Abstract
Dealing with solid waste has always been a global concern, and construction waste is one of the most important parts. Addressing how to properly dispose of construction waste, reduce its negative environmental impact, and achieve effective resource recycling has emerged as an urgent problem to be solved. Technological innovation underpins efficient waste reduction, reuse, and recycling, but existing research often overlooks systematic and quantitative measurements of innovation initiatives. This study uncovers the development status and trends of construction waste recycling (CWR) technology, identifies key points and potential innovation directions for technological development, and also explores practical strategies to promote technological innovation and industrial growth. Through patent analysis, this study uncovers the current status of technological innovation within China’s CWR industry. A text mining approach is employed to analyze patent texts related to core technologies, explore topic contents, and identify topic intensities and evolution trends. A comparative analysis between China and the global dominant countries in CWR reveals China’s technological strengths and weaknesses. The results indicate that patent applications in China’s CWR industry are substantial, with a rapid growth rate, while its global competitiveness remains weak. The applicants are widely distributed, with traditional enterprises demonstrating strong innovation capabilities, while emerging and small-to-medium enterprises lack vitality. The industry has potential advantages in developing resource recycling devices and construction wastewater treatment technology, but the technological foundation in some other core technologies is weak. This study offers an overview of technological innovation initiatives in the CWR industry, representing a breakthrough in existing research. The findings will assist policymakers in formulating evidence-driven strategies to promote CWR.
1. Introduction
Solid waste is a rapidly expanding problem worldwide, and how to deal with this residual waste has become a hot topic. As an essential part of the solid waste stream, construction waste treatment has become the focus of academia and industry [1]. Construction waste, a generic term for engineering sediment, engineering mud, engineering waste, demolition waste, and decoration waste [2], consists of abandoned soil, scrap materials, and other byproducts generated during the construction, expansion, reconstruction, and demolition of various buildings, structures, and pipe networks as well as residential decoration and renovation [3]. In China, the annual municipal construction waste generation surpasses two billion tons, nearly eightfold the volume of household refuse and accounting for approximately 40% of total municipal solid waste [4]. With the ongoing demolition of old buildings, this figure is expected to continue rising. Untreated construction waste is complex in composition, and its harmful substances, such as asbestos, mercury, and lead-containing coatings, pose a severe threat to the environment and human health [5]. Moreover, improper waste disposal, whether from construction or demolition, is quite wasteful [6]. Over the past few decades, China’s construction waste has caused significant environmental damage [7]. In Shenzhen, a megalopolis of China, approximately 84% of construction waste was landfilled, with over half disposed of in unlicensed landfills or illegally dumped [8]. Similarly, it was found that most construction waste was buried or haphazardly placed near construction sites [9]. Effectively managing construction waste is crucial for the government to address this growing challenge.
A practical approach to managing construction waste entails resource reuse and recycling [10]. CWR is the most environmentally friendly method in terms of global warming potential [11]. Over recent years, China’s rapid urbanization has driven a sharp increase in the generation of construction waste. The industry consensus is that approximately 90% of construction waste can be recycled [12]. However, in China, the average treatment rate of construction waste in most cities ranges from 3% to 10%, significantly lagging behind other powerful economies like Japan, South Korea, Germany, and the United States [13]. China’s entry into the field of CWR is relatively recent. Factors including low technological sophistication in resource recycling and a lack of awareness regarding resource conservation have severely impeded the advancement of CWR [14]. As such, CWR in China remains nascent [13,15]. Enhancing CWR technology and optimizing its management framework is imperative. Recycling construction waste and realizing the closed-cycle utilization of the waste can facilitate the sustainable development of the construction industry [16]. Given this context, this study aims to uncover the development status and trends of CWR technology, identify key points and potential innovation directions for technological development, and explore practical strategies to promote technological innovation and industrial growth.
With rising global awareness of sustainable development and environmental protection, construction waste management has become a hot topic worldwide [17]. Scholars are increasingly devoted to exploring relevant policy mechanisms, enhancing disposal efficiency, and developing low-cost recycling technologies. However, few researchers have focused on the progress of CWR technology. Some scholars have summarized the research status of construction waste management, either holistically or in specific parts. For instance, bibliometric analysis is used to identify hotspots in published articles on construction waste management [18]. A quantitative analysis of journal papers is conducted to discuss hotspots and research gaps [19]. Text mining methods combined with big data are employed to track research trends and explore recent focal points [20]. While these studies have yielded valuable insights, most have approached the field’s overall or partial status and focus from a publication-based perspective. A comprehensive understanding of the technological landscape and innovation trends in CWR remains limited.
Technological progress is considered the critical factor affecting the optimization and practice of construction waste management [21]. Some scholars have also adopted this perspective to examine the factors influencing stakeholders’ decision-making regarding technological innovation in the CWR field [22]. Scholars regard patents as a symbol of technological progress and innovation [23]. As a resource of basic knowledge, patents can help identify current trends and opportunities in emerging technologies [24]. Patent analysis has become mature and widely used in various fields, such as automation technology [25], medicine [26], and new energy vehicles [27]. However, in the CWR field, the application of this method is less prevalent. Some scholars have studied the trend of construction waste management from the perspective of bibliometrics, but it can only reveal the situation in the academic community [28]. Enterprises are the actual entities that handle construction waste, and the core driving force for enterprises to effectively utilize resources is technologies, which form patents. However, there is still a significant gap in identifying the development trend of CWR technology through a systematic patent analysis. Measuring the characteristics and dynamics of CWR technological innovation is conducive to clarifying its current and future situation macroscopically, interpreting underlying causes, providing evidence-based policy suggestions for the government, providing references for enterprise R&D, and improving the overall performance of CWR [29].
Given this, this study aims to uncover the development status and trends of CWR technology, identify key points and potential innovation directions for technological development, and explore practical strategies to promote technological innovation and industrial growth. Considering that China’s average treatment of construction waste varies greatly by region and is much lower than that of some other global economies, this study conducts a comparative analysis to explore whether China’s patent situation is different from theirs and the existing problems in China’s CWR industry. On the one hand, the research comprehensively reveals the macro characteristics and dynamics of CWR technology from multiple dimensions by collecting and analyzing patent data from 1983 to 2023. Through the Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) model, a text mining method, the study conducts in-depth text analysis on patents related to core technologies, exploring critical technology fields and innovation topics that can drive further advancements. On the other hand, through a comparative analysis of China and the global dominant countries in CWR technology, we have identified China’s technological advantages and disadvantages, providing a scientific reference and basis for policy-making, industrial development strategy adjustment, and scientific research direction determination.
The contribution of this study lies in its comprehensive analysis of China’s research status and core competitiveness in the field of CWR technologies by employing a series of data analysis methods. This study also provides a new perspective for measuring the development of technological innovation in the CWR industry. The findings help to grasp the overarching technological landscape and emerging innovation trends in the CWR industry. On a practical level, this research provides policymakers with data-driven support and strategic recommendations while offering enterprises guidance for technological development. The findings also contribute to promoting the overall upgrading and sustainable growth of the CWR industry.
The remainder of the article is organized as follows. Section 2 is the literature review. Section 3 details the methods and strategies used in the research. Section 4 comprehensively evaluates the macro characteristics and dynamics of CWR technology. Section 5 explores key technology fields and innovation topics through text mining. Section 6 discusses China’s technological strengths and weaknesses and proposes targeted suggestions. Section 7 concludes the research and outlines limitations and future directions.
2. Literature Review
In the past decade, CWR has become a hot topic in academia and industry. Experts have conducted in-depth research and continuous innovation around how to efficiently utilize construction waste as resources. The current technological innovations in the CWR industry primarily concentrate on developing and optimizing specific technologies [30]. These advancements notably encompass: (1) Precise separation and sorting technology [31,32], a pivotal process that facilitates the efficient and accurate separation and sorting of diverse components in construction waste, ultimately enhancing resource reuse and recycling efforts. Notably, the effectiveness of this separation and sorting process directly and profoundly impacts the quality of downstream products. (2) Low-carbon gel material technology [33,34] employs high-activity recycled powder derived from crushing, screening, and processing construction waste as a mineral admixture to partially replace cement, reducing the usage of both cement and sand and significantly lowering carbon emissions. (3) Aggregate recycling and application technology [35,36] involves using recycled coarse and fine aggregates obtained through processes such as crushing and sieving construction waste to partially replace sand and reduce its usage [37]. (4) Lightweight material energy conversion technology [38] entails the extraction of lightweight constituents from construction waste, followed by a high-temperature pyrolysis process within an advanced energy conversion system. This methodology yields valuable energy products, including charcoal and combustible gases, and also effectively manages secondary pollution, facilitating energy conservation, minimizing consumption, and enhancing overall efficiency. (5) Integrated application technology for recycled products [39] harnesses construction waste as the primary raw material, transforming it into diverse eco-friendly products such as mortar, concrete, foamed cement, ceramsite concrete, fired bricks, permeable paving bricks, grass-planting tiles, hollow blocks, imitation granite tiles, landscaping stones, integrated insulation and decoration blocks, and prefabricated walls.
However, the recycling and utilization of construction waste is not without potential risks that warrant careful consideration. Here are several key concepts that warrant particular attention. Downcycling refers to a specific form of resource recycling in which discarded items or materials are reused in a manner that results in reduced quality or economic value compared to the original material. A study focusing on Switzerland revealed that the majority of mineral materials from construction waste are currently downcycled for low-value applications such as road construction, rather than being utilized in higher-value building projects [40]. This practice fails to maximize the material’s potential and results in suboptimal resource efficiency. Value retention options (VROs) are defined as a set of operational principles designed to maximize the preservation of product and material resource value through tiered circular strategies. In practice, lower-tier VROs (e.g., recycling and energy recovery) dominate policy and business implementations, typically resulting in substantial value depreciation of resources [41]. Although the circular economy (CE) aims to reduce resource consumption and environmental pressures through strategies like recycling and reuse, its actual effectiveness may be significantly undermined by rebound effects. For instance, the use of recycled materials may lead to heavier product designs, ultimately increasing total waste generation [42].
At present, research on technological innovation in the CWR industry primarily revolves around refining and enhancing individual technologies, often neglecting a comprehensive overview of technology innovations as an interconnected system. Specifically, the research focus seems narrow, centering on specific technologies, strategies, and their effectiveness in particular contexts. Although these studies have undoubtedly yielded valuable insights, they inherently limit our ability to grasp the overarching technological landscape and emerging innovation trends in the CWR industry. Therefore, we have applied patent analysis methodologies to the CWR domain to investigate current technological innovations. Furthermore, recognizing the limitations of traditional research methods in handling exponentially growing data volumes in the big data era, we have additionally employed text mining techniques to analyze core technology patent texts. This research provides a new perspective for measuring the development of technological innovation in the CWR industry and guiding its future development in this industry.
3. Methodology
This study aims to uncover the development status and trends of CWR technology, identify key points and potential innovation directions for technological development, and explore practical strategies to promote technological innovation and industrial growth. This study first gathers patent data from the incoPat database as the basis for patent analysis. It then applies text mining to core technology patents to identify topics and calculate topic intensity, revealing evolutionary trends. Finally, a comparative analysis between China and other leading countries in the CRW field reveals China’s technological strengths and weaknesses. The research framework is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Research framework.
3.1. Patent Analysis
As an essential indicator of technological innovation, a patent contains technical information, such as inventor, applicant, and application date. Scholars often use patents to measure the innovation capacity of a region or a specific field [23]. Patents possess novelty, creativity, and practicality and contain the technical and commercial knowledge required for technological development and innovative activities [43]. Patent data are generally regarded as the latest and most reliable source of knowledge [44] and are often considered a standard indicator to measure innovation activities in the field, which can accurately judge technological development and industry trends. Patent analysis is a series of methods based on patent data that reveal innovation dynamics and technology trends [45] in a specific technology field. With the progress of big data, the accuracy and depth of patent analysis will be further enhanced, bringing more revelations to global technology innovation and intellectual property management.
This study selects the incoPat database as the source of patent data, which covers a wide range of patent information from countries worldwide [46]. The database ensures the high quality and integrity of the data and facilitates subsequent preprocessing for LDA topic modeling. Since the study focuses on technological innovation, it collects only invention patents from 1983 to 2023. The complete information of invention patents typically becomes publicly available 3 to 18 months after the filing date, while utility model patents require 1 to 15 months for full disclosure. Due to pending publication, the study’s dataset does not include patent applications submitted in 2024. Details of the search query criteria and the retrieved patent information are reported in Appendix A (Table A1). This study focuses on the patent data of China and other countries that have advantages in CWR technology. Based on the ranking of the relevant literature and patents, Japan, South Korea, the United States, and Germany were selected as the leading countries for comparative analysis with China. After conducting an advanced search and removing duplicates in the incoPat database, 88,555 patents related to global CWR technology were obtained, of which 57,857 were from China, 9736 from Japan, 5097 from South Korea, 3829 from the United States, and 1444 from Germany.
3.2. Text Mining: LDA Topic Model
3.2.1. Model Setup
LDA is a topic model based on Bayesian learning proposed by Blei et al. [47] and a document topic generation model suitable for short text processing [48]. It can excavate hidden topic structures from document collection and is widely used in text mining and natural language processing [49]. The LDA topic model is based on the following assumptions: (1) Documents are generated by the underlying topic distribution. (2) A set of potential word distributions defines each topic. The LDA topic model attempts to infer the hidden topics in the document collection based on the co-occurrence of terms and describes the distribution of these topics. Through the LDA topic model, researchers can reveal the hidden structure of a large amount of text data and identify the main topics in the document collection to deeply understand the intrinsic meaning of the text data [50].
Topic models represent an exemplary approach for comprehensively evaluating various research domains [51]. The LDA model is widely used in exploring the evolution of policy and research, and it is expected to be better applied to technology topic analysis [52]. For instance, some scholars employ the LDA topic model to investigate the development and evolution of renewable energy policies in China [53]. Some scholars use it to discover the trends in artificial intelligence [54]. This study aims to reveal the current status and evolution of the CWR field.
The main software utilized in this study is PyCharm 2022.3. For data cleaning, the jieba library and a collected stop-word library are employed. Subsequently, pandas and numpy are leveraged for data analysis, sklearn library is used for LDA modeling, and matplotlib alongside pyLDAvis is utilized for visualization [55]. Figure 2 illustrates the experimental framework for LDA modeling.
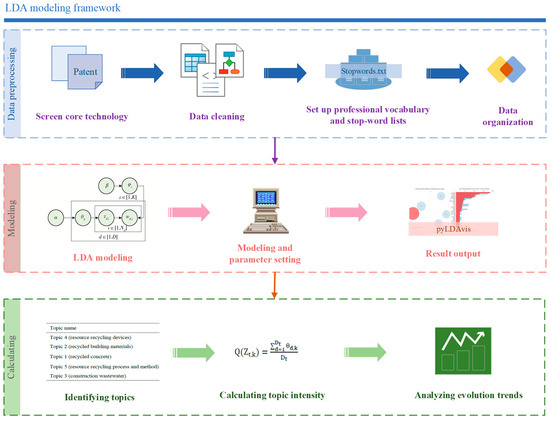
Figure 2.
Experimental framework for LDA modeling.
3.2.2. Data Preprocessing
Data preprocessing includes four steps.
- (1)
- Screening core technologies. In the CWR industry, the core patented technology can better represent the technical field of CWR, so the core patented technology is selected first;
- (2)
- Cleaning data. The text modeling of patent abstracts for core technologies in CWR excludes data with an empty “abstract” field. Next, unify the abstract language and generate the “abstract” field;
- (3)
- Setting up professional vocabulary and stop-word lists. Building a professional vocabulary dictionary in CWR is necessary to process patent texts professionally. Next, a stop-word list is established to avoid interfering with the correct segmentation of professional vocabulary in subsequent processing. Four commonly used stop-word lists are collected and integrated. In addition, non-professional vocabulary that appeared in the data is supplemented and added to the stop-word list;
- (4)
- Organizing data. After the required data are converted into phrase form, they are set into the text form needed for LDA topic modeling to facilitate subsequent experimental operations for topic analysis.
3.2.3. Modeling and Parameter Setting
In LDA topic modeling, there are four key parameters to be set: the number of topics K, the hyperparameter α of document-topic distribution, the hyperparameter β of topic-word distribution, and the number of iterations.
The perplexity is usually used to evaluate the fit of the model [56], and according to the perplexity the appropriate number of topics K is chosen. Generally, a maximum number of topics is set, and then the perplexity is calculated from K = 1 to the maximum number of topics. As the number of topics increases, the perplexity will gradually decrease and stabilize [53]. According to the experimental results, the number of topics whose perplexity decreases and tends to stabilize is selected as the final K value [47]. In this experiment, after multiple experiments and consideration of topic interpretability, the final number of topics is determined as K = 10.
For the hyperparameters of the document topic distribution and the hyperparameters of the topic word distribution, the default values are usually adopted, i.e., α = 1/K and β = 1/K. To ensure the modeling effect, the number of iterations should be set to a relatively large number, so it is set to 1000 times in this experiment.
3.2.4. Topic Intensity
Topic intensity reflects the active degree of related patent research, and a higher topic intensity means more patent applications and higher research interest in this technical field at a specific time. By analyzing the evolution of topic intensity, researchers can understand the research status in this field from a time perspective [57]. By calculating the topic intensity, we can understand the evolution of certain topics, which can help decision-makers track innovation and knowledge flows [58]. Most studies use the number of topic documents to indicate topic intensity [59]. The topic intensity calculation method proposed by Jian et al. [60] is adopted in this study. The details are shown in Equation (1).
where represents the topic intensity in the current period, represents the probability of the kth topic in the dth document, and represents the number of documents in the period t.
4. Overview of CWR Technology Patents
4.1. Statistical Insights from China
The number of patent applications, technology distribution, and applicants for Chinese patents are analyzed first.
4.1.1. Patent Applications
Figure 3 shows China’s patent application trend in CWR technology from 1983 to 2023. From 1983 to 2001, the number of patent applications in the CWR field was small. After 2001, due to a series of policies that were successively issued, such as the “Tenth Five-Year Plan for National Environmental Protection” and “Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Waste”, the number of patent applications began to accelerate. The “Circular economy promotion law of the People’s Republic of China” promulgated in 2009 requires the comprehensive utilization or harmless treatment of construction and demolition waste. The “Industrial specification on construction and demolition waste recycling (provisional)” promulgated in 2016 marked a milestone in the normalization development of the CWR industry [16]. The number of patent applications increased significantly, reaching a peak in 2020. After 2020, the number of patent applications in this technological field began to decline yearly, possibly due to the COVID-19 epidemic and the lag in patent disclosure.
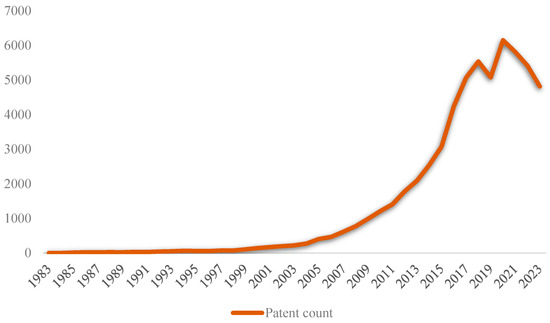
Figure 3.
Patent application trend of CWR technology in China from 1983 to 2023.
4.1.2. Applicant Analysis
Figure 4 shows the share of different types of patent applicants. There are 61,915 different patent applicants. Statistics show that enterprise applicants dominate, with a total of 35,914 applicants, accounting for 58.01% of all applicants. Next is universities, accounting for 23.09% of all applicants. Research institutes and individual applicants also account for a certain proportion of patent applications, accounting for 14.99% and 3.40%, respectively. A few government agencies and other organizations have applied for relevant patents, accounting for only 0.51% of all applicants. It can be found that enterprises play an important role in China’s CWR industry. Through technological innovation and research and development (R&D), construction and demolition waste (CDW) recycling enterprises can enhance the efficiency and quality of recycled products, reduce environmental pollution, and maximize CDW utilization [61].
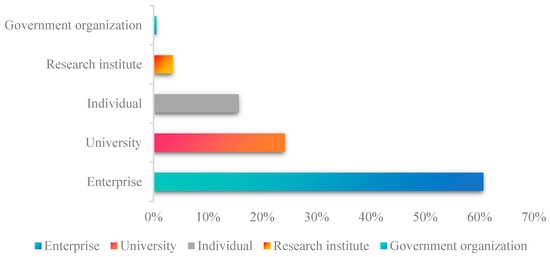
Figure 4.
The share of different types of Chinese patent applicants.
Applicants are ranked according to the number of patent applications, and the top 10 applicants are identified, as shown in Table 1. It can be seen that five are enterprise applicants, and the other five are universities. Here, enterprises are typically defined as legally registered corporate entities with business licenses and profit-driven commercial organizations. Enterprises have the strongest R&D and innovation capabilities in the CWR field. The top three are from enterprises. China State Construction Engineering Group has the largest number of patent applicants, 655, followed by China Metallurgical Group Corporation and Xi’an Construction Engineering Group, with 623 and 536, respectively. The three enterprises are far ahead in the number of patent applications, indicating that they have a leading position in the technological innovation of CWR in China and are the backbone of the industry’s technology development. Universities also show strong momentum in patent applications, among which Wuhan University of Technology has the largest number of applications, with 426, ranking fourth. Enterprises should play a more critical role as the main applicants that use CWR technology. The right part of Table 1 shows the top 12 enterprises regarding the number of patent applications for CWR technology.

Table 1.
Top 10 Chinese applicants and top 12 applicants from Chinese enterprises.
Currently, Chinese enterprises are still dominated by traditional enterprises in the research and development of CWR technology. Ten of the top 12 enterprises were established before 2010, all state-owned enterprises. It has a great relationship with China’s policy proposal. For example, China issued the Urban Construction Waste Management Regulations in 2005 to promote CWR, harmless treatment, and reduction treatment. Later, in 2008, the Ministry of Construction formulated the Technical Standards for Construction Waste Treatment, which clarified the technical specifications for all links of construction waste from the starting point to collection to transportation, treatment, and disposal. However, overall, the popularity of CWR technology in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and private enterprises is still low. Only two non-state-owned enterprises appear on the list and rank last, which indicates that China’s future focus and layout should be strengthened towards SMEs.
4.2. Comparative Analysis
This study selects Japan, South Korea, the United States, and Germany as China’s main competitors in the CWR field for comparative analysis, aiming to reveal China’s strengths and weaknesses in this field and accordingly put forward suggestions for promoting China’s CWR industry development.
4.2.1. Patent Applications
Regarding the number of invention patents in the CWR industry from 1983 to 2023, China tops the list (57,857), followed by Japan (9736), South Korea (5097), the United States (3829), and Germany (1444).
In recent years, China’s CWR industry has developed rapidly, and it has a substantial number of patents. Here we compare the trends in patent applications between China and four other countries. Considering that China’s patent volume significantly exceeds that of some other countries, displaying all five countries on the same figure might obscure the trend lines’ variations. Therefore, we present China’s patent data separately from the other four countries.
From a comparative observation of Figure 3 and Figure 5, it can be seen that China’s research and development started later than other countries in the CWR field, and the number of patent applications consistently ranked last before 2006. By 2007, patent applications in China had risen rapidly. However, countries like Germany and Japan pioneered CWR technologies. In Germany, recycled materials account for over 80% of the total waste mass flow [2].
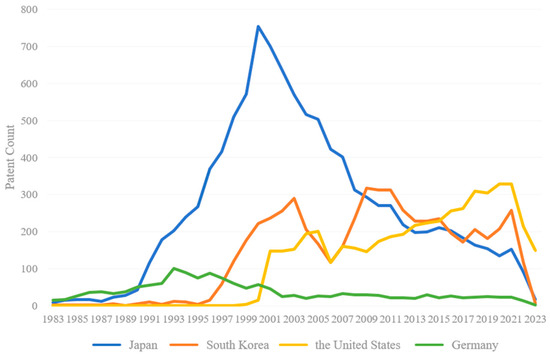
Figure 5.
Patent application trends of CWR technology in four leading countries.
Japan’s patent application trend exhibited a growth pattern, peaking in 2000, followed by a subsequent decline. Japan has been a leading nation in recycling concrete waste, with research indicating a continuous increase in the recycling rate of various construction and demolition waste from 1995 to 2003 [62]. Although a late starter in CWR, South Korea experienced rapid development during its initial stage, achieving a historical peak in 2009. The United States, slightly lagging behind South Korea in developing CWR technology, initiated significant growth in 2000 and has maintained a fluctuating upward trend since, culminating in a historical peak in 2021. Conversely, Germany was the earliest pioneer in this field, achieving notable advancements in the early 1990s. From 1983 to 1993, Germany’s technological innovation followed an upward trajectory, reaching a historical peak before subsequently experiencing fluctuations and a decline.
When the other four countries experienced faster growth in their patent applications during the early stages, China’s growth was slower until a surge occurred around 2006. When the yearly number of patent applications in other countries gradually declined, indicating a slight weakening in their patent application growth, China entered a high-speed development stage, surpassed Japan to become the global leader in the number of applications, and continued to rise steadily, reaching a sub-peak in 2018. This indeed aligns with China’s national circumstances, as the country has established a series of policies and regulations in recent years to promote better management of construction and demolition waste [63]. Although there was a decline in 2019, it increased in 2020 and reached a historical peak. Subsequently, the growth rate slowed, and the annual number of applications declined.
4.2.2. Applicant Analysis
Figure 6 shows the top 20 applicants in five countries. There are 16 Chinese applicants, including five enterprises and 11 universities. The other four patent applicants are all Japanese companies. As can be seen from the figure, China has developed rapidly in CWR technology in the last ten years and has taken the leading position in patent applications, among which CSCEC, MCC, XACEG, and Wuhan University of Technology are far ahead of the global patent applicants. Studies indicate that Japan maintains a leading position in concrete recycling and hosts sufficient specialized recycling companies in this sector [62]. Japan’s Taiheiyo cement corporation ranked fifth among the global applicants with 422 patents. As an old cement and industrial materials manufacturing company founded in 1881, it has been promoting the practice of environmental protection and sustainable development for a long time, transforming all kinds of construction waste into building materials. In 2001, it sold Eco-Cement and launched the recycling business of municipal waste incineration ashes, utilizing these ashes and other waste materials as raw inputs for eco-cement production. In addition, the Mitsubishi Group of Japan, as an enterprise established in 1870, has also demonstrated that its contribution to CWR can be traced back to the end of the twentieth century and the beginning of the twenty-first century.
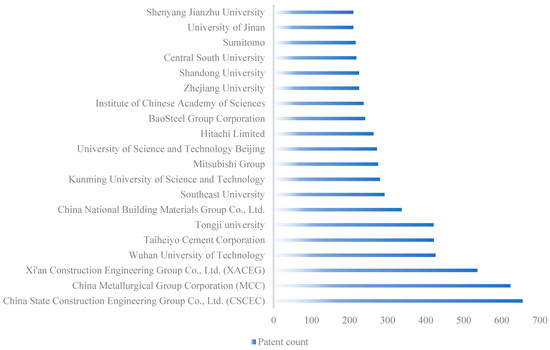
Figure 6.
Top 20 patent applicants in five countries.
As a comprehensive enterprise, Mitsubishi Group has been pursuing the development and application of environmental protection technology to realize the recycling and reuse of waste. Hitachi and Sumitomo, the other two Japanese enterprises on the list, also had an early start and development. These enterprises are in a leading position in the ecological manufacture and recycling of concrete, which is the goal that China can learn from in the future.
4.2.3. Multidimensional View of Patents
The study will analyze the patent characteristics of CWR technology in China, Japan, South Korea, the United States, and Germany in six dimensions, including average number of citations, average number of citations received, patent validity ratio, average number of simple patent family, average number of patent claims, and average technical value. The specific results are shown in Table 2. All the data presented in the table are statistically derived from the incoPat database.

Table 2.
Statistical results of indicators related to patent characterization in five countries.
- (1)
- Average number of citations
The average number of patent citations in the United States is 8.21 times, ranking first among the five. China ranks second, with an average number of patent citations of 4.69 times, followed by Germany and Japan. South Korea ranks last, with an average number of patent citations of only 1.16 times. It demonstrates that the United States has a relatively strong and comprehensive foundation in CWR technology [64].
- (2)
- Average number of citations received
The United States remains first, with an average of 11.03 citations received, followed by Japan with 6.04 and Germany with 5.87. China ranks fourth, with an average of 5.02 citations received, while South Korea remains at the bottom. It indicates that although the development time of the United States is similar to that of China in terms of CWR technology, it has a more substantial influence. In contrast, China’s influence in the global CWR field needs to be improved despite its rapid development and many patents [63].
- (3)
- Average number of simple patent families
The United States ranks first, with an average of 4.18 simple patent families, followed by Germany, South Korea, and Japan, all having similar average numbers of simple patent families. However, China ranks last among these five countries, with only 1.68 simple patent families, proving that China’s protection of intellectual property rights in this field is insufficient, and its strategic position and competitiveness are weak. In the next step, China should focus on planning and developing the layout of the CWR industry.
- (4)
- Average number of patent claims
The United States leads the other four countries with an average number of 22.15 patent claims. Germany ranks second; South Korea and Japan rank third and fourth, respectively. China ranked last with 7.41. It can be seen that the United States has strong innovation in CWR technology. In contrast, China’s innovation in this technology field is relatively weak, showing its competitiveness in the international market of CWR is weak [29].
- (5)
- Average technical value
The United States ranks first with 8.7, followed by Japan and South Korea, China ranks fourth with an average value of 6.03, and Germany ranks last. It can be seen that China’s innovation ability in CWR technology has made a low contribution to the development of related industries and the economy in China. In contrast, the development of the United States in this field has well promoted the development of associated industries and the economy.
- (6)
- Patent validity ratio
The United States still has the highest patent validity, reaching 36.8%, followed by South Korea with 30.5%, China with 27.86%, ranking third among the five countries, Japan with 16.31%, and Germany’s patent validity is only 3.31%.
Overall, the United States ranks first in the six indicators. In contrast, China ranks low in several indicators and is in a weak position, especially in the number of simple patent families and the number of patent claims, and the technical value is only slightly higher than the last. It shows that although China far exceeds the other four countries in the total number of patents, there is still a considerable gap between China and the other four countries regarding technological innovation, influence, and overall competitiveness of patents.
5. Topic Analysis of CWR Patents
5.1. Topic Extraction
To better analyze the development of core technologies of the CWR industry, this study obtained corresponding patents based on international patent classification (IPC) codes selected by co-occurrence analysis (see Figure A1 in Appendix B) and used LDA topic models to analyze topics of these core technologies.
A total of 19,349 valid patent data of China’s CWR industry are screened. LDA topic modeling is carried out, five technical topics are identified, and keywords of each topic are extracted. After deleting repeated keywords, the main keywords for each topic are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Keywords for patents in China’s CWR industry.
The distribution of topics and keywords cannot be intuitively seen from the above table, so this study uses pyLDAvis to visualize the distribution more intuitively [65]. Figure 7 shows the distribution of the five topics. As can be seen from the figure, Topic 1 has the highest proportion in the CWR field, while the other four topics have similar proportions. Additionally, Topic 1 and Topic 2 are very close in the diagram, indicating that they share more identical or similar keywords and are closely related. In contrast, Topic 1 is far from the other three topics, showing they are quite different in concept.
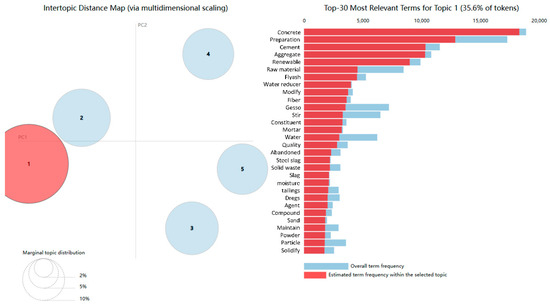
Figure 7.
Topic distribution.
Through comparing and understanding keywords, five core topics are summarized from Topic 1 to Topic 5: recycled concrete, recycled building materials, construction wastewater, resource recycling devices, and resource recycling process and method. According to statistical analysis, in the distribution of core technology topics, Topic 4 ranks first with 5588 core technology patent data, while Topic 2 ranks second with 4964 core technologies, followed by Topic 1 with 4954 core technology patent data, Topic 5 with 2418 core technology patent data, and Topic 3 ranks last with 1425 core technology patent data.
5.2. Topic Intensity
The study will analyze the topic intensity of core technologies in China’s CWR industry during the 40 years from 1983 to 2023, and the results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Topic intensity for patents in China’s CWR industry.
The table shows that the distribution of China’s CWR industry in the past 40 years can be roughly divided into three levels. Topic 4 (resource recycling devices) ranks first, with a topic intensity of 0.27 and the highest research heat, indicating that the current research hotspots in China are focused on the design and development of construction waste resource recycling and reuse devices. The intensities of Topic 2 (recycled building materials) and Topic 1 (recycled concrete) are close, and their heat is second only to that of Topic 4 (resource recycling devices). However, the fourth-ranked Topic 5 (resource recycling process and method) has a significant gap compared to the top three, with a topic intensity of only 0.133, half of Topic 4. The last-ranked topic is Topic 3 (construction wastewater). It proves that these two topics are low in popularity in the development process of China’s CWR and are not the critical research directions of current scholars.
In the LDA visualization results, Topic 1 occupies the largest area, yet computational analysis using the topic intensity formula reveals Topic 4 demonstrates the greatest intensity. This seemingly contradictory phenomenon actually reflects two distinct statistical dimensions within the topic model. The size of the area reflects the frequency and importance of the topic in all the documents [66]. The topic intensity is based on the average statistics of the topic probabilities in the document collection, and it can reflect the average intensity of a certain topic within a specific time period.
5.3. Evolution Trends of Topic Intensity
Each year is taken as a time window to analyze the evolution of topic intensity in China’s CWR industry from 2013 to 2023. The intensity changes of different topics over time are obtained through calculation, and the line chart of the intensity-changing trend of core technical topics is drawn in Figure 8a. From 2013 to 2023, the heat of these five topics changed significantly, and each has its leading period. Topic 1 maintained its position as the most prominent theme for two consecutive years (2014–2015). Topic 2 demonstrated higher research popularity in 2017 and 2019, surpassing other topics. Topic 3 emerged as the leading topic in 2018 and regained significant attention between 2021 and 2022. Topic 4 showed notable popularity only in 2016, while Topic 5, after being the top theme in 2013, regained its leading position in 2020.
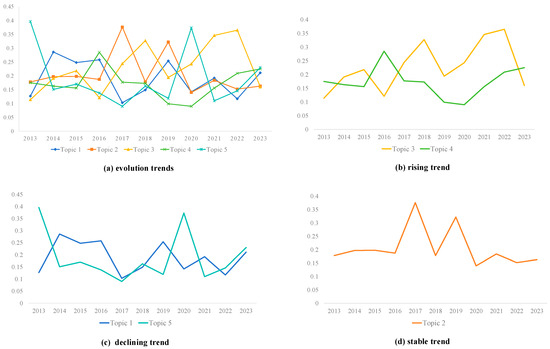
Figure 8.
Evolution trends of topic intensity.
After preliminary data analysis, the study divided the evolution of topic intensity into three trends of rising, stable, and declining for further observation and analysis.
- (1)
- Rising trend
As shown in Figure 8b, Topic 3 (construction wastewater) and Topic 4 (resource recycling devices) exhibited a generally rising trend from 2013 to 2023. Topic 3 demonstrated a fluctuating rise over time. Although there was a fluctuation from 2013 to 2022, the topic intensity increased from 0.114 to 0.365. While the topic intensity declined in 2023, judging from the trend of previous years, the heat for this topic will continue to rise. Construction wastewater mainly originates from construction activities, such as car washing water, concrete mixing station cleaning water, and other water-containing pollutants generated during construction. If discharged without proper treatment, the wastewater can seriously pollute the environment and degrade surface water and groundwater quality. However, the existing construction wastewater treatment technology and equipment encounter numerous challenges, including overly complicated treatment processes, high operating costs, low economic benefits, and frequent manual field maintenance [67,68]. These issues hinder the widespread adoption and promotion of construction wastewater treatment technology, which has been a significant factor contributing to the low popularity of this topic in recent years. In the next step, the government should provide financial and policy support for addressing construction wastewater issues to facilitate breakthroughs and advancements for this topic in China.
Although the topic intensity of Topic 4 showed a slight downward trend from 2013 to 2020, it continued to increase after 2020, rising from 0.09 to 0.225, which is still an increase compared with 0.175 in 2013. In addition, the peak topic intensity during this period appeared at 0.285 in 2016. As the core of converting construction waste into renewable resources, recycling devices play an essential role in the CWR industry. In the 13th Five-Year Plan for Building Energy Conservation and Green Building Development proposed by the Chinese government in 2017, it is pointed out that by 2020, more than half of the construction area of new buildings should be green buildings, and the proportion of recycled building materials used in new buildings should reach or exceed 40%. After 2020, the heat of resource recycling devices in China continues to grow, inseparable from a series of policies issued by the Chinese government.
- (2)
- Declining trend
As shown in Figure 8c, Topic 1 (recycled concrete) and Topic 5 (resource recycling process and method) exhibited a generally declining trend from 2013 to 2023. Specifically, Topic 1 showed a downward trend, with its topic intensity decreasing from 0.127 in 2013 to 0.117 in 2022. The topic intensity peaked at 0.286 in 2014 and reached its lowest value of 0.103 in 2017. After crushing, cleaning, and grading, waste concrete can be mixed and reused in specific proportions [69]. By adding cement and other components, these materials can be utilized to produce new recycled concrete. On 22 September 2020, China put forward the “dual carbon” target for the first time, and the application of recycled concrete is a crucial means to achieve carbon neutrality and sustainable development. Recycled concrete can alleviate the environmental burden caused by construction waste and effectively conserve natural resources, which indicates that research interest in recycled concrete will continue to grow in the future development of CWR in China.
Overall, Topic 5 exhibits a declining trend. As shown in Figure 8c, the topic intensity of Topic 5 reached as high as 0.396 in 2013 but dropped to 0.151 in 2014. It peaked again in 2020, with a topic intensity of 0.373, before returning to 0.11. Resource recycling processes and methods constitute the core approach to managing construction waste. However, their popularity has declined due to various stakeholder-associated factors, including the government, construction units, resource recycling enterprises, and research institutes. It is also important to note a new concept: design for disassembly (DfD). DfD is a design method developed in the manufacturing industry, aiming to cope with shrinking material and energy resources as well as increasing waste [70]. It is a strategy of eliminating rather than dealing with waste. DfD and some industrialized construction methods (such as prefabrication and standardization) can significantly reduce waste, promote direct reuse of materials, and reduce reliance on downstream recycling processes [71]. This can explain why the popularity of Topic 5 is gradually declining. Since implementing the Thirteenth Five-Year Plan, China has made significant progress in the field of the circular economy, and the recycling technology for renewable resources has improved dramatically. By 2023, the comprehensive utilization rate of construction waste in some cities has exceeded 50%. Nevertheless, compared with the international advanced level, there is still a notable gap in this field in China. At the same time, the total amount of construction waste in China is still increasing at a high speed every year. Therefore, developing and improving resource recycling processes and methods is imperative. In the next few years, resource recycling processes and methods of construction waste will gradually become a hot topic in the research field.
- (3)
- Stable trend
Figure 8d illustrates that Topic 2 (recycled building materials) has fluctuated yet is generally stable from 2013 to 2023. During this period, Topic 2 experienced two notable fluctuations: the first occurred between 2016 and 2018, with a peak intensity of 0.376, and the second followed closely between 2018 and 2019, reaching a peak intensity of 0.322. However, the intensity of Topic 2 remained relatively stable most of the time, with a value of 0.178 in 2013 and 0.164 in 2023. At present, China’s research in the field of recycled building materials is extensive, encompassing the use of polystyrene-related waste as building insulation materials [72,73], the processing of waste masonry and concrete into recycled aggregate concrete, the utilization of waste glass as an aggregate to produce recycled glass concrete, and the transformation of waste wood into particleboard. Applying these building recycled materials can effectively reduce pollution to the natural environment and conserve natural resources. It demonstrates good sustainable ecological practices, enhances environmental protection, and supports a practical circular economy. For example, Fengtai District in Beijing has released the “Fengtai District Carbon Peak Implementation Plan”, proposing that by 2025, the proportion of green and recycled building materials should reach 70%. Although the enthusiasm for research on this topic in China has slightly declined in recent years, the increase observed in 2023 indicates that there is still great potential and space for the future development of building recycled materials.
5.4. Comparative Analysis
This study screened the patent data of the CWR industry from 1983 to 2023 from China, Japan, South Korea, the United States, and Germany and conducted a comparative study on the core technology topics of CWR in these five countries in the past ten years. Based on the IPC codes selected, the LDA topic is used for in-depth analysis.
Table 5 shows the topics and keywords generated using the LDA model for the five countries. A total of 20 keywords were generated for each topic, and the top five non-repeated keywords were taken as the primary keywords. At the same time, through the comparison and understanding of the core patent vocabulary, the five core technology topic names are obtained.

Table 5.
Overall topic intensity for the five countries.
The topic intensity of the overall core technologies of these five countries is calculated, and the results are shown in Table 5. Within the scope of the five countries, Topic 3 (recycled building materials) is currently the hottest core technical field, with a topic intensity of 0.259, followed by Topic 1 (resource recycling devices). Topic 2 (construction wastewater), Topic 5 (resource recycling process and method), and Topic 4 (recycled concrete) are all not exceeding 0.2. Despite Topic 4 having 11,548 core technologies, more than Topic 5, its topic intensity is weaker, and its popularity is the lowest among the five countries.
The topic intensities of these countries are shown in Figure 9. Overall, among the five core technological topics, all five countries have their strengths and patent achievements. Among them, China shows a high degree of enthusiasm in Topic 1 (resource recycling devices), ranking first, second in Topic 3 (recycled building materials), third in Topic 4 (recycled concrete), and last in Topic 2 (construction wastewater) and Topic 5 (resource recycling process and method). Japan has demonstrated the highest research enthusiasm in Topic 2 and Topic 4. This finding aligns with previous studies identifying Japan as the leading nation in concrete recycling [62]. South Korea has the highest research enthusiasm in Topic 3, and the United States has the highest in Topic 5. Although Germany is not in the first place, it has a relatively even performance across these five topics and shows good research enthusiasm in all five directions.
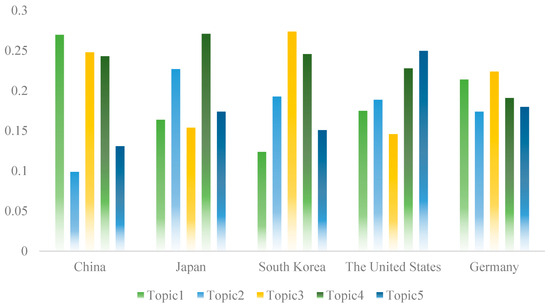
Figure 9.
Topic intensity in the five countries.
6. Discussion and Implications
Through patent analysis and LDA topic modeling, the study has traced the development status and trends of CWR technology and figured out the key points and potential innovation directions of technology development. The results are as follows.
6.1. Strengths and Weaknesses
6.1.1. Strengths
First, the number of patent applications is substantial, and the growth rate is rapid. By comparing the number of patent applications between China and four other countries, it is evident that China has been the leader in patent applications since 2007. The number of patents has rapidly increased from 614 in 2007 to 6152 in 2020, an increase of nearly ten times in less than 20 years, far exceeding the growth rates of the other four countries during the same period. Meanwhile, although the United States is still experiencing positive growth, the other three countries, Japan, South Korea, and Germany, are all experiencing either negative growth or remaining stable.
Second, the applicants are widely distributed, and the traditional enterprises have strong innovation capabilities. Currently, enterprises still account for a large proportion of technological innovation in the CWR industry in China, and universities and other applicants have submitted significantly fewer patent applications for developing CWR technology than enterprises. At the same time, by observing the list of enterprise applicants, it can also be seen that under the incentive of the “dual carbon” target and the support of various policies, traditional enterprises such as CSCEC and MCC play an essential role in promoting the development of construction waste resource technology and the application of green materials, which is also the result of a series of reforms such as the replacement of old growth drivers with new ones in China. Meanwhile, these large traditional enterprises will also play a crucial role in supporting the development of SMEs and emerging enterprises in this field.
Third, it has potential advantages in developing resource recycling devices and construction wastewater treatment technology. China is currently experiencing rapid development in the above two areas. Especially in resource recycling devices, China has shown the greatest enthusiasm among the five countries and demonstrates good development prospects in this area. The growing focus on construction wastewater treatment also indicates that China’s attention to this area is gradually increasing, indicating significant market potential.
6.1.2. Weaknesses
First, while patent applications in China’s CWR industry are significant, its global competitiveness remains weak. Over the past two decades, the industry in China has undergone rapid development, accompanied by a substantial surge in patent applications. However, when benchmarked against the patent characteristics of the other four leading countries, China ranks fourth in terms of the number of citations received and the technical value of its patents. This indicates that the influence of China’s patent applications on the CWR industry is still insufficient. Furthermore, China ranks at the bottom among these five countries regarding the number of patent claims and simple patent families, which reveals that its research and development endeavors in this field are still constrained, resulting in insufficient innovation capabilities. Consequently, the industry faces a challenge characterized by a high volume of patents but a lack of robust innovation.
Second, emerging enterprises and SMEs exhibit a lack of vitality. When examining the patent applicant ranking list in China, it becomes evident that most applications still originate from traditional state-owned enterprises. Only a fraction of emerging enterprises and SMEs appear on the list, accompanied by a notably small number of patent applications. This situation is neither favorable for advancing nor applying CWR technology in China, nor does it contribute positively to increasing the recycling rate of construction waste in China.
Third, the technological foundation is weak, especially in some core technologies. China started late in the CWR industry and is still in its infancy development stage. As a result, the technological foundation remains relatively weak, which is also a key factor contributing to China’s low recycling rate of construction waste. Generally speaking, the development of the five core technologies in China is uneven. Although China has invested substantially in R&D for resource recycling devices, it ranks at the bottom among five countries in the core technology areas of construction wastewater treatment and resource recycling processes and methods, with a notable gap compared to other countries. Furthermore, it does not demonstrate an obvious advantage in the other two core technology areas.
6.2. Policy Implications
First, the policies and regulations related to the CWR industry need specific improvement. Drawing from the experiences of Japan, South Korea, the United States, and Germany, formulating specific policies and regulations is critical for promoting CWR management. By observing these developed countries’ practices, we find that in the industry’s initial stage, the government often leads by regulating enterprises’ waste disposal behavior through mandatory laws and regulations and encouraging participation in recycling activities through tax policies and other incentives. China has implemented relevant laws and regulations, including the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Solid Waste Pollution, the Regulations on the Management of Urban Construction Waste, and the Circular Economy Promotion Law of the People’s Republic of China. However, compared with leading countries, China’s approach to CWR management, though grounded in relevant laws and regulations, still lacks sufficient guidance and targeted measures, and there is an urgent need for improvement in administrative means to regulate stakeholders’ behavior.
Second, promote the technological development and innovation of the resource reuse and recycling industry. China still faces some challenges in CWR, such as the absence of a standard system adapted to China’s specific conditions and inadequate efforts in integrating and standardizing processes and technologies [13]. Enterprises and research institutes find it challenging to make significant breakthroughs through their efforts. Therefore, the government should introduce policies to invest in and encourage R&D in specific technical fields of recycling enterprises. At the same time, the government should rationally plan the technical layout of China’s CWR industry, regulate and oversee the recycling technology market, guide enterprises to develop core technologies through targeted incentives, and enhance the innovation and development of core technologies related to construction wastewater treatment and resource recycling processes and methods, thereby enabling China to achieve this industry’s balanced development and discard inferior technologies.
Third, give greater attention to supporting emerging enterprises and SMEs. Currently, the development of the CWR industry in China is primarily led by traditional state-owned enterprises, while the growth of emerging enterprises remains insufficient. However, relying solely on traditional state-owned enterprises is not feasible for accelerating the achievement of the “dual carbon” target and enhancing the recycling rate of construction waste. In underdeveloped cities, construction waste is still predominantly backfilled, landfilled, and incinerated, resulting in a severe environmental burden and wasting resources [63]. The government should encourage local SMEs and emerging enterprises to develop recycling technologies for construction waste through corresponding policies, aiming for a comprehensive improvement in the recycling rate of construction waste and hoping to spread this improvement from cities to villages. Meanwhile, considering the funding needs for R&D in CWR technology, the government can provide financial support to enterprises, universities, and research institutes by investing in R&D funds, facilitating industry–university research cooperation, and fostering a win-win situation.
7. Conclusions
This study retrieved the invention patent data of the global CWR industry from 1983 to 2023 through the incoPat patent database and selected China and the other four leading countries regarding patent application quantity: Japan, South Korea, the United States, and Germany. Overall, this article first analyzes the relevant patent texts of China’s CWR industry and summarizes the current development status of China in this field. Then, it compares and analyzes China with other countries from multiple perspectives, outlines the strengths and weaknesses of China’s CWR industry, and presents significant policy implications for promoting the future development of CWR management.
The research found three main strengths in China’s CWR industry: (1) The number of patent applications is substantial, and the growth rate is rapid. (2) The applicants are widely distributed, and traditional enterprises have strong innovation capabilities. (3) It has potential advantages in developing resource recycling devices and construction wastewater treatment technology. The weaknesses of China’s CWR industry are mainly concentrated in three aspects: (1) While patent applications in China’s CWR industry are significant, its global competitiveness remains weak. (2) Emerging enterprises and SMEs exhibit a lack of vitality. (3) The technological foundation is weak, especially in some core technologies. This study offers an overview of technological innovation initiatives in the CWR industry, representing a breakthrough in existing research.
This study also yielded several policy implications. There is an urgent need for improvement in administrative means to regulate stakeholders’ behaviors. The government should promote technological development and innovation in the resource reuse and recycling industry and give greater attention to supporting emerging enterprises and SMEs. Nevertheless, this study is limited to a comparative analysis of patent filings in five selected countries, potentially overlooking jurisdictions with lower patent volumes but strategically significant patents. Unlike traditional literature reviews, patent analysis is confined to legally disclosed inventions, thereby excluding non-patented proprietary technologies that may represent core innovations. Also, the reliance on keyword-based retrieval in patent databases may have resulted in partial omission of relevant patents. Additionally, this study primarily focuses on innovation dynamics and development trends of CWR technology without considering influencing factors and underlying mechanisms that drive this process. These limitations will be addressed in future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Y. and L.L.; methodology, M.L.; software, M.L.; validation, M.Y., L.L. and S.C.; formal analysis, M.L.; investigation, S.C.; resources, L.L.; data curation, M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, M.Y. and S.C.; visualization, S.C.; supervision, M.Y.; project administration, M.Y.; funding acquisition, M.Y. and L.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72304278), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2023QG100), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 22CX06069A), Humanities and Social Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No. 24YJC630105), and Outstanding Youth Innovation Team Foundation of Shandong Province (No. 2022RW036).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Search Query Criteria and the Retrieved Patent Information

Table A1.
Search query criteria and the retrieved patent information.
Table A1.
Search query criteria and the retrieved patent information.
| Data repository | IncoPat Patent Database |
| Data crawling query | Keywords: construction waste, construction material waste, construction demolition waste, construction and demolition waste, construction trash, construction garbage, construction litter, construction rubbish IPC codes: A23K, A43B, A61L, A62D, B01D, B03B, B02C, B03C, B07B, B08B, B09B, B09C, B22F, B29B, B29C, B29D, B62D, B63B, B63J, B65B, B65F, B65G, C01B, C02F, C04B, C05D, C05F, C08J, C09D, C09K, C10B, C10G, C10L, C11B, C11D, C14C, C21B, C21C, C22B, C25C, D01C, D01F, D01G, D06B, D06F, D06L, D21B, D21C, D21H, E01C, E01H, E02B, E03C, E03F, E04B, E02D, E04D, E04F, E06B, E21B, E21F, F01N, F02B, F23B, F23C, F23G, F23J, F24F, F25J, F27B, G08B, G21C, G21F, H01B, H01J, H01M |
| Data retrieved duration | January 1983–December 2023 |
| Document type | Invention patents |
Appendix B. Technology Distribution Analysis
Given the connection between IPC codes, Gephi 0.9.2 software was used to draw the IPC code co-occurrence network of China’s CWR technology. IPC codes that show a strong correlation in the co-occurrence network often represent more critical and core technology systems. Due to the large number of patents in the CWR field in China and the large number of IPC codes, when drawing the IPC code co-occurrence network, this study selected a relatively large proportion of IPC codes for better visualization and observation. As shown in Figure A1, the more times the IPC codes appear, the larger the network nodes are, and the stronger the correlations between the nodes are, the thicker the network edges are.
Figure A1.
IPC code co-occurrence network of China’s CWR technology.
References
- Zhang, K.; Qing, Y.; Umer, Q.; Asmi, F. How construction and demolition waste management has addressed sustainable development goals: Exploring academic and industrial trends. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez-Martos, J.-L.; Styles, D.; Schoenberger, H.; Zeschmar-Lahl, B. Construction and demolition waste best management practice in Europe. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossink, B.A.G.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Construction Waste: Quantification and Source Evaluation. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 1996, 122, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Promotes Construction Waste Management and Recycling. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-12/09/content_5659650.htm (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Alsheyab, M.A.T. Recycling of construction and demolition waste and its impact on climate change and sustainable development. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, W. Identifying factors influencing demolition waste generation in Hong Kong. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Duan, H.; Zheng, L.; Wang, J.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, G. Demolition waste generation and recycling potentials in a rapidly developing flagship megacity of South China: Prospective scenarios and implications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Li, J. Construction and demolition waste management: China’s lessons. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Yu, B.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Chen, Z.; Ya, Y. Research trend of the application of information technologies in construction and demolition waste management. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Shen, L.; Li, Q. Emergy analysis of the recycling options for construction and demolition waste. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, O.; Pasqualino, J.C.; Castells, F. Environmental performance of construction waste: Comparing three scenarios from a case study in Catalonia, Spain. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, M.; Ronkanen, M.; Kärki, T. Sorting efficiency in mechanical sorting of construction and demolition waste. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Kua, H.; Geng, Y.; Bleischwitz, R.; Ren, J. Construction and demolition waste management in China through the 3R principle. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Li, M.; Yu, D. Bibliometric analysis of construction and demolition waste recycling: Review and prospects. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Eng. Sustain. 2022, 175, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Li, B.; Zhou, T.; Wanatowski, D.; Piroozfar, P. An empirical study of perceptions towards construction and demolition waste recycling and reuse in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Zuo, J.; Li, J. Key policies to the development of construction and demolition waste recycling industry in China. Waste Manag. 2020, 108, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, A.T.W.; Shen, L.; Liu, G. Quantifying construction and demolition waste: An analytical review. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Sang, P. A bibliometric review of studies on construction and demolition waste management by using CiteSpace. Energy Build. 2022, 258, 111822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Q. Science mapping approach to assisting the review of construction and demolition waste management research published between 2009 and 2018. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 140, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xie, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, B.; He, Q. Tracing the Trends of General Construction and Demolition Waste Research Using LDA Modeling Combined With Topic Intensity. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 899705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Jha, K.N.; Vyas, G. Proposing building information modeling-based theoretical framework for construction and demolition waste management: Strategies and tools. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2020, 22, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Tan, L. Mechanisms driving technological innovation behavior in construction and demolition waste remanufactured products via self-determination theory. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 38, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.P.; Li, M.; Turner, S.F.; Hatfield, D.E.; Cardinal, L.B. Mapping Patent Usage in Management Research: The State of Prior Art. J. Manag. 2020, 46, 1121–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, Y.S. Profiling technology development process using patent data analysis: A case study. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2012, 24, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Daim, T.; Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Shaikh, R.; Kassi, D.F. Monitoring the development trend and competition status of high technologies using patent analysis and bibliographic coupling: The case of electronic design automation technology. Technol. Soc. 2022, 71, 102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Porter, A.L. Analyzing patent topical information to identify technology pathways and potential opportunities. Scientometrics 2015, 102, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.-C.; Xu, J.-H.; Fan, Y. Characteristics and key trends of global electric vehicle technology development: A multi-method patent analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Umer, Q.; Zhou, R.; Asmi, A.; Asmi, F. How publications and patents are contributing to the development of municipal solid waste management: Viewing the UN Sustainable Development Goals as ground zero. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, D. Cross-domain function analysis and trend study in Chinese construction industry based on patent semantic analysis. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 162, 120331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, A.T.; Di Maio, F.; Vahidi, A.; Rem, P. Innovative technologies for recycling End-of-Life concrete waste in the built environment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fu, Y.; Lu, W.; Pan, Y. Augmented reality-enabled human-robot collaboration to balance construction waste sorting efficiency and occupational safety and health. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodampegama, S.; Hou, L.; Asadi, E.; Zhang, G.; Setunge, S. Revolutionizing construction and demolition waste sorting: Insights from artificial intelligence and robotic applications. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 202, 107375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Morales, J.; Burciaga-Diaz, O.; Gomez-Zamorano, L.Y.; Escalante-Garcia, J.I. Transforming construction and demolition waste concrete as a precursor in sustainable cementitious materials: An innovative recycling approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 204, 107474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Yang, D.; Wang, C.; Ma, Z. Upcycling of construction waste powder for sustainable ultra-high performance engineered cementitious composites: Effects of waste powder source and content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 349, 128789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandru, U.; Bahurudeen, A.; Senthilkumar, R. Systematic comparison of different recycled fine aggregates from construction and demolition wastes in OPC concrete and PPC concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 75, 106768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malazdrewicz, S.; Ostrowski, K.A.; Sadowski, L. Self-compacting concrete with recycled coarse aggregates from concrete construction and demolition waste-Current state-of-the art and perspectives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo, P.W.C.; Silva, Y.F.; Araya-Letelier, G.; Hernández, H. Valorization of Recycled Aggregate and Copper Slag for Sustainable Concrete Mixtures: Mechanical, Physical, and Environmental Performance. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chu, C.; Song, L.; Gao, X.; Huang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hou, L.; Ju, M.; et al. From prospecting to mining: A review of enabling technologies, LCAs, and LCCAs for improved construction and demolition waste management. WASTE Manag. 2023, 159, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodaei, H.; Olson, C.; Patino, D.; Rico, J.; Jin, Q.; Boateng, A. Multi-objective utilization of wood waste recycled from construction and demolition (C&D): Products and characterization. WASTE Manag. 2022, 149, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliem, D.; Scheidegger, A.; Kopainsky, B. Closing the mineral construction material cycle—An endogenous perspective on barriers in transition. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reike, D.; Vermeulen, W.J.V.; Witjes, S. The circular economy: New or Refurbished as CE 3.0?—Exploring Controversies in the Conceptualization of the Circular Economy through a Focus on History and Resource Value Retention Options. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.G.; Trevisan, A.H.; Pigosso, D.C.A.; Mascarenhas, J. The rebound effect of circular economy: Definitions, mechanisms and a research agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, T.; Lin, A.-L.; Su, H.-N. Analyzing Status Quo of Technology Fusion by Using Patents: A Global and Technical Assessment. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 7101–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Su, H.-N. The innovative fulcrums of technological interdisciplinarity: An analysis of technology fields in patents. Technovation 2019, 84–85, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breschi, S.; Lissoni, F.; Malerba, F. Knowledge-relatedness in firm technological diversification. Res. Policy 2003, 32, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Zhang, G.; Mei, L. General purpose technology R&D specialization and supply chain cross-industry expansion: The moderation effect of technology portfolio breadth and depth. Technol. Soc. 2025, 82, 102889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, K. Word network topic model: A simple but general solution for short and imbalanced texts. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2016, 48, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, H. Leveraging Global and Local Topic Popularities for LDA-Based Document Clustering. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 24734–24745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Ren, X.; Yang, S.; Han, Q.; Zhao, P.; Yang, X. Latent Dirichlet Allocation Model Training with Differential Privacy. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 1290–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomojiri, D.; Takaya, K.; Ise, T. Temporal trends and spatial distribution of research topics in anthropogenic marine debris study: Topic modelling using latent Dirichlet allocation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Z. Heterogeneity evaluation of China’s provincial energy technology based on large-scale technical text data mining. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, W. Evolution of renewable energy laws and policies in China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Xiang, B. Discovering topics and trends in the field of Artificial Intelligence: Using LDA topic modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 225, 120114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goloshchapova, I.; Poon, S.-H.; Pritchard, M.; Reed, P. Corporate social responsibility reports: Topic analysis and big data approach. Eur. J. Financ. 2019, 25, 1637–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Qi, Y. Selection of the Optimal Number of Topics for LDA Topic Model—Taking Patent Policy Analysis as an Example. Entropy 2021, 23, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Feng, L. Technology Hotspot Tracking: Topic Discovery and Evolution of China’s Blockchain Patents Based on a Dynamic LDA Model. Symmetry 2021, 13, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Tsutsui, S.; Ding, Y.; Ma, F. Understanding the topic evolution in a scientific domain: An exploratory study for the field of information retrieval. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Qian, L.; Qin, W.; Wei, J.; Shen, C. Evolution analysis of online topics based on ‘word-topic’ coupling network. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 3767–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, F.; Yajiao, W.; Yuanyuan, D. Microblog topic evolution computing based on LDA algorithm. Open Phys. 2018, 16, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Zuo, J. Assessment of promotional strategies for construction and demolition waste recycled products based on hybrid simulation system. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 112, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y. Comparing the implementation of concrete recycling in the Australian and Japanese construction industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Le, K.N.; Li, W. Challenges in current construction and demolition waste recycling: A China study. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 610–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.; El Asmar, M.; Aldaaja, M. An Analysis of the Impact of the Circular Economy Application on Construction and Demolition Waste in the United States of America. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Two decades of the evolution of China’s green building policy: Insights from text mining. Build. Res. Inf. 2023, 51, 158–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsironis, G.; Cox, R.; Jolly, M.; Salonitis, K.; Tsagarakis, K.P. Exploring circular economy in the United Kingdom based on LinkedIn data from company profiles. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 503, 145355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, E.; Babaei, A.; Mehrnia, M.R.; Shayegan, J.; Safdari, M.-S. Municipal wastewater treatment by semi-continuous and membrane algal-bacterial photo-bioreactors. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, R.; Hou, R.; Zhou, B.; Chen, H. Construction of an algal-bacterial symbiosis system and its application to municipal wastewater treatment: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 196, 106846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Soomro, M.; Evangelista, A.C.J. A review of recycled aggregate in concrete applications (2000–2017). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapska, K.; Rüther, P.; Loli, A.; Gradeci, K. Design for Disassembly: A systematic scoping review and analysis of built structures Designed for Disassembly. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 48, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, H.; Díaz, L.; Rodríguez-Grau, G. Examining building deconstruction: Introducing a holistic index to evaluate the ease of disassembly. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 218, 108215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kytinou, V.K.; Metaxa, Z.S.; Zapris, A.G.; Kosheleva, R.I.; Prokopiou, V.D.; Alexopoulos, N.D. Exploitation of extruded polystyrene (XPS) waste for lightweight, thermal insulation and rehabilitation building applications. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 20, 100580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, A.; Pang, S.D.; Kang, S.-H.; Moon, J. Lightweight structural cement composites with expanded polystyrene (EPS) for enhanced thermal insulation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 102, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).