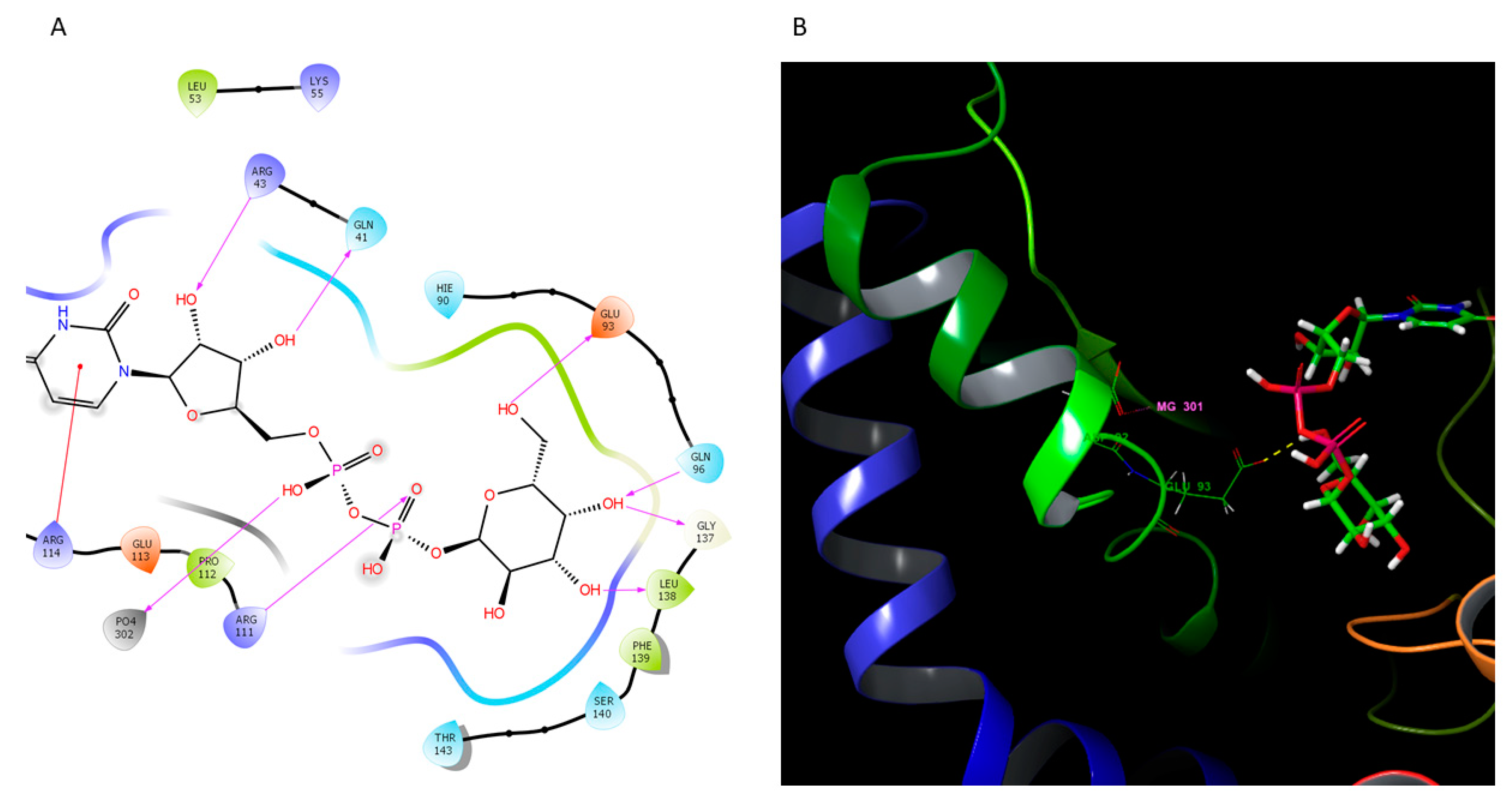

| O-Type Antigen | A-Type Antigen | K-Type Antigen | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biological function | Protection in a hostile environment, interaction with the environment, structural support to the cell | Protection in a hostile environment | Interaction with the environment |
| Structural information | Fully described | Two incompatible proposals | Unknown |
| Genomic information | Fully described | Partially described | Locus sequenced, function of individual genes unknown |
| Gene a | Protein Function b |
|---|---|
| HMPREF1322_0447 | undecaprenyl/decaprenyl-phosphate α-N-acetylglucosaminyl 1-phosphate transferase |
| HMPREF1322_0448 | UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosamine dehydrogenase |
| HMPREF1322_0449 | O-antigen ligase domain-containing protein |
| HMPREF1322_0450 | glycosyltransferase family 1 protein |
| HMPREF1322_0451 | hypothetical protein |
| HMPREF1322_0454 | aminoglycoside 3-N-acetyltransferase |
| HMPREF1322_0455 | hypothetical protein |
| HMPREF1322_RS09085 | serine acetyltransferase |
| HMPREF1322_0456 | hypothetical protein |
| HMPREF1322_0457 | hypothetical protein |
| HMPREF1322_0458 | glycosyltransferase family 2 protein |
| HMPREF1322_0459 | glycosyltransferase |
| HMPREF1322_0460 | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase (non-hydrolyzing) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swietnicki, W.; Caspi, R. Prediction of Selected Biosynthetic Pathways for the Lipopolysaccharide Components in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030374
Swietnicki W, Caspi R. Prediction of Selected Biosynthetic Pathways for the Lipopolysaccharide Components in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Pathogens. 2021; 10(3):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030374
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwietnicki, Wieslaw, and Ron Caspi. 2021. "Prediction of Selected Biosynthetic Pathways for the Lipopolysaccharide Components in Porphyromonas gingivalis" Pathogens 10, no. 3: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030374
APA StyleSwietnicki, W., & Caspi, R. (2021). Prediction of Selected Biosynthetic Pathways for the Lipopolysaccharide Components in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Pathogens, 10(3), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030374







