Defining the Prion Type of Fatal Familial Insomnia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. PET Blot
4.3. Western Blot, Membrane Adsorption Assay, and Stability Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prusiner, S.B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science 1982, 216, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lugaresi, E.; Medori, R.; Montagna, P.; Baruzzi, A.; Cortelli, P.; Lugaresi, A.; Tinuper, P.; Zucconi, M.; Gambetti, P. Fatal Familial Insomnia and Dysautonomia with Selective Degeneration of Thalamic Nuclei. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambetti, P.; Parchi, P.; Petersen, R.B.; Chen, S.G.; Lugaresi, E. Fatal Familial Insomnia and Familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease: Clinical, Pathological and Molecular Features. Brain Pathol. 1995, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchi, P.; Castellani, R.; Cortelli, P.; Montagna, P.; Chen, S.G.; Petersen, R.B.; Manetto, V.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; McLean, M.J.; Sheller, J.R.; et al. Regional distribution of protease-resistant prion protein in fatal familial insomnia. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 38, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, L.G.; Petersen, R.B.; Tabaton, M.; Brown, P.; LeBlanc, A.C.; Montagna, P.; Cortelli, P.; Julien, J.; Vital, C.; Pendelbury, W.W. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Disease phenotype determined by a DNA polymorphism. Science 1992, 258, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateishi, J.; Brown, P.; Kitamoto, T.; Hoque, Z.M.; Roos, R.; Wollman, R.; Cervenáková, L.; Gajdusek, D.C. First experimental transmission of fatal familial insomnia. Nature 1995, 376, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Tschöke, S.; Kranefuss, N.; Dröse, W.; Hause-Reitner, D.; Giese, A.; Groschup, M.H.; Kretzschmar, H.A. The paraffin-embedded tissue blot detects PrP(Sc) early in the incubation time in prion diseases. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasnianski, A.; Sanchez Juan, P.; Ponto, C.; Bartl, M.; Heinemann, U.; Varges, D.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Zerr, I. A proposal of new diagnostic pathway for fatal familial insomnia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monari, L.; Chen, S.G.; Brown, P.; Parchi, P.; Petersen, R.B.; Mikol, J.; Gray, F.; Cortelli, P.; Montagna, P.; Ghetti, B.; et al. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Different prion proteins determined by a DNA polymorphism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2839–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parchi, P.; Castellani, R.; Capellari, S.; Ghetti, B.; Young, K.; Chen, S.G.; Farlow, M.; Dickson, D.W.; Sima, A.A.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Molecular basis of phenotypic variability in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medori, R.; Tritschler, H.J.; LeBlanc, A.; Villare, F.; Manetto, V.; Chen, H.Y.; Xue, R.; Leal, S.; Montagna, P.; Cortelli, P. Fatal familial insomnia, a prion disease with a mutation at codon 178 of the prion protein gene. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wemheuer, W.M.; Benestad, S.L.; Wrede, A.; Schulze-Sturm, U.; Wemheuer, W.E.; Hahmann, U.; Gawinecka, J.; Schütz, E.; Zerr, I.; Brenig, B.; et al. Similarities between Forms of Sheep Scrapie and Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Are Encoded by Distinct Prion Types. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 2566–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wemheuer, W.M.; Wrede, A.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Types and Strains: Their Essential Role in Understanding Protein Aggregation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wemheuer, W.M.; Wrede, A.; Gawinecka, J.; Zerr, I.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Filtration of Protein Aggregates Increases the Accuracy for Diagnosing Prion Diseases in Brain Biopsies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breyer, J.; Wemheuer, W.M.; Wrede, A.; Graham, C.; Benestad, S.L.; Brenig, B.; Richt, J.A.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Detergents modify proteinase K resistance of PrP Sc in different transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs). Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanusso, G. Evidence from Molecular Strain Typing. In Proceedings of the Prion Conference PRION20210; Taylor & Francis Open Access: Salzburg, Austria, 2010; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, A.; Mohri, S.; Kai, H.; Tamaoka, A.; Kobayashi, A.; Mizusawa, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Shimizu, H.; Murayama, S.; et al. Two distinct prions in fatal familial insomnia and its sporadic form. Brain Commun. 2019, 1, fcz045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchi, P.; Giese, A.; Capellari, S.; Brown, P.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Windl, O.; Zerr, I.; Budka, H.; Kopp, N.; Piccardo, P.; et al. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchi, P.; Capellari, S.; Chin, S.; Schwarz, H.B.; Schecter, N.P.; Butts, J.D.; Hudkins, P.; Burns, D.K.; Powers, J.M.; Gambetti, P. A subtype of sporadic prion disease mimicking fatal familial insomnia. Neurology 1999, 52, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rumeileh, S.; Redaelli, V.; Baiardi, S.; Mackenzie, G.; Windl, O.; Ritchie, D.L.; Didato, G.; Hernandez-Vara, J.; Rossi, M.; Capellari, S.; et al. Sporadic Fatal Insomnia in Europe: Phenotypic Features and Diagnostic Challenges. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skora, L.; Fonseca-Ornelas, L.; Hofele, R.V.; Riedel, D.; Giller, K.; Watzlawik, J.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Urlaub, H.; Becker, S.; Zweckstetter, M. Burial of the polymorphic residue 129 in amyloid fibrils of prion stop mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 2994–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Telling, G.C.; Parchi, P.; DeArmond, S.J.; Cortelli, P.; Montagna, P.; Gabizon, R.; Mastrianni, J.; Lugaresi, E.; Gambetti, P.; Prusiner, S.B. Evidence for the conformation of the pathologic isoform of the prion protein enciphering and propagating prion diversity. Science 1996, 274, 2079–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Windl, O.; Dempster, M.; Estibeiro, J.P.; Lathe, R.; de Silva, R.; Esmonde, T.; Will, R.; Springbett, A.; Campbell, T.A.; Sidle, K.C.; et al. Genetic basis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the United Kingdom: A systematic analysis of predisposing mutations and allelic variation in the PRNP gene. Hum. Genet. 1996, 98, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
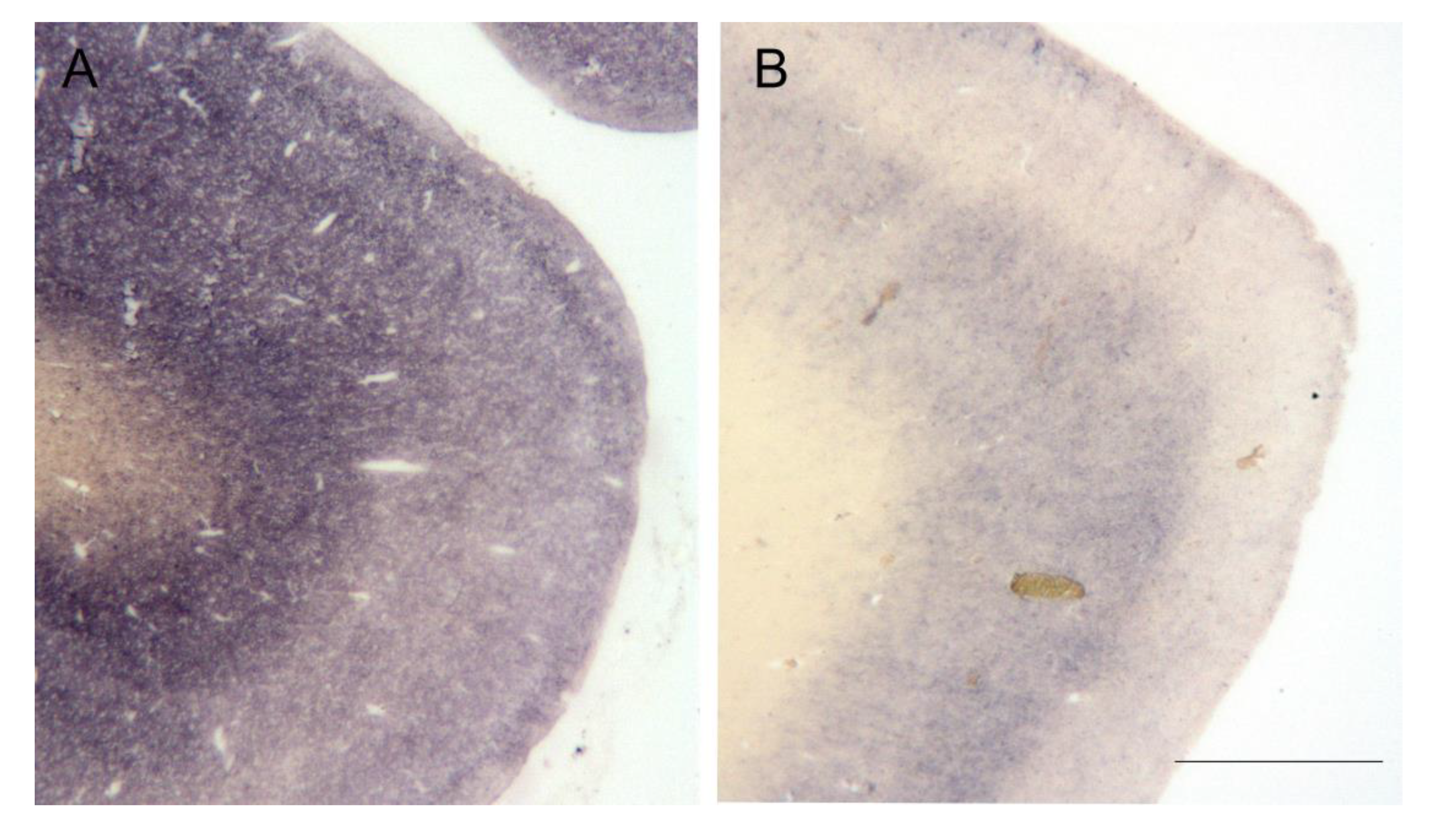
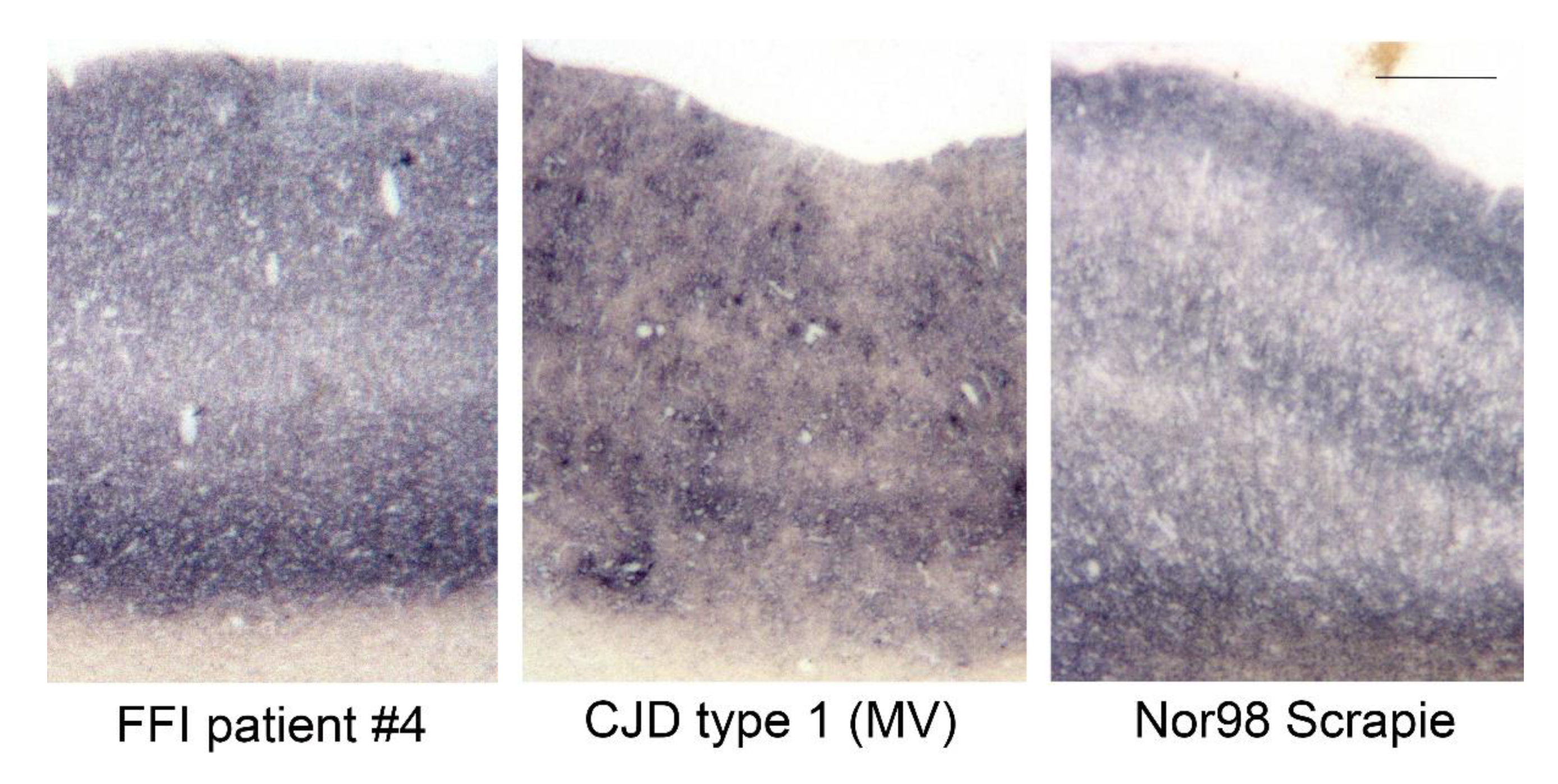
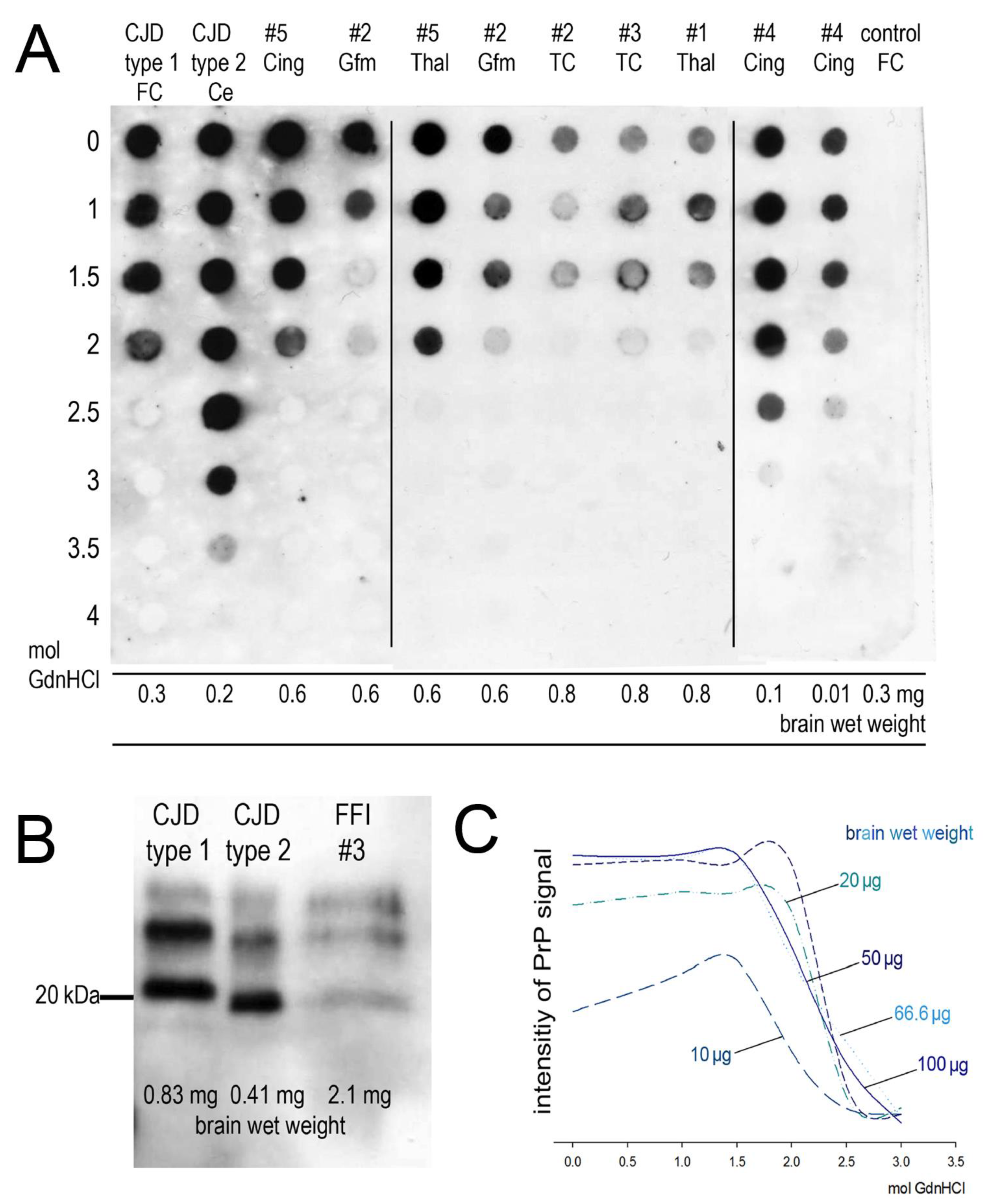
| Case Number | Codon 129 Polymorphism | Brain Regions Available for Homogenates |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | MV | Gyrus cinguli, Gyrus temporalis inferior, Gyrus frontalis medius, Gyrus frontalis superior, mediodorsal thalamic nuclei |
| #2 | MM | Gyrus cinguli, Gyrus temporalis inferior, Gyrus frontalis medius, Gyrus frontalis superior |
| #3 | MM | Gyrus temporalis inferior, Gyrus frontalis superior |
| #4 | MM | Gyrus cinguli, Gyrus temporalis inferior, Gyrus frontalis medius, Gyrus frontalis superior, mediodorsal thalamic nuclei, Nucleus caudatus, Cerebellum |
| #5 | MV | Gyrus cinguli, Gyrus temporalis inferior, Gyrus frontalis medius, Gyrus frontalis superior, mediodorsal thalamic nuclei, Nucleus caudatus, Cerebellum |
| #6 | MM | Gyrus frontalis superior |
| Case Number | Brain Area | MAA | Stability MAA | Western Blot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Gyrus cinguli | positive | not possible | n.d. |
| Gyrus temporalis inferior | positive | not possible | n.d. | |
| Gyrus frontalis medius | positive | not possible | n.d. | |
| Gyrus frontalis superior | positive | not possible | not possible | |
| mediodorsal thalamic nuclei | positive | possible | typical FFI signature | |
| #2 | Gyrus cinguli | positive | not possible | n.d. |
| Gyrus temporalis inferior | positive | possible | n.d. | |
| Gyrus frontalis medius | positive | possible | typical FFI signature | |
| Gyrus frontalis superior | positive | possible | typical FFI signature | |
| #3 | Gyrus temporalis inferior | positive | possible | typical FFI signature |
| Gyrus frontalis superior | positive | possible | typical FFI signature | |
| #4 | Gyrus cinguli | positive | possible | typical FFI signature |
| Gyrus temporalis inferior | positive | possible | n.d. | |
| Gyrus frontalis medius | positive | possible | n.d. | |
| Gyrus frontalis superior | positive | possible | typical FFI signature | |
| mediodorsal thalamic nuclei | positive | possible | n.d. | |
| Nucleus caudatus | positive | possible | n.d. | |
| Cerebellum | negative | not possible | not possible | |
| #5 | Gyrus cinguli | positive | possible | typical FFI signature |
| Gyrus temporalis inferior | positive | possible | typical FFI signature | |
| Gyrus frontalis medius | positive | possible, but not sufficient for final determination of stability | n.d. | |
| mediodorsal thalamic nuclei | positive | possible | n.d. | |
| Nucleus caudatus | positive | not possible | n.d. | |
| Cerebellum | positive | not possible | n.d. | |
| #6 | Gyrus frontalis superior | positive | not possible | not possible |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jürgens-Wemheuer, W.; Wrede, A.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W. Defining the Prion Type of Fatal Familial Insomnia. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101293
Jürgens-Wemheuer W, Wrede A, Schulz-Schaeffer W. Defining the Prion Type of Fatal Familial Insomnia. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101293
Chicago/Turabian StyleJürgens-Wemheuer, Wiebke, Arne Wrede, and Walter Schulz-Schaeffer. 2021. "Defining the Prion Type of Fatal Familial Insomnia" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101293
APA StyleJürgens-Wemheuer, W., Wrede, A., & Schulz-Schaeffer, W. (2021). Defining the Prion Type of Fatal Familial Insomnia. Pathogens, 10(10), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101293






