Effects of Local and Systemic Immune Challenges on the Expression of Selected Salivary Genes in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles coluzzii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Salivary Candidate Selection
2.2. Molecular Features and Prediction Analyses
2.3. Transcriptional Profiling by Local and Systemic Bacterial Challenges
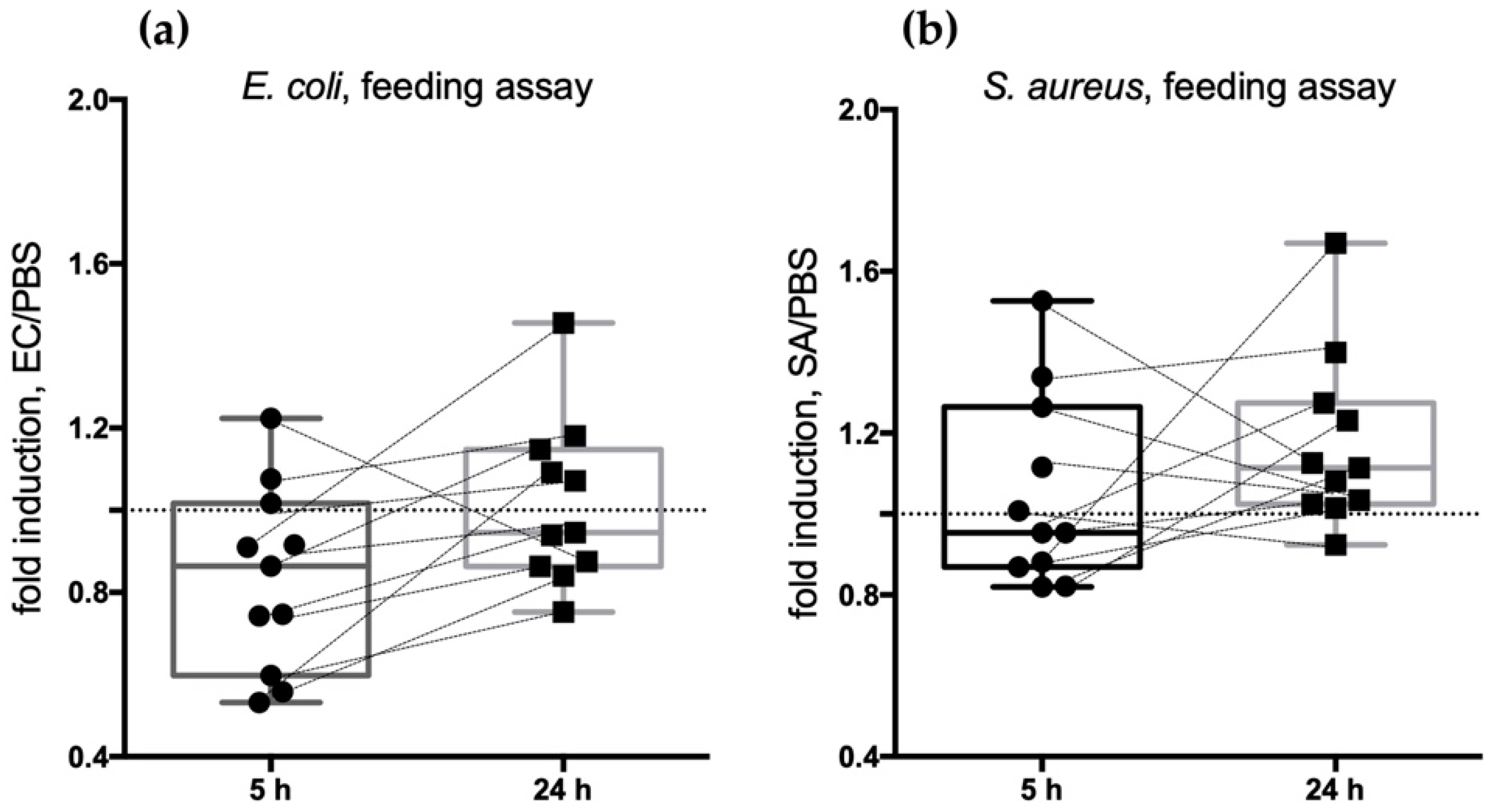
2.3.1. Feeding Assays Reveal an Early Transcriptional Increase of SG+ Candidates
2.3.2. Injection Assays Reveal a Late Transcriptional Increase of SG+ Candidates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatic Analysis and Candidate Selection
4.2. Mosquito Rearing
4.3. Immune Challenges
4.4. Transcriptional Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribeiro, J.; Arcà, B. From Sialomes to the Sialoverse: An Insight into Salivary Potion of Blood-Feeding Insects. Adv. Insect Phys. 2009, 37, 59–118. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffolano, J.G.; Haselton, A.T. The Adult Dipteran Crop: A Unique and Overlooked Organ. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Mans, B.J.; Arca, B. An insight into the sialome of blood-feeding Nematocera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. Engl. 2010, 40, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Martin-Martin, I.; Arcà, B.; Calvo, E. A Deep Insight into the Sialome of Male and Female Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreira-Ferro, C.K.; Daffre, S.; James, A.; Marinotti, O. A lysozyme in the salivary glands of the malaria vector Anopheles darlingi. Insect Mol. Biol. 1998, 7, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, G.; Seeley, D.; Wolf, A.; Kafatos, F.C. Malaria infection of the mosquito Anopheles gambiae activates immune-responsive genes during critical transition stages of the parasite life cycle. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6115–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, A.; Rossignol, P. Mosquito salivary glands: Parasitological and molecular aspects. Parasitol. Today 1991, 7, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, W.A. Mosquito Sugar Feeding and Reproductive Energetics. Annu. Rev. Entomol. Annu. Rev. 1995, 40, 443–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffolano, J.G. Chapter Two—Fly Foregut and Transmission of Microbes; Jurenka, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 27–95. [Google Scholar]
- Rosinski-Chupin, I.; Briolay, J.; Brouilly, P.; Perrot, S.; Gomez, S.M.; Chertemps, T.; Roth, C.W.; Keime, C.; Gandrillon, O.; Couble, P.; et al. SAGE analysis of mosquito salivary gland transcriptomes during Plasmodium invasion. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Modahl, C.M.; Tan, S.T.; Xiang, B.W.W.; Missé, D.; Vial, T.; Kini, R.M.; Pompon, J.F. JNK pathway restricts DENV2, ZIKV and CHIKV infection by activating complement and apoptosis in mosquito salivary glands. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro-Silva, R.; Borges, L.; Coelho, L.P.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Valdés, J.J.; Rosário, V.D.; De La Fuente, J.; Domingos, A. Gene expression changes in the salivary glands of Anopheles coluzzii elicited by Plasmodium berghei infection. Paras. Vect. 2015, 8, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, J.M.; Francischetti, I.M. Role of arthropod saliva in blood feeding: Sialome and post-sialome perspectives. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanfrancotti, A.; Lombardo, F.; Santolamazza, F.; Veneri, M.; Castrignanò, T.; Coluzzi, M.; Arcà, B. Novel cDNAs encoding salivary proteins from the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. FEBS Lett. 2002, 517, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arcà, B.; Lombardo, F.; Capurro, M.; della Torre, A.; Dimopoulos, G.; James, A.; Coluzzi, M. Trapping cDNAs encoding secreted proteins from the salivary glands of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1516–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arcà, B.; Lombardo, F.; Struchiner, C.J.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. Anopheline salivary protein genes and gene families: An evolutionary overview after the whole genome sequence of sixteen Anopheles species. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Srivastava, P.; Sirisena, P.; Dubey, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Shrinet, J.; Sunil, S. Mosquito Innate Immunity. Insects 2018, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, D.R.; Clark, K.D. Bombyx mori and Aedes aegypti form multifunctional immune Complexes that integrate Pattern recognition, melanization, coagulants, and hemocyte recruitment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulet, P.; Hetru, C.; Dimarcq, J.-L.; Hoffmann, D. Antimicrobial peptides in insects; structure and function. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1999, 23, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Patočka, J.; Kuča, K. Insect Antimicrobial Peptides, a Mini Review. Toxins 2018, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomay, L.C.; Michel, K. Mosquito Immunobiology: The Intersection of Vector Health and Vector Competence. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, M.; Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J.A. Antimicrobial peptide defense in Drosophila. BioEssays 1997, 19, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J. The Host Defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 697–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christophides, G.; Zdobnov, E.; Barillas-Mury, C.; Birney, E.; Blandin, S.; Blass, C.; Brey, P.T.; Collins, F.H.; Danielli, A.; Dimopoulos, G.; et al. Immunity-Related Genes and Gene Families in Anopheles gambiae. Science 2002, 298, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meister, S.; Kanzok, S.M.; Zheng, X.-L.; Luna, C.; Li, T.-R.; Hoa, N.T.; Clayton, J.R.; White, K.P.; Kafatos, F.C.; Christophides, G.K.; et al. Immune signaling pathways regulating bacterial and malaria parasite infection of the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11420–11425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De, T.D.; Sharma, P.; Thomas, T.; Singla, D.; Tevatiya, S.; Kumari, S.; Schauhan, C.; Rani, J.; Srivastava, K.; Kaur, R.; et al. Interorgan molecular communication strategies of “Local” and “Systemic” innate immune responses in mosquito Anopheles stephensi. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Souza-Neto, J.; Cosme, R.T.; Rovira, J.; Ortiz, A.; Pascale, J.M.; Dimopoulos, G. Reciprocal Tripartite Interactions between the Aedes aegypti Midgut Microbiota, Innate Immune System and Dengue Virus Influences Vector Competence. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillyer, J.F. Mosquito immunity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 708, 218–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arcà, B.; Lombardo, F.; Valenzuela, J.G.; Francischetti, I.M.B.; Marinotti, O.; Coluzzi, M.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. An updated catalogue of salivary gland transcripts in the adult female mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 3971–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendes-Sousa, A.F.; Queiroz, D.C.; Vale, V.F.; Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Valenzuela, J.G.; Gontijo, N.F.; Andersen, J.F. An Inhibitor of the Alternative Pathway of Complement in Saliva of New World Anopheline Mosquitoes. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, D.A.; Nolan, T.; Fischer, B.; Pinder, A.; Crisanti, A.; Russell, S. A comprehensive gene expression atlas of sex- and tissue-specificity in the malaria vector, Anopheles gambiae. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlachou, D.; Schlegelmilch, T.; Christophides, G.; Kafatos, F.C. Functional Genomic Analysis of Midgut Epithelial Responses in Anopheles during Plasmodium Invasion. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabere, M.N.; Noble, W.S. Empirical comparison of web-based antimicrobial peptide prediction tools. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waghu, F.H.; Barai, R.S.; Gurung, P.; Idicula-Thomas, S. CAMPR3: A database on sequences, structures and signatures of antimicrobial peptides. Nucl. Acids Res. 2015, 44, D1094–D1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzou, P.; Ohresser, S.; Ferrandon, D.; Capovilla, M.; Reichhart, J.-M.; Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Imler, J.-L. Tissue-Specific Inducible Expression of Antimicrobial Peptide Genes in Drosophila Surface Epithelia. Immunity 2000, 13, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agaisse, H.; Petersen, U.-M.; Boutros, M.; Mathey-Prevot, B.; Perrimon, N. Signaling Role of Hemocytes in Drosophila JAK/STAT-Dependent Response to Septic Injury. Dev. Cell 2003, 5, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillyer, J.F. Transcription in mosquito hemocytes in response to pathogen exposure. J. Biol. 2009, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizioli, J.; Bulet, P.; Charlet, M.; Lowenberger, C.; Blass, C.; Müller, H.-M.; Dimopoulos, G.; Hoffmann, J.; Kafatos, F.; Richman, A. Cloning and analysis of a cecropin gene from the malaria vector mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2000, 9, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimopoulos, G.; Christophides, G.; Meister, S.; Schultz, J.; White, K.P.; Barillas-Mury, C.; Kafatos, F.C. Genome expression analysis of Anopheles gambiae: Responses to injury, bacterial challenge, and malaria infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8814–8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baxter, R.H.G.; Contet, A.; Krueger, K. Arthropod Innate Immune Systems and Vector-Borne Diseases. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, H.-Y.; Chowdhury, M.; Huang, Y.-D.; Yu, X.-Q. Insect antimicrobial peptides and their applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5807–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, H.-Y.; Deng, X.-J.; Yang, W.-Y.; Zhou, C.-Z.; Cao, Y.; Yu, X.-Q. Gloverins of the silkworm Bombyx mori: Structural and binding properties and activities. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, C.; Gao, B.; Fang, Q.; Ye, G.; Zhu, S. Antimicrobial peptide-like genes in Nasonia vitripennis: A genomic perspective. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Genes | Expression Profile | Full | Precursor | Mature | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name 1 | AGAP ID | SG+ | SG F/M | U | AA | kDa | SP | AA | kDa | pI | AA | kDa | pI |
| hyp6.2 secreted salivary basic pep. | AGAP006495 | X | 85 | 9.3 | 27 | 58 | 6.3 | 10.41 | 35 | 4.0 | 11.57 | ||
| hyp17 hypothetical salivary pr. 17 | AGAP000151 | X | 77 | 8.1 | 29 | 48 | 4.9 | 10.83 | |||||
| hyp15 hypothetical salivary pr. 15 | AGAP000152 | X | 78 | 9.9 | 30 | 48 | 4.9 | 10.55 | |||||
| sg2a salivary protein | AGAP006504 | X | 173 | 17.6 | 18 | 155 | 15.6 | 7.02 | 54 | 5.2 | 5.52 | ||
| sg2 salivary protein | AGAP006506 | X | 114 | 11.8 | 20 | 94 | 9.7 | 3.49 | |||||
| hyp55.3 putative 55.3 salivary pr. | AGAP005822 | X | 513 | 55.2 | 21 | 492 | 52.9 | 8.73 | 276 | 29.8 | 8.77 | ||
| hyp12 hypothetical salivary pr. 12 | AGAP008306 | X | 92 | 10.0 | 21 | 71 | 7.9 | 4.47 | |||||
| hyp10 hypothetical salivary pr. 10 | AGAP008307 | X | 90 | 10.0 | 19 | 67 | 7.5 | 5.42 | 63 | 7.0 | 5.77 | ||
| hyp14.5 sim. to Cx. 14.5 sal. Pep. | AGAP004883 | X | 180 | 19.7 | 26 | 154 | 16.8 | 8.07 | |||||
| hyp14.5-1 sim. to Cx. 14.5 sal. Pep. | AGAP001174 | X | 154 | 17.2 | 20 | 134 | 14.9 | 6.15 | |||||
| hyp13 hypothetical pr. 13 | AGAP003474 | X | 56 | 6.2 | 22 | 34 | 3.8 | 4.75 | 19 | 2.0 | 3.77 | ||
| Ag_sal_Lyzo1 sal. Lysozyme | AGAP007347 | X | 140 | 15.3 | 20 | 120 | 13.3 | 8.91 | |||||
| Cecropin | AGAP000693 | X | 58 | 6.1 | 23 | 35 | 3.6 | 10.79 | |||||
| CAMP R3—Prediction of Antimicrobial Peptides | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM 1 | RF 1 | DA 1 | ANN 1 | |||||
| PRE | MAT | PRE | MAT | PRE | MAT | PRE | MAT | |
| 0.057 | 0.193 | 0.062 | 0.304 | 0.006 | 0.048 | NAMP | NAMP | hyp6.2_AGAP006495 |
| 0.062 | 0.062 | 0.055 | 0.055 | 0.015 | 0.015 | NAMP | NAMP | hyp17_AGAP000151 |
| 0.092 | 0.092 | 0.149 | 0.149 | 0.028 | 0.028 | AMP | AMP | hyp15_AGAP000152 |
| 0.316 | 0.316 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.006 | 0.006 | NAMP | NAMP | hyp12_AGAP008306 |
| 0.298 | 0.269 | 0.099 | 0.052 | 0.088 | 0.166 | AMP | AMP | hyp10_AGAP008307 |
| 1.000 | 0.445 | 0.917 | 0.504 | 1.000 | 0.102 | NAMP | NAMP | sg2a_AGAP006504 |
| 0.324 | 0.324 | 0.858 | 0.858 | 0.937 | 0.937 | NAMP | NAMP | sg2_AGAP006506 |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.913 | 0.932 | 0.000 | 1.000 | AMP | AMP | hyp55.3_AGAP005822 |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.945 | 0.945 | 1.000 | 1.000 | AMP | AMP | hyp14.5_AGAP004883 |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.970 | 0.970 | 1.000 | 1.000 | AMP | AMP | hyp14.5-1_AGAP001174 |
| 0.601 | 0.579 | 0.287 | 0.115 | 0.080 | 0.189 | NAMP | NAMP | hyp13_AGAP003474 |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.873 | 0.873 | 1.000 | 1.000 | AMP | AMP | LysC1_AGAP007347 |
| 0.985 | 0.985 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.999 | 0.999 | AMP | AMP | Cec_AGAP000693 |
| GENE 1 | VB ID | pF | qPCR F | pR | qPCR R | SIZE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hyp6.2 secreted sal. basic pep. | AGAP006495 | 06495_F | CATTGCTTGTGGTGCTGTCC | 06495_R | AAGTGCTGCCGACATTACCA | 87 |
| hyp17 hypothetical sal. pr. 17 | AGAP000151 | 00151_F | TGTCTGCTGCTCTTCATCGC | 00151_R | TGGGGTCGCTCTTTTGTCAT | 99 |
| hyp15 hypothetical sal. pr. 15 | AGAP000152 | 00152_F | GGGCAGAGACCGAAATACCA | 00152_R | CCAGTCAGTGCCATCCTAGC | 99 |
| sg2a salivary protein | AGAP006504 | 06504_F | AAATGGTCAGCAAGGACGAG | 06504_R | ATGCCTCCATTCTGTTGTCC | 96 |
| sg2 salivary protein | AGAP006506 | 06506_F | TGCCGAACCTTGGTAATCTG | 06506_R | ACGCATCGGTAAAGTTCGTC | 96 |
| hyp55.3 putative 55.3 sal. pr. | AGAP005822 | 05822_F | GACGGCAAGAAAGTTGAAGC | 05822_R | TGACGTTGGTGAGTCGTTTG | 104 |
| hyp12 hypothetical sal. pr. 12 | AGAP008306 | 08306_F | AGAAACTGCAGCTCACGAAC | 08306_R | TGCACAGAGCACAACAACAG | 78 |
| hyp10 hypothetical sal. pr. 10 | AGAP008307 | 08307_F | GTCACCATGGAAGACCCCCGTACCGAGCT | 08307_R | GTCACCCGGGGCGAATATCCTTTGTACAGT | 204 |
| hyp14.5 sim. to Cx 14.5 sal. pep. | AGAP004883 | 04883_F | GCTCAAAAAGCTTCGCAGAG | 04883_R | TCGGATTATCTGGCAGGAAG | 102 |
| hyp14.5-1 sim. to Cx 14.5 sal. pep. | AGAP001174 | 01174_F | TCTACAAGGCGCAGAATGTG | 01174_R | TGGGCCGAATTACACTCATC | 100 |
| hyp13 hypothetical pr. 13 | AGAP003474 | 03474_F | GTCACCATGGGGAACGAAATCATACAAAA | 03474_R | GTCACCCGGGTTGCGATCCGGAGTCACTGT | 105 |
| Ag_sal_Lyzo1 sal. lysozyme | AGAP007347 | 07347_F | ACGGCATCTTCCAGATCAAC | 07347_R | GACGTTTGTGGATCAGCTTG | 138 |
| Cecropin | AGAP000693 | 00693_F | GTCACCATGGGACGGCTGAAGAAGCTGGG | 00693_R | GTCACCCGGGACCGAGCGCCTTAACGCCTG | 104 |
| Ag_RpS7 | AGAP010592 | AgS7_qF | GTGCGCGAGTTGGAGAAGA | AgS7_qR | ATCGGTTTGGGCAGAATGC | 77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bevivino, G.; Arcà, B.; Lombardo, F. Effects of Local and Systemic Immune Challenges on the Expression of Selected Salivary Genes in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles coluzzii. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101300
Bevivino G, Arcà B, Lombardo F. Effects of Local and Systemic Immune Challenges on the Expression of Selected Salivary Genes in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles coluzzii. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101300
Chicago/Turabian StyleBevivino, Giulia, Bruno Arcà, and Fabrizio Lombardo. 2021. "Effects of Local and Systemic Immune Challenges on the Expression of Selected Salivary Genes in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles coluzzii" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101300
APA StyleBevivino, G., Arcà, B., & Lombardo, F. (2021). Effects of Local and Systemic Immune Challenges on the Expression of Selected Salivary Genes in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles coluzzii. Pathogens, 10(10), 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101300








