Abstract
Pneumonia and inflammatory diseases of the pulmonary system such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma continue to cause significant morbidity and mortality globally. While the etiology of these diseases is highly different, they share a number of similarities in the underlying inflammatory processes driving disease pathology. Multiple recent studies have identified failures in efferocytosis—the phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells—as a common driver of inflammation and tissue destruction in these diseases. Effective efferocytosis has been shown to be important for resolving inflammatory diseases of the lung and the subsequent restoration of normal lung function, while many pneumonia-causing pathogens manipulate the efferocytic system to enhance their growth and avoid immunity. Moreover, some treatments used to manage these patients, such as inhaled corticosteroids for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the prevalent use of statins for cardiovascular disease, have been found to beneficially alter efferocytic activity in these patients. In this review, we provide an overview of the efferocytic process and its role in the pathophysiology and resolution of pneumonia and other inflammatory diseases of the lungs, and discuss the utility of existing and emerging therapies for modulating efferocytosis as potential treatments for these diseases.
1. Introduction
Apoptosis (programmed cell-death) is a highly organized process that is critical for the removal of excessive cells produced during development, for the normal turnover of cells during tissue maintenance, and for the removal of damaged cells during the resolution of pathological events such as infections and inflammation [1]. Every day over a hundred billion cells undergo apoptosis in the adult human body and are replaced by newly formed cells to promote cellular homeostasis. Despite this high burden, clearance of these cells is highly efficient, leaving few uncleared apoptotic cells that can be detected in vivo, even in tissues such as the thymus, which have high rates of cell turnover [2]. This prompt, efficient, and immunologically silent removal of apoptotic bodies by phagocytes is termed “efferocytosis”, and is necessary to prevent secondary necrosis and the subsequent release of proinflammatory alarmins such as adenosine, and autoantigens, which can potentially induce autoimmunity [3]. Efferocytosis is performed by many cell types—termed “efferocytes”—with macrophages functioning as the primary efferocyte in many tissues, while epithelial cells, monocytes, and endothelial cells exhibit efferocytic activity in some tissues [4]. Phenotypically, efferocytosis shares many similarities with the phagocytosis of pathogens [5]. Apoptotic cells are recognized by cell-surface receptors which induce the engulfment of the apoptotic cell into a plasma membrane-derived vacuole termed an “efferosome”. Similar to pathogen-containing phagosomes, these efferosomes undergo a step-wise maturation pathway that delivers the degradative enzymes required to destroy the apoptotic cell (reviewed in [6]). Efferocytosis and phagocytosis are defined by the nature of the target particle being removed by the phagocyte—apoptotic cells in the case of the former, and foreign particulates in the case of the latter—and share many similarities in their cellular and signaling processes. However, there are also differences between efferocytosis and phagocytosis and, therefore, in this review we will refer to efferocytosis/efferosomes when referring to the clearance of apoptotic cells, and phagocytosis/phagosomes when referring to the clearance of microbes and other foreign particulates [3,7,8].
Defects in efferocytosis are known to contribute to many inflammatory and infectious diseases, including lung diseases such as pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cystic fibrosis [9,10]. One of the first investigations into the role of efferocytosis in human pneumonia patients determined that the efferocytic capacity of the patients’ alveolar macrophages correlated more strongly with the recovery of normal lung function than did other markers of disease severity, identifying defective efferocytosis as a contributing factor to the sustained lung injury experienced by some pneumonia patients [11]. Although efferocytosis can be enhanced using existing therapeutics such as glucocorticoids, the use of these agents during infections is controversial as the immunosuppressive action of these drugs impedes some aspects of host defense [12,13,14]. Furthermore, despite the conserved nature of efferocytosis, some of its molecular mechanisms are not fully understood. In this review, we provide an update on the mechanisms and current knowledge gaps of efferocytosis, explore the relationship between efferocytosis and pneumonia, and review the different strategies employed by pneumonia-causing pathogens to influence the efferocytic process to promote their growth. Elucidating the relationship between efferocytosis and pneumonia will inform future therapeutic efforts for manipulating efferocytosis to improve patient outcomes.
2. Overview of Apoptosis
Apoptosis, the programmed death of cells, continually occurs under physiological conditions and serves to uphold the homeostasis of tissues through removing damaged or unneeded cells [1,15]. The induction of apoptosis can occur via two different signaling pathways—an intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway activated by cell stresses including DNA damage and erroneous protein folding in the ER, and an extrinsic pathway activated by the ligation of cell-surface death receptors by ligands expressed on immune cells (reviewed in [16,17]). Apoptosis is coordinated by cysteine aspartic proteases (caspases) which, when activated from their inactive procaspase zymogen forms, cleave various proteins at aspartic acid residues in a cascade leading to the controlled disassembly of intracellular components [18]. Caspases involved in apoptosis are broadly subclassified as initiator caspases (caspase-2, -8, -9 and -10), or executioner caspases (caspase-3, -6 and -7). Initiator caspases are activated by both the intrinsic and extrinsic cell death pathways. In the intrinsic pathway, cell stress pathways inactivate anti-apoptotic proteins, allowing pro-apoptotic Bcl-family proteins to converge on the mitochondria [19,20]. Here, these proteins induce the release of cytochrome C through the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore [21,22]. In the cytosol, cytochrome C complexes with inactive Apoptotic Protease Activating Factor 1 (APAF-1) monomers, inducing the binding of ATP by APAF-1 and the assembly of APAF-1 into a heptamer. Each APAF-1 monomer in this complex, termed the apoptosome, recruits a single molecule of procaspase-9, with this clustering of procaspase-9 allowing cleavage of the pro-domain from neighboring procaspase-9 proteins, thus activating the caspase-9 molecules within the apoptosome [23]. Active caspase-9 in turn cleaves and activates the executioner caspase, caspase-3 [24]. The extrinsic (death receptor) pathway is stimulated by extracellular ligands produced by immune cells that bind to the corresponding death receptors on the dying cells [25,26,27]. The two main receptor-mediated reactions of extrinsic apoptosis are fatty acid synthase ligand and receptor (FasL/FasR) and tumor necrosis factor and receptor (TNF-α/TNFR). Binding of a death ligand with its corresponding death receptor recruits multiple procaspase-8 monomers, which then auto-activate [28]. Active caspase-8 cleaves Bid to form tBid, with both active caspase-8 and tBid recruited to the small amount of charged cardiolipin present on the cytosolic face of the outer mitochondrial membrane. tBid then induces the translocation of additional cardiolipin to the cytosolic facet of the mitochondrial membrane, increasing the surface charge of the mitochondria. This increase in surface charge recruits additional pro-apoptotic proteins and cationic signaling molecules, which ultimately activates the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and initiates apoptosome formation [29,30]. It is not known at this time whether this increase in mitochondrial surface charge occurs during activation of the intrinsic pathway. This activation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore is not required in all cell types, with direct activation of procaspase-3 by caspase-8-mediated cleavage sufficient to induce apoptosis in some cells [31].
Both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converge on the activation of executioner caspases. Once active, these caspases cleave a variety of intracellular targets [18]. Some of these produce active forms of the cleaved proteins, which aid in the disassembly of the cell—e.g., myosin cleavage promotes membrane blebbing [32]—with the activity of these cleaved targets leading to the morphological hallmarks of apoptosis including DNA fragmentation, destruction of cytoskeletal elements, release of ligands recognized by efferocytes, and ultimately, cell death [33,34,35]. After this processing by executioner caspases, the apoptotic cell fragments condense into subcellular membrane-bound vesicles, known as apoptotic bodies, which contain degraded proteins, DNA fragments, and other cellular contents. The final step of apoptosis is efferocytosis, which removes apoptotic bodies prior to the release of intracellular components—thereby reducing the risk of collateral damage to neighboring cells. Efferocytosis (“to bring to the grave” [36]) keeps tissues clear of apoptotic corpses. Efferocytic defects lead to the persistence of apoptotic cells that eventually succumb to secondary necrosis, wherein they lose their membrane integrity via an autolytic process [8,37,38].
The trigger for this transition from the execution phase of apoptosis to secondary necrosis is thought to be ATP depletion in late apoptosis, brought on by a loss of cellular energetics due to mitochondrial dysfunction [39,40,41]. In secondary necrosis, ATP depletion occurs concurrently with ROS production and elevated cytosolic Ca2+, resulting in the activation of non-caspase proteases and other enzymes, ultimately rupturing the plasma membrane [42,43,44,45]. The pathogenic consequences of secondary necrosis can be divided into two types: First, membrane rupture results in leakage of cytotoxic pro-inflammatory and immunogenic molecules called damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) or alarmins. These DAMPs include ATP and HMGB1, which are released from the cytosol (ATP) and nucleus (HMGB1) when the membrane integrity of apoptotic cells is lost. These DAMPs can also be released during lytic forms of cell death (e.g., necrosis and pyroptosis, discussed later in this review), and exert their pro-inflammatory effect by activating innate immune cells and inducing tissue injury [46]. Second, autoantigens released after membrane rupture can be taken up by antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells and be presented to autoreactive CD4+ T cells [37,47]. Activation of autoreactive CD4+ T cells can then drive the onset of autoimmune disease, including the activation of B cells to produce autoantibodies, and the activation of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, which together facilitate an autoimmune response. Moreover, in the case of infection, failed efferocytosis may promote the release of the pathogen and infection of neighboring cells [48,49]. Thus, effective efferocytosis is crucial in preventing these immunogenic outcomes.
3. Mechanisms of Efferocytosis
While being separate processes, efferocytosis and phagocytosis share many mechanistic similarities. The term “phagocytosis” refers to the receptor-mediated ingestion of large (>0.5 μm) foreign particles into a plasma membrane-derived vesicle known as a phagosome (reviewed in [50]), and shares many of the same uptake and degradative mechanisms as efferocytosis. In most cases, phagocytosis and efferocytosis are performed by professional phagocytic cells such as macrophages, neutrophils, monocytes and dendritic cells—although nonprofessional “neighboring” phagocytes such as epithelial cells, fibroblasts and endothelial cells function as efferocytes in some tissues [51]. Efferocytosis is dependent on several signaling processes that together divide efferocytosis into four sequential steps: “find-me” signals released by apoptotic cells which recruit phagocytes, “eat-me” signals on the apoptotic cell surface which allow for receptor-mediated recognition and engulfment of the dying cell, efferosome formation and maturation that degrades the engulfed material, and anti-inflammatory post-engulfment signaling [52,53].
3.1. Release of “Find-Me” Signals by Apoptotic Cells
For efferocytosis to occur, an efferocyte must first migrate to the apoptotic cell. As in response to pathogens, the migration of efferocytes is controlled by chemoattractant “find-me” signals including chemokines and soluble factors such as nucleotides and lipids which are released into the local environment (Figure 1A). Once released, “find me” signals diffuse and form a chemotactic gradient that allows for the directional migration of efferocytes to the apoptotic cell [54,55,56,57]. Activation of the caspase-3 and -7 results in the release of these soluble mediators [52]. Currently, four find-me signals have been identified, which include CX3CL1 (fractalkine), triphosphate nucleotides (ATP and UTP), sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), and lysophosphatidylcholine (LysoPC), which are released at different stages of apoptosis [55,56,58,59]. Elliot et al. found that ATP and UTP release occurs in early apoptosis and induces the directional migration of monocytes towards apoptotic cells in vitro and in vivo, with recognition of these nucleotides occurring through the P2Y2 receptor [56]. During apoptosis, caspase-3 and -7 cleave the C-terminal tail of plasma membrane Pannexin-1 (Panx1) channels while the membrane of these cells is still intact, resulting in the opening of the Panx1 channel and release of cytosolic nucleotides into the extracellular milieu where they act as chemoattractants [34]. Another early “find-me” signal released by some early-stage apoptotic cells is CX3CL1, which is released in a caspase-dependent fashion and is recognized by CX3CR1 on efferocytes [58,60]. In addition to acting as a “find me” signal, CX3CL1 also promotes efferocytosis by stimulating expression of MFG-E8 in responding efferocytes, with the MFG-E8 acting as an opsonin that bridges “eat me” signals on apoptotic cells to efferocytic receptors [61].
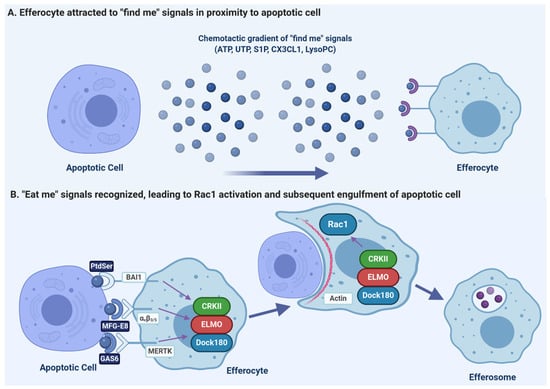
Figure 1.
Efferocytosis requires efferocytes to migrate to sites of apoptosis where the apoptotic cells are then engulfed. (A) Apoptotic cells release multiple chemoattractants which recruit efferocytes. These include nucleotide-tri-phosphates (ATP, UTP), lipids (S1P, LysoPC), and chemokines (CX3CL1). (B) The engulfment of apoptotic cells is primarily driven by the recognition of phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) on the apoptotic cell, either directly by receptors such as BAI1, or via opsonins (MFG-E8 and Gas6) which bridge the PtdSer to efferocytic receptors such as αvβ3 integrin or MERTK. These efferocytic receptors then activate the canonical phagocytic receptor signaling cascade, activating a complex of CRKII, ELMO and DOCK180 which then activates the GTPase Rac1. Rac1 drives the reorganization of the efferocyte actin cytoskeleton such that the efferocyte engulfs the apoptotic cell into a plasma-membrane derived vacuole called the “efferosome”. Figure prepared with BioRender (biorender.com).
The find-me signals LysoPC and S1P are lipid chemotactic factors produced by apoptotic cells in later stages of apoptosis [54]. LysoPC is produced from plasma membrane phosphatidylcholine following caspase-3 mediated activation of calcium-independent phospholipase A2. Following its production, LysoPC is released from the cell by ATP-binding cassette transporter C1 and is recognized by the G2A receptor on macrophages [55,62]. Through caspase-1-dependent upregulation of S1P Kinases (SphK) 1 and 2, S1P is generated from sphingosine, released from apoptotic cells, and promotes chemotaxis of macrophages via the S1P receptor (S1PR) [63]. In addition to serving as a “find-me” signal, S1P-induced signaling promotes an anti-inflammatory gene expression phenotype in macrophages, elevating the expression of anti-inflammatory mediators and inhibiting pro-inflammatory mediator production [63]. S1P also directly promotes efferocytosis through inducing the release of erythropoietin (EPO) from apoptotic cells which, via EPO-EPOR signaling, induces upregulation of efferocytic receptors such as MFG-E8 and MERTK by efferocytes [64].
3.2. Recognition of Apoptotic Cells via “Eat-Me” Signals
Once attracted by “find-me” signals to the proximity of apoptotic cells, efferocytes recognize specific cell surface ligands on apoptotic cells, termed “eat-me” signals, which differentiate apoptotic cells from neighboring healthy cells displaying “don’t-eat-me” signals such as CD47 [65,66,67]. Efferocytes have various engulfment receptors on their surface that specifically recognize these “eat-me” signals, either directly or via opsonins which act as a “bridge” between the “eat-me” signal and the receptor. During apoptosis, activated executioner caspases cleave different substrates resulting in characteristic morphological changes to the apoptotic cell that allow for this recognition. While a variety of “eat-me” ligands have been studied including cell-surface calreticulin, altered glycosylation patterns of ICAM-1, oxidized lipids, and C1q, the most characteristic and ubiquitously seen marker of apoptosis is exposure of phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) on the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane [68,69,70,71,72,73].
In eukaryotic cells, phospholipids are asymmetrically distributed between the inner and outer leaflets of the plasma membrane [30,74]. In healthy cells, PtdSer is confined to the inner cytoplasmic leaflet by the activity of ATP-dependent flippase enzymes which shuttle PtdSer from the outer to the inner leaflet [75,76]. During apoptosis, PtdSer exposure on the apoptotic cell surface is promoted by the action of two caspase-dependent processes: caspases 3/7 inactivate the flippases ATP11A and ATP11C, and simultaneously activates Xkr8 scramblase, resulting in PtdSer translocation to the outer leaflet [77,78,79]. Once exposed, PtdSer is recognized by many receptors expressed by efferocytes (Figure 1B). Receptors that bind directly to PtdSer include members of the T cell immunoglobulin mucin (TIM) receptor family such as TIM-1, TIM-3, and TIM-4 [80], brain angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1) [81], stabilin 2 [82], members of the CD300 family [83], and the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) [84]. Other efferocytic receptors indirectly recognize PtdSer via soluble opsonins such as sCD93 [85], MFG-E8 [86], CCN1 [87], GAS6 [88], and Protein S [88]. After binding to the “eat-me” signals on the apoptotic cell surface, sCD93 is recognized by αxβ2 integrin [85], MFG-E8 and CCN1 are recognized by αvβ3/5 integrins [86,87], while GAS6 and ProS1 are recognized by the TAM (Tyro3, Axl, MERTK) tyrosine kinase family of receptors [88,89,90]. In addition to facilitating the recognition of apoptotic cells by phagocytes, PtdSer also triggers an anti-inflammatory response consisting of secretion of interleukin (IL)-10, and transforming growth factor β (TGFβ), and inhibits the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα and IL-1β [91,92].
In some instances, healthy cells may have a high amount of PtdSer or other “eat-me” signals on their surface but do not undergo efferocytosis [93,94]. These healthy cells are protected from inappropriate efferocytic uptake by the presence of surface proteins, termed “don’t-eat-me” signals, which bind to receptors on efferocytes to prevent internalization. These “don’t-eat-me” signals include CD47, CD31, and CD24 [66,95,96]. CD47 is recognized by the signal-regulatory protein-α (SIRPα), CD24 is recognized by SIGLEC10, and CD31 prevents engulfment through homotypic interactions with CD31 on efferocytes [67]. In the case of CD47, the most well-studied “don’t-eat-me” signal, the CD47-SIRPα interaction triggers a dephosphorylation cascade which antagonizes efferocytic receptor signaling, ultimately blocking the myosin II and Rac1 activity required for the cytoskeletal rearrangement that mediates apoptotic cell engulfment [66]. As such, any cell that undergoes efferocytosis must first lose their “don’t-eat-me” signals. Dying cells have a reduced expression of CD31 and CD47, thus reducing the inhibitory effect of these “don’t-eat-me” signals [97]. How these “don’t-eat-me” signals are regulated during apoptosis is unclear, although the decrease in CD31 and CD47 is caspase-mediated [97].
The receptors and signaling pathways regulating efferocytosis in response to other “eat me” signals are not as well understood as the receptors and signaling mediated by PtdSer-recognizing receptors. Recognition of oxidized lipids occurs via scavenger receptors such as CD36 and SR-B1 [72,98]. ICAM-1 is recognized by β2 integrins [99], while calreticulin is a ligand for C1q and/or LPR [73,100]. Other ligands likely exist—for example, we recently demonstrated that sCD93 acts as an opsonin between apoptotic cells and αxβ2 integrin on the efferocyte, but while we were able to demonstrate that this ligand was not PtdSer, the identity of sCD93’s ligand remains elusive [85]. CD36 and β2 integrins utilize variants of the canonical phagocytic signaling pathway, discussed below [101,102], while the efferocytic signaling pathways induced by C1q and LPR are unclear.
3.3. Receptor Signaling and Internalization
Once “eat-me” signals are recognized, signal transduction pathways are activated which reorganize the efferocyte actin cytoskeleton at the site of apoptotic cell contact, driving the engulfment of the apoptotic cell (reviewed in [5]). While there are many efferocytic receptors, they appear to utilize the same signaling pathway as canonical pathogen-recognizing phagocytic receptors. This pathway is initiated by two receptor-proximal signals—Src-family kinases and formation of the second messenger phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)trisphosphate (PIP3) by PI-3-kinase (PI3K) [103,104,105]. These pathways activate a host of downstream effectors, converging on the activation of the RHO family GTPase Rac1 [103]. The activation of Rac1 requires the formation of a functional Rac1 guanine exchange factor complex, usually composed of a complex of DOCK180 and ELMO1, on the cell membrane (Figure 1B, [81,106,107]). DOCK180 is recruited to the membrane by PIP3, after which it binds to ELMO1 via an SH3 domain; this complex forms a bipartite guanine-nucleotide exchange factor which then activates Rac1 [106]. Efferocytic receptors which use the CrkII-ELMO-Dock180 Rac1-activating pathway include integrin αvβ3/5, MERTK, and BAI1 [81,108,109]. Activation of Rac1 by the ELMO1/DOCK180 complex reorganizes the cortical actin cytoskeleton through Arp2/3 induced actin polymerization [82,105,107]. This polymerization drives extensions of the plasma membrane around the apoptotic cell, first forming a cup-like structure, which over time completely envelops the apoptotic cell. This membrane extension can require the addition of membrane to the forming cup, which is delivered via the focal exocytosis of ER- and endosome-derived vesicles, with these fusion events mediated by Arf6, Rab13 and Rab35 (reviewed in [6]). Fusion of the enveloping membrane and closure of the phagocytic cup forms a discrete cytosolic vacuole, termed the “efferosome”, containing the apoptotic cell. This process appears to be identical to the engulfment process of phagocytosis, with the same canonical signaling pathway activated by both efferocytic and phagocytic receptors and driving an engulfment process relying on the same cytoskeletal rearrangements and Rab-mediated membrane delivery.
3.4. Efferosome Maturation
Once the apoptotic cell is internalized, the resulting efferosome proceeds through a tightly regulated maturation process that degrades the internalized contents through the sequential fusion of the efferosome with early endosomes, late endosomes and ultimately lysosomes. This delivers hydrolytic enzymes and vacuolar ATPases, which produce an increasingly acidic luminal environment that bestows the efferosome with potent degradative capabilities. Each stage of this process is facilitated by the action of Rab GTPases (reviewed in detail in [6]).
The first maturation step after engulfment is fusion of the nascent efferosome with early endosomes (Figure 2). This is driven by the Rab GTPase Rab5, which is activated on the early efferosome by the GEF Rabex-5 [110]. Once activated, Rab5 recruits and activates several Rab5 effector proteins, including the type III PI3K Vps34, which catalyzes the generation of the signaling lipid phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P) [111]. The accumulation of PI3P on the cytosolic leaflet of the early efferosome recruits and activates other Rab5 effectors, such as endosomal early antigen 1 (EEA1) and rabenosyn-5, which together trigger the formation of the class C COre Vacuole/Endosome Tether complex (CORVET) on the efferosome membrane [111,112,113,114]. This complex bridges active Rab5 on the efferosome to Rab5 on early endosomes, thereby driving the SNARE-dependent fusion of the efferosome with early endosomes. This begins the delivery of the degradative enzymes which will ultimately destroy the apoptotic cell [115,116].
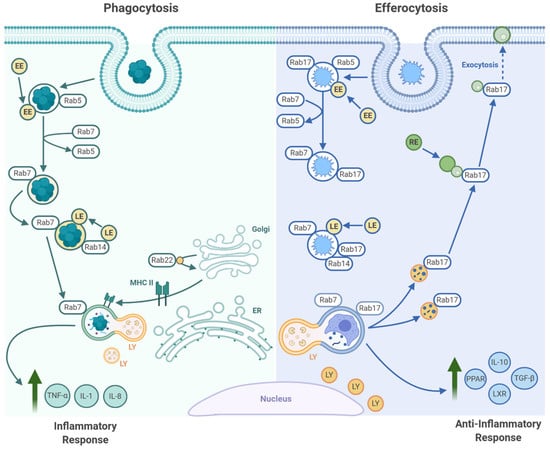
Figure 2.
Maturation of pathogen-containing phagosomes and apoptotic cell-containing efferosomes. Following pathogen phagocytosis (left), the microbes are contained within a membrane-bound phagosome, which recruits the GTPase Rab5. Rab5 then mediates fusion of the phagosome with early endosomes (EE), after which Rab5 is exchanged for Rab7 on the phagosome surface. Rab7 then mediates fusion of the phagosome with late endosomes (LE) and lysosomes (LY), thereby killing and degrading the microbe. Microbe-recognizing pattern recognition receptors induce the expression of inflammatory cytokines and drive macrophage polarization towards a more inflammatory phenotype. In some cell types (macrophages and dendritic cells), this inflammatory signaling also induces MHC II expression. MHC II is then trafficked to the phagosomes, where it is loaded with microbe-derived antigens that can then be presented to T cells. The initial stages of efferocytosis are similar to phagocytosis in that Rab5 and Rab7 drive fusion of the efferosome with endosomes and lysosomes, but differs in that Rab17 is also recruited to the efferosome. At the later stages of maturation, Rab17 mediates the fragmentation of the efferosome and the transport of these efferosome fragments to the recycling endosomal system (RE), where these materials are absorbed. Efferocytic receptors and efferosome-derived materials activate transcription factors that induce the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines and mediate the metabolic reprogramming of the efferocyte to enable the engulfment of additional apoptotic cells. Figure prepared with BioRender (biorender.com).
Approximately five minutes after engulfment, the early efferosome transitions to a late efferosome marked by an exchange of Rab5 for Rab7 (Figure 2, [117]). A complex of Monensin and Brefeldin A Hypersensitive 1a/b (Mon1a/b) and Sensitive to Caffeine Ca2+ and Zn2+ (Ccz-1) promotes the inactivation and release of Rab5. In parallel, the Mon1a/b/Ccz-1 complex recruits and activates Rab7 [118,119]. Once activated, Rab7 recruits a set of effectors different from those recruited by Rab5. This includes Rab-interacting lysosomal protein (RILP) and oxysterol-binding protein related-protein 1 (ORPL1), which interact with dynein/dynactin to transport the late efferosome to the perinuclear region of the cells where fusion between the efferosome and lysosomes occurs [118,120,121]. Through these effectors, Rab7 also promotes recruitment of the HOmotypic fusion and Protein Sorting complex (HOPS), a large multimeric tethering complex necessary to dock and fuse the efferosome with Rab7-bearing late endosomes and lysosomes (reviewed in [114]). This complex bridges Rab7 on the efferosome with Rab7 on late endosomes and lysosomes, thus enabling SNARE-mediated fusion of late endosomes and lysosomes with the efferosome. These fusion events deliver V-ATPases, which lowers the luminal pH to 5.0 or lower, and hydrolytic enzymes including nucleases, cathepsins, and lipases, to the efferosome [122,123]. The high acidity of the luminal environment produced by the V-ATPases not only serves to facilitate degradation of the apoptotic cell debris but also works synergistically to activate the hydrolases acquired from the lysosomes. Together, the hydrolytic enzymes and acidic environment, along with production of oxygen radicals by NADPH oxidase, results in the complete degradation of the internalized apoptotic cell [124,125].
During pathogen phagocytosis, the highly acidic compartment that forms after phagosome-lysosome fusion (the phagolysosome [126,127]) matures further, forming into an MHC class II loading compartment (MIIC) [128,129,130]. Here, pathogen-derived antigens are loaded on to MHC II, and then exported to the cell surface for presentation to antigen-specific CD4+ T cells (reviewed in [129]). However, this process does not occur following efferocytosis, as efferocytosis is anti-inflammatory and non-immunogenic. Our group recently determined that this key difference in pathogen phagocytosis versus apoptotic cell efferocytosis is driven by the recruitment of Rab17 onto the early efferosome [131,132]. Rab17 persists on the efferosome throughout maturation, where following lysosome fusion and degradation of the apoptotic cell, Rab17 mediates trafficking of the efferosome from the perinuclear region to the cell periphery [133]. Here, the apoptotic cell contents are shuttled to the recycling endosome, where the degraded materials are thought to either be absorbed by the efferocyte or expelled via exocytosis. This may act to enhance the recovery of amino acids, lipids, sugars and proteins from the apoptotic cell, while simultaneously limiting immunogenic loading of autoantigens onto MHC II [132,133]. While the specific mechanism which allows Rab17 to be persistently recruited to the efferosome remains unknown, it is established that MIIC formation requires TLR signaling, and Rab17 knockdown enables MHC II recruitment to efferosomes, suggesting that Rab17 may antagonize MIIC formation and is displaced from phagosomes via a TLR-dependent signaling mechanism [132,134,135]. It is currently unknown how Rab17 prevents MHC II recruitment to the phagosome, with this process currently being under investigation in our lab.
4. Efferocyte Metabolism, Polarization, and Inflammation
While the normal outcome of phagosome maturation is the initiation of inflammatory signaling, efferosome maturation is characterized by the opposite—the secretion of anti-inflammatory and pro-tissue healing factors. This includes upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines including TGF-β, IL-10, and release of lipid mediators including prostaglandin E2 and I2 (PGE2, PGI2) [91,136]. In addition, efferocytosis also inhibits secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-8, through suppression of the nuclear factor-κ B (NF-ĸB) transcription [91,137]. Further anti-inflammatory influence comes from activation of the TAM family of efferocytic receptors such as MERTK, which upregulate the expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 and -3 (SOCS1 and SOCS3), which attenuate inflammatory responses by inhibiting STAT-dependent transcription [138,139].
4.1. Efferocyte Metabolism and Polarization
Changes in efferocyte behavior following efferocytosis is not limited to the production of anti-inflammatory mediators, and indeed, following efferocytosis, these cells undergo large-scale metabolic and transcriptional reprogramming. Efferocytic receptor signaling induces the upregulation of liver X receptor (LXR) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) nuclear receptors [140,141,142]. LXR and PPAR receptors are generally co-expressed in phagocytic cells under basal conditions, although when singly-expressed, activation of one receptor induces the expression of the other [143,144]. LXR and PPAR receptors bind to many of the same ligands—mostly lipid-derived metabolites—with activation of both leading to the preferential formation of heterodimers over homodimers. Once dimerized, the receptors bind to their target gene promotors, with the homodimeric and heterodimeric forms recognizing the same DNA sequence [145]. Signaling of the heterodimers are best understood, as these are most often found in efferocytes, where they enhance the expression of efferocytic receptors and cholesterol exporters. These receptors can also suppress gene expression, for example inhibiting pro-inflammatory gene transcription through suppressing the transcription of STAT-3 [146,147,148,149]. While heterodimer-mediated transcription seems to be most common in efferocytes, competition between homodimers for DNA binding sites may also have an important role in determining the response of efferocytes to apoptotic cell engulfment. For example, active LXR can displace PPAR homodimers, thereby preventing the PPAR-mediated inhibition of fatty acid β-oxidation [150]. The role of these receptors in pathogen phagocytosis are less well understood. PPAR activation with synthetic ligands enhances the expression of macrophage NADPH oxidase, myeloperoxidase, and upregulates CD36 which, in addition to acting as an efferocytic receptor, can act as a phagocytic receptor for eukaryotic pathogens such as malaria [151,152,153]. The role of LXRs in phagocytosis appears to be context dependent. LXR agonists in the absence of other inflammatory stimuli enhance phagocyte responsiveness to pathogens through upregulating TLR receptors and reactive oxygen species production, but the effect of LXR signaling rapidly becomes strongly anti-inflammatory upon exposure of the phagocyte to inflammatory cytokines or pathogens [154,155].
These changes in efferocyte metabolism are critical for efficient and on-going efferocytosis. The high metabolic burden placed on efferocytes—a doubling or more of their lipid and sterol content every time an apoptotic cell is engulfed—requires a significant alteration to the efferocytes’ metabolism. This includes upregulation of the mitochondrial electron transport chain and enzymes for lipid β-oxidation, allowing efferocytes to derive most of their energy from lipolysis, while also reducing their lipid content [156]. In parallel, macrophages upregulate the cholesterol exporters ABCA1 and ABCG1, enhancing their export of cholesterol to HDL [157,158]. This enhanced metabolic capacity is required for efferocytes to engage in multiple rounds of efferocytosis. Indeed, inhibition of these pathways limits the ability of efferocytes to engulf multiple apoptotic cells, as the cellular stresses from the buildup of apoptotic cell-derived lipids and sterols prevents further rounds of efferocytosis [159,160]. This phenomenon is not limited to in vitro studies, and indeed, is partially responsible for the pathology of atherosclerosis. In atherosclerosis, the accumulation of lipids and sterols in subvascular macrophages induces the expression of the transcription factor GATA2. GATA2 then suppresses the transcription of efferocytic receptors (e.g., αxβ2), efferocytic signaling molecules (e.g., Src-family kinases), regulators of efferosome maturation (e.g., Rab7), and hydrolytic enzymes required for degradation of apoptotic cells (e.g., vacuolar ATPase, [161]). The loss of these efferocytic regulators then limits the clearance of apoptotic cells, allowing for the accumulation of dead, cholesterol-laden macrophages that comprise the bulk of atherosclerotic plaques.
In macrophages, this anti-inflammatory and metabolic reprogramming results in a unique polarization state different from the classically-defined inflammatory (M1) and alternatively activated (M2) polarization states. Indeed, transcriptomic analysis of tissue macrophages fails to find cells with gene expression patterns similar to in vitro polarized M0/M1/M2 macrophages and, rather, the transcriptomic profile of tissue-resident macrophages varies greatly between tissues [162]. However, while tissue resident macrophages vary greatly between tissues, the subset of macrophages in each tissue specialized for efferocytosis share a common transcriptional “core” characterized by expression of the scavenger receptors CD206 and CD163 (recognizing mannose and hemoglobin-haptoglobin, respectively) and the efferocytic receptors Tim-4 and MERTK. This “core” signature was not found in M0/M1/M2 polarized cells, nor was it found in non-efferocytic macrophages from the same tissues [162]. It is unclear if a similar transcriptional pattern emerges when non-professional efferocytes engulf apoptotic cells.
4.2. Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators
In responses to engulfing an apoptotic cell, efferocytes produce several anti-inflammatory proteinaceous, gaseous and lipid-based mediators, which act on neighboring cells in a paracrine fashion. In the human respiratory system, this anti-inflammatory response is driven primarily by Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators (SPMs), lipid mediators derived from dietary essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (reviewed in [163,164]). Examples of SPMs include arachidonic acid-derived lipoxins, and omega-3 fatty acid-derived resolvins, maresins, and protectins. SPMs are formed during acute inflammation, when lipid mediator class-switching drives polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism from the production of pro-inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes, to production of pro-resolving SPMs [165,166]. In the lung, SPMs can be synthesized via a number of cell types, with lipoxins being produced by epithelial cells, eosinophils, and monocytes/macrophages [167,168], while resolvins can be produced by endothelial cells and leukocytes [169,170], and maresins by macrophages [171]. SPMs are stereoselective agonists of their cognate G-protein coupled receptors, which are expressed by leukocytes [172]. Consequentially, SPMs can act in both a paracrine and autocrine fashion, and indeed, the induction of SPM synthesis following efferocytosis has been proposed to generate a positive feedback loop that reinforces the anti-inflammatory signaling induced by efferocytic receptors (reviewed in [164]). In the inflamed lung, SPMs decrease leukocyte infiltration while increasing efferocytic clearance of apoptotic leukocytes and increasing the production of anti-microbial peptides [173,174]. While there are multiple classes of SPMs, resolvins are the best understood and have well-established roles in regulating efferocytosis and inflammation. Moreover, exposure to pathogenic bacteria, such as S. aureus and E. coli, has been shown to stimulate human alveolar macrophages in the lungs to produce SPMs, notably, resolvin D1 (RvD1) and resolvin D2 (RvD2), to mitigate inflammation [175].
ALX/FPR2, ERV, BLT1, DRV1 and DRV2 are high-affinity receptors for resolvins (reviewed in [176]). These receptors are primarily expressed on human airway epithelial cells and on innate immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils [64,173]. ALX/FPR2 and DRV1 are high-affinity RvD1 receptors, while ERV, BLT1 and DRV2 are high-affinity RvE1 and, potentially, RvE2 receptors [174]. While these receptors bind to different types of resolvins, they share the common anti-inflammatory functions including promoting efferocytosis and bacterial phagocytosis, while limiting neutrophil recruitment and migration. The expression of these high affinity resolvin receptors are regulated by cytokines and epigenetic changes which occur in response to inflammation. While acute inflammation tends to increase the expression of these receptors, chronic airway inflammation suppresses resolvin receptor expression, which in turn, hinders the homeostatic effects of resolvins [174,177].
Furthermore, some patients with bacterial pneumonia will subsequently develop respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), prolonging inflammatory responses in the lungs [177]. In humans, the underlying cellular mechanisms involved in the development of chronic inflammation in patients with bacterial pneumonia are not completely established. However, murine models of bacterial pneumonia demonstrated that resolvin administration enhances the resolution of inflammation. Specifically, resolvins were shown to promote efferocytosis of apoptotic leukocytes and reduce neutrophil recruitment to the lungs in murine models [178]. Interestingly, human chronic inflammatory diseases of the lung such as asthma, cystic fibrosis and COPD, exhibit a similar defect in SPM activity to patients with acute inflammation from ARDS and respiratory failure following bacterial pneumonia [174]. Notably, the persistent inflammation exhibited in asthma, cystic fibrosis and COPD is due, in part, to insufficient levels of SPMs or their receptors in the airways of these patients [178].
5. Alveolar Macrophages and Efferocytosis in the Lung
In the proximal airways, the clearance of debris is overseen by pulmonary mechanisms such as the mucociliary apparatus, while the distal airways and lungs are kept clear by phagocytosis and efferocytosis. In healthy lungs, efferocytosis is predominantly mediated by alveolar macrophages located in the mucus layer and interstitial space, and are the most prevalent alveolar professional phagocytes, making up 95% of cells retrieved by bronchoalveolar lavage [179]. Unlike some macrophage populations, alveolar macrophages are long-lived and have a high capacity for self-renewal [180]. Other alveolar efferocytes include recruited monocytes and dendritic cells, as well as non-professional phagocytes such as epithelial and mesenchymal cells [181]. Together, these cells both maintain homeostasis in the airway and aid in the recovery from tissue injury.
Under homeostatic conditions, few apoptotic cells are found in the airways due to the efficient clearance by alveolar efferocytes [182]. Even during acute lung inflammation, which typically features high levels of immune cell apoptosis, few uncleared apoptotic cells are found within the lung [183]. Alveolar macrophages differ from other tissue-resident macrophages; in particular, alveolar macrophages in the non-inflamed lung have a reduced ability to engulf both efferocytic and phagocytic targets compared to other tissue-resident macrophages from other organs. In addition, alveolar macrophages do not respond in an inflammatory fashion after engulfing single bacteria. This reduced responsiveness is thought to prevent inflammatory damage to the vulnerable alveolus following inhalation of cellular debris, non-pathogenic bacteria, and harmless particulates [179,184,185]. In comparison, most other tissue macrophages will readily engulf efferocytic and/or phagocytic targets in large numbers, and respond with a robust activation of inflammatory genes in response to single bacteria [186,187]. This reduced activity of alveolar macrophages is the result of the local airway microenvironment which influences both the expression pattern of efferocytic receptors and overall efferocytic capacity of alveolar macrophages, and is mediated by both soluble mediators and cell-cell interactions. Type II alveolar epithelial cells in the lower airways secrete pulmonary surfactant fluid containing the lung collectins pulmonary surfactant-associated protein (SP)-A and SP-D, which bathes the alveolar macrophages [188]. SP-A and SP-D act as ligands for the SIRPα receptor on efferocytes which inhibits efferocytosis [180,188]. In addition, SP-A and SP-D and promote an anti-inflammatory state by inhibiting formation of the C1 complex required for activating complement, and by blocking TLR2 and TLR4 interactions also prevents NF-ĸB signaling [189,190,191]. Finally, IL-10 is constitutively expressed by lung epithelial cells [192], thereby producing an intracellular milieu that suppresses alveolar macrophage activity.
This tonic inhibition is also mediated by cell contact-dependent processes through molecules expressed by the airway epithelium. Type II alveolar epithelial cells express CD200, which binds to CD200 receptors on alveolar macrophages to block the MAPK and JNK inflammatory pathways [193]. TGF-β is expressed by lung epithelium, and is tethered to the surface of these cells, providing a contact-dependent activation of the TGF-β receptor [194]. While the mechanisms underlying this decrease in alveolar macrophage suppression remain unclear, research has suggested that the damage to the respiratory epithelium and consequent reduction in exposed epithelial cell ligands may relieve this suppressive effect on macrophages, allowing them to engage in more efficient phagocytosis and efferocytosis. Restoration of the lung epithelium then restores normal expression of IL-10 and CD200, restoring the tonic suppression of alveolar macrophages following the resolution of inflammation [195,196]. In addition, the high concentration of multiple inflammatory signals present during an infectious or inflammatory event transcriptionally suppresses some of the tonic inhibitory pathways. For example, TNF-α suppresses the transcription factors necessary for IL-10 expression [197]. Thus, through a combination of transcriptional regulation and the loss of lung epithelial cells, the tonic inhibitory environment in the lung is downregulated during inflammation, thereby “freeing” alveolar macrophages to take on an inflammatory phenotype.
During pneumonia, alveolar macrophages have been reported to exhibit a significant efferocytic capacity, but it is unclear how this is induced [11]. While alveolar macrophages appear to take on an inflammatory phenotype during events such as infection, a large portion of the macrophages in the inflamed lung are derived from the differentiation of blood-derived monocytes into inflammatory and pro-fibrotic macrophages [198,199]. Moreover, the recent description of a new lung-resident macrophage population challenges the view that alveolar macrophages are the predominant cell type responsible for efferocytosis in the lung [198]. These nerve- and airway-associated macrophages are found in the lung’s interstitium and maintain an anti-inflammatory and pro-efferocytic phenotype even under inflammatory conditions. This may indicate that it is the monocyte-derived or interstitial lung-resident macrophages, and not the airway-resident alveolar macrophages, that are the primary mediators of efferocytosis in the lung.
6. Impaired Efferocytosis in Lung Disease
An increased number of uncleared apoptotic cells have been detected in the airways of patients with several chronic inflammatory lung diseases, with alveolar macrophages from these individuals exhibiting defects in efferocytosis. Some evidence suggests that impaired apoptotic cell clearance may be upstream to the sustained lung inflammation of these diseases, and causally contributes to their pathogenesis [200].
6.1. Chronic Obstrructive Pulmonary Disorder
COPD is the chronic inflammation of the airways maintained by the continuous accumulation of activated neutrophils, macrophages and T cells, which cause irreversible small-airway obstruction, peribronchial fibrosis, and emphysema. In COPD, the efferocytic uptake of apoptotic bronchial epithelial, immune and endothelial cells by alveolar macrophages in the lungs is significantly reduced, with a corresponding accumulation of apoptotic cells [9,201]. This efferocytic defect was found to be more pronounced in COPD patients who smoke, with cigarette smoking being the number one risk factor for COPD [202]. In addition, the reductions in efferocytic potential were also associated with altered expression of CD31, CD44, and CD91/LRP-1—key proteins involved in apoptotic cell recognition and binding [202]. While the mechanisms underlying these efferocytic defects remain unidentified, potential contributors include alteration of PtdSer-recognizing efferocytic receptors and opsonins [203], increased levels of HMGB1 in the airways [204], and downregulation of SP-D during chronic lung inflammation [205].
6.2. Asthma
Asthma is another obstructive pulmonary disease characterized by hyperresponsiveness to airway allergens and subsequent recruitment of eosinophils and chronic inflammation. As with COPD, asthma is also associated with an increased number of uncleared apoptotic epithelial cells [206]. Alveolar macrophages in patients with severe asthma have reduced production of anti-inflammatory prostaglandins which, alongside secondary necrosis, may contribute to the chronicity of inflammation [206]. The role of efferocytosis in the pathogenesis of asthma remains poorly understood, but interestingly, glucocorticoids are known to enhance efferocytosis in asthma patients, suggesting that improved efferocytosis may be partially responsible for the positive effects of glucocorticoids in asthmatic patients [1].
6.3. Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. The loss of CFTR, a chloride ion channel, produces thicker respiratory mucous, promotes bacterial colonization, leading to chronic neutrophilic inflammation and impaired mucociliary clearance [207]. Similar to asthma and COPD, CF patients have an accumulation of uncleared apoptotic cells in the airway, primarily uncleared apoptotic neutrophils. These neutrophils release elastase, both during extracellular trap formation and during secondary necrosis, with this elastase reducing efferocytosis through cleavage of efferocytic receptors [10,208,209]. Other potential contributors to this efferocytic defect include increased levels of HMGB1 in the extracellular space [210], and increased RhoA activity through cytokine-mediated decreases in the expression of the RhoA negative regulator FAM13A, and cytokine-induced STAT1-mediated transcription of RhoA itself [211,212].
6.4. Lung Cancer
Through its immunosuppressive effects, efferocytosis also plays a role in promoting the tumor microenvironment and tumorigenesis and progression [213]. Macrophages are the primary immune cell found in tumor microenvironments. PtdSer receptors, such as the TAM and TIM family receptors, are expressed on these cells and are frequently stimulated by apoptotic cells within the tumor environment. This triggers the anti-inflammatory signaling pathways downstream of these receptors, leading to the increased production of anti-inflammatory and pro-healing cytokines. This altered inflammatory environment promotes tumor growth and survival, while dampening T cell-mediated tumor immunity (reviewed in [214]). Indeed, efferocytic receptors are often overexpressed directly by cancers cells, including small and non-small cell lung carcinoma, and contribute to drug resistance to antitumor therapies [215].
6.5. Community-Aquired Pneumonia
Since efferocytosis is essential for resolution of lung inflammation, it follows that it may be an important factor in the differing outcomes of pneumonia patients. In one prospective cohort study, the recovery of lung function after community acquired pneumonia (CAP) was found to be positively correlated with the rate of efferocytosis exhibited by patients’ alveolar macrophages [11]. Another study using a double-infection mouse model of secondary pneumonia found that, following recovery from primary pneumonia caused by Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, or the influenza A virus, alveolar macrophages have a severely impaired phagocytic capacity associated with an increased susceptibility to secondary infection upon re-exposure to causative organisms [210]. Renewal of the alveolar macrophage population with this functional impairment was from locally renewing tissue-resident macrophages which had undergone epigenetic reprogramming. This epigenetic reprogramming was induced by sustained secondary inflammatory mediator signaling and enhanced SIRPα expression and activity from the post-pneumonia lung environment, rather than bacterial pathogen products from primary pneumonia [210]. Upon reinfection and induction of pneumonia, the reprogrammed alveolar macrophages had reduced phagocytic capacity. While inhibition of SIRPα-CD47 interactions may have potentially therapeutic application for preventing hospital-acquired pneumonia, further functional analyses of alveolar macrophages in different models is warranted. Unlike COPD, asthma and CF, pneumonia is driven entirely by infection of the lung. As such, some of the pathology of pneumonia may be a result of pathogen manipulation of the efferocytic system.
7. Pathogen Manipulation of Efferocytosis
Through the clearance of apoptotic cells, efferocytosis prevents secondary necrosis and induces an anti-inflammatory state through the release of anti-inflammatory mediators PGE2, IL-10 and TGF-β. This ultimately promotes the resolution of inflammation and healing following an infection. In addition, induction of apoptosis and subsequent apoptotic cell engulfment is critical for destruction of certain intracellular pathogens, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which would otherwise disseminate freely following the death of infected cells [48]. While it is tempting to consider efferocytosis as a potential therapeutic target for enhancing the clearance of pneumonia-causing pathogens and improving lung function following pneumonia, pathogens engage in species-specific manipulation of cell death and efferocytic pathways. Therefore, it is important to understand how pathogens manipulate cell death and efferocytic pathways, and efferocytosis targeting therapies will likely need to be employed in an organism-specific manner.
7.1. Subverting Efferocytosis
Although efferocytosis can have an antimicrobial effect and clear pathogens by removing apoptotic phagocytes, some pathogens have developed strategies to avoid efferocytosis through the action of secreted virulence effectors that alter host cell processes.
7.1.1. Streptococcus pneumoniae: Inducing Apoptosis to Limit Microbicidal Activity
While the anti-inflammatory state induced by efferocytosis effectively maintains immune homeostasis, it may also inhibit the mounting of an antimicrobial immune response and increase the susceptibility to other infections. Pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumoniae induce apoptosis, with the subsequent efferocytosis of the infected cells and the PGE2 production this induces in alveolar macrophages, inhibiting bacterial killing through reduced production of microbicidal H2O2 in the efferosome. This inhibition occurs through PGE2 receptors EP-2 and EP-4, which inhibit H2O2 production via cAMP and PKA signaling [216,217]. While these studies did not identify the mechanism by which S. pneumoniae induced cAMP/PKA activity inhibits H2O2 production, PGE2 has a similar effect on responses to Klebsiella pneumoniae, where PKA activation blocks translocation of the p47phox subunit of NADPH oxidase to the phagosome, thereby preventing formation of active NADPH oxidase and the resulting generation of superoxide and H2O2 [218].
7.1.2. Legionella, Salmonella and Tuberculosis: Inhibiting Apoptosis
A strategy employed by pathogens to avoiding efferocytosis is inhibiting apoptosis. To inhibit macrophage apoptosis, Legionella pneumophila secretes LegK1—a bacterial effector—into the cytosol of the infected macrophage. This activates NF-κB mediated transcription in the infected cell, increasing the expression of the anti-apoptotic gene plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 which then prevents apoptosis of the infected cell [219]. Salmonella enterica secretes its effector SopB into the cytosol of infected epithelial cells, where it inhibits apoptosis by activating the anti-apoptotic kinase Akt [220]. One pathway contributing to survival of some virulent forms of M. tuberculosis functions by inhibiting macrophage apoptosis through activity of its NADH oxidoreductase NDH-1, a component of the mycobacteria electron transport chain which directly neutralizes ROS. By eliminating the ROS produced by infected macrophages, NDH-1 prevents ROS-induced macrophage apoptosis [221,222]. For these pathogens, inhibiting apoptosis both prolongs their growth period in the infected cell and leads to dissemination via the eventual necrotic lysis of the infected cell.
7.1.3. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Manipulating Cell Death Pathways
Other pathogens avoid efferocytosis by manipulating the cell death process itself. Klebsiella pneumoniae, a common cause of nosocomial pneumonia, utilizes multiple mechanisms to manipulate cell death and prevents its clearance by efferocytosis. K. pneumoniae impairs the efferocytosis of infected neutrophils by increasing the activity of flippases, preventing PtdSer externalization and therefore recognition by efferocytes (Figure 3A [223]). In some K. pneumoniae strains, this is accomplished by a suppression of signaling via the extrinsic apoptosis pathway, leading infected neutrophils to proceed down the necroptotic cell death pathway. Necroptosis occurs when the extrinsic apoptosis pathway is activated under conditions where initiator caspase-8 (and therefore apoptosis) cannot be activated. This results in activation of RIPK1 and RIPK3, which induce the polymerization of MLKL, thus forming pores in the plasma membrane and mitochondria that lyse the cell (reviewed in [224]). Thus, necroptosis spills the bacterium into the interstitium rather than allowing its uptake and clearance through efferocytosis [223]. In addition to activating necroptosis, K. pneumoniae also inhibits the pyroptotic cell death pathway to limit inflammation. Pyroptosis is an inflammatory form of lytic cell death that is triggered by the presence of cytosolic bacterial products. Pyroptosis is initiated by bacterial product-mediated activation of the inflammasome—a cytosolic bacterial sensor—which then cleaves and activates caspases-1,-4 and -5 [225]. Additionally, caspases 4 and 5 can be directly activated by LPS-mediated polymerization [226]. Unlike other caspases, these caspases do not induce apoptosis and rather mediate the cleavage-induced secretion of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 [227]. This secretion involves two caspase-mediated events: 1) the cleavage of pro- IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into their active form, and 2) cleavage of GSDMN, which in its cleaved form polymerizes into a pore in the plasma membrane through which IL-1β and IL-18 are secreted [228]. However, ongoing pore formation can permeabilize the infected cell, leading to its osmotic swelling and eventual lysis (reviewed in [224]). K. pneumoniae can avoid both efferocytic and pyroptotic clearance by inducing IL-10 expression in infected cells. This provides both an anti-apoptotic signal and inhibits inflammasome activation, thereby limiting both apoptotic and pyroptotic cell death [229]. It is important to note that while PtdSer recognition is involved in the clearance of necrotic and pyroptotic cells, these cell death pathways are highly inflammatory and therefore engulfment of these cells likely does not have the same anti-inflammatory effects as efferocytosis does [230].
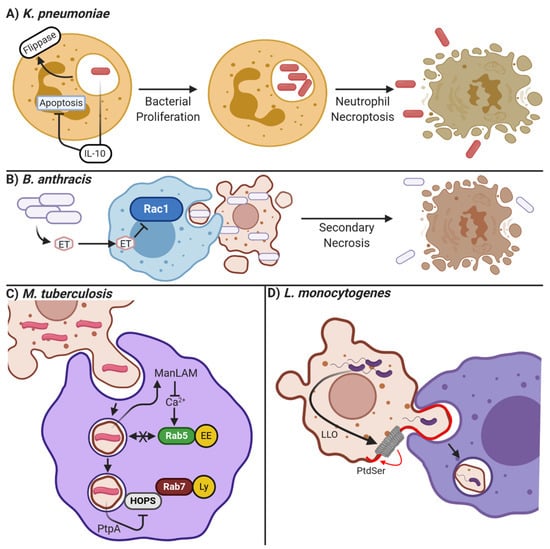
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of bacterial manipulation of apoptosis and efferocytosis. (A) K. pneumonia suppresses neutrophil apoptosis through inducing the expression of IL-10, and efferocytosis through activation of membrane flippases, which prevent PtdSer from accumulating on the cell surface. This allows the bacteria to reproduce in the neutrophil, eventually escaping via lytic necroptotic cell death. (B) B. anthracis secretes edema toxin (ET) which can enter neighboring cells and inhibit Rac1-mediated cytoskeletal reorganization. This prevents the efferocytosis of B. anthracis-infected apoptotic cells, allowing for additional bacteria growth and their eventual release following secondary necrosis of the infected cell. (C) M. tuberculosis is often engulfed by macrophages inside of apoptotic bodies derived from infected cells. M. tuberculosis can then proliferate within the efferosome by ManLAM-mediated inhibition of calcium-dependent fusion of early endosomes (EE) to the efferosome, and PtpA mediated inactivation of the HOPS complex required for Rab7-mediated fusion of lysosomes (LS). (D) L. monocytogenes releases a pore-forming toxin LLO (grey ring) which induces blebbing and PtdSer externalization on infected cells. Neighboring macrophages engulf these blebs, thereby becoming infected with L. monocytogenes. Figure prepared with BioRender (biorender.com).
7.1.4. Staphylococcus aureus: Cell- Specific Manipulation of Apoptosis and Efferocytosis
S. aureus is a gram-positive bacterium whose infection of hosts can cause CAP and a host of other diseases involving colonization of different organ systems [231]. While most S. aureus is phagocytically cleared by neutrophils, a subset remains viable within the human neutrophil’s phagosomes. The still-viable S. aureus induces upregulation of “don’t-eat-me” signal CD47 on the surface of infected neutrophils, thus inhibiting internalization by efferocytes and promoting necroptosis and bacteria dispersal [232]. Through the action of virulence factors such as alpha toxin, S. aureus further inhibits neutrophil efferocytosis by alveolar macrophages in infected lungs, independently of CD47 upregulation, by altering infected neutrophils’ expression and localization of the apoptotic cell opsonin CCN1 and the “eat me” signal DD1α [233]. This is in contrast to S. aureus-infected macrophages, where S. aureus is a potent inducer of apoptosis. Apoptosis of infected macrophages then accelerates bacterial spread, as additional macrophages will be subsequently infected via the efferocytosis of S. aureus-bearing apoptotic cells [234].
7.1.5. Francisella novicida and Bacillus anthracis: Inhibiting Efferocytic Receptors
Francisella novicida is an intracellular Gram-negative bacteria that causes pneumonia characterized by necrotic infiltrates in the lung, particularly in immunocompromised patients [235]. Once F. novicida infects a macrophage, the efferocytic receptor CD36 is downregulated via an unknown mechanism, leading to the accumulation of necrotic debris in the lung and continued infection [236]. Another pathogen that inhibits signaling through efferocytic receptors is Bacillus anthracis, which has been shown to inhibit the activation and phosphorylation of Rac1 downstream of the MERTK and αVβ5 integrin signaling via its virulence factor edema toxin (Figure 3B [105,237]). Thus, the efferocytic uptake of infected apoptotic cells is inhibited as the requisite actin cytoskeletal rearrangements needed to engulf an apoptotic cell are inhibited. This prolongates infection and increases damage from secondary necrosis.
7.1.6. Altered Efferosome Maturation
Another mechanism used by pathogens to avoid efferocytosis is interfering with efferosome/phagosome maturation, thus allowing the pathogen to grow within the phagocyte. Different pathogens can target different steps of the maturation pathway. Perhaps the most well-studied of these pathogens is M. tuberculosis, which survives within macrophages through the action of multiple effectors. Upon inhalation, alveolar macrophages promptly phagocytose M. tuberculosis, where M. tuberculosis then arrests phagosome maturation at several stages. Through modulating the action of GTPases Rab14 and Rab22, fusion of the nascent phagosome with endosomes is inhibited [238]. In addition, the mannosylated lipoarabinomannan (ManLAM) glycolipid secreted into the host cytoplasm by M. tuberculosis inhibits intracellular calcium signaling, preventing activation of Rab5 and its effectors such as EEA1, further inhibiting phagosome/efferosome fusion with endosomes (Figure 3C [239]). Other M. tuberculosis effectors such as EsxG, EsxH, and PtPa target different elements in the maturation process [240,241]. EsxG and EsxH both target the endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT), inhibiting the transport of phagosomes [240] while the phosphatase PtpA secreted into the host cytoplasm dephosphorylates the HOPS complex (Figure 3C), inhibiting the docking of phagosomes with lysosomes, and directly inhibits phagosome acidification by blocking V-ATPase pump assembly [241,242]. Other pathogens, such as L. pneumophila and S. enterica, target phagosome-lysosome fusion as well through the activity of their virulence factors (reviewed in [243]). Since phagocytosis and efferocytosis share similar maturation mechanisms, the effectors produced by these pathogens to evade microbicidal destruction of phagosome maturation may also allow for their survival following efferocytosis of infected cells.
7.2. Manipulating Efferocytosis
While some pathogens have evolved strategies to evade efferocytic elimination, others may exploit host efferocytic mechanisms for their own replication and spread. Through a process termed “apoptotic mimicry”, certain enveloped viruses such as HIV-1, Ebola, Dengue, and vaccinia acquire PtdSer in their viral envelope by budding from PtdSer-rich organelles. The presence of PtdSer in their membranes then allows for these viruses to bind to efferocytic receptor expressing cells, facilitating viral entry [244,245]. Using this strategy, viruses avoid the host’s pro-inflammatory innate and adaptive immune responses, and instead activate the anti-inflammatory signaling cascades of efferocytosis. The parasite Leishmania major utilizes a similar mechanism of immune evasion by infecting neutrophils, inducing apoptosis, and gaining entry to the healthy efferocytes that are recruited to the apoptotic infected cell [246]. Similarly, the bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes secretes the pore-forming toxin listeriolysin O (LLO, Figure 3D) within the cell cytoplasm, resulting in the budding of host-derived L. monocytogenes containing vesicles with exposed PtdSer [247]. Subsequent recognition by efferocytic receptors promotes cell-to-cell spread to uninfected efferocytes. Upon infection of a macrophage, Yersinia pestis—the cause of the plague—makes use of “find-me” signaling by inducing production of S1P such that, after release from the dying macrophage, new uninfected macrophages can be found in close proximity for subsequent infection [248]. Thus, pathogens can exploit efferocytosis to disseminate and grow in an immunologically silent manner, both within the lung and in other tissues.
8. Therapeutic Interventions that Manipulate Efferocytosis
8.1. Existing Therapeutics
Currently, there are several therapeutic interventions that have the potential to manipulate efferocytosis during pneumonia and other inflammatory diseases of the lungs. These treatments—statins and glucocorticoids—function to both enhance alveolar macrophage efferocytosis and to restore lung homeostasis through anti-inflammatory effects.
Statins affect efferocytosis through antagonizing the RhoA pathway, which normally suppresses apoptotic cell engulfment. RhoA, a member of the Rho GTPase family, tightly controls efferocytosis [249,250]. To be functional, RhoA must be covalently modified via prenylation, which attaches a lipid moiety required for RhoA recruitment to the plasma membrane [249,251]. Here, RhoA antagonizes the actin reorganization driven by Rac-1, thereby abrogating efferocytic cup formation and the engulfment of apoptotic cells [249,252]. While statins are typically used to reduce circulating cholesterol levels, the immunomodulatory effects of statins are independent of cholesterol, and instead result from inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase—the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. Normally, HMG-CoA reductase converts HMG-CoA to mevalonate, with mevalonate then used either in the synthesis of cholesterol, or as a precursor for the prenyl moiety that is attached to RhoA [253]. By limiting the synthesis of this moiety, RhoA cannot be prenylated, thereby preventing this negative regulator of efferocytosis from being recruited to the plasma membrane [251,254,255]. As a result, Rac-1 can mediate efferocytic cup formation and apoptotic cell engulfment unopposed by RhoA activity [252,256]. Simvastatin, for example, was observed to inhibit RhoA in murine lungs infused with apoptotic cells, with simvastatin reducing the fibrosis and damage that otherwise follows infusion of apoptotic cells into the airways [256]. Notably, the effects of simvastatin were also shown in alveolar macrophages from human patients with COPD [201]. These studies indicate that statins may enhance alveolar macrophage efferocytosis in an HMG-CoA reductase-dependent manner to restore lung tissue homeostasis following infection and inflammation [252,257]. This phenomenon has been observed in human patients, where during pneumonia there is a strong correlation between the efferocytic capacity of alveolar macrophages and recovery of lung function following pneumonia. In these patients, those on statins fared better than similar patients not on statins, showing improvements in both efferocytic capacity and recovery of lung function [11]. This demonstrates the potential utility of statins for improving efferocytosis and lung function following inflammatory insults.
Similarly, glucocorticoids enhance alveolar macrophage efferocytosis through interactions with the RhoA pathway [13,249]. Glucocorticoids are small lipophilic molecules that exert their actions through binding to intracellular glucocorticoid receptors. Following binding, the glucocorticoid receptor translocates to the nucleus where it acts as a transcription factor. Synthetic glucocorticoids, such as fluticasone, have been shown to increase the apoptotic cell uptake in murine and human alveolar macrophages through a process termed glucocorticoid augmented efferocytosis (GCAE, [12,13]). GCAE has been shown to enhance alveolar macrophage efferocytosis through multiple mechanisms including limiting the activation of the efferocytosis inhibitor RhoA [258], increased efferocytic and scavenger receptor expression [12,259], and upregulation of pro-efferocytic metabolism through increased expression of LXR and PPAR receptors [260]. This includes upregulation of the efferocytic receptor MERTK—the predominant efferocytic receptor in many tissues including the lung [261,262,263,264,265,266]. In humans, the upregulation of MERTK by dexamethasone has been shown to directly enhance the efferocytic capacity of alveolar macrophages [261,267].
While statins and glucocorticoids improve the efferocytic capacity of alveolar macrophage and may therefore aid in the recovery from pneumonia, these agents have potentially adverse side effects. Statins and glucocorticoids are notorious for their immunosuppressive properties, which may lead to adverse effects such as the recurrence of infection. Statins, in addition to their immunosuppressive effect, may also impair other pro-resolving processes, thus delaying the recovery of lung function [268]. Moreover, statins are known to have adverse side effects, especially in organ systems beyond the lungs. For instance, the reduction of mevalonate levels can lead to deficiencies in mevalonate-derived isoprenoids such as coenzyme Q [269]. This decrease in coenzyme Q levels can lead to impairment of the mitochondrial electron transport chain and antioxidant production, leading to issues with cellular respiration and oxygen depletion, and in severe cases, rhabdomyolysis [270,271]. To minimize these off-target effects, inhaled and intratracheally-administered statins were investigated in murine models of asthma [272,273]. The results confirmed that murine lung epithelial cells contained enzymes required to activate statins. Importantly, these results demonstrated few off-target effects in these murine models [272,273]. Notably, the effects of inhaled statins in humans with asthma remains inconclusive [274], necessitating further studies to determine whether the beneficial effects of inhaled and/or intratracheally-administered statins are observed in other diseases, including pneumonia. Therefore, while statins are generally tolerable, these adverse side effects may be life-threatening and therefore may limit the suitability of statins as a drug for modulating efferocytosis during lung infection or inflammation.
Glucocorticoids have been associated with increased risk of infections, including the recurrence of pneumonia in some patients. Previous human studies demonstrated that hydrocortisone was associated with reduced production of inflammatory cytokines, while dexamethasone was associated with reduced antimicrobial activity [14,275]. Notably, inhaled corticosteroids—which are essential therapeutic agents for patients with COPD—were associated with increased cases of CAP. This finding was further illustrated in studies of murine models of pneumonia, where inhaled fluticasone reduced alveolar macrophage destruction of pneumococci, resulting in increased risk of infection and disease [276]. While glucocorticoids may be effective in temporarily enhancing alveolar macrophage efferocytosis following pneumonia and other associated lung diseases [13], they may have long-term adverse effects on immunity, resulting in increased risk of infection.
8.2. Novel Therapeutic Targets
Due to the adverse side effects of statins and glucocorticoids, novel therapies for enhancing pulmonary efferocytosis are required. These novel therapeutics should aim to carefully mimic the anti-inflammatory and pro-healing effects of efferocytosis, while seeking to minimize off-target effects such as increased risk of infection. Two efferocytosis-enhancing therapeutic opportunities that meet these criteria are resolvins and anti-CD47 therapy.
Resolvins have been shown to play a significant role in the recovery of lung tissues to homeostasis following disease, in particular RvD1 after Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Application of exogenous RvD1 reduced both bacterial growth and neutrophil infiltration, in both acute and long-term murine models of pneumonia [173]. While further studies of the therapeutic potential of resolvins are required in humans, these findings suggest that RvD1 may be a plausible therapeutic target in treating bacterial pneumonia due to its role in inhibiting inflammation and enhancing tissue healing in murine lung models [277,278,279,280]. To date, no human clinical trials with resolvins have been reported, but these compounds are well tolerated in mice [281]. Human trials have focused on improving resolvin production in patients by administration of the dietary fatty acids used as substrates for resolvin synthesis; these treatments increase circulating resolvin levels and are generally well tolerated [282].
CD47 is broadly expressed across most cell types where it acts as a “don’t-eat-me” signal via engaging SIRPα on efferocytes [66]. The engagement of SIRPα recruits phosphatases to the efferocyte plasma membrane which antagonizes protein and lipid kinase activity induced by efferocytic receptors [283,284]. The inhibition of efferocytosis by SIRPα signaling is thought to underly many diseases that are characterized by defective efferocytosis [285,286], and as such, anti-CD47 therapy has been explored as a potential therapeutic approach for treating these diseases [287,288]. For example, atherosclerosis—which is characterized by the accumulation of uncleared apoptotic macrophages beneath the heart vasculature—is responsive to anti-CD47 therapy [285], with this therapy reversing the efferocytic defects that arise early in disease [161]. Importantly, anti-CD47 therapy appears to be well-tolerated by patients, suggesting that this treatment may be suitable for many efferocytosis-associated diseases [289,290]. However, anti-CD47 therapy should be used with caution, as both anemia and thrombocytopenia have been observed in human trials of anti-CD47 therapeutics [291]. Anemia and thrombocytopenia following infusion of anti-CD47 is a result of the expression of CD47 on erythrocytes and platelets; on the former, CD47 normally acts to prevent the efferocytic clearance of non-senescent erythrocytes by splenic macrophages, while on the latter, CD47 prevents spontaneous platelet activation. Blockade of CD47 on these cells then allows for their clearance by macrophages, and whether these side effects can be avoided by using inhaled, rather than injected, CD47-targeting therapeutics has not been tested [292,293,294]. In the lung, anti-CD47 therapy is being investigated in murine models of acute (LPS-induced lung injury) and long-term (E. coli pneumonia) lung injury [295]. So far, these studies demonstrated that blocking CD47 enhanced innate and adaptive immune responses to lung infection. Furthermore, anti-CD47 therapy improved apoptotic cell clearance and T cell responses in both acute and long-term murine models of lung infections, reducing pulmonary edema and bacteremia [295]. These findings suggest that blocking CD47 may be a plausible therapeutic approach for enhancing lung efferocytosis and, thus, lung recovery from inflammation and infection.
9. Conclusions
This review provided an update on the current mechanisms of efferocytosis, a highly organized process that is essential for the phagocytic removal of apoptotic cell bodies following inflammatory diseases, including the inflammation resulting from pneumonia. Efferocytosis plays an important, but poorly understood role in the pathogenesis of pneumonia, with this effect potentially aggravated by pathogens which manipulate the efferocytic system to enhance their survival. While there are many gaps in this research, such as the lack of human studies regarding the therapeutic potential of various efferocytosis-modifying treatments, current literature shows promise in the use of existing and novel therapeutics in enhancing recovery after pneumonia in murine models, with some evidence showing a similar benefit in human patients.
Author Contributions
All authors wrote sections of this article and reviewed the completed document. B.H. supervised the preparation of the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ontario Lung Association and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Project Grant (PJT-162203) to BH.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, and the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- D’Arcy, M.S. Cell Death: A Review of the Major Forms of Apoptosis, Necrosis and Autophagy. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter-Hufford, A.; Ravichandran, K.S. Clearing the Dead: Apoptotic Cell Sensing, Recognition, Engulfment, and Digestion. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubbrey, A.L.; Curtis, J.L. Efferocytosis and Lung Disease. Chest 2013, 143, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korns, D.; Frasch, S.C.; Fernandez-Boyanapalli, R.; Henson, P.M.; Bratton, D.L. Modulation of Macrophage Efferocytosis in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2011, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannagan, R.S.; Jaumouillé, V.; Grinstein, S. The Cell Biology of Phagocytosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 7, 61–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taefehshokr, N.; Yin, C.; Heit, B. Rab GTPases in the Differential Processing of Phagocytosed Pathogens versus Efferocytosed Apoptotic Cells. Histol. Histopathol. 2020, 18252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, M.; Nagata, S. Efferocytosis and Autoimmune Disease. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandivier, R.W.; Henson, P.M.; Douglas, I.S. Burying the Dead: The Impact of Failed Apoptotic Cell Removal (Efferocytosis) on Chronic Inflammatory Lung Disease. Chest 2006, 129, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demedts, I.K.; Demoor, T.; Bracke, K.R.; Joos, G.F.; Brusselle, G.G. Role of Apoptosis in the Pathogenesis of COPD and Pulmonary Emphysema. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandivier, R.W.; Fadok, V.A.; Hoffmann, P.R.; Bratton, D.L.; Penvari, C.; Brown, K.K.; Brain, J.D.; Accurso, F.J.; Henson, P.M. Elastase-Mediated Phosphatidylserine Receptor Cleavage Impairs Apoptotic Cell Clearance in Cystic Fibrosis and Bronchiectasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootton, D.G.; Diggle, P.J.; Court, J.; Eneje, O.; Keogan, L.; Macfarlane, L.; Wilks, S.; Woodhead, M.; Gordon, S.B. Recovery from Pneumonia Requires Efferocytosis Which Is Impaired in Smokers and Those with Low Body Mass Index and Enhanced by Statins. Thorax 2016, 71, 1052–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, M.; Stolberg, V.R.; Freeman, C.M.; Kady, M.R.; Alikaj, H.; McCloskey, L.; Curtis, J.L. Glucocorticoid-Augmented Efferocytosis Reduces Pneumococcal Killing by Human Alveolar Macrophages by Blocking Phagosome Acidification. In C31. Mechanistic Insights into Lung Infection, Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society International Conference Abstracts, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–23 May 2018; American Thoracic Society: New York, NY, USA, 2018; p. A4701. [Google Scholar]
- Stolberg, V.R.; McCubbrey, A.L.; Freeman, C.M.; Brown, J.P.; Crudgington, S.W.; Taitano, S.H.; Saxton, B.L.; Mancuso, P.; Curtis, J.L. Glucocorticoid-Augmented Efferocytosis Inhibits Pulmonary Pneumococcal Clearance in Mice by Reducing Alveolar Macrophage Bactericidal Function. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Xiong, W.; Wen, Q.; Ma, L. Glucocorticoids Suppress Antimicrobial Autophagy and Nitric Oxide Production and Facilitate Mycobacterial Survival in Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.R.; Llambi, F. Cell Death Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraz, Y.; Adan, A.; Kartal Yandim, M.; Baran, Y. Major Apoptotic Mechanisms and Genes Involved in Apoptosis. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 8471–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, O.; Wells, J.A. Caspases and Their Substrates. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Bhalla, K.; Kim, C.N.; Ibrado, A.M.; Cai, J.; Peng, T.I.; Jones, D.P.; Wang, X. Prevention of Apoptosis by Bcl-2: Release of Cytochrome c from Mitochondria Blocked. Science 1997, 275, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluck, R.M.; Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Green, D.R.; Newmeyer, D.D. The Release of Cytochrome c from Mitochondria: A Primary Site for Bcl-2 Regulation of Apoptosis. Science 1997, 275, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Zhao, Y.; Barber, M.J.; Kuharsky, D.K.; Yin, X.M. Bid-Induced Cytochrome c Release Is Mediated by a Pathway Independent of Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore and Bax. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39474–39481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, D.; Pires, F.; Plin, C.; Tillement, J.-P. Role of the Permeability Transition Pore in Cytochrome C Release from Mitochondria during Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rat Liver. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.M.; Adrain, C.; Duriez, P.J.; Creagh, E.M.; Martin, S.J. Analysis of the Composition, Assembly Kinetics and Activity of Native Apaf-1 Apoptosomes. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2134–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. An APAF-1. Cytochrome c Multimeric Complex Is a Functional Apoptosome That Activates Procaspase-9. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11549–11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, N.; Yonehara, S.; Ishii, A.; Yonehara, M.; Mizushima, S.; Sameshima, M.; Hase, A.; Seto, Y.; Nagata, S. The Polypeptide Encoded by the CDNA for Human Cell Surface Antigen Fas Can Mediate Apoptosis. Cell 1991, 66, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; O’Rourke, K.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Gentz, R.; Ebner, R.; Ni, J.; Dixit, V.M. The Receptor for the Cytotoxic Ligand TRAIL. Science 1997, 276, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.M.; Eby, M.; Jasmin, A.; Bookwalter, A.; Murray, J.; Hood, L. Death Receptor 5, a New Member of the TNFR Family, and DR4 Induce FADD-Dependent Apoptosis and Activate the NF-KappaB Pathway. Immunity 1997, 7, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, T.; Strasser, A.; Jost, P.J. Fas Death Receptor Signalling: Roles of Bid and XIAP. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, Z.T.; Gonzalvez, F.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Vaz, F.M.; Gottlieb, E. BID Is Cleaved by Caspase-8 within a Native Complex on the Mitochondrial Membrane. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, B.; Yeung, T.; Grinstein, S. Changes in Mitochondrial Surface Charge Mediate Recruitment of Signaling Molecules during Apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. 2011, 300, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozören, N.; El-Deiry, W.S. Defining Characteristics of Types I and II Apoptotic Cells in Response to TRAIL. Neoplasia 2002, 4, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Katayama, T.; Kohama, K.; Endo, Y.; Sawasaki, T. Myosin Phosphatase Is Inactivated by Caspase-3 Cleavage and Phosphorylation of Myosin Phosphatase Targeting Subunit 1 during Apoptosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enari, M.; Sakahira, H.; Yokoyama, H.; Okawa, K.; Iwamatsu, A.; Nagata, S. A Caspase-Activated DNase That Degrades DNA during Apoptosis, and Its Inhibitor ICAD. Nature 1998, 391, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandilos, J.K.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Chekeni, F.B.; Armstrong, A.J.; Walk, S.F.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Bayliss, D.A. Pannexin 1, an ATP Release Channel, Is Activated by Caspase Cleavage of Its Pore-Associated C-Terminal Autoinhibitory Region. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11303–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, H.; Luo, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, F.; Huang, S.; Li, H. Caspase-Mediated Cleavage of C53/LZAP Protein Causes Abnormal Microtubule Bundling and Rupture of the Nuclear Envelope. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCathelineau, A.M.; Henson, P.M. The Final Step in Programmed Cell Death: Phagocytes Carry Apoptotic Cells to the Grave. Essays Biochem. 2003, 39, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, S.G.; Geng, K.; Kasikara, C.; Kumar, S.; Sriram, G.; Wu, Y.; Birge, R.B. Contribution of Defective PS Recognition and Efferocytosis to Chronic Inflammation and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, E.B. Mechanisms of Failed Apoptotic Cell Clearance by Phagocyte Subsets in Cardiovascular Disease. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.T. Secondary Necrosis: The Natural Outcome of the Complete Apoptotic Program. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.T.; do Vale, A.; dos Santos, N.M.N. Secondary Necrosis in Multicellular Animals: An Outcome of Apoptosis with Pathogenic Implications. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Berghe, T.; Vanlangenakker, N.; Parthoens, E.; Deckers, W.; Devos, M.; Festjens, N.; Guerin, C.J.; Brunk, U.T.; Declercq, W.; Vandenabeele, P. Necroptosis, Necrosis and Secondary Necrosis Converge on Similar Cellular Disintegration Features. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, J.I. Plasma Membrane Calcium Pump Regulation by Metabolic Stress. World J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 1, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.; Steenbergen, C. Mechanisms Underlying Acute Protection from Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 581–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, B.S.; Belenghi, B.; Levine, A. Oxidative Stress Increased Respiration and Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species, Resulting in ATP Depletion, Opening of Mitochondrial Permeability Transition, and Programmed Cell Death. Plant. Physiol. 2002, 128, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.S.; Yoon, Y.; Robotham, J.L.; Anders, M.W.; Sheu, S.-S. Calcium, ATP, and ROS: A Mitochondrial Love-Hate Triangle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachet, M.; Liang, Y.Y.; Oehler, R. The Immune Response to Secondary Necrotic Cells. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Molinaro, C.; Johnson, N.; Casiano, C.A. Secondary Necrosis Is a Source of Proteolytically Modified Forms of Specific Intracellular Autoantigens: Implications for Systemic Autoimmunity. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2642–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.J.; Booty, M.G.; Rosebrock, T.R.; Nunes-Alves, C.; Desjardins, D.M.; Keren, I.; Fortune, S.M.; Remold, H.G.; Behar, S.M. Efferocytosis Is an Innate Antibacterial Mechanism. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaji, N.; Sattentau, Q.J. Efferocytosis of Pathogen-Infected Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, C.; Uribe-Querol, E. Phagocytosis: A Fundamental Process in Immunity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9042851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Plüddemann, A. Macrophage Clearance of Apoptotic Cells: A Critical Assessment. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.R.; Koster, K.M.; Murphy, P.S. Efferocytosis Signaling in the Regulation of Macrophage Inflammatory Responses. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, K.S. Find-Me and Eat-Me Signals in Apoptotic Cell Clearance: Progress and Conundrums. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauber, K.; Bohn, E.; Kröber, S.M.; Xiao, Y.; Blumenthal, S.G.; Lindemann, R.K.; Marini, P.; Wiedig, C.; Zobywalski, A.; Baksh, S.; et al. Apoptotic Cells Induce Migration of Phagocytes via Caspase-3-Mediated Release of a Lipid Attraction Signal. Cell 2003, 113, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, C.; Waibel, M.; Keppeler, H.; Lehmann, R.; Xu, G.; Halama, A.; Adamski, J.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Wesselborg, S.; Lauber, K. Release of Lysophospholipid “find-Me” Signals during Apoptosis Requires the ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1. Autoimmunity 2012, 45, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.R.; Chekeni, F.B.; Trampont, P.C.; Lazarowski, E.R.; Kadl, A.; Walk, S.F.; Park, D.; Woodson, R.I.; Ostankovich, M.; Sharma, P.; et al. Nucleotides Released by Apoptotic Cells Act as a Find-Me Signal to Promote Phagocytic Clearance. Nature 2009, 461, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, B.; Robbins, S.M.; Downey, C.M.; Guan, Z.; Colarusso, P.; Miller, B.J.; Jirik, F.R.; Kubes, P. PTEN Functions to “prioritize” Chemotactic Cues and Prevent “Distraction” in Migrating Neutrophils. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truman, L.A.; Ford, C.A.; Pasikowska, M.; Pound, J.D.; Wilkinson, S.J.; Dumitriu, I.E.; Melville, L.; Melrose, L.A.; Ogden, C.A.; Nibbs, R.; et al. CX3CL1/Fractalkine Is Released from Apoptotic Lymphocytes to Stimulate Macrophage Chemotaxis. Blood 2008, 112, 5026–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, D.R.; Alvarez, S.E.; Paugh, S.W.; Mitra, P.; Yu, J.; Griffiths, R.; Barbour, S.E.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Apoptosis Induces Expression of Sphingosine Kinase 1 to Release Sphingosine-1-Phosphate as a “Come-and-Get-Me” Signal. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 2629–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.S.; Jaumouillé, V.; Heit, B.; Doodnauth, S.A.; Patel, S.; Huang, Y.-W.; Grinstein, S.; Robinson, L.A. Cytoskeletal Confinement of CX3CL1 Limits Its Susceptibility to Proteolytic Cleavage by ADAM10. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 3884–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.R.; Ravichandran, K.S. The Dynamics of Apoptotic Cell Clearance. Dev. Cell 2016, 38, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, P.; Oskeritzian, C.A.; Payne, S.G.; Beaven, M.A.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Role of ABCC1 in Export of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate from Mast Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16394–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Gan, W.; Liu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Wang, J.; Shi, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Erythropoeitin Signaling in Macrophages Promotes Dying Cell Clearance and Immune Tolerance. Immunity 2016, 44, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Lim, J.-H.; Cho, M.-S.; Kang, J.L. PPARγ Activation Following Apoptotic Cell Instillation Promotes Resolution of Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis via Regulation of Efferocytosis and Proresolving Cytokines. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 1031–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segawa, K.; Nagata, S. An Apoptotic “Eat Me” Signal: Phosphatidylserine Exposure. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Bian, Z.; Shi, L.; Niu, S.; Ha, B.; Tremblay, A.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Paluszynski, J.; Liu, M.; et al. Loss of Cell Surface CD47 Clustering Formation and Binding Avidity to SIRPα Facilitate Apoptotic Cell Clearance by Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.K.; Discher, D.E. Inhibition of “Self” Engulfment through Deactivation of Myosin-II at the Phagocytic Synapse between Human Cells. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadok, V.A.; Warner, M.L.; Bratton, D.L.; Henson, P.M. CD36 Is Required for Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells by Human Macrophages That Use Either a Phosphatidylserine Receptor or the Vitronectin Receptor (Alpha v Beta 3). J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 6250–6257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fadok, V.A.; Voelker, D.R.; Campbell, P.A.; Cohen, J.J.; Bratton, D.L.; Henson, P.M. Exposure of Phosphatidylserine on the Surface of Apoptotic Lymphocytes Triggers Specific Recognition and Removal by Macrophages. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Païdassi, H.; Tacnet-Delorme, P.; Garlatti, V.; Darnault, C.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Gaboriaud, C.; Arlaud, G.J.; Frachet, P. C1q Binds Phosphatidylserine and Likely Acts as a Multiligand-Bridging Molecule in Apoptotic Cell Recognition. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Liu, J.; Piao, C.; Shao, J.; Du, J. ICAM-1 Suppresses Tumor Metastasis by Inhibiting Macrophage M2 Polarization through Blockade of Efferocytosis. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.E.; Sun, M.; Zhang, R.; Febbraio, M.; Silverstein, R.; Hazen, S.L. Oxidized Phosphatidylserine-CD36 Interactions Play an Essential Role in Macrophage-Dependent Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2613–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardai, S.J.; McPhillips, K.A.; Frasch, S.C.; Janssen, W.J.; Starefeldt, A.; Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.; Bratton, D.L.; Oldenborg, P.-A.; Michalak, M.; Henson, P.M. Cell-Surface Calreticulin Initiates Clearance of Viable or Apoptotic Cells through Trans-Activation of LRP on the Phagocyte. Cell 2005, 123, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segawa, K.; Suzuki, J.; Nagata, S. Flippases and Scramblases in the Plasma Membrane. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2990–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S.; Suzuki, J.; Segawa, K.; Fujii, T. Exposure of Phosphatidylserine on the Cell Surface. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.G.; Koivusalo, M.; Ma, X.; Wohland, T.; Grinstein, S. Phosphatidylserine Dynamics in Cellular Membranes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2198–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, J.; Imanishi, E.; Nagata, S. Xkr8 Phospholipid Scrambling Complex in Apoptotic Phosphatidylserine Exposure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9509–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, K.; Kurata, S.; Yanagihashi, Y.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Matsuda, F.; Nagata, S. Caspase-Mediated Cleavage of Phospholipid Flippase for Apoptotic Phosphatidylserine Exposure. Science 2014, 344, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, J.; Denning, D.P.; Imanishi, E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Nagata, S. Xk-Related Protein 8 and CED-8 Promote Phosphatidylserine Exposure in Apoptotic Cells. Science 2013, 341, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannagan, R.S.; Canton, J.; Furuya, W.; Glogauer, M.; Grinstein, S. The Phosphatidylserine Receptor TIM4 Utilizes Integrins as Coreceptors to Effect Phagocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Tosello-Trampont, A.-C.; Elliott, M.R.; Lu, M.; Haney, L.B.; Ma, Z.; Klibanov, A.L.; Mandell, J.W.; Ravichandran, K.S. BAI1 Is an Engulfment Receptor for Apoptotic Cells Upstream of the ELMO/Dock180/Rac Module. Nature 2007, 450, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Kim, I.-S. Stabilin Receptors: Role as Phosphatidylserine Receptors. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Tian, L.; Voss, O.H.; Margulies, D.H.; Krzewski, K.; Coligan, J.E. CD300b Regulates the Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells via Phosphatidylserine Recognition. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1746–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friggeri, A.; Banerjee, S.; Biswas, S.; de Freitas, A.; Liu, G.; Bierhaus, A.; Abraham, E. Participation of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products in Efferocytosis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6191–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, J.W.D.; Lau, D.H.C.; Liu, E.Y.; Ellins, J.; Vrieze, A.M.; Pawlak, E.N.; Dikeakos, J.D.; Heit, B. Soluble CD93 Is an Apoptotic Cell Opsonin Recognized by Ax Β2. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandrot, E.F.; Anand, M.; Almeida, D.; Atabai, K.; Sheppard, D.; Finnemann, S.C. Essential Role for MFG-E8 as Ligand for Alphavbeta5 Integrin in Diurnal Retinal Phagocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12005–12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.-I.; Kim, K.-H.; Lau, L.F. The Matricellular Protein CCN1 Mediates Neutrophil Efferocytosis in Cutaneous Wound Healing. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.O.; Obin, M.S.; Heeb, M.J.; Burgess, B.L.; Abrams, T.A. Both Protein S and Gas6 Stimulate Outer Segment Phagocytosis by Cultured Rat Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2005, 81, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, B.; Muñoz, X.; Recarte-Pelz, P.; García, N.; Luque, A.; Krupinski, J.; Sala, N.; de Frutos, P.G. Expression of the Vitamin K-Dependent Proteins GAS6 and Protein S and the TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Human Atherosclerotic Carotid Plaques. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morizono, K.; Xie, Y.; Olafsen, T.; Lee, B.; Dasgupta, A.; Wu, A.M.; Chen, I.S.Y. The Soluble Serum Protein Gas6 Bridges Virion Envelope Phosphatidylserine to the TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl to Mediate Viral Entry. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadok, V.A.; Bratton, D.L.; Konowal, A.; Freed, P.W.; Westcott, J.Y.; Henson, P.M. Macrophages That Have Ingested Apoptotic Cells in vitro Inhibit Proinflammatory Cytokine Production through Autocrine/Paracrine Mechanisms Involving TGF-Beta, PGE2, and PAF. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire-de-Lima, C.G.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Gardai, S.J.; Bratton, D.L.; Schiemann, W.P.; Henson, P.M. Apoptotic Cells, through Transforming Growth Factor-Beta, Coordinately Induce Anti-Inflammatory and Suppress pro-Inflammatory Eicosanoid and NO Synthesis in Murine Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 38376–38384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevers, E.M.; Comfurius, P.; van Rijn, J.L.; Hemker, H.C.; Zwaal, R.F. Generation of Prothrombin-Converting Activity and the Exposure of Phosphatidylserine at the Outer Surface of Platelets. Eur. J. Biochem. 1982, 122, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segawa, K.; Suzuki, J.; Nagata, S. Constitutive Exposure of Phosphatidylserine on Viable Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19246–19251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.; Heinisch, I.; Ross, E.; Shaw, K.; Buckley, C.D.; Savill, J. Apoptosis Disables CD31-Mediated Cell Detachment from Phagocytes Promoting Binding and Engulfment. Nature 2002, 418, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, C.A. CD24—A Novel ‘Don’t Eat Me’ Signal. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Dote, K.; Higai, K.; Matsumoto, K. Decreases in CD31 and CD47 Levels on the Cell Surface during Etoposide-Induced Jurkat Cell Apoptosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigotti, A.; Acton, S.L.; Krieger, M. The Class B Scavenger Receptors SR-BI and CD36 Are Receptors for Anionic Phospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16221–16224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesolek, H.L.; Bui, T.M.; Lee, J.J.; Dalal, P.; Finkielsztein, A.; Batra, A.; Thorp, E.B.; Sumagin, R. Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 Functions as an Efferocytosis Receptor in Inflammatory Macrophages. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.; Tacnet-Delorme, P.; Kleman, J.-P.P.; Millet, A.; Frachet, P. Calreticulin Release at an Early Stage of Death Modulates the Clearance by Macrophages of Apoptotic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, B.; Kim, H.; Cosío, G.; Castaño, D.; Collins, R.; Lowell, C.A.; Kain, K.C.; Trimble, W.S.; Grinstein, S. Multimolecular Signaling Complexes Enable Syk-Mediated Signaling of CD36 Internalization. Dev. Cell 2013, 24, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Gomez, A.; Cabañas, C.; Lafuente, E.M. Phagocytic Integrins: Activation and Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Yancey, P.G.; Babaev, V.R.; Blakemore, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, L.; Fazio, S.; Linton, M.F. Macrophage SR-BI Mediates Efferocytosis via Src/PI3K/Rac1 Signaling and Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Necrosis. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, H.; Kaushik, N.; Yoo, K.; Shim, J.; Kwon, M.; Choi, M.-Y.; Yoon, T.; Kang, S.; Lee, S. MerTK Mediates STAT3-KRAS/SRC-Signaling Axis for Glioma Stem Cell Maintenance. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, S.J.; Colwill, K.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Pawson, T.; Thompson, D.A. MERTK Interactions with SH2-Domain Proteins in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugnera, E.; Haney, L.; Grimsley, C.; Lu, M.; Walk, S.F.; Tosello-Trampont, A.-C.; Macara, I.G.; Madhani, H.; Fink, G.R.; Ravichandran, K.S. Unconventional Rac-GEF Activity Is Mediated through the Dock180-ELMO Complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Ravichandran, K.S. Dock180-ELMO Cooperation in Rac Activation. Methods Enzymol. 2006, 406, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Singh, S.; Georgescu, M.-M.; Birge, R.B. A Role for Mer Tyrosine Kinase in Alphavbeta5 Integrin-Mediated Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.L.; Kim, J.I.; Birge, R.B. Alphavbeta5 Integrin Recruits the CrkII-Dock180-Rac1 Complex for Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, M.; Nakaya, M.; Nakamura, T.; Nagata, S.; Matsuda, M. Imaging of Rab5 Activity Identifies Essential Regulators for Phagosome Maturation. Nature 2008, 453, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, O.V.; Botelho, R.J.; Rameh, L.; Brachmann, S.M.; Matsuo, T.; Davidson, H.W.; Schreiber, A.; Backer, J.M.; Cantley, L.C.; Grinstein, S. Distinct Roles of Class I and Class III Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinases in Phagosome Formation and Maturation. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforidis, S.; McBride, H.M.; Burgoyne, R.D.; Zerial, M. The Rab5 Effector EEA1 Is a Core Component of Endosome Docking. Nature 1999, 397, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eathiraj, S.; Pan, X.; Ritacco, C.; Lambright, D.G. Structural Basis of Family-Wide Rab GTPase Recognition by Rabenosyn-5. Nature 2005, 436, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleine Balderhaar, H.J.; Ungermann, C. CORVET and HOPS Tethering Complexes—Coordinators of Endosome and Lysosome Fusion. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becken, U.; Jeschke, A.; Veltman, K.; Haas, A. Cell-Free Fusion of Bacteria-Containing Phagosomes with Endocytic Compartments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20726–20731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, A.; Gaullier, J.M.; D’Arrigo, A.; Stenmark, H. The Rab5 Effector EEA1 Interacts Directly with Syntaxin-6. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 28857–28860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinchen, J.M.; Ravichandran, K.S. Identification of Two Evolutionarily Conserved Genes Regulating Processing of Engulfed Apoptotic Cells. Nature 2010, 464, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.; Rocha, N.; Zwart, W.; Jordens, I.; Janssen, L.; Kuijl, C.; Olkkonen, V.M.; Neefjes, J. Activation of Endosomal Dynein Motors by Stepwise Assembly of Rab7-RILP-P150Glued, ORP1L, and the Receptor βIII Spectrin. J. Biol. 2007, 176, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langemeyer, L.; Borchers, A.-C.; Herrmann, E.; Füllbrunn, N.; Han, Y.; Perz, A.; Auffarth, K.; Kümmel, D.; Ungermann, C. A Conserved and Regulated Mechanism Drives Endosomal Rab Transition. eLife 2020, 9, e56090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalupo, G.; Alifano, P.; Roberti, V.; Bruni, C.B.; Bucci, C. Rab-Interacting Lysosomal Protein (RILP): The Rab7 Effector Required for Transport to Lysosomes. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.E.; Bucci, C.; Vieira, O.V.; Schroer, T.A.; Grinstein, S. Phagosomes Fuse with Late Endosomes and/or Lysosomes by Extension of Membrane Protrusions along Microtubules: Role of Rab7 and RILP. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 6494–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, G.P.; Botelho, R.J.; Butler, J.R.; Moltyaner, Y.; Chien, P.; Schreiber, A.D.; Grinstein, S. Phagosomal Maturation, Acidification, and Inhibition of Bacterial Growth in Nonphagocytic Cells Transfected with FcgammaRIIA Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 28436–28444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, S.; Faulhaber, A.; Sieber, C.; Pfeifer, D.; Hochberg, T.; Gansz, M.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Dauth, S.; Brix, K.; Saftig, P.; et al. The Endolysosomal Cysteine Cathepsins L and K Are Involved in Macrophage-Mediated Clearance of Staphylococcus Aureus and the Concomitant Cytokine Induction. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savina, A.; Jancic, C.; Hugues, S.; Guermonprez, P.; Vargas, P.; Moura, I.C.; Lennon-Duménil, A.-M.; Seabra, M.C.; Raposo, G.; Amigorena, S. NOX2 Controls Phagosomal PH to Regulate Antigen Processing during Crosspresentation by Dendritic Cells. Cell 2006, 126, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, P.; Demaurex, N.; Dinauer, M.C. Regulation of the NADPH Oxidase and Associated Ion Fluxes during Phagocytosis. Traffic 2013, 14, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desjardins, M.; Huber, L.A.; Parton, R.G.; Griffiths, G. Biogenesis of Phagolysosomes Proceeds through a Sequential Series of Interactions with the Endocytic Apparatus. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 124, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairn, G.D.; Grinstein, S. How Nascent Phagosomes Mature to Become Phagolysosomes. Trends Immunol. 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegazza, A.R.; Zajac, A.L.; Twelvetrees, A.; Holzbaur, E.L.F.; Amigorena, S.; Marks, M.S. TLR-Dependent Phagosome Tubulation in Dendritic Cells Promotes Phagosome Cross-Talk to Optimize MHC-II Antigen Presentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15508–15513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegazza, A.R.; Magalhaes, J.G.; Amigorena, S.; Marks, M.S. Presentation of Phagocytosed Antigens by MHC Class I and II. Traffic 2013, 14, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddami, M.; Mayrhofer, G.; Cleland, L.G. MHC Class II Compartment, Endocytosis and Phagocytic Activity of Macrophages and Putative Dendritic Cells Isolated from Normal Tissues Rich in Synovium. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Matsui, T.; Fukuda, M. Rabex-5 Protein Regulates Dendritic Localization of Small GTPase Rab17 and Neurite Morphogenesis in Hippocampal Neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9835–9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Kim, Y.; Argintaru, D.; Heit, B. Rab17 Mediates Differential Antigen Sorting Following Efferocytosis and Phagocytosis. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Argintaru, D.; Heit, B. Rab17 Mediates Intermixing of Phagocytosed Apoptotic Cells with Recycling Endosomes. Small GTPases 2019, 10, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blander, J.M.; Medzhitov, R. Toll-Dependent Selection of Microbial Antigens for Presentation by Dendritic Cells. Nature 2006, 440, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Haber, C.; Levin-Konigsberg, R.; Zhu, Y.; Bi-Karchin, J.; Balla, T.; Grinstein, S.; Marks, M.S.; Mantegazza, A.R. Phosphatidylinositol-4-Kinase IIα Licenses Phagosomes for TLR4 Signaling and MHC-II Presentation in Dendritic Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28251–28262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voll, R.E.; Herrmann, M.; Roth, E.A.; Stach, C.; Kalden, J.R.; Girkontaite, I. Immunosuppressive Effects of Apoptotic Cells. Nature 1997, 390, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibrewal, N.; Wu, Y.; D’mello, V.; Akakura, R.; George, T.C.; Varnum, B.; Birge, R.B. Autophosphorylation Docking Site Tyr-867 in Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Allows for Dissociation of Multiple Signaling Pathways for Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells and down-Modulation of Lipopolysaccharide-Inducible NF-KappaB Transcriptional Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3618–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Han, J.-Y.; Byun, J.; Park, H.-J.; Park, E.-M.; Chong, Y.H.; Cho, M.-S.; Kang, J.L. Inhibiting Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Suppresses STAT1, SOCS1/3, and NF-ΚB Activation and Enhances Inflammatory Responses in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fang, L.; Wu, H.-M.; Ding, P.-S.; Xu, K.; Liu, R.-Y. Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Negatively Regulates Lipoteichoic Acid-Induced Inflammatory Response via PI3K/Akt and SOCS3. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 76, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rébé, C.; Raveneau, M.; Chevriaux, A.; Lakomy, D.; Sberna, A.-L.; Costa, A.; Bessède, G.; Athias, A.; Steinmetz, E.; Lobaccaro, J.M.; et al. Induction of Transglutaminase 2 by a Liver X Receptor/Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha Pathway Increases the Clearance of Apoptotic Cells by Human Macrophages. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukundan, L.; Odegaard, J.I.; Morel, C.R.; Heredia, J.E.; Mwangi, J.W.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Goh, Y.P.S.; Eagle, A.R.; Dunn, S.E.; Awakuni, J.U.H.; et al. PPAR-Delta Senses and Orchestrates Clearance of Apoptotic Cells to Promote Tolerance. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, N.A.; Bensinger, S.J.; Hong, C.; Beceiro, S.; Bradley, M.N.; Zelcer, N.; Deniz, J.; Ramirez, C.; Díaz, M.; Gallardo, G.; et al. Apoptotic Cells Promote Their Own Clearance and Immune Tolerance through Activation of the Nuclear Receptor LXR. Immunity 2009, 31, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, A.; Boisvert, W.A.; Lee, C.-H.; Laffitte, B.A.; Barak, Y.; Joseph, S.B.; Liao, D.; Nagy, L.; Edwards, P.A.; Curtiss, L.K.; et al. A PPARγ-LXR-ABCA1 Pathway in Macrophages Is Involved in Cholesterol Efflux and Atherogenesis. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, M.; Mallmann, M.R.; Xue, J.; Staratschek-Jox, A.; Vorholt, D.; Krebs, W.; Sommer, D.; Sander, J.; Mertens, C.; Nino-Castro, A.; et al. High-Resolution Transcriptome of Human Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boergesen, M.; Pedersen, T.Å.; Gross, B.; van Heeringen, S.J.; Hagenbeek, D.; Bindesbøll, C.; Caron, S.; Lalloyer, F.; Steffensen, K.R.; Nebb, H.I.; et al. Genome-Wide Profiling of Liver X Receptor, Retinoid X Receptor, and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α in Mouse Liver Reveals Extensive Sharing of Binding Sites. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croasdell, A.; Duffney, P.F.; Kim, N.; Lacy, S.H.; Sime, P.J.; Phipps, R.P. PPARγ and the Innate Immune System Mediate the Resolution of Inflammation. PPAR Res. 2015, 2015, 549691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johann, A.M.; von Knethen, A.; Lindemann, D.; Brüne, B. Recognition of Apoptotic Cells by Macrophages Activates the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma and Attenuates the Oxidative Burst. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majai, G.; Sarang, Z.; Csomós, K.; Zahuczky, G.; Fésüs, L. PPARgamma-Dependent Regulation of Human Macrophages in Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Hou, J.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Mihalic, K.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, W.; et al. Transcriptional Inactivation of STAT3 by PPARgamma Suppresses IL-6-Responsive Multiple Myeloma Cells. Immunity 2004, 20, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, T.; Shimano, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Yahagi, N.; Amemiya-Kudo, M.; Matsuzaka, T.; Nakakuki, M.; Yatoh, S.; Iizuka, Y.; Tomita, S.; et al. Cross-Talk between Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) Alpha and Liver X Receptor (LXR) in Nutritional Regulation of Fatty Acid Metabolism. II. LXRs Suppress Lipid Degradation Gene Promoters through Inhibition of PPAR Signaling. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teissier, E.; Nohara, A.; Chinetti, G.; Paumelle, R.; Cariou, B.; Fruchart, J.-C.; Brandes, R.P.; Shah, A.; Staels, B. Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor α Induces NADPH Oxidase Activity in Macrophages, Leading to the Generation of LDL with PPAR-α Activation Properties. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W.F.; Kumar, A.P.; Piedrafita, F.J. The Human Myeloperoxidase Gene Is Regulated by LXR and PPARα Ligands. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serghides, L.; Kain, K.C. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma-Retinoid X Receptor Agonists Increase CD36-Dependent Phagocytosis of Plasmodium Falciparum-Parasitized Erythrocytes and Decrease Malaria-Induced TNF-Alpha Secretion by Monocytes/Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 6742–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walcher, D.; Kümmel, A.; Kehrle, B.; Bach, H.; Grüb, M.; Durst, R.; Hombach, V.; Marx, N. LXR Activation Reduces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression in Human CD4-Positive Lymphocytes. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, C.; Rigamonti, E.; Nohara, A.; Gervois, P.; Teissier, E.; Fruchart, J.-C.; Staels, B.; Chinetti-Gbaguidi, G. Liver X Receptor Activation Potentiates the Lipopolysaccharide Response in Human Macrophages. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Weinberg, S.; DeBerge, M.; Gainullina, A.; Schipma, M.; Kinchen, J.M.; Ben-Sahra, I.; Gius, D.R.; Yvan-Charvet, L.; Chandel, N.S.; et al. Efferocytosis Fuels Requirements of Fatty Acid Oxidation and the Electron Transport Chain to Polarize Macrophages for Tissue Repair. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 443–456.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costet, P.; Lalanne, F.; Gerbod-Giannone, M.C.; Molina, J.R.; Fu, X.; Lund, E.G.; Gudas, L.J.; Tall, A.R. Retinoic Acid Receptor-Mediated Induction of ABCA1 in Macrophages. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 7756–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvan-Charvet, L.; Pagler, T.A.; Seimon, T.A.; Thorp, E.; Welch, C.L.; Witztum, J.L.; Tabas, I.; Tall, A.R. ABCA1 and ABCG1 Protect against Oxidative Stress-Induced Macrophage Apoptosis during Efferocytosis. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaud, M.; Ivanov, S.; Vujic, N.; Duta-Mare, M.; Aira, L.-E.; Barouillet, T.; Garcia, E.; Orange, F.; Dugail, I.; Hainault, I.; et al. Lysosomal Cholesterol Hydrolysis Couples Efferocytosis to Anti-Inflammatory Oxysterol Production. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1369–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdagul, A.; Subramanian, M.; Wang, X.; Crown, S.B.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; Darville, L.; Kolluru, G.K.; Rymond, C.C.; Gerlach, B.D.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Macrophage Metabolism of Apoptotic Cell-Derived Arginine Promotes Continual Efferocytosis and Resolution of Injury. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 518–533.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Vrieze, A.M.; Rosoga, M.; Akingbasote, J.; Pawlak, E.N.; Jacob, R.A.; Hu, J.; Sharma, N.; Dikeakos, J.D.; Barra, L.; et al. Efferocytic Defects in Early Atherosclerosis Are Driven by GATA2 Overexpression in Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, N.A.; Quintana, J.A.; García-Silva, S.; Mazariegos, M.; González de la Aleja, A.; Nicolás-Ávila, J.A.; Walter, W.; Adrover, J.M.; Crainiciuc, G.; Kuchroo, V.K.; et al. Phagocytosis Imprints Heterogeneity in Tissue-Resident Macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1281–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basil, M.C.; Levy, B.D. Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators: Endogenous Regulators of Infection and Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalli, J.; Serhan, C.N. Pro-Resolving Mediators in Regulating and Conferring Macrophage Function. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, B.D.; Clish, C.B.; Schmidt, B.; Gronert, K.; Serhan, C.N. Lipid Mediator Class Switching during Acute Inflammation: Signals in Resolution. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, A.D.; Di Battista, J.A. The Cardinal Role of the Phospholipase A(2)/Cyclooxygenase-2/Prostaglandin E Synthase/Prostaglandin E(2) (PCPP) Axis in Inflammostasis. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 60, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, B.D.; Romano, M.; Chapman, H.A.; Reilly, J.J.; Drazen, J.; Serhan, C.N. Human Alveolar Macrophages Have 15-Lipoxygenase and Generate 15(S)-Hydroxy-5,8,11-Cis-13-Trans-Eicosatetraenoic Acid and Lipoxins. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Hamberg, M.; Samuelsson, B. Lipoxins: Novel Series of Biologically Active Compounds Formed from Arachidonic Acid in Human Leukocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 5335–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Bianchini, F.; Aliberti, J.; Sher, A.; Chiang, N.; Hong, S.; Yang, R.; Petasis, N.A.; Serhan, C.N. Stereochemical Assignment, Antiinflammatory Properties, and Receptor for the Omega-3 Lipid Mediator Resolvin E1. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Clish, C.B.; Brannon, J.; Colgan, S.P.; Chiang, N.; Gronert, K. Novel Functional Sets of Lipid-Derived Mediators with Antiinflammatory Actions Generated from Omega-3 Fatty Acids via Cyclooxygenase 2-Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs and Transcellular Processing. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Yang, R.; Martinod, K.; Kasuga, K.; Pillai, P.S.; Porter, T.F.; Oh, S.F.; Spite, M. Maresins: Novel Macrophage Mediators with Potent Antiinflammatory and Proresolving Actions. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Langmead, C.J.; Riddy, D.M. New Advances in Targeting the Resolution of Inflammation: Implications for Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediator GPCR Drug Discovery. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codagnone, M.; Cianci, E.; Lamolinara, A.; Mari, V.C.; Nespoli, A.; Isopi, E.; Mattoscio, D.; Arita, M.; Bragonzi, A.; Iezzi, M.; et al. Resolvin D1 Enhances the Resolution of Lung Inflammation Caused by Long-Term Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvall, M.G.; Bruggemann, T.R.; Levy, B.D. Bronchoprotective Mechanisms for Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in the Resolution of Lung Inflammation. Mol. Aspects Med. 2017, 58, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werz, O.; Gerstmeier, J.; Libreros, S.; De la Rosa, X.; Werner, M.; Norris, P.C.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Human Macrophages Differentially Produce Specific Resolvin or Leukotriene Signals That Depend on Bacterial Pathogenicity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirault, J.; Bäck, M. Lipoxin and Resolvin Receptors Transducing the Resolution of Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondue, B.; Vosters, O.; de Nadai, P.; Glineur, S.; De Henau, O.; Luangsay, S.; Van Gool, F.; Communi, D.; De Vuyst, P.; Desmecht, D.; et al. ChemR23 Dampens Lung Inflammation and Enhances Anti-Viral Immunity in a Mouse Model of Acute Viral Pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozinovski, S.; Uddin, M.; Vlahos, R.; Thompson, M.; McQualter, J.L.; Merritt, A.-S.; Wark, P.A.B.; Hutchinson, A.; Irving, L.B.; Levy, B.D.; et al. Serum Amyloid A Opposes Lipoxin A4 to Mediate Glucocorticoid Refractory Lung Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, T.; Grabiec, A.M.; Kaur, M.; Bell, T.J.; Fujino, N.; Cook, P.C.; Svedberg, F.R.; MacDonald, A.S.; Maciewicz, R.A.; Singh, D.; et al. The Axl Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Is a Discriminator of Macrophage Function in the Inflamed Lung. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussell, T.; Bell, T.J. Alveolar Macrophages: Plasticity in a Tissue-Specific Context. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Subramaniam, R.; Chen, H.; Smith, A.; Keshava, S.; Shams, H. Boosting Efferocytosis in Alveolar Space Using BCG Vaccine to Protect Host against Influenza Pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, Y.; Tuder, R.M.; Cool, C.D.; Lynch, D.A.; Flores, S.C.; Voelkel, N.F. Endothelial Cell Death and Decreased Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 in Emphysema. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, S.; Leemans, J.C.; Florquin, S.; Branger, J.; Maris, N.A.; Pater, J.; van Rooijen, N.; van der Poll, T. Alveolar Macrophages Have a Protective Antiinflammatory Role during Murine Pneumococcal Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, P.G. Inhibitory Activity of Unstimulated Alveolar Macrophages on T-Lymphocyte Blastogenic Response. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1978, 118, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupane, A.S.; Willson, M.; Chojnacki, A.K.; Vargas E Silva Castanheira, F.; Morehouse, C.; Carestia, A.; Keller, A.E.; Peiseler, M.; DiGiandomenico, A.; Kelly, M.M.; et al. Patrolling Alveolar Macrophages Conceal Bacteria from the Immune System to Maintain Homeostasis. Cell 2020, 183, 110–125.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, K.M.; Bush, S.J.; Hume, D.A. Network Analysis of Transcriptomic Diversity amongst Resident Tissue Macrophages and Dendritic Cells in the Mouse Mononuclear Phagocyte System. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emam, M.; Cánovas, A.; Islas-Trejo, A.D.; Fonseca, P.A.S.; Medrano, J.F.; Mallard, B. Transcriptomic Profiles of Monocyte-Derived Macrophages in Response to Escherichia Coli Is Associated with the Host Genetics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, W.J.; McPhillips, K.A.; Dickinson, M.G.; Linderman, D.J.; Morimoto, K.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Oldham, K.M.; Vandivier, R.W.; Henson, P.M.; Gardai, S.J. Surfactant Proteins A and D Suppress Alveolar Macrophage Phagocytosis via Interaction with SIRP Alpha. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Nishitani, C.; Mitsuzawa, H.; Ariki, S.; Takahashi, M.; Ohtani, K.; Wakamiya, N.; Kuroki, Y. Mannose Binding Lectin and Lung Collectins Interact with Toll-like Receptor 4 and MD-2 by Different Mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, L.N.; Azad, A.K.; Parsa, K.V.L.; Crowther, J.E.; Tridandapani, S.; Schlesinger, L.S. Pulmonary Surfactant Protein A Regulates TLR Expression and Activity in Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7847–7858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, M.; Nishitani, C.; Sano, H.; Yamada, C.; Mitsuzawa, H.; Shimizu, T.; Saito, T.; Smith, K.; Crouch, E.; Kuroki, Y. Human Pulmonary Surfactant Protein D Binds the Extracellular Domains of Toll-like Receptors 2 and 4 through the Carbohydrate Recognition Domain by a Mechanism Different from Its Binding to Phosphatidylinositol and Lipopolysaccharide. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 8657–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, S.; Jose, P.; Avdiushko, M.G.; Kaplan, A.M.; Cohen, D.A. Inhibition of IL-10 Receptor Function in Alveolar Macrophages by Toll-like Receptor Agonists. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihrshahi, R.; Barclay, A.N.; Brown, M.H. Essential Roles for Dok2 and RasGAP in CD200 Receptor-Mediated Regulation of Human Myeloid Cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4879–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munger, J.S.; Huang, X.; Kawakatsu, H.; Griffiths, M.J.; Dalton, S.L.; Wu, J.; Pittet, J.F.; Kaminski, N.; Garat, C.; Matthay, M.A.; et al. The Integrin Alpha v Beta 6 Binds and Activates Latent TGF Beta 1: A Mechanism for Regulating Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis. Cell 1999, 96, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sluijs, K.F.; van Elden, L.J.R.; Nijhuis, M.; Schuurman, R.; Pater, J.M.; Florquin, S.; Goldman, M.; Jansen, H.M.; Lutter, R.; van der Poll, T. IL-10 Is an Important Mediator of the Enhanced Susceptibility to Pneumococcal Pneumonia after Influenza Infection. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 7603–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelgrove, R.J.; Goulding, J.; Didierlaurent, A.M.; Lyonga, D.; Vekaria, S.; Edwards, L.; Gwyer, E.; Sedgwick, J.D.; Barclay, A.N.; Hussell, T. A Critical Function for CD200 in Lung Immune Homeostasis and the Severity of Influenza Infection. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, H.G.; Roostalu, U.; Walter, G.J.; Gullick, N.J.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Roberts, C.A.; Sumner, J.; Baeten, D.L.; Gerwien, J.G.; Cope, A.P.; et al. TNF-α Blockade Induces IL-10 Expression in Human CD4+ T Cells. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ural, B.B.; Yeung, S.T.; Damani-Yokota, P.; Devlin, J.C.; de Vries, M.; Vera-Licona, P.; Samji, T.; Sawai, C.M.; Jang, G.; Perez, O.A.; et al. Identification of a Nerve-Associated, Lung-Resident Interstitial Macrophage Subset with Distinct Localization and Immunoregulatory Properties. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wen, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Single-Cell Landscape of Bronchoalveolar Immune Cells in Patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysko, O.; Vandenabeele, P.; Krysko, D.V.; Bachert, C. Impairment of Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells and Its Role in Chronic Airway Diseases. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, S.; Hodge, G.; Scicchitano, R.; Reynolds, P.N.; Holmes, M. Alveolar Macrophages from Subjects with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Are Deficient in Their Ability to Phagocytose Apoptotic Airway Epithelial Cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2003, 81, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, S.; Hodge, G.; Ahern, J.; Jersmann, H.; Holmes, M.; Reynolds, P.N. Smoking Alters Alveolar Macrophage Recognition and Phagocytic Ability: Implications in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.P.; Tuder, R.M. Role of Apoptosis in Amplifying Inflammatory Responses in Lung Diseases. J. Cell Death 2010, 2010, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hou, C.; Zhao, H.; Liu, L.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Lv, Y.; Shen, X.; Liang, Z.; Cai, S.; Zou, F. High Mobility Group Protein B1 (HMGB1) in Asthma: Comparison of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Healthy Controls. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schagat, T.L.; Wofford, J.A.; Wright, J.R. Surfactant Protein A Enhances Alveolar Macrophage Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.-L.N.; Malcolm, K.C.; Kotaru, C.; Tilstra, J.A.; Westcott, J.Y.; Fadok, V.A.; Wenzel, S.E. Defective Apoptotic Cell Phagocytosis Attenuates Prostaglandin E2 and 15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid in Severe Asthma Alveolar Macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, J.R.; Rommens, J.M.; Kerem, B.; Alon, N.; Rozmahel, R.; Grzelczak, Z.; Zielenski, J.; Lok, S.; Plavsic, N.; Chou, J.L. Identification of the Cystic Fibrosis Gene: Cloning and Characterization of Complementary DNA. Science 1989, 245, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yipp, B.G.; Petri, B.; Salina, D.; Jenne, C.N.; Scott, B.N.V.; Zbytnuik, L.D.; Pittman, K.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Wu, K.; Meijndert, H.C.; et al. Infection-Induced NETosis Is a Dynamic Process Involving Neutrophil Multitasking in Vivo. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, K.D.; Goosmann, C.; Lubojemska, A.; Zychlinsky, A.; Papayannopoulos, V. A Myeloperoxidase-Containing Complex Regulates Neutrophil Elastase Release and Actin Dynamics during NETosis. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquilly, A.; Jacqueline, C.; Davieau, M.; Mollé, A.; Sadek, A.; Fourgeux, C.; Rooze, P.; Broquet, A.; Misme-Aucouturier, B.; Chaumette, T.; et al. Alveolar Macrophages Are Epigenetically Altered after Inflammation, Leading to Long-Term Lung Immunoparalysis. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiselmeier, N.E.; Kraynack, N.C.; Corey, D.A.; Kelley, T.J. Statin-Mediated Correction of STAT1 Signaling and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Cystic Fibrosis Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Corvol, H.; Rousselet, N.; Thompson, K.E.; Berdah, L.; Cottin, G.; Foussigniere, T.; Longchampt, E.; Fiette, L.; Sage, E.; Prunier, C.; et al. FAM13A Is a Modifier Gene of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Phenotype Regulating Rhoa Activity, Actin Cytoskeleton Dynamics and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Cyst Fibros 2018, 17, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaught, D.B.; Stanford, J.C.; Cook, R.S. Efferocytosis Creates a Tumor Microenvironment Supportive of Tumor Survival and Metastasis. Cancer Cell Microenviron. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birge, R.B.; Boeltz, S.; Kumar, S.; Carlson, J.; Wanderley, J.; Calianese, D.; Barcinski, M.; Brekken, R.A.; Huang, X.; Hutchins, J.T.; et al. Phosphatidylserine Is a Global Immunosuppressive Signal in Efferocytosis, Infectious Disease, and Cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, W.; Wang, R.; Liang, X.; Ma, C.; Gao, L. TIM-4 Promotes the Growth of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in a RGD Motif-Dependent Manner. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salina, A.C.; Souza, T.P.; Serezani, C.H.; Medeiros, A.I. Efferocytosis-Induced Prostaglandin E2 Production Impairs Alveolar Macrophage Effector Functions during Streptococcus Pneumoniae Infection. Innate Immun. 2017, 23, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, A.I.; Serezani, C.H.; Lee, S.P.; Peters-Golden, M. Efferocytosis Impairs Pulmonary Macrophage and Lung Antibacterial Function via PGE2/EP2 Signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serezani, C.H.; Chung, J.; Ballinger, M.N.; Moore, B.B.; Aronoff, D.M.; Peters-Golden, M. Prostaglandin E2 Suppresses Bacterial Killing in Alveolar Macrophages by Inhibiting NADPH Oxidase. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losick, V.P.; Isberg, R.R. NF-KappaB Translocation Prevents Host Cell Death after Low-Dose Challenge by Legionella Pneumophila. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2177–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, C.E.; Chong, A.; Cooper, K.G.; Starr, T.; Steele-Mortimer, O. A Second Wave of Salmonella T3SS1 Activity Prolongs the Lifespan of Infected Epithelial Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.L.; Velmurugan, K.; Cowan, M.J.; Briken, V. The Type I NADH Dehydrogenase of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Counters Phagosomal NOX2 Activity to Inhibit TNF-Alpha-Mediated Host Cell Apoptosis. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, S.M.; Martin, C.J.; Booty, M.G.; Nishimura, T.; Zhao, X.; Gan, H.-X.; Divangahi, M.; Remold, H.G. Apoptosis Is an Innate Defense Function of Macrophages against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jondle, C.N.; Gupta, K.; Mishra, B.B.; Sharma, J. Klebsiella Pneumoniae Infection of Murine Neutrophils Impairs Their Efferocytic Clearance by Modulating Cell Death Machinery. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.; Vince, J.E. Pyroptosis versus Necroptosis: Similarities, Differences, and Crosstalk. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, S.M.; Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Molecular Mechanisms and Functions of Pyroptosis, Inflammatory Caspases and Inflammasomes in Infectious Diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viganò, E.; Diamond, C.E.; Spreafico, R.; Balachander, A.; Sobota, R.M.; Mortellaro, A. Human Caspase-4 and Caspase-5 Regulate the One-Step Non-Canonical Inflammasome Activation in Monocytes. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroja-Mazo, A.; Martín-Sánchez, F.; Gomez, A.I.; Martínez, C.M.; Amores-Iniesta, J.; Compan, V.; Barberà-Cremades, M.; Yagüe, J.; Ruiz-Ortiz, E.; Antón, J.; et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome Is Released as a Particulate Danger Signal That Amplifies the Inflammatory Response. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; She, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shi, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.-C.; Shao, F. Pore-Forming Activity and Structural Autoinhibition of the Gasdermin Family. Nature 2016, 535, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codo, A.C.; Saraiva, A.C.; Dos Santos, L.L.; Visconde, M.F.; Gales, A.C.; Zamboni, D.S.; Medeiros, A.I. Inhibition of Inflammasome Activation by a Clinical Strain of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Impairs Efferocytosis and Leads to Bacterial Dissemination. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Shi, W.; Liang, B.; Chen, C.; Wu, R.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J. Efficient Engulfment of Necroptotic and Pyroptotic Cells by Nonprofessional and Professional Phagocytes. Cell Discov. 2019, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, W.H.; Wunderink, R.G.; Williams, D.J.; Zhu, Y.; Anderson, E.J.; Balk, R.A.; Fakhran, S.S.; Chappell, J.D.; Casimir, G.; Courtney, D.M.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee-Wacker, M.C.; Rigby, K.M.; Kobayashi, S.D.; Porter, A.R.; DeLeo, F.R.; Nauseef, W.M. Phagocytosis of Staphylococcus Aureus by Human Neutrophils Prevents Macrophage Efferocytosis and Induces Programmed Necrosis. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4709–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, T.S.; Jones-Nelson, O.; Hotz, M.; Cheng, L.; Miller, L.S.; Suzich, J.; Stover, C.K.; Sellman, B.R.S. Aureus Blocks Efferocytosis of Neutrophils by Macrophages through the Activity of Its Virulence Factor Alpha Toxin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannagan, R.S.; Heit, B.; Heinrichs, D.E. Intracellular Replication of Staphylococcus Aureus in Mature Phagolysosomes in Macrophages Precedes Host Cell Death, and Bacterial Escape and Dissemination. Cell. Microbiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares, C.A.; Sharma, J.; Li, Q.; Rangel, E.L.; Morris, E.G.; Enriquez, M.I.; Teale, J.M. Defect in Efferocytosis Leads to Alternative Activation of Macrophages in Francisella Infections. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, K.M.; Oghumu, S.; Satoskar, A.A.; Gunn, J.S.; van Rooijen, N.; Satoskar, A.R. Respiratory Infection with Francisella Novicida Induces Rapid Dystrophic Cardiac Calcinosis (DCC). FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 53, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Dumas, E.K.; Lawrence, C.; Pate, L.; Longobardi, S.; Wang, X.; James, J.A.; Kovats, S.; Farris, A.D. Bacillus Anthracis Edema Toxin Inhibits Efferocytosis in Human Macrophages and Alters Efferocytic Receptor Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyei, G.B.; Vergne, I.; Chua, J.; Roberts, E.; Harris, J.; Junutula, J.R.; Deretic, V. Rab14 Is Critical for Maintenance of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Phagosome Maturation Arrest. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 5250–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Z.A.; Denning, G.M.; Kusner, D.J. Inhibition of Ca(2+) Signaling by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Is Associated with Reduced Phagosome-Lysosome Fusion and Increased Survival within Human Macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, A.; Zahra, A.; Thompson, V.; Sirisaengtaksin, N.; Wells, A.; Porto, M.; Köster, S.; Penberthy, K.; Kubota, Y.; Dricot, A.; et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Type VII Secreted Effector EsxH Targets Host ESCRT to Impair Trafficking. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Bach, H.; Sun, J.; Hmama, Z.; Av-Gay, Y. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase (PtpA) Excludes Host Vacuolar-H+-ATPase to Inhibit Phagosome Acidification. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA 2011, 108, 19371–19376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, H.; Papavinasasundaram, K.G.; Wong, D.; Hmama, Z.; Av-Gay, Y. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Virulence Is Mediated by PtpA Dephosphorylation of Human Vacuolar Protein Sorting 33B. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, V.; Av-Gay, Y. Intracellular Growth of Bacterial Pathogens: The Role of Secreted Effector Proteins in the Control of Phagocytosed Microorganisms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amara, A.; Mercer, J. Viral Apoptotic Mimicry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.L.; Blackburn, J.W.D.; Taruc, K.; Kipp, A.; Dirk, B.S.; Hunt, N.R.; Barr, S.D.; Dikeakos, J.D.; Heit, B. Antagonistic Coevolution of MER Tyrosine Kinase Expression and Function. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 1613–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabiec, A.M.; Hussell, T. The Role of Airway Macrophages in Apoptotic Cell Clearance Following Acute and Chronic Lung Inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czuczman, M.A.; Fattouh, R.; van Rijn, J.M.; Canadien, V.; Osborne, S.; Muise, A.M.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Higgins, D.E.; Brumell, J.H. Listeria Monocytogenes Exploits Efferocytosis to Promote Cell-to-Cell Spread. Nature 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifuzzaman, M.; Ang, W.X.G.; Choi, H.W.; Nilles, M.L.; St John, A.L.; Abraham, S.N. Necroptosis of Infiltrated Macrophages Drives Yersinia Pestis Dispersal within Buboes. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubbrey, A.L.; Sonstein, J.; Ames, T.M.; Freeman, C.M.; Curtis, J.L. Glucocorticoids Relieve Collectin-Driven Suppression of Apoptotic Cell Uptake in Murine Alveolar Macrophages through Downregulation of SIRPα. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Baen, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-J.; Choi, Y.-H.; Kang, J.L. The TAM-Family Receptor Mer Mediates Production of HGF through the RhoA-Dependent Pathway in Response to Apoptotic Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 3254–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, G.; Dagher, M.C.; Geiszt, M.; Settleman, J.; Ligeti, E. Role of Prenylation in the Interaction of Rho-Family Small GTPases with GTPase Activating Proteins. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 10542–10549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, K.; Janssen, W.J.; Fessler, M.B.; McPhillips, K.A.; Borges, V.M.; Bowler, R.P.; Xiao, Y.-Q.; Kench, J.A.; Henson, P.M.; Vandivier, R.W. Lovastatin Enhances Clearance of Apoptotic Cells (Efferocytosis) with Implications for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 7657–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesen, J.A.; Rodwell, V.W. The 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl Coenzyme-A (HMG-CoA) Reductases. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akula, M.K.; Ibrahim, M.X.; Ivarsson, E.G.; Khan, O.M.; Kumar, I.T.; Erlandsson, M.; Karlsson, C.; Xu, X.; Brisslert, M.; Brakebusch, C.; et al. Protein Prenylation Restrains Innate Immunity by Inhibiting Rac1 Effector Interactions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Xu, J.; Ma, L. Simvastatin Enhances Chemotherapy in Cervical Cancer via Inhibition of Multiple Prenylation-Dependent GTPases-Regulated Pathways. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Choi, Y.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Kang, J.L. Simvastatin Treatment Boosts Benefits of Apoptotic Cell Infusion in Murine Lung Fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, K.-S.; Cushman, H.J.; Akaike, M.; Woo, C.-H.; Wang, X.; Qiu, X.; Fujiwara, K.; Abe, J.-I. ERK5 Activation in Macrophages Promotes Efferocytosis and Inhibits Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2014, 130, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xiong, R.; Chen, X.; Li, P.; Ning, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, N.; Zhou, Y. The Glucocorticoid Dexamethasone Inhibits U937 Cell Adhesion and Neutrophil Release via RhoA/ROCK1-Dependent and Independent Pathways. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, A.; Scott, T.; Li, J.; Gaskell, R.; Dikwa, A.B.; Shah, R.; Montero-Fernandez, M.A.; Lea, S.; Singh, D. Effects of Corticosteroids on COPD Lung Macrophage Phenotype and Function. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabuczi, É.; Sarang, Z.; Szondy, Z. Glucocorticoids Enhance Prolonged Clearance of Apoptotic Cells by Upregulating Liver X Receptor, Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-δ and UCP2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizzo, G.; Hilliard, B.A.; Monestier, M.; Cohen, P.L. Efficient Clearance of Early Apoptotic Cells by Human Macrophages Requires M2c Polarization and MerTK Induction. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3508–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Thorp, E.B.; Doran, A.C.; Sansbury, B.E.; Daemen, M.J.A.P.; Dorweiler, B.; Spite, M.; Fredman, G.; Tabas, I. MerTK Receptor Cleavage Promotes Plaque Necrosis and Defective Resolution in Atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investing. 2017, 127, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorp, E.; Cui, D.; Schrijvers, D.M.; Kuriakose, G.; Tabas, I. Mertk Receptor Mutation Reduces Efferocytosis Efficiency and Promotes Apoptotic Cell Accumulation and Plaque Necrosis in Atherosclerotic Lesions of Apoe-/- Mice. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wittchen, E.S.; Monaghan-Benson, E.; Hahn, C.; Earp, H.S.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Burridge, K. The Role of Endothelial MERTK during the Inflammatory Response in Lungs. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohning, M.P.; Thomas, S.M.; Barthel, L.; Mould, K.J.; McCubbrey, A.L.; Frasch, S.C.; Bratton, D.; Henson, P.M.; Janssen, W.J. Phagocytosis of Microparticles by Alveolar Macrophages during Acute Lung Injury Requires MerTK. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, L.M.; Perron, G.; Won, S.-Y.; Michell-Robinson, M.A.; Rezk, A.; Ludwin, S.K.; Moore, C.S.; Hall, J.A.; Bar-Or, A.; Antel, J.P. MerTK Is a Functional Regulator of Myelin Phagocytosis by Human Myeloid Cells. J. Immunol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodrea, J.; Majai, G.; Doró, Z.; Zahuczky, G.; Pap, A.; Rajnavölgyi, É.; Fésüs, L. The Glucocorticoid Dexamethasone Programs Human Dendritic Cells for Enhanced Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Neutrophils and Inflammatory Response. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, R. Immune Modulatory Effects of Statins. Immunology 2018, 154, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltowski, J.; Jamroz-Wisniewska, G.W. Adverse Effects of Statins—Mechanisms and Consequences. Available online: https://www.eurekaselect.com/69865/article (accessed on 8 December 2020).
- Deichmann, R.; Lavie, C.; Andrews, S. Coenzyme Q10 and Statin-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Ochsner J. 2010, 10, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, U. Statin-Induced Delayed Rhabdomyolysis. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulbah, A.S.; Ong, H.X.; Lee, W.-H.; Colombo, P.; Young, P.M.; Traini, D. Biological Effects of Simvastatin Formulated as PMDI on Pulmonary Epithelial Cells. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeki, A.A.; Bratt, J.M.; Chang, K.Y.; Franzi, L.M.; Ott, S.; Silveria, M.; Fiehn, O.; Last, J.A.; Kenyon, N.J. Intratracheal Instillation of Pravastatin for the Treatment of Murine Allergic Asthma: A Lung-Targeted Approach to Deliver Statins. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeki, A.A.; Elbadawi-Sidhu, M. Innovations in Asthma Therapy: Is There a Role for Inhaled Statins? Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giron, D.J.; Schmidt, J.P.; Pindak, F.F. Effect of Progesterone and Testosterone on Interferon Production and on the Viral Infection-Enhancing Activity of Estrone and Hydrocortisone. Infect. Immun. 1971, 4, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, C.M.; Morrison, R.L.; D’Souza, A.; Teng, X.S.; Happel, K.I. Inhaled Fluticasone Propionate Impairs Pulmonary Clearance of Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Mice. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, X.; Leanse, L.G.; Dai, T.; Wang, Z. Co-Delivery of Resolvin D1 and Antibiotics with Nanovesicles to Lungs Resolves Inflammation and Clears Bacteria in Mice. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rymut, N.; Heinz, J.; Sadhu, S.; Hosseini, Z.; Riley, C.O.; Marinello, M.; Maloney, J.; MacNamara, K.C.; Spite, M.; Fredman, G. Resolvin D1 Promotes Efferocytosis in Aging by Limiting Senescent Cell-Induced MerTK Cleavage. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isopi, E.; Mattoscio, D.; Codagnone, M.; Mari, V.C.; Lamolinara, A.; Patruno, S.; D’Aurora, M.; Cianci, E.; Nespoli, A.; Franchi, S.; et al. Resolvin D1 Reduces Lung Infection and Inflammation Activating Resolution in Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Levy, B.D. Resolvins: Natural Agonists for Resolution of Pulmonary Inflammation. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.J.; Luther, J.; Bohr, S.; Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Li, M.; King, K.R.; Chung, R.T.; Yarmush, M.L. A Novel Resolvin-Based Strategy for Limiting Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, M.; Linder, T.; Ott, J.; Walmrath, H.-D.; Lohmeyer, J.; Vadász, I.; Marsh, L.M.; Herold, S.; Reichert, M.; Buchbinder, A.; et al. Immunomodulation by Lipid Emulsions in Pulmonary Inflammation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, G.P.; Parsons, K.R.; Howard, C.J. Cloning of Two Members of the SIRP Alpha Family of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Binding Proteins in Cattle That Are Expressed on Monocytes and a Subpopulation of Dendritic Cells and Which Mediate Binding to CD4 T Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon-Wilson, E.F.; Kee, W.J.; Willis, A.C.; Barclay, A.N.; Simmons, D.L.; Brown, M.H. CD47 Is a Ligand for Rat Macrophage Membrane Signal Regulatory Protein SIRP (OX41) and Human SIRPalpha 1. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, Y.; Volkmer, J.-P.; McKenna, K.; Civelek, M.; Lusis, A.J.; Miller, C.L.; Direnzo, D.; Nanda, V.; Ye, J.; Connolly, A.J.; et al. CD47-Blocking Antibodies Restore Phagocytosis and Prevent Atherosclerosis. Nature 2016, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Wang, J.; Willingham, S.B.; Martin, R.; Wernig, G.; Weissman, I.L. Anti-CD47 Antibodies Promote Phagocytosis and Inhibit the Growth of Human Myeloma Cells. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2538–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cham, L.B.; Torrez Dulgeroff, L.B.; Tal, M.C.; Adomati, T.; Li, F.; Bhat, H.; Huang, A.; Lang, P.A.; Moreno, M.E.; Rivera, J.M.; et al. Immunotherapeutic Blockade of CD47 Inhibitory Signaling Enhances Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to Viral Infection. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cham, L.B.; Adomati, T.; Li, F.; Ali, M.; Lang, K.S. CD47 as a Potential Target to Therapy for Infectious Diseases. Antibodies 2020, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.D.S.; Banerjee, S.; Kruglov, O.; Viller, N.N.; Horwitz, S.M.; Lesokhin, A.; Zain, J.; Querfeld, C.; Chen, R.; Okada, C.; et al. Targeting CD47 in Sézary Syndrome with SIRPαFc. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, C.K.; Staves, J.; Roberts, C.; Johnson, H.; Vyas, P.; Goodnough, L.T.; Murphy, M.F. The Effects of Monoclonal Anti-CD47 on RBCs, Compatibility Testing, and Transfusion Requirements in Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Transfusion 2019, 59, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, F.; Tseng, S.; Narayanan, C.; Shura, L.; Willingham, S.; Howard, M.; Prohaska, S.; Volkmer, J.; et al. Pre-Clinical Development of a Humanized Anti-CD47 Antibody with Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Potential. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, S.; van Rooijen, N.; Saxena, R.K. Reduced Expression of CD47 during Murine Red Blood Cell (RBC) Senescence and Its Role in RBC Clearance from the Circulation. Transfusion 2007, 47, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-L.; Liu, D.-Q.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zen, K. Down-Regulation of Platelet Surface CD47 Expression in Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Infection-Induced Thrombocytopenia. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansell, S.; Chen, R.W.; Flinn, I.W.; Maris, M.B.; O’Connor, O.A.; Johnson, L.D.; Irwin, M.; Petrova, P.S.; Uger, R.A.; Sievers, E.L. A Phase 1 Study of TTI-621, a Novel Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Targeting CD47, in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Hematologic Malignancies. Blood 2016, 128, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Johansen, M.; Looney, M.R.; Brown, E.J.; Matthay, M.A. CD47 Deficiency Protects Mice from Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Escherichia Coli Pneumonia. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 6947–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).