Abstract
The concept of Industry 4.0 has considerably altered the way organisations operate and has impacted every aspect of life. Furthermore, the fast-growing trend of information technology (IT) transformation in organisations and huge IT investment by Malaysian government have triggered the significance of IT risk and its related controls. Besides, technology-enabled auditing and IT-oriented audit procedures have become crucial when performing audit tasks in an electronic environment. Although many initiatives are being implemented to improve technology usage, audit technology use among auditors is still low and auditors are not attaining sufficient progress in the use of technology. This implies the current strategies and policies may not effectively support technology implementation. In the same vein, the under-utilisation of technologies was reported due to inadequate governance. Thus, this study intends to investigate the impact of IT governance on audit technology performance. IT governance is a mechanism to stimulate anticipated behavior in the use of technology among the employees of an organisation. Surveys using closed-ended questionnaires were distributed to approximately 309 Malaysia public sector auditors. The results show that IT governance mechanisms such as IT strategy and management support significantly influence the audit technology performance. IT governance does play a significant role in assuring the successful utilisation of audit technology.
1. Introduction
Technological innovation has been playing a significant role in every organisation in recent years. The notion of Industry 4.0 has considerably altered the way organisations operate and this fourth industrial revolution (4IR) has impacted every aspect of life. Earlier industrial revolutions were focusing in improving manufacturing operations (Industry 1.0), mass productions using electrical energy (Industry 2.0) and automation of uniform job functions (Industry 3.0). The main purpose of Industry 4.0 is to attain betterment in term of automation and operational efficiency as well as effectiveness (Ślusarczyk 2018). Basically, 4IR is connected with digitalization within and between people and devices as well as the use of advance technologies in accelerating the efficiency and effectiveness of operations and activities plus gaining autonomous performance in the work process through the use of machines (Paprocki 2016). Interestingly, the concept of Industry 4.0 was developed in 2011 as a government initiative by the German Federal Government in promoting technological innovation to boost the German economy. Finally, Industry 4.0 instigated much attention and become a famous mantra.
In line with the growing attention on the digitalization of work processes particularly involving public sector services, there are growing initiatives by the Malaysian government in ICT-related projects to escalate an effective and efficient public service delivery. Thus, IT-related investments have increased among government agencies and has triggered the significance of IT investment in public service delivery and the expected return from these investments is also an important concern among government agencies and citizens. However, in most of the ICT projects being evaluated, the major issue was system underutilisation in terms of functionality. The audit assessment on e-Project Monitoring II, e-PBT (e-Local Authority), and 1Bestari projects, for example, yielded interesting facts such as, underutilisation of the system functions due to lack of knowledge, lack of training, delayed in project implementation due to the additional scope of work or change requests by users, system specifications were not clearly defined, and databases were not updated due to lack of monitoring from the central agency (NADM 2015).
Importantly, most of the issues were related to inadequate governance measures as stipulated in the circulars. The Malaysian Administrative Modernisation and Management Planning Unit (MAMPU) circular has required all government agencies to have committees to deal with ICT-related issues such as a steering committee, technical committee, and project management team. Nevertheless, in most cases, the agencies do not set up these committees because project owners assumed that the project implementation team is sufficient to manage the projects, and in cases where the committees are set up, their roles are uninformed (NADM 2015). The key purposes associated with technology-related governance are reducing risk, assisting performance achievement, and monitoring the technology-related investments.
As organisations rely on IT to some degree to conduct their business, IT governance (ITG) has gained importance in recent years as a key aspect of governance (Bhattacharjya and Chang 2007). IT governance is important for an organisation to attain its organisation objectives specifically related to IT investment. In order to employ effective IT governance, a set of ITG mechanisms is compulsory (e.g., IT steering committee, IT organisational structure) that are able to boost actions consistent with the organisation’s missions. These ITG mechanisms focus on several technological issues such as the way significant information system (IS) related practices being implemented and the way the strategies are aligned into practices (Weill and Ross 2004). IT transformation can affect the existing governance systems, leading to a reduction in the capacity and capability of IT in a public sector organisation if this transformation ignores the people and assets devoted to the systems (Al-Omari and Barnes 2014). This governance is imperative to warrant the successful implementation of public service delivery to accomplish corporate goals, whereby the decision-making process and monitoring system are aligned with the organisational goals and citizen expectation (Mukhtar and Ali 2011).
2. Motivation of Study
Highly computerised accounting systems have had implications for current audit practices and has led to the necessity of new audit procedures to evaluate control in order to mitigate new business risks (Soral and Jain 2011). The new requirement of audit standards has increased the needs of technology-oriented audit procedures (Masli et al. 2010). As digitalisation gaining more attention in the business, auditors need to embrace analytics quickly (Protiviti 2018). Although benefit from IT-related audit procedures being widely recognised some auditors are still failing in performing technology enabled audit tasks. Furthermore, there is evidence by academic scholars of the slower adoption of technology-related auditing (Smidt et al. 2018; Bierstaker et al. 2014; Ahmi and Kent 2013) and this is supported by professional literature which suggests auditors are not attaining sufficient progress in their technology-related competency and technology-enabled audit performance (Protiviti 2016a) as well as the use of analytics in the auditing remain low (Protiviti 2018). Within the Malaysia context, the Auditor General of Malaysia has expressed in his recent concern over the under-utilisation of audit technology among public sector auditors (Buang 2015) and most of the public sector auditors are still focusing on traditional IT control rather than advanced IT controls (Mahzan and Veerankutty 2011). A study was conducted in Malaysia indicating lower audit technology usage among private auditors (Rosli et al. 2013).
However, human capital in an organisation is the crucial important factor in speeding innovativeness, performance and competitiveness (Kovaľová 2016). Significantly, the key challenges facing the audit function were the evolving technologies and risk related to information security, limited qualified human resources capabilities and skills, inadequate reporting structures for IT audit function and insufficient IT infrastructure, misalignment between technology and organisation performance, and limited audit methodology related to IT risk assessment, as well as restricted use of technology in data analytics (Protiviti 2016b).
Multiple initiatives are being undertaken to improve the use of technology among auditors, but IT utilisation among the auditors are still low. It may also indicate that the current strategies and policies may not effectively support technology implementation. Major factors that cause IT project failure re related to the inadequate governance mechanism, specifically no clear direction on IT business performance, insufficient management support, improper IT plans and a lack of IT support services (Nawi et al. 2011; Amind et al. 2012). Knowing the high-cost and low-success rate, it is crucial to understand reasons for these issues and for a strategy towards success vital to be discovered. Nevertheless, the review indicates that reasons for the slower adoption of technology-enabled auditing has yet been investigated, although the importance of audit technology in improving the auditors’ task in the electronic environment has been recognised widely.
IT governance is defined as a framework that determines the decisions rights and accountability to stimulate anticipated behaviour in the use of technology. As such, effective IT governance stimulates and influences the workforces in technology usage and warrants compliance with an organisation’s missions and norms (Weill and Ross 2004). Governments with ineffective IT governance may cause in low performance of technology assets such as ambiguous information quality, unproductive operational costs, delay in IT project and the closing down of its IT department (Nfuka and Rusu 2011).
Thus effective IT governance anticipates playing a role in improving the performance of technology-enabled auditing through the effective management of organisational resources. Effective IT governance has a set of mechanisms that involve structures, process, and communication. These mechanisms involve the formation of executive teams, committees and IT support services to assure clear strategic direction is established and technology-related issues are handled appropriately. Well-disseminated IT strategies and policies are designed to ensure employees’ behaviours are consistent with organisational objectives (Weill and Ross 2004). Consequently, this study anticipates inspecting the influence of these governance mechanisms on the audit technology performance. Although studies have investigated the influence of governance mechanism on IT-related activities, none of the studies have investigated the impact of IT governance on IT-related activities in audit organisation specifically for the audit task.
This study attempts to understand the influence of effective IT governance on the performance of audit technology among Malaysian external public sector auditors. Literature reviews were performed in the area related to the information system, auditing, and governance with the aim of gaining a better understanding of the value of governance of IT-related activities. The finding of the study is expected to enrich the existing body of knowledge on the significant impact of IT governance in assuring the successful utilisation of audit technology.
3. Literature Reviews
3.1. The Concept of Governance in Information Technology
The United Nations Development Program described governance as “the exercise of economic, political, and administrative authority to manage a country’s affairs at all levels. It comprises mechanisms, processes, and institutions through which citizens and groups articulate their interests, exercise their legal rights, meet their obligations, and mediate their differences” (UNDP 1997, p. 12). From the auditing literature, governance “is the framework, principles, structure, processes, and practices to set direction and monitor compliance and performance aligned with the overall purpose and objectives of an enterprise” (ISACA 2009). IT governance is a part of the wider concept of corporate governance, which emphasises the effective management and use of technology to accomplish business performance. ITG is generally denoted as a subsection of corporate governance (Heart et al. 2010). ITG is defined as a framework that determines the decisions rights and accountability to stimulate anticipated behaviour in the use of technology. Effective ITG stimulates and influences the workforce in technology usage and warrants compliance with the business vision, norms, and beliefs (Weill and Ross 2004). The IT Governance Institute (ITGI) recognises ITG as an accountability of the board of controllers and senior management and it defines ITG as “an integral part of enterprise governance and consists of the leadership and organisational structures and processes that ensure that the organisation’s IT sustains and extends the organisation’s strategies and objectives” (ITGI 2003, p. 10). The key aims related to ITG are reducing risk, sustaining goal achievement, and monitoring of IT investments (Al-Omari and Barnes 2014).
3.2. IT Governance (ITG) Effectiveness
Organisations with effective ITG have dynamically developed a set of ITG mechanisms that motivates behaviour in line with the organisation missions, strategies, values, norms, and culture. According to Weill and Ross (2004), effective governance only takes place when an organisation has a set of mechanisms which involve structures, process, and communication. An effective ITG comprises of IT structures, management participation, well-disseminated IT strategies and IT policies as well as clearly defined performance indicators (Nfuka and Rusu 2010). Furthermore, top management participation in IT decision making, the establishment of IT steering committees in handling IT related issues to ensure they are in line with organisational goals, and the use of key performance indicators related to IT have significantly measured the effectiveness of IT governance (Ferguson et al. 2013). IT strategies and IT plans are able to ensure that IT investments have been evaluated for relevant risk and assist the business expectation (Wilkin and Chenhall 2010; Ali and Green 2012). Some studies have found IS support service through the availability of IT experts and IS consultants play a significant role in in the successful implementation of the system (Law et al. 2010).
3.3. Audit Technology Performance
Technology-related auditing is considered among the top priority area in the audit function, particularly in the use of audit technology (Protiviti 2016a). The auditor needs to incorporate ‘state-of-art’ audit technology to enhance the audit process (Rose et al. 2017). The most frequently recommended audit technology often promoted by professionals and standards are Computer Assisted Audit Tools (CAATs). The most widely used audit technology, particularly during the technology enabled auditing, are: (i) test data, parallel stimulation and integrated test facility assessing the internal logic of the financial application directly and to test a program is functioning as intended and correctly; (ii) generalised audit software being used to access client electronic files, extract related data, and conduct substantive tests to examine the details of transaction and balances, and perform analytical reviews to identify unusual transactions; (iii) system control audit review files (SCARF) and embedded audit modules being installed into the system to evaluate flows of transaction and identify exceptional transactions (Hall 2015).
Thus, this study intends to develop contextualised measures and view an effective system/technology/application from the user perspective which highlights the ability of audit technology in enhancing the job performance of the auditors and increasing the quality of the audit. Additionally, the type of system being assessed is related to technology that supports the implementation of audit tasks in a digital environment focusing on the automation of individual job functions usually by a single user. Based on the literature reviews, technology/system/application effectiveness or success was evaluated based on the IS Success Model by DeLone and McLean (1992). The measurement of IS success is critical to understands the value and efficacy of IS investment and its management (DeLone and McLean 2003). This process model consists of six interrelated dimensions namely system quality, information quality, use, user’s satisfaction, individual impact and organisational impact (DeLone and McLean 1992). Audit technology performance or success was measured using 2 constructs of this model which are user satisfaction and individual impact that represent the net benefit derived from the use of technology.
A study conducted in Hong Kong among certified accountants on the successful use of accounting information systems indicated that information quality, system quality, and service quality do impact organisational performance (Gorla et al. 2010). A study examined the successful use of a mandatory taxation information system in Greek and noted that there is a strong association with system quality, information quality, service quality, perceived usefulness and user satisfaction except for system quality and user satisfaction (Floropoulos et al. 2010). From the employee satisfaction perspective, a survey was conducted among 10,000 employees and noted that service quality, information quality, user satisfaction, use, individual impact and organisational impact contribute to the successful utilisation of employee portals (Urbach et al. 2010). Reviews show that the DeLone and McLean IS Success model is robust because of the findings from studies among different users and involving different information systems indicating similar results in measuring the successful utilisation of technology. Thus, this study utilised the IS Success model to evaluate audit technology performance.
In summary, audit technology performance may further be improved when audit organisations established an effective IT governance mechanism by guiding auditors with an appropriate IT strategy and IT policy as well as assisting the auditors with an adequate IT support service. Besides, audit organisation may effectively manage IT related issues through the formation of an IT committee and being further supported by senior management. This is anticipated to encourage a positive behaviour toward the use of technology during the audit task among the auditors.
3.4. IT Governance and Performance
The implementation of ITG anticipated to improve the operational and supply chain processes efficiently within and across the organisation (Ilebrand et al. 2010); and well-organized ITG may have progressive effects on organisation performance (Weill and Ross 2004). There are some signs that the implementation of ITG mechanisms may lead organisations to manage and use the technology in business more efficiently than the organisation in which IT governance is not effective. ITG mechanisms are able to assist in risk mitigations and IT business value creation. ITG mechanisms may enhance the administration of IT-related activities by assuring technology usage is in line with business objectives, IT being managed effectively, and IT outcomes being monitored effectively. As such, an effective IT Governance mechanism able to influence organisational performance (Lunardi et al. 2014) and enhanced technology-related activities (Heart et al. 2010) and governance practices (Haes and Grembergen 2009). Liang et al. (2011) found that IT governance maturity enables strategic alignment which in turn yields better performance. Thus, effective IT governance mechanisms can improve system performance.
From the auditing context, effective IT governance mechanisms anticipate impacting the audit work process which may result in better job performance and productivity through the effective utilisation of audit technology during the audit task in the digital environment. Effective IT governance lays a foundation for the audit organisation and its workforce to follow a desirable behaviour and motivate the behaviour to be in line with the organisation’s mission in providing quality audit opinions. In addition, senior management support, clear strategies, and policies as a part of a governance mechanism in controlling the organisation’s activities are considered to be significant drivers for audit technology usage (Mahzan and Lymer 2014). IT support services also play a significant role in assuring the audit technology usage (Ahmi and Kent 2013) as well as supporting the cultural impact of the technology performance. Accordingly, effective use of audit technology during the audit task through the existence of effective IT governance may enhance audit task efficiency and improve the quality of audit opinion in addition to job performance.
Interestingly, studies examining the role of IT governance in IT-related activities in public sector audit organisations have been limited. Most of the literature on the role of IT governance were focused mainly on its impact towards organisation performance. No attempt was done to explore the potential of effective IT governance on individual behaviour specifically from an auditing context. Thus, this study anticipates enriching the existing knowledge by integrating the issues of IT-related investment and IT governance to highlight the importance of IT governance for the success of IT initiatives in audit organisations.
4. Hypothesis Development and Research Model
Agency theory is utilized to elucidate the phenomena, as literature showed agency theory being predominantly used in public sector accountability research (Schillemans and Busuioc 2015) and being very much related to governance issues such as monitoring mechanisms (Maijoor 2000). Accountability refers to relationships between two (or more) persons, where one is obliged to be responsible for his or her behaviour to the other(s), and some specific mechanisms are arranged to make him or her behave in an accountable manner (Dubnick and Frederickson 2010). Therefore, principals create some mechanisms to bind the degree of such behaviour. Furthermore, principals also observe the conduct of management with the intention of discouraging unrelated activities and introduce mechanisms to bond the interest of both parties (Peirson 1990). An IT governance mechanism was established by the government through government circulars and a high-level governing committee (e.g., parliamentary members meeting) in order to oversee the behaviour of civil servants being in line with the government mission and objectives. This IT governance mechanism acts as the mechanism on behalf of principals (i.e., government) in monitoring the behaviour of management. The Auditor General of Malaysia who represents the management is responsible for administering the organisation’s activities through effective work processes and reporting such activities to the governing committees.
Implementation of ITG mechanisms may lead organisations to manage and use the technology in business more efficiently than the organisation in which IT governance is not effective. Effective ITG mechanisms may enhance the administration of IT-related activities by assuring technology is in line with business objectives, IT being managed effectively and IT outcomes being monitored effectively (Lunardi et al. 2017). Senior management support is important in creating a supportive climate and allocating sufficient resources for the successful utilisation of technologies (Wang et al. 2010; Low et al. 2011) and being significant drivers in making decisions on technology adoption in audit organisations (Mahzan and Lymer 2014; Ahmi and Kent 2013). Further, reviews indicated that IT strategy as the technology-related strategic policy is providing guidance and direction on IT-related activities (Nfuka and Rusu 2010) and IT Committee as a supporting mechanism for managing IS related activities (Ferguson et al. 2013; Ali and Green 2012) are important mechanisms for effective governance. IT support services also play an important role in assuring the usage of audit technology among the auditors (Vasarhelyi and Romero 2014). Thus, organisations should effectively govern the organisational IT-related activities with appropriate infrastructure in supporting technology utilisation among the auditors and recommended provision of an IT support service in order to enhance auditors confidence in utilising audit technology i.e., CAATs during the audit task (Bierstaker et al. 2014). This IT governance construct denotes the mechanism that inspires actions concurrent with the organisation’s mission, strategy, and culture related to IT which influences the successful use of technology during the audit task.
Therefore, organisations need to focus on effective ITG before attempting to improve technology-related activities. An effective IT governance mechanism anticipated influencing audit technology performance. Accordingly, it is hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
There is a positive relationship between effective IT governance and audit technology performance.
H1a.
There is a positive relationship between management support and audit technology performance.
H1b.
There is a positive relationship between effective IT strategy and audit technology performance.
H1c.
There is a positive relationship between effective IT committee and audit technology performance.
H1d.
There is a positive relationship between effective IT support service and audit technology performance.
5. Research Method
The unit of analysis for this study includes the public sector auditor in National Audit Department of Malaysia (NADM) who represents the majority of public sector auditors in the country. Data were collected through cluster sampling by segregating audit staffs function into administration and audit functions. After a discussion with the NADM representative, a total of 1535 auditors with organisation’s email addresses were considered as targeted respondents. Using the Cohen (1988) table, the minimum sample required was approximately 306. Based on the literature, particularly involving online web-surveys in public services, 20% to 30% were presumed to be reasonable (Baruch and Holtom 2008; Saunders et al. 2009). A multistage method of data collection was conducted, whereby a total of 1518 questionnaires were emailed and personally administered. A link with the web survey was randomly attached to 1427 official e-mails, with 14 email addresses invalid, and 97 paper-based questionnaires were handed over to the auditors in audit branches in the headquarters of Putrajaya. The data collection was carried out for two months. About 309 questionnaires were collected with a response rate of 22.07%. The usable questionnaires met the minimum required sample size.
SmartPLS 3.0 software was used to assess the relationship among the research constructs by performing partial least square (PLS) analysis (Hair et al. 2016) which is a structural equation modeling (SEM) technique that permits concurrent analysis within latent constructs and between measurement items. PLS-SEM was believed to be an appropriate data analysis technique as (i) this study intends to investigate the predictive association between independent and dependent variables, and (ii) new measures and structural paths were added into the conceptual model based on previous literature.
The constructs were measured using a 5-point Likert scale of 1—strongly disagree and 5—strongly agree. All instruments were adopted from previous studies and modified to meet the objective and research setting. The questionnaire consists of multiple item measurement scales adapted from previous literature. The dependent variable for this study was audit technology performance which as explained through the IS Success Model by DeLone and McLean (1992). Item measurements consist of two constructs mainly adapted from Hussein et al. (2007) which are: user satisfaction and individual impact.
IT governance is signified by IT Committee, IT strategy, IT support service and senior management support which may stimulate the implementation of technological innovation (Havelka and Merhout 2013). In the same vein, this construct denotes the mechanism that inspires action concurrent with the organisation’s mission, strategy and culture that is related to IT which influences the adoption and use of technology. These measurement items have been validated on its reliability and validity in previous literature, specifically in governance and IS literature (Ifinedo 2011; Li et al. 2015). The measurement items used for this construct were modified from IS literature (Li et al. 2015; Kim et al. 2009), governance literature (Ali and Green 2012; Ferguson et al. 2013) and auditing literature (Ahmi and Kent 2013) to fit the purpose of the research context and the respective questionnaires as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Measurement items for IT governance.
This research is a cross-sectional quantitative study, with hypotheses testing, and the types of investigation is a causal relationship, using questionnaires requesting auditors to provide their insight on the perceived importance of each IT governance mechanism in influencing their decision on audit technology usage. In addition, auditors were requested to rate the extent to which they agreed with the statements in the questionnaire regarding audit technology usage on their job performance.
6. Data Analysis
The structural equation modelling technique was a second generation multi-variate data analysis method selected to test the research model, and partial least square (PLS) using SmartPLS (Ringle et al. 2015) was employed as the statistical tool to examine the measurement and structural model as it can accommodate no assumptions on data distribution and survey research is not normally distributed (Chin et al. 2003). The assessment on the research model was firstly tested on the measurement model (validity and reliability of the measures) and secondly, the evaluations were done on the structural model (testing the hypothesized relationships) (see Hair et al. 2016; Ramayah et al. 2011). Furthermore, the relationship between variables was analysed using SmartPLS 3 Software bootstrapping analysis (resampling = 2000) in order to test the level of significance, t-values for all paths. Bootstrapping analysis is used to evaluate the quality of the measurement models and the structural model results in PLS-SEM based on a set of non-parametric evaluation criteria (Hair et al. 2016). Hair et al. (2014) explained that “in bootstrapping, subsamples are randomly drawn (with replacement) from the original set of data. Each subsample is then used to estimate the model. This process is repeated until a large number of random subsamples have been created, typically more 5000. The parameter estimates (in this case, the indicator weights) estimated from the subsamples are used to derive standard errors for the estimates”.
6.1. Respondents’ Profile
The sample of this study consist of 309 respondents. The respondents’ profile is as per Table 2. The majority of respondents were working at state government (40.4%) and federal government (34.0%) levels. Almost 76.7% respondents were female and the remainder were males (23.3%). Most of the respondents were support staff (68.0%) who are the field auditors who performed the technology-enabled auditing directly followed by middle managers (22.0%) who were involved in supervising and monitoring the work of support staff as well as senior managers (10.0%) who led and gave directions on the audit job function. Almost 87.1% of the respondents had auditing experiences 5 years and more which displays that they have the necessary knowledge to respond well. Additionally, about 45.0% of the respondents had experience using audit technology over 5 years and more, and virtually 62.1% of the auditors were perceived to have adequate IT skills.

Table 2.
Demographic profile (N = 309).
6.2. Assessment of Measurement Model
Two types of assessments were performed in assessing the measurement model which include construct validity, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. As recommended by Hair et al. (2016) the assessment was done by examining loadings, average extracted (AVE) and composite reliability (Yeap et al. 2016).
Construct validity signifies how well the results obtained from the use of measure fit the theories around which the test is designed (Sekaran and Bougie 2010). A satisfactory measurement model tends to have internal consistency reliability above the threshold value of 0.708 (Hair et al. 2014). However, Hair et al. (2016) contended that with any outer loading values between 0.4 and 0.7 although considered weak, the researchers should carefully examine the effects of item removal on the composite reliability (CR) as well as content validity of the constructs and should only consider for removal from the scale those that when deleting the indicator lead to an increase in CR. Most of the loading of items were more than 0.70 (significant at p < 0.01) and met the fit criteria.
Furthermore, the AVE value of 0.5 or higher indicates the construct achieve adequate convergent validity (Bagozzi and Yi 1988; Fornell and Larcker 1981) and the construct is able to explain more than half of the variance of its indicators. The loadings for all the items were more than 0.5 and the composite reliabilities were all greater than 0.7 (Hair et al. 2010). The AVE measures the variance captured by the indicators relative to measurement error and the AVE for this study was in the range from 0.623 to 0.979. Table 3 summarizes the results and shows that all the 5 constructs are valid measures for the respective constructs.

Table 3.
Results of the measurement model.
Discriminant validity of the constructs of this study was assessed using Fornell and Larcker’s technique and the heterotrait-monotrait (HTMT) technique. Measurement model has discriminant validity if the square root of AVE of each construct exceeded the correlation between the items and all other items (Fornell and Larcker 1981). The results of Fornell and Larcker’s technique indicates that the square roots of the AVE of the construct (represented diagonally and in bold) are higher than the correlation (represented off-diagonally) for all reflective constructs.
Further assessment using HTMT techniques as suggested by Henseler et al. (2015) was conducted as per Table 4 which specifies that all the values were less than the HTMT.85 value of 0.85 (Kline 2011) or HTMT.90 value of 0.90 (Gold et al. 2001), thus specifies that discriminant validity has been met. In summary, the measurement model demonstrated adequate convergent validity and discriminant validity.

Table 4.
Discriminant validity using heterotrait-monotrait (HTMT) criterion (Henseler et al. 2015).
6.3. Assessment of Structural Model
The assessment of the structural model of this study was analysed using five-step procedures proposed by Hair et al. (2014) which includes assessment of collinearity issues; path co-efficient; coefficient of determination (R2); effect size f2; and predictive relevance (Q2).
Even if the discriminant validity requirements are met, issues on lateral collinearity may mislead the results due to the strong causal effect (Kock and Lynn 2012). The variance inflation factor (VIF) measures the collinearity among the indicators. The result on the VIF values of each construct indicates that the score of VIF is below the recommended threshold value of 5 (Hair et al. 2014) and there were no issues of collinearity issues in the structural model.
The relationship between variables was investigated by running the SmartPLS 3 Software algorithm and was further analyses using SmartPLS 3 Software bootstrapping of 2000 was applied in order to test the level of significance and t-statistics for all path. Table 5 summarizes the results on R2, f2, Q2 and the respective t-values and the results of the path analysis as shown in Figure 1.

Table 5.
Hypothesis Testing.
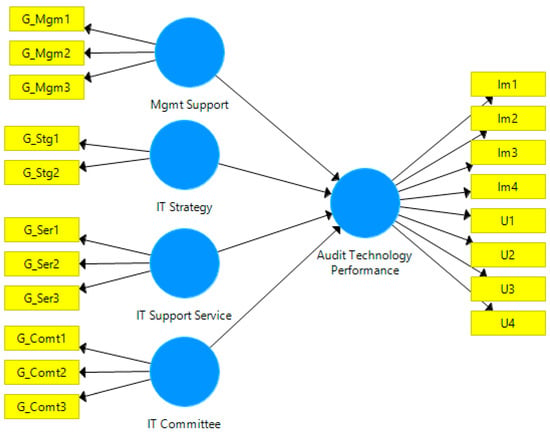
Figure 1.
Research model of the study.
The results indicate that the effective IT governance component which consist of the IT strategy (β = 0.325, p < 0.05) and management support (β = 0.266, p < 0.05) were positively related to audit technology performance and explained 38.1% of the variance in audit technology performance. However, IT committee and IT support service do not influence the audit technology performance. Thus, the H1a and H1d were supported. The R2 value was above the 0.35 value as recommended by Cohen (1988) indicating this is a substantial model.
Although the p-value is being used to measure the statistical significance of each relationship between exogenous constructs and endogenous constructs, it is unable to reveal the size of the effect which also refers as substantive significance (Sullivan and Feinn 2012). To measure the magnitude of the effect size, this study employed Cohen (1988) rule of thumb which is 0.02, 0.15 and 0.35, representing small, medium and large effect. Based on the results of f2 effect size in Table 4, it showed that only management support has small effect sizes. Hair et al. (2010) have highlighted that the effect size is problematic to establish based on the rule of thumb because the effect size depends on the model complexity and research context as well as the research field (Sullivan and Feinn 2012).
Furthermore, this study tested the predictive relevance (Q2) of the model. The predictive Q2 test is a measure to investigate the predictive power of exogenous constructs over endogenous constructs using the blindfolding technique (Geisser 1974; Stone 1974). A value of Q2 bigger than zero for a specific reflective endogenous construct shows the path model’s predictive relevance for a particular dependent construct (Hair et al. 2016). By applying the blindfolding procedure as suggested by Hair et al. (2014), the result shows that the research model has medium predictive relevance (Q2 = 23.2%).
6.4. Importance Performance Matrix Analysis (IPMA)
As an extension of the results of this study, a post-hoc importance-performance matrix analysis (IPMA) was performed using audit technology performance as the target construct or outcome variable. The IPMA goal is to identify predecessors that have a relatively high importance for the target construct (i.e., those that have a strong total effect) but also a relatively low performance (i.e., low average latent variable scores). The aspects underlying these constructs represent potential areas of improvement that may receive high attention. IPMA contrasts structural model total effects on a specific target construct with the average latent variable scores of this construct’s predecessors. The total effects represent the predecessor constructs’ importance in shaping the target construct while their average latent variable scores represent their performance (Hair et al. 2016).
Based on Figure 2, it can be observed that IT strategy and management support are very important IT governance elements in determining the successful utilisation of audit technology during the audit task. Besides, both constructs also show good performance influencing the audit technology performance. The other two constructs, particularly on IT support service and IT committee. have relatively little relevance as well as intermediate performance in influencing the audit technology performance.
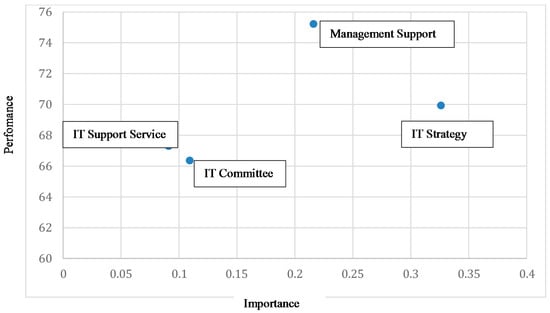
Figure 2.
Importance-performance matrix analysis (IPMA) for audit technology performance.
7. Discussion and Conclusions
7.1. Discussion
The originality of this research lies in the impact of IT governance on audit technology performance since there were no studies that have investigated the proposed relationship from the context of public sector auditing. This study proves that the IT governance mechanism consists of IT strategyand management support which are important factors influencing audit technology performance among the Malaysian public sector auditors using the partial least square (PLS) technique in testing the hypotheses. The paper investigates the goodness of measure by assessing the reliability and validity of the measures of the constructs. The results indicate the measures used in the study exhibited convergent and discriminant validity. In addition, the reliability of the measures was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability which indicate all the measures’ reliability values are at par with the criteria set by the established scholars.
Most of the previous studies focused only on certain measures such as top management support, IT support service, IT policies and being individually tested as a factor that influences the technology usage (Buchwald et al. 2014; Grover and Kohli 2012; Tsai et al. 2015). Some literature focused on the influence of IT governance towards organisation performance/job performance/technology performance (Lunardi et al. 2014; Liang et al. 2011). This is the first study that integrates the measures related to the IT governance construct particularly on top management support, IT strategy, IT committee and IT support service which have been tested individually. An effective IT governance mechanism is able to articulate and reinforce the use of technology by aligning the organisation resources and capabilities to stimulate anticipated behaviours on technology usage (Wilkin and Chenhall 2010; Weill and Ross 2004).
The findings of the paper confirmed that IT governance is an important accountability mechanism to induce anticipated behaviour in the use of technology among the workforce. The IT governance mechanism displays direct influences on the audit technology performance. Most of the items used to measure this construct were adopted from auditing literature and IS literature on technology adoption which is being examined separately as the antecedents in technology adoption literature.
The results indicate that management support as stated in previous literature influence the technology usage (Ghobakhloo and Tang 2015). IT strategy does influence the technology usage consistent with earlier research findings (Widuri et al. 2014; Nkhoma and Dang 2013). However, IT committee and IT support service do not influence the technology performance which is inconsistent with earlier findings (Ferguson et al. 2013; Law et al. 2010).
Consequently, audit organisations should strengthen the IT governance mechanism by specifying the decision rights and accountability framework to encourage desirable behaviour in using IT among the public sector auditors (Weill and Ross 2004). On the other hand, management should provide adequate assistance through effective IT plans by providing adequate resources in the successful use of audit technology during the audit task. In addition, requirements and pressure imposed on the use of technology during auditing should be supported by management and a clear IT strategy should in place to achieve successful utilisation of audit technology.
Active management supports and clear roles of IT plan may ease in optimising the performance of IT initiatives (Buchwald et al. 2014). In line with this finding, effective IT governance is anticipated to optimize the audit technology usage among the public sector auditors by assisting the organisation to formulate and formalise the understanding and application of IT (Wilkin and Chenhall 2010) by means of IT strategy and IT Plan. Reviews also indicated that when organisation effectively aligned its IT activities and IT-supported process to inspire actions concurrent with organisation strategy and culture, it may improve the technology-related performance (Tsai et al. 2015).
Effective IT-related communication policies and IT plans (IT governance mechanism) are important elements (Huang et al. 2010) as well as management participation (Nfuka and Rusu 2010) to instill effective use of audit technology among public sector auditors. IT governance arrangements are able to monitor IT investment in order to sustain a desired outcome and expectation of stakeholders (Al-Omari and Barnes 2014). When performing complex auditing, auditors should be given reliable assistance from IT support services thru the availability of IT expert and IT consultant (Law et al. 2010) in order to enhance audit technology usage.
Besides, when management wants to improve audit technology performance, an IT strategy should be given first priority. Thus it is important to an audit organisation to develop, disseminate and create awareness about IT strategy. Furthermore, managers should assure the technology-related activities in audit organisation are in line with the organisation IT strategy. Besides, participation and support from senior management are crucial in order to achieve better performance on audit technology usage among the public sector auditors.
7.2. Contribution
A significant theoretical contribution of this study was the introduction of the IT governance mechanism influencing the audit technology performance. This is the first study that presents and specifies some drivers of technology usage such as top management support, IT committee, and IT strategy into a construct representing IT governance which is being anticipated to boost actions consistent with the organisation’s mission, approach, standards, rules and culture (Weill and Ross 2004).
Another substantial methodological implication involves the choice of statistical analysis. This research is among very few audit technology researchers which utilised PLS-SEM (SEM). By using SmartPLS 3.0 software, this research was able to establish the joint impact of IT governance and the audit technology performance.
From the managerial perspective, a public sector audit organisation should strengthen governance related to technology by developing an appropriate IT strategy and IT plan for the auditors to be guided in performing technology-related activities during the audit task. Besides, organisations should establish and strengthen the IT support services in assisting the auditors to perform their job function more effectively. Furthermore, it is important that organisations clearly indicate their requirements and priorities related to technology-related training in their IT strategy and IT plan to enhance the use of audit technology. In addition, compliance with professional standards should be scrutinised by the IT committee carefully to assure adherence to technology-enabled auditing.
7.3. Limitations and Future Research Direction
There are several limitations to this study. The first limitation of this study relates to the sample representativeness. The current study is limited to samples from the National Audit Department of Malaysia which represents the majority of public sector auditors who are performing an external audit function and generalising the findings to all public sector auditors in Malaysia or across the world. This should be done with caution and more studies need to be conducted to support the findings of the study due to the different context of public sector audit organisations and related law and regulations. Secondly, this study showed small effect sizes for the majority of the relationship (ƒ: 0.02–0.09) which may be due to the sample size of the study (n = 309). Lower effect size might have been due to the absence of other relevant variables in the research model.
In summary, the findings of the study are expected to enrich the existing body of knowledge on the significant role of IT governance in assuring the successful use of audit technology among public sector auditors.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, T.R.; Investigation, F.V.; Supervision, N.A.A.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmi, Aidi, and Simon Kent. 2013. The utilisation of generalized audit software (GAS) by external auditors. Managerial Auditing Journal 28: 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Syaiful, and Peter Green. 2012. Effective information technology (IT) governance mechanisms: An IT outsourcing perspective. Information Systems Frontiers 14: 179–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Omari, Loai, and Paul Barnes. 2014. IT governance stability in a political changing environment: Exploring potential impacts in the public sector. Journal of Information Technology Management 25: 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Amid, Amin, Morteza Moalagh, and Ahad Zare Ravasan. 2012. Identification and classification of ERP critical failure factors in Iranian industries. Information Systems 37: 227–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, Richard P., and Youjae Yi. 1988. On the evaluation of structural equation models. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 16: 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjya, Jyotirmoyee, and Vaneesa Chang. 2007. Evolving IT governance practices for aligning IT with business—A case study in an Australian institution of higher education. Journal of Information Science and Technology 4: 24–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bierstaker, James, Diane Janvrin, and David Jordan Lowe. 2014. What factors influence auditors’ use of computer-assisted audit techniques? Advances in Accounting 30: 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruch, Yehuda, and Brooks C. Holtom. 2008. Survey response rate levels and trends in organizational research. Human Relations 61: 1139–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buang, Ambrin. 2015. Country paper leveraging technology to enhance audit quality and effectiveness National Audit Department of Malaysia. Paper presented at the 6th ASOSAI Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, February 12. [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald, Arne, Nils Urbach, and Frederik Ahlemann. 2014. Business value through controlled IT: Toward an integrated model of IT governance success and its impact. Journal of Information Technology 29: 128–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Wynne W., Barbara L. Marcolin, and Peter R. Newsted. 2003. A partial least squares latent variable modeling approach for measuring interaction effects: Results from a Monte Carlo simulation study and an electronic-mail emotion/adoption study. Information Systems Research 14: 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Jacob. 1988. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed. Hillsdale: Lawrence Earlbaum Associates. [Google Scholar]
- DeLone, William H., and Ephraim R. McLean. 1992. Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable. Information Systems Research 3: 60–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLone, William H., and Ephraim R. McLean. 2003. The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. Journal of Management Information Systems 19: 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dubnick, Melvin J., and H. George Frederickson. 2010. Accountable agents: Federal performance measurement and third-party government. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory 20: i143–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, Colin, Peter Green, Ravi Vaswani, and Gang Wu. 2013. Determinants of effective information technology governance. International Journal of Auditing 17: 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floropoulos, Jordan, Charalambos Spathis, Dimitrios Halvatzis, and Maria Tsipouridou. 2010. Measuring the success of the Greek taxation information system. International Journal of Information Management 30: 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, Claes, and David F. Larcker. 1981. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. Journal of Marketing Research 18: 382–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisser, Seymour. 1974. A predictive approach to the random effect model. Biometrika 61: 101–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, Morteza, and Sai Hong Tang. 2015. Information system success among manufacturing SMEs: Case of developing countries. Information Technology for Development 21: 573–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, Andrew H., Arvind Malhotra, and Albert H. Segars. 2001. Knowledge management: An organizational capabilities perspective. Journal of Management Information Systems 18: 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorla, Narasimhaiah, Toni M. Somers, and Betty Wong. 2010. Organizational impact of system quality, information quality, and service quality. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems 19: 207–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, Varun, and Rajiv Kohli. 2012. Cocreating IT value: New capabilities and metrics for multifirm environments. MIS Quarterly 36: 225–32. [Google Scholar]
- Haes, Steven De, and Wim Van Grembergen. 2009. An exploratory study into IT governance implementations and its impact on business/IT alignment. Information Systems Management 26: 123–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, Joseph F., Jr., William C. Black, Barry J. Babin, and Rolph E. Anderson. 2010. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed. London: Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, Joseph F., Jr., G. Tomas M. Hult, Christian Ringle, and Marko Sarstedt. 2014. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). Los Angeles: Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, Joseph F., Jr., G. Tomas M. Hult, Christian Ringle, and Marko Sarstedt. 2016. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, James A. 2015. Information Technology Auditing, 4th ed. Boston: Cengage Learning. [Google Scholar]
- Havelka, Douglas, and Jeffrey W. Merhout. 2013. Internal information technology audit process quality: Theory development using structured group processes. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems 14: 165–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heart, Tsipi, Hanan Maoz, and Nava Pliskin. 2010. From governance to adaptability: The mediating effect of IT executives’ managerial capabilities. Information Systems Management 27: 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, Jörg, Christian Ringle, and Marko Sarstedt. 2015. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 43: 115–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Rui, Robert W. Zmud, and R. Leon Price. 2010. Influencing the effectiveness of IT governance practices through steering committees and communication policies. European Journal of Information Systems 19: 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, Ramlah, Nor Shahriza Abdul Karim, and Mohd Hasan Selamat. 2007. The impact of technological factors on information systems success in the electronic-government context. Business Process Management Journal 13: 613–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifinedo, Princely. 2011. Examining the influences of external expertise and in-house computer/IT knowledge on ERP system success. Journal of Systems and Software 84: 2065–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilebrand, Nicklas, Tor Mesøy, and Remco Vlemmix. 2010. Using IT to enable a lean transformation. McKinsey on Business Technology 18: 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Information System Audit and Controls Association (ISACA). 2009. In Summary: The Taking Governance Forward Mapping Initiative. ISACA Journal 1: 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- IT Governance Institute (ITGI). 2003. Board Briefing on IT Governance, 2nd ed. Rolling Meadows: Information Systems Assurance and Control Association (ISACA). [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Hyo-Jeong, Michael Mannino, and Robert J. Nieschwietz. 2009. Information technology acceptance in the internal audit profession: Impact of technology features and complexity. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems 10: 214–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, Rex. 2011. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 3rd ed. New York: Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, Ned, and Gary Lynn. 2012. Lateral collinearity and misleading results in variance-based SEM: An illustration and recommendations. Journal of the Association for Information Systems 13: 546–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaľová, Marcela. 2016. People in the Process of Innovation and as the Factor Increasing Business Performance. Forum Scientiae Oeconomia 4: 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Law, Chuck C. H., Charlie C. Chen, and Bruce J. P. Wu. 2010. Managing the full ERP life-cycle: Considerations of maintenance and support requirements and IT governance practice as integral elements of the formula for successful ERP adoption. Computers in Industry 61: 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Xiaolin, Sharma Pillutla, Huaming Zhou, and Dong-Qing Yao. 2015. Drivers of adoption and continued use of e-procurement systems: Empirical evidence from China. Journal of Organizational Computing and Electronic Commerce 25: 262–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Ting-Peng, Yi-Chieh Chiu, Shelly P. J. Wu, and Deimar Straub. 2011. The impact of IT governance on organizational performance. Paper presented at the 7th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Detroit, MI, USA, August 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Low, Chinyao, Yahsueh Chen, and Mingchang Wu. 2011. Understanding the determinants of cloud computing adoption. Industrial Management and Data Systems 111: 1006–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, Guilherme Lerch, Joao Luiz Becker, Antonio Carlos Gastaud Maçada, and Pietro Cunha Dolci. 2014. The impact of adopting IT governance on financial performance: An empirical analysis among Brazilian firms. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems 15: 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, Guilherme Lerch, Antonio Carlos Gastaud Maçada, João Luiz Becker, and Wim Van Grembergen. 2017. Antecedents of IT Governance effectiveness: An empirical examination in Brazilian firms. Journal of Information Systems 31: 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahzan, Nurmazilah, and Andy Lymer. 2014. Examining the adoption of computer-assisted audit tools and techniques: Cases of generalized audit software use by internal auditors. Managerial Auditing Journal 29: 327–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahzan, Nurmazilah, and Farida Veerankutty. 2011. IT auditing activities of public sector auditors in Malaysia. African Journal of Business Management 5: 1551–63. [Google Scholar]
- Maijoor, Steven. 2000. The internal control explosion. International Journal of Auditing 4: 101–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masli, Adi, Gary F. Peters, Vernon J. Richardson, and Juan Manuel Sanchez. 2010. Examining the potential benefits of internal control monitoring technology. The Accounting Review 85: 1001–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, Ramlah, and Noor Azman Ali. 2011. Quality governance of human aspects of quality initiatives in the public service sector. Current Issues of Business and Law 6: 111–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Audit Department of Malaysia (NADM). 2015. IT Audit-Issues, Lesson Learnt and Actions for A Successful IT System Implementation. Paper presented at the 24th Meeting of the INTOSAI Working Group on IT Audit, Warsaw, Poland, June 29–July 1. [Google Scholar]
- Nawi, Haslinda Sutan Ahmad, Azizah Abdul Rahman, and Othman Ibrahim. 2011. Government’s ICT project failure factors: A revisit. Paper presented at International Conference on Research and Innovation in Information Systems (ICRIIS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, November 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nfuka, Edephonce N., and Lazar Rusu. 2010. Critical success factors for effective IT governance in the public sector organizations in a developing country: The case of Tanzania. Paper presented at European Conference on Information Systems, Pretoria, South Africa, August 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Nfuka, Edephonce N., and Lazar Rusu. 2011. The effect of critical success factors on IT governance performance. Industrial Management and Data Systems 111: 1418–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkhoma, Mathews Z., and Duy P. T. Dang. 2013. Contributing factors of cloud computing adoption: A Technology-Organisation-Environment framework approach. International Journal of Information Systems and Engineering 1: 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Paprocki, Wojciech. 2016. Industry 4.0 Concept and Its Application in the Conditions of the Digital Economy. Digitization of the Economy and Society. Opportunities and Challenges for Infrastructure Sectors. Gdańsk: European Financial Congress, pp. 39–57. [Google Scholar]
- Peirson, Graham. 1990. A Report on Institutional Arrangements for Accounting Standard Setting in Australia. Melbourne: Australian Accounting Research Foundation. [Google Scholar]
- Protiviti. 2016a. Arriving at Internal Audit’s Tipping Point Amid Business Transformation: Assessing the Results of the 2016 Internal Audit Capabilities and Needs Survey—And a Look at Key Trends over the Past Decade. Available online: http://www.protiviti.com/en-US/Documents/Surveys/2016-Internal-Audit-Capabilities-and-Needs-Survey-Protiviti.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2017).
- Protiviti. 2016b. A Global Look at IT Audit Best Practices: Assessing the International Leaders in an Annual ISACA/Protiviti Survey. Available online: http://www.protiviti.com/en-US/Documents/Surveys/5th-Annual-IT-Audit-Benchmarking-Survey-ISACA-Protiviti.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2017).
- Protiviti. 2018. Analytic in Auditing Is a Game Changer. Available online: https://www.protiviti.com/sites/default/files/united_kingdom/insights/2018-internal-audit-capabilities-and-needs-survey-protiviti-global_version.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2018).
- Ramayah, Thurasamy, Jason Wai Chow Lee, and Julie Boey Chyaw. 2011. Network collaboration and performance in the tourism sector. Service Business 5: 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, Christian M., Sven Wende, and Jan-Michael Becker. 2015. SmartPLS 3. Boenningstedt, Germany. Available online: http://www.smartpls.com (accessed on 28 July 2016).
- Rose, Anna M., Jacob M. Rose, Kerri-Ann Sanderson, and Jay C. Thibodeau. 2017. When should audit firms introduce analyses of Big Data into the audit process? Journal of Information Systems 31: 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, Khairina, Paul H. P. Yeow, and Siew Eu-Gene. 2013. Adoption of audit technology in audit firms. Paper presented at 24th Australasian Conference on Information Systems (ACIS), Melbourne, Australia, December 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, Mark, Philip Lewis, and Andrian Thornhill. 2009. Research Methods for Business, 5th ed. Harlow: Prentice Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Schillemans, Thomas, and Madalina Busuioc. 2015. Predicting public sector accountability: From agency drift to forum drift. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory 25: 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaran, Uma, and Roger Bougie. 2010. Research Method for Business, 5th ed. New York: John Wiley and Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Ślusarczyk, Beata. 2018. Industry 4.0—Are we ready? Polish Journal of Management Studies 17: 232–48. [Google Scholar]
- Soral, G., and Monika Jain. 2011. Impact of ERP system on auditing and internal control. The International Journal’s Research: Journal of Social Sciences and Management 1: 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, Mervyn. 1974. Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) 36: 111–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, Gail M., and Richard Feinn. 2012. Using effect size—Or why the P value is not enough. Journal of Graduate Medical Education 4: 279–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Wen-Hsien, Yu-Wei Chou, Jun-Der Leu, Der Chao Chen, and Tsen-Shu Tsaur. 2015. Investigation of the mediating effects of IT governance-value delivery on service quality and ERP performance. Enterprise Information Systems 9: 139–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). 1997. Governance for Sustainable Human Development: A Policy Document. New York: United Nations, Available online: http://pogar.org/publications/other/undp/governance/undppolicydoc97-e.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2016).
- Urbach, Nils, Stefan Smolnik, and Gerold Riempp. 2010. An empirical investigation of employee portal success. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems 19: 184–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasarhelyi, Miklos A., and Silvia Romero. 2014. Technology in audit engagements: A case study. Managerial Auditing Journal 29: 350–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Yu-Min, Yi-Shun Wang, and Yong-Fu Yang. 2010. Understanding the determinants of RFID adoption in the manufacturing industry. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 77: 803–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, Peter, and Jeanne W. Ross. 2004. IT Governance: How Top Performers Manage IT Decision Rights for Superior Results. Boston: Harvard Business School Press. [Google Scholar]
- Widuri, Rindang, Brendan O’Connell, and Prem W. S. Yapa. 2014. Adoption and use of generalized audit software by Indonesian audit firms: Some preliminary findings. Paper presented at the 4th Annual International Conference on Accounting and Finance (AF 2014), Singapore, April 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin, Carla L., and Robert H. Chenhall. 2010. A review of IT governance: A taxonomy to inform accounting information systems. Journal of Information Systems 24: 107–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, Jasmine A. L., Thurasamy Ramayah, and Pedro Soto-Acosta. 2016. Factors propelling the adoption of m-learning among students in higher education. Electronic Markets 26: 323–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidt, Louis, Aidi Ahmi, Leandi Steenkamp, D. P. van der Nest, and Dave Lubbe. 2018. A Maturity-level Assessment of Generalised Audit Software: Internal Audit Functions in Australia. Australian Accounting Review. forthcoming. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).