Abstract
Schools provide a place of learning for adolescents and can be considered safe havens. However, in some cases, African American adolescents are subjected to discrimination by peers and teachers, which can impact their own academic engagement and abilities. Applying a risk and resilience framework, the present study examined the relationship between adolescents’ perceptions of school-based discrimination and academic outcomes in a sample of African American middle school students. Adolescents’ reports of perceived school-based discrimination and racial socialization were identified as predictors of academic outcomes (i.e., academic persistence, academic self-efficacy, and academic self-concept). The study also investigated whether racial socialization moderated the relationship between school-based discrimination and achievement outcomes. The study sample comprised 74 African American adolescents (49% female) and one of their parents. Hierarchical regressions showed that racial discrimination by peers was negatively related to academic outcomes. Furthermore, we found that dimensions of racial socialization buffered the effects of school-based discrimination on academic outcomes. Implications for the importance of investigating race-related factors in the academic outcomes of African American youth will be discussed.
Although schools should be safe havens for youth to learn and develop, many African American youth experience school as a place where they are treated negatively by their peers and teachers. African American youth report more perceived school-based discrimination than youth of other racial backgrounds, with negative consequences for their psychosocial and academic outcomes (Chavous et al. 2008; Cogburn et al. 2011; Fisher et al. 2000; Wong et al. 2003). Parents may be able to mitigate some of the negative effects of discrimination through their ethnic-racial socialization practices (Bynum et al. 2007; Dotterer et al. 2009; White-Johnson et al. 2010), which include discussions aimed at helping youth to negotiate a stigmatized identity.
Guided by a risk and resilience framework, this paper considers how adolescents’ experiences with racial discrimination in school relate to their academic outcomes. If teachers are grading students more harshly or peers are excluding students from social activities because they are Black, they may withdraw from school or feel less positively about their academic abilities. However, we are also considering how adaptive coping mechanisms can also be linked to the relationship. In particular, if parents are providing messages about ethnic pride and preparing children for possible discrimination, youth may be better able to cope with those experiences. Therefore, we sought to examine how parents’ messages about race moderate the effects of school-based discrimination on academic outcomes.
1. Conceptual Underpinnings
Applying risk and resilience frameworks that highlight mechanisms is important to consider for adolescent outcomes. This is especially true when considering outcomes for youth of color. Hence, we turned to Spencer’s (1995) Phenomenological Variant of Ecological Systems Theory (PVEST) and a resilience framework (Fergus and Zimmerman 2005). The PVEST framework considers the effects of contextual issues (e.g., social, cultural) on the development of African American youth (Spencer 1999). Within the PVEST framework, Spencer et al. (2003) highlight the importance of examining contributors of risk (e.g., racial discrimination) and how they have been found to be directly related to adverse outcomes. Additionally, Spencer et al. (1997), highlight the importance of coping responses that are pertinent for youth of color. Within the current study, we examine the effects of the perceptions of school-based discrimination by both peers and teachers, which is conceptualized as net stress engagement within the PVEST framework. These net stress factors may be linked to a reduction in positive academic outcomes for the youth. On the other hand, the protective factor of ethnic-racial socialization may mitigate the effects of perceived racial discrimination for the youth and be linked to more adaptive outcomes, such as higher academic achievement and positive academic self-efficacy and self-concept. The model by Fergus and Zimmerman (2005) also highlights the importance of protective and compensatory factors for youth outcomes. Protective factors are those assets or resources that reduce the impact of a negative outcome. Fergus and Zimmerman (2005) provide the example of how parental support may be a protective factor between the effects of poverty on violent behavior. In this example, the presence of parental support may reduce the effects of poverty on reported violent behavior. Within the compensatory model, Fergus and Zimmerman (2005) identify compensatory factors as those that provide a direct effect of a promotive factor on an outcome that is independent of the effect of the risk factor. For example, Fergus and Zimmerman discuss how adult monitoring may be viewed as a compensatory factor in the relation between poverty and violent behavior. We expect racial-ethnic socialization to function as either a protective or compensatory factor for African American adolescents.
2. School-Based Racial Discrimination
Experiences with racial discrimination are quite common for African American youth. In fact, African American youth report more racial discrimination in school than youth of other races (Fisher et al. 2000; Romero and Roberts 1998). Furthermore, the negative academic consequences of a negative racial climate and discrimination are well-documented (Byrd 2015; Chavous et al. 2008; Wang and Huguley 2012; Wong et al. 2003). For example, Wong et al. (2003) found adolescents’ perceptions of discrimination by peers and teachers were associated with lower academic motivation and poor self-esteem. Similarly, other research has found linkages among school-based discrimination, academic self-concept, and school importance (Chavous et al. 2008). In addition, general racial discrimination has been associated with lower academic achievement in African Americans (Neblett et al. 2006). When adolescents perceive discrimination in school and in other public spaces, it impacts their beliefs and attitudes towards school as well as their school performance.
School-based racial discrimination may be especially relevant in middle school. In many cases, African American students move from settings that are relatively homogenous racially to schools that are more racially diverse, increasing the potential for them to face unfair treatment based on their race. Studies show that students in the numerical minority are at greater risk for being bullied as they move into more diverse schools (Graham and Juvonen 2002) and that discrimination is more frequently reported in racially diverse schools than in less diverse schools (Bellmore et al. 2012). This is because, in homogenous schools, there is less opportunity for students to act on potential stereotypes and prejudice they have about other racial groups. Even if they do not move into more diverse settings, older students tend to perceive more discrimination than younger students (Fisher et al. 2000; Seaton et al. 2008). Furthermore, studies of bullying show that victimization occurs more frequently in middle school than in high school (Bradshaw et al. 2007; Rose et al. 2009). As school-based discrimination and bullying are similar experiences, we would also expect racial discrimination to be higher in middle school compared to high school. Thus, students are at a greater risk for experiencing the negative outcomes associated with discrimination as they enter middle school.
Studies of school-based discrimination distinguish between the associations on academic outcomes with regards to peer-based and teacher-based discrimination (Benner and Graham 2013; Medvedeva 2010). In particular, a study by Benner and Graham (2013) found that, for a sample of Latino, African American, and Asian American youth, discrimination from adults was associated with lower grades and less school engagement, whereas discrimination from peers was associated with poorer psychological well-being. Furthermore, Medvedeva (2010) found that, in a sample of children of immigrants, those who reported more discrimination by peers were more likely to report poorer language skills, compared to those who reported discrimination by teachers. Those who reported more discrimination by teachers reported higher proficiency in language skills. Although these studies have focused on the source of racial discrimination, both studies have used multiracial samples; hence, we do not know if the source of the discrimination is also an important factor in the lives of African American youth. This may be a vital piece when considering the aspects that play a role in the successes and barriers in the academic outcomes of African American children and youth.
3. Ethnic-Racial Socialization
Ethnic-racial socialization has been defined as the transmission of verbal and nonverbal messages, attitudes, and behaviors related to race and ethnicity (Hughes et al. 2006; Lesane-Brown 2006). African American parents are more likely to talk to their children about race than parents of other ethnicities (Hughes et al. 2006). In their seminal literature review on ethnic-racial socialization, Hughes et al. (2006) identified four main dimensions of ethnic-racial socialization. Of these four, we focus on two that we believe are most relevant to youth experiences of racial discrimination, specifically experiences of discrimination in school—cultural socialization and preparation for bias. Cultural socialization messages focus on the cultural history and traditions of the group. They include efforts to instill a sense of racial/ethnic pride in the child. The preparation for bias dimension encompasses messages aimed at making the child aware of racial discrimination and offering strategies for coping with those experiences. Studies have shown that, as African American children transition to adolescence, the frequency of preparation for bias increases (Hughes and Chen 1997) Additionally, African American youth continue to receive cultural socialization messages in adolescence (Hughes and Chen 1997).
Research has found that a major motivation for ethnic-racial socialization among ethnic minority parents is to buffer children from the negative effects of racial discrimination (Peters 2002; Suizzo et al. 2008). It is likely that parental discussions of group history and accomplishments bolster group pride and protect self-concept in the face of negative treatment from others (Hughes et al. 2006). In addition, scholars suggest that when youths are prepared for discrimination, they are less shocked by the experience and better prepared with explicit coping strategies (Hughes and Johnson 2001). Empirical studies have demonstrated that ethnic-racial socialization reduces the effects of racial discrimination on adolescent well-being (Fischer and Shaw 1999; Harris-Britt et al. 2007). For example, Harris-Britt et al. (2007) found that preparation for bias and cultural socialization moderated the effects of racial discrimination on self-esteem in a sample of African American adolescents. Similarly, Fischer and Shaw (1999) found that when African American youth experienced more racial discrimination, but received fewer preparation for bias messages, they tended to report poorer mental health. It should be noted that these studies address the buffering effects of ethnic-racial socialization on psychological well-being, but these relationships have not been well-established with academic outcomes. For instance, Neblett et al. (2006) examined whether ethnic-racial socialization attenuated the effects of racial discrimination on academic outcomes and did not find any evidence to support this claim. In addition, the study by Neblett et al. (2006) focused on adolescents’ perceptions of general racial discrimination on academic outcomes, whereas the current study focuses on African American adolescents’ experiences with school-based discrimination (e.g., peers, teachers).
4. The Present Study
In this study, we were interested in understanding how ethnic-racial socialization may buffer well-established negative relationships between perceived racial discrimination and academic outcomes. Our study hypotheses are as listed. First, adolescents’ perceptions of racial discrimination by peers will be negatively related to their academic outcomes. Second, adolescents’ perceptions of racial discrimination by teachers will also be negatively associated with academic outcomes. Finally, adolescents’ reports of the frequency of their parents’ ethnic-racial socialization messages will moderate the relationship between racial discrimination by peers and academic outcomes. Academic outcomes were identified as academic competence, academic efficacy, academic persistence, and academic preparedness.
5. Method
5.1. Sample
The sample consisted of 74 African American middle school (grades 6–8) students and their parents. Within our sample, 37 (50%) of the adolescents were male. Each child had one parent participating in the study. Sixty-two (83%) of the parents identified themselves as the child’s mother, whereas 12 (13%) of the parents identified themselves as the child’s father. When asked to report their current educational level, approximately 8% of parents reported having a GED or high school degree, 8% of parents reported an associate’s degree, 18% of parents reported having some college, 37% of parents reported having a college degree, and 26% of parents reported having either a Masters or Doctoral degree. Forty-one (56%) of the parents reported being married and 32 (32%) of the parents reported being single; this included those parents who were either single, never married, or divorced. The median household income for our full sample was $50,000–59,999. This was higher than the national average for household income in U.S., which was $49,445 in 2010 (DeNavas-Walt et al. 2010).
Parents and their children were recruited from two small towns in the Midwest. The first town consisted of 113,934 individuals, of which 73% have been identified as White and 8% as African Americans. The median household income for the families in this town is approximately $55,000. The school district of the first town had similar racial demographics to the city. Approximately 73% of students in the school district were White and 7.8% of students were African American (ProximityOne 2010). The second town was smaller in comparison to the first town. In 2010, there were 19,435 individuals residing in the town, approximately 62% of whom were White and 29% identified as African American. The 2010 median household income for the families in this town was $33,406. The school district within this town had approximately 63% of its student body identifying as White and 29% identifying as African American/Black (ProximityOne 2010).
5.2. Measures
5.2.1. Predictor Variables
Perceived School-Based Discrimination assessed adolescents’ perceptions of racial discrimination committed by their teachers and peers. This measure was developed by Eccles et al. for the Maryland Adolescent Development in Contexts Study (MADICS; Wong et al. 2003). There are two subscales to this measure: One assesses perceived teacher discrimination and the other assesses perceived peer discrimination. The five-item perceived teacher discrimination scale asked adolescents how often they were treated negatively by their teachers in the classroom because they are Black, such as not being called on in class. The four-item perceived peer discrimination scale assessed negative race-related treatment by peers at school because they are Black, including not being picked for teams. Participants were asked to indicate their responses on a five-point scale from 1 = “Never” to 5 = “Almost every day”. Cronbach’s alphas were 0.86 and 0.82 respectively for the current sample. Please see Appendix A and Appendix B.
Ethnic-Racial Socialization was measured using the Hughes and Chen (1997) measure of adolescents’ perceptions of their parents’ ethnic-racial socialization messages and practices. The measure is comprised of two subscales, which are preparation for bias and cultural socialization. The four-item preparation for bias subscale assessed parental messages related to possible discrimination and racial coping. Preparation for bias items included: “Talked to you about the fight for equality among Blacks”; “Said that people might try to limit him/her because of race”.
The seven-item cultural socialization subscale measured parental messages about cultural pride and heritage. Cultural socialization items included: “Talked about being proud to be Black”; “Read Black storybooks”. High scores on these subscales indicated a greater frequency of providing the child with racial socialization messages. Both scales had adequate internal consistency for the current sample (Preparation for bias scale = 0.91 and cultural socialization scale = 0.77).
5.2.2. Outcome Variables
Academic Persistence was adapted from the Wellborn (1991) measure of classroom persistence. This scale examines adolescents’ re-engagement with material after difficulty or failure. Participants were asked to rate their answers on a four-point scale (1 = “not at all true” to 4 = “very true”). A sample item from this measure is: “If I can’t get a problem right the first time, I just keep trying”. Academic persistence had an alpha of 0.73 for the current sample.
The Academic Self-Concept was adapted from Nicholls (1979) measure on children’s reports of self-concept. This measure taps into children’s perceptions of their own academic abilities in school subjects relative to their age mates. Participants were asked to rate their ability in comparison to other children the same age (e.g., “In reading I am…”) on a seven-point scale, ranging from “much worse” to “much better”. The scale comprised the average of the responses to the five items that include self-concept ratings in math, reading, general intelligence, grades, and writing.
The Academic Efficacy measure was developed by Hoover-Dempsey and Sandler (2005). This seven-item measure assesses children’s beliefs about their abilities to successfully complete their schoolwork. Children were asked to indicate how often they felt each of the statements on a sour-point scale, ranging from 1 = “never” to 4 = “always”. A sample item is: “Homework is easy for me”. The alpha for the current sample of this measure was 0.84.
Perceptions of Academic Ability was also adapted from the Nicholls (1979) measure of children’s academic self-concept. This scale asked parents to report their perceptions of their children’s academic ability in school subjects, relative to classmates. Similar to the youth scale, this scale was composed of parents’ perceptions of their child’s abilities in math, reading, general intelligence, grades, and writing. Parents were asked to rate their children on a seven-point scale and the scale had an alpha of 0.88 for the current study.
Perceptions of Academic Preparedness was created by Rowley (2004). This scale comprised two items that assess parents’ perceptions of their child’s preparation for homework and for tests. This scale had an alpha of 0.80 for the current study. Parents were asked to rate their child’s preparedness on a five-point scale.
6. Procedure
The current study was part of the Middle School Experiences Study (MSES), a larger study of race-related factors in African American middle schoolers’ achievement motivation. Letters were mailed to families within middle schools in the two different districts. The letters were sent to those who self-identified as having a child who was African American. Interested individuals were asked to contact us either via email or phone. Participants were enrolled in the study following a brief screening for eligibility. Surveys were completed either in the participant’s home or at the research lab and took, on average, an hour and half to complete. Adolescents completed questionnaires that asked about their experiences with racial discrimination, academic achievement and perceptions of racial socialization practices by their parents. Parents completed a similar set of surveys that included reporting their educational level and the frequency of participation in racial socialization messages and practices. At the completion of the survey, adolescents were given a free movie pass and parents received a $25 gift card.
7. Data Analysis Plan
In order to examine the relationships among racial discrimination, racial socialization, and academic outcomes, a series of hierarchical regressions were conducted (Cohen et al. 2003) using IBM Statistical Packages for Social Sciences version 24 (IBM Corporation 2016). Ethnic-racial socialization and racial discrimination variables were standardized, as suggested by Frazier et al. (2004). The regressions investigated the relationship between peer racial discrimination, teacher discrimination, racial socialization, and academic outcomes. The first step consisted of control variables, which were parental education and gender. The second step comprised the standardized variables of peer racial discrimination and one of the racial socialization subscales. An interaction term was created, multiplying each racial socialization subscale by peer racial discrimination, and was entered into the third step. The two racial socialization scales were examined in separate regressions because of concerns related to multi-collinearity. Additional regressions were structured similarly, except they included teacher racial discrimination. Simple slopes analyses were conducted to probe the interactions for significance, as suggested by Preacher et al. (2006).
8. Results
8.1. Preliminary Analysis
Preliminary analyses were conducted on the study variables (see Table 1). Correlations indicated that peer discrimination was positively related to reports of perceived teacher discrimination (r = 0.66, p < 0.01). Furthermore, reports of cultural socialization were positively related to preparation for bias messages (r = 0.75, p < 0.01). Both correlations were expected, based on the similarities between the scales. In terms of the variables of interest, perceived peer discrimination had weak to moderate correlations with each outcome. However, the correlations for academic persistence, self-concept, and self-efficacy were opposite the expected directions. For example, the correlation between perceived peer discrimination and academic persistence was 0.28 (p < 0.05). Teacher discrimination had somewhat weaker correlations with the outcomes, and was only significantly correlated with academic preparedness (r = −0.28, p < 0.05). However, all of the correlations were in the expected directions.

Table 1.
Means, Standard Deviations, and Correlations of Study Variables.
8.2. Hierarchical Regressions
Hypothesis 1.
The first hypothesis predicted that perceived racial discrimination by peers would be negatively associated with academic outcomes.
Separate regressions were conducted for preparation for bias (Table 2) and cultural socialization (Table 3). In those analyses that included preparation for bias, we found that perceived peer discrimination was negatively associated with academic persistence (b = −0.14; p < 0.05), academic self-concept (b = −0.32; p < 0.05), and parent perceptions of academic ability (b = −0.25; p < 0.05). Perceived peer discrimination was not significantly associated with academic self-efficacy or academic preparedness. These results suggest that those individuals who reported more peer discrimination were less persistent on academic tasks and had poorer academic self-concept. Interestingly, the findings indicate that preparation for bias was negatively associated with parents’ reports of perceptions of academic ability, suggesting that youth who perceived more preparation for bias had parents who felt their children had lower academic ability compared to their classmates. These results were qualified by significant interactions between perceived peer discrimination and preparation for bias that will be discussed under Hypothesis 3.

Table 2.
Perceived Peer Discrimination by Preparation for Bias: Academic Outcomes.

Table 3.
Perceived Peer Discrimination by Cultural Socialization: Academic Outcomes.
Cultural socialization was included in the next set of hierarchical regressions (Table 3). Peer discrimination was negatively related to academic persistence (b = −0.19; p < 0.05) and academic ability (b = −0.27; p < 0.05), indicating that those individuals who reported perceiving that they were discriminated against their peers were less likely to be engaged at school in the face of previous failure. Furthermore, those individuals who perceived more discrimination by peers had parents who perceived their academic ability to be lower. Again, these outcomes were qualified by significant interactions with cultural socialization that will be further probed under Hypothesis 3. In these regressions, peer discrimination was not significantly associated with academic self-concept, academic self-efficacy, or academic preparedness.
Hypothesis 2.
The second hypothesis was that perceived racial discrimination by teachers would be negatively linked to academic outcomes.
Two different analyses were conducted, examining preparation for bias and cultural socialization separately. In the analyses, including preparation for bias, perceived teacher discrimination was not significantly associated with any of youth-reported academic outcomes (Table 4). In the analyses that included cultural socialization (Table 5), perceived teacher discrimination was negatively related to academic persistence (b = −0.13; p < 0.05). We also found that teacher discrimination was negatively related to academic self-concept and self-efficacy; however, these findings were marginally significant and were qualified by significant interactions with cultural socialization. Perceived teacher discrimination was not significantly related to parent-reported academic ability and was marginally related to academic preparedness.

Table 4.
Perceived Teacher Discrimination by Preparation for Bias: Academic Outcomes.

Table 5.
Perceived Teacher Discrimination by Cultural Socialization: Academic Outcomes.
Hypothesis 3.
The final hypothesis was that ethnic-racial socialization would moderate the relationship between racial discrimination and academic outcomes.
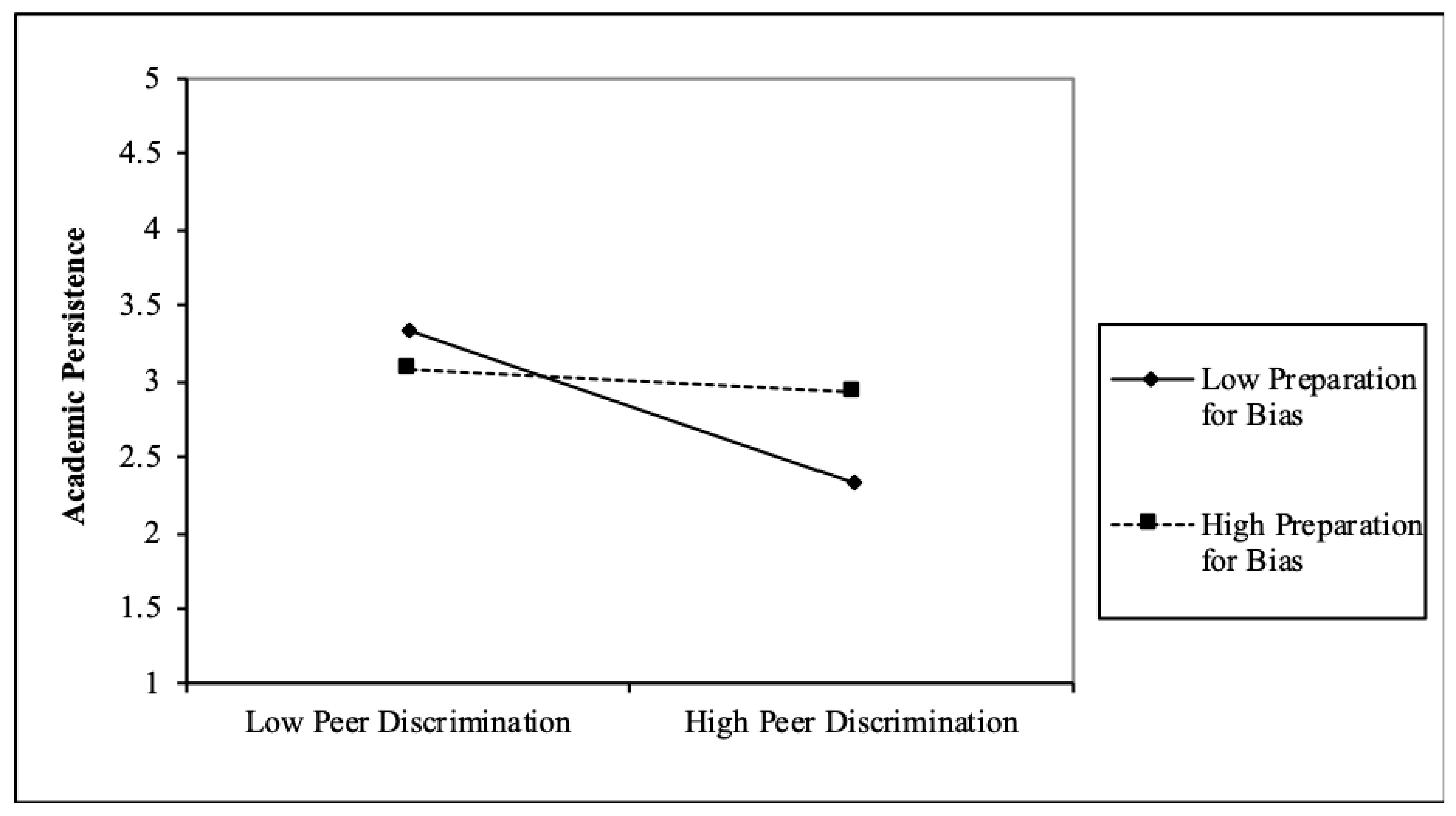
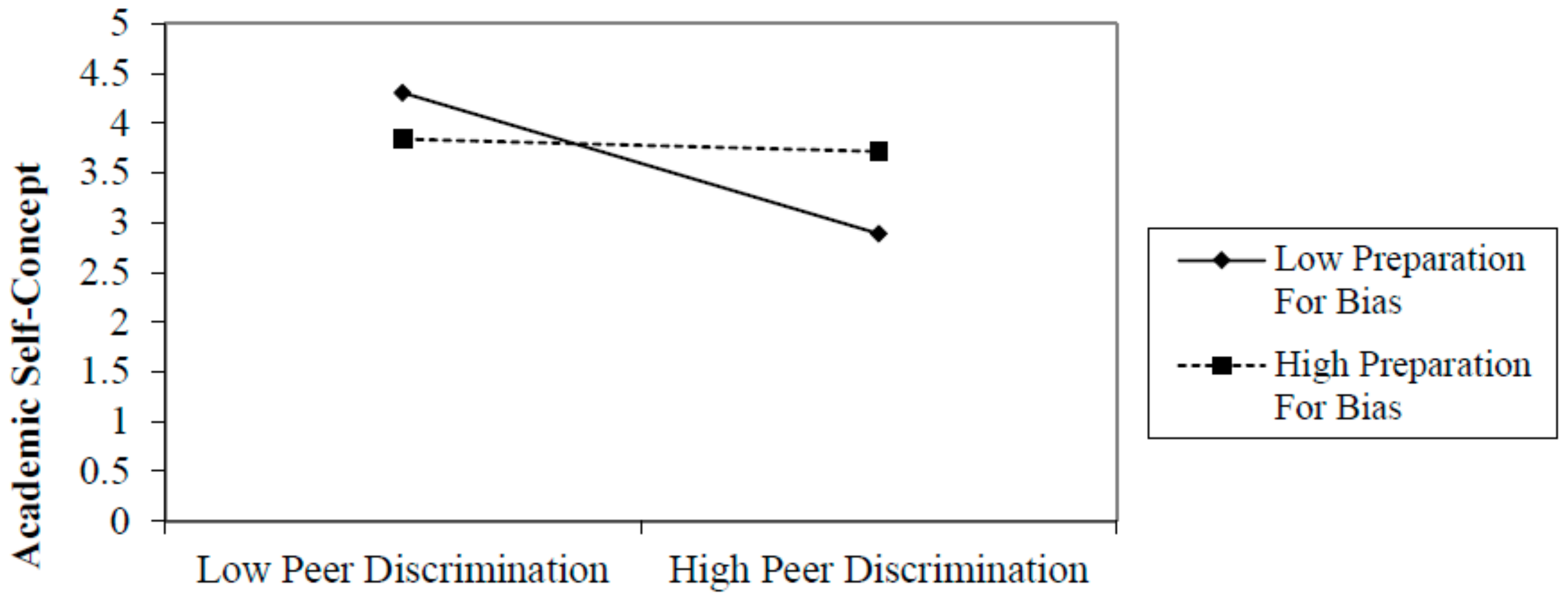
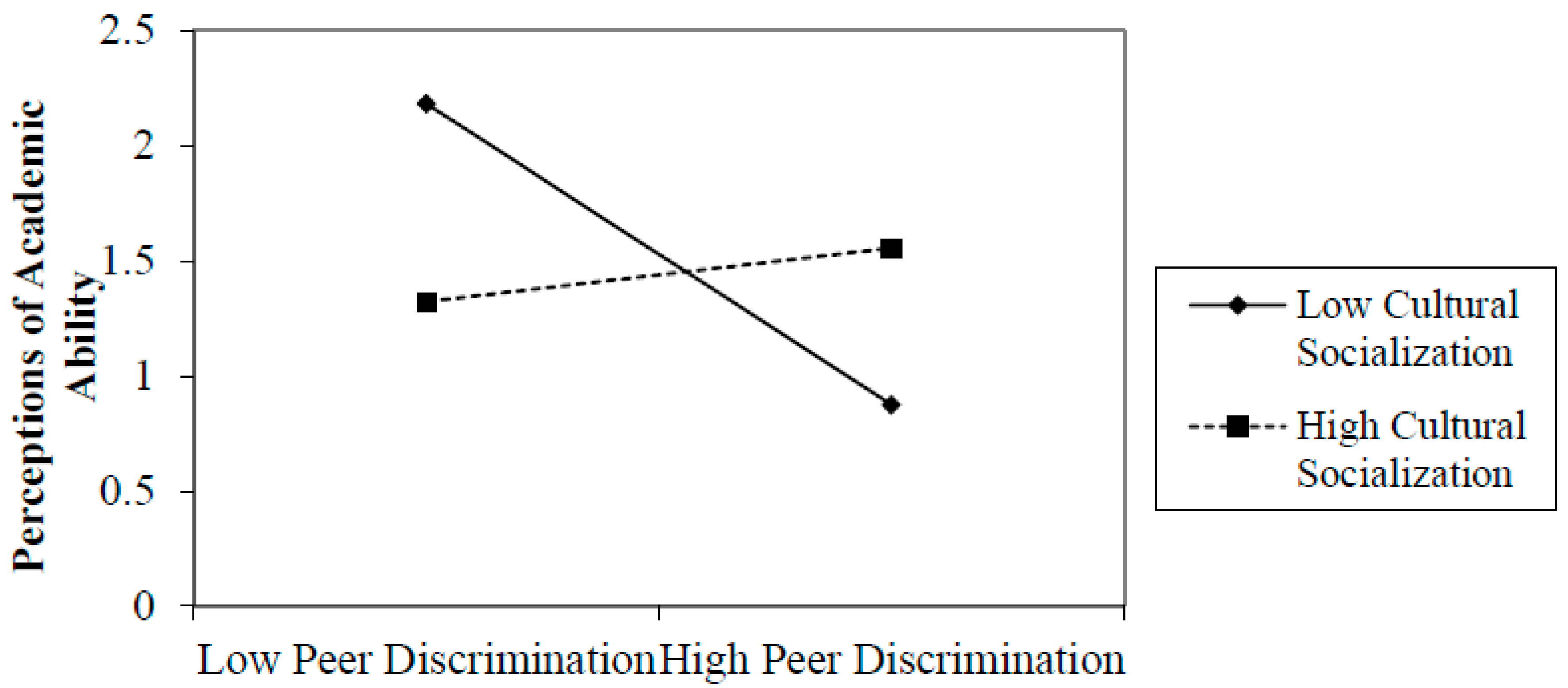
First, we investigated whether preparation for bias mitigates the effects of peer discrimination on academic outcomes (Table 2). We found that preparation for bias buffers the effects of peer discrimination on all youth-reported academic outcomes. In particular, there was a significant negative relationship between peer discrimination and academic persistence when preparation for bias is low (B = −0.50, SE = 0.14, β = −0.30; p < 0.05). However, for those with high levels of preparation for bias, peer discrimination and academic persistence were not related (B = −0.08, SE = 0.06, β = −0.16; p = NS). Similarly, we found that when preparation for bias was low, peer discrimination had a negative effect on academic self-efficacy (B = −0.63, SE = 0.25, β = −0.73; p < 0.05), whereas there was no significant relation between peer discrimination and academic self-efficacy when preparation for bias was high (B = 0.02, SE = 0.11, β = 0.03; p = NS). Finally, when preparation for bias was low, the relationship between peer discrimination and academic self-concept was negative (B = −0.35, SE = 0.16, β = −0.68; p < 0.05), but this connection was nonsignificant when preparation for bias was high. These findings suggest preparation for bias socialization buffers youth from the negative effects of peer racial discrimination on academic persistence, self-efficacy, and self-concept. Additionally, we found that cultural socialization messages and practices mitigated the effects of peer discrimination on academic outcomes in ways similar to preparation for bias practices (see Table 3). In each of these analyses, we found that the relationships of peer discrimination to these academic outcomes were negative when cultural socialization was relatively low (B = −0.29, −0.40, −0.50, and −0.19; p < 0.05) and nonsignificant when cultural socialization was relatively high. Since the interactions in this study are similar in nature, we have presented examples of several significant interactions (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3).
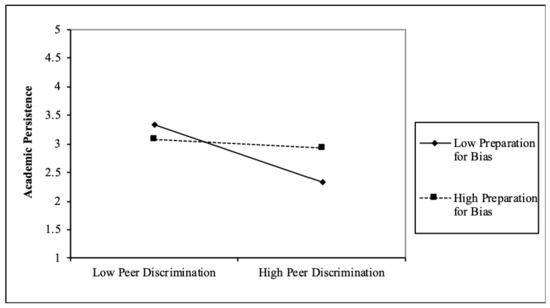
Figure 1.
Academic Persistence–Moderation: Preparation for Bias.
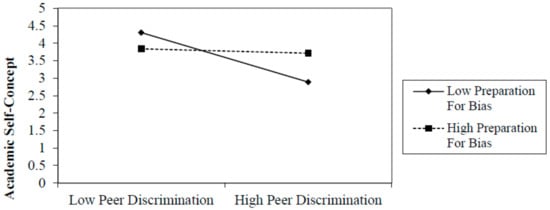
Figure 2.
Academic Self-Concept: Moderation–Preparation for Bias.
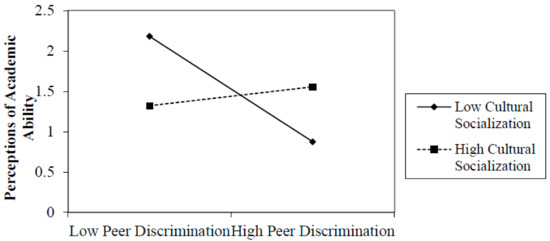
Figure 3.
Perceptions of Academic Ability: Cultural Socialization by Peer Discrimination.
9. Discussion
Adolescence is marked by developmental transitions in areas such as socioemotional development, peer group, and academic achievement. Since race becomes more salient around adolescence for African Americans (Tatum 1997), youth begin to notice both nonverbal and verbal cues surrounding race (Rosenbloom and Way 2004). School-based discrimination, such as not being called upon or treated differently than their European American counterparts, can impact the academic outcomes of African American students (Chavous et al. 2008; Wong et al. 2003). Some research has found that ethnic-racial socialization does not moderate the effects of general racial discrimination on academic outcomes (Neblett et al. 2006). However, this particular study examined the effects of perceptions of general racial discrimination and did not study the effects of school-based discrimination specifically. The current study examined the effects of school-based discrimination (e.g., peers, teachers) on academic outcomes. Specifically, this study focused on the effects of discrimination by teachers and discrimination by peers separately, in an effort to investigate if the relations of discrimination to outcomes varies according to the source. Other studies have focused on discrimination by peers or adults, but did not find differential outcomes by source (Greene et al. 2006; Niwa et al. 2014). Furthermore, this study examined whether two different dimensions of ethnic-racial socialization mitigate the effects of school-based discrimination on academic outcomes. Additionally, the two studies that found different outcomes in relation to the source of discrimination (peers vs. teachers) both consisted of multiracial samples (Benner and Graham 2013; Medvedeva 2010), whereas the current study focused on an African American sample to understand how racial discrimination may be associated with academic outcomes for African American adolescents.
We hypothesized that, consistent with previous studies (e.g., Chavous et al. 2008; Medvedeva 2010; Wong et al. 2003), peer-based discrimination would be negatively associated with academic outcomes. The results from this study suggest that youth who perceived more peer discrimination reported lower academic persistence. Moreover, youth who reported more discrimination by peers had parents who perceived their children to have lower academic ability. This finding was consistent across the regressions with cultural socialization and preparation for bias. Research suggests that students who feel discriminated against by peers (and teachers) feel a lower sense of connection to other people at school (Byrd and Chavous 2011; Hurtado and Carter 1997), and that feelings of belonging predict other motivational outcomes (Deci et al. 1991). Peer discrimination was also significantly associated with academic self-concept in the preparation for bias regression and, marginally, with academic self-concept in the cultural socialization regression. This finding echoes the research of Wong et al. (2003) in a middle school sample and Dotterer et al. (2009) in a middle and high school sample. Thus, our findings confirm existing research. We did not, however, find direct relationships between peer discrimination and academic self-efficacy, and peer discrimination’s relationship with perceptions of academic ability and academic preparedness were inconsistent across regressions.
We also hypothesized that teacher discrimination would be negatively linked to academic outcomes. However, youths’ reports of teacher discrimination were generally not associated with outcomes for the preparation for bias regressions and only marginally associated with outcomes for the cultural socialization regressions. This is surprising, given the findings for peer discrimination and the strong correlation between perceptions of peer and teacher discrimination. However, it may be that youth had more direct and frequent experiences with their peers. Nevertheless, the direction of the effects supports our hypothesis, and there were some significant interactions between teacher discrimination and ethnic-racial socialization.
Finally, we predicted that ethnic-racial socialization would mitigate the effects of school-based discrimination on academic outcomes. With regards to peer discrimination, youth reports of preparation for bias were found to buffer the relation between peer discrimination and the following academic outcomes: Academic persistence, self-concept, and self-efficacy. In addition, youth reports of cultural socialization mitigated the association between peer discrimination and youth-reported academic outcomes (e.g., academic persistence, self-concept, and self-efficacy). Moreover, cultural socialization attenuated the effects of peer discrimination on parents’ perceptions of academic ability. It may be that youth who received messages from their parents that prepared them for racial barriers and bias were prepared to overcome the consequences of discrimination by peers. These findings are similar to those indicated by Sanders (1997), who found that African American youth who were more aware of racism were also the highest achievers. Surprisingly, with regards to teacher discrimination, it was not preparation for bias messages, but cultural socialization that was found to mitigate the effects on academic outcomes. Additionally, cultural socialization mitigated the effects of teacher discrimination on parents’ perceptions of academic ability. For African American youth, it may be that racial discrimination presents a negative view of who they are, while racial socialization gives them a positive view of themselves to fall back on.
10. Limitations and Future Directions
A strength of this study was its focus on school-based discrimination and inclusion of parent reports of academic ability in addition to student self-report. Though this paper adds to the current literature, there are a few limitations that must be noted. To reduce the possibility of bias in self-reports, future studies should focus on measures collected from teachers, peers, and parents to fully understand the impact of school-based discrimination. Teacher and peer perceptions of discrimination may provide greater depth in understanding the relationship between the classroom environment and student outcomes (Byrd and Andrews 2016). This study was also cross-sectional in nature and can only provide the reader with a glimpse of what is occurring currently. It could be that African American parents were providing racial socialization messages to their children in response to discussions about school-based discrimination. Thus, longitudinal designs should be employed in future research to understand the connection between ethnic-racial socialization, racial discrimination, and academic outcomes from the beginning to the end of middle school. By studying these variables longitudinally, we will have a better understanding of the protective nature of ethnic-racial socialization within the context of racial discrimination. Furthermore, by employing longitudinal designs, we can pinpoint when perceptions of racial discrimination are the most salient and influential for this developmental stage. Future work should also consider other outcomes that are not related to self-report, such as achievement, teacher ratings of behavior, or sports achievement.
11. Implications
The current study adds to a growing body of literature that has shown the positive impact of ethnic-racial socialization on academic achievement in African American adolescents within the school context. Although previous research has investigated the relation between racial discrimination, racial socialization, and academic outcomes (Neblett et al. 2006), very few studies have examined both parent and youth reports of academic achievement with regards to racial discrimination and ethnic-racial socialization. The present study provides evidence that racial discrimination in school, specifically by peers, may be associated with negative academic outcomes for African American youth. Furthermore, results indicate that both dimensions of ethnic-racial socialization may buffer the effects of discrimination by peers on academic outcomes for African American youth. Additionally, cultural socialization mitigated the effects of teacher discrimination on academic outcomes, suggesting that messages about racial pride may offset the effects of discrimination in the school context. For African American youth, the inclusion of Afrocentric educational practices and its emphasis on cultural pride may be a way in which schools can work in tandem with parents in reinforcing messages youth may receive at home. Additionally, having messages about culture and ethnicity may be important in offsetting the negative consequences for students who are at risk for dropping out or do not feel a sense of belonging. By including ethnic-racial socialization practices, in particular messages about ethnic heritage or cultural pride in the school curriculum, may foster better academic achievement for African American youth, providing them pathways to success.
Author Contributions
M.B. came up with the manuscript idea, collected the data, cleaned and analyzed the data and was the primary authors on all the sections of the manuscript. C.B. helped with the collection of data, the analysis of the data as well as writing of the introduction, results and discussion. S.R. is the principal investigator on the project, she also created some of the parent academic involvement scales, she also helped with the writing of the introduction and the discussion as well as confirming the analyses of the results.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Teacher Discrimination Items
- Teachers call on you less often than they call on other kids because you are Black?
- Teachers grade you harder than they grade other kids because you are Black?
- You get disciplined more harshly by teachers than other kids do because you are Black?
- Teachers think you are less smart than you really are because you are Black?
- How stressful is it for you when teachers at your school treat you in these ways?
Appendix B. Peer Discrimination Items
- At school, how often do you feel like you are not picked for certain teams or other school activities because you are Black?
- At school, how often do you feel that you get in fights with some kids because you are Black?
- At school, how often do you feel that kids do not want to hang out with you because you are Black?
- How stressful is it for you when other kids at school treat you in these ways?
References
- Bellmore, Amy, Adrienne Nishina, Ji-in You, and Ting-Lan Ma. 2012. School context protective factors against peer ethnic discrimination across the high school years. American Journal of Community Psychology 49: 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benner, Aprile D., and Sandra Graham. 2013. The antecedents and consequences of racial/ethnic discrimination during adolescence: Does the source of Discrimination matter? Developmental Psychology 49: 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, Catherine P., Anne L. Sawyer, and Lindsey M. O’Brennan. 2007. Bullying and peer victimization at school: Perceptual differences between students and school staff. School Psychology Review 36: 361–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bynum, Mia Smith, Thomaseo Burton, and Candace Best. 2007. Racism experiences and psychological functioning in African American college freshmen: Is racial socialization a buffer? Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology 13: 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, Christy M. 2015. Associations of intergroup interactions and school racial socialization with academic motivation. Journal of Educational Research 108: 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, Christy M., and Dorinda J. Carter Andrews. 2016. Variations in students’ perceived reasons for, sources of, and forms of in-school discrimination: A latent class analysis. Journal of School Psychology 57: 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, Christy M., and Tabbye Chavous. 2011. Racial identity, school racial climate, and school intrinsic motivation among African American youth: The importance of person-context congruence. Journal of Research and Adolescence 21: 849–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavous, Tabbye M., Deborah Rivas-Drake, Ciara Smalls, Tiffany Griffin, and Courtney Cogburn. 2008. Gender matters too: The influences of school racial discrimination and racial identity on academic engagement outcomes among African American adolescents. Developmental Psychology 44: 637–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogburn, Courtney D., Tabbye M. Chavous, and Tiffany M. Griffin. 2011. School-based racial and gender discrimination among African American adolescents: Exploring gender variation in frequency and implications for adjustment. Race and Social Problems 3: 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, Patricia, Stephen G. West, and Leona S. Aiken. 2003. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. [Google Scholar]
- Deci, Edward L., Robert J. Vallerand, Luc G. Pelletier, and Richard M. Ryan. 1991. Motivation and education: The self-determination perspective. Educational Psychologist 26: 325–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNavas-Walt, Carmen, Bernadette D. Proctor, and Jessica C. Smith. 2010. U.S. Census Bureau, Current population reports, P60–239. In Income, Poverty and Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2010; Washington: U.S Government Printing Office. [Google Scholar]
- Dotterer, Aryn M., Susan M. McHale, and Ann C. Crouter. 2009. Sociocultural factors and school engagement among African American youth: The roles of racial discrimination, racial socialization, and ethnic identity. Applied Developmental Science 13: 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fergus, Stevenson, and Marc A. Zimmerman. 2005. Adolescent resilience: A framework for understanding healthy development in the face of risk. Annual Review of Public Health 26: 399–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, Ann R., and Christina M. Shaw. 1999. African Americans’ mental health and perceptions of racist discrimination: The moderating effects of racial socialization experiences and self-esteem. Journal of Counseling Psychology 46: 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, Celia B., Scyatta A. Wallace, and Rose E. Fenton. 2000. Discrimination distress during adolescence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence 29: 679–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, Patricia A., Andrew P. Tix, and Kenneth E. Barron. 2004. Testing moderator and mediator effects in counseling psychology research. Journal of Counseling Psychology 51: 115–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, Sandra, and Jaana Juvonen. 2002. Ethnicity, peer harassment, and adjustment in middle school: An exploratory study. The Journal of Early Adolescence 22: 173–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, Melissa L., Niobe Way, and Kerstin Pahl. 2006. Trajectories of perceived adult and peer discrimination among Black, Latino, and Asian American adolescents: Patterns and psychological correlates. Developmental Psychology 42: 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Britt, April, Cecelia R. Valrie, Beth Kurtz-Costes, and Stephanie J. Rowley. 2007. Perceived racial discrimination and self-esteem in African American youth: Racial socialization as a protective factor. Journal of Research on Adolescence 17: 669–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover-Dempsey, Kathleen V., and Howard M. Sandler. 2005. Final Performance Report for OERI Grant # R305T010673: The Social Context of Parental Involvement: A Path to Enhanced Achievement; Washington: Project Monitor, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education.
- Hughes, Diane, and Lisa Chen. 1997. When and what parents tell their children about race: An examination of race-related socialization among African American families. Applied Developmental Science 1: 200–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, Diane, and Deborah Johnson. 2001. Correlates in children’s experiences of parents’ racial socialization behaviors. Journal of Marriage and the Family 63: 981–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, Diane, James Rodriguez, Emilie P. Smith, Deborah J. Johnson, Howard C. Stevenson, and Paul Spicer. 2006. Parents’ ethnic-racial socialization practices: A review of research and directions of future study. Developmental Psychology 42: 747–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, Sylvia, and Deborah Faye Carter. 1997. Effects of college transition and perceptions of the campus racial climate on Latino college students’ sense of belonging. Sociology of Education 70: 324–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corporation. 2016. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 24. Armonk: IBM Corporation. [Google Scholar]
- Lesane-Brown, Chase L. 2006. A review of race socialization within Black families. Developmental Review 26: 400–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, Maria. 2010. Perceived discrimination and linguistic adaptation of adolescent children of immigrants. Journal of Youth and Adolescence 39: 940–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neblett, Enrique W., Jr., Cheri L. Philip, Courtney D. Cogburn, and Robert M. Sellers. 2006. African American adolescents’ discrimination experiences and academic achievement: Racial socialization as a cultural compensatory and protective factor. Journal of Black Psychology 32: 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, John G. 1979. Development of perception of own attainment and causal attributions for success and failure in reading. Journal of Educational Psychology 71: 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, Erika Y., Niobe Way, and Diane L. Hughes. 2014. Trajectories of ethnic-racial discrimination among ethnically diverse early adolescents: Associations with psychological and social adjustment. Child Development 85: 2339–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, Marie F. 2002. Racial socialization of young Black children. In Black Children: Social Educational and Parental Environments, 2nd ed. Edited by Harriette P. McAdoo. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Preacher, Kristopher J., Patrick J. Curran, and Daniel J. Bauer. 2006. Computational tools for probing interaction effects in multiple linear regression, multilevel modeling, and latent curve analysis. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics 31: 437–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ProximityOne. 2010. Michigan School District Demographic Files. Available online: http://proximityone.com/mi_sdc.htm (accessed on 29 September 2014).
- Romero, Andrea J., and Robert E. Roberts. 1998. Perception of discrimination and ethnocultural variables in a diverse group of adolescents. Journal of Adolescence 21: 641–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, Chad Allen, Dorothy Lynn Espelage, and Lisa E. Monda-Amaya. 2009. Bullying and victimisation rates among students in general and special education: A comparative analysis. Educational Psychology 29: 761–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, Susan Rakosi, and Niobe Way. 2004. Experiences of discrimination among African American, Asian American and Latino adolescents in an urban high school. Youth and Society 35: 420–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, S. J. 2004. Academic preparedness scales. Unpublished Manuscript. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, Mavis G. 1997. Overcoming obstacles: Academic achievement as a response to racism and discrimination. Journal of Negro Education 66: 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, Eleanor K., Cleopatra H. Caldwell, Robert M. Sellers, and James S. Jackson. 2008. The prevalence of perceived discrimination among African American and Caribbean Black youth. Developmental Psychology 44: 1288–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, Margaret Beale. 1995. Old issues and new theorizing abut African American youth: A phenomenological variant of ecological systems theory. In Black Youth: Perspectives on Their Status in the United States. Edited by Ronald L. Taylor. Westport: CT Praeger, pp. 37–69. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, Margaret Beale. 1999. Social and cultural influences on school adjustment: The application of identity-focused cultural ecological perspective. Educational Psychologist 34: 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, Margaret Beale, Davido Dupree, and Tracey Hartmann. 1997. A phenomenological variant of ecological systems theory (PVEST): A self-organization perspective in context. Development and Psychopathology 9: 817–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, Margaret Beale, Davido Dupree, Michael Cunningham, Vinay Harpalani, and Michèle Muñoz-Miller. 2003. Vulnerability to violence: A contextually-sensitive developmental perspective on African American adolescents. Journal of Social Issues 59: 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suizzo, Marie-Anne, Courtney Robinson, and Erin Pahlke. 2008. African American mothers’ socialization beliefs and goals with young children: Themes of history, education, and collective independence. Journal of Family Issues 29: 287–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatum, Beverly Daniel. 1997. Why Are All the Black Kids Sitting Together in the Cafeteria? New York: Basic Books. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Ming-Te, and James P. Huguley. 2012. Parental racial socialization as a moderator of the effects of racial discrimination on educational success among African American adolescents. Child Development 83: 1716–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellborn, James G. 1991. Engaged and Disaffected Action: The Conceptualization and Measurement of Motivation in the Academic Domain. Unpublished Ph.D. dissertation, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA. [Google Scholar]
- White-Johnson, Rhonda L., Kahlil R. Ford, and Robert M. Sellers. 2010. Parental racial socialization profiles: Association with demographic factors, racial discrimination, childhood socialization, and racial identity. Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology 16: 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Carol A., Jacquelynne S. Eccles, and Arnold Sameroff. 2003. The influence of ethnic discrimination and ethnic identification on African American adolescents’ school and socioemotional adjustment. Journal of Personality 71: 1197–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).