First Report of Uncinaria hamiltoni in Orphan Eastern Mediterranean Monk Seal Pups in Greece and Its Clinical Significance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Evaluation
2.2. Body Condition and Body Mass Evaluation
2.3. Hematology and Biochemistry
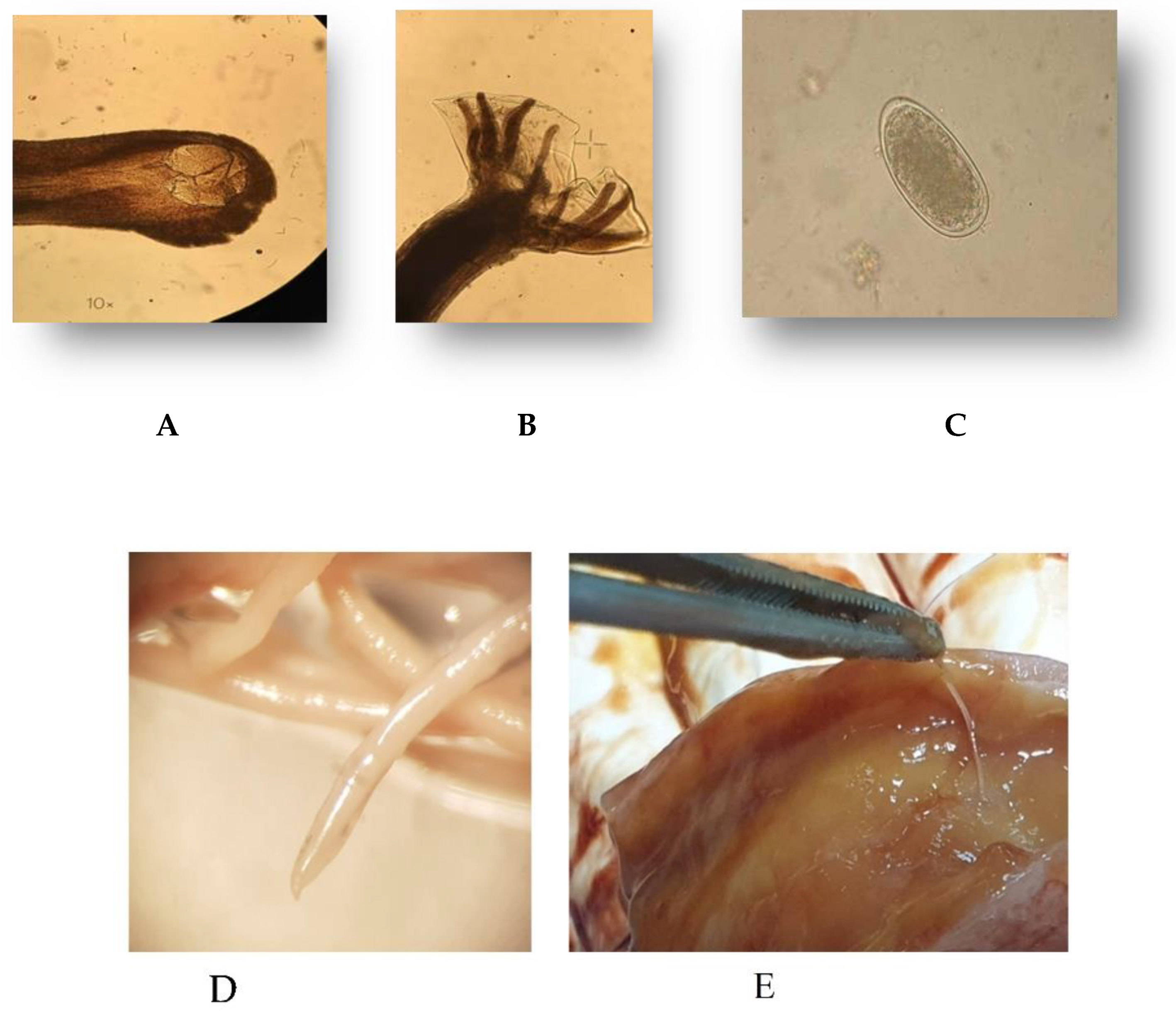
2.4. Parasitological-Coprological Examination
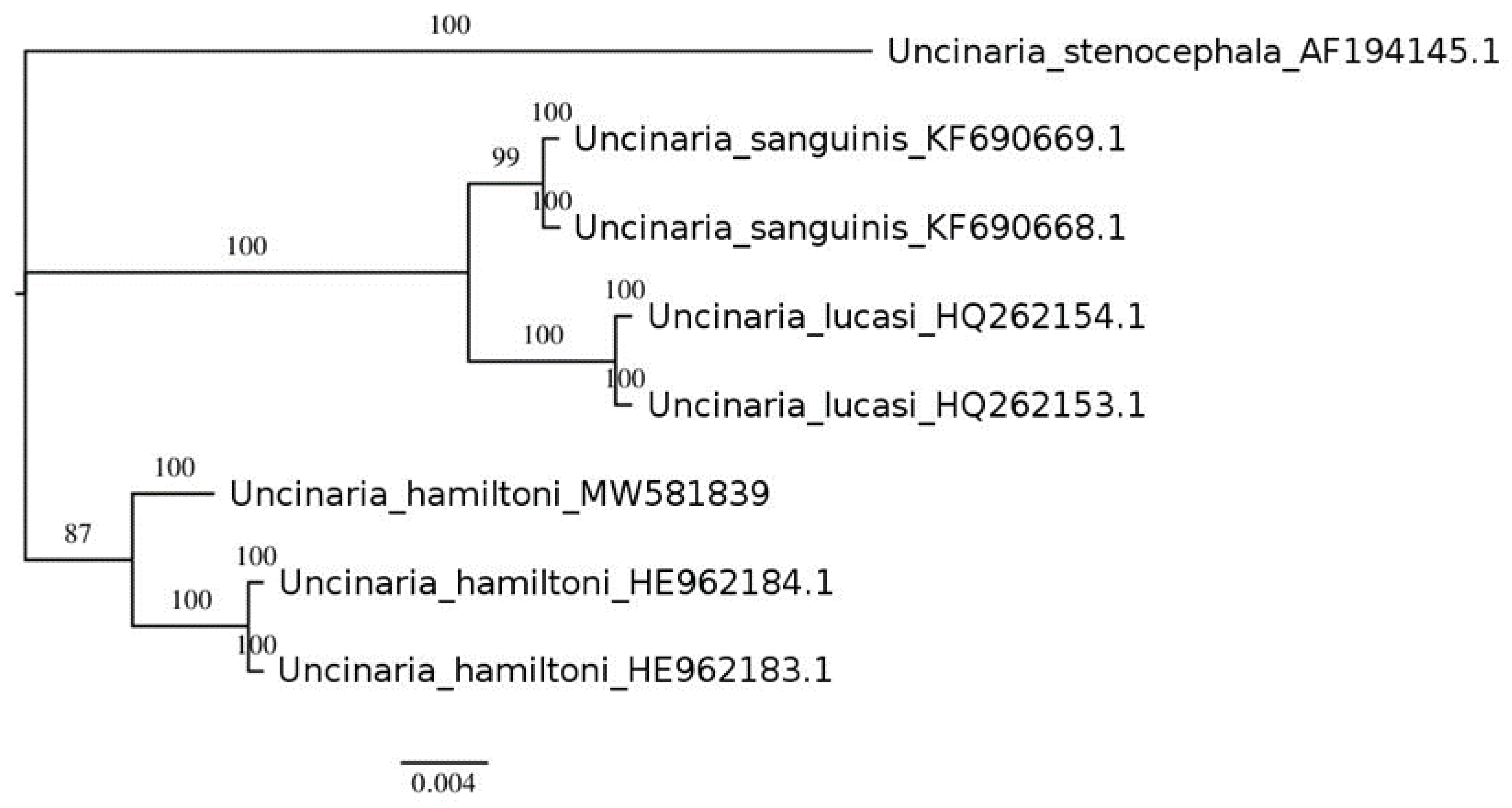
2.5. Molecular Identification
2.6. Treatment
3. Discussion
3.1. Parasitic Species Identification
3.2. Parasite Transmission
3.3. Clinical Significance
3.4. Importance of Parasitic Burden
3.5. Treatment
3.6. Parasite–Host Interaction
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Age Estimation
4.2. Weight Evaluation and Body Mass Index
4.3. Coprological Examination
4.4. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karamanlidis, A.A.; Dendrinos, P. Monachus monachus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015. 2015. Available online: https://www.marinemammalhabitat.org/portfolio-item/cilician-basin/ (accessed on 2 December 2021). [CrossRef]
- Karamanlidis, A.A.; Adamantopoulou, S.; Tounta, E.; Dendrinos, D. Monachus monachus Eastern Mediterranean subpopulation. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019. 2019. Available online: https://www.marinemammalhabitat.org/portfolio-item/turkish-straits-system-and-prebosphoric-imma/ (accessed on 2 December 2021). [CrossRef]
- Karamanlidis, A.A.; Dendrinos, P.; Fernández de Larrinoa, P.; Gücü, A.C.; Johnson, W.M.; Kiraç, C.O.; Pires, R. The Mediterranean monk seal Monachus monachus: Status, biology, threats, and conservation priorities. Mamm. Rev. 2016, 46, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, H.; Dendrinos, D.; Marcou, M.; Michaelides, S.; Karamanlidis, A.A. Re-establishment of the Mediterranean monk seal Monachus monachus in Cyprus: Priorities for conservation. Oryx 2019, 55, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendrinos, D.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Adamantopoulou, S.; Koemtzopoulos, K.; Komninou, A.; Tounta, E. LIFE-IP 4 NATURA: Integrated Actions for the Conservation and Management of Natura 2000 Sites, Species, Habitats and Ecosystems in Greece. Deliverable Action A.1: Action Plan for the Mediterranean Monk Seal (Monachus monachus); Hellenic Ministry of Environment and Energy: Athens, Greece, 2020; pp. 1–105.
- Waltzek, T.B.; Cortés-Hinojosa, G.; Wellehan, J.F.X., Jr.; Gray, G.C. Marine mammal zoonoses: A review of disease manifestations. Zoon Public Health 2012, 59, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, F. Zoonoses in wildlife: Integrating ecology into management. Adv. Parasitol. 2009, 68, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Population biology of infectious diseases: Part I. Nature 1979, 280, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, R.M.; Anderson, R.M. Population biology of infectious diseases: Part II. Nature 1979, 280, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, H.G.; Zuk, M. For Host’s Sake: The Pluses of Parasite Preservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefèvre, T.; Lebarbenchon, C.; Gauthier-Clerc, M.; Missé, D.; Poulin, R.; Thomas, F. The ecological significance of manipulative parasites. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, A.P. Parasitism and the regulation of host populations. In Parasitism and Ecosystems; Thomas, F., Renaud, F., Guégan, J.-F., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, F.; Poulin, R.; de Meeu}s, T.; Guégan, J.-F.; Renaud, F. Parasites and ecosystem engineering: What roles could they play? Oikos 1999, 84, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, F.; Sheih, A.; West, J.D.; Kerr, B. Coevolutionary cycling of host sociality and pathogen virulence in contact networks. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 261, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvell, C.D.; Kim, K.; Burkholder, J.M.; Colwell, R.R.; Epstein, P.R.; Grimes, D.J.; Hofmann, E.E.; Lipp, E.K.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Overstreet, R.M.; et al. Emerging marine diseases—Climate links and anthropogenic factors. Science 1999, 285, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuk, M.; McKean, K.A. Sex differences in parasite infections: Patterns and processes. Int. J. Parasit. 1996, 26, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.E.J. Patterns in parasite epidemiology: The peak shift. Parasitol. Today 1998, 14, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, S.J.; Bjornstad, O.N.; Cattadori, I.M.; Boag, B.; Hudson, P.J. Seasonality, cohort-dependence and the development of immunity in a natural host-nematode system. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B-Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, N.U.; James, I.M.; Alphonsus, N.O.; Nkiruka, R.U. A review of host-parasite relationships. Ann. Res. Rev. Zool. 2015, 5, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziej-Sobocińska, M.; Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Lachowicz, J.; Borowik, T.; Kowalczyk, R. Influence of management and biological factors on the parasitic invasions in the wild—Spread of blood-sucking nematode Ashworthius sidemi in European bison (Bison bonasus). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2016, 5, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kołodziej-Sobocińska, M.; Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Pyziel, A.M.; Kowalczyk, R. Increased parasitic load in captive-released European bison (Bison bonasus) has important implications for reintroduction programs. Ecohealth 2018, 15, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziej-Sobocińska, M. Factors affecting the spread of parasites in populations of wild European terrestrial mammals. Mamm. Res. 2019, 64, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, P.J.; Dobson, A.P.; Lafferty, K.D. Is a healthy ecosystem one that is rich in parasites? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafferty, K.D. Ecosystem consequences of fish parasites. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.A.; Lymbery, A.J.; Smith, A. Parasites, emerging disease and wildlife conservation. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszak, P.; Cunningham, A.A.; Hyatt, A.D. Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife—Threats to biodiversity and human health. Science 2000, 287, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvell, C.D.; Mitchell, C.E.; Ward, J.R.; Altizer, S.; Dobson, A.P.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Samuel, M.D. Climate warming and disease risk for terrestrial biota. Science 2002, 296, 2158–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.F.; Sax, D.F.; Lafferty, K.D. Evidence for the role of infectious disease in species extinction and endangerment. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George-Nascimento, M.; Lima, M.; Ortiz, E. Phenotypic differentiation among hookworms Uncinaria sp. (Nematoda: Ancylostomatidae) in sympatric and allopatric populations of South American sea lions Otaria byronia, and fur seals Arctocephalus australis (Carnivora: Otariidae). Mar. Biol. 1992, 112, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, A.; Lyons, E.T.; Pagan, C.; Hyman, D.; Lewis, E.E.; Beckmen, K.; Bell, C.M.; Castinel, A.; Delong, R.L.; Duignan, P.J.; et al. Molecular systematics of pinniped hookworms (Nematoda: Uncinaria): Species delimitation, host associations and host-induced morphometric variation. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2013, 43, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.; Pagan, C.; Nadler, S.A. Host Population Expansion and the Genetic Architecture of the Pinniped Hookworm Uncinaria lucasi. J. Parasitol. 2020, 106, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, D.; Carter, S.; Gaus, C.; Muller, J.; Dennison, W. Organochlorine and heavy metal concentrations in blubber and liver tissue collected from Queensland (Australia) dugong (Dugong dugon). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, A.D.; Higgins, D.P.; Slapeta, J.; Gray, R. Uncinaria sanguinis sp. n. (Nematoda: Ancylostomatidae) from the endangered Australian sea lion, Neophoca cinerea (Carnivora: Otariidae). Folia Parasitol. 2014, 61, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, S.A.; Hoberg, E.P.; Hudspeth, D.S.; Rickard, L.G. Relationships of Nematodirus species and Nematodirus battus isolates (Nematoda: Trichostrongyloidea) based on nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences. J. Parasitol. 2000, 86, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, C.W. Uncinariasis (Anchylostomiasis) in man and animals in the United States. Tex. Med. News 1901, 10, 523–532. [Google Scholar]
- Baylis, M.A. A new species of the nematode genus Uncinaria from a sea lion, with some observations on related species. Parasitology 1933, 25, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylis, H.A. A re-description of Uncinaria lucasi Stiles, a hookworm of seals. Parasitology 1947, 38, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguel, M.; Gottdenker, N. The diversity and impact of hookworm infections in wildlife. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, B.T.; Marcus, A.D.; Higgins, D.P.; Gongora, J.; Gray, R.; Šlapeta, J. Unexpected absence of genetic separation of a highly diverse population of hookworms from geographically isolated hosts. Inf. Genet. Evol. 2014, 28, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, A.D.; Higgins, D.P.; Gray, R. Epidemiology of hookworm (Uncinaria sanguinis) infection in free-ranging Australian sea lion (Neophoca cinerea) pups. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3341–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, A.D.; Higgins, D.P.; Gray, R. Health assessment of free-ranging endangered Australian sea lion (Neophoca cinerea) pups: Effect of haematophagous parasites on haematological parameters. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 184, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, A.D.; Higgins, D.P.; Gray, R. Ivermectin treatment of free-ranging endangered Australian sea lion (Neophoca cinerea) pups: Effect on hookworm and lice infection status, haematological parameters, growth, and survival. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2743–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, E.T.; DeLong, R.L.; Nadler, S.A.; Laake, J.L.; Orr, A.J.; DeLong, B.L.; Pagan, C. Investigations of peritoneal and intestinal infections of adult hookworms (Uncinaria spp.) in northern fur seal (Callorhinus ursinus) and California sea lion (Zalophus californianus) pups on San Miguel Island, California (2003). Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmina, T.A.; Kuzmin, Y. Description of Uncinaria lyonsi n. sp. (Nematoda: Ancylostomatidae) from the California sea lion Zalophus californianus lesson (Carnivora: Otariidae). Syst. Parasitol. 2015, 90, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berón-Vera, B.; Crespo, E.A.; Raga, J.A.; Pedraza, S.N. Uncinaria hamiltoni (Nematoda: Ancylostomatidae) in South American sea lions, Otaria flavescens, from Northern Patagonia, Argentina. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castinel, A.; Duignan, P.J.; Pomroy, W.E.; Lyons, E.T.; Nadler, S.A.; Dailey, M.D.; Wilkinson, I.S.; Chilvers, B.L. First report and characterization of adult Uncinaria spp. in New Zealand Sea Lion (Phocarctos hookeri) pups from the Auckland Islands, New Zealand. Parasitol. Res. 2006, 98, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echenique, J.; Pereira, E.; Prado, J.; Schild, A.L.; Valente, A.L. New host and geographical records for Parafilaroides normani (Nematoda: Filaroididae) Dailey, 2009 in South American fur seal, Arctocephalus australis, from southern Brazil. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Whitehouse, K.; Spraker, T.R.; Lyons, E.; Melin, S.R.; Gulland, F.; Delong, R.L.; Amos, W. Contrasting effects of heterozygosity on survival and hookworm resistance in California sea lion pups. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lion, S.; van Baalen, M.; Wilson, W.G. The evolution of parasite manipulation of host dispersal. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, M.-A.; Vincent, C.; Womble, J.N.; Steingass, S.M.; Desportes, G. Harbour Seals: Population Structure, Status, and Threats in a Rapidly Changing Environment. Oceans 2021, 2, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, R.; Chandradeva, N.; Gkafas, G.; Raga, J.A.; Fernández, M.; Aznar, F.J. Transmission and predictors of burden of lungworms of the striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba) in the Western Mediterranean. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castinel, A.; Duignan, P.J.; Lyons, E.T.; Pomroy, W.E.; Gibbs, N.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Chilvers, B.L.; Wilkinson, I.S. Epidemiology of hookworm (Uncinaria spp.) infection in New Zealand (Hooker’s) sea lion (Phocarctos hookeri) pups on Enderby Island, Auckland Islands (New Zealand) during the breeding seasons from 1999/2000 to 2004/2005. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, E.T.; Spraker, T.R.; De Long, R.L.; Ionita, M.; Melin, S.R.; Nadler, S.A.; Tolliver, S.C. Review of research on hookworms (Uncinaria lucasi Stiles, 1901) in northern fur seals (Callorhinus ursinus Linnaeus, 1758). Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, O.W.; Lyons, E.T. Life cycle of Uncinaria lucasi Stiles, 1901 (Nematoda: Ancylostomatidae) of fur seals, Callorhinus ursinus Linn., on the Pribilof Islands, Alaska. J. Parasitol. 1965, 51, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, E.T.; DeLong, R.L.; Melin, S.R.; Tolliver, S.C. Uncinariasis in northern fur seal and California sea lion pups from California. J. Wildl. Dis. 1997, 33, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lyons, E.T.; Melin, S.R.; DeLong, R.L.; Orr, A.J.; Gulland, F.M.; Tolliver, S.C. Current prevalence of adult Uncinaria spp. in northern fur seal (Callorhinus ursinus) and California sea lion (Zalophus californianus) pups on San Miguel Island, California, with notes on the biology of these hookworms. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 97, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, E.T.; Spraker, T.R.; Olson, K.D.; Tolliver, S.C.; Bair, H.D. Prevalence of hookworms (Uncinaria lucasi Stiles) in northern fur seal (Callorhinus ursinus Linnaeus) pups on St. Paul Island, Alaska, USA: 1986–1999. Comp. Parasitol. 2000, 67, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Dendrinos, P.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Kotomatas, S.; Legakis, A.; Tounta, E.; Matthiopoulos, J. Pupping habitat use in the Mediterranean monk seal: A long-term study. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2007, 23, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, F.J.; Balbuena, J.A.; Fernández, M.; Raga, J.A. Living together: The parasites of marine mammals. In Marine Mammals: Biology and Conservation; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Irvine, R.J. Parasites and the dynamics of wild mammal populations. Anim. Sci. 2006, 82, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordes, F.; Morand, S. The impact of multiple infections on wild animal hosts: A review. Infect. Ecol. Epidem. 2011, 1, 7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Papastamataki, P.A.; Bliziotis, I.A. A bibliometric analysis of research productivity in Parasitology by different world regions during a 9-year period (1995–2003). BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D. Pet roundworms and hookworms: A continuing need for global warming. Parasite Vectors 2012, 5, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Beaumier, C.M.; Gillespie, P.M.; Strych, U.; Hayward, T.; Bottazzi, M.E. Advancing a vaccine to prevent hookworm disease and anemia. Vaccine 2016, 34, 3001e3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyes, M.C. Pathology of the northern fur seal. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1965, 147, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, R.T.; Geiger, S.M.; Bethony, J.; Mendez, S. Comparative immunology of human and animal models of hookworm infection. Parasite Immunol. 2006, 28, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, A.; Constant, S.L.; Bethony, J.M. Immunobiology of hookworm infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microb. 2005, 43, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Castinel, A.; Duignan, P.J.; Pomroy, W.E.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Gibbs, N.J.; Chilvers, B.L.; Wilkinson, I.S. Neonatal mortality in New Zealand sea lions (Phocarctos hookeri) at Sandy Bay, Enderby Island, Auckland Islands from 1998 to 2005. J. Wildl. Dis. 2007, 43, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spraker, T.R.; DeLong, R.L.; Lyons, E.T.; Melin, S.R. Hookworm enteritis with bacteremia in California sea lion pups on San Miguel Island. J. Wildl. Dis. 2007, 43, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguel, M.; Muñoz, F.; Perez-Venegas, D.; Müller, A.; Paves, H.; Howerth, E.; Gottdenker, N. The life history strategy of a fur seal hookworm in relation to pathogenicity and host health status. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2018, 7, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, E.T.; DeLong, R.L.; Spraker, T.R.; Melin, S.R.; Tolliver, S.C. Observations in 2001 on hookworms (Uncinaria spp.) in otariid pinnipeds. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 89, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, M.S. Hookworms (Uncinaria sp.) in Juan Fernandez fur seal pups (Arctocephalus philippii) from Alejandro Selkirk Island, Chile. J. Parasitol. 1998, 84, 1305–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraci, J.R. Functional hematology of the harp seal Pagophilus groenlandicus. Physiol. Zool. 1971, 44, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumble, S.J.; Castellini, M.A. Blood chemistry, hematology, and morphology of wild harbor seal pups in Alaska. J. Wildl. Manag. 2002, 66, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boily, F.; Beaudoin, S.; Measures, L.N. Hematology and serum chemistry of harp (Phoca groenlandica) and hooded seals (Cystophora cristata) during the breeding season, in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, Canada. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.A.; Burns, J.M.; Schreer, J.F.; Hammill, M.O. A longitudinal and cross-sectional analysis of total body oxygen store development in nursing harbor seals (Phoca vitulina). J. Comp. Physiol. B 2007, 177, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, D.J.; Gulland, F.M.D.; Rios, C.A.; Hall, A.J. Hematology and serum chemistry in stranded and wild-caught harbor seals in central California: Reference intervals, predictors of survival, and parameters affecting blood variables. J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, M.E.; Fadely, B.S.; Gelatt, T.S.; Rea, L.D.; Loughlin, T.R. Serum chemistry reference ranges for Steller sea lion (Eumetopias jubatus) pups from Alaska: Stock differentiation and comparisons within a North Pacific sentinel species. Ecohealth 2014, 10, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.; Canfield, P.; Rogers, T. Serum proteins in the leopard seal, Hydrurga leptonyx, in Prydz Bay, Eastern Antarctica and the coast of NSW, Australia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B-Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 142, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beldomenico, P.M.; Telfer, S.; Gebert, S.; Lukomski, L.; Bennett, M.; Begon, M. The dynamics of health in wild field vole populations: A haematological perspective. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hufschmid, J.; Beveridge, I.; Handasyde, K.A. Haematology and serum biochemistry of adult free-ranging mountain brushtail possums (Trichosurus cunninghami), including correlations with season, sex, age, habitat type and disease status. Aust. J. Zool. 2014, 61, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, E.T. Biology of the Hookworm, Uncinaria lucasi Stiles, 1901, in the Northern fur Seal Callorhinus ursinus Linn. on the Pribilof Islands, Alaska; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, A. Ecological study on the hookworm, Uncinaria lucasi, of northern fur seal, Callorhynus ursinus, in Bering Island, Russia. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 45, 109–110. [Google Scholar]
- Seguel, M.; Paves, H.; Paredes, E.; Schlatter, R. Causes of mortality in South American fur seal pups (Arctophoca australis gracilis) at Guafo Island, southern Chile (2004–2008). Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2013, 29, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Orts, J.S.; Montero, F.E.; Juan-García, A.; García, N.A.; Crespo, E.A.; Raga, J.A.; Aznar, F.J. Intestinal helminth fauna of the South American sea lion Otaria flavescens and fur seal Arctocephalus australis from northern Patagonia, Argentina. J. Helminthol. 2012, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, E.T. Historic importance of some aspects of research by O. Wilford Olsen on hookworms (Uncinaria lucasi) in northern fur seals (Callorhinus ursinus) and Steller sea lions (Eumatopias jubatus) in 1951 on St. Paul Island, Alaska. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 95, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilvers, B.L.; Duignan, P.J.; Robertson, B.C.; Castinel, A.; Wilkinson, I.S. Effects of hookworms (Uncinaria sp.) on the early growth and survival of New Zealand sea lion (Phocarctos hookeri) pups. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, R.L.; Orr, A.J.; Jenkinson, R.S.; Lyons, E.T. Treatment of northern fur seal (Callorhinus ursinus) pups with ivermectin reduces hookworm-induced mortality. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2009, 25, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguel, M.; Paredes, E.; Paves, H.; Molina, R.; Henríquez, F.; de Groote, F.; Schlatter, R. Pathological findings in South American fur seal pups (Arctocephalus australis) found dead at Guafo Island, southern Chile. J. Comp. Pathol. 2011, 145, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, E.T.; Keyes, M.C.; Conlogue, J. Activities of Dichlorvos or Disophenol against Hookworm (Uncinaria-lucasi) and Sucking Lice of Northern Fur Seal Pups (Callorhinus-ursinus) on St. Paul Island, Alaska. J. Wildl. Dis. 1978, 14, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, E.T.; Kim, K.C.; Keyes, M.C. Variable activity of disophenol against hookworms and lice of northern fur seal pups on St. Paul Island, Alaska. J. Wildl. Dis. 1980, 16, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigg, M.A.; Lyons, E.T. Clinical observations on three northern fur seal pups treated with dichlorvos. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1981, 179, 1284–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Kolevatova, A.L.; Bukina, L.A.; Vasenin, Y.A. Diseases and parasites of the northern fur seal. In The Northern fur Seal Taxonomy, Morphology, Ecology, Behavior; Sokolov, V.E., Ed.; Russian Academy of Sciences: Moscow, Russia, 1998; Volume 2, pp. 862–892. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gulland, F.M.D.; Dierauf, L.A.; Whitman, K.L. CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine; Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, S.A.; Hayman, D.T.S.; Gray, R.; Roe, W.D. Risk Factors for New Zealand Sea Lion (Phocarctos hookeri) Pup Mortality: Ivermectin Improves Survival for Conservation Management. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijks, J.M.; Hoffman, J.I.; Kuiken, T.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Amos, W. Heterozygosity and lungworm burden in harbour seals (Phoca vitulina). Heredity 2008, 100, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkafas, G.A.; de Jong, M.; Exadactylos, A.; Raga, J.A.; Aznar, F.J.; Hoelzel, A.R. Sex-specific impact of inbreeding on pathogen load in the striped dolphin. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20200195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Whitehouse, K.; Petetti, L.; Duignan, P.; Castinel, A. Hookworm infection, anaemia and genetic variability of the New Zealand sea lion. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanlidis, A.A.; Gaughran, S.; Aguilar, A.; Dendrinos, P.; Huber, D.; Pires, R.; Schultz, J.; Skrbinšek, T.; Amato, G. Shaping species conservation strategies using mtDNA analysis: The case of the elusive Mediterranean monk seal (Monachus monachus). Biol. Conserv. 2016, 193, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanlidis, A.A.; Skrbinšek, T.; Amato, G.; Dendrinos, D.; Gaughran, S.; Kasapidis, P.; Kopatz, A.; Vik Stronen, A. Genetic and demographic history define a conservation strategy for Earth’s most endangered Pinniped, the Mediterranean monk seal Monachus monachus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkafas, G.A.; Exadactylos, A.; Rogan, E.; Raga, J.A.; Reid, R.; Hoelzel, A.R. Biogeography and temporal progression during the evolution of striped dolphin population structure in European waters. J. Biogeogr. 2017, 44, 2681–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, D.; Barbiers, R. Impact of emerging and zoonotic diseases on mammal management. In Wild Mammals in Captivity: Principles and Techniques for Zoo Management, 2nd ed.; Kleiman, D.G., Ed.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010; pp. 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Androukaki, E.; Fatsea, E.; t’ Hart, L.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Tounta, E.; Kotomatas, S. Growth and development of Mediterranean monk seal pups during rehabilitation. Monac. Guard 2002, 5, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguti, S. Systema Helminthum; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1961; Volume III. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.C.; Chabaud, A.G.; Willmott, S. Keys to the Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates. Parasites Vectors 2009, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 21, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MrBayes 2.1: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, J.G.; Jarvis, P.D.; Fernández-Sánchez, J.; Kaine, B.T.; Woodhams, M.D.; Holland, B.R. Is the general time-reversible model bad for molecular phylogenetics? Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Arrival | Release/Death | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survived | Died | Survived | Died | |
| Age | 24.9 (3–90) | 19.8 (5–65) | 143.1 days (104–194) | 31.9 days (8–70) |
| Rehabilitation Time | n/a | n/a | 118.3 days (25–174) | 12.7 days (0–63) |
| Length | 113.8 cm (105–124) | 109.5 (90–123) | 136.8 cm (123–145) | 111.4 (91–123) |
| Weight | 18.2 kg (13–29.9) | 16.3 kg (9–27) | 55.4 kg (43.2–60) | 16.7 (8–27) |
| BMI | 0.160 (0.111–0.253) | 0.148 (0.100–0.225) | 0.405 (0.345–0.456) | 0.149 (0.141–0.225) |
| Expected “Healthy” Mean BMI | 0.186 (0.162–0.257) | 0.180 (0.164–0.230) | 0.316 (0.273–0.372) | 0.193 (0.167–0.235) |
| % Difference from “healthy” | −14.1% (−34.5%–15.2%) | −17.0% (−51.6%–26.1%) | 29.0% (1.4%–47.4%) | −22.6% (−53.2%–25.3%) |
| n | 16 | 15 | 16 | 15 |
| Hematological and Biochemical Parameters | Range | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Blood Cells (RBC) × 1,000,000/μL | 3.94 | 0.78 | 4.72 | 2.8 | 1.08 |
| Hemoglobin (Hgb) gr/dL | 126.3 | 2.7 | 129 | 18.42 | 29.79 |
| Hematocrit (Hct)-Packed Cell Volume (PCV) % | 46.7 | 9.3 | 55.7 | 34.3 | 11.67 |
| Mean corposcular volume (MCV) fl | 26 | 102 | 128 | 117.61 | 8.29 |
| Mean corposcular hemoglobin (MCH) pg | 18.3 | 30.3 | 48.6 | 38.33 | 5.65 |
| Mean corp hemoglobin consentration (MCHC) g/dL | 15 | 25.5 | 40.5 | 32.69 | 4.85 |
| White Blood Cells (WBC) × 1000/μL | 18.9 | 11.7 | 30.6 | 21.02 | 5.41 |
| Neutrophils % | 76.8 | 10.5 | 87.3 | 67.62 | 21.37 |
| Lymphocytes % | 72.74 | 8.76 | 81.5 | 28.03 | 20.45 |
| Monocytes % | 20 | 0 | 20 | 5.92 | 5.35 |
| Eosinophils % | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0.82 | 0.97 |
| Vasophils % | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.44 |
| Platelets ×1000/μL | 665 | 194 | 859 | 571.06 | 213.22 |
| Total Proteins g/dL | 3.9 | 3.3 | 7.2 | 5.71 | 1.07 |
| Urea mg/dL | 137 | 20.0 | 157 | 66.88 | 46.02 |
| Creatinine mg/dL | 1.7 | 0.2 | 1.9 | 0.67 | 0.38 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) U/L | 1001 | 38 | 1039 | 162.94 | 234.99 |
| Alanine transaminase (ALT) U/L | 319 | 19 | 338 | 71.05 | 81.79 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) U/L | 123 | 34 | 157 | 71 | 39.66 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH U/L | 4134.8 | 811 | 4945.8 | 1974.75 | 1377.14 |
| Calcium mg/dL | 2 | 8.6 | 10.6 | 9.58 | 0.65 |
| Phosphorus mg/dL | 1.7 | 5.7 | 7.4 | 6.68 | 0.55 |
| Cholesterole mg/dL | 2186 | 119 | 2305 | 448.35 | 751.44 |
| Triglycerides mg/dL | 82 | 37 | 119 | 69.175 | 28.9 |
| Albumins g/dL | 3.2 | 0.4 | 3.6 | 2.4 | 1.19 |
| Glucose mg/dL | 162 | 5 | 167 | 69.9 | 46.94 |
| Potassium mmol/L | 1.79 | 4.21 | 6 | 5.1 | 0.6 |
| Sodium mmol/L | 13.8 | 136.3 | 150.1 | 145.7 | 4.78 |
| Number of Mediterranean Monk Seal Pups | Body Condition | Mean Number of Hookworm Eggs/10 Micr Fields | Hematocrit (PCV) | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Critical x < −35% | 112 | 9–18% | 5 Died |
| 11 | Poor 15% < x < −35% | 24 | 18–28% | 3 Died 8 Survived |
| 15 | Good/Fair x > −15% | 10 | 28–55.7% | 7 Died 8 Survived |
| Species | COI | ITS | D2/D3 28S |
|---|---|---|---|
| U. lucasi | MT154514.1 [31] MT154516.1 [31] | HQ262154.1 [30] HQ262153.1 [30] | HQ261827.1 [30] HQ261823.1 [30] |
| U. hamiltoni | MW581887 (this study) | HE962184.1 [30] HE962183.1 [30] MW581839 (this study) | HQ261869.1 [30] HQ261867.1 [30] MW581843 (this study) |
| U. sanguinis | KF693746.1 [32] KF693748.1 [32] | KF690669.1 [33] KF690668.1 [33] | N/A |
| Day 0 (Arrival) | Day 15 | Day 30 | Day 45 | Day 60 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survived | Died during 1st week) | Survived | Died | Survived | Died | Survived | Died | Survived | Died | |
| Mean PCV % No of pups | 35.3 (n = 16) | 31.1 (n = 15) | 37.9 (n = 16) | 0 | 40.1 (n = 16) | 0 | 41.9 (n = 16) | 0 | 42.9 (n = 16) | 0 |
| Egg count (mean per 10 optical field) | 17.0 | 47.0 | 5.0 | NA | 0 | NA | 0 | NA | 0 | NA |
| Drug given (oral) | fenbendazole 10 mg/kg b.w. × 3 days or mebendazole 20 mg/kg b.w. × 2 days and amoxycillin+clavulanic 12 mg/kg b.w. or metronidazole 10 mg/kg b.w. × 10 days | fenbendazole 10 mg/kg b.w. or mebendazole 20 mg/kg b.w. | fenbendazole 10 mg/kg b.w. or mebendazole 20 mg/kg b.w. | No treatment | No treatment | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komnenou, A.T.; Gkafas, G.A.; Kofidou, E.; Sarantopoulou, J.; Exadactylos, A.; Tounta, E.; Koemtzopoulos, K.; Dendrinos, P.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Gulland, F.; et al. First Report of Uncinaria hamiltoni in Orphan Eastern Mediterranean Monk Seal Pups in Greece and Its Clinical Significance. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121581
Komnenou AT, Gkafas GA, Kofidou E, Sarantopoulou J, Exadactylos A, Tounta E, Koemtzopoulos K, Dendrinos P, Karamanlidis AA, Gulland F, et al. First Report of Uncinaria hamiltoni in Orphan Eastern Mediterranean Monk Seal Pups in Greece and Its Clinical Significance. Pathogens. 2021; 10(12):1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121581
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomnenou, Anastasia Th., George A. Gkafas, Evangelia Kofidou, Joanne Sarantopoulou, Athanasios Exadactylos, Eleni Tounta, Kimon Koemtzopoulos, Panagiotis Dendrinos, Alexandros A. Karamanlidis, Frances Gulland, and et al. 2021. "First Report of Uncinaria hamiltoni in Orphan Eastern Mediterranean Monk Seal Pups in Greece and Its Clinical Significance" Pathogens 10, no. 12: 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121581
APA StyleKomnenou, A. T., Gkafas, G. A., Kofidou, E., Sarantopoulou, J., Exadactylos, A., Tounta, E., Koemtzopoulos, K., Dendrinos, P., Karamanlidis, A. A., Gulland, F., & Papadopoulos, E. (2021). First Report of Uncinaria hamiltoni in Orphan Eastern Mediterranean Monk Seal Pups in Greece and Its Clinical Significance. Pathogens, 10(12), 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121581









