Nasopharyngeal Carriage and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of Staphylococcus aureus among Children under Five Years in Accra
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Site, Design, and Sample Processing
2.2. Isolation and Phenotypic Identification of Bacteria
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
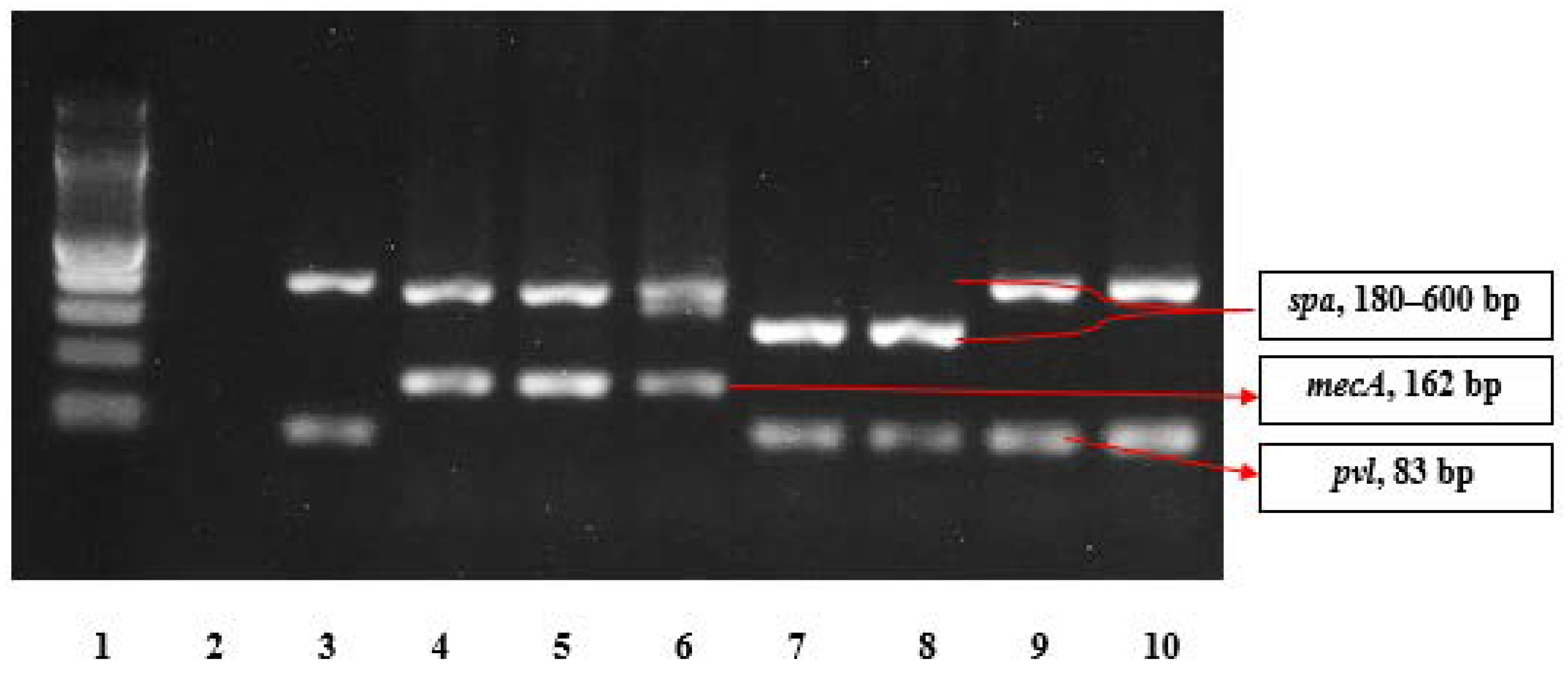
2.4. Molecular Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Demographics of the Study Population
3.2. Nasopharyngeal Staphylococcus aureus Carriage
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of the S. aureus Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thapa, S.; Gokhale, S.; Sharma, A.L.; Sapkota, L.B.; Ansari, S.; Gautam, R.; Shrestha, S.; Neopane, P. Burden of bacterial upper respiratory tract pathogens in school children of Nepal. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2017, 4, e000203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiberman, A.; Dagan, R.; Leibovitz, E.; Yagupsky, P.; Fliss, D.M. The bacteriology of the nasopharynx in childhood. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1999, 49, S151–S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, A.; Gelaw, B.; Shiferaw, Y.; Tigabu, Z. Nasopharyngeal carriage rate and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of potential pathogenic bacteria among pediatric outpatients at Gondar University teaching hospital, Ethiopia. J. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2013, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogden, K.A.; Guthmiller, J.M.; E Taylor, C. Human polymicrobial infections. Lancet 2005, 365, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettigrew, M.M.; Gent, J.F.; Revai, K.; Patel, J.A.; Chonmaitree, T. Microbial interactions during upper respiratory tract infections. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Almudervar, A.; Casey, J.R.; Pichichero, M.E. Nasopharyngeal bacterial interactions in children. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevaranjan, N.; Whelan, F.J.; Puchta, A.; Ashu, E.; Rossi, L.; Surette, M.G.; Bowdish, D.M.E. Streptococcus pneumoniae colonization disrupts the microbial community within the upper respiratory tract of aging mice. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.L.; McDougal, L.K.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Mayer, K.H.; Patel, J.B.; Sennott, J.M.; Fontana, J.L. High frequencies of clindamycin and tetracycline resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Pulsed-Field Type USA300 isolates collected at a Boston ambulatory health center. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bambeke, F.; Reinert, R.R.; Appelbaum, P.C.; Tulkens, P.M.; E Peetermans, W. Multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae infections. Drugs 2007, 67, 2355–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, H.F.; DeLeo, F.R. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 7, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayie, N.T.K.D.; Arhin, R.E.; Newman, M.J.; Dalsgaard, A.; Bisgaard, M.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Slotved, H.-C. Penicillin resistance and serotype distribution of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Ghanaian children less than six years of age. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampane-Donkor, E.; Badoe, E.V.; Annan, J.A.; Nii-Trebi, N.I. Colonisation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in a cohort of HIV infected children in Ghana. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2017, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, E.S.; Kotey, F.C.N.; Dayie, N.T.K.D.; Duodu, S.; Tetteh-Quarcoo, P.B.; Osei, M.-M.; Tette, E.M.A. Colonization of HIV-infected children with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, V.A.; Pesewu, G.A.; Kotey, F.C.N.; Boakye, A.N.; Duodu, S.; A Tette, E.M.; Nyarko, M.Y.; Donkor, E.S. Staphylococcus aureus Nasal colonization among children with sickle cell disease at the Children’s Hospital, Accra: Prevalence, risk factors, and antibiotic resistance. Pathogens 2020, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkor, E.S.; Newman, M.J.; Oliver-Commey, J.; Bannerman, E.; Dayie, N.T.K.D.; Badoe, E.V. Invasive disease and paediatric carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Ghana. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 42, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkor, E.S.; Kotey, F.C.N. Bacterial bloodstream infections. In Studies on Components of Blood & Their Functions; Open Access eBooks: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2020; Volume 1, Chapter 5; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-81-935757-8-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sucher, A.J.; Chahine, E.B.; Nelson, M.; Sucher, B.J. Prevnar 13, the new 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Ann. Pharmacother. 2011, 45, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, L.M.; Farley, M.M.; Schaffner, W.; Thomas, A.; Reingold, A.; Harrison, L.H.; Lynfield, R.; Bennett, N.M.; Petit, S.; Gershman, K.; et al. Prevention of antibiotic-nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae with conjugate vaccines. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 205, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasa, N.B.; Grijalva, C.G.; Arbogast, P.G.; Talbot, T.R.; Craig, A.S.; Griffin, M.R.; Schaffner, W. Nearly complete elimination of the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine serotypes in Tennessee. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, E.S.; Dayie, N.T.K.D.; Badoe, E.V. Vaccination against pneumococcus in West Africa: Perspectives and prospects. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2013, 6, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, D.M.; Malley, R.; Lipsitch, M. Serotype replacement in disease after pneumococcal vaccination. Lancet 2011, 378, 1962–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiertsema, S.P.; Kirkham, L.-A.S.; Corscadden, K.J.; Mowe, E.N.; Bowman, J.; Jacoby, P.; Francis, R.W.; Vijayasekaran, S.; Coates, H.; Riley, T.; et al. Predominance of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in children with otitis media following introduction of a 3+0 pneumococcal conjugate vaccine schedule. Vaccine 2011, 29, 5163–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.M.; Deloria-Knoll, M.; Kassa, H.T.; O’Brien, K.L. Impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on nasopharyngeal carriage and invasive disease among unvaccinated people: Review of evidence on indirect effects. Vaccine 2013, 32, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shak, J.R.; Vidal, J.E.; Klugman, K.P. Influence of bacterial interactions on pneumococcal colonization of the nasopharynx. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogaert, D.; Van Belkum, A.; Sluijter, M.; Luijendijk, A.; De Groot, R.; Rümke, H.C.; A Verbrugh, H.; Hermans, P.W.M. Colonisation by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus in healthy children. Lancet 2004, 363, 1871–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regev-Yochay, G.; Dagan, R.; Raz, M.; Carmeli, Y.; Shainberg, B.; Derazne, E.; Rahav, G.; Rubinstein, E. Association between carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus in children. JAMA 2004, 292, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, B.; Araque, M.; Jongh, C.V.D.G.-D.; Escalona, F.; Correa, M.; Morillo-Puente, S.; Vielma, S.; Hermans, P.W.M. Epidemiology of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus colonization in healthy Venezuelan children. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 30, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.M.; Ambler, J.; Mitchell, S.L.; Castanheira, M.; Dingle, T.; Hindler, J.A.; Koeth, L.; Sei, K.; Hardy, D.; Zimmer, B.; et al. CLSI Methods Development and Standardization Working Group best practices for evaluation of antimicrobial susceptibility tests. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01934-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss-Mandel, A.; Regev-Yochay, G. Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae interaction and response to pneumococcal vaccination: Myth or reality? Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2015, 12, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navne, J.E.; Koch, A.; Slotved, H.-C.; Andersson, M.; Melbye, M.; Ladefoged, K.; Børresen, M. Effect of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on nasopharyngeal carriage by respiratory pathogens among Greenlandic children. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2017, 76, 1309504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzenze, S.A. Effect of introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine immunization on nasopharyngeal colonization of Streptococcus pneumoniae in South Africa (Doctoral dissertation). Wits Inst. Environ. D-Space 2015, 212, 386. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global antimicrobial resistance surveillance system (GLASS) report: Early implementation 2017–2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/searo/amr/global-antimicrobial-resistance-surveillance-system---glass-report-early-implementation-2017-2018.pdf?sfvrsn=7e629fec_6 (accessed on 15 June 2018).
- Pizzutto, S.J.; Hare, K.M.; Upham, J.W. Bronchiectasis in children: Current concepts in immunology and microbiology. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Gu, F.-F.; Guo, X.-K.; Ni, Y.-X.; Xe, P.; Han, L.-Z. Antimicrobial resistance and molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus causing childhood pneumonia in Shanghai. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elixhauser, A.; Steiner, C. Infections with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in US Hospitals, 1993–2005. In Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Brief #35. 2007 July; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2007. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK61977 (accessed on 13 August 2020).
- Klevens, R.M.; Edwards, J.R.; Richards, C.L.; Horan, T.C.; Gaynes, R.P.; Pollock, D.A.; Cardo, D.M. Estimating health care-associated infections and deaths in U.S. Hospitals, 2002. Public Health Rep. 2007, 122, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kraker, M.E.; Wolkewitz, M.; Davey, P.G.; Koller, W.; Berger, J.; Nagler, J.; Icket, C.; Kalenic, S.; Horvatic, J.; Seifert, H.; et al. Clinical impact of antimicrobial resistance in European hospitals: Excess mortality and length of hospital stay related to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1598–1605. Available online: https://www.um.edu.mt/library/oar/handle/123456789/45465 (accessed on 13 August 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantes, R.; Mu, Y.; Belflower, R.; Aragon, D.; Dumyati, G.; Harrison, L.H.; Lessa, F.C.; Lynfield, R.; Nadle, J.; Petit, S.; et al. Emerging infections program–active bacterial Core surveillance MRSA surveillance investigators. National burden of invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections, United States, 2011. JAMA Int. Med. 2013, 173, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gargasson, J.B.; Nyonator, F.K.; Adibo, M.; Gessner, B.D.; Colombini, A. Costs of routine immunization and the introduction of new and underutilized vaccines in Ghana. Vaccine 2015, 33, A40–A46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denno, D.M.; Frimpong, E.; Gregory, M.; Steel, R.W. Nasopharyngeal carriage and susceptibility patterns of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Kumasi, Ghana. West Afr. J. Med. 2004, 21, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimkugel, J.; Forgor, A.A.; Gagneux, S.; Pflüger, V.; Flierl, C.; Awine, E.; Naegeli, M.; Dangy, J.; Smith, T.; Hodgson, A.; et al. An Outbreak of Serotype 1 Streptococcus pneumoniae Meningitis in northern Ghana with features that are characteristic of Neisseria meningitides meningitis epidemics. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, E.S. Molecular typing of the pneumococcus and its application in epidemiology in sub-Saharan Africa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, H.; Aanensen, D.M.; Wijngaard, v.d.C.C.; Spratt, B.G.; Harmsen, D.; Friedrich, A.W.; the European Staphylococcal Reference Laboratory Working Group. Geographic Distribution of Staphylococcus aureus causing invasive infections in Europe: A molecular-epidemiological analysis. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.F.; Leech, J.M.; Rogers, T.R.; McLoughlin, R.M. Staphylococcus aureus Colonization: Modulation of host immune response and impact on human vaccine design. Front. Immunol. 2014, 4, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddinger, R.M.; Luke-Marshall, N.R.; Sauberan, S.L.; Hakansson, A.P.; Campagnari, A.A. Streptococcus pneumoniae modulates Staphylococcus aureus biofilm dispersion and the transition from colonization to invasive disease. mBio 2018, 9, e02089–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkor, E.S.; Jamrozy, D.; Mills, R.O.; Dankwah, T.; Amoo, P.K.; Egyir, B.; Badoe, E.V.; Twasam, J.; Bentley, S.D. A genomic infection control study for Staphylococcus aureus in two Ghanaian hospitals. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayie, N.T.K.D.; Tettey, E.Y.; Newman, M.J.; Bannerman, E.; Donkor, E.S.; Labi, A.-K.; Slotved, H.-C. Pneumococcal carriage among children under five in Accra, Ghana, five years after the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.R.; Stegger, M.; Sørum, M. spa typing directly from a mecA, spa and pvl multiplex PCR assay—a cost-effective improvement for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus surveillance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.C.; De Lencastre, H. Multiplex PCR strategy for rapid identification of structural types and variants of the mec element in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, D.; Claus, H.; Witte, W.; Rothgänger, J.; Turnwald, D.; Vogel, U. Typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a university hospital setting by using novel software for spa repeat determination and database management. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5442–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deurenberg, R.H.; Vink, C.; Driessen, C.; Bes, M.; London, N.; Etienne, J.; Stobberingh, E.E.; Bes, M. Rapid detection of Panton-Valentine leukocidin from clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus strains by real-time PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 240, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegger, M.; Andersen, P.S.; Kearns, A.; Pichon, B.; Holmes, M.A.; Edwards, G.; Laurent, F.; Teale, C.; Skov, R.; Larsen, A.R. Rapid detection, differentiation and typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus harbouring either mecA or the new mecA homologue mecA (LGA251). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-J. Nasal carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus during the first 2 years of life in children in northern Taiwan. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyir, B.; Guardabassi, L.; Esson, J.; Nielsen, S.S.; Newman, M.J.; Addo, K.K.; Larsen, A.R. Insights into nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus in an urban and a rural community in Ghana. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egyir, B.; Oteng, A.A.; Owusu, E.; Newman, M.J.; Addo, K.K.; Rhod-Larsen, A. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus from Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) patients in Accra, Ghana. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwambana-Adams, B.A.; Barer, M.R.; Bottomley, C.; A Adegbola, R.; Antonio, M. Early acquisition and high nasopharyngeal co-colonisation by Streptococcus pneumoniae and three respiratory pathogens amongst Gambian new-borns and infants. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojang, A.; Kendall, L.; Usuf, E.; Egere, U.; Mulwa, S.; Antonio, M.; Greenwood, B.; Hill, P.C.; Roca, A. Prevalence and risk factors for Staphylococcus aureus nasopharyngeal carriage during a PCV trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, D.A.; Sá-Leão, R.; Miragaia, M.; De Lencastre, H. Large screening of CA-MRSA among Staphylococcus aureus colonizing healthy young children living in two areas (urban and rural) of Portugal. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, I.; Moez, H.J.; Alikhani, M.Y. Nasal carriage of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and their antibiotic susceptibility patterns in children attending day-care centers. Acta Microbiol. Et Immunol. Hung. 2011, 58, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumental, S.; Deplano, A.; Jourdain, S.; De Mendonça, R.; Hallin, M.; Nonhoff, C.; Rottiers, S.; Vergison, A.; Denis, O. Dynamic pattern and genotypic diversity of Staphylococcus aureus nasopharyngeal carriage in healthy pre-school children. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, K.; Zhang, T.; Vu, B.N.T.; Dao, T.T.; Tran, T.K.; Nguyen, D.N.T.; Tran, H.K.T.; Nguyen, C.K.T.; Fox, A.; Horby, P.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus nasopharyngeal carriage in rural and urban northern Vietnam. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 108, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottomley, C.; Bojang, A.; Smith, P.G.; Darboe, O.; Antonio, M.; Foster-Nyarko, E.; Kampmann, B.; Greenwood, B.; D’Alessandro, U.; Roca, A. The impact of childhood vaccines on bacterial carriage in the nasopharynx: A longitudinal study. Emerg. Themes Epidemiol. 2015, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiku, T.K.; Asmah, R.H.; Rodrigues, O.; Goka, B.Q.; Obodai, E.; A Adjei, A.; Donkor, E.S.; Armah, G.E. Aetiology of acute lower respiratory infections among children under five years in Accra, Ghana. Pathogens 2015, 4, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, V.T.; Jefferies, J.M.; Clarke, S.C.; Faust, S.N. Nasopharyngeal bacterial carriage in the conjugate vaccine era with a focus on pneumococci. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, J.W.; Gordon, J. Production of hydrogen peroxide by bacteria. Biochem. J. 1922, 16, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev-Yochay, G.; Trzciński, K.; Thompson, C.M.; Malley, R.; Lipsitch, M. Interference between Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus: In vitro hydrogen peroxide-mediated killing by Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 4996–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.M.; Huang, S.S.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Hinrichsen, V.L.; Pelton, S.I.; Kleinman, K.; Hanage, W.P.; Lipsitch, M.; McAdam, A.J.; Finkelstein, J.A. Epidemiology and risk factors for Staphylococcus aureus colonization in children in the post-PCV7 era. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramdani-Bouguessa, N.; Bes, M.; Meugnier, H.; Forey, F.; Reverdy, M.-E.; Lina, G.; Vandenesch, F.; Tazir, M.; Etienne, J. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains resistant to multiple antibiotics and carrying the Panton-Valentine Leukocidin genes in an Algiers Hospital. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, D.O.; Adeyanju, A.; Schaumburg, F.; Akinyoola, A.L.; Lawal, O.O.; Amusa, Y.B.; Köck, R.; Becker, K. Characterization of colonizing Staphylococcus aureus isolated from surgical wards’ patients in a Nigerian university hospital. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risk, R.; Naismith, H.; Burnett, A.; E Moore, S.; Cham, M.; Unger, S. Rational prescribing in paediatrics in a resource-limited setting. Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, K.P.; Boamah, E.A.; Abdulai, M.A.; Buabeng, K.O.; Mahama, E.; Dzabeng, F.; Gavor, E.; Annan, E.A.; Owusu-Agyei, S.; Ghana Antimicrobial Resistance Working Group; et al. Knowledge of antibiotic resistance and antibiotic prescription practices among prescribers in the Brong Ahafo Region of Ghana; a cross-sectional study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2017, 17, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, E.S.; Newman, M.J.; Frimpong, E.; A Opintan, J.; Asamoah-Adu, A. Resistance to antimicrobial drugs in Ghana. Infect. Drug Resist. 2011, 4, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibach, D.; Nagel, M.; Hogan, B.; Azuure, C.; Krumkamp, R.; Dekker, D.; Gajdiss, M.; Brunke, M.; Sarpong, N.; Owusu-Dabo, E.; et al. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus among children in the Ashanti Region of Ghana. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziekan, G.; Hahn, A.; Thüne, K.; Schwarzer, G.; Schäfer, K.; Daschner, F.D.; Grundmann, H. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a teaching hospital: Investigation of nosocomial transmission using a matched case-control study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2000, 46, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowcroft, N.S.; Ronveaux, O.; Monnet, D.L.; Mertens, R. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and antimicrobial use in Belgian hospitals. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 1999, 20, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breurec, S.; Fall, C.; Pouillot, R.; Boisier, P.; Brisse, S.; Diene-Sarr, F.; Djibo, S.; Etienne, J.; Fonkoua, M.C.; Perrier-Gros-Claude, J.D.; et al. Epidemiology of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus lineages in five major African towns: High prevalence of Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Eiff, C.; Friedrich, A.W.; Peters, G.; Becker, K. Prevalence of genes encoding for members of the staphylococcal leukotoxin family among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2004, 49, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Phenotype | Resistance Phenotype | CLI Result | ERY Result | Double Disc Diffusion Test Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D+ | Inducible MLSB | S | R | Flattened, D-shaped clear zone around the CLI disc close to resistant ERY disc |
| D− | MS | S | R | Susceptible zone around the CLI disc and resistant zone around ERY disc |
| R | Constitutive MLSB | R | R | Resistance zones around the CLI and ERY discs |
| S | No Resistance | S | S | Susceptible clear zones around both discs |
| Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mecA | mecA P4 mecA P7 | 5′-TCCAGATTACAACTTCACCAGG-3′ 5′-CCACTTCATATCTTGTAACG-3′ | 162 | Oliveira and de Lencastre [49] |
| spa * | spa 113F spa 1514R | 5′-TAAAGACGATCCTTCGGTGAGC-3′ 5′-CAGCAGTAGTGCCGTTTGCTT-3′ | 180–600 | Harmsen et al. [50] |
| pvl | pvlF pvlR | 5′-GCTGGACAAAACTTCTTGGAATAT-3′ 5′-GATAGGACACCAATAAATTCTGGATTG-3′ | 83 | Deurenberg et al. [51] |
| Age Group (Months) | Age Group (Years) | Number of Children | Carriage Prevalence of S. aureus | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total (%) | |||
| 0–12 | 0–1 | 2 | 3 | 5 (1.2) | 3 (3.2%) |
| 13–24 | 1.1–2 | 31 | 25 | 56 (13.7) | 14 (14.7%) |
| 25–36 | 2.1–3 | 86 | 86 | 172 (42.0) | 28 (29.5%) |
| 37–48 | 3.1–4 | 70 | 59 | 129 (31.5) | 31 (32.9%) |
| 49–60 | 4.1–5 | 21 | 27 | 48 (11.7) | 19 (20%) |
| Total | 210 | 200 | 410 | 95 | |
| Bacterial Pathogen | Number | Prevalence (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Coagulase negative Staphylococci | 194 | 47.3 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 95 | 23.2 |
| Diphtheroids | 22 | 5.4 |
| Micrococcus species | 15 | 3.7 |
| Moraxella species | 6 | 1.5 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 13 | 3.2 |
| Citrobacter species | 6 | 1.5 |
| Escherichia coli | 2 | 0.9 |
| Enterobacter species | 2 | 0.9 |
| Pseudomonas species | 2 | 0.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dayie, N.T.K.D.; Osei, M.-M.; Opintan, J.A.; Tetteh-Quarcoo, P.B.; Kotey, F.C.N.; Ahenkorah, J.; Adutwum-Ofosu, K.K.; Egyir, B.; Donkor, E.S. Nasopharyngeal Carriage and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of Staphylococcus aureus among Children under Five Years in Accra. Pathogens 2021, 10, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020136
Dayie NTKD, Osei M-M, Opintan JA, Tetteh-Quarcoo PB, Kotey FCN, Ahenkorah J, Adutwum-Ofosu KK, Egyir B, Donkor ES. Nasopharyngeal Carriage and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of Staphylococcus aureus among Children under Five Years in Accra. Pathogens. 2021; 10(2):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020136
Chicago/Turabian StyleDayie, Nicholas T. K. D., Mary-Magdalene Osei, Japheth A. Opintan, Patience B. Tetteh-Quarcoo, Fleischer C. N. Kotey, John Ahenkorah, Kevin Kofi Adutwum-Ofosu, Beverly Egyir, and Eric S. Donkor. 2021. "Nasopharyngeal Carriage and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of Staphylococcus aureus among Children under Five Years in Accra" Pathogens 10, no. 2: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020136
APA StyleDayie, N. T. K. D., Osei, M.-M., Opintan, J. A., Tetteh-Quarcoo, P. B., Kotey, F. C. N., Ahenkorah, J., Adutwum-Ofosu, K. K., Egyir, B., & Donkor, E. S. (2021). Nasopharyngeal Carriage and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of Staphylococcus aureus among Children under Five Years in Accra. Pathogens, 10(2), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020136





