Influence of N-glycosylation on Expression and Function of Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein gB
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
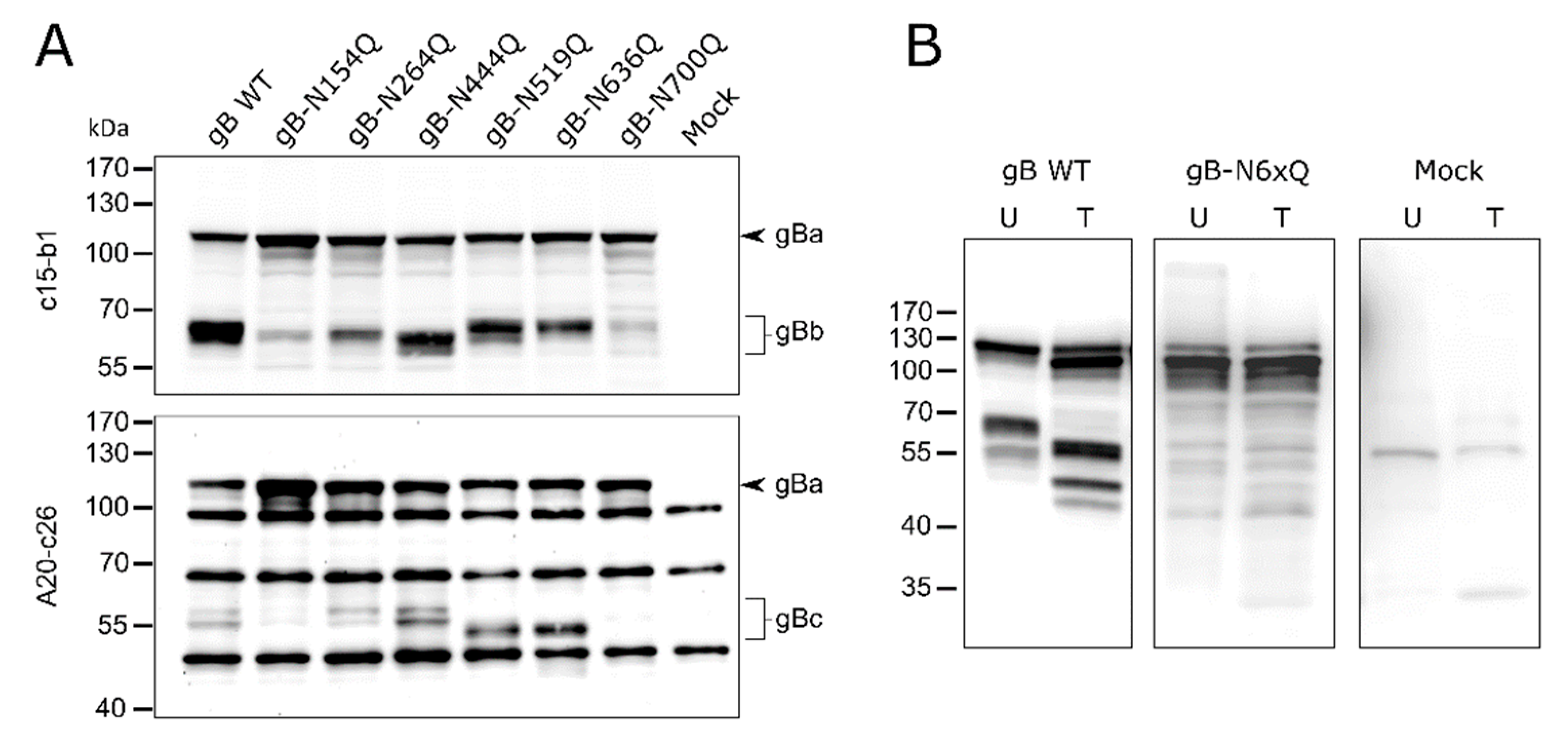
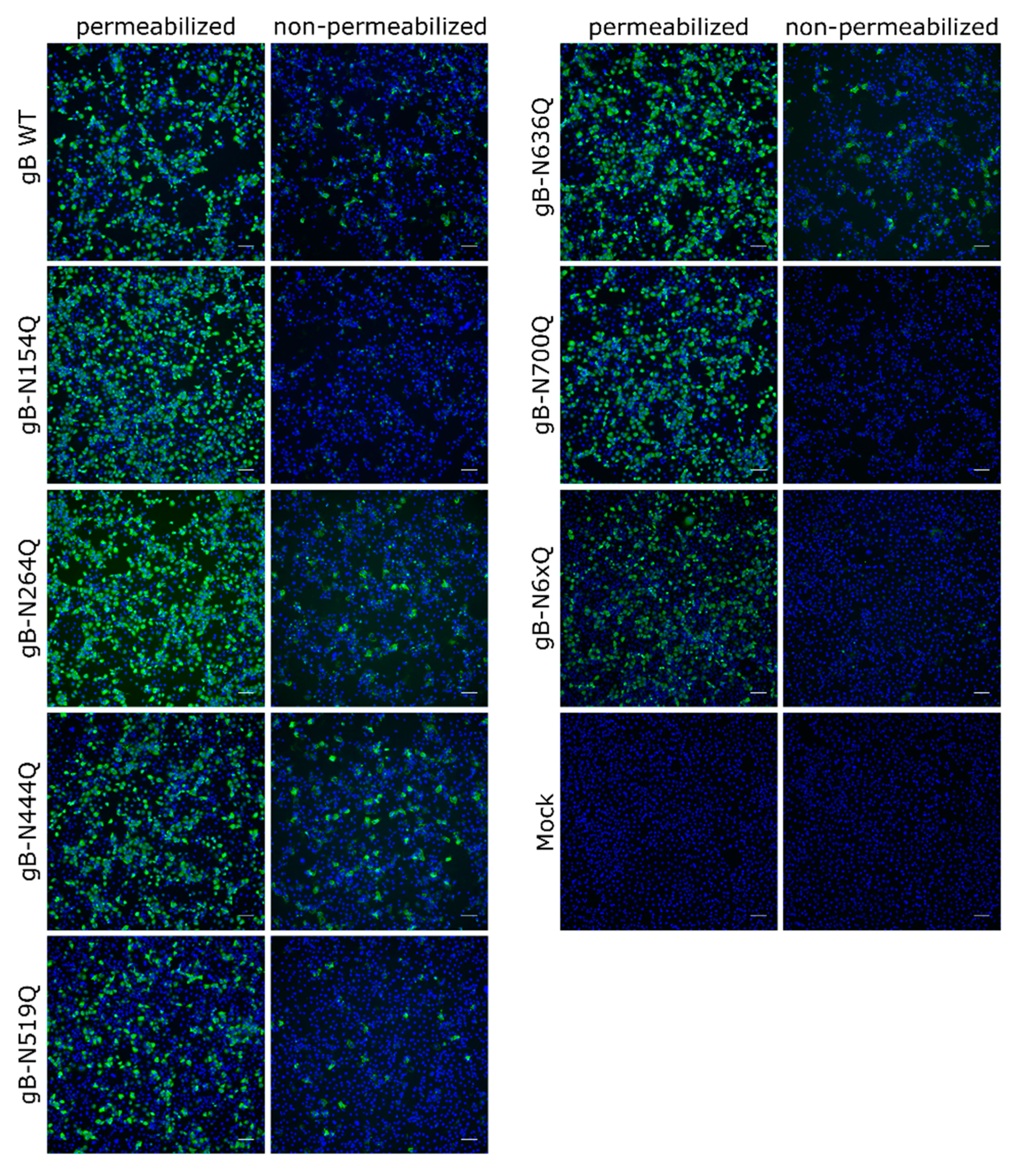
2.1. Effect of N-Glycosylation Site Mutations on gB Processing and Expression
2.2. In Vitro Fusion Activity of gB N-Glycosylation Mutants
2.3. Impact of gB N-Glycosylation Site Mutations on Virus Entry
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Viruses
4.2. Expression Plasmids and Generation of PrV gB N-Glycosylation Mutants
4.3. Western Blot Analyses
4.4. PNGase F Digestion for Glycosylation Analysis
4.5. In Vitro Cell–Cell Fusion Assays
4.6. Trans-Complementation Assay
4.7. Comparative Indirect Immunofluorescence Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davison, A.J. Herpesvirus Systematics. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettenleiter, T.C. Pseudorabies Virus. In Encyclopedia of Virology; Mahy, B.W.J., Van Regenmortel, M.H.V., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 341–351. [Google Scholar]
- Sehl, J.; Teifke, J.P. Comparative Pathology of Pseudorabies in Different Naturally and Experimentally Infected Species-a Review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.C. Viral Membrane Fusion. Virology 2015, 479–480, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallbracht, M.; Backovic, M.; Klupp, B.G.; Rey, F.A.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Common Characteristics and Unique Features: A Comparison of the Fusion Machinery of the Alphaherpesviruses Pseudorabies Virus and Herpes Simplex Virus. Adv. Virus Res. 2019, 104, 225–281. [Google Scholar]
- Spear, P.G.; Longnecker, R. Herpesvirus Entry: An Update. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10179–10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.A.; Jackson, J.O.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. Fusing Structure and Function: A Structural View of the Herpesvirus Entry Machinery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummenacher, C.; Carfi, A.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Entry of Herpesviruses into Cells: The Enigma Variations. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 790, 178–195. [Google Scholar]
- Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Cascade of Events Governing Cell-Cell Fusion Induced by Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoproteins Gd, Gh/Gl, and Gb. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12292–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasiu, D.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Cairns, T.M.; Reilly, B.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Bimolecular Complementation Reveals That Glycoproteins Gb and Gh/Gl of Herpes Simplex Virus Interact with Each Other During Cell Fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18718–18723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampfer, S.D.; Heldwein, E.E. Stuck in the Middle: Structural Insights into the Role of the Gh/Gl Heterodimer in Herpesvirus Entry. Curr. Opin Virol. 2013, 3, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraghty, R.J.; Krummenacher, C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Spear, P.G. Entry of Alphaherpesviruses Mediated by Poliovirus Receptor-Related Protein 1 and Poliovirus Receptor. Science 1998, 280, 1618–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.I.; Warner, M.S.; Lum, B.J.; Spear, P.G. Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Entry into Cells Mediated by a Novel Member of the Tnf/Ngf Receptor Family. Cell 1996, 87, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, T.M.; Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Lou, H.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Ditto, N.T.; Bruun, B.; Browne, H.; Bennett, L.; Wu, C.; et al. Localization of the Interaction Site of Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoprotein D (Gd) on the Membrane Fusion Regulator, Gh/Gl. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00983-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, R.J.; Atanasiu, D.; Cairns, T.M.; Gallagher, J.R.; Krummenacher, C.; Cohen, G.H. Herpes Virus Fusion and Entry: A Story with Many Characters. Viruses 2012, 4, 800–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasiu, D.; Whitbeck, J.C.; de Leon, M.P.; Lou, H.; Hannah, B.P.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Bimolecular Complementation Defines Functional Regions of Herpes Simplex Virus Gb That Are Involved with Gh/Gl as a Necessary Step Leading to Cell Fusion. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3825–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalin, H.B.; Heldwein, E.E. Interplay between the Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Gb Cytodomain and the Gh Cytotail During Cell-Cell Fusion. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12262–12272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallbracht, M.; Brun, D.; Tassinari, M.; Vaney, M.C.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Guardado-Calvo, P.; Haouz, A.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Rey, F.A.; et al. Structure-Function Dissection of the Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein B Fusion Loops. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01203-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, F.; Hu, X.; Tan, F.; Qi, J.; Peng, R.; Wang, M.; Chai, Y.; Hao, L.; Deng, J.; et al. Two Classes of Protective Antibodies against Pseudorabies Virus Variant Glycoprotein B: Implications for Vaccine Design. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldwein, E.E.; Lou, H.; Bender, F.C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Harrison, S.C. Crystal Structure of Glycoprotein B from Herpes Simplex Virus 1. Science 2006, 313, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.L.; Xing, Y.; Chen, D.H.; Roh, S.H.; Pintilie, G.D.; Bushnell, D.A.; Sommer, M.H.; Yang, E.; Carfi, A.; Chiu, W.; et al. A Glycoprotein B-Neutralizing Antibody Structure at 2.8 a Uncovers a Critical Domain for Herpesvirus Fusion Initiation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backovic, M.; Jardetzky, T.S. Class Iii Viral Membrane Fusion Proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 714, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontana, J.; Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Gallagher, J.R.; Cox, R.G.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Brown, L.M.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. The Fusion Loops of the Initial Prefusion Conformation of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Fusion Protein Point toward the Membrane. MBio 2017, 8, e01268-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, B.; Prazak, V.; Vasishtan, D.; Jefferys, E.E.; Hernandez-Duran, A.; Vallbracht, M.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Backovic, M.; Rey, F.A.; et al. The Prefusion Structure of Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoprotein B. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shivakoti, S.; Atanasov, I.; Tao, C.L.; Hui, W.H.; Zhou, K.; Yu, X.; Li, W.; Luo, M.; et al. Different Functional States of Fusion Protein Gb Revealed on Human Cytomegalovirus by Cryo Electron Tomography with Volta Phase Plate. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. Swiss-Model: Homology Modelling of Protein Structures and Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. Ucsf Chimerax: Meeting Modern Challenges in Visualization and Analysis. Protein. Sci. 2018, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Bowden, T.A.; Wilson, I.A.; Crispin, M. Exploitation of Glycosylation in Enveloped Virus Pathobiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 1480–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Hu, K.; He, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X.; Du, T.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q. Contribution of N-Linked Glycans on Hsv-2 Gb to Cell-Cell Fusion and Viral Entry. Virology 2015, 483, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallbracht, M.; Rehwaldt, S.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Fuchs, W. Functional Role of N-Linked Glycosylation in Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein Gh. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00084-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornfeld, R.; Kornfeld, S. Assembly of Asparagine-Linked Oligosaccharides. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1985, 54, 631–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helenius, A.; Aebi, M. Roles of N-Linked Glycans in the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 1019–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.S.; Ohshima, N.; Stanfield, R.L.; Yu, W.; Iba, Y.; Okuno, Y.; Kurosawa, Y.; Wilson, I.A. Receptor Mimicry by Antibody F045-092 Facilitates Universal Binding to the H3 Subtype of Influenza Virus. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Suzuki, Y. Evidence for N-Glycan Shielding of Antigenic Sites During Evolution of Human Influenza a Virus Hemagglutinin. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3446–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, O.C.; Montgomery, D.; Ito, K.; Woods, R.J. Analysis of the Sars-Cov-2 Spike Protein Glycan Shield Reveals Implications for Immune Recognition. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Allen, J.D.; Wrapp, D.; McLellan, J.S.; Crispin, M. Site-Specific Glycan Analysis of the Sars-Cov-2 Spike. Science 2020, 369, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, A.C.; Tortorici, M.A.; Frenz, B.; Snijder, J.; Li, W.; Rey, F.A.; DiMaio, F.; Bosch, B.J.; Veesler, D. Glycan Shield and Epitope Masking of a Coronavirus Spike Protein Observed by Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Tortorici, M.A.; Snijder, J.; Yoshioka, C.; Walls, A.C.; Li, W.; McGuire, A.T.; Rey, F.A.; Bosch, B.J.; Veesler, D. Glycan Shield and Fusion Activation of a Deltacoronavirus Spike Glycoprotein Fine-Tuned for Enteric Infections. J. Virol. 2018, 92, JVI.01628-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Frabutt, D.A.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Hu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zheng, S.; Xiang, S.H.; et al. Mechanistic Understanding of N-Glycosylation in Ebola Virus Glycoprotein Maturation and Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 5860–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panico, M.; Bouche, L.; Binet, D.; O’Connor, M.J.; Rahman, D.; Pang, P.C.; Canis, K.; North, S.J.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Chertova, E.; et al. Mapping the Complete Glycoproteome of Virion-Derived Hiv-1 Gp120 Provides Insights into Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Binding. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Pauthner, M.; Andrabi, R.; Rantalainen, K.; Berndsen, Z.; Diedrich, J.K.; Menis, S.; Sok, D.; Bastidas, R.; Park, S.R.; et al. Differential Processing of Hiv Envelope Glycans on the Virus and Soluble Recombinant Trimer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes-Garfias, C.R.; Shan, C.; Luo, H.; Muruato, A.E.; Medeiros, D.B.A.; Mays, E.; Xie, X.; Zou, J.; Roundy, C.M.; Wakamiya, M.; et al. Functional Analysis of Glycosylation of Zika Virus Envelope Protein. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondotte, J.A.; Lozach, P.Y.; Amara, A.; Gamarnik, A.V. Essential Role of Dengue Virus Envelope Protein N Glycosylation at Asparagine-67 During Viral Propagation. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7136–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallbracht, M.; Schröter, C.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Transient Transfection-Based Fusion Assay for Viral Proteins. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whealy, M.E.; Robbins, A.K.; Enquist, L.W. The Export Pathway of the Pseudorabies Virus Gb Homolog Gii Involves Oligomer Formation in the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Protease Processing in the Golgi Apparatus. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfer, U.; Kruft, V.; Sawitzky, D.; Hampl, H.; Wittmann-Liebold, B.; Habermehl, K.O. Processing of Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein Gii. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3122–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixdorf, R.; Klupp, B.G.; Karger, A.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Effects of Truncation of the Carboxy Terminus of Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein B on Infectivity. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 7137–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, M.; Granzow, H.; Fuchs, W.; Klupp, B.G.; Mundt, E.; Karger, A.; Mettenleiter, T.C. The Pseudorabies Virus Ul11 Protein Is a Virion Component Involved in Secondary Envelopment in the Cytoplasm. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5339–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdonaite, I.; Wandall, H.H. Global Aspects of Viral Glycosylation. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K. Proteolytic Cleavage of Glycoprotein B Is Dispensable for in Vitro Replication, but Required for Syncytium Formation of Pseudorabies Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Blissard, G.W. Functional Analysis of the Autographa Californica Multiple Nucleopolyhedrovirus Gp64 Terminal Fusion Loops and Interactions with Membranes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9617–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strive, T.; Borst, E.; Messerle, M.; Radsak, K. Proteolytic Processing of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein B Is Dispensable for Viral Growth in Culture. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Grantham, M.L.; Smith, M.S.; Anderson, E.S.; Cardelli, J.A.; Muggeridge, M.I. Truncation of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Glycoprotein B Increases Its Cell Surface Expression and Activity in Cell-Cell Fusion, but These Properties Are Unrelated. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9271–9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mettenleiter, T.C.; Spear, P.G. Glycoprotein Gb (Gii) of Pseudorabies Virus Can Functionally Substitute for Glycoprotein Gb in Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, S.W.; Backovic, M.; Klupp, B.G.; Rey, F.A.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Fuchs, W. Functional Characterization of Glycoprotein H Chimeras Composed of Conserved Domains of the Pseudorabies Virus and Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Homologs. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, P.; Schachter, H.; Taniguchi, N. N-Glycans. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Cold Spring Harbor: Suffolk County, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bieberich, E. Synthesis, Processing, and Function of N-Glycans in N-Glycoproteins. Adv. Neurobiol. 2014, 9, 47–70. [Google Scholar]
- Berndsen, Z.T.; Chakraborty, S.; Wang, X.; Cottrell, C.A.; Torres, J.L.; Diedrich, J.K.; Lopez, C.A.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; van Gils, M.J.; Paulson, J.C.; et al. Visualization of the Hiv-1 Env Glycan Shield across Scales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28014–28025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodora, D.L.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Influence of Asparagine-Linked Oligosaccharides on Antigenicity, Processing, and Cell Surface Expression of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Glycoprotein D. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 5184–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodora, D.L.; Cohen, G.H.; Muggeridge, M.I.; Eisenberg, R.J. Absence of Asparagine-Linked Oligosaccharides from Glycoprotein D of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Results in a Structurally Altered but Biologically Active Protein. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4424–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodora, D.L.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Characterization of a Recombinant Herpes Simplex Virus Which Expresses a Glycoprotein D Lacking Asparagine-Linked Oligosaccharides. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4432–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.S.; Vatter, A.E. A Comparison of Herpes Simplex and Pseudorabies Viruses. Virology 1959, 7, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klupp, B.G.; Nixdorf, R.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein M Inhibits Membrane Fusion. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6760–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpara, M.L.; Tafuri, Y.R.; Parsons, L.; Shamim, S.R.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Legendre, M.; Enquist, L.W. A Wide Extent of Inter-Strain Diversity in Virulent and Vaccine Strains of Alphaherpesviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettenleiter, T.C. Glycoprotein Giii Deletion Mutants of Pseudorabies Virus Are Impaired in Virus Entry. Virology 1989, 171, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Name | Sequence (5′➔3′) |
|---|---|
| gB Ka N154Q F | CTCGCAGGGGCGCCAGTTCACGGAGGGG |
| gB Ka N264Q F | CGGCTGGCACACCACCCAGGACACCTACACC |
| gB Ka N444Q F | CGGCGGCGCTACCAGAACACGCACGTGCTGG |
| gB Ka N519Q F | CGCCGGCCGTCCAGGGCACGGGGCACC |
| gB Ka N636Q F | CACCTTCGAGCACCAGGGCACGGGCGTG |
| gB Ka N700Q F | CGCGGGTGACCCTGCAGCTGACGCTGCTGG |
| 130 | CGTGCCCGTCCCCGTGCAGGAGATC |
| 134 | CCATCTACCGGCGGCGCTACAACAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vallbracht, M.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Influence of N-glycosylation on Expression and Function of Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein gB. Pathogens 2021, 10, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010061
Vallbracht M, Klupp BG, Mettenleiter TC. Influence of N-glycosylation on Expression and Function of Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein gB. Pathogens. 2021; 10(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010061
Chicago/Turabian StyleVallbracht, Melina, Barbara G. Klupp, and Thomas C. Mettenleiter. 2021. "Influence of N-glycosylation on Expression and Function of Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein gB" Pathogens 10, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010061
APA StyleVallbracht, M., Klupp, B. G., & Mettenleiter, T. C. (2021). Influence of N-glycosylation on Expression and Function of Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein gB. Pathogens, 10(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010061






