Proteomic Discovery of VEEV E2-Host Partner Interactions Identifies GRP78 Inhibitor HA15 as a Potential Therapeutic for Alphavirus Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of VEEV TC-83 Expressing E2 with a N-Terminal V5-Epitope Tag
2.2. VEEV E2 Interactome Characterization
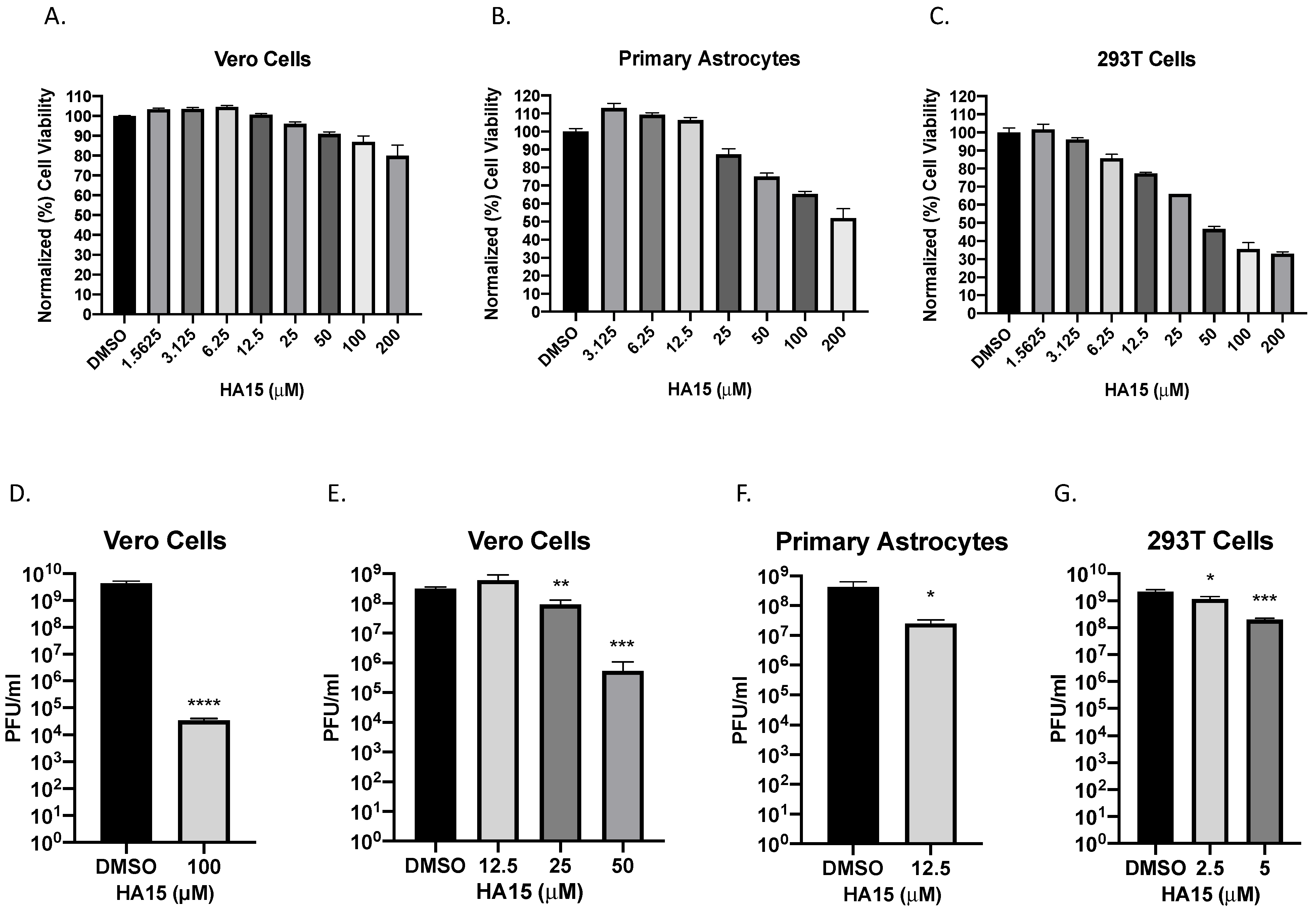
2.3. Inhibition of GRP78 through HA15 Treatment Reduces VEEV TC-83 Infectious Titers
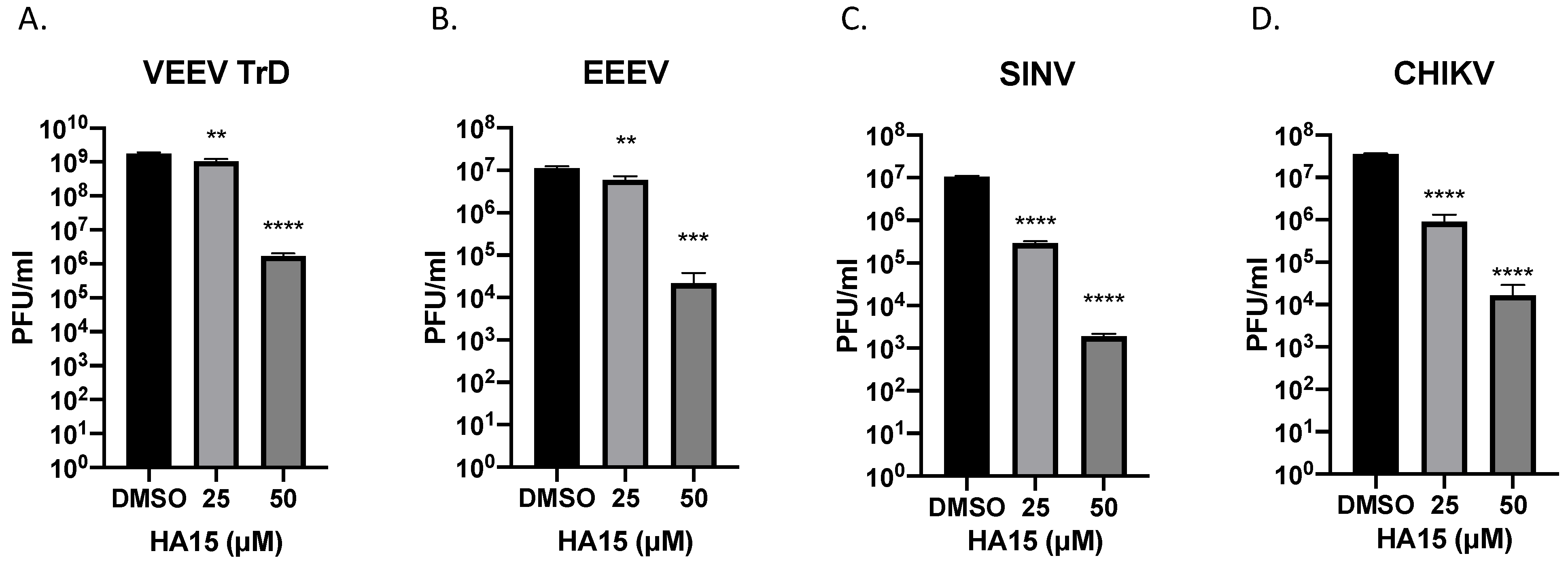
2.4. HA15 Is a Broad-Spectrum Alphavirus Inhibitor
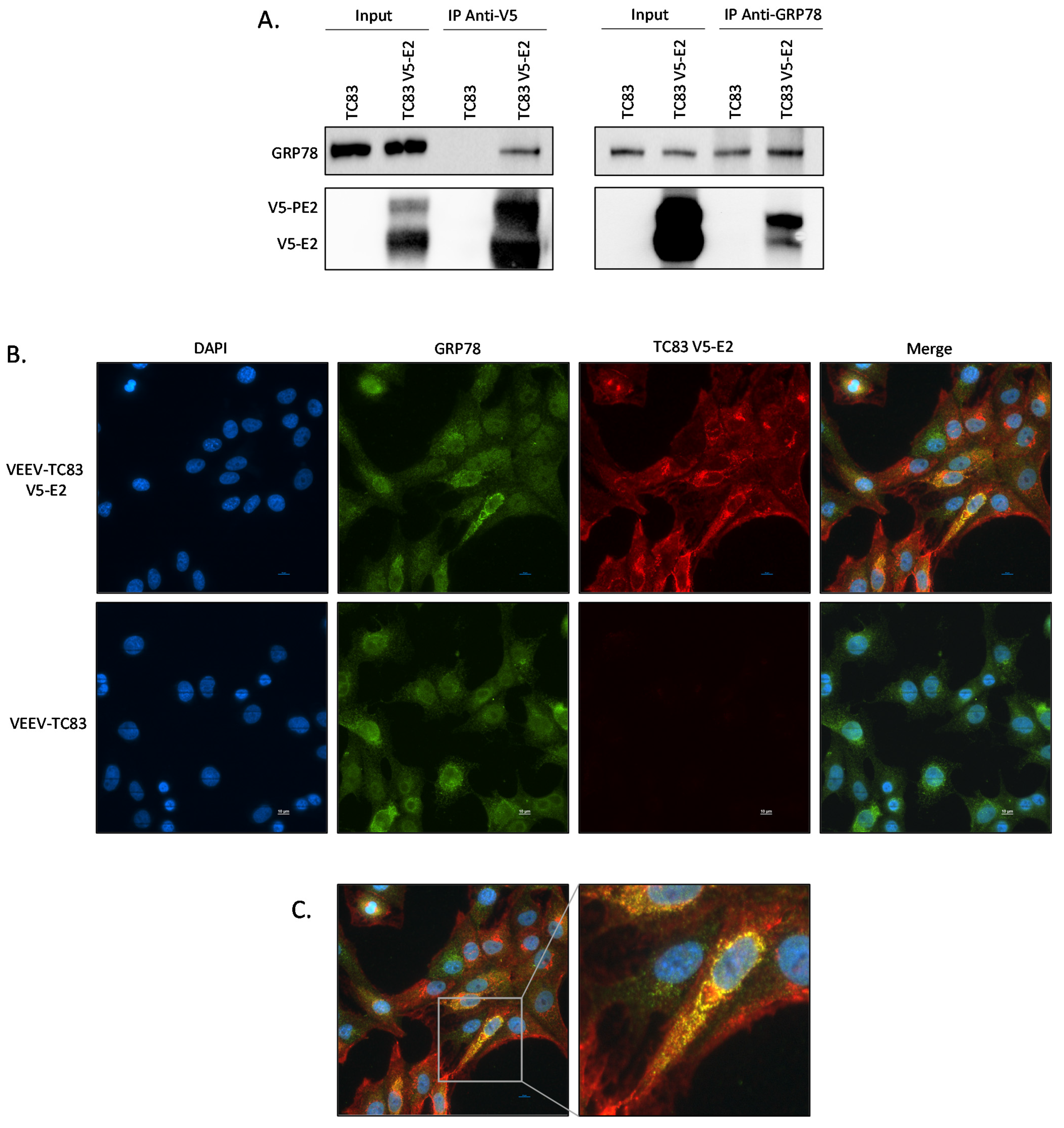
2.5. E2 Glycoprotein of VEEV TC-83 Interacts with GRP78
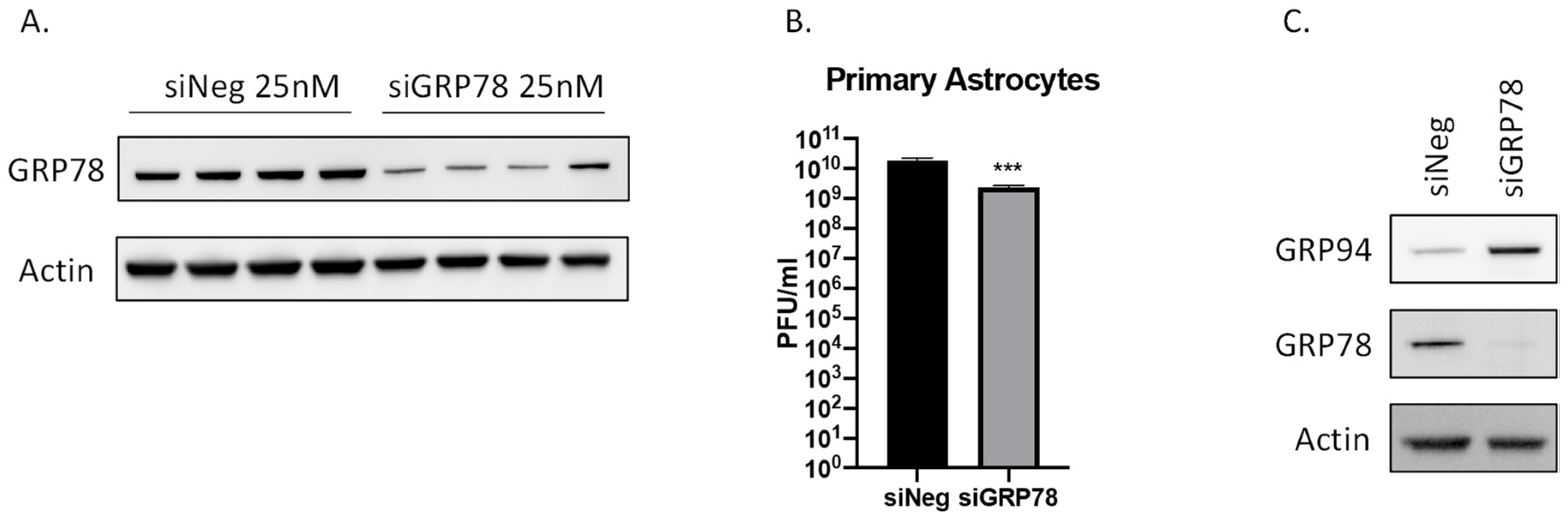
2.6. siRNA Mediated Knockdown of GRP78 Inhibits VEEV TC-83
2.7. HA15 Treatment Has a Significant Impact on Late Steps of the VEEV Life Cycle
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Viruses and Infections
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Immunoprecipitation
4.5. Mass Spectrometry
4.6. Cell Viability Assays
4.7. Inhibitor Treatments
4.8. Immunofluorescent Microscopy
4.9. siRNA Mediated Knockdown
4.10. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weaver, S.C.; Barrett, A.D. Transmission cycles, host range, evolution and emergence of arboviral disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Manuja, A.; Gulati, B.R.; Virmani, N.; Tripathi, B.N. Zoonotic viral diseases of equines and their impact on human and animal health. Open Virol. J. 2018, 12, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.H.; Strauss, E.G. The alphaviruses: Gene expression, replication, and evolution. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 491–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicher, T.; Delitz, M.; Schneider, A.B.; Wolfinger, M.T. Dynamic molecular epidemiology reveals lineage-associated single-nucleotide variants that alter rna structure in chikungunya virus. Genes 2021, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Ferro, C.; Barrera, R.; Boshell, J.; Navarro, J.C. Venezuelan equine encephalitis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2004, 49, 141–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, S.E.; Dineley, K.T.; Paessler, S. Neurological sequelae resulting from encephalitic alphavirus infection. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morens, D.M.; Folkers, G.K.; Fauci, A.S. Eastern equine encephalitis virus—Another emergent arbovirus in the united states. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Zhang, W.; Gabler, S.; Chipman, P.R.; Strauss, E.G.; Strauss, J.H.; Baker, T.S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. Mapping the structure and function of the e1 and e2 glycoproteins in alphaviruses. Structure 2006, 14, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoff, H.; Simons, K. Location of the spike glycoproteins in the semliki forest virus membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3988–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, B.D.; Bakovic, A.; Callahan, V.; Narayanan, A.; Kehn-Hall, K. New world alphavirus protein interactomes from a therapeutic perspective. Antivir. Res. 2019, 163, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimstra, W.B.; Nangle, E.M.; Smith, M.S.; Yurochko, A.D.; Ryman, K.D. Dc-sign and l-sign can act as attachment receptors for alphaviruses and distinguish between mosquito cell- and mammalian cell-derived viruses. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12022–12032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, K.A.; Klimstra, W.B.; Johnston, R.E. Mutations in the e2 glycoprotein of venezuelan equine encephalitis virus confer heparan sulfate interaction, low morbidity, and rapid clearance from blood of mice. Virology 2000, 276, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimstra, W.B.; Ryman, K.D.; Johnston, R.E. Adaptation of sindbis virus to bhk cells selects for use of heparan sulfate as an attachment receptor. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7357–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoshitzky, S.R.; Pegoraro, G.; Chi, X.O.; Dong, L.; Chiang, C.Y.; Jozwick, L.; Clester, J.C.; Cooper, C.L.; Courier, D.; Langan, D.P.; et al. Sirna screen identifies trafficking host factors that modulate alphavirus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezo, M.; Lehraiki, A.; Millet, A.; Rouaud, F.; Plaisant, M.; Jaune, E.; Botton, T.; Ronco, C.; Abbe, P.; Amdouni, H.; et al. Compounds triggering er stress exert anti-melanoma effects and overcome braf inhibitor resistance. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ni, M.; Lee, B.; Barron, E.; Hinton, D.R.; Lee, A.S. The unfolded protein response regulator grp78/bip is required for endoplasmic reticulum integrity and stress-induced autophagy in mammalian cells. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Mao, C.; Lee, B.; Lee, A.S. Grp78/bip is required for cell proliferation and protecting the inner cell mass from apoptosis during early mouse embryonic development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 5688–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flodby, P.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Marconett, C.N.; Laird-Offringa, I.A.; Minoo, P.; Lee, A.S.; Zhou, B. The 78-kd glucose-regulated protein regulates endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis and distal epithelial cell survival during lung development. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, G.M.; Leclerc, G.J.; Kuznetsov, J.N.; DeSalvo, J.; Barredo, J.C. Metformin induces apoptosis through ampk-dependent inhibition of upr signaling in all lymphoblasts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, I.M.; Abdelmalek, D.H.; Elfiky, A.A. Grp78: A cell’s response to stress. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozpedek, W.; Pytel, D.; Mucha, B.; Leszczynska, H.; Diehl, J.A.; Majsterek, I. The role of the perk/eif2alpha/atf4/chop signaling pathway in tumor progression during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Curr. Mol. Med. 2016, 16, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.P.; Ng, M.L.; Vasudevan, S.G. Differential unfolded protein response during chikungunya and sindbis virus infection: Chikv nsp4 suppresses eif2alpha phosphorylation. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, B.; Lin, S.C.; Carey, B.D.; Jacobs, J.L.; Dinman, J.D.; Van Hoek, M.L.; Adams, A.A.; Kehn-Hall, K. Egr1 upregulation following venezuelan equine encephalitis virus infection is regulated by erk and perk pathways contributing to cell death. Virology 2020, 539, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, C. Grp78 at the centre of the stage in cancer and neuroprotection. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wati, S.; Soo, M.L.; Zilm, P.; Li, P.; Paton, A.W.; Burrell, C.J.; Beard, M.; Carr, J.M. Dengue virus infection induces upregulation of grp78, which acts to chaperone viral antigen production. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12871–12880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.Y.; Yang, G.H.; Ryu, C.J.; Hong, H.J. Molecular chaperone grp78/bip interacts with the large surface protein of hepatitis b virus in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2784–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Earl, P.L.; Moss, B.; Doms, R.W. Folding, interaction with grp78-bip, assembly, and transport of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchkovich, N.J.; Maguire, T.G.; Yu, Y.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Alwine, J.C. Human cytomegalovirus specifically controls the levels of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone bip/grp78, which is required for virion assembly. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongwichit, S.; Sornjai, W.; Jitobaom, K.; Greenwood, M.; Greenwood, M.P.; Hitakarun, A.; Wikan, N.; Murphy, D.; Smith, D.R. A functional interaction between grp78 and zika virus e protein. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, S.P.; Shurtleff, A.C.; Costantino, J.A.; Tritsch, S.R.; Retterer, C.; Spurgers, K.B.; Bavari, S. Hspa5 is an essential host factor for ebola virus infection. Antivir. Res. 2014, 109, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.P.; Van Krieken, R.; Carlos, A.J.; Lee, A.S. The stress-inducible molecular chaperone grp78 as potential therapeutic target for coronavirus infection. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 452–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.P.; Chang, C.M.; Hung, C.Y.; Tsai, M.C.; Schuyler, S.C.; Wang, R.Y. Japanese encephalitis virus co-opts the er-stress response protein grp78 for viral infectivity. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Chan, C.M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, J.; Au-Yeung, R.K.; Sze, K.H.; Yang, D.; Shuai, H.; et al. Middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus and bat coronavirus hku9 both can utilize grp78 for attachment onto host cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 11709–11726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinney, R.M.; Chang, G.J.; Tsuchiya, K.R.; Sneider, J.M.; Roehrig, J.T.; Woodward, T.M.; Trent, D.W. Attenuation of venezuelan equine encephalitis virus strain tc-83 is encoded by the 5’-noncoding region and the e2 envelope glycoprotein. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, L.; Pinkham, C.; De la Fuente, C.; Brahms, A.; Shafagati, N.; Wagstaff, K.M.; Jans, D.A.; Tamir, S.; Kehn-Hall, K. Selective inhibitor of nuclear export (sine) compounds alter new world alphavirus capsid localization and reduce viral replication in mammalian cells. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorchakov, R.; Wang, E.; Leal, G.; Forrester, N.L.; Plante, K.; Rossi, S.L.; Partidos, C.D.; Adams, A.P.; Seymour, R.L.; Weger, J.; et al. Attenuation of chikungunya virus vaccine strain 181/clone 25 is determined by two amino acid substitutions in the e2 envelope glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6084–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Gardner, C.L.; Watson, A.M.; Ryman, K.D.; Klimstra, W.B. Stable, high-level expression of reporter proteins from improved alphavirus expression vectors to track replication and dissemination during encephalitic and arthritogenic disease. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, A.; Kehn-Hall, K. Viral concentration determination through plaque assays: Using traditional and novel overlay systems. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, e52065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Accession # | Description | % Coverage | # of Peptides | PSMs | # of Unique Peptides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein Folding | |||||
| NP_005338.1 | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein precursor [Homo sapiens] | 28.13 | 14 | 18 | 13 |
| NP_005337.2 | heat shock 70 kDa protein 1B [Homo sapiens] | 16.69 | 9 | 11 | 6 |
| NP_005518.3 | heat shock 70 kDa protein 1-like [Homo sapiens] | 8.74 | 5 | 5 | 2 |
| NP_004273.1 | BAG family molecular chaperone regulator 2 [Homo sapiens] | 7.58 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| XP_016875853.1 | heat shock protein 105 kDa isoform X6 [Homo sapiens] | 1.90 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| NP_001210.1 | calumenin isoform a precursor [Homo sapiens] | 4.13 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| XP_016868148.1 | calumenin isoform X1 [Homo sapiens] | 7.93 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Metabolism/ATP production | |||||
| NP_001244263.1 | ATP synthase subunit alpha, mitochondrial isoform b precursor [Homo sapiens] | 3.77 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| NP_001677.2 | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial precursor [Homo sapiens] | 22.87 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| Translation | |||||
| NP_000995.1 | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P2 [Homo sapiens] | 33.91 | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| NP_000967.1 | 60S ribosomal protein L12 [Homo sapiens] | 23.64 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| NP_000959.2 | 60S ribosomal protein L4 [Homo sapiens] | 5.15 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| NP_003964.3 | 60S ribosomal protein L14 [Homo sapiens] | 5.58 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Cytoskeleton | |||||
| NP_001017992.1 | beta-actin-like protein 2 [Homo sapiens] | 6.91 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Complement | |||||
| NP_001203.1 | complement component 1 Q subcomponent-binding protein, mitochondrial precursor [Homo sapiens] | 10.64 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Vesicle Transport | |||||
| NP_004729.1 | vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C isoform 1 [Homo sapiens] | 5.76 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| NP_004152.1 | ras-related protein Rab-1A isoform 1 [Homo sapiens] | 8.29 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ubiquitination | |||||
| NP_001268646.1 | polyubiquitin-B precursor [Homo sapiens] | 20.96 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| NP_066289.3 | polyubiquitin-C [Homo sapiens] | 21.02 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| NP_001129064.1 | ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S27a precursor [Homo sapiens] | 10.26 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| NP_001307947.1 | ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40 isoform 1 precursor [Homo sapiens] | 12.50 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrera, M.D.; Callahan, V.; Akhrymuk, I.; Bhalla, N.; Zhou, W.; Campbell, C.; Narayanan, A.; Kehn-Hall, K. Proteomic Discovery of VEEV E2-Host Partner Interactions Identifies GRP78 Inhibitor HA15 as a Potential Therapeutic for Alphavirus Infections. Pathogens 2021, 10, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030283
Barrera MD, Callahan V, Akhrymuk I, Bhalla N, Zhou W, Campbell C, Narayanan A, Kehn-Hall K. Proteomic Discovery of VEEV E2-Host Partner Interactions Identifies GRP78 Inhibitor HA15 as a Potential Therapeutic for Alphavirus Infections. Pathogens. 2021; 10(3):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030283
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrera, Michael D., Victoria Callahan, Ivan Akhrymuk, Nishank Bhalla, Weidong Zhou, Catherine Campbell, Aarthi Narayanan, and Kylene Kehn-Hall. 2021. "Proteomic Discovery of VEEV E2-Host Partner Interactions Identifies GRP78 Inhibitor HA15 as a Potential Therapeutic for Alphavirus Infections" Pathogens 10, no. 3: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030283
APA StyleBarrera, M. D., Callahan, V., Akhrymuk, I., Bhalla, N., Zhou, W., Campbell, C., Narayanan, A., & Kehn-Hall, K. (2021). Proteomic Discovery of VEEV E2-Host Partner Interactions Identifies GRP78 Inhibitor HA15 as a Potential Therapeutic for Alphavirus Infections. Pathogens, 10(3), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030283






