Evaluating Color Perception in Indoor Cultural Display Spaces of Traditional Chinese Floral Arrangements: A Combined Semantic Differential and Eye-Tracking Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background and Significance
1.2. Literature Review
1.2.1. Spatial Environmental Color Design
1.2.2. Spatial Environmental Color Application Evaluation
1.2.3. Spatial and Cultural Translation of Traditional Colors
1.3. Research Objectives
- (1)
- To propose a method for extracting and modernly translating traditional cultural colors based on historical images and documentary materials.
- (2)
- To construct a multi-factor evaluation framework for display space colors that integrates subjective Semantic Differential evaluations and objective eye-tracking data.
- (3)
- To quantitatively analyze the differences between different color schemes across perception dimensions and explore the correlations between the metrics.
2. Materials and Methods
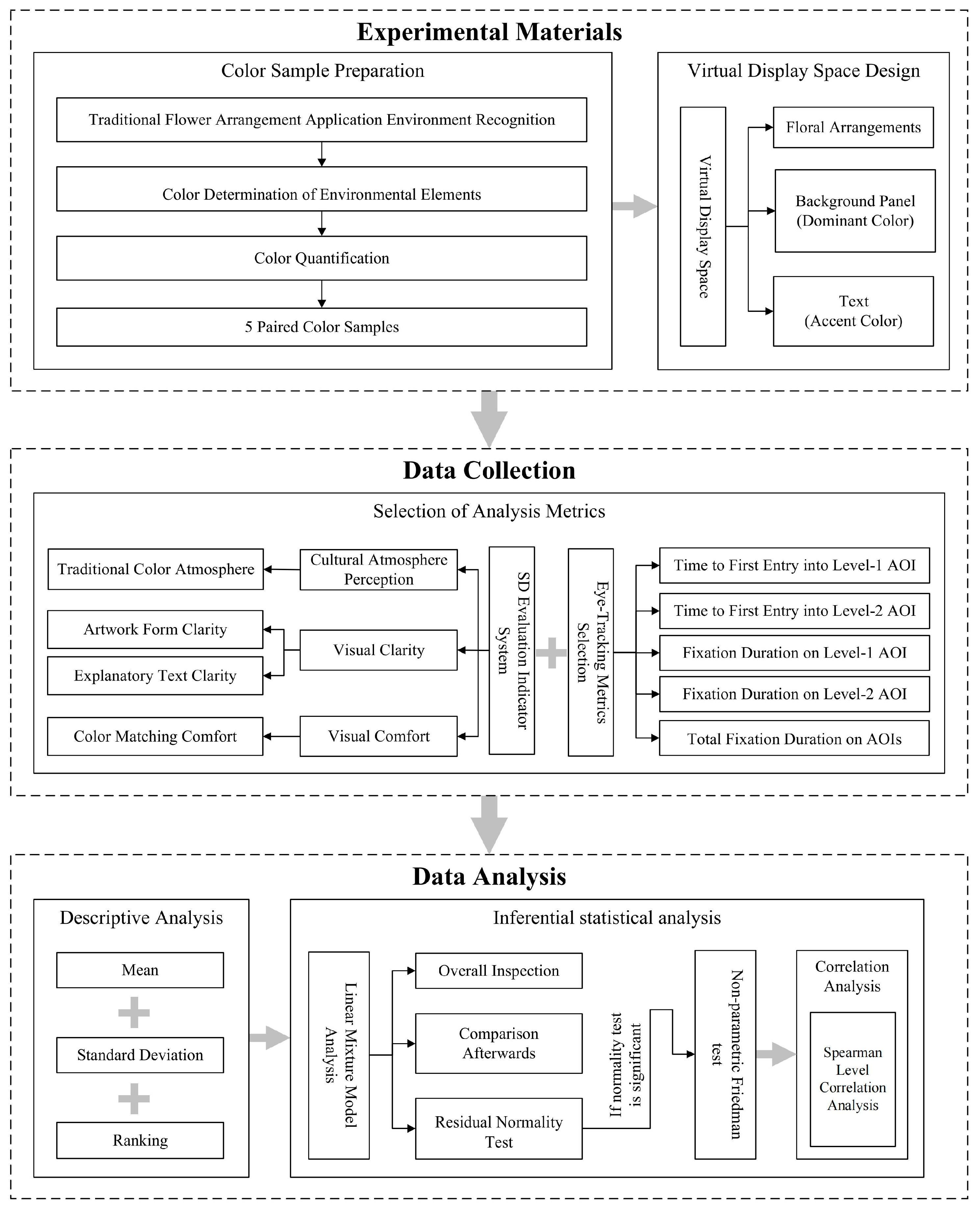
2.1. Technical Route
2.2. Virtual Display Space Color Design
2.2.1. Color Extraction and Matching
2.2.2. Virtual Display Space Design
2.3. Combined Semantic Differential Method and Eye-Tracking Analysis Method
2.3.1. Semantic Differential Evaluation System Establishment
2.3.2. Eye-Tracking Metrics Selection
2.4. Data Collection
2.4.1. Participant Recruitment
2.4.2. Experimental Environment and Apparatus
2.4.3. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. SD Evaluation Results
3.1.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.1.2. Linear Mixed Model Analysis
3.1.3. Non-Parametric Tests
3.2. Eye-Tracking Survey Results
3.2.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2.2. Linear Mixed Model Analysis
3.2.3. Non-Parametric Tests
3.3. Correlation Analysis
3.3.1. Internal Correlation Analysis of Subjective Perception
3.3.2. Internal Correlation Analysis of Eye-Tracking Indicators
3.3.3. Internal Correlation Analysis of Subjective Perception and Eye-Tracking Behavior
4. Discussion
4.1. Subjective Perception Differences and Internal Associations of Traditional Color Schemes
4.2. Attention Allocation Mechanisms Reflected in Eye-Tracking Behavior Patterns
4.3. Separation of Subjective Perception and Objective Eye-Tracking Behavior
4.4. Research Limitations and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Adj. | Adjusted |
| AOI | Areas of Interest |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| CIE | Commission Internationale de l‘Éclairage |
| CMYK | Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key (black) |
| FD | Fixation Duration |
| HSB | Hue, Saturation, Brightness |
| LMM | Linear Mixed Model |
| M | Mean |
| N | Sample size |
| p | Probability value |
| RGB | Red, Green, Blue |
| rs | Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| η2 | Eta-squared |
| χ2 | Chi-square statistic |
References
- Hwang, Y.; Kim, H.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Gim, J. Color saturation effect in hotel images: Moderating roles of travel purpose and busy mindset. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2025, 42, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, E. Effects of coloured lighting on pleasure and arousal in relation to cultural differences. Light. Res. Technol. 2022, 54, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.L.; Yun, Y.X.; Ren, L.J. Research on the Assessment of Architectural Colors in Cultural Heritage Blocks Based on Computer Vision: A Case Study of Tianjin. Land 2025, 14, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitgood, S. An analysis of visitor circulation: Movement patterns and the general value principle. Curator Mus. J. 2006, 49, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.I. Analysis of color symbology from the perspective of cultural semiotics focused on Korean costume colors according to the cultural changes. Color Res. Appl. 2007, 32, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roppola, T. Designing for the Museum Visitor Experience; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.H.; Li, J.X.; Chen, L.D.; Shan, Q.; Jin, Y.; Ren, G.P. A study on color visual perception of museum exhibition space based on eye movement experiments. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1431161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.E. Nine Ways to Reduce Cognitive Load in Multimedia Learning. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 38, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippopoulos, P.I.; Drivas, I.C.; Tselikas, N.D.; Koutrakis, K.N.; Melidi, E.; Kouis, D. A Holistic Approach for Enhancing Museum Performance and Visitor Experience. Sensors 2024, 24, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reppa, I.; Williams, K.E.; Greville, W.J.; Saunders, J. The relative contribution of shape and colour to object memory. Mem. Cogn. 2020, 48, 1504–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küller, R.; Mikellides, B.; Janssens, J. Color, Arousal, and Performance—A Comparison of Three Experiments. Color Res. Appl. 2009, 34, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.C.; Chao, C.J. Effects of simulated driving task screen background color combinations on visual performance and visual fatigue. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2024, 47, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haas, B.; Iakovidis, A.L.; Schwarzkopf, D.S.; Gegenfurtner, K.R. Individual differences in visual salience vary along semantic dimensions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11687–11692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.M.; Zhou, Z.C.; Xu, Y.Y. Design Element Preferences in Public Facilities: An Eye Tracking Study. Land 2023, 12, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.C.; Chen, J.M.; Huang, R.Y.; Shen, M.H.; Lu, M.C.; Liu, C.J. Numerical Analysis on Color Preference and Visual Comfort from Eye Tracking Technique. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 861610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.S.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, B.H.; Han, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, B. Assessment of Color Perception and Preference with Eye-Tracking Analysis in a Dental Treatment Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovillo, G.; Rapuano, M.; Milite, A.; Ruggiero, G. Perceived Quality in the Automotive Industry: Do Car Exterior and Interior Color Combinations Have an Impact? Appl. Syst. Innov. 2024, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.H.; Yang, Y.X.; Yu, J.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Lin, B.R. Effects of eye illuminance and correlated color temperature on subjective visual comfort, mood, and alertness in high-space buildings. Build. Environ. 2025, 283, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Li, L.K.; Jiang, Y.T.; Liu, X.; Yang, H. Quantitative analysis methods for evaluating colour on architectural heritage: Survey of colour restoration and perception of the Wen Yuan Ge in the Forbidden City. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Research on Restorative Color Extraction and Design Application Based on Spatial Environment Perception. Art Des. 2024, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.K. Research on the Colored Paintings of the “Yingzao Fashi”; Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H. Regulations and Examples of Polychrome Painting Materials for Palace Architecture; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Sun, H.; Li, J. Research on Architectural Color and Visual Comfort in Historic Landscape Areas. Buildings 2023, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, G. Reconstruction in the Pictorial Space: Architectural Structures and Urban Depictions of Cairo in Orientalist Paintings. METU J. Fac. Archit. 2025, 42, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Zhang, M.R.; Liu, J.; Kaya, M.G.A.; Tang, K.Y. Non-destructive pigment analysis of mural paintings from the Song and Jin Dynasties in Baode County. J. Archaeol. Sci.-Rep. 2025, 61, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Committee of the Complete Collection of Song Dynasty Paintings (Ed.) Complete Song Dynasty Paintings; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2008; ISBN 978730808866. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.X.; He, J.Z. Interpretation of the “Yingzao Fashi”; Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Illustrations of the “Yingzao Fashi” (Vol. 2); China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Camgöz, N.; Yener, C.; Güvenç, D. Effects of hue, saturation, and brightness: Part 2: Attention. Color Res. Appl. 2004, 29, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedel, M.; Pieters, R.; van der Lans, R. Modeling Eye Movements During Decision Making: A Review. Psychometrika 2023, 88, 697–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Durmus, D. The Effect of Color Contrast on the Visual Clarity of Images of Complex Indoor Environments. Buildings 2025, 15, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Shen, M.T.; Huang, Y.M. Exploring the Impact of Facade Color Elements on Visual Comfort in Old Residential Buildings in Shanghai: Insights from Eye-Tracking Technology. Buildings 2024, 14, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humar, I.; Gradisar, M.; Turk, T.; Erjavec, J. The impact of color combinations on the legibility of text presented on LCDs. Appl. Ergon. 2014, 45, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Shen, M.T.; Huang, Y.M. Combining Eye-Tracking Technology and Subjective Evaluation to Determine Building Facade Color Combinations and Visual Quality. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Luo, M.R. Visual comfort models based on coloured text and neutral background combinations. Vis. Res. 2025, 227, 108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spering, M.; Montagnini, A.; Gegenfurtner, K.R. Competition between color and luminance for target selection in smooth pursuit and saccadic eye movements. J. Vis. 2008, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Guo, H.Y.; Song, Z.T.; Yang, N.; Wang, R.; Guo, F. The Influence of the Relationship Between Landmark Symbol Types, Annotations, and Colors on Search Performance in Mobile Maps Based on Eye Tracking. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E.; Maier, A. The attentional guidance of individual colours in increasingly complex displays. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 81, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Wang, P.H.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, Y. Investigating Influence of Visual Elements of Arcade Buildings and Streetscapes on Place Identity Using Eye-Tracking and Semantic Differential Methods. Buildings 2023, 13, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sik-Lanyi, C.; Halmosi, B.; Ara, J.; Szucs, J.; Guzzvinecz, T. Assessing Memory Colors of University Students. Infocommunications J. 2024, 16, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, Y. A study on comparative analysis of perception of color between Korean and Malaysia: Focusing on Youth. J. Basic Des. Art 2013, 14, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
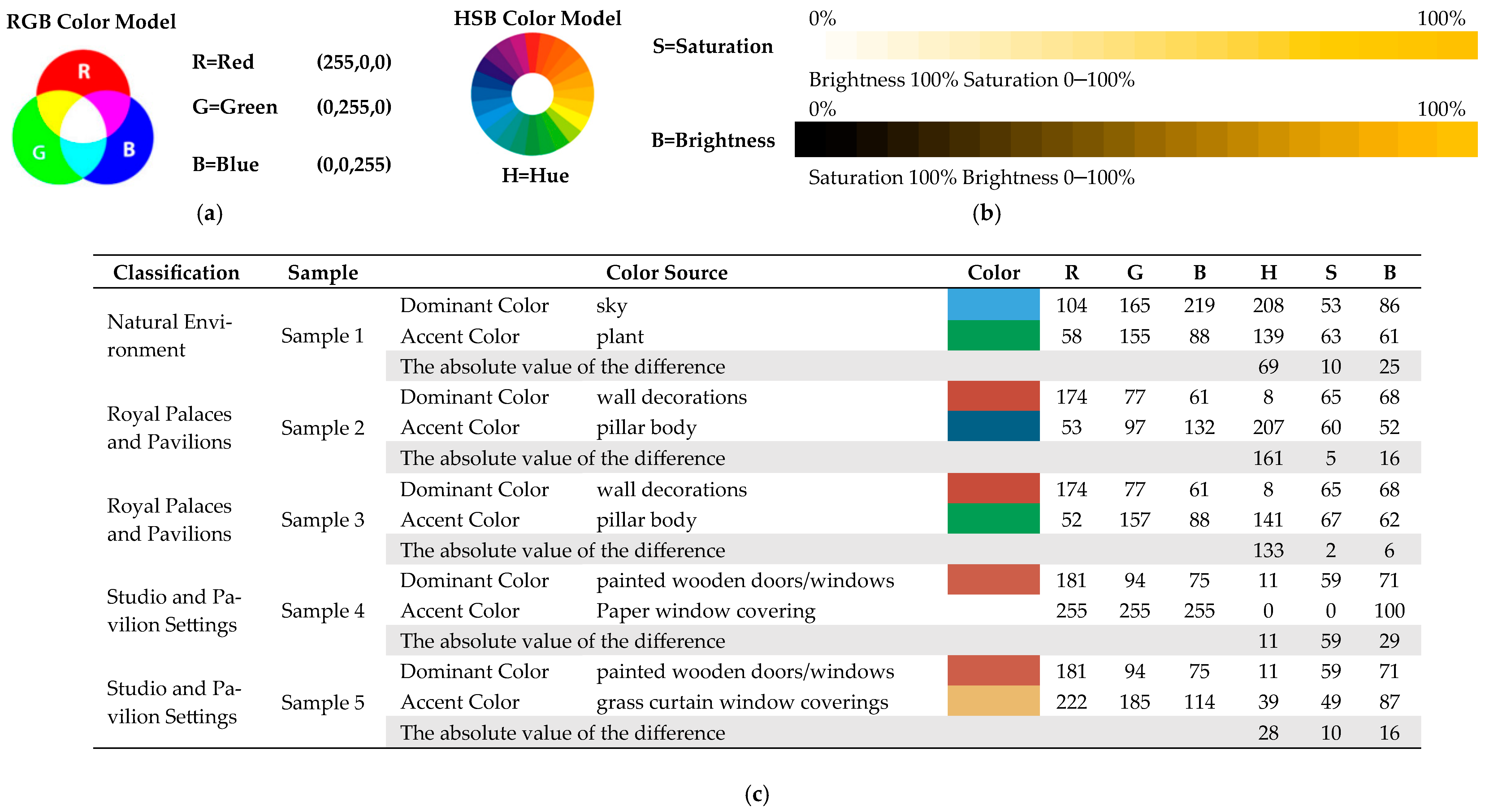
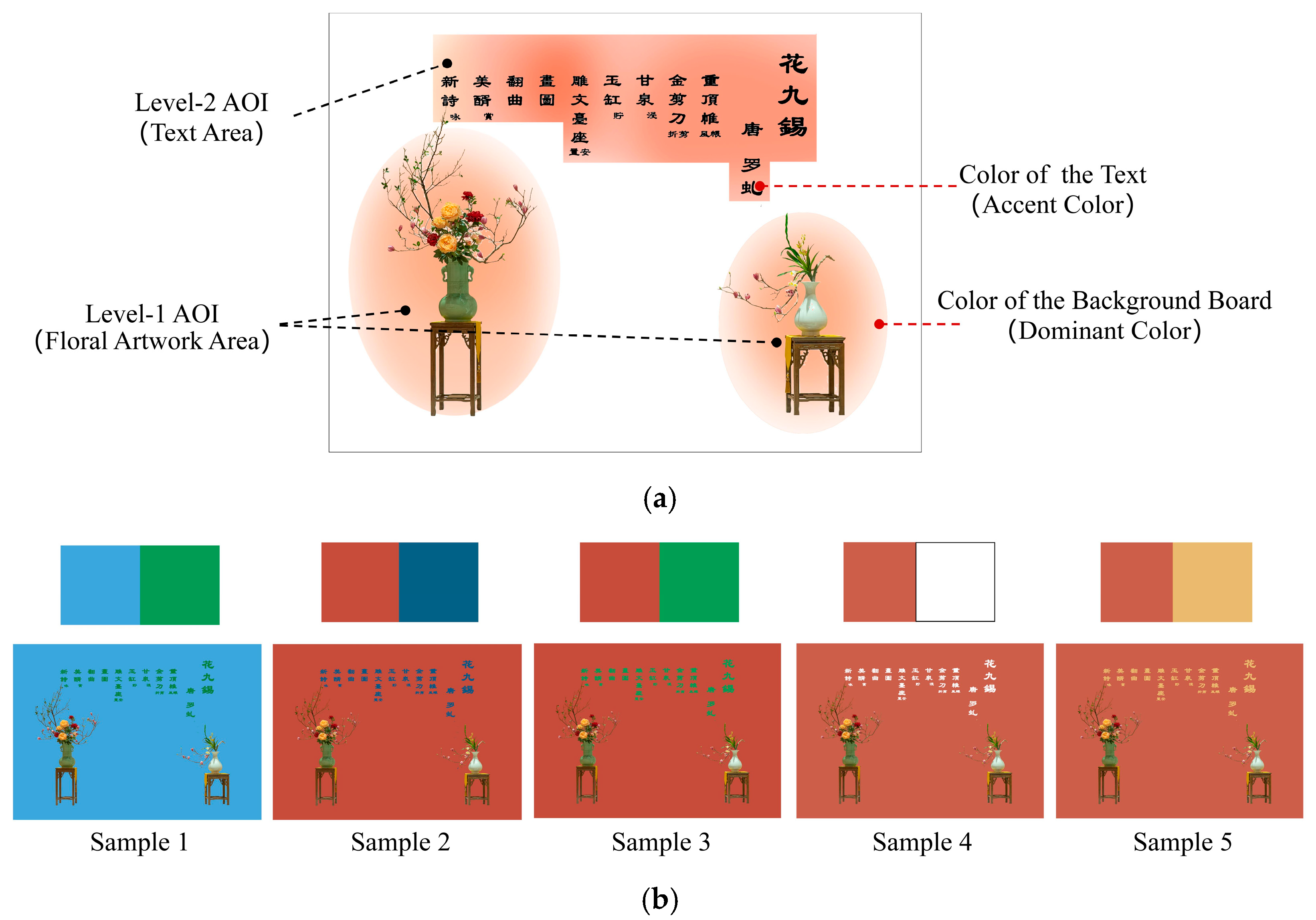
| Ambient Background Content | Summary of Components | Some Corresponding Painting Examples | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Painting Title * | Collection Location | ||
| Natural Environment | Dominant Color: Sky Accent Color: Plant | Listening to the Qin (Ting Qin Tu) | The Palace Museum, Beijing |
| Literary Gathering (Wen Hui Tu) | National Palace Museum, Taipei | ||
| Listening to the Ruan (Ting Ruan Tu) | National Palace Museum, Taipei | ||
| Antiquarian Gathering Around a Stove (Wei Lu Bo Gu Tu) | National Palace Museum, Taipei | ||
| Royal Palaces and Pavilions | Dominant Color: Wall decorations Accent Color: pillar body | Han Palace (Han Gong Tu) | National Palace Museum, Taipei |
| Autumn in the Han Palace (Han Gong Qiu Tu) | Long Museum, Shanghai | ||
| Emperor Ming Huang’s Summer Palace (Minghuang Bi Shu Tu) | Osaka City Museum of Fine Arts | ||
| Emperor Ming Huang Cockfighting (Minghuang Dou Ji Tu) | Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art | ||
| Studio and Pavilion Settings | Dominant Color: Painted wooden doors/windows Accent Color: paper/silk window coverings | Chatting in a Riverside Pavilion (Xi Ting Ke Hua Tu) | The Palace Museum, Beijing |
| Enjoying the Scroll by the Breeze (Feng Yan Zhan Juan Tu) | National Palace Museum, Taipei | ||
| Study of Heavenly Fragrance (Tian Xiang Shu Wu Tu) | National Palace Museum, Taipei | ||
| Reading the Book of Changes by the Winter Window (Han Chuang Du Yi Tu) | Duoyunxuan, Shanghai | ||
| Evaluation Dimension | Evaluation Indicator | Adjective Pair | Evaluation Scale 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural Atmosphere Perception | Traditional Cultural Atmosphere | Song Dynasty traditional-Contemporary avant-garde | Very traditional (5 pts)-Relatively traditional (4 pts)-Neutral (3 pts)-Relatively avant-garde (2 pts)-Very avant-garde (1 pt) |
| Visual Comfort | Color Matching Comfort | Comfortable color-Uncomfortable color | Very comfortable (5 pts)-Relatively comfortable (4 pts)-Neutral (3 pts)-Relatively uncomfortable (2 pts)-Very uncomfortable (1 pt) |
| Visual Clarity | Artwork Form Clarity | Clear form-Blurred form | Very clear (5 pts)-Relatively clear (4 pts)-Neutral (3 pts)-Relatively blurred (2 pts)-Very blurred (1 pt) |
| Explanatory Text Clarity | Clear text-Blurred text | Very clear (5 pts)-Relatively clear (4 pts)-Neutral (3 pts)-Relatively blurred (2 pts)-Very blurred (1 pt) |
| Metric Name | Description | Perceptual Process | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to First Entry into Level-1 AOI | The duration before the eyes first fixate on the floral arrangement area. | Information Search | Seconds (s) |
| Time to First Entry into Level-2 AOI | The duration before the eyes first fixate on the text description area. | Information Search | Seconds (s) |
| Fixation Duration on Level-1 AOI | The total duration of eye fixations on the floral arrangement area. | Information Processing | Seconds (s) |
| Fixation Duration on Level-2 AOI | The total duration of eye fixations on the text description area. | Information Processing | Seconds (s) |
| Total Fixation Duration on AOIs | The total duration of eye fixations on all AOIs. | Information Processing | Seconds (s) |
| Variable | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Sample 4 | Sample 5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M 1 | SD 2 | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | ||
| Cultural Atmosphere Perception | Traditional Cultural Atmosphere Perception | 2.550 | 1.081 | 2.820 | 1.131 | 3.200 | 1.080 | 3.370 | 1.014 | 4.140 | 0.842 |
| Visual Comfort | Color Matching Comfort Level | 2.510 | 1.277 | 2.350 | 1.032 | 2.630 | 1.167 | 3.390 | 1.017 | 4.040 | 0.789 |
| Visual Clarity | Artwork Form Clarity | 3.370 | 1.167 | 3.000 | 1.190 | 3.060 | 1.107 | 3.470 | 1.063 | 3.310 | 1.122 |
| Explanatory Text Clarity | 2.080 | 0.909 | 2.410 | 1.257 | 3.200 | 1.154 | 4.670 | 0.851 | 4.240 | 0.969 | |
| Overall Mean Score | 2.628 | 1.109 | 2.645 | 1.153 | 3.023 | 1.127 | 3.725 | 0.986 | 3.933 | 0.931 | |
| Dependent Variable | Numerator df | Denominator df | F | Significance (p) | Partial η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Cultural Atmosphere Perception | 4 | 192 | 23.635 | <0.001 | 0.330 |
| Color Matching Comfort Level | 4 | 192 | 26.002 | <0.001 | 0.351 |
| Artwork Form Clarity | 4 | 192 | 2.485 | 0.045 | 0.049 |
| Explanatory Text Clarity | 4 | 192 | 69.199 | <0.001 | 0.590 |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.265 | 0.653 *2 | 0.816 * | 1.592 * | |
| 2 | −0.265 | 0.388 | 0.551 * | 1.327 * | |
| 3 | −0.653 * | −0.388 | 0.163 | 0.939 * | |
| 4 | −0.816 * | −0.551 * | −0.163 | 0.776 * | |
| 5 | −1.592 * | −1.327 * | −0.939 * | −0.776 * |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −0.163 | 0.122 | 0.878 *2 | 1.531 * | |
| 2 | 0.163 | 0.286 | 1.041 * | 1.694 * | |
| 3 | −0.122 | −0.286 | 0.755 * | 1.408 * | |
| 4 | −0.878 * | −1.041 * | −0.755 * | 0.653 * | |
| 5 | −1.531 * | −1.694 * | −1.408 * | −0.653 * |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −0.367 | −0.306 | 0.102 | −0.061 | |
| 2 | 0.367 | 0.061 | 0.469 | 0.306 | |
| 3 | 0.306 | −0.061 | 0.408 | 0.245 | |
| 4 | −0.102 | −0.469 | −0.408 | −0.163 | |
| 5 | 0.061 | −0.306 | −0.245 | 0.163 |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.327 | 1.122 *2 | 2.592 * | 2.163 * | |
| 2 | −0.327 | 0.796 * | 2.265 * | 1.837 * | |
| 3 | −1.122 * | −0.796 * | 1.469 * | 1.041 * | |
| 4 | −2.592 * | −2.265 * | −1.469 * | −0.429 | |
| 5 | −2.163 * | −1.837 * | −1.041 * | 0.429 |
| Variable | Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test | Shapiro–Wilk Test | Judgment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Cultural Atmosphere Perception | p = 0.200 * > 0.050 | p = 0.325 > 0.050 | Residuals follow a normal distribution |
| Color Matching Comfort Level | p = 0.010 < 0.050 | p = 0.187 > 0.050 | Residual distribution does not follow a normal distribution 2 |
| Artwork Form Clarity | p = 0.200 * > 0.050 | p = 0.103 > 0.050 | Residuals follow a normal distribution |
| Explanatory Text Clarity | p < 0.001 < 0.050 | p = 0.005 < 0.050 | Residual distribution does not follow a normal distribution |
| Variable | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Sample 4 | Sample 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M 1 | SD 2 | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Time to First Entry into Level-1 AOI (s) | 0.654 | 0.903 | 1.676 | 3.225 | 2.643 | 3.910 | 2.348 | 3.623 | 1.905 | 3.508 |
| Time to First Entry into Level-2 AOI (s) | 4.020 | 5.819 | 3.542 | 5.248 | 2.911 | 4.992 | 4.632 | 6.166 | 2.875 | 4.816 |
| Fixation Duration on Level-1 AOI (s) | 5.762 | 2.923 | 5.421 | 3.223 | 5.574 | 3.312 | 4.749 | 3.399 | 4.774 | 2.942 |
| Fixation Duration on Level-2 AOI (s) | 2.939 | 3.165 | 3.735 | 3.566 | 3.332 | 3.435 | 2.692 | 2.582 | 4.187 | 3.273 |
| Total Fixation Duration on AOIs (s) | 8.701 | 3.378 | 9.156 | 3.347 | 8.906 | 3.400 | 7.441 | 3.681 | 8.962 | 3.341 |
| Dependent Variable | Numerator Df | Denominator Df | F | Significance (p) | Partial η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to First Entry into Level-1 AOI (s) | 4 | 192 | 3.429 | 0.010 | 0.067 |
| Time to First Entry into Level-2 AOI (s) | 4 | 192 | 2.264 | 0.064 | 0.045 |
| Fixation Duration on Level-1 AOI (s) | 4 | 192 | 1.734 | 0.144 | 0.035 |
| Fixation Duration on Level-2 AOI (s) | 4 | 192 | 3.173 | 0.015 | 0.062 |
| Total Fixation Duration on AOIs (s) | 4 | 192 | 6.318 | <0.001 | 0.116 |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.021 | 1.989 *2 | 1.694 * | 1.251 | |
| 2 | −1.021 | 0.967 | 0.673 | 0.229 | |
| 3 | −1.989 * | −0.967 | −0.295 | −0.738 | |
| 4 | −1.694 * | −0.673 | 0.295 | −0.443 | |
| 5 | −1.251 | −0.229 | 0.738 | 0.443 |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.796 | 0.393 | −0.247 | 1.248 | |
| 2 | −0.796 | −0.403 | −1.042 | 0.452 | |
| 3 | −0.393 | 0.403 | −0.640 | 0.855 | |
| 4 | 0.247 | 1.042 | 0.640 | 1.495 *2 | |
| 5 | −1.248 | −0.452 | −0.855 | −1.495 * |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.455 | 0.206 | −1.259 *2 | 0.261 | |
| 2 | −0.455 | −0.250 | −1.715 * | −0.194 | |
| 3 | −0.206 | 0.250 | −1.465 * | 0.055 | |
| 4 | 1.259 * | 1.715 * | 1.465 * | 1.521 * | |
| 5 | −0.261 | 0.194 | −0.055 | −1.521 * |
| Variable | Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test | Shapiro–Wilk Test | Judgment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to First Entry into Level-1 AOI (s) | p < 0.001 < 0.050 | p = < 0.001 < 0.050 | Residual distribution does not follow a normal distribution |
| Time to First Entry into Level-2 AOI (s) | p < 0.001 < 0.050 | p = < 0.001 < 0.050 | Residual distribution does not follow a normal distribution |
| Fixation Duration on Level-1 AOI (s) | p = 0.200 * 2 > 0.050 | p = 0.860 > 0.050 | Residuals follow a normal distribution |
| Fixation Duration on Level-2 AOI (s) | p < 0.001 < 0.050 | p < 0.001 < 0.050 | Residual distribution does not follow a normal distribution |
| Total Fixation Duration on AOIs (s) | p = 0.200 * > 0.050 | p = 0.036 < 0.050 | Residual distribution does not follow a normal distribution 3 |
| Metrics | Traditional Cultural Atmosphere Perception | Color Matching Comfort Level | Artwork Form Clarity | Explanatory Text Clarity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Color Atmosphere Perception | Correlation coefficient | 1 | 0.471 **2 | 0.133 * | 0.290 ** |
| Significance (two-tailed) | <0.001 | 0.037 | <0.001 | ||
| Color Matching Comfort Level | Correlation coefficient | 0.471 ** | 1 | 0.216 ** | 0.443 ** |
| Significance (two-tailed) | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Artwork Form Clarity | Correlation coefficient | 0.133 * | 0.216 ** | 1 | 0.245 ** |
| Significance (two-tailed) | 0.037 | 0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Explanatory Text Clarity | Correlation coefficient | 0.290 ** | 0.443 ** | 0.245 ** | 1 |
| Significance (two-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Metrics | Time to First Entry into Level-1 AOI (s) | Time to First Entry into Level-2 AOI (s) | Fixation Duration on Level-1 AOI (s) | Fixation Duration on Level-2 AOI (s) | Total Fixation Duration on AOIs (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to First Entry into Level-1 AOI (s) | Correlation coefficient | 1 | −0.307 **,2 | −0.251 ** | 0.076 | −0.163 * |
| Significance (two-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.235 | 0.011 | ||
| Time to First Entry into Level-2 AOI (s) | Correlation coefficient | −0.307 ** | 1 | 0.112 | −0.574 ** | −0.347 ** |
| Significance (two-tailed) | <0.001 | 0.079 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Fixation Duration on Level-1 AOI (s) | Correlation coefficient | −0.251 ** | 0.112 | 1 | −0.367 ** | 0.482 ** |
| Significance (two-tailed) | <0.001 | 0.079 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Fixation Duration on Level-2 AOI (s) | Correlation coefficient | 0.076 | −0.574 ** | −0.367 ** | 1 | 0.560 ** |
| Significance (two-tailed) | 0.235 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0 | ||
| Total Fixation Duration on AOIs (s) | Correlation coefficient | −0.163 * | −0.347 ** | 0.482 ** | 0.560 ** | 1 |
| Significance (two-tailed) | 0.011 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Metrics | Traditional Cultural Atmosphere Perception | Color Matching Comfort Level | Artwork Form Clarity | Explanatory Text Clarity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to First Entry into Level-1 AOI (s) | Correlation coefficient | 0.069 | 0.106 | −0.014 | 0.093 |
| Significance (two-tailed) | 0.280 | 0.099 | 0.831 | 0.148 | |
| Time to First Entry into Level-2 AOI (s) | Correlation coefficient | 0.036 | −0.026 | 0.051 | 0.046 |
| Significance (two-tailed) | 0.580 | 0.691 | 0.424 | 0.476 | |
| Fixation Duration on Level-1 AOI (s) | Correlation coefficient | −0.104 | −0.081 | −0.115 | −0.092 |
| Significance (two-tailed) | 0.105 | 0.209 | 0.071 | 0.152 | |
| Fixation Duration on Level-2 AOI (s) | Correlation coefficient | 0.047 | 0.124 | 0 | −0.033 |
| Significance (two-tailed) | 0.461 | 0.053 | 1 | 0.607 | |
| Total Fixation Duration on AOIs (s) | Correlation coefficient | −0.008 | 0.050 | −0.090 | −0.123 |
| Significance (two-tailed) | 0.904 | 0.437 | 0.161 | 0.054 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Yuan, K.; Fan, P.; Qin, H.; Gong, W. Evaluating Color Perception in Indoor Cultural Display Spaces of Traditional Chinese Floral Arrangements: A Combined Semantic Differential and Eye-Tracking Study. Buildings 2026, 16, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010181
Yuan K, Fan P, Qin H, Gong W. Evaluating Color Perception in Indoor Cultural Display Spaces of Traditional Chinese Floral Arrangements: A Combined Semantic Differential and Eye-Tracking Study. Buildings. 2026; 16(1):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010181
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Kun, Pingfang Fan, Han Qin, and Wei Gong. 2026. "Evaluating Color Perception in Indoor Cultural Display Spaces of Traditional Chinese Floral Arrangements: A Combined Semantic Differential and Eye-Tracking Study" Buildings 16, no. 1: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010181
APA StyleYuan, K., Fan, P., Qin, H., & Gong, W. (2026). Evaluating Color Perception in Indoor Cultural Display Spaces of Traditional Chinese Floral Arrangements: A Combined Semantic Differential and Eye-Tracking Study. Buildings, 16(1), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010181





