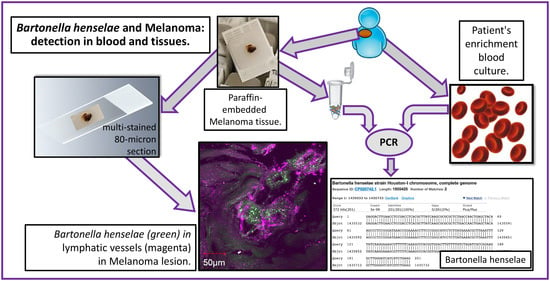
Bartonella henselae Detected in Malignant Melanoma, a Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographics of Melanoma Patients
2.2. Bartonella spp. Seroreactivity, Enrichment Blood Culture, and PCR
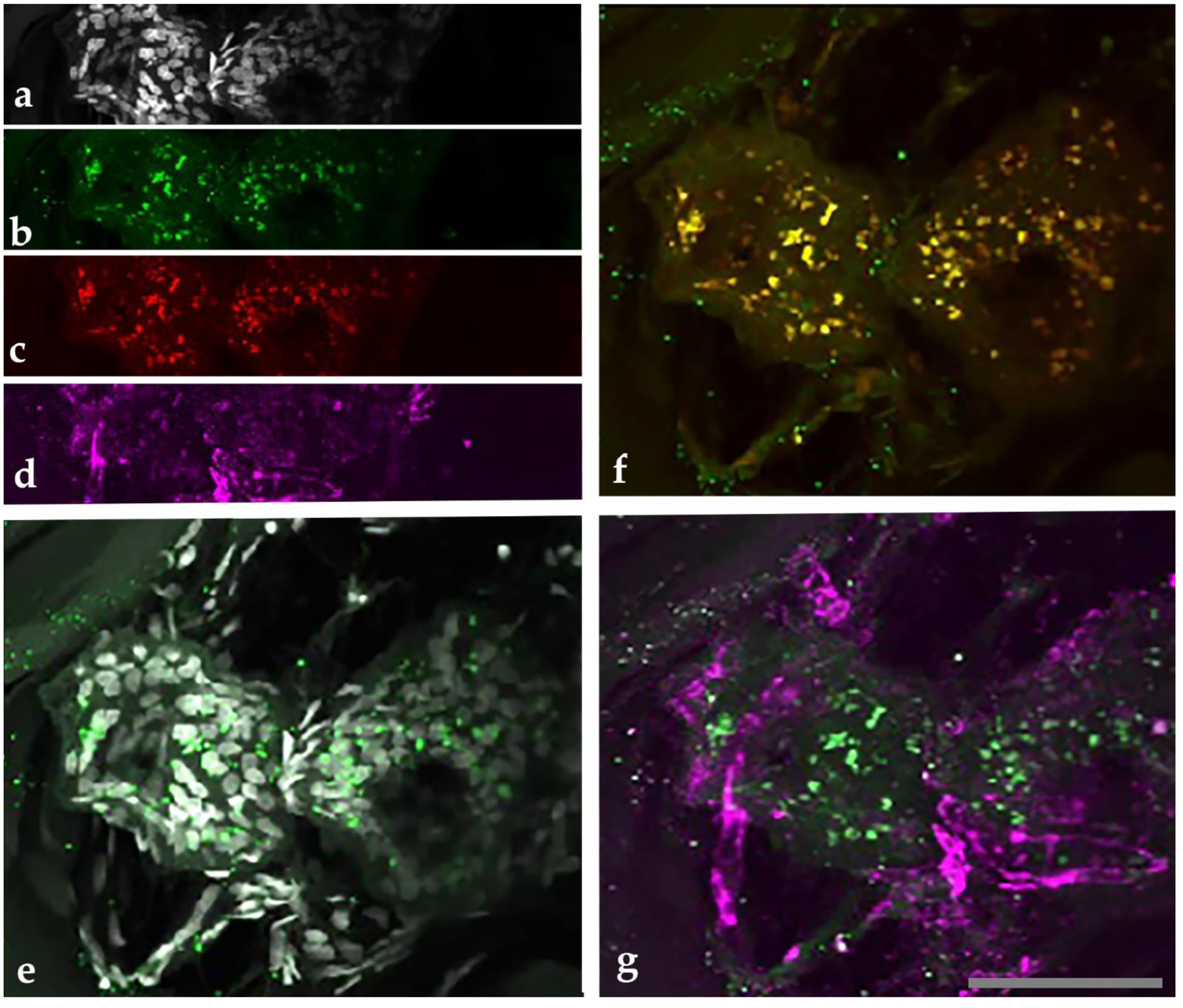
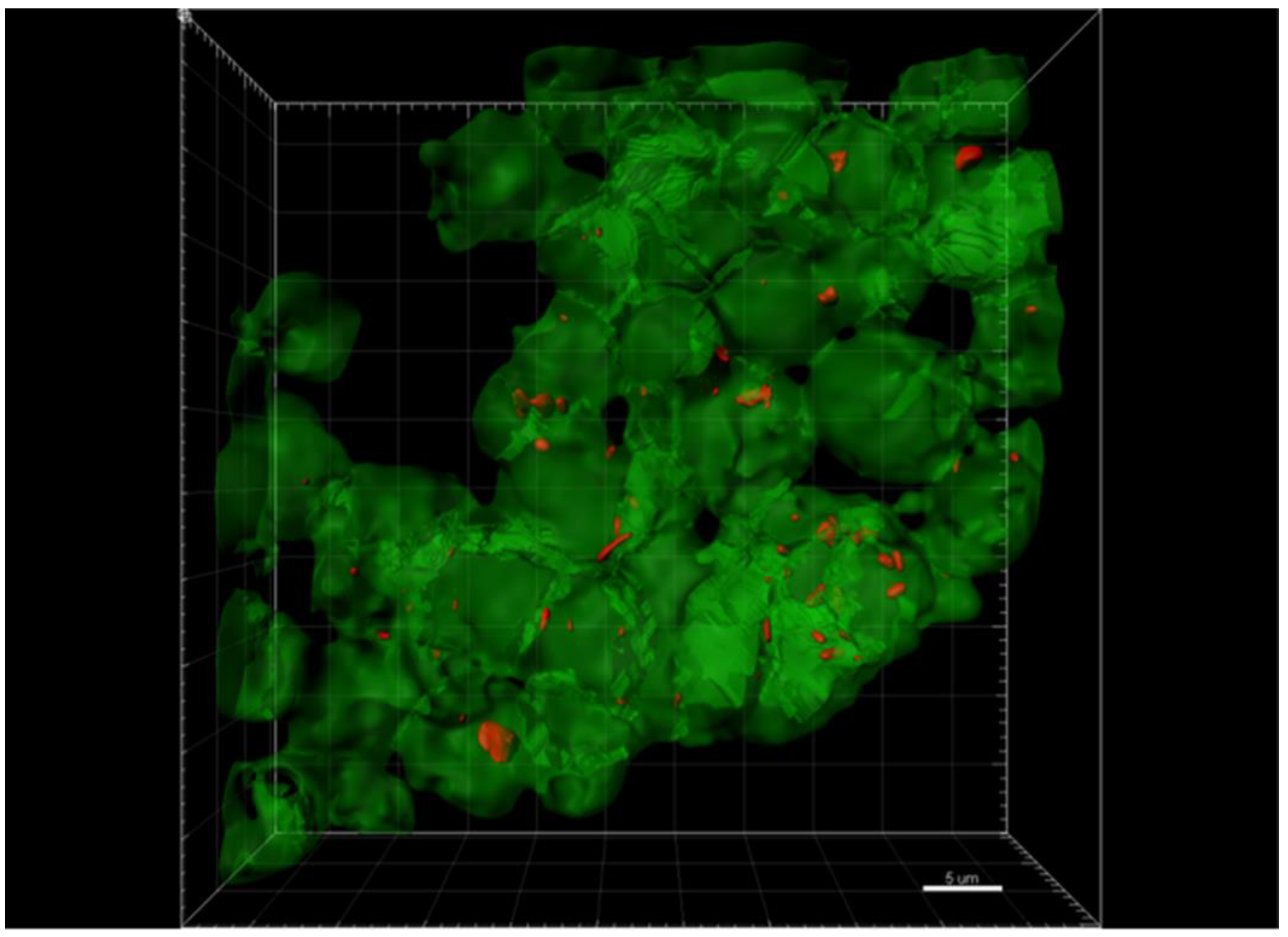
2.3. Confocal Immunohistochemistry of Melanoma Tissues
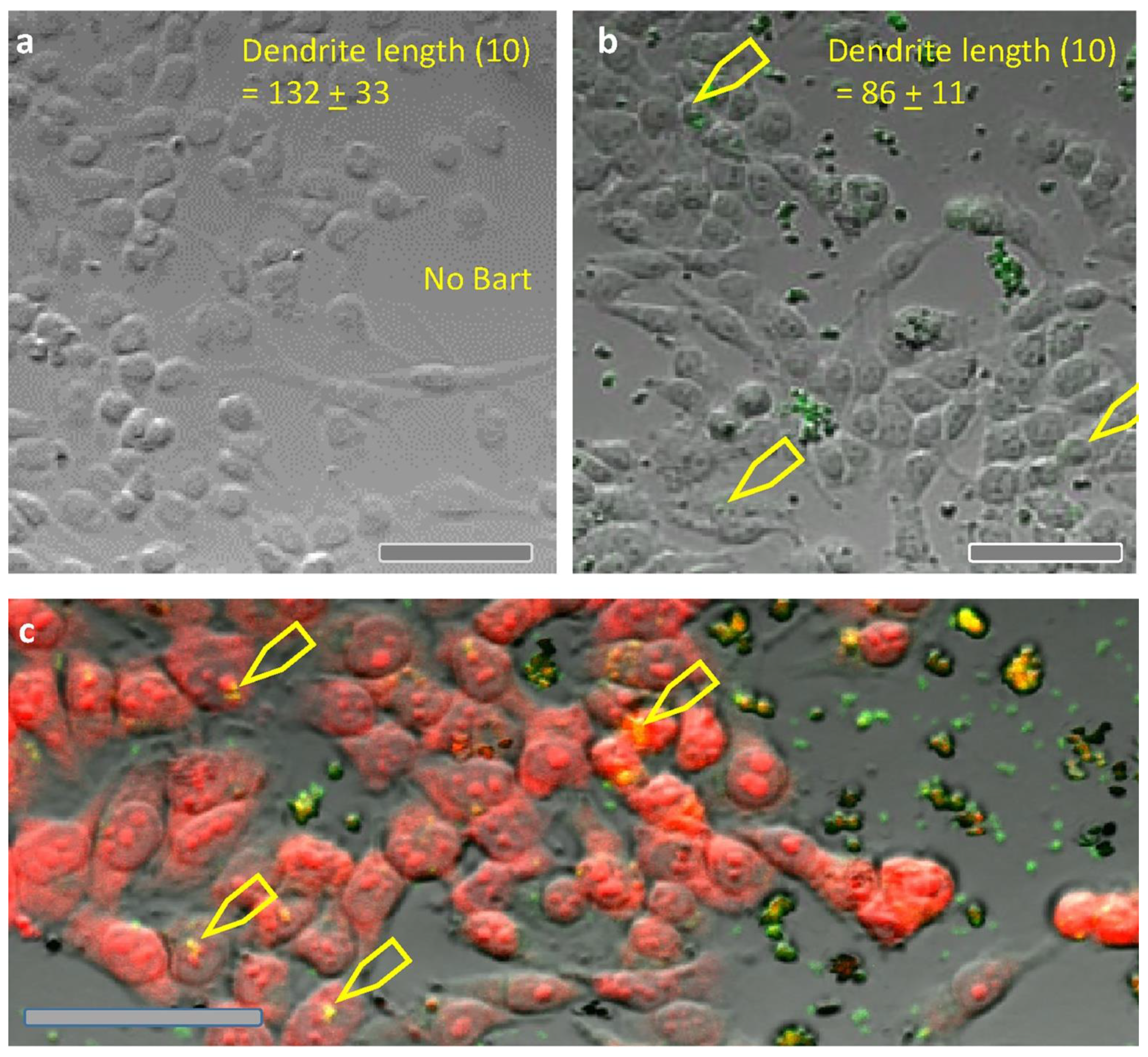
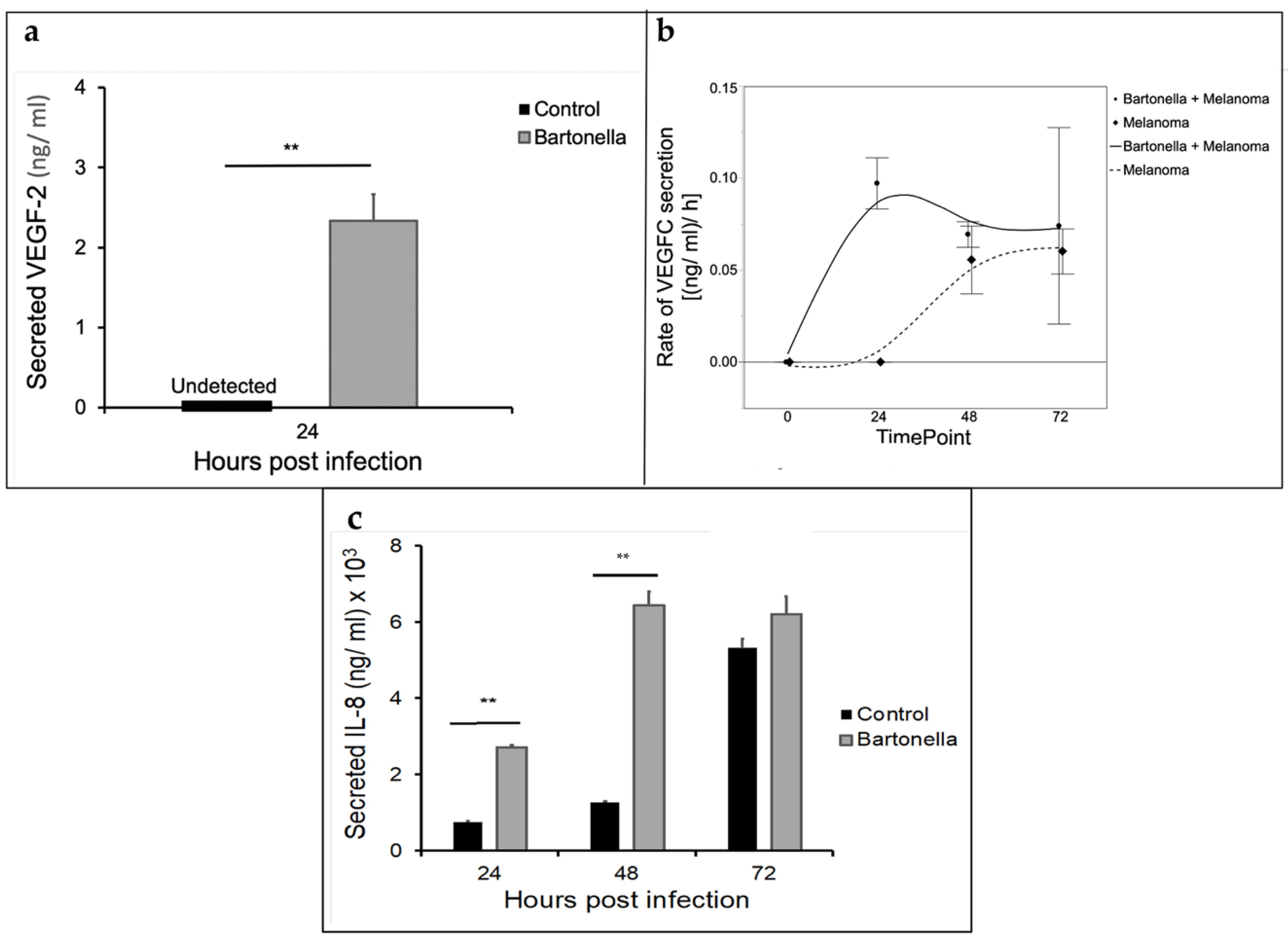
2.4. Co-Culture of B. henselae with Melanoma Cells (A375)
2.5. Cytokine Analysis of Melanoma A375 Cells Co-Infected with B. henselae
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Timeline
4.2. Patients and Samples
4.3. Conventional PCR (PCR) and Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis
4.4. PCR Analysis of DNA Extracted from Formalin-Fixed Tissue
4.5. Multi-Staining and Confocal Imaging of Tissues and Co-Cultures
4.6. Co-Culture of Melanoma Cells and B. henselae
4.7. Cytokine Analysis
4.8. Statistical Methods
4.9. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eggermont, A.M.; Spatz, A.; Robert, C. Cutaneous melanoma. Lancet 2014, 383, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbasis, L.; Stefanaki, I.; Stratigos, A.J.; Evangelou, E. Non-genetic risk factors for cutaneous melanoma and keratinocyte skin cancers: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2016, 84, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejman, D.; Livyatan, I.; Fuks, G.; Gavert, N.; Zwang, Y.; Geller, L.T.; Rotter-Maskowitz, A.; Weiser, R.; Mallel, G.; Gigi, E.; et al. The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type-specific intracellular bacteria. Science 2020, 368, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, L. When human cells meet bacteria: Precision medicine for cancers using the microbiota. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1157–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopala, S.V.; Vashee, S.; Oldfield, L.M.; Suzuki, Y.; Venter, J.C.; Telenti, A.; Nelson, K.E. The Human Microbiome and Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martel, C.; Ferlay, J.; Franceschi, S.; Vignat, J.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Plummer, M. Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2008: A review and synthetic analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, D.L. Bacteria and cancer: Cause, coincidence or cure? A review. J. Transl. Med. 2006, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.-E.; Chiu, C.-T.; Rayner, C.K.; Wu, K.-L.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Hu, M.-L.; Chuah, S.-K.; Tai, W.-C.; Liang, C.-M.; Wang, H.-M. Associated factors in Streptococcus bovis bacteremia and colorectal cancer. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejea, C.M.; Fathi, P.; Craig, J.M.; Boleij, A.; Taddese, R.; Geis, A.L.; Wu, X.; Shields, C.E.D.; Hechenbleikner, E.M.; Huso, D.L.; et al. Patients with familial adenomatous polyposis harbor colonic biofilms containing tumorigenic bacteria. Science 2018, 359, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullman, S.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Sicinska, E.; Clancy, T.E.; Zhang, X.; Cai, D.; Neuberg, D.; Huang, K.; Guevara, F.; Nelson, T.; et al. Analysis of Fusobacterium persistence and antibiotic response in colorectal cancer. Science 2017, 358, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Albina, E.; Citti, C.; Cosson, J.-F.; Jacques, M.-A.; Lebrun, M.-H.; Le Loir, Y.; Ogliastro, M.; Petit, M.-A.; Roumagnac, P.; et al. Shifting the paradigm from pathogens to pathobiome: New concepts in the light of meta-omics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tinoco, R.; Elmén, L.; Segota, I.; Xian, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Sahu, A.; Zarecki, R.; Marie, K.; Feng, Y.; et al. Gut microbiota dependent anti-tumor immunity restricts melanoma growth in Rnf5−/− mice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Jeon, C.O. Promotion and induction of liver cancer by gut microbiome-mediated modulation of bile acids. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Spencer, C.N.; Nezi, L.; Reuben, A.; Andrews, M.C.; Karpinets, T.V.; Prieto, P.A.; Vicente, D.; Hoffman, K.; Wei, S.C.; et al. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti—PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, V.; Fessler, J.; Bao, R.; Chongsuwat, T.; Zha, Y.; Alegre, M.-L.; Luke, J.J.; Gajewski, T.F. The commensal microbiome is associated with anti—PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salava, A.; Aho, V.; Pereira, P.; Koskinen, K.; Paulin, L.; Auvinen, P.; Lauerma, A. Skin microbiome in melanomas and melanocytic nevi. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2016, 26, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrázek, J.; Mekadim, C.; Kučerová, P.; Švejstil, R.; Salmonová, H.; Vlasáková, J.; Tarasová, R.; Čížková, J.; Červinková, M. Melanoma-related changes in skin microbiome. Folia Microbiol. 2018, 64, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lax, A.J.; Thomas, W. How bacteria could cause cancer: One step at a time. Trends Microbiol. 2002, 10, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheslock, M.A.; Embers, M.E. Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regier, Y.; O’Rourkef, F.; Kempf, V.A.J. Bartonella spp.—A chance to establish one Health concepts in veterinary and human medicine. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Fernández, A.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Solano-Gallego, L. Bartonella infections in cats and dogs including zoonotic aspects. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.; Kasten, R. Bartonellosis, an increasingly recognized zoonosis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, B.B.; Boulouis, H.-J.; Maruyama, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella Spp. in Pets and Effect on Human Health. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, C.; Ruiz, J. Carrion’s Disease: The Sound of Silence. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwensen, J.F.; Nielsen, R.H.; Helleberg, M. Bacillary angiomatosis in a solid organ transplant recipient. IDCases 2019, 18, e00649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G. Bartonella quintana and Bartonella vinsonii subsp. vinsonii bloodstream co-infection in a girl from North Carolina, USA. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitassi, L.H.U.; Diniz, P.P.V.D.P.; Scorpio, D.G.; Drummond, M.R.; Lania, B.G.; Barjas-Castro, M.L.; Gilioli, R.; Colombo, S.; Sowy, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; et al. Bartonella spp. Bacteremia in Blood Donors from Campinas, Brazil. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lantos, P.M.; Maggi, R.G.; Ferguson, B.; Varkey, J.; Park, L.P.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Woods, C.W. Detection of Bartonella Species in the Blood of Veterinarians and Veterinary Technicians: A Newly Recognized Occupational Hazard? Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.; Linder, K.; Day, M.; Maggi, R.; Chomel, B.; Kempf, V. Koch’s Postulates and the Pathogenesis of Comparative Infectious Disease Causation Associated with Bartonella species. J. Comp. Pathol. 2013, 148, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Bradley, J.M.; Maggi, R.G.; Lashnits, E.; Reicherter, P. Bartonella Associated Cutaneous Lesions (BACL) in People with Neuropsychiatric Symptoms. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.A.; Balakrishnan, N.; Linder, K.E.; Messa, J.B.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Concurrent Bartonella henselae infection in a dog with panniculitis and owner with ulcerated nodular skin lesions. Vet. Dermatol. 2014, 26, 60-e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.K.; Alfert, M.; Castrillon, D.H.; Shen, Q.; Holash, J.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Chin, L. Excessive tumor-elaborated VEGF and its neutralization define a lethal paraneoplastic syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7481–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Ericson, M.; Maggi, R.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Vasculitis, cerebral infarction and persistent Bartonella henselae infection in a child. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacnik, P.W.; Baker, C.M.; Herron, M.J.; Kren, B.T.; Blazar, B.R.; Wilcox, G.L.; Hordinsky, M.K.; Beitz, A.J.; Ericson, M.E. Tumor-induced mechanical hyperalgesia involves CGRP receptors and altered innervation and vascularization of DsRed2 fluorescent hindpaw tumors. Pain 2005, 115, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, V.A.J.; Volkmann, B.; Schaller, M.; Sander, C.A.; Alitalo, K.; Rieß, T.; Autenrieth, I.B. Evidence of a leading role for VEGF in Bartonella henselae-induced endothelial cell proliferations. Cell. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seubert, A.; Schulein, R.; Dehio, C. Bacterial persistence within erythrocytes: A unique pathogenic strategy of Bartonella spp. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 291, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meghari, S.; Rolain, J.; Grau, G.E.; Platt, E.; Barrassi, L.; Mège, J.; Raoult, D. Antiangiogenic Effect of Erythromycin: An In Vitro Model of Bartonella quintana Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulliainen, A.T.; Dehio, C. Persistence of Bartonella spp. stealth pathogens: From subclinical infections to vasoproliferative tumor formation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 563–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, M.; Latz, A.; Ballhorn, W.; Kempf, V.A.J. Development of a Specific and Sensitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay as an In Vitro Diagnostic Tool for Detection of Bartonella henselae Antibodies in Human Serum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteo, J.A.; Maggi, R.; Portillo, A.; Bradley, J.; García-Álvarez, L.; San-Martín, M.; Roura, X.; Breitschwerdt, E. Prevalence of Bartonella spp. by culture, PCR and serology, in veterinary personnel from Spain. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.D.; Miller, M.A.; Dusold, D.; Ramos-Vara, J. Effects of Prolonged Formalin Fixation on the Immunohistochemical Detection of Infectious Agents in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissues. Vet. Pathol. 2010, 47, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hong, J.; Li, Y.; Hua, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, C.; Du, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, C. Inhibition of phagocytosis and pyroptosis of macrophages promotes Bartonella invasion into the blood stream through lymphatic circulation. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 215, jiw526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Mahoud, S.; Bakheet, A.M.H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.; Tang, J. Pathway-related molecules of VEGFC/D-VEGFR3/NRP2 axis in tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 461, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehio, C. Recent progress in understanding Bartonella-induced vascular proliferation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truttmann, M.C.; Rhomberg, T.A.; Dehio, C. Combined action of the type IV secretion effector proteins BepC and BepF promotes invasome formation of Bartonella henselae on endothelial and epithelial cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felcht, M.; Thomas, M. Angiogenesis in malignant melanoma. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2015, 13, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehio, C.; Meyer, M.; Berger, J.; Schwarz, H.; Lanz, C. Interaction of Bartonella henselae with endothelial cells results in bacterial aggregation on the cell surface and the subsequent engulfment and internalisation of the bacterial aggregate by a unique structure, the invasome. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, F.; Mändle, T.; Urbich, C.; Dimmeler, S.; Michaelis, U.R.; Brandes, R.P.; Flötenmeyer, M.; Döring, C.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Lauber, K.; et al. Reprogramming of myeloid angiogenic cells by B artonella henselae leads to microenvironmental regulation of pathological angiogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J.E.; Nekorchuk, D.M. Bartonella-associated endothelial proliferation depends on inhibition of apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4656–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Bai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Hong, J.; Yang, Z.; Cui, L.; Hua, X.; Yuan, C. Depolymerization of Cytokeratin Intermediate Filaments Facilitates Intracellular Infection of HeLa Cells by Bartonella henselae. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mccord, A.M.; Resto-Ruiz, S.I.; Anderson, B.E. Autocrine Role for Interleukin-8 in Bartonella henselae-induced Angiogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5185–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Sykes, J.E.; Boulouis, H.-J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Clinical Impact of Persistent Bartonella Bacteremia in Humans and Animals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 990, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varanat, M.; Maggi, R.; Linder, K.; Breitschwerdt, E. Molecular Prevalence of Bartonella, Babesia and Hemotropic Mycoplasma sp. in Dogs with Splenic Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maluki, A.; Breitschwerdt, E.; Bemis, L.; Greenberg, R.; Mozayeni, B.R.; Dencklau, J.; Ericson, M. Imaging analysis of Bartonella species in the skin using single-photon and multi-photon (second harmonic generation) laser scanning microscopy. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, Z.; Ji, M.; Tan, A.-C.; Bemis, J.; Tse, J.-V.; Huang, G.; Park, J.; Ji, C.; Chen, J.; et al. MIR29B regulates expression of MLLT11 (AF1Q), an MLL fusion partner, and low MIR29B expression associates with adverse cytogenetics and poor overall survival in AML. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 153, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry, 4th ed.; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
| Patient No: | Age (Years) | Gender | Occupation | Oregon Residency (Years) | Year of Melanoma Diagnosis | Patient Reported Co-Morbidities * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 81 | F | Housewife | 64 | 29 December 2011 Malignant melanoma (superficial spreading type) | Breast cancer, dementia, cholecystectomy, hysterectomy, arteriosclerosis |
| 2 | 77 | M | Dentist | 77 | 2008 Metastatic | Hairy cell leukemia, lung cancer, depression, diabetes, hypertension, hypothyroid, chronic pain |
| 3 | 71 | M | Truck driver/boiler operator | 71 | 23 August 2006 Malignant melanoma (superficial spreading type) | Depression, diabetes, 2 heart attacks, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia |
| 4 | 68 | M | Painter/truckdriver | 5 | Primary 2008 ** Metastatic 2009 Malignant melanoma (invasive) | Thrombosis, heart bypass, heart attack, diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia |
| 5 | 71 | M | Physician | 39 | 17 March 2010 Malignant melanoma (in situ lentigo malignant type) | Carpel tunnel syndrome, acromioplasty, basal cell/squamous cell, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia |
| 6 | 85 | F | Nurse | 80 | Primary 15 August 2006 Malignant melanoma (nodular) Recurrence 2011 and 2012 | Breast Cancer, depression, hysterectomy, diabetes, replaced heart valve (bovine), hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, cholelithiasis |
| 7 | 31 | M | Cook | 14 | First lesion 2 January 2008 Malignant melanoma (invasive) Second lesion 16 February 2012 ** Malignant melanoma (invasive) Third lesion 7 February 2018 Malignant melanoma (superficial spreading type) | Appendectomy |
| 8 | 77 | M | Timber worker | 42 | Primary 17 December 2007 Malignant melanoma (superficial spreading type) Second lesion 3 January 2008 Malignant melanoma | Diabetes, Hypertension, Hypercholesterolemia, Asthma |
| Reciprocal IFA Antibody Titers To: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient No: | Bartonella vinsonii berkhoffii | Bartonella henselae Houston 1 | Bartonella henselae San Antonio 2 | Bartonella koehlerae | Bartonella Alphaproteobacteria Growth Medium (BAPGM) Enrichment Blood Culture/PCR * |
| 1 | 64 | <16 | 64 | <16 | Negative |
| 2 | 64 | <16 | 128 | <16 | B. henselae (qPCR) |
| 3 | 128 | <16 | 32 | <16 | Negative |
| 4 | <16 | <16 | <16 | <16 | B. henselae (cPCR) |
| 5 | <16 | <16 | <16 | <16 | Negative |
| 6 | <16 | <16 | 64 | <16 | Negative |
| 7 | <16 | <16 | <16 | <16 | B. henselae (cPCR) |
| 8 | 64 | 16 | 64 | 64 | Negative |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ericson, M.E.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Reicherter, P.; Maxwell, C.; Maggi, R.G.; Melvin, R.G.; Maluki, A.H.; Bradley, J.M.; Miller, J.C.; Simmons, G.E., Jr.; et al. Bartonella henselae Detected in Malignant Melanoma, a Preliminary Study. Pathogens 2021, 10, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030326
Ericson ME, Breitschwerdt EB, Reicherter P, Maxwell C, Maggi RG, Melvin RG, Maluki AH, Bradley JM, Miller JC, Simmons GE Jr., et al. Bartonella henselae Detected in Malignant Melanoma, a Preliminary Study. Pathogens. 2021; 10(3):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030326
Chicago/Turabian StyleEricson, Marna E., Edward B. Breitschwerdt, Paul Reicherter, Cole Maxwell, Ricardo G. Maggi, Richard G. Melvin, Azar H. Maluki, Julie M. Bradley, Jennifer C. Miller, Glenn E. Simmons, Jr., and et al. 2021. "Bartonella henselae Detected in Malignant Melanoma, a Preliminary Study" Pathogens 10, no. 3: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030326
APA StyleEricson, M. E., Breitschwerdt, E. B., Reicherter, P., Maxwell, C., Maggi, R. G., Melvin, R. G., Maluki, A. H., Bradley, J. M., Miller, J. C., Simmons, G. E., Jr., Dencklau, J., Joppru, K., Peterson, J., Bae, W., Scanlon, J., & Bemis, L. T. (2021). Bartonella henselae Detected in Malignant Melanoma, a Preliminary Study. Pathogens, 10(3), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030326