1. Introduction
There is a critical mass of international evidence reporting on the growing rates of access, use and adoption of smartphones, mobile applications (“apps”), social media, and wearable devices by young people (
Anderson and Jiang 2018;
Swist et al. 2015;
Wartella et al. 2016). In the UK, for example, young people aged 12–15 spend 21 h per week online, where 83% own a smartphone, and 74% are reported to be active users of social media (
Ofcom 2017). The significance of these technologies in young people’s lives suggests that they are likely to play a highly influential role in the development of young people’s healthy lifestyle behaviors (
Fullagar et al. 2017;
Patton et al. 2016). Yet, there are few robust empirical accounts on young people’s engagement with social media, apps, and wearable devices in the areas of physical activity, diet/nutrition, and body image (
Hausmann et al. 2017;
Holmberg et al. 2016). Despite the breadth of information and devices available (
Millington 2017), we know very little about how social media, apps, and wearable health devices support or hinder young people’s physical activity, diet/nutrition, and body image behaviors (
Hausmann et al. 2017;
Holmberg et al. 2016). As a result, adults tend to be only acutely aware of the availability, importance, and potential health-related impacts of digital health technologies, while having insufficient knowledge or understanding to be able to support young people to use digital health technologies responsibly and effectively (
Third et al. 2017). Furthermore, there is little guidance from research or policy, across international contexts (
Shaw et al. 2015;
Third et al. 2017). This means that many young people may be unnecessarily exposed to risks, and there is little understanding of how social media, apps, and wearable devices can be used as positive health promotion tools.
This paper reports on
young people’s perspectives and experiences of engaging with and using health-related social media, apps, and wearable devices, and how young people perceive that these technologies influence their knowledge and behaviors in the areas of physical activity, diet/nutrition, and body image. The paper synthesizes findings from three separate projects that took place in the UK and that involved over 1600 young people. Grounded in knowledge translation (see
Holt et al. 2017), the paper is an important and initial step in terms of understanding the overall role and influence of digital health technologies in young people’s lives, particularly from young people’s perspectives, and from a large data set. The original data is reported elsewhere (see
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming;
Goodyear et al. 2018a,
2018b,
2018c,
2017;
Kerner and Goodyear 2017), so the purpose of this paper is to add new insights by looking across the three datasets to identify new insights that can help to inform policy and practice and generate further questions for research. The paper is therefore useful for those who have an interest in better understanding, engaging with, and supporting young people’s health and wellbeing in a digital age.
The paper is organized into two sections. First, an overview of the existing evidence base on young people’s engagement with digital technologies is provided. In this section, findings are also summarized from three separate projects that took place in the UK and that accumulated over 1600 young people’s perspectives and experiences of health-related social media and health-related apps and devices. In the second section, new guidance and direction for research, policy, and practice are provided that explain how relevant adults (including teachers, parents/guardians, health professionals/practitioners, policy-makers, and researchers) can better understand, engage with, and support young people’s uses of digital health technologies.
2. Young People and Digital Health Technologies
Young people are overwhelming positive about the role of digital technologies in their lives and tend to view digital technology as a central resource for communication, information and entertainment (
Boyd 2014;
Ito et al. 2010;
Third et al. 2014,
2017;
Turkle 2017). Young people are reported to value the specific affordances of accessibility and efficiency, the immediacy of information and interaction, and the ability to access personalized information, that they perceive to be tailored to their individual needs (
Gardner and Davis 2014;
Third et al. 2014). For many young people, smartphones, apps, and social media are situated, embedded, and habitual parts of their daily lives (
Boyd 2014;
Ito et al. 2010;
Turkle 2017). Social media, apps, and portable devices can therefore be summarized as connected spaces for young people, where communication, friendship, play, self-expression, and learning occurs (
Handyside and Ringrose 2017;
Ito et al. 2010;
Maclssac et al. 2018).
Young people’s interest in accessing health-related information from technology and the media is well-established, particularly in fields researching gender, culture, media, and sport and exercise pedagogy (
Armour 2014;
Oliver and Kirk 2016). Certainly, there is an abundance of literature reporting on the profound influence of magazines on the perception of body image (
Oliver and Kirk 2016). Extending passive media (e.g., through magazines, websites, TV), however, social media, apps, and wearable devices are user-generated and participatory spaces where young people can co-produce views and behaviors (
Boyd 2014;
Ito et al. 2010). These are also digital/online spaces where commercial, government, community, and individual contexts overlap (
Freishtat and Sandlin 2010) and where health-related information can be created, shared, and accessed by medical professionals, celebrities, organizations/trusts, governments (
Fullagar et al. 2017;
Rich and Miah 2014,
2017) and, potentially, young people. The breadth of information available is also vast. Alongside the plethora of health information that is shared on social media, there are currently over 160,000 health apps on the major apps stores focused on aspects of wellness, diet, and exercise (
Lupton 2017). In addition, there are numerous wearable health-related devices, such as the Fitbit or the Nike Fuel Band, that can be paired with health-related apps to monitor, track, and record health behaviors. Thus, while the specific health-related information that is available (e.g., images that related to body image) may appear to be similar between passive and contemporary technologies, the medium differs. Social media, apps, and wearable devices alter the types and quantities of health-related information that is accessible, and they provide opportunities for young people to create health-related content in highly visible and often very public spaces (
Maclssac et al. 2018;
Walsh 2017).
To date, most empirical evidence has predominantly focused on the quality/validity of health apps/devices (see
Kerner and Goodyear 2017), the types of digital platforms young people use, and/or the time young people spend on digital devices or social media (
RPSH 2017;
Ofcom 2017;
Shaw et al. 2015). Evidence has also been limited to one-off short-duration intervention studies, analysis of parent/guardian and teacher perspectives, and/or evidence from survey data or observational methods (
James 2014;
Mascheroni et al. 2014;
Wartella et al. 2016). Yet the existing evidence-base currently neglects the very dynamic and participatory ways in which young people use digital technologies (see
Boyd 2014). It is also evident that the use of digital health technologies in clinical and educational settings tend to only have limited impacts on young people’s health-related knowledge and behaviors (
Kerner and Goodyear 2017).
Despite limited evidence, there is a tendency in research and policy to be either overtly positive or overtly negative. On the one hand, digital technologies are increasingly being promoted as cost-effective preventative solutions to rising levels of obesity, sedentary behavior and associated non-communicable diseases (see
Rich and Miah 2017). On the other hand, there have been strong calls to limit, control, or manage young people’s uses of social media and apps (
Boyd 2014;
RPSH 2017). For example, there is an abundant literature reporting on the negative impacts of social media, in areas including reduced psychological and physical health due to sedentary lifestyle, loss of sleep and cognitive impairment; risks for mental health, such as anxiety, stress and body dissatisfaction; and impact on cognitions such as negative self-perception, bullying, and social isolation (
Shaw et al. 2015). There is, therefore, a lack of clear direction and guidance for relevant adults on how to support young people’s uses of digital health technologies. The risk of this gap in research and policy is that we continue to view digital health technologies either in terms of the “solution” or as quite deterministic resources in young people’s lives, where young people’s agency and actions are seldom taken into account (
Goodyear et al. 2017).
In order to better frame and shape the use of digital health technologies by young people, and to offer support that will be effective, new insights are required from the perspectives of young people about how they engage with and navigate digital health technologies. This paper offers new insights into the complex relationship between young people and digital health technologies by drawing conclusions from research that engaged with young people’s perspectives and sought to better understand young people’s experiences of health-related social media, apps, and wearable devices.
2.1. Young People’s Perspectives and Experiences of Digital Health Technologies
An overview is now provided on three separate projects that focused on young people’s perspectives and experiences of health-related social media, apps, and wearable health devices. Project 1 focused on young people’s engagement with health-related social media. Project 2 focused on young people’s experiences of using health-related apps and wearable devices in their daily lives. Project 3 focused on how young people used a wearable Fitbit device and the associated Fitbit app during an 8-week intervention. Further conceptual, methodological and empirical detail can be found in: (
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming;
Goodyear et al. 2018a,
2018b,
2018c,
2017;
Kerner and Goodyear 2017).
2.2. An Overview of the Conceptual Frameworks
Across all three projects the guiding conceptual focus was on pedagogy, and how young people’s uses of social media, apps, and wearable devices influenced their health-related knowledge and behaviors in the areas of physical activity, diet/nutrition, and body image. In projects 1 and 2, the initial framing of pedagogy was guided by the concept of public pedagogy. According to
Giroux (
2004) and more recently,
Rich and Miah (
2014,
2017), the concept of public pedagogy can be used to explain learning in informal technologically-mediated spaces by focusing on issues related to embodiment, power, and relationality. Yet, to date, most conceptualizations of public pedagogy have been grounded in passive media contexts (e.g.,
Andersson and Olson 2014). Little work has been done in connecting the concept of public pedagogies to empirical data that is related to contemporary user-driven technologies, such as apps or social media (
Andersson and Olson 2014;
Freishtat and Sandlin 2010), particularly in the context of health and young people.
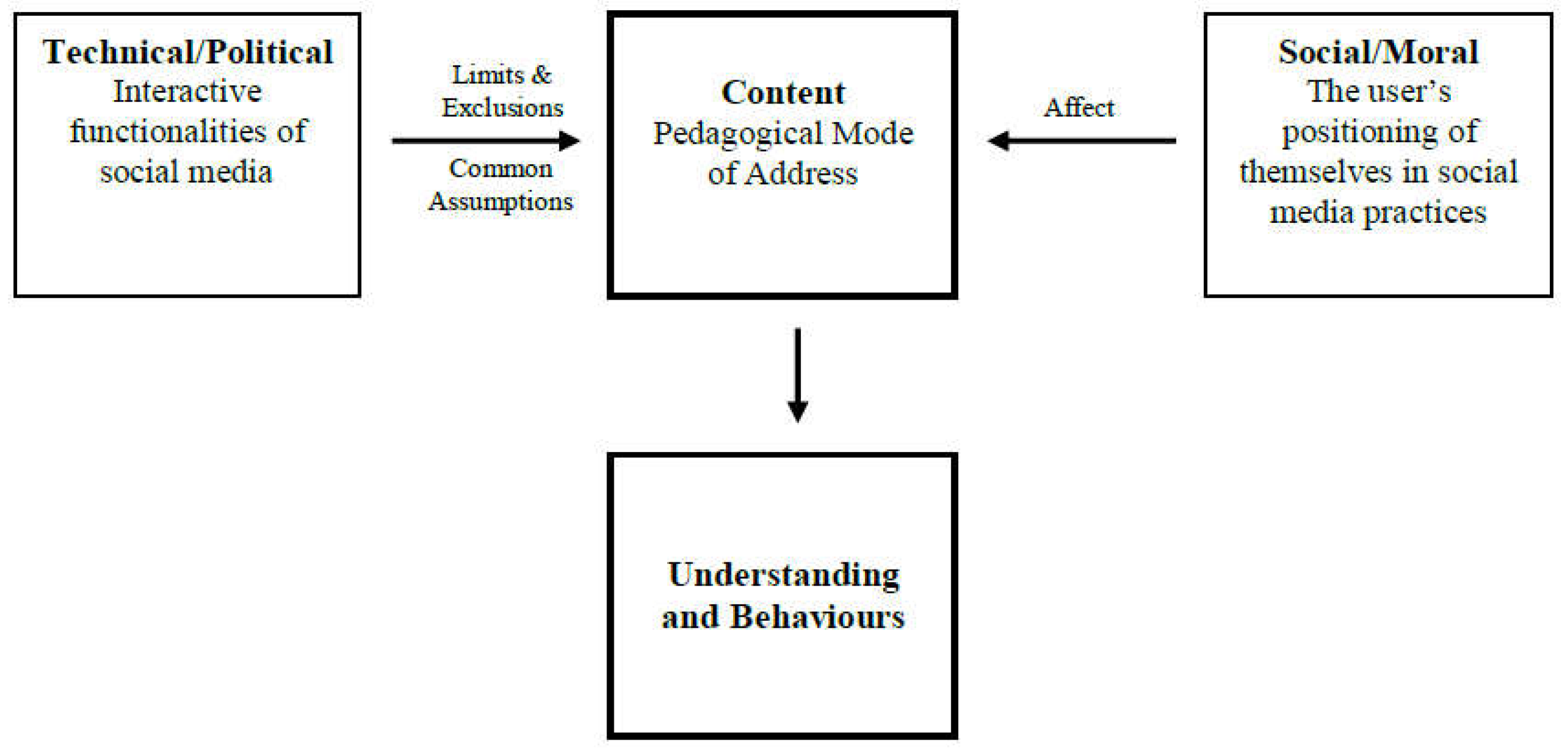
In projects 1 and 2, the analysis of the data led to the development of an extended framing of pedagogy and public pedagogy. In particular, anthropological (see
Miller et al. 2016) and communication theory (see
Lomborg 2017) frameworks directed a focus toward content, and both the dynamic interaction with and generation of content as a key analytical lens. At the same time, elements of
Giroux (
2004) and
Rich and Miah’s (
2014,
2017) conceptualizations of public pedagogy were relevant to the data and the analysis process; in particular, concepts related to embodiment, power, and relationality. The conceptual framework that guided the analysis and was developed from the data in projects 1 and 2 is presented in
Figure 1. This framework focuses on the interplay between the user (i.e., the young person) and the interactive functionalities of digital technologies (e.g., likes, followers) in the construction of health-related content, and how health-related content influences knowledge and behaviors (
Goodyear et al. 2018a).
In project 3, a focus on pedagogy was guided by concepts related to surveillance, self-surveillance, and resistance. These concepts were informed by the work of Foucault (
Foucault [1977] 2008) and his work on power and surveillance. In turn, the concepts of surveillance, self-surveillance, and resistance were applied to the data to interpret how young people engaged with and responded to the disciplinary and regulatory interactive functionalities of the Fitbit device and Fitbit app, such as the ability to monitor, record, and track step count, active minutes, and calorie intake. In addition, motivational constructs from self-determination theory were applied to the analysis of the data to interpret how young people’s uses of the Fitbit device and Fitbit app influenced their motivation for physical activity. In particular, the data analysis focused on concepts related to competence, autonomy, and relatedness. Similar to projects 1 and 2, the combination of Foucouldian and self-determination frameworks sought to examine the dynamic relationship between young people and the interactive functionalities of technology.
2.3. An Overview of the Methods
A participatory and iterative research design was common across the three projects, and was adopted to generate rich, in-depth, and detailed insights into young people’s perspectives and experiences of health-related social media, apps, and wearable devices. In total, 1691 young people aged 13–18 were involved and data collection took place in 12 schools and in 18 classes across the UK. The schools were located in the West Midlands and the South East and North West of England. Of the 12 schools, 3 were private, 4 were state schools, and 5 were academies, of which 2 were faith schools. The schools were located in diverse socio-economic contexts and included students from a range of ethnic backgrounds. Data collection took place in citizenship/PSHE or physical education lessons and had the aim of providing a broad sample of young with a diverse range of health-related needs, interests, and experiences.
A culturally responsive relational and reflexive approach to ethics was adopted across the three projects (
Lahman et al. 2011;
Sparkes and Smith 2014). In applying this approach, a number of steps were followed: (i) cultural differences were valued and recognized in terms of the participants’ age, expertise with digital mediums and differences between their contexts and situations (culturally responsive); (ii) the research aims were balanced with care and concern for young people (relational); (iii) the methods adopted were sensitive to the interactions of self, others, and situations and the researchers were adaptive to situations that emerged during the research process ensuring participant safety, privacy, and dignity, whilst simultaneously seeking to address power imbalances (reflexive) (
Lahman et al. 2011;
Sparkes and Smith 2014). This ethical approach ensured that ethical decision making was contextualized within the digital cultures and contexts inhabited by young people and sought to promote autonomy and agency of the young people involved in the research.
Project 1 aimed to understand the types of health-related information young people accessed and attended to on social media, and the impacts young people reported on their health-related knowledge and behaviors. Data collection involved 1346 young people (age 13–18) from 10 UK schools. Data were initially collected from participatory class activities (n = 236; age 13–15; m = 101, f = 135) and were generated from questionnaires and a digital pinboard using Pinterest. Using the data generated, further data were then generated from 19 focus group elicitation interviews (n = 84; age 13–15; m = 35, f = 49) and a survey (n = 1016; age, 13–16; m = 334; f = 676). Following this, a smaller group of young people (n = 41; age 13–15; m = 19; f = 32) participated in a workshop to analyze the data generated and to create guidance for adults on how their uses of social media should be supported. Data from the workshop were generated from questionnaires (n = 104; m = 40; f = 104) and resources that the young people created (that included, video recorded interviews (n = 2), newspaper articles (n = 4), and movies (n = 4)). Combined, the data collected from class activities, interviews, the survey, and workshops provided an empirically rich data set on the health-related information young people accessed and attended to. The data sets were then analyzed using an adapted content-led pedagogical framework (see
Figure 1,
Goodyear et al. 2018a).
Project 2 aimed to generate evidence on: (i) the types of digital health apps and devices young people use to inform their health-related understandings and behaviors; and (ii) the forms of digital health information young people attend to/ignore and how these choices inform their health-related understandings and behaviors. Data collection involved 245 young people (age 13–18) from 10 UK schools. Data were collected initially from participatory class activities (n = 235; age 13–15; m = 100, f = 135) and data were generated from questionnaires and a small group task that involved young people creating a health app. Using the data generated, further data were then collected from 19 focus group elicitation interviews (n = 83; m = 42, f = 41). Similar to project 1, when combined, the data collected from class activities and interviews provided an empirically rich data set on the types of apps, devices young people use, and the types of information that influence their knowledge and behaviors. The data from class activities and interviews were analyzed using an adapted content-led pedagogical framework (see
Figure 1,
Goodyear et al. 2018a).
Project 3 aimed to understand the motivational influence of the Fitbit device and Fitbit app on young people’s physical activity behaviors, and how these technologies influenced young people’s health-related knowledge and behaviors. The Fitbit device and app were selected on the basis of the popularity of these devices in society at the time of the study. The project involved 100 young people (age 13–14; m = 47; f = 53) wearing a Fitbit device and using the Fitbit app for a period of 8 weeks. Pre- and post-questionnaires were completed by all of the young people in the study to assess their motivation toward physical activity. Nine focus group interviews were also completed at the end of the 8-week period. The quantitative data were analyzed through a repeated measures multivariant analysis and qualitative data were analyzed through a deliberative strategy informed by a Foucouldian framework of surveillance, self-surveillance, and resistance.
A relativist approach was adopted to guide validity across the three projects (
Smith and McGannon 2018). Following this approach, the following traits existed: (i) width through the comprehensiveness of evidence from a wide sample of participants and from diverse contexts, as well multiple data collection methods, (ii) credibility through pre- and post-test and iterative phased designs, where the methods were co-constructed with young people, alongside a deliberative analytical process between the researchers (
Englund 2006); and (iii) coherence in terms of the alignment between theory, research questions, and methods.
2.4. Key Findings
In this section, an overview of the key findings from the three projects is presented in order to generate new insights from existing data. These summative findings were generated from a deliberative analytical strategy (
Englund 2006) that involved comparing and contrasting the key data themes from each project. Key points of insight were identified from each project data set and were then grouped into categories that shared common characteristics. The grouping of data into categories took place over a number of iterations and to a point of saturation in agreement between the authors. As a result, five overarching key findings were identified and are discussed in the following sub-sections. It should be noted that it is not assumed that the key findings developed from this analytical process are the only plausible reading of the data from the three projects. The analytical process adopted in this paper sought to ensure a level of rigor and validity, and in a way that would ensure that the key findings presented could stand up to interrogation (
Smith and McGannon 2018). A level of bias is also acknowledged in the analytical process, given that the data has been analyzed within each individual project and then re-analyzed by the same authors.
2.4.1. Young People Access Different Types of Health-Related Information from a Range of “Trusted” and Unregulated Sources
Evidence from the three projects clearly showed that young people are exposed to a range of health-related information on social media, apps, and wearable health devices, and in the areas of physical activity, diet/nutrition, and body image. The common types of information young people see on social media and health-related apps are related to physical activity workouts, diet/nutritional supplements, and/or body changes or transformations. For example, young people see images and/or videos on social media related to 30-day body transformations that are a result of using a particular supplement, engaging with a specific diet, and/or are the result of a physical activity workout schedule (
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming;
Goodyear et al. 2018a).
Across social media, apps, and wearable devices, the source of the information varies. On social media, young people access health-related information that is created, shared, and promoted by governments, commercial brands, celebrities, sports men and women, health organizations/trusts, and their peers or other young people of a similar age. For example, young people have seen and engaged with promotional physical activity videos shared by health organisations/trusts, such as ThisGirlCan; images of celebrities working out in the gym, such as the Kardashians; images of the food young people their age are eating; and/or diet drinks promoted by commercial brands, such as FitTea (
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming;
Goodyear et al. 2018a). In terms of health-related apps, young people tend to engage with and use information that is shared via established apps on the two major app stores. For example, young people access information related to calorie and water intake, diet recipes, workouts/exercises, sleep, and the menstrual cycle from apps such as MyFitnessPal, 7-min Workout, Clue, and Apple Health (
Goodyear et al. 2018c). By using wearable health devices and their associated health-related apps, such as Fitbits, young people access information that is more personalized to their individual health-related behaviors, such as step count, calorie intake, and/or the number of active minutes they have achieved per day (
Goodyear et al. 2017,
2018c;
Kerner and Goodyear 2017).
Evidence across the three projects therefore highlights that young people are actively using digital health technologies and they are, in turn, exposed to a range of different types of health-related information. There is evidence that young people access health-related information from regulated or “trusted sources” (e.g., governments or health trusts/organizations) and unregulated sources (e.g., peers or celebrities).
2.4.2. Young People Reported That Their Uses of Digital Health Technologies Influenced Their Physical and Mental Health in Both Potentially Positive and Negative Ways
Young people reported that their engagement with health-related social media, apps, and wearable devices can influence young people to alter/change their physical activity behaviors and diet/nutritional behaviors, and the perceptions of their body image. Variance existed, however, in the ways in which young people reported that their uses of digital health technologies influenced their knowledge and behaviors.
It was apparent in the data sets that young people valued the accessibility of health-related information and perceived that they could access information that was relevant and/or personalized to their individual health-related needs (
Goodyear et al. 2018a,
2018c). In particular, the young people reported on the benefits of being able to access information related to diets or workouts that provided them with short duration and simple solutions to become “healthier” (
Goodyear et al. 2018a,
2018c). This type of health-related information was reported to meet their lifestyle needs by overcoming school and homework pressures that often constrained the time they had to engage with physical activity (
Goodyear et al. 2018a). The health-related information accessed by young people was also reported to be motivational. The young people could access images and videos of real people engaging with exercise and, for some, this provided a level of inspiration to engage with physical activity (
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming). Motivational impacts were also evident in young people’s uses of wearable devices, where there was evidence to suggest that peer-based competitions using the Fitbit device and Fitbit app motivated some young people to increase their levels of physical activity (
Goodyear et al. 2017;
Kerner and Goodyear 2017).
Data from the three projects provided evidence that the ways in which young people used social media, apps, and wearable health devices could lead to potentially negative and harmful impacts on health-related knowledge and behaviors. There was an overwhelming sense that the health-related information that was shared by young people their age or of a similar age promoted negative feelings about their bodies. On social media, peer selfies influenced young people to compare their bodies to others and were reported to create a level of peer-pressure to conform to a particular body type (
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming;
Goodyear et al. 2018a). By using a Fitbit, some of the young people reported on the negative effects of peer-comparison that occurred during peer-based step competitions. In particular, peer-comparison led to a reduced desire to engage with physical activity (
Goodyear et al. 2017;
Kerner and Goodyear 2017).
The potential for young people’s uses of digital health technologies to lead to potential harmful impacts on their health was furthermore evident from the narrow and normative understandings about health that the young people communicated. For example, some young people were reported to use different types of diet teas that were promoted to them as ways of developing a skinny, toned, or slim thick appearances (
Goodyear et al. 2018a). Some young people also associated health with not being fat and being slim, and used the Fitbit device and Fitbit app as a way of regulating their calorie intake and exercise behaviors to conform to these normative understandings of health (
Goodyear et al. 2017). Young people, therefore, tended to associate health with body image, and social media, apps, and wearable devices were used by young people to change/alter their body image in ways that they perceived could help them to become “healthier”.
The evidence suggests that digital health technologies are very powerful mediums that can change and alter young people’s health-related understandings and behaviors. Young people reported that the influences of social media, apps, and wearable devices are not always negative and not all young people are exposed to risk. There is evidence from across the three projects on the positive health-related outcomes young people experience from social media, apps, and wearable devices, and these need to be acknowledged alongside risk-related impacts that tended to be associated with peer-comparison and body image.
2.4.3. Young People Are Critical Users and Generators of Digital Health Technologies, and Yet They Are Vulnerable at the Same Time
The data indicated that young people are critical users and generators of digital health technologies, and that they are able to assess the relevance of health-related information to their personal and individual health-related needs. At the same time, there was evidence that some young people found themselves in a position of vulnerability and chose to act on health-related information that could result in potentially negative impacts.
Many of the young people reported that they do not act on or use all of the health-related information that they see on social media, apps, and wearable devices. On social media, it was reported by the young people that they swipe past most of the information that they see related to physical activity, diet/nutrition, and/or body image (
Goodyear et al. 2018a). Moreover, while young people may download or purchase health-related apps and wearable devices, there was evidence to suggest that these are often disregarded after an initial assessment of the relevance of the information, or as a result of a short period of using the app or device (
Goodyear et al. 2017,
2018c). It was reported that the decision about whether to engage with health-related information was often related to young people’s critical judgements about whether the information was tailored to their individual needs and/or their individual status of health. For example, many of the young people were critically aware that most of the information available on social media and via health-related apps was targeted and designed for adult populations (
Goodyear et al. 2018a,
2018c). In addition, young people were critically aware that differences existed between individuals in how they respond to exercises and diets. Some of the young people were critical of short-duration exercises or diet schedules, reporting that they were not tailored to their body weight, size, or exercise capabilities and thus would have limited and/or sustained impact (
Goodyear et al. 2018a,
2018c). Many young people, therefore, critically assess the relevance of health-related information to their bodies and status of health, and only choose to act on information if it is perceived to be relevant.
There was clear evidence that some young people find themselves in a position of vulnerability, where they are influenced to act on health-related information from social media, apps, and wearable devices that is potentially harmful for their health. For many young people, their ability to think and act in critical ways appeared to be influenced by their peers, their prior knowledge about health, and the health-related practices they experience in schools and/or from their family members. For example, the ways in which health-related information is mobilized and shared through peer networks had a powerful influence on the ways in which young people perceive the information to be credible and useful to their health (
Goodyear et al. 2018a,
2018c). It was also apparent that young people’s growing interest in health-related social media, apps, and wearable devices occurred alongside a growing level of curiosity about their bodies and their health. If young people had particular body image concerns or desires, they turned to digital health technologies for health-related information (
Goodyear et al. 2017,
2018a,
2018c). The problematic issue is when young people find, select, and use information that meets their personal needs, but may be harmful for their health. For example, young people reported that they used and engaged with workouts on social media that were designed for bodybuilders due to a desire to get more “buff” (
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming).
Young people, therefore, engage with health-related social media, apps, and wearable devices in different ways. Young people are able to make critical judgements about the relevance of information to their bodies and their health. Yet, young people’s critical skills vary, and such variance appears to be influenced by practices that exist on digital technologies (such as peer networks) and factors such as prior knowledge and/or school and family practices related to health.
2.4.4. Young People’s Health-Related Knowledge and Behaviours Are Influenced by Content
Across the three projects, there is evidence that young people’s knowledge and behaviors are influenced by different forms of content. Content differs to information as it is representative of something that individuals do in digital/online spaces (
Miller et al. 2016), where content is constructed at the interplay between: (i) the user and (ii) the interactive functionalities of the technology (
Figure 1,
Goodyear et al. 2018a). For example, a distinction between information and content can be understood between an image that presents information of a 30-day workout versus suggested or recommended content. The difference between the image-based information and suggested or recommended content is that suggested or recommended content was actively shaped by the involvement of the young person. Suggested or recommended content refers to how a young person’s initial search for information (i.e., the user), such as the 30-day workout, results in a vast amount of partially related material being promoted to a young person’s account via algorithms (interactive functionalities) (
Goodyear et al. 2018a). Content is therefore shaped by the young person’s uses of technology and the interactive functions of the technology.
By exploring young people’s engagement with health-related social media, five forms of content were identified: automatically sourced content, that includes pre-selected content that is promoted to young people via their peer networks; suggested or recommended content, as outlined above; peer content, that describes the influence of selfies and images or videos created and shared by young people; likes, that operate as a form of endorsement and affirmation; and reputable content, that refers to how health-related information is framed to young people through particular social media accounts (
Goodyear et al. 2018a,
2018b). These five forms of content were also apparent in young people’s uses of health-related apps and wearable devices. There was evidence of similarity between automatically sourced content, suggested content, and peer content (
Goodyear et al. 2017,
2018c).
The ways in which content influenced young people’s health-related knowledge and behaviors occurred through the same user and interactive features that lead to the construction of content (
Goodyear et al. 2018a). In young people’s uses of social media, content appeared to be influential because it operated through affect, promoted common sense assumptions, and limited and/or excluded young people’s access to a wide range of health-related information. For example, in the case of suggested or recommended content, young people’s knowledge and understandings were influenced by affect (a young person’s desire to search for information) and the limits and exclusions of information (algorithms).
Affect and prior knowledge of health appeared to be key factors that could explain the reasons why different young people respond in different ways to health-related information. For example, while one young person may search for information on social media due to body image concerns, another young person may not be interested in this content and/or may draw on their prior knowledge to determine whether the partially promoted material is useful to their individual needs (
Goodyear et al. 2018a,
2018c). There was also evidence of this critical variance in terms of affect and prior knowledge in the ways in which young people used and engaged with the Fitbit device and Fitbit app. While some young people used Fitbits to meet normative standards of health, others drew on their prior knowledge to critique the health-related information that was available. For example, some young people reported that the Fitbit device was incapable of measuring their health as it did not capture data that related to all of their physical activity behaviors, such as their engagement with swimming (
Goodyear et al. 2017).
An examination into content can explain how young people’s knowledge and behaviors are influenced by their varying uses and engagement with health-related social media, apps, and wearable devices. Content acknowledges the reflexive relationship between the young person and the technology, and shows how young people are actively involved in the ways in which digital health technologies shape their health-related knowledge and behaviors.
2.4.5. Young People Are Able to Offer Relevant Adults Guidance on the Types of Support They Require to Use Digital Health Technologies Safely and Effectively
Schools, teachers, and parents/guardians are important to young people for their potential to provide support for using digital health technologies. Yet the current support that is reported to be available to young people in schools and by parents/guardians varies, and in many respects, was suggested by young people to require improvement.
There was an overwhelming sense that young people perceive adults to have insufficient knowledge and understanding about the ways in which young people use and navigate social media, apps, and wearable devices. It was reported that schools/teachers, parents/guardians, and the media often fail to understand or adequately address the health-related pressures that young people experience from digital health technologies (
Goodyear et al. 2017,
2018b). For example, young people tend to perceive that their uses of social media are misinterpreted by teachers and parents/guardians (
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming;
Goodyear et al. 2018b). School-based programs focused on cyberbullying were also reported to be ineffective, as they do not address wider pressures that young people experience on a more frequent and daily basis, such as peer-pressure and the associated effects of body dissatisfaction (
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming;
Goodyear et al. 2018b). Young people suggest that adults need to be more understanding of their uses of social media, apps, and wearable devices and begin to offer support in ways that reflect their needs and that does not dismiss social media as a positive health resource in their lives (
Goodyear and Armour, forthcoming;
Goodyear et al. 2018b).
Although young people were generally supportive of receiving guidance from adults, they were also dismissive of teachers attempts to use and incorporate digital health technologies into their physical education lessons. Young people reported that the use of Fitbits had no educational value in the context of schools, and they were highly skeptical of teachers using wearable health devices or apps to monitor their steps and calorie intake (
Goodyear et al. 2017). The young people claimed that their teacher’s role was to support their knowledge and understanding of how to be healthy, and not to record, monitor, or track their health-related behaviors (
Goodyear et al. 2017). If digital health technologies were to be used in schools and in physical education, the young people argued that targets needed to be personalized and based on measures that reflected an individual’s needs and abilities (
Goodyear et al. 2017).
The evidence highlights that young people can provide adults with direction on the types of support that they require to use digital health technologies safely and effectively. The young people point toward a clear need for adults to be more understanding about the ways in which they use social media, apps, and wearable devices, and the ways in which their health-related knowledge and behaviors are influenced. Yet, although young people are interested in digital health technologies, this interest does not always translate to an interest in the use of digital health technologies in formal educational settings. The findings suggest that health-related data, including step count, may be considered by some young people as personal. This suggests there is a need to appreciate that where digital health technologies are used in formal educational settings, young people may be reluctant to share their data. Building this recognition into pedagogical strategies could be an important way to engage some young people in positive health-related educational activities.
3. Discussion
This paper has synthesized the evidence from three projects to identify additional insights into the ways in which young people engage with health-related social media, apps, and wearable devices, and the impacts they report on their health-related knowledge and behaviors. In contrast to most research that has tended to neglect the voices of young people and has, instead, articulated adult’s concerns about the risk-related impacts of digital health technologies (
Boyd 2014;
Mascheroni et al. 2014;
Third et al. 2017), this paper has provided multiple and layered insights from the perspectives and experiences of young people. The findings reveal that social media, apps, and wearable devices are considered by many young people as positive and educational health resources in their lives. There was evidence of a range of health-related benefits, and young people can be understood as critically aware users, consumers, and generators of digital health knowledge. Yet, young people use and experience health-related social media, apps, and wearable devices in different ways, and there was also evidence of health-related risks and the potential for young people’s uses of digital health technologies to result in harmful impacts on their health-related knowledge and behaviors. The potential for risk and opportunity were influenced by a range of personal, social, and contextual factors, and the ways in which health-related content are presented and promoted to young people via digital health technologies. Relevant adults must therefore be more understanding of the positive role of digital health technologies in young people’s lives, without excluding an awareness of the potential for risk-related impacts.
The challenge for relevant adults is to provide support to young people in ways that allow them to maximize the opportunities of digital health technologies, while simultaneously protecting young people from harm. Yet despite the evidence from these three studies and the clear messages for adults, evidence from wide-scale evaluations and systematic reviews consistently identifies that adults lack the knowledge and skills they need to provide support for young people in ways that are relevant and effective (
Livingstone et al. 2018;
Third et al. 2014). There is also limited direction and guidance from research and policy on how adults can support young people to navigate digital health technologies responsibly and effectively (
Shaw et al. 2015;
Third et al. 2017). The remainder of this paper is focused on providing direction and guidance for research, policy, and practice on how relevant adults (including teachers, parents/guardians, health professionals/practitioners, policy-makers and researchers) can better understand and support young people’s engagement with digital health technologies.
The first point of guidance is that policy and practice communities must engage with on-going conversations with young people about digital health technologies. The evidence reported in this paper demonstrated that young people engage with digital/online environments in highly complex and sophisticated ways. It was also apparent that young people enjoyed the levels of autonomy that they currently experience in accessing health information from social media, apps, and wearable devices and the capabilities to access information that they perceive to be relevant to their health-related needs. The ways in which young people navigate and make use of digital health environments can therefore provide new insights into how their behaviors and knowledge are being shaped by digital health technologies and, potentially, how young people are shaping the design, experiences, and uses of digital health technologies. Indeed, young people can provide insight into whether their health-related needs, hopes, and wishes are being fulfilled and the role, or future role, of technology in supporting, hindering, and/or harnessing these needs.
The second point of guidance is that
young people people’s very specific levels and forms of expertise in digital technologies must be recognized and accommodated. It was clear from the three projects that young people are avid users and drivers of this contemporary, participatory, and user driven online culture and, to some extent, they can be understood as highly skilled and knowledgeable about digital health environments. Young people are also likely to remain at the vanguard of technology adoption, where their skills and knowledge of digital/online environments are likely to continue to outpace most of their adult counterparts (
Boyd 2014;
Ito et al. 2010;
Livingstone et al. 2018). Young people, therefore, appear to be best placed to help relevant adults better understand how they use and navigate digital environments. There was also evidence from the young people to suggest that adults who would be seen to recognize and accommodate young people’s expertise would be better-informed about the risks and opportunities of digital health technologies and how to support young people to use these technologies safely and effectively.
The third point of guidance is that in designing educative and health support for young people, it is essential that these forms of support are co-designed and co-constructed with young people. There are currently significant drives in research and policy to harness the use of digital technologies in clinical and educational settings (
Fullagar et al. 2017;
Rich and Miah 2017), and there is evidence of clear enthusiasm by practitioners to use digital technologies in physical activity and health settings (
Casey et al. 2016;
Koekoek and Hilvoorde 2018). Yet, and similar to previous research (
Depper and Howe 2017), the evidence reported on in this paper shows that young people adopt a highly skeptical stance about the use of technology in formal educational settings. At the same time, there was evidence that some of the young people had very normative, narrow, and reductionist understandings of health and used health-related information from unregulated sources, particularly on social media. It is well-established that developing and enhancing young people’s health-related knowledge is something that key adults should be in a position to support, and this includes qualified professionals in schools, such as physical educators (
Armour 2014). By bridging young people’s perspectives on technology integration with relevant adults’ expertise in health education, appropriate, relevant, and effective forms of support for young people could be developed. In practice, inspiration might be taken from a strengths-based curriculum approaches (
McCuaig et al. 2013) and/or activist approaches to working with youth (
Oliver and Kirk 2016). It is clear, however, that further evidence is required on the pedagogical strategies that support young people’s learning about their health-related uses of digital technologies (
Casey et al. 2016,
2017).
The fourth and final point of guidance is that international researchers and policy makers have a responsibility to strengthen the evidence-base on the ways in which young people use and navigate digital health technologies. Similar to
Rich and Miah (
2014,
2017), the evidence reported on in this paper has demonstrated the value of a pedagogically informed approach to interpret how young people’s health-related knowledge and behaviors are influenced by digital health technologies. A focus on pedagogy accommodated young people’s perspectives and experiences of digital health technologies, and offered detailed insights into how and why young people learn within digitally-mediated environments. Furthermore, a pedagogical lens provided understandings into relationality (
Rich and Miah 2014), with the data across three studies showing how young people’s varying needs, contexts, and situations shape the ways in which they engage with digital health technologies and how they report such engagement can influence their knowledge and behaviors. The evidence base on pedagogically driven approaches to interpreting digital health technologies is, however, limited (
Rich and Miah 2017). To date, most research on digital technologies has been dominated by a focus on the technology and how specific affordances affect knowledge and behaviors (
Rich and Miah 2014,
2017). As a result, there is a lack of detailed insights into the complex pedagogical processes that can generate effective learning, how young people’s interactions with technology shape their knowledge and behaviors and, in turn, how these interactions shape how technology is used.
To develop the rigor and robustness of pedagogically informed frameworks, further empirical data is required on the ways in which diverse groups of young people from diverse contexts use and navigate digital health technologies. Across different cultures and contexts, there is evidence to suggest that young people’s uses of technology differs, and the meanings they assign to different forms of content varies (
Miller et al. 2016). Beyond the three projects reported on in this paper, however, there are few robust empirical accounts on the types of health-related information young people find, select, and use from social media, apps, and wearable devices, and how young people use these technologies in a way that influences their health-related knowledge and behaviors (
Hausmann et al. 2017;
Wartella et al. 2016). New empirical evidence would therefore further contribute to understandings about how young people’s uses of digital health technologies influence their knowledge and behaviors, and would contribute to the design of relevant and effective educative forms of support for young people.