Abstract
Scan-to-BIM is the process of converting point cloud data into a Building Information Model (BIM) that has proven essential for the AEC industry. Scan-to-BIM consists of two fundamental tasks—semantic segmentation and 3D reconstruction. Deep learning has proven useful for semantic segmentation, and its integration into the Scan-to-BIM workflow can benefit the automation of BIM reconstruction. Given the rapid advancement of deep learning algorithms in recent years, it is crucial to analyze how their accuracy impacts reconstruction quality. In this study, we compare the performance of five deep learning models—PointNeXt, PointMetaBase, PointTransformer V1, PointTransformer V3, and Swin3D—and examine their influence on wall reconstruction. We propose a novel yet simple workflow that integrates deep learning and RANSAC for reconstructing walls, a fundamental architectural element. Interestingly, our findings reveal that even when semantic segmentation accuracy is lower, reconstruction accuracy may still be high. Swin3D consistently outperformed the other models in both tasks, while PointNeXt, despite weaker segmentation, demonstrated high reconstruction accuracy. PTV3, with its faster performance, is a viable option, whereas PTV1 and PointMetaBase delivered subpar results. We provide insights into why this occurred based on the architectural differences among the deep learning models evaluated. To ensure reproducibility, our study exclusively utilizes open-source software and Python 3.11 for processing, allowing future researchers to replicate and build upon our workflow.
1. Introduction
Inadequate building information interoperability in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector raises costs by USD 6.12 per square foot for new construction and USD 0.23 per square foot for operations and maintenance, totalling USD 15.8 billion in additional expenses annually, according to a National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) study [1]. Building Information Modelling (BIM) facilitates knowledge sharing and interoperability between different stakeholders and has brought significant advancements to the AEC industry, particularly in the design and construction of new structures [2]. An ‘As-designed BIM’ is generated during the design of new structures. However, the operations and maintenance phase in a structure’s life cycle is the longest [3], and an ‘As-built-BIM’ provides essential data for the operation and maintenance of a structure. As-designed BIM creation is a simple process that is becoming increasingly popular, but for structures without an as-designed BIM or structures whose as-built circumstances deviate from the as-designed BIM, creating as-built BIMs is a challenging but essential process [4]. An as-built BIM is created using collected point cloud data of existing building structures, and this process of transforming raw point cloud data into detailed and accurate 3D models is called Scan-to-BIM [5]. Scan-to-BIM consists of four fundamental tasks—pre-processing, semantic segmentation, extracting measurements, and 3D reconstruction (Figure 1) [6].
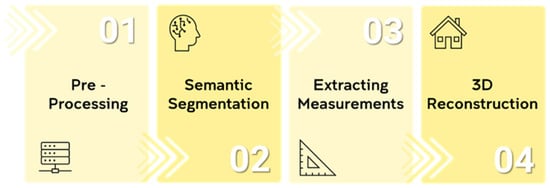
Figure 1.
Scan-to-BIM workflow.
As the raw point cloud datasets are large and noisy, they need to be pre-processed. Depending on the scanner, different pre-processing steps are applied—outlier removal (data cleaning or filtering), down-sampling (reducing the size by retaining critical features), normal estimation, data augmentation, etc. [7]. Pre-processing also depends on the input requirements for semantic segmentation. Semantic segmentation involves classifying each point in the point cloud data into predefined categories [8]. The semantic segmentation step is essential to identify different structural and non-structural elements in the point cloud data, such as walls, doors, windows, floors, ceilings, furniture, etc. Once identified, the third step, i.e., extracting measurements, is most important to generate accurate BIMs. The segmented point cloud is clustered into individual building elements, and their dimensions, orientation, and placement are extracted. These measurements are used for 3D reconstruction. Along with creating the BIM, reconstruction involves defining the spatial relations to create a valid BIM. Accuracy checks can be carried out after the semantic segmentation step and the reconstruction step.
Over the past decade, significant strides have been made in the development of deep learning models for semantic segmentation, enabling more precise and efficient point cloud analysis [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. However, for BIM reconstruction, extracting measurements of structural elements from segmented point clouds and 3D reconstruction of these elements are two critical processes for accurate model building of existing structures. Thus, the question arises: how does semantic segmentation accuracy influence the correctness of reconstructed models?
This study aims to fill this gap by evaluating how varying levels of segmentation accuracy affect the accuracy of 3D reconstruction, focusing specifically on the reconstruction of walls, which are fundamental architectural elements. Our intention is to discuss how the architecture of different deep learning algorithms would impact wall reconstruction. This would enable future researchers to select appropriate algorithms for improving the Scan-to-BIM process.
We begin with a review of existing deep learning algorithms, followed by a summary of the past research work for wall reconstruction. In Section 2, we compare five deep learning models and review their impact on the accuracy of reconstructed models. We also provide a novel workflow of how deep learning models can be used in the Scan-to-BIM process. Section 3 presents and analyses the results. Finally, a discussion of the employed deep learning algorithms is provided in Section 4, followed by a conclusion and recommendations for future work in Section 5.
1.1. Background
The creation of a BIM has three important data requirements—the semantic information of points, the geometry of elements, and spatial relationships [6].
1.1.1. Semantic Segmentation
To obtain semantic information, researchers have targeted the geometry of objects to differentiate different elements in point cloud data. The use of RGB-D images combined with texture for semantic segmentation has been used in several studies [17,18,19]. Object classifiers have gained popularity, and classification algorithms have been developed to segment the indoor scene. An interactive context-aware image segmentation and labelling algorithm was developed to extract semantic regions from RGBD images [20]. Texture information-based box classifiers were introduced, but accurately segmenting a complex scene with clutter into boxes is challenging [21]. Researchers have also developed an indoor scene segmentation approach that utilizes a graph-cut algorithm to extend classification labels from features to the entire scene [22]. A search-classify algorithm was introduced using iterative region growing [23]. Studies have also used conditional random fields for the classification of patches based on contextual relations [24,25]. Shape descriptors are another method for single object classification in an indoor environment. Global fitting techniques such as the Hough transform [26] and RANSAC [27] aim to fit a primitive shape to partial or noisy data using a robust process. Markov Random Fields were used in this context by computing the classification of a point from its local descriptor and neighbours [28,29]. However, these segmentation methods are primitive and cannot be applied to complex indoor scenes consisting of furniture. Missing information or occlusions due to furniture makes these methods difficult to implement in a real-world dataset.
Deep learning algorithms have proven successful in many applications where the extraction of complex data patterns is required [30]. This has led to substantial performance in semantic segmentation tasks for images [31]. The deep learning models for semantic segmentation tasks use an encoder–decoder network structure with skip connections inspired by UNets. UNets have gained popularity due to their simple structure with a contracting path (encoder) and an expansive path (decoder) that can be used for semantic segmentation tasks. Skip connections connect the encoder and decoder paths and thus preserve the high-resolution features and improve localization by combining both paths’ features [32]. Point clouds are an important type of geometric data structure for 3D data. As they are irregular and unordered, deep learning architectures that leverage the geometric structure properties need to be used [33].
Researchers have tried to apply CNNs to higher-dimensional regular domains by converting point clouds to voxels [34,35]. This is the most straightforward way to handle the irregularity of point clouds. This process of converting them into regular data as uniform grid voxels is called the voxelization of point cloud data. Popular deep learning techniques that have proven successful in image classification and segmentation tasks can be applied to these voxelized data using 3D convolutional kernel networks. Voxnet [36] and 3D Shapenets [34] were the first to convert raw point cloud data into volumetric representation, i.e., a 3D grid, to process point cloud data using deep learning models. Researchers observed that while applying convolutions to these datasets, most activations occur at the boundary layer of the objects. Thus, to exploit this sparsity property of the point clouds, octrees have been used. An octree splits the voxels according to the density of the data. This helps reduce computations and increase efficiency. OctNets [36] uses a unique hybrid grid-tree structure that uses multiple shallow octrees and can process high-resolution input data.
To prevent voluminous transformations, state-of-the-art deep neural networks have been designed to directly manipulate irregular raw point cloud data rather than pass them through an intermediate process, i.e., voxelization. This was challenging due to the unordered input. PointNet [12] was a pioneer in handling point cloud data directly by using a symmetric function on the features extracted after operating on each point independently. The authors of PointNet developed an extension of it—PointNet++ [37]. It operates on neighbourhoods of points rather than individual points. Using sampling and grouping methods, local areas in the point cloud were found, and PointNet was applied to these groups. Thus, the local context, along with the global context of point clouds, was exploited. Multiscale Consolidation Units [38] were developed to investigate how PointNet can be implemented for large-scale spatial contexts by enlarging the receptive field. Feature Network [13] investigated the feature space by understanding the neighbourhood’s role in the point cloud data. Inspired by the SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) architecture, PointSIFT [39] was developed to understand scale variance and orientation of the shapes in a 3D space. It was integrated into PointNet architecture.
Inspired by PointNet, PointCNN [40] uses X-Conv transformation, and CNN operations are applied to the transformed features. KPConv [41] proposes deformable kernel point convolutions that can adapt to the local geometry of the points by varying the kernel points. Many deep learning models, however, do not consider the geometric relationships of points as they are largely treated on individual points. Describing the relationship between the points and neighbours through the generation of edge features was the idea presented in the Edge Convolution network in Dynamic Graph CNN [9]. LSANet [42] also tried to understand the point cloud using local spatial aware layers. It tried to understand the distribution of the local areas instead of the points. To deal with noisy data, Adaptive Sampling [43] was introduced. To reduce the memory computations and effectively apply these methods on large-scale point clouds, RandLA-Net [44] was developed. It provides an end-to-end trainable network by loading the entire scene and thus does not require pre-processing of the point clouds. With improved training and augmentation schemes, PointNeXt [45] revisited PointNet++ by fully exploring its potential. The authors focused on training and scaling strategies and improved the performance of PointNet++.
As self-attention transformer networks are good with positional information, the PointTransformer [46] network explored the use of transformer networks for 3D point cloud understanding. To avoid overfitting issues as the network goes deeper, the authors improved the PointTransformer network by using group vector attention in version 2 of PointTransformer [15]. To leverage the local attention network and voxel hashing, the FastTransformer [11] network was introduced that uses centroid-aware voxelization and devoxelization techniques. Researchers argued that most existing approaches could be unified within a single meta-architecture, PointMeta, which abstracts point cloud processing into four meta-functions: neighbour update, neighbour aggregation, point update, and position embedding. Based on this framework, they developed PointMetaBase, a simplified and efficient building block implementing these functions [47].
Building on recent progress in large-scale 3D representation learning, it has been observed that scaling plays a more critical role in model performance than complex architecture design. Consequently, Point Transformer V3 (PTV3) [48] was developed to emphasize simplicity and computational efficiency. By focusing on scalable elements, PTV3 replaces exact neighbour search using KNN with more efficient serialized neighbour mapping. This mapping leverages structured point cloud patterns, streamlining performance without compromising essential functionality at scale. The Stratified Transformer [49] modifies the Swin Transformer architecture to be compatible with 3D point cloud data by implementing a stratified strategy, which enhances the receptive field and handles long-range contexts. Additionally, it incorporates contextual relative positional encoding to enrich self-attention by embedding positional information more effectively. To handle signal irregularity and memory complexity, a Swin3D block [50] was developed that performs memory-efficient self-attention and contextual relative signal encoding. The 3D Swin Transformer is used as the backbone network that enables efficient self-attention on sparse voxels with linear memory complexity, making the backbone scalable to large models and datasets.
The selection of the model depends on the user’s requirements. Every model has its advantages and disadvantages, and based on the system configurations, input data, and complexity of the models, one can decide which model to choose for semantic segmentation. Deep learning algorithms can be integrated into the Scan-to-BIM process to obtain semantic information. This study will compare the performance of five deep learning models and discuss how they influence reconstruction accuracy.
1.1.2. Wall Reconstruction
Wall detection is an important step in the reconstruction process as it specifies the framework of the room. Buildings are mostly composed of planes, and thus, plane detection algorithms play a crucial role in wall detection. Different algorithms have been used previously to detect flat surfaces from point cloud data, including RANSAC, region growing, graph-based clustering, and projection techniques [51,52,53,54].
The RANSAC (Random Sampling Consensus) algorithm [55] is one of the most popular and simpler methods in plane detection within a point cloud. It can effectively estimate point cloud plane parameters and fit planes with a certain robustness. However, RANSAC is highly sensitive to initial sample selection, leading to over-segmentation and the detection of multiple planes where a single continuous surface exists. To improve on this, MLESAC was introduced as a modified version of RANSAC. It uses maximum likelihood estimation to determine the plane and is more suitable for complex geometries [56].
Another effective technique for detecting planes is region-growing. It begins with an initial point and clusters points that are in the neighbourhood having similar criteria like proximity, local plane distance, normal, etc. [57]. As walls are assumed to be vertical, normal vector-based analysis is a popular approach for wall detection. Cell decomposition and normal vector-based filtering were used to detect walls by differentiating them from floors, ceilings, and inclined surfaces [58].
Planar segments can also be structured into a graph, and a conditional random field algorithm can be applied to cluster them [59]. Using density signatures along the vertical axis to detect wall instances is also effective [60]. Projection-based methods involve projecting point clouds onto a surface to detect vertical line patterns indicative of walls [61,62]. These methods can be helpful in handling different wall geometries but struggle with occlusions due to furniture and over-segmentation.
To overcome this, unlike traditional workflows where walls are detected directly using raw point cloud data, this study employs RANSAC after semantic segmentation to improve wall detection. The combination of deep learning and geometric algorithms for wall detection remains relatively unexplored. This study has tried to integrate existing deep learning-based segmentation approaches with RANSAC, a traditional geometric detection algorithm (Figure 2).
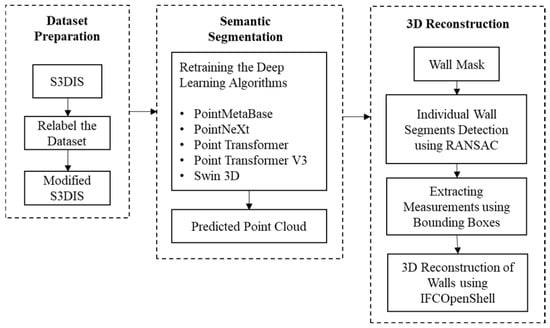
Figure 2.
Overall methodology employed in this study.
After detection, reconstruction is carried out by extracting measurements such as the length, width, height, orientation, and position of individual walls. Previous studies have used Dynamo to reconstruct walls using these measurements [63].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Preparation
Semantic segmentation on the S3DIS (Stanford 3D Indoor Scene Dataset) dataset has been explored for over a decade. S3DIS [64] comprises six large-scale indoor areas from three different buildings containing 271 rooms. Each point in the point cloud scene is labelled with 12 semantic class categories—structural elements (wall, floor, ceiling, beam, and column) and commonly found elements or furniture (door, sofa, desk, chair, bookcase, and board). The rest of the points are categorized as ’clutter’. Two versions of this dataset have been released—raw and aligned. The raw dataset uses the depth coordinate system, and every point contains both its spatial coordinates (x, y, z) and colour information (r, g, b). The aligned version is similar to the raw version, except each point cloud is rotated such that the x-axis is aligned along the entrance of the room, the y-axis is perpendicular to the entrance wall, and the z-axis remains the vertical axis. This alignment forms a canonical coordinate system that allows us to exploit the consistent structures.
Since previous studies struggle with reconstruction due to furniture, the S3DIS dataset (Figure 3) was modified by re-labelling the furniture categories—sofa, desk, chair, bookcase, and board as ‘clutter’. The modified dataset thus had eight categories—wall, floor, ceiling, beam, column, door, window, and clutter (Figure 4). Five deep learning models were re-trained on this modified dataset. By simplifying the dataset and re-labelling furniture items as “clutter”, the study narrows its focus to key architectural elements and the classified furniture points can be removed. This could improve the model’s ability to more accurately identify architectural features, which are critical in Scan-to-BIM [30].

Figure 3.
Raw point cloud data.
Figure 4.
Re-labelled point cloud data.
2.2. Semantic Segmentation
2.2.1. Selection of Algorithms
Researchers have developed state-of-the-art (SOTA) deep learning algorithms to improve the accuracy and efficiency of semantic segmentation on the S3DIS dataset. The S3DIS Benchmark [65] ranked these algorithms based on their mean IoU (Intersection over Union) scores. To compare their performance, we selected five algorithms providing different accuracies and architectures in our study (Table 1). The five algorithms—PointNeXt, Point Transformer V1 (PTV1), Point Transformer V3 (PTV3), and Swin3D—were chosen based on their varying accuracies on the S3DIS Benchmark and distinct architectural characteristics. These include differences in their core ideas, neighbour search strategies, feature extraction methods, spatial encoding techniques, and neighbour aggregation processes.

Table 1.
Summary of deep learning models’ architecture.
PointNeXt: PointNeXt builds upon the foundational ideas introduced by PointNet and PointNet++, which revolutionized point cloud processing by enabling convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to work directly with unordered point data. Before PointNet, traditional deep learning models struggled with point clouds because they are unstructured, i.e., they lack a regular grid-like structure, unlike images. Since point clouds are unordered, the introduction of permutation invariance by PointNet made it possible to use CNNs to process point clouds directly in their unstructured format [12]. Permutation invariance confirms that the final output remains consistent even if the order of the points is changed. For ‘n’ number of inputs, the input permutations can be ‘n!’. To make the output invariant to input permutations, a symmetric function can be used i.e., functions with a commutative property [Equation (1)]. PointNet used a max function to aggregate features, resulting in a global feature.
While PointNet was groundbreaking, it lacked the ability to capture local spatial relationships. This limitation led to the development of PointNet++, which introduced a hierarchical structure to learn features at multiple scales. PointNet++ improved upon the original PointNet by using set abstraction layers to aggregate features from neighbouring points of local regions and then applying the PointNet architecture. It introduced a sampling and grouping strategy followed by feature propagation. Iterative Farthest Point Sampling (FPS) uses the greedy approach as it starts with a random point and then repeatedly selects the point that is furthest from all previously chosen points, adding it to the sample set until the desired number of points is reached. These sampled points act as centroids for local regions, allowing the network to focus on important features within the point cloud. It then performs grouping by constructing local region sets of the neighbouring points around the centroids. For feature extraction, a mini PointNet network is applied to each local region, extracting features specific to that neighbourhood. This grouping process is repeated at multiple levels, where the features extracted from lower-level groupings are then used as input for grouping at a higher level, progressively capturing more global features. Thus, PointNet++ used a hierarchical spatial structure to better capture the locality [37]. Despite these advancements, PointNet++ had limitations in terms of scalability and efficiency.
PointNeXt revisited the training strategies and model scaling strategies that were not present during the time of PointNet++ and tweaked the earlier PointNet++ model with this learning to achieve SOTA performance [45]. It introduced residual connections, inverted bottleneck design, and separable MLPs into PointNet++ to efficiently scale it up and improve it, making it the next version of PointNets. Residual connections are inspired by ResNets [66], where skip connections are added to help train deeper models without suffering from vanishing gradients. Similar to MobileNetV2 [67], PointNeXt applied inverted bottlenecks instead of traditional dense layers. Using this, the model expands the feature dimensions before compressing them, allowing it to capture richer features with fewer parameters. Along with that, unlike standard fully connected layers, depth-wise separable MLPs [68] were used to reduce computational costs. Instead of processing all features together, separable MLPs apply a lightweight depth-wise operation followed by a pointwise operation, significantly reducing the number of parameters. Thus, PointNeXt improved upon PointNet++ by introducing key architectural optimizations that enhance model scalability and efficiency. PointNeXt shares the same Set Abstraction and Feature Propagation blocks as PointNet++ while adding an additional MLP layer at the beginning and the proposed Inverted Residual MLP (InvResMLP) appended after the first SA block, per stage for effective and efficient model scaling (Figure 5).

Figure 5.
Basic architecture of PointNeXt. FPS selects a subset of representative points. InvResMLPs extract features from the neighbourhood of each selected point. Max Pooling/Stratified Sampling aggregates the local features. Hierarchical Feature Learning repeats the steps at different scales and resolutions.
PTV1: Inspired by the transformer models’ progress in NLPs, a transformer network for 3D point clouds was designed. Unlike earlier point-based models like PointNet and PointNet++, which relied on MLPs and pooling operations, PTV1 utilized self-attention mechanisms to dynamically aggregate features from neighbouring points (Figure 6). The self-attention mechanism enables each point in a cloud to selectively focus on the most relevant neighbouring points based on learned feature relationships. Since point clouds are unordered sets embedded in a 3D space, self-attention, being inherently a set operator, is well suited for unordered data like point clouds. Self-attention dynamically adjusts based on feature similarity rather than fixed neighbourhood rules. Each point in the cloud interacts with its local neighbourhood by evaluating feature similarity, with attention weights emphasizing more important neighbours [69].

Figure 6.
Basic architecture of PTV1. KNN Search finds the nearest neighbours for each point. Point-wise MLPs apply MLPs to each point to transform its features. Self-Attention (Vector) computes attention weights between points based on their features and relative positions. RPE encodes the relative positions between points. Self-Attention Weights aggregates neighbour features using attention weights and processes them using MLPs.
PTV1 uses vector self-attention to aggregate features from surrounding points. Instead of assigning equal importance to all neighbours, the model learns feature-specific attention weights. This enables the model to prioritize local geometries like edges. It incorporates relative positional encoding to improve spatial awareness, where is trainable [Equation (2)].
It calculates spatial distances and orientations between points to improve feature learning. This approach helps in understanding spatial locality, i.e., nearby points have greater influence on each other compared to distant ones. Thus, the authors showed that since point clouds are essentially sets embedded in a 3D metric space, a self-attention operator, being fundamentally a set operator, is a natural fit [46].
PointMetaBase: The authors argued that most existing approaches—PointNet++ [37], DGCNN [9], PointCNN [40], Point Transformer [46], ASSANet [70], PointNeXt [45], PosPool [71]—could be fit into a single meta-architecture, PointMeta. PointMeta abstracted the general pipeline into four meta functions—neighbour update, neighbour aggregation, point update, and position embedding (Figure 7). The first step, neighbour update, involves grouping and updating the neighbours for each point. Neighbour aggregation focuses on combining the features of neighbouring points for the centre point. The point update function typically employs an MLP to further refine point features, while the position embedding function introduces positional awareness into the model. Within this general framework, an in-depth analysis was carried out and best practices were summarized to design a building block and implement the four meta functions as simply as possible, and this block was called PointMetaBase [47].
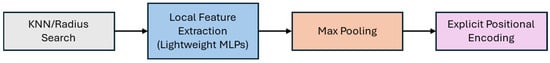
Figure 7.
Basic architecture of PointMetaBase. KNN/Radius Search finds neighbours for each point. Local Feature Extraction extracts features from each point using Lightweight MLPs. Max Pooling aggregates neighbour features. Explicit Positional Encoding encodes positional information.
For the Neighbour Updates step, the framework emphasized using efficient grouping strategies such as radius-based grouping or KNN searches, ensuring dynamic neighbourhood updates that adapt based on spatial relationships during feature extraction. In neighbour aggregation, firstly, max pooling was identified as a computationally efficient and effective method for aggregating features from neighbours, offering strong performance in capturing local geometric patterns, and secondly, reusing intermediate features was suggested to reduce computational redundancy during aggregation. For point updates, Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) are recommended for feature refinement at the point level, as they are lightweight and capable of enhancing feature expressiveness. The authors emphasize simplicity in designing point update mechanisms. For position embedding, the framework adopted Explicit Positional Encoding (EPE) from the Point Transformer, which encodes relative positional information, such as spatial distances and orientations between points, to improve spatial awareness. EPE ensures that nearby points have a stronger influence on each other compared to distant ones, improving the model’s ability to capture local details. Placing MLP layers before grouping operations was found to improve feature quality before neighbour aggregation. Thus, the set abstraction module, PointMetaSA, was refined into a reduction block that efficiently down-samples features while maintaining critical geometric details. Model scaling techniques were adapted from PointNeXt.
PTV3: PTV3 is aimed at overcoming the trade-off between accuracy and efficiency in point cloud processing (Figure 8). Earlier Point Transformer versions used KNN-based neighbour searching. This involves computing distances between points repetitively, thus leading to high computational costs and memory inefficiencies. PTV3 tackled this bottleneck by using serialized neighbourhoods. It organizes points into structured patterns based on space-filling curves (e.g., Z-order and Hilbert curves). Space-filling curves are ways to map higher-dimensional spaces into a one-dimensional space [72]. These curves pass through every point within a higher-dimensional space and preserve spatial proximity to a certain extent. As it reduces the number of computations, this makes it a faster and more scalable alternative to KNN.
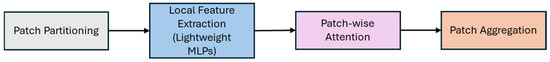
Figure 8.
Basic architecture of PTV3. Patch Partitioning divides the point cloud into patches using space-filling curves. Local Feature Extraction extracts features of each point within each patch using Lightweight MLPs. Patch-wise Attention computes attention within each patch and between patches. Patch Aggregation aggregates information from different patches.
PTV3 made the model simpler by introducing a patch attention mechanism that groups points into non-overlapping points and performs attention with each individual patch [48]. A patch is a group of points in the point cloud that are spatially or structurally related. They are treated as a single unit for further processing. Instead of calculating attention across the entire point cloud, this mechanism performs self-attention within each patch independently. The points are divided into distinct, non-overlapping groups, and thus, there is no duplication of points between patches. A self-attention mechanism allows the model to weigh the importance of each point within a patch based on its features and improves local feature aggregation.
PTV3’s patch attention mechanism consists of two methods—patch grouping and patch interaction. Patch grouping organizes the points into structured patches. It is the process of dividing the point cloud into smaller, non-overlapping regions or patches. These patches maintain spatial relationships and eliminate computationally expensive neighbour searches. Each patch contains a subset of points that are processed together, reducing the scope of attention operations to a smaller subset of points. Points are organized into patches based on specific rules or patterns, which may or may not involve spatial proximity.
Patch interaction allows the exchange of information between patches. It ensures that the global context is still captured despite independent localized processing. Thus, patch interaction involves transferring aggregated features from one patch to another, helping the model learn relationships between distant points or patches. By integrating these concepts, PTV3 achieves a balance between efficiency and performance.
Swin3D: The Swin3D architecture is a hierarchical transformer and consists of four key modules: voxelization, initial feature embedding, Swin3D blocks, and down-sampling [50]. Voxelization converts the unstructured point cloud into a multiscale sparse voxel grid with five hierarchical levels. At the finest level, each voxel has a representative point randomly selected from within it. The features of the lower level are aggregated at the coarser level. The representative point at the coarser level is the one closest to the center. The sparse voxel grids reduce computations by focusing only on non-empty voxels. The representative points are the inputs for initial feature embedding. During the initial feature embedding stage, raw input features—including point positions, colours, and normals—are mapped into a high-dimensional space using sparse convolution. A 3 × 3 × 3 sparse convolution kernel is applied at the finest voxel level, followed by batch normalization (BN) to stabilize training and a ReLU activation function to introduce non-linearity. The input feature for each voxel is obtained by concatenation of its positional offset (the difference between the representative point and voxel centre) with the point features. Thus, absolute point positions are not used as the objective is to learn local geometric patterns rather than global spatial coordinates.
The core of Swin3D is the Swin3D block that is inspired by the Swin Transformer. The Swin3D block includes S-MSA3D (self-attention on regular windows) and SW-MSA3D (shifted window attention). Regular windows process non-overlapping regions and shifted windows process the boundaries for the interaction between neighbouring regions. This captures both local features within windows and the global features across the regions.
Contextual relative signal encoding (cRSE), improving on the standard relative positional encoding (RPE), enhances self-attention by encoding not only spatial positions but also other features, such as colour or surface normal. This helps in learning both geometric and feature-based patterns. Finally, the down-sample module aggregates voxel features hierarchically. Features are aggregated to higher dimensions using normalization and fully connected layers and then pooled from neighbouring voxels using KNN pooling, preserving key spatial information. Swin3D’s hierarchical design, memory-efficient attention, and ability to process multiscale voxel features make it a SOTA deep learning model (Figure 9).

Figure 9.
Basic architecture of Swin3D. Sparse Voxelization converts the point cloud into a sparse voxel representation. Sparse Convolutions extract local features. Shifted Window Attention computes attention within shifted windows. cRSE encodes contextual signal encoding.
2.2.2. Training
The modified S3DIS dataset was divided into training (Areas 1, 2, 3, and 4), validation (Area 6), and testing (Area 5) sets. Models PointMetaBase and PointNeXt were trained on 100 epochs, batch size of 8 on the axis aligned S3DIS modified dataset. PTV1, PTV3, and Swin3D were run on 3000 epochs, batch sizes of 4, 2, and 4, respectively, on the raw modified dataset. The deep learning model parameters were kept the same as suggested by the authors of the deep learning algorithms. Figure 11a, Figure 12a, Figure 13a, Figure 14a and Figure 15a show the prediction output of Office 18 of Area 5 for the five deep learning models, respectively.
2.2.3. Evaluation
The evaluation of the semantic segmentation process was conducted using three key metrics: overall accuracy (oAcc), mean class-wise accuracy (mAcc), and mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) [45,46,47,48,50]. This evaluation is the same as provided by the authors of the respective deep learning models.
Overall Accuracy measures the percentage of correctly classified points across all categories, providing a general evaluation of the model’s performance. However, it may not fully reflect the accuracy of individual classes, especially in cases of class imbalance. Mean class-wise accuracy addresses this by calculating accuracy separately for each class and then averaging the results, ensuring that no single class dominates the evaluation. Mean Intersection over Union further refines the assessment by measuring the overlap between predicted and actual segmentation, penalizing both false positives and false negatives. This makes IoU particularly useful for understanding segmentation quality at a more detailed level. Together, these metrics provide a comprehensive evaluation, balancing overall performance with class-specific accuracy and segmentation consistency.
The segmented point cloud from Area 5 was used to compute the accuracy of the deep learning models and for 3D reconstruction. The predicted labels were compared with the original S3DIS dataset labels and the accuracy was calculated.
2.3. Wall Reconstruction
Walls define the structure of a room or space. In the process of Scan-to-BIM automation, walls are among the first architectural elements reconstructed [73]. After a wall is reconstructed, different architectural elements can be reconstructed with reference to the wall such as windows and doors. Thus, in this study, we introduced a simple workflow for the reconstruction of walls that integrates the predicted outputs of deep learning models with RANSAC to cluster individual wall segments (Figure 10).
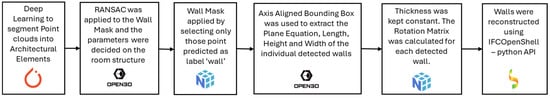
Figure 10.
Workflow used for wall reconstruction.
2.3.1. Wall Mask
A wall mask was applied to extract points classified as walls by the deep learning models (Figure 11b, Figure 12b, Figure 13b, Figure 14b and Figure 15b). A wall mask helps isolate only the points classified as walls, removing unnecessary data like furniture, ceilings, or floors. Once the walls are extracted, further processing, such as plane fitting, bounding box generation, and measurement extraction (e.g., height, width, and orientation), becomes more accurate without interference from other structures. It thus reduces false positives from clutter/furniture or other structural elements. This approach improves wall detection and accuracy in reconstruction.
2.3.2. Individual Wall Detection
Within each space, RANSAC was utilized to identify distinct wall structures. RANSAC uses iterative sample learning and tries to fit the best possible planes in the data. It begins by randomly selecting three non-collinear points to define a plane. Using these points, the necessary parameters for the plane equation are computed. Next, the deviation of all points in the cloud from the identified plane is measured based on a distance estimate. Points that fall within a predefined threshold are classified as inliers. The algorithm then records the plane along with the points that have the highest number of inliers. This process is repeated iteratively for a set number of iterations to ensure robust plane detection.
Separating individual walls makes it easier to extract the dimensions and orientation that are the key parameters for wall reconstruction using IFCOpenShell. The number of detected planes and the tolerance parameter varied across different spaces in Area 5, depending on their type. For instance, hallways typically contained two walls, whereas offices generally featured four walls. The RANSAC algorithm’s parameters were kept consistent for each space to ensure a fair comparison with the results from the five deep learning models. This approach ensured that the same plane detection process was applied uniformly across all models within a given space.
2.3.3. Extracting Measurements
Bounding boxes are used for separating instances in point cloud data for object detection [74]. An axis-aligned bounding box (AABB) was used to extract the measurements of these individual walls (Figure 11c, Figure 12c, Figure 13c, Figure 14c and Figure 15c). It encloses the detected wall points within a box aligned to the global coordinate system. The box edges are always parallel to the X, Y, and Z axes. It does not rotate to fit an object’s shape but encloses it within a fixed orientation. The AABB is determined by finding the minimum (xmin, ymin, zmin) and maximum (xmax, ymax, zmax) coordinates of the enclosed points. These values define the length, width, and height of the box.
The bounding box coordinates and dimensions were used to calculate the length (horizontal extent), height (vertical extent), and position (coordinates in 3D space) of the walls. The plane equations were used to find parallel and perpendicular walls, their tilt and the axis with which they are aligned. A rotation matrix was computed using these measurements. The thickness of the walls was kept constant at 0.2 m. Thus, the length, height, and rotation matrix were extracted to reconstruct 3D walls.
2.3.4. Reconstruction
In this study, we used IFCOpenShell to reconstruct walls. IFCOpenShell is an open-source software library designed for working with Industry Foundation Classes (IFC), a standard data format used in Building Information Modelling (BIM) (IfcOpenShellthe open-source IFC toolkit and geometry engine). An IFCOpenShell python script was utilized to create IFC models of walls using the extracted measurements. An ‘IFCWallClass’ was employed for the reconstruction of the walls. The reconstruction of walls was carried out for 60 spaces in Area 5 for each of the five models. The built 3D models and the code for every space can be provided on request.
The study employed a novel workflow for wall reconstruction. It is relatively simple and less computationally intensive and utilizes open-source tools. Thus, this workflow can be easily implemented for such comparative studies.
2.3.5. Accuracy Assessment
When assessing the accuracy of a 3D model using point cloud-to-model distance analysis, three key statistical metrics are commonly used: maximum distance, mean distance, and standard deviation. These metrics help evaluate how well a reconstructed model aligns with the reference point cloud [73,74].
Maximum distance refers to the largest deviation between any point in the point cloud and the corresponding nearest surface in the 3D model. It represents the worst-case error, highlighting the most extreme discrepancy. The mean distance is the sum of all point-to-model distances divided by the total number of points. It represents the typical error in the model. Standard deviation measures the variation or spread of the point distances. It quantifies how consistent or scattered the deviations are. A low standard deviation indicates that most points are close to the mean, meaning the errors are uniformly small. A high standard deviation suggests that some areas of the model fit well, while others have significant errors.
The points labelled as the wall class in the S3DIS dataset were extracted and used for accuracy assessment [73]. Since they are provided by the authors they are considered as ground truth. Open3D was used to conduct deviation analysis [75,76]. It requires the IFC Walls to be converted to ‘.obj’ files. Blender [77] is open-source software that allows for analysis of ifc, ply, and obj file types. Thus, Blender made it easier to compare the results and carry out the file conversions.
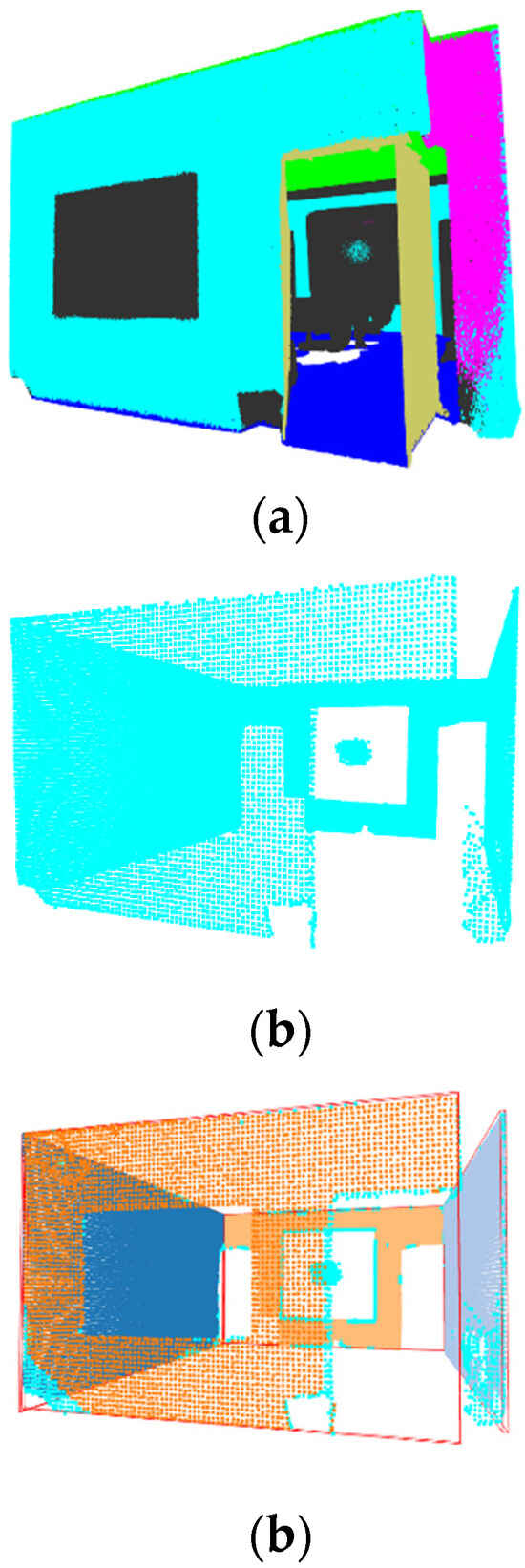
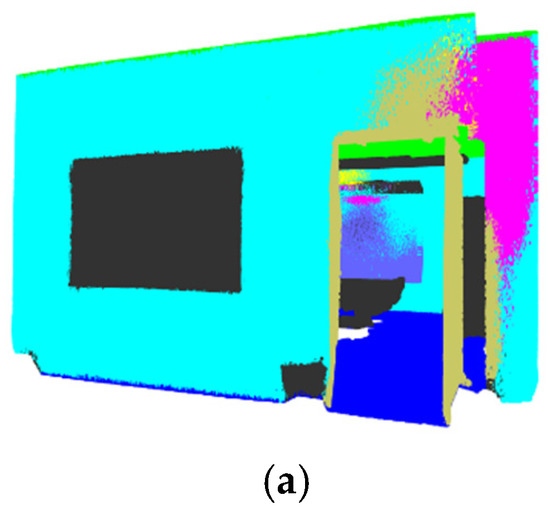
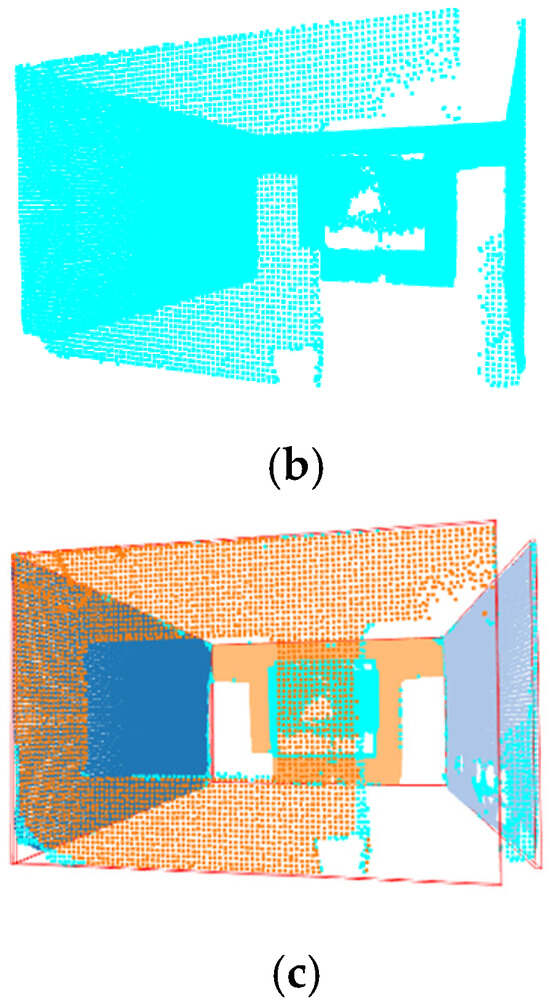
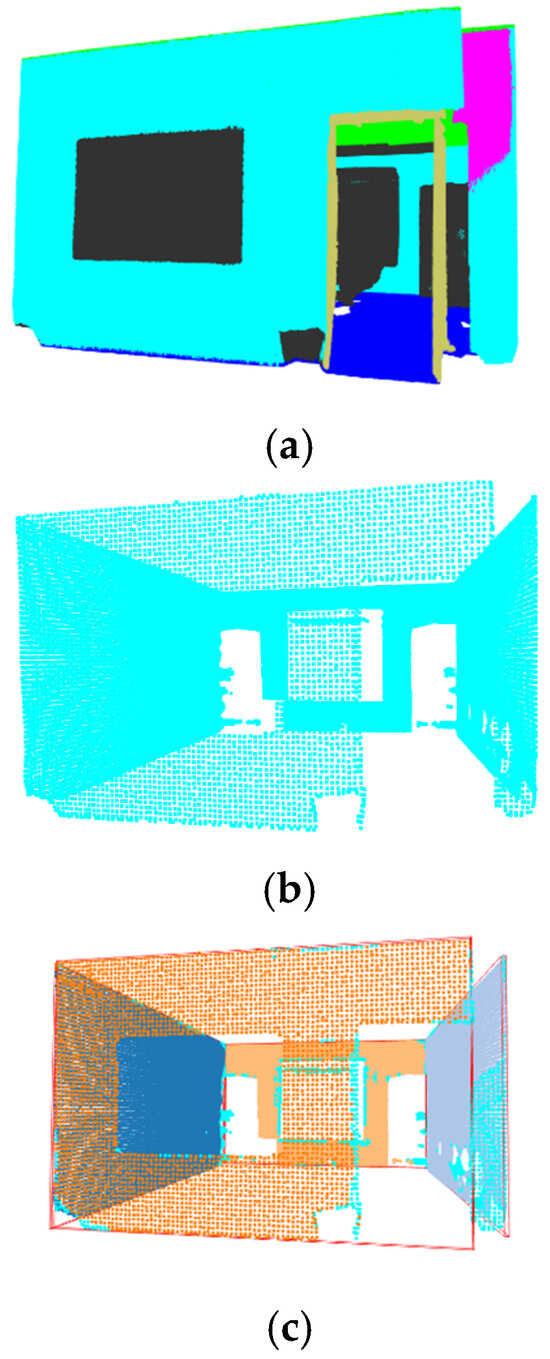
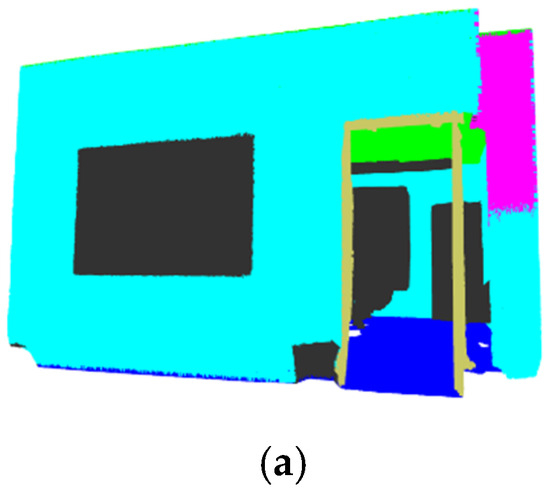
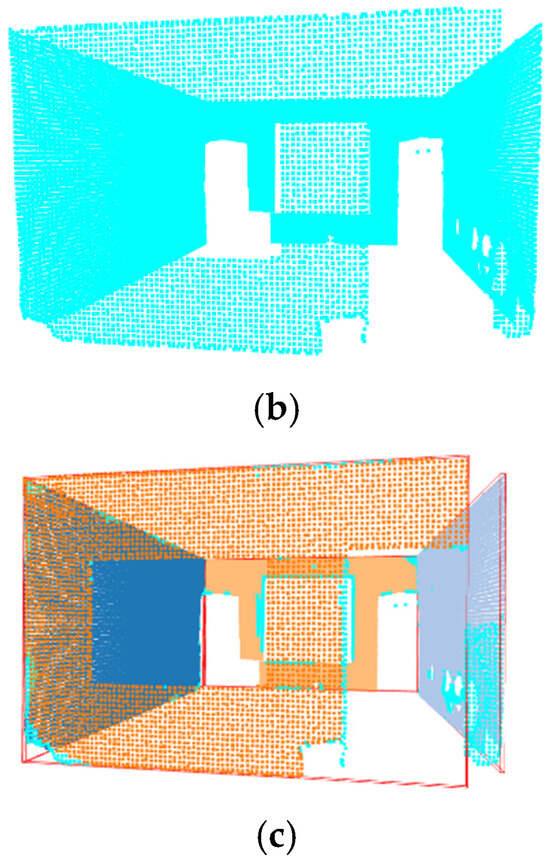
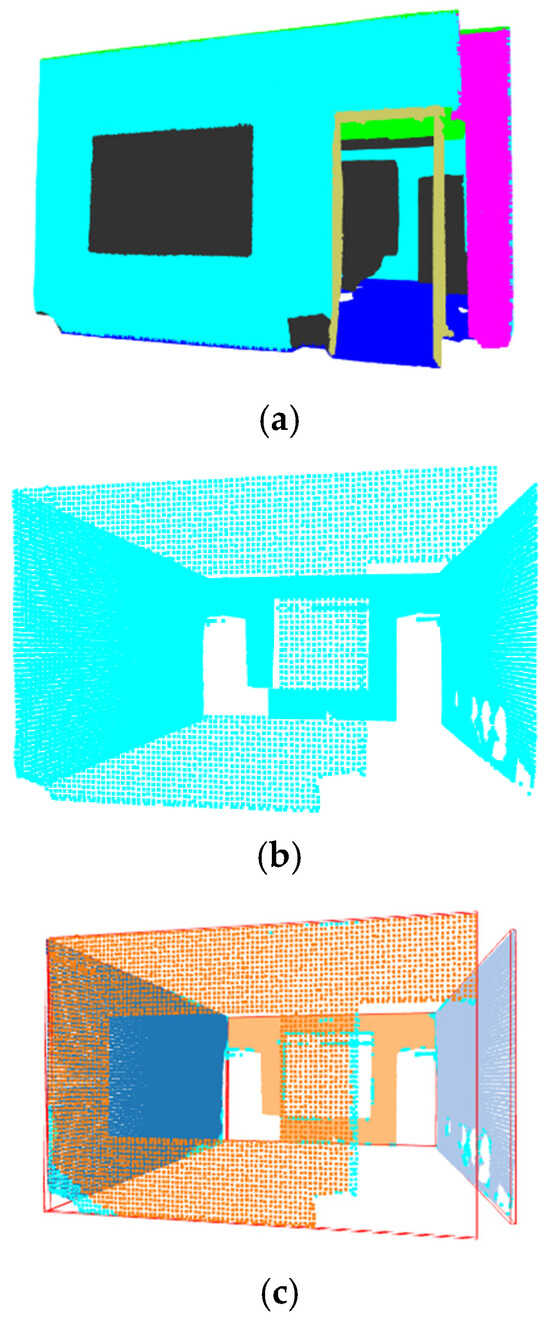

Figure 11.
(a) PointMetaBase Prediction—Office 18. (b) PointMetaBase Wall Mask—Office 18. (c) PointMetaBase Wall Detection—Office 18.


Figure 12.
(a) PointNeXt Prediction—Office 18. (b) PointNeXt Wall Mask—Office 18. (c) PointNeXt Wall Detection—Office 18.

Figure 13.
(a) PTV1 Prediction—Office 18. (b) PTV1 Wall Mask—Office 18. (c) PTV1 Wall Detection—Office 18.


Figure 14.
(a) PTV3 Prediction—Office 18. (b) PTV3 Wall Mask—Office 18. (c) PTV3 Wall Detection—Office 18.

Figure 15.
(a) Swin3D Prediction—Office 18. (b) Swin3D Wall Mask—Office 18. (c) Swin3D Wall Detection—Office 18.
3. Results
Since the focus is on wall reconstruction, the accuracy of wall classes (Wall IoU) was also examined (Table 2). This helps in understanding how well the segmentation model performed specifically on the wall class and how it influenced the final reconstruction quality.

Table 2.
Accuracy assessment for semantic segmentation.
Based on the results (Table 2), we can see that Swin3D performed the best on the wall classes and has the highest mIoU score. It is followed by PTV3 and PointMetaBase. Both have better mIoU and Wall IoU as compared to PTV1 and PointNeXt.
After reconstruction of the walls, Open3D was used to perform a deviation analysis of the 3D model with respect to the ground truth point cloud data of the walls. Heatmaps were generated for individual space to help visualize the results (Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18, Figure 19 and Figure 20). Maximum distance, mean distance and standard deviation for each space and each deep learning model were noted. An overall average of all of the spaces for the five deep learning models is presented (Table 3).
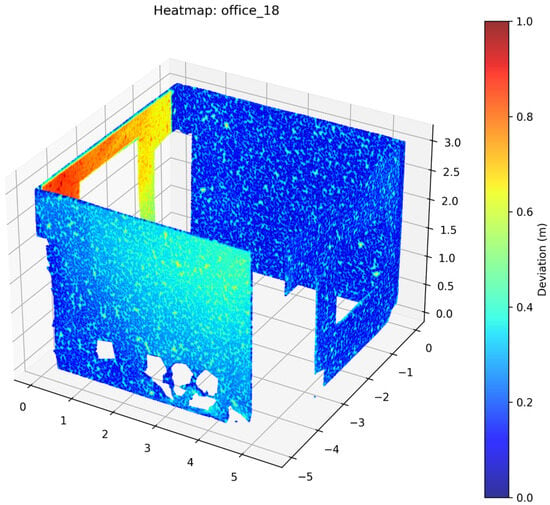
Figure 16.
Deviation Heatmap—PointMetaBase—Office 18.
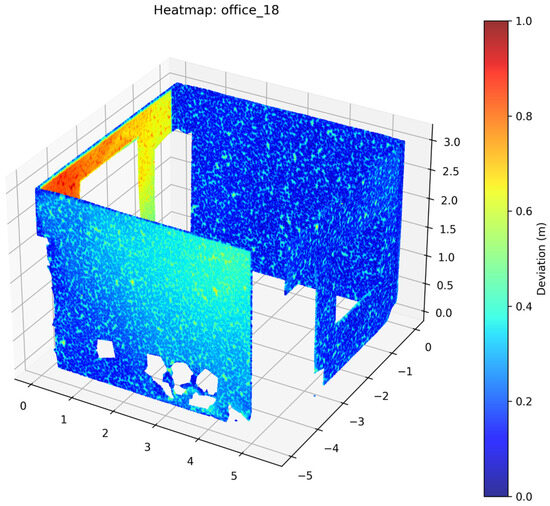
Figure 17.
Deviation Heatmap—PointNeXt—Office 18.
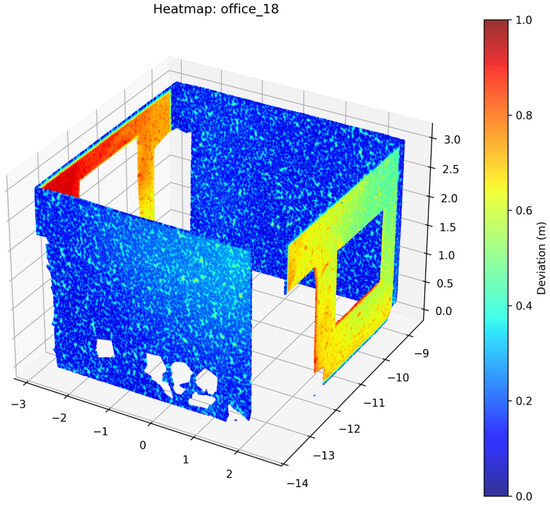
Figure 18.
Deviation Heatmap—PTV1—Office 18.
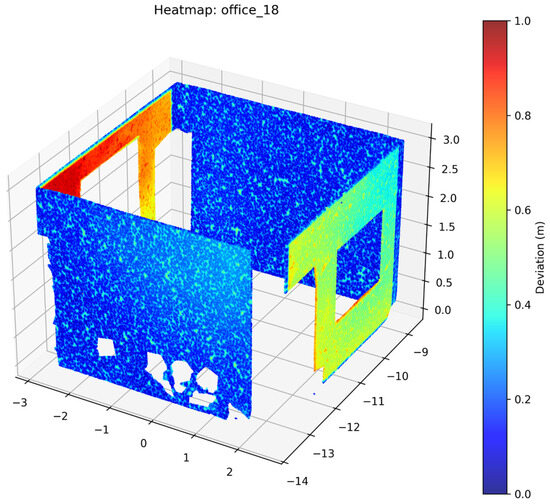
Figure 19.
Deviation Heatmap—PTV3—Office 18.
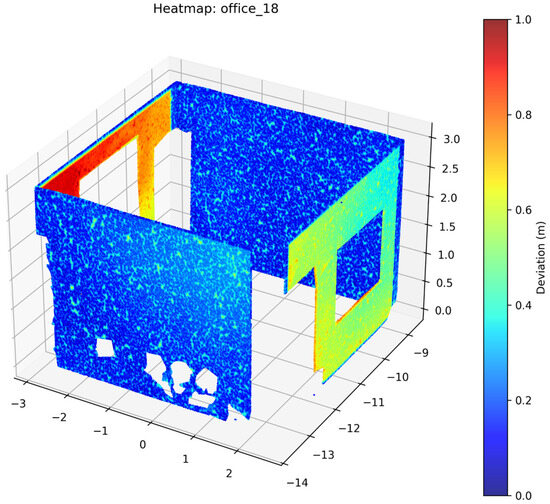
Figure 20.
Deviation Heatmap—Swin3D—Office 18.

Table 3.
Deviation analysis of the 3D models.
The results show that Swin3D performed the best; however, PointNeXt is a close second followed by PTV3. PointMetaBase and PTV1 have comparatively lower accuracies. Comparing the results of semantic segmentation and the 3D models, we can observe that PointNeXt, even if it not performing well on semantic segmentation, could still be used to build fairly accurate models.
A visual analysis of Office 23 is also provided below to gain an understanding of how the lower accuracy of the semantic segmentation prediction results impacted the deviation of the reconstructed models (Figure 21, Figure 22, Figure 23, Figure 24, Figure 25, Figure 26, Figure 27, Figure 28, Figure 29 and Figure 30).
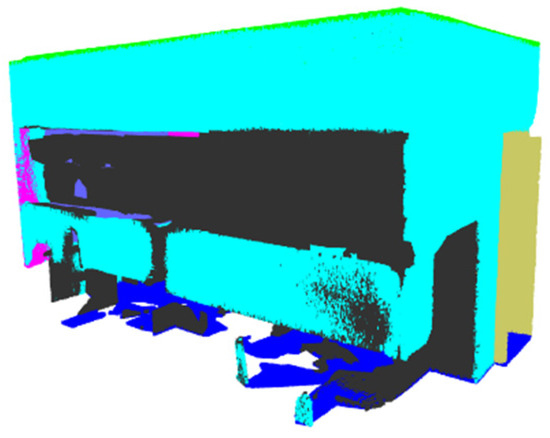
Figure 21.
Prediction—PointMetaBase—Office 23.
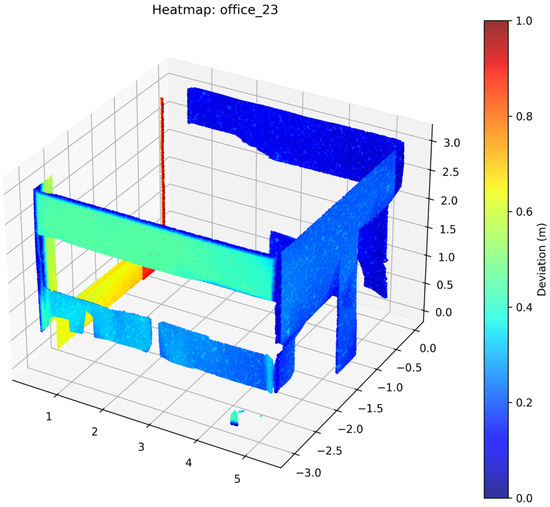
Figure 22.
Deviation Heatmap—PointMetaBase—Office 23.
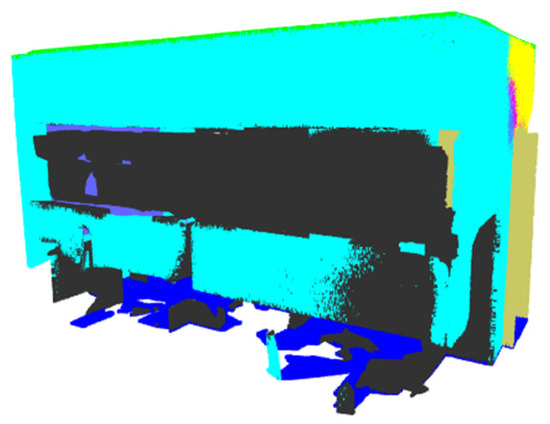
Figure 23.
Prediction—PointNeXt—Office 23.
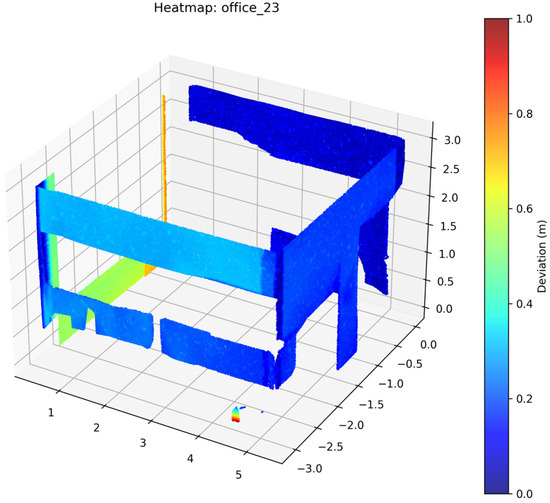
Figure 24.
Deviation Heatmap—PointNeXt—Office 23.
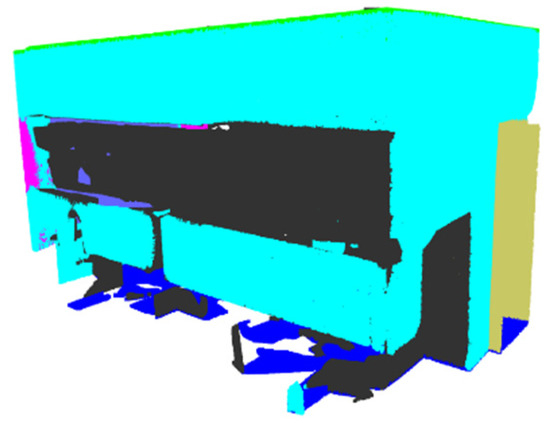
Figure 25.
Prediction—PTV1—Office 23.
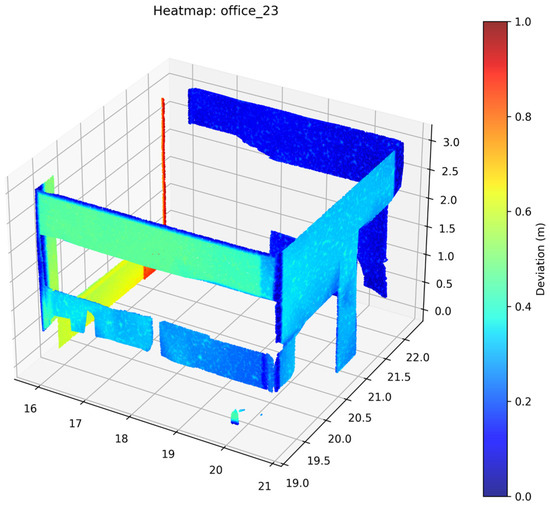
Figure 26.
Deviation Heatmap—PTV1—Office 23.
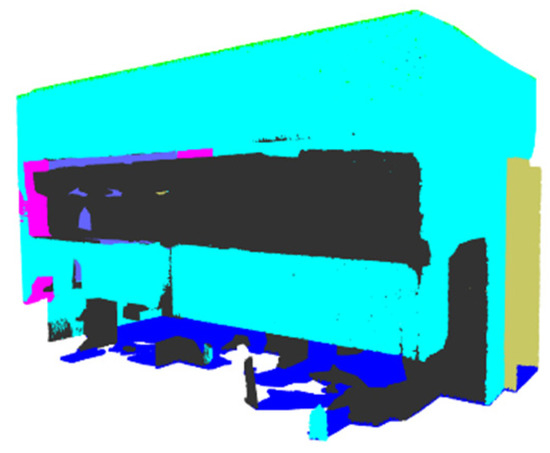
Figure 27.
Prediction—PTV3—Office 23.
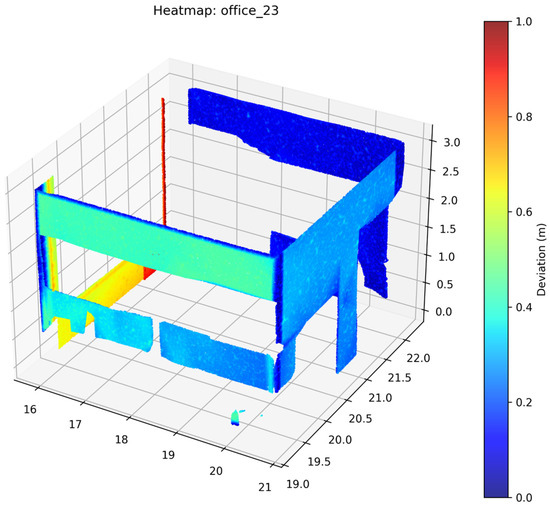
Figure 28.
Deviation Heatmap—PTV3—Office 23.
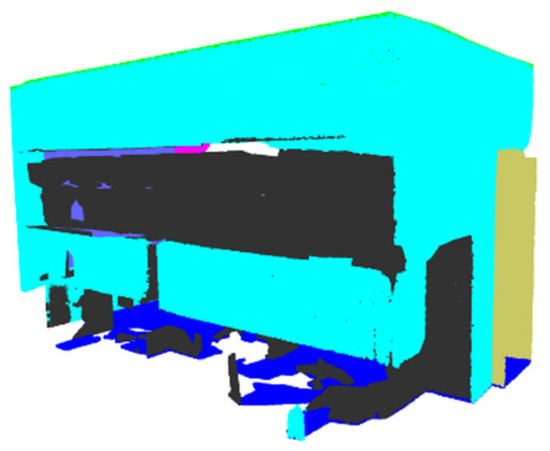
Figure 29.
Prediction—Swin3D—Office 23.
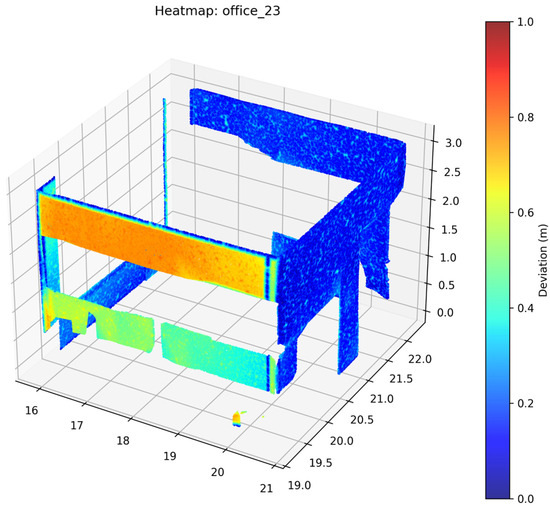
Figure 30.
Deviation Heatmap—Swin3D—Office 23.
The evaluation of the five deep learning models for semantic segmentation and 3D reconstruction of walls shows that segmentation accuracy and geometric accuracy are connected in a complicated way. While Swin3D consistently outperforms other models in both tasks, an interesting observation is that PointNeXt, despite weaker segmentation performance, achieves strong reconstruction accuracy. This suggests that different deep learning model architectures impact segmentation and reconstruction performance differently. Understanding these factors would provide insights into why certain models perform better in one and worse in another, which is discussed in the next section.
4. Discussion
The results from Table 2 show that Swin3D achieved the highest mAcc, mIoU, and Wall IoU, making it the most effective model for architectural segmentation. PTV3 and PointMetaBase followed closely, with PTV1 and PointNeXt trailing behind. However, as shown in Table 3, PointNeXt unexpectedly emerged as the second-best model, with relatively low deviations, despite its lower segmentation accuracy. This suggests that semantic segmentation accuracy does not always directly translate to better reconstruction, underlining the importance of the architecture of the models. Every model’s performance in segmentation and 3D reconstruction is determined by its architectural design, feature extraction, and spatial awareness methods.
The goal of segmentation is to classify each individual point in the point cloud correctly. This requires the ability to distinguish fine details between elements spaced close together, whereas the goal of reconstruction is to create an accurate 3D model of the overall shape. This requires the ability to capture the structures and geometries that are less sensitive to minor misclassification of points as long as the overall geometry remains intact. Semantic segmentation accuracy is highly sensitive to boundaries between objects. Small errors in segmentation along the boundaries between objects can impact accuracy significantly. Reconstruction is more influenced by the global structure. Even if some points are misclassified, the overall shape can still be reconstructed reasonably well if the dominant geometric features are captured.
Swin3D, being a hierarchical transformer-based model, uses voxels to represent point cloud data. These sparse voxel grids at multiple hierarchical levels improve the model’s spatial understanding. It uses a Swin Transformer Block to perform shifted window attention and represents both local and global features effectively. Its cRSE integration has improved its capability to encode geometric and feature-based information. This helps the model better understand spatial relationships and awareness. Overall, the model is able to learn key spatial information and geometric patterns. Thus, this hierarchically structured approach promises high segmentation accuracy and reliable 3D reconstructions, making Swin3D the best-performing model overall.
PointNeXt is the next version of PointNet++ and introduces residual connections, inverted bottlenecks, and depth-wise separable MLPs to improve the efficiency of the model. As it processes point clouds directly using an MLP-based approach, it focuses more on localized feature extraction. A lack of a global mechanism, as seen in transformer-based models, limits its segmentation accuracy. Despite this limitation, it performs well on reconstruction tasks. This is because it preserves its geometric consistency through hierarchical grouping and set abstraction layers. It progressively enriches spatial features using these layers. Depth-wise separable MLPs encode fine geometric details, preserving the local structural patterns. This suggests that while PointNeXt may not classify points with the highest accuracy, it maintains the integrity of spatial structures, making it effective for 3D reconstruction tasks. Even if semantic segmentation misclassified the wall classes as doors and columns due to their proximity to them (Figure 31), the wall structure overall did not change as the RANSAC considered all wall points lying on the plane (Figure 32). The portion above the door was classified correctly and thus led to proper plane detection, leading to accurate reconstruction (Figure 31).
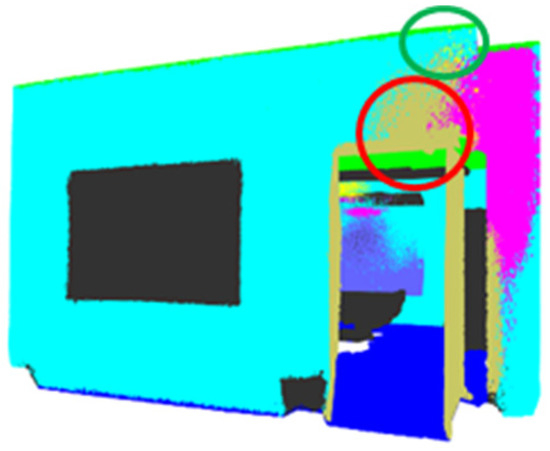
Figure 31.
Misclassification of points. The red circle highlights the misclassified points, and the green circle shows the points that were correctly classified, due to which the wall was detected accurately.
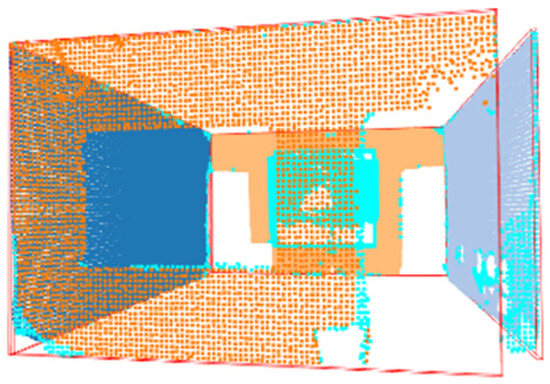
Figure 32.
Accurate plane detection even if points were misclassified.
PTV1 introduced transformers and the self-attention mechanism for point cloud processing. It uses vector self-attention and dynamically learns features and their dependencies for neighbouring points. This method is useful for contextual learning. However, as it uses fixed-radius or KNN-based aggregation, it becomes computationally expensive and less adaptable. Point clouds have varying point densities, and using a fixed-radius neighbourhood selection method makes it impossible to generalize these densities well. Thus, PTV1 struggles both in semantic segmentation and 3D reconstruction tasks.
PointMetaBase introduced a dynamic framework by analyzing the meta functions for different deep learning models and incorporating the best methods. It has four meta-functions: neighbour update, neighbour aggregation, point update, and position embedding. This design is adaptable but its feature extraction methods are not able to capture fine details. Thus, its performance is moderate for semantic segmentation tasks. Its neighbourhood aggregation method relies on max pooling. This may lead to over-simplification of global features and might be the cause of higher errors in reconstruction. When compared to Swin3D, its position encoding is not as robust as cRSE and could thus be one cause of lower spatial awareness.
PTV3 introduces a patch attention mechanism and serialized neighbourhoods to improve PTV1 and increase the efficiency of transformer-based models. PTV3 uses space-filling curves, instead of KNN-based neighbourhood searches, to obtain structured patterns of points. Its patch grouping processes point at local patches and capture local geometry. The patch interaction mechanism helps in understanding the global features and preserves spatial dependencies. This patch-based attention mechanism has enabled PTV3 to achieve balanced performance in both segmentation and 3D reconstruction. Although Swin3D outperforms it, PTV3 remains a viable alternative when efficiency is prioritized.
The proposed workflow for wall reconstruction uses the predicted outputs from deep learning models to identify and extract wall classes. Following semantic segmentation, the next step involves clustering the points labelled as walls into individual wall segments, achieved using methods such as RANSAC, which is widely popular for planar segment extraction. Traditional Scan-to-BIM methods have struggled with furniture/clutter and other architectural elements (Section 1.1.2). However, as this workflow utilizes only wall-classified points from deep learning predictions, it bypasses issues associated with non-wall classes.
In the broader Scan-to-BIM process, establishing wall topology is essential following wall reconstruction [78]. The proposed workflow does not address wall topology and presents itself as a foundational method that the authors of future studies can further develop and refine. It can also be used as a framework for comparative analysis to evaluate how other deep learning models perform across various datasets.
The accuracy assessment within this workflow specifically compares ground truth points labelled as walls to their corresponding reconstructed wall surfaces, focusing on deviations to measure reconstruction accuracy. This is essential to understand whether the walls are reconstructed at the precise location and have accurate dimensions and orientation. It is important to note that this assessment approach evaluates wall reconstruction accuracy but does not confirm the overall accuracy of the resulting BIM model. An accurate BIM model requires verification of wall continuity, adjacency, and connectivity [79]. While these aspects are critical, they represent subsequent steps in the Scan-to-BIM workflow and are beyond the current study’s scope, which primarily aims to assess the performance of different deep learning models.
5. Conclusions
Our intentions with this study were as follows: (1) Provide a summary of deep learning algorithms for the semantic segmentation of point cloud data; (2) put forth a workflow for wall reconstruction that can help future researchers automate the Scan-to-BIM process; (3) evaluate the impact of semantic segmentation accuracy on the 3D reconstruction of walls; and (4) discuss how the architecture of deep learning algorithms might have impacted the accuracy of wall reconstruction.
Based on the analysis, Swin3D is the best model overall. It performed well in both segmentation and 3D reconstruction. It is an ideal choice for users requiring high accuracy in both tasks. PointNeXt can be used when efficiency for reconstruction is prioritized over segmentation accuracy. Despite showing lower segmentation scores, it produced stable and reliable 3D models. PTV3 balances accuracy and efficiency, making it a strong alternative when computational resources are limited. PointMetaBase and PTV1 performed worse in both tasks, making them less suitable for structural segmentation and reconstruction. In this study, we focused on wall reconstruction only and did not consider opening/void detection and reconstruction (doors, windows) of the walls. For a comprehensive comparison, future researchers can use the novel workflow put forth in this study for the reconstruction of other architectural elements such as doors, windows, floors, and ceilings.
According to this study, deep learning models with semantic segmentation with a certain level of accuracy (mIoU > 65%) can also create reliable 3D models. Reconstruction algorithms must be focused on to create better 3D models as semantic segmentation only provides semantic information. However, geometric information and planar detection are the important aspects of reconstruction.
Thus, the focus of research on Scan-to-BIM should focus more on improving the reconstruction algorithms that generate valid and reliable BIM models. Achieving accuracy in segmentation alone does not guarantee that the resulting 3D model will be geometrically correct or meet the standards of a complete BIM model. Post-segmentation, the data may need to be further processed to ensure it aligns with the rules and parameters of the BIM. This includes ensuring that all elements are properly connected and that structural integrity is maintained in the model.
Integrating deep learning-based segmentation with traditional geometric reconstruction methods could be one solution. As segmentation accuracy improves, it will be important to pair these advancements with equally robust and adaptive reconstruction techniques. By focusing on these improvements, we can move closer to fully automated and highly accurate Scan-to-BIM processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and streamlining workflows in the AEC industry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K. and J.P.; methodology, M.K. and J.P.; software, J.P.; validation, M.K. and J.P.; formal analysis, J.P.; investigation, J.P.; resources, J.P.; data curation, J.P.; writing—original draft preparation, J.P.; writing—review and editing, M.K.; visualization, J.P.; supervision, M.K.; project administration, M.K.; funding acquisition, M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BIM | Building Information Model/Modelling |
| AEC | Architecture, Engineering, and Construction |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| RGBD | Red Green Blue Depth |
| RANSAC | Random Sampling Consensus |
| SIFT | Scale Invariant Feature Transform |
| PTV1 | Point Transformer Version 1 |
| PTV3 | Point Transformer Version 3 |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbour |
| S3DIS | Stanford 3D Indoor Scene Dataset |
| SOTA | State-of-the-art |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| FPS | Farthest Point Sampling |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| EPE | Explicit Positional Encoding |
| BN | Batch Normalization |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| cRSE | Contextual Relative Signal Encoding |
| RPE | Relative Positional Encoding |
| oAcc | Overall Accuracy |
| mAcc | Mean Class-wise Accuracy |
| mIoU | Mean Intersection Over Union |
| AABB | Axis-Aligned Bounding Box |
| IFC | Industry Foundation Class |
References
- Eastman, C. BIM Handbook: A Guide to Building Information Modeling for Owners, Managers, Designers, Engineers and Contractors; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Adekunle, S.A.; Aigbavboa, C.; Ejohwomu, O.A. SCAN TO BIM: A systematic literature review network analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1218, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwodo, M.N.; Anumba, C.J. A review of life cycle assessment of buildings using a systematic approach. Build. Environ. 2019, 162, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pətrəucean, V.; Armeni, I.; Nahangi, M.; Yeung, J.; Brilakis, I.; Haas, C. State of research in automatic as-built modelling. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourguechon, C.; MacHer, H.; Landes, T. Automation of As-Built Bim Creation from Point Cloud: An Overview of Research Works Focused on Indoor Environment. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 43, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borruso, G.; Huang, W.; Balletto, G.; Banfi, F.; Mura, M. Procedural Point Cloud Modelling in Scan-to-BIM and Scan-vs-BIM Applications: A Review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmelar, P.; Rejfek, L.; Nguyen, T.N.; Ha, D.H. Advanced Methods for Point Cloud Processing and Simplification. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Z. A Review of Deep Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation for Point Cloud. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 179118–179133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. 2019, 38, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Fu, C.W.; Jia, J. Pointweb: Enhancing local neighborhood features for point cloud processing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5560–5568. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.; Jeong, Y.; Cho, M.; Park, J. Fast Point Transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16928–16937. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann, F.; Kontogianni, T.; Schult, J.; Leibe, B. Know What Your Neighbors Do: 3D Semantic Segmentation of Point Clouds; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 395–409. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shan, J. Graph attention convolution for point cloud semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10288–10297. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Lao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H. Point Transformer V2: Grouped Vector Attention and Partition-based Pooling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 33330–33342. [Google Scholar]
- Camuffo, E.; Michieli, U.; Milani, S. Learning from Mistakes: Self-Regularizing Hierarchical Representations in Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 27, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.; Fox, D. Object Recognition in 3D Point Clouds Using Web Data and Domain Adaptation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.; Bo, L.; Ren, X.; Fox, D. A large-scale hierarchical multi-view RGB-D object dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.; Batra, S.; Gould, S.; Klingbeil, E.; Le, Q.; Wellman, A.; Ng, A.Y. High-accuracy 3D sensing for mobile manipulation: Improving object detection and door opening. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 2816–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Xu, W.; Zhou, K.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Guo, B. An Interactive Approach to Semantic Modeling of Indoor Scenes with an RGBD Camera. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedau, V.; Hoiem, D.; Forsyth, D. Thinking Inside the Box: Using Appearance Models and Context Based on Room Geometry. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; Volume 6316, pp. 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberman, N.; Fergus, R. Indoor scene segmentation using a structured light sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Xie, K.; Sharf, A. A search-classify approach for cluttered indoor scene understanding. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Huber, D. Using context to create semantic 3D models of indoor environments. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, BMVC 2010, Aberystwyth, UK, 31 August–3 September 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galleguillos, C.; Rabinovich, A.; Belongie, S. Object categorization using co-occurrence, location and appearance. In Proceedings of the 26th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosselman, G.; Gorte, B.G.H.; Sithole, G.; Rabbani, T. Recognising structure in laser scanning point clouds. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2004, 36, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel, R.; Degener, P.; Klein, R. Completion and reconstruction with primitive shapes. Comput. Graph. Forum 2009, 28, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, D.; Bagnell, J.A.; Vandapel, N.; Hebert, M. Contextual classification with functional Max-Margin Markov Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelov, D.; Taskar, B.; Chatalbashev, V.; Koller, D.; Gupta, D.; Heitz, G.; Ng, A.Y. Discriminative learning of Markov random fields for segmentation of 3D scan data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; pp. 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H. Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Overview on Techniques, Taxonomy, Applications and Research Directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Georgiou, T.; Lew, M.S. A review of semantic segmentation using deep neural networks. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2018, 7, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Zhu, X. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. IEEE Access 2015, 9, 16591–16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Bennamoun, M. Deep Learning for 3D Point Clouds: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 4338–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Song, S.; Khosla, A.; Yu, F.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Xiao, J. 3D ShapeNets: A Deep Representation for Volumetric Shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Niessner, M.; Dai, A.; Yan, M.; Guibas, L.J. Volumetric and Multi-View CNNs for Object Classification on 3D Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.-S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.-X.; Sun, C.-Y.; Tong, X. O-CNN: Octree-based convolutional neural networks for 3D shape analysis. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.R.Q.; Hao, Y.; Leonidas, S.; Guibas, J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann, F.; Kontogianni, T.; Hermans, A.; Leibe, B. Exploring Spatial Context for 3D Semantic Segmentation of Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, C. PointSIFT: A SIFT-like Network Module for 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.00652. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Bu, R.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Di, X.; Chen, B. PointCNN: Convolution on X-Transformed Points. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2018), Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.; Qi, C.R.; Deschaud, J.-E.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Guibas, L.J. KPConv: Flexible and Deformable Convolution for Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CFV International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6410–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Z.; Li, X.-Y.; Fan, D.-P.; Wang, K.; Lu, S.-P.; Cheng, M.-M. LSANet: Feature Learning on Point Sets by Local Spatial Aware Layer. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.05442. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zheng, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Cui, S. PointasNL: Robust point clouds processing using nonlocal neural networks with adaptive sampling. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CFV Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5588–5597. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Rosa, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. RandLA-Net: Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, G.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Mai, J.; Hammoud, H.A.A.K.; Elhoseiny, M.; Ghanem, B. PointNeXt: Revisiting PointNet++ with Improved Training and Scaling Strategies. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 23192–23204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, J.; Torr PH, S.; Koltun, V. Point Transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual Conference, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Zheng, X.; Li, L.; Chao, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ji, R. Meta Architecture for Point Cloud Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17682–17691. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, P.-S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Ouyang, W.; He, T.; Zhao, H. Point Transformer V3: Simpler, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Qi, X.; Jia, J. Stratified Transformer for 3D Point Cloud Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8490–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-Q.; Guo, Y.-X.; Xiong, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Wang, P.-S.; Tong, X.; Guo, B. Swin3D: A Pretrained Transformer Backbone for 3D Indoor Scene Understanding. Comput. Vis. Media 2025, 11, 83–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Xie, L.; Chen, D. Modeling indoor spaces using decomposition and reconstruction of structural elements. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2017, 83, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, G.; Su, F.; Li, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, D.; Zuo, X.; Ying, S. Automatic Indoor Reconstruction from Point Clouds in Multi-room Environments with Curved Walls. Sensors 2019, 19, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrus, R.; Claici, S.; Wendt, A. Automatic Room Segmentation from Unstructured 3-D Data of Indoor Environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macher, H.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P. From Point Clouds to Building Information Models: 3D Semi-Automatic Reconstruction of Indoors of Existing Buildings. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torr, P.H.S.; Zisserman, A. MLESAC: A New Robust Estimator with Application to Estimating Image Geometry. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2000, 78, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjatoleslami, S.A.; Kittler, J. Region growing: A new approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1998, 7, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, C.; Wyss, G.; Pajarola, R. Robust normal estimation in unstructured 3D point clouds by selective normal space exploration. Vis. Comput. 2018, 34, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassier, M.; Vergauwen, M. Unsupervised reconstruction of Building Information Modeling wall objects from point cloud data. Autom. Constr. 2020, 120, 103338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previtali, M.; Díaz-Vilariño, L.; Scaioni, M. Indoor Building Reconstruction from Occluded Point Clouds Using Graph-Cut and Ray-Tracing. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesau, S.; Lafarge, F.; Alliez, P. Indoor scene reconstruction using feature sensitive primitive extraction and graph-cut. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 90, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Su, F.; Yang, F.; Zhu, H.; Li, D.; Zuo, X.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Ying, S. Reconstruction of Three-Dimensional (3D) Indoor Interiors with Multiple Stories via Comprehensive Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Automated BIM generation for large-scale indoor complex environments based on deep learning. Autom. Constr. 2024, 162, 105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armeni, I.; Sener, O.; Zamir, A.R.; Jiang, H.; Brilakis, I.; Fischer, M.; Savarese, S. 3D Semantic Parsing of Large-Scale Indoor Spaces (a) Raw Point Cloud (b) Space Parsing and Alignment in Canonical 3D Space (c) Building Element Detection Enclosed Spaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- S3DIS Benchmark (Semantic Segmentation)|Papers with Code. Available online: https://paperswithcode.com/sota/semantic-segmentation-on-s3dis (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3295222.3295349 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Qian, G.; Al Kader Hammoud, H.A.; Li, G.; Thabet, A.; Ghanem, B. ASSANet: An Anisotropic Separable Set Abstraction for Efficient Point Cloud Representation Learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 28119–28130. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, X. A Closer Look at Local Aggregation Operators in Point Cloud Analysis; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12368, pp. 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, M. Space-Filling Curves; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassier, M.; Klein, R.; Van Genechten, B.; Vergauwen, M. IfcWall Reconstruction from Unstructured Point Clouds. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 4, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Clark, R.; Hu, Q.; Wang, S.; Markham, A.; Trigoni, N. Learning Object Bounding Boxes for 3D Instance Segmentation on Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- IfcOpenShell—The Open Source IFC Toolkit and Geometry Engine. Available online: https://ifcopenshell.org/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Open3D Primary (Unknown) Documentation. Available online: https://www.open3d.org/docs/latest/index.html (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- blender.org—Home of the Blender Project—Free and Open 3D Creation Software. Available online: https://www.blender.org/ (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Bassier, M.; Vergauwen, M. Topology Reconstruction of BIM Wall Objects from Point Cloud Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshelham, K.; Díaz-Vilariño, L. 3D Modelling of Interior Spaces: Learning the Language of Indoor Architecture. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).