Highlights
- Eco-friendly geopolymer foams are developed from silica fume, natural zeolite, and H2O2.
- The addition of a stabilizer produces smaller and more homogeneous pore sizes.
- The technical properties highly depend on porosity and pore size distribution.
- The samples produced showed good compressive strength and low thermal conductivity.
- These foams could be a sustainable substitute for thermal insulation.
Abstract
The need for environmentally friendly and energy-efficient building materials has increased significantly. This study synthesizes geopolymer foams with enhanced thermal insulation properties using silica fume and natural zeolite tuff. Zeolite’s porous structure and active sites improve polymerization and strengthen the foam, while silica fume reacts with NaOH to release sodium silicate, forming a durable geopolymer matrix. Foam porosity is introduced by generating oxygen gas from H2O2 and NaOH, with calcium stearate stabilizing the foam structure. Comparative analysis of the compressive strength, bulk density, porosity, and thermal conductivity shows that incorporating H2O2 and calcium stearate significantly reduces thermal conductivity (from 0.19 to 0.06 W/m·K) while ensuring a highly porous system (66–82.6% porosity) with adequate mechanical strength (1.6–3.39 MPa). These findings highlight the potential of the developed geopolymer foam for sustainable insulation applications.
1. Introduction
The rapid progress of urbanization and industrialization is developing environmental concerns, particularly in the construction industry [1,2]. Key issues include excessive reliance on non-renewable energy sources and the resulting greenhouse gas emissions, necessitating innovative solutions [3,4]. Statistical evidence indicates a substantial rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, rising from approximately 285 parts per million in 1850 to 419 parts per million by 2023 [5,6]. This increase is expected to rise by 50% until the year 2050 [7]. Significantly, buildings are a major contributor to global climate change, accounting for approximately 39% of worldwide carbon dioxide emissions [8]. This highlights the essential role of construction decisions in aligning with and advancing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations [9].
In current construction practices, a diverse wall insulation material is employed, ranging from polymer foams to glass foams and concrete foams [10,11,12]. Despite their popularity, these materials introduce specific challenges that extend beyond financial considerations. For instance, polymer foams, while widely used, exhibit a shorter lifespan and are susceptible to flammability [13,14]. Additionally, the production of glass foams and the calcination process for the cement component in concrete foams require high temperatures [15], contributing not only to significant energy consumption but also to the release of harmful gases, such as CO2, into the atmosphere [16]. Hence, the growing demand for environmentally sustainable thermal insulation materials, such as geopolymer foams, is increasingly dominant in addressing environmental concerns.
Geopolymer foams are distinguished by their semi-crystalline three-dimensional silico-aluminate porous structure, these materials are created by activating precursors of aluminosilicate through an alkali solution [17,18]. The production process of geopolymer foams is not only straightforward but also eco-friendly, as it is produced from industrial solid waste, forming a geopolymer slurry [19]. Notably, a low-temperature method is used to prepare geopolymer paste, reducing the amount of hazardous gas released into the atmosphere during the production process [20]. Presently, two primary approaches are employed for geopolymer foam preparation: physical and chemical foaming methods [21]. The physical foaming method entails mixing the paste with precast foam generated by a foaming agent, leading to the formation of numerous pores within the paste once it cures and hardens [22]. On the other hand, the chemical foaming approach involves mixing the paste with chemical foaming agents such as H2O2 and aluminum powder, which cause the paste to react and release gases like H2 and O2, resulting in pore formation [23].
The production of geopolymer foams from natural materials like metakaolin [24,25,26] or industrial waste such as fly ash [27,28,29,30], blast furnace slag [31,32], construction and demolition waste [33,34] waste glass [35,36,37], and silica fume [38,39,40] is a cost-effective and eco-friendly method [41]. These foams are suitable for a variety of applications due to their lightweight nature, superior thermal insulation, and fire resistance [42,43]. Their chemical durability, environmentally friendly composition, and low cost (as they can be produced from cheap materials like silica fume and natural zeolite) further enhance their appeal, offering tailored solutions for diverse needs, from construction to aerospace [44]. Silica fumes emerge as a by-product during the manufacturing of elemental silicon or alloys that incorporate silicon within electric arc furnaces [45]. On the other hand, natural zeolite tuffs, volcanic rocks characterized by crystalline aluminosilicate minerals, are renowned for their outstanding adsorption and cation exchange capacities [46]; however, the low-content natural zeolite is an excellent building material for porous bricks [47] and ceramic foams formation. These materials stand out as both cost-effective and easily accessible resources
This research introduces an innovative approach to developing high-performance geopolymer foams by strategically combining zeolite and Si-rich raw materials. This design leverages zeolite not only for its high porosity, ion-exchange capacity, and reactive surface sites [48,49], which enhance polymerization and structural integrity, but also for its ability to form a stable, interconnected network within the foam. This unique feature improves both strength and durability. Additionally, the inclusion of Si-rich materials plays a main role in increasing the formation of strong Si–O–Si bonds [50], which further enhance the foam’s mechanical strength, rigidity, and thermal stability. By optimizing the interaction between these materials, this study presents a novel strategy for producing geopolymer foams with superior structural and thermal properties, advancing the field of sustainable and high-performance materials.
The aim of this study is to develop sustainable geopolymer foams using natural zeolite tuffs and silica fume, which represents a novel and sustainable approach to advanced material synthesis, addressing a critical gap in the current literature. This research introduces an innovative combination of natural zeolite—an abundant, environmentally friendly material—with silica fume, a by-product of industrial processes, to create a geopolymer foam that significantly reduces the environmental impact. The incorporation of H2O2 as a foaming agent further adds novelty by facilitating controlled pore formation through the decomposition process, contributing to the foam’s unique properties. Additionally, the use of calcium stearate as a stabilizer enhances the foam’s stability and durability. The synergistic action of H2O2 and calcium stearate provides precise control over key material characteristics, such as porosity, mechanical strength, and thermal properties. This innovative approach not only addresses a critical knowledge gap in sustainable construction materials but also holds significant promise for reducing the environmental impact. By enabling the eco-friendly production of these materials, it effectively minimizes waste while enhancing energy-efficient thermal insulation in buildings, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient built environment [51,52,53].
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials
Natural zeolite, sourced from Tokaj Mountain, Hungary, is first collected in large granules and then fragmented into smaller pieces. The fractured tuff undergoes ball milling to attain a finely powdered texture. To maintain its quality for later use, the finely ground material is packaged in plastic bags. Silica fume, gathered from industrial sites as waste, is directly employed in the synthesis process. The 98% pure sodium hydroxide, acquired from Donauchem GmbH in Germany in granular form, is directly applied in the experimental processes as the alkaline activator. H2O2 serves as a foaming agent, and calcium stearate is chosen as the foam stabilizer due to its good integration with the geopolymer framework.
A CILAS715 laser-based particle analyzer (QUANTACHROME, Odelzhausen, Germany) was employed to assess the distribution of particle sizes. The crystalline structure was examined through X-ray diffraction (XRD) using CuKα radiation at 15 kV and 20 mA, performed with a Miniflex II diffractometer (Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan). The quantitative phase composition of the samples was analyzed using both analytical and refined peak shape profile fitting techniques. This analysis was carried out using the Powder Diffraction File (PDF) database provided by the International Center for Diffraction Data (ICDD) as a reference using Topas software, version 6 to ensure precise phase identification and quantification.
The elemental composition of the raw powder was analyzed through wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (WDXRF), employing the advanced capabilities of the 200 Supermini Rigaku system (Japan). This high-precision instrument featured a palladium X-ray tube, operating at 200 W power, 50 kV voltage, and 4 mA current. The measurements were performed on 4 g pressed pellet samples, ensuring optimal signal detection. Data acquisition and processing were carried out using ZSX Primus IV software, enabling accurate and comprehensive quantification of the oxide content.
The fractured surface microstructure was examined through optical microscopy using an AxioCam ERc 5s (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). The morphology of the raw powders was analyzed with a Carl Zeiss EVO MA10 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM, Jena, Germany) integrated with an EDAX Genesis Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) system. Prior to imaging, SEM samples were coated with a thin gold layer to enhance conductivity. Pore size distribution from optical microscope photos was analyzed using ImageJ 1.54. software. A Bruker Tensor 27 Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) instrument was employed to observe changes in the functional groups, covering a spectral range of 400 cm⁻1 to 4000 cm⁻1.
The Archimedes method, following ASTM C-642 standards, was used to determine the bulk density and porosity. Compressive strength tests on cured geopolymer foams were conducted in accordance with ASTM C-39, utilizing a universal testing machine (Instron 1121, Canton, MA, USA) at a loading rate of 1 mm/min. For each condition, five samples were tested to calculate the average values and standard deviations. Thermal conductivity was measured using a C-Therm TCi meter on thin sections of 20 mm × 20 mm × 15 mm, prepared after a 28-day curing period. Each sample was tested three times to obtain average values.
The analysis of the particle size distribution and XRD diffractogram in Figure 1 provides valuable insights into the composition and characteristics of silica fume and natural zeolite powders. The median particle diameter of silica fume natural zeolite is determined to be 17.30 μm and 6.50 μm, respectively. Examining the XRD patterns of natural zeolite (Figure 1b), it is evident that clinoptilolite-zeolite (PDF No. 00-003-0010) constitutes the primary mineral in the natural zeolite tuff, comprising approximately 27.75% of the sample. Other significant constituents include cristobalite (PDF No. 01-077-1317) at around 27.15%, illite (PDF No. 00-009-0334) at 18.03%, and montmorillonite (PDF No. 01-089-7539) at 17.45%. Quartz (PDF No. 01-086-1629) and calcite (PDF No. 00-051-1524) are present in minor quantities, as outlined in Table 1. Contrastingly, the XRD analysis of silica fume indicates low percentages of crystalline mineral phases such as cristobalite and SiC. The material is predominantly composed of amorphous silica, accounting for 91% of its composition.
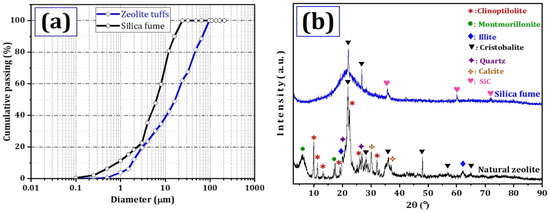
Figure 1.
X-ray diffractogram for (a) natural zeolite and (b) silica fume.

Table 1.
The phase composition of zeolite tuff as analyzed by XRD.
The XRF analysis detailed in Table 2 offers valuable information about the zeolite tuff’s composition, revealing it as a siliceous tuff with approximately 70.66% silica, 12.9% alumina, and 2.46% K2O. Additionally, it contains various contaminants such as calcium oxide, potassium oxide, iron oxide, and sodium oxide. In contrast, the XRF analysis of silica fume highlights a high content of SiO2, exceeding 97%. This composition contains impurities such as alumina (Al2O3), iron oxide (Fe2O3), potassium oxide (K2O), calcium oxide (CaO), and sodium oxide (Na2O).

Table 2.
Oxide content (wt%) of the raw materials as detected by XRF.
The SEM analysis in Figure 2 provided a detailed look at the microscopic features of both natural zeolite and silica fume powders. The zeolite particles displayed a fascinating irregularity in shape. Smaller particles clumped together, forming uneven, layered structures. Some particles were angular, while others were unevenly shaped, highlighting the diverse range of structures. In contrast, silica fume particles presented a more uniform appearance. They were generally semi-spherical, though a variety of sizes were observed. Their surfaces were well defined, with some exceptions where particles appeared irregular or rough. This observation, along with the broad range of particle sizes evident in the SEM images, aligns well with the findings from the separate particle size analysis (Figure 1a).
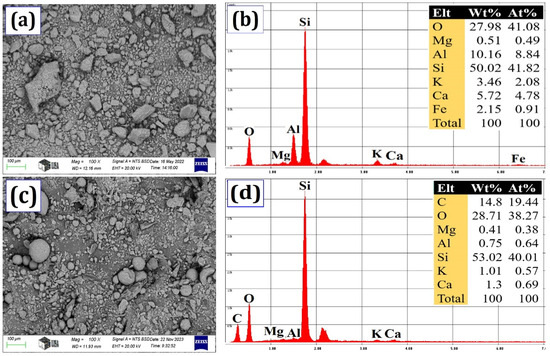
Figure 2.
(a) SEM of natural zeolite, (b) EDS of natural zeolite, (c) SEM of silica fume, and (d) EDS of silica fume.
The EDS analysis (Figure 2b,d) revealed the chemical composition of the two materials. The natural zeolite was mainly made up of silica, oxygen, and alumina, with trace amounts of other oxide elements also identified. Similarly, the EDS spectrum of silica fume (Figure 2d) revealed silicon as the dominant element, followed by oxygen. Carbon was also present, along with trace amounts of magnesium, aluminum, potassium, and calcium.
2.2. Development of the Geopolymer Foams
The chemical foaming preparation process of geopolymer foams, as outlined in Figure 3, involves several sequential steps. Initially, a homogenous mixture is achieved by milling 50 wt% of natural zeolite with 50 wt% silica fume in a planetary ball mill for 15 min at 200 rpm. Subsequently, the produced mixture is treated with 15 M NaOH solution, prepared by dissolving a stoichiometric amount of NaOH granules in distilled water (Table 3). The NaOH content in the mixture is 25.2 g, ensuring the necessary alkalinity for effective geopolymerization. Regarding the water-to-solid (W/S) ratio, a value of 0.42 was chosen to balance workability, reaction kinetics, and final porosity. This ratio facilitates adequate mixing and moldability while promoting the optimal dissolution of raw materials, enhancing polymerization reactions, and achieving the desired pore structure in the final geopolymer foam. The resulting mixture is thoroughly mixed using a laboratory overhead mixer operating at 1000 rpm for 5 min, facilitating dissolution and polycondensation reactions that generate a viscous slurry, accompanied by heat evolution due to the exothermic nature of the reaction. Firstly, sodium hydroxide dissolves the silica fume, releasing reactive silicate species like sodium silicate, which becomes available for subsequent chemical reactions [54]. The resulting soluble sodium silicate acts as an effective binder, playing a basic role in the development and strengthening of geopolymeric systems. Following this, varying proportions (0.15 and 0.30 wt%) of calcium stearate foam stabilizer are introduced into the slurry and mixed for an additional 5 min at 1000 rpm. Successively, H2O2 foaming agent (0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.00, and 1.25 wt%) is added to generate O2 gas bubbles within the mixture, which is thoroughly mixed for an additional 2 min. The resulting evenly distributed viscous slurry is then molded in a silicon rubber mold with dimensions of 20 mm × 20 mm × 15 mm. The foam-forming mixture is subsequently cured at 60 °C for 48 h; during which, chemical reactions form the geopolymer structure while gas bubbles expand, yielding a porous material. Following curing, the sample is demolded, shaped using a table saw, and further cured as necessary for specific applications. The chosen composition resulted from preliminary trials optimizing the reactivity, workability, and stability of the geopolymer slurry.
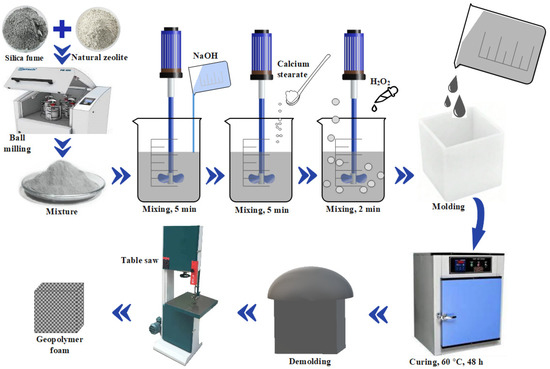
Figure 3.
Geopolymer foams preparation procedure.

Table 3.
Mixture design of geopolymer foams.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Identification of the Cured Samples
XRD analysis serves as a crucial tool for investigating the complex mineral compositions and phase transitions within geopolymer foams. Typically, the positioning of characteristic peaks within XRD spectra depends on the crystal structure, while the intensity correlates with the mineral concentration. Notably, the XRD spectra show that, when alkali activation occurs, the wide amorphous hump that spans 15–30° in the case of raw materials (as seen in Figure 4) changes to a discrete hump that is positioned towards somewhat higher angles (20–35°). This phenomenon is attributed to the occurrence of polycondensation reactions and the subsequent formation of N-A-S-H gel in geopolymerization [55,56]. This chemical process consumes free water, resulting in an increase in alkalinity, thus facilitating the dissolution of aluminum (Al) and silicon (Si) from natural zeolite and silica fume. Consequently, this dissolution aids in gel formation and effectively stabilizes the structural integrity of foam pores. Despite the incorporation of foaming agents such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and a foam stabilizer like calcium stearate, minimal impact on the phase composition is observed, suggesting stable mineralogical phases. The result also confirms the presence of small peaks of montmorillonite (PDF No. 00-003-0010), clinoptilolite (PDF No. 01-089-7539), quartz (PDF No. 01-086-1629), and cristobalite (PDF No. 01-077-1317). These peaks potentially signify the presence of unreacted compounds from the geopolymer raw materials.
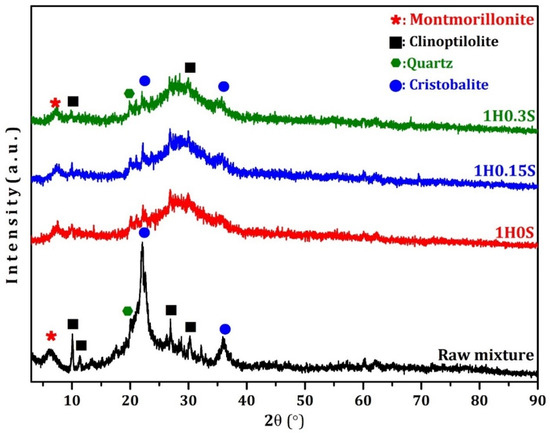
Figure 4.
XRD analysis of the raw mixture and produced geopolymer foams.
3.2. FT-IR
To examine the structural alterations prompted by alkali activation, the samples underwent evaluation via FTIR analysis. Figure 5 compares the FTIR spectra of the raw mixture to the FTIR spectra of the alkali-activated samples containing varying concentrations of foaming agent and stabilizer. The peak at 449 cm−1 was identified as the in-plane bending vibration peak of the Si-O bond [57]. An interesting observation is the disappearance of the 794 cm−1 peak, which exists in the FTIR investigation of the raw materials, attributed to the Si-O bond in the SiO4 tetrahedron [58]. This disappearance post-geopolymerization was attributed to the dissolution of the raw mixture. Additionally, the appearance of Si-O bonds was confirmed by the presence of a peak at 864 cm−1, indicative of asymmetric vibrations of Si-O bonds [59], while the band at 1450 cm−1 was attributed to the asymmetric stretching of the O-C-O bond within CO32− groups, resulting from the interaction between atmospheric carbon dioxide and the alkali solution present during geopolymer formation [60]. The prominent band in the 860–1200 cm−1 range was linked to the asymmetric stretching vibrations of Si–O–T tetrahedra (T = Al and Si). During geopolymerization, the matrix structure experienced a substitution of tetrahedral [AlO4] for the original [SiO4] tetrahedra in the raw powders. This substitution altered the environment surrounding the [SiO4] tetrahedra, causing absorption peaks to move to lower frequencies as a result of increased Si–Al substitution. Consequently, the approximately 970 cm−1 wavelength was identified as the asymmetric stretching band of Si–O–T vibration, serving as a distinctive marker for geopolymer formation [61,62]. Further bands observed include those at 3657 cm−1, corresponding to OH stretching within the three-dimensional porous structure of the geopolymer, and at 1652 cm−1, indicating OH bending of bound water [63].
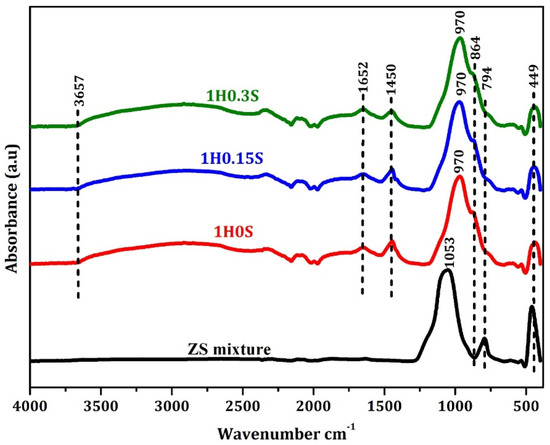
Figure 5.
FTIR analysis of the raw mixture and the resulting geopolymer foams.
3.3. Characterization of the Produced Geopolymer Foams
3.3.1. The Influence of Zeolite (Clinoptilolite) and Silica Fume in the Development of Geopolymer Foams
Using natural zeolite and silica fume raises a geopolymer’s Si concentration, which significantly affects how links develop inside the geopolymer structure. During alkali activation, sodium hydroxide dissolves silica fume, releasing reactive silicate species, including sodium silicate, which then participate in further reactions [64]. The soluble sodium silicate generated can act as a binder, contributing to the development of geopolymeric systems. A high silicon content increases the availability of silica (SiO2) species, promoting the creation of Si–O–Si bonds during the polymerization process. This results in a more silicate-rich network with stronger covalent linkages, contributing to enhanced structural integrity [65]. However, an excess of Si can also limit the amount of alumina (Al2O3) available for Si–O–Al linkages, which are important for charge balancing and flexibility in the geopolymer structure. As a consequence, the material may become more rigid and brittle, reducing its toughness but increasing its compressive strength and durability. However, zeolite in the raw mixture can significantly enhance the polymerization reaction due to its unique structural properties. Zeolites are crystalline aluminosilicates with a highly porous framework and abundant active sites, which can facilitate the dissolution and enhance the structural integrity in the geopolymer mix [66]. These active sites accelerate the interaction between silica and alumina precursors, promoting the formation of polymeric chains during geopolymerization. The ion exchange capacity of zeolites also plays a crucial role by improving the availability of reactive cations, which can balance the charge and aid in the formation of a more stable, interconnected network [67]. This leads to faster polymerization, enhanced densification of the geopolymer matrix, and eventually improves the material’s mechanical strength and durability.
3.3.2. Effects of the Concentration of Hydrogen Peroxide
The optical images, SEM images, and pore size distribution of the geopolymer foams are illustrated in Figure 6. The examination of the geopolymer foams revealed a distinctive spherical pore morphology, characterized by a size range spanning from 0.1 to 4.0 mm. The microstructure of the foam is impacted by the quantity of foaming agent incorporated into the geopolymer paste, responsible for generating gas that forms the cellular structure. Notably, there is a tendency for pore sizes and porosity to escalate with the increase in foaming agent volume. The average pore sizes highly increase with increasing the content of foaming agent with less homogeneous pore size distribution. Throughout the process of foam formation, the foaming agents play a crucial role by introducing gas bubbles into the geopolymer mixture. During the setting or curing process, these gas bubbles become trapped inside the matrix, thereby generating pores within the material. Amplifying the volume of the foaming agent can result in the introduction of more gas bubbles, creating a high degree of bubble coalescence wherein adjacent bubbles merge together, leading to larger, uneven cells and reduced foam stability. Observations in the samples containing 0.7–1.2 wt% H2O2 included the coalescence of spherical pores into more intricate shapes and the occurrence of cracking, as indicated by arrows. A critical porosity value indicates a microstructural change in accordance with the percolation theory. A network of interconnected pores with more complex configurations replaces single-celled and closed pores, which are usually ellipsoidal or roughly spherical in form [68].
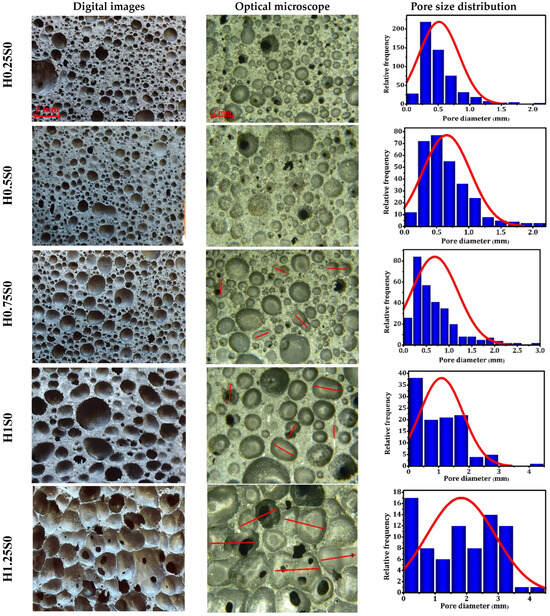
Figure 6.
Digital images, optical images, and pore size distribution of the geopolymer foams prepared without a stabilizer.
3.3.3. Influence of the Addition of the Surfactant
The addition of a surfactant to the geopolymer paste influences the structure of the foams by stabilizing the gas bubbles. The microstructures characteristics of geopolymer foams made with calcium stearate as a stabilizer are shown in Figure 7. When 0.15 wt% and 0.30 wt% calcium stearate were used, the resulting samples appeared uniform upon visual examination, displaying a network of well-developed smaller macropores evenly distributed throughout. An open macroporous structure is formed when certain pores are connected by open faces. The layer between these mostly spherical pores was thinner compared to foams without a stabilizer, attributed to higher porosity and foam stabilization. The average pore sizes differed among samples containing 1 wt% H2O2: about 1.09 mm for those without a stabilizer, 0.46 mm for those with 0.15 stabilizer, and 0.13 mm for those with 0.30 stabilizer-based geopolymer foams (see Figure 7). This variation in foam morphology can be explained by how gas bubbles are stabilized in the paste. Calcium stearate molecules adhere strongly to the mixture particles, altering the gas–liquid interface and significantly increasing the paste viscosity. Additionally, calcium stearate functions as a surfactant, reducing the liquid phase’s surface tension in the foam. Consequently, the interface becomes rigid, restricting fluid leakage through pore borders and resulting in thicker films between the pores. This preserves the foam’s structure over time, preventing collapse or shrinkage. Furthermore, calcium stearate aids in the uniform dispersion of other components, such as blowing agents and powder mixture, throughout the foam matrix [69]. This ensures minimal variations in foam density, maintains consistent properties across the foam, and enhances the overall quality.
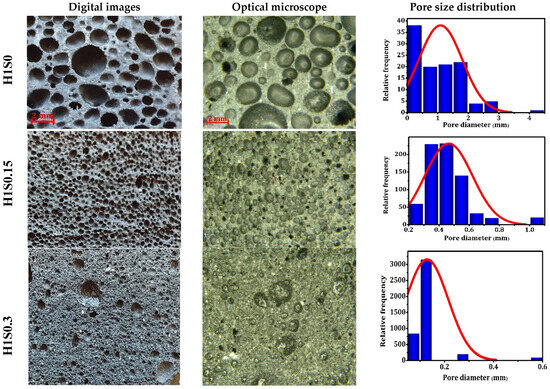
Figure 7.
Digital images, optical images, and pore distribution of the geopolymer specimens prepared with a stabilizer.
3.4. Technical Properties of the Produced Geopolymer Foams
3.4.1. Density
The effect of both the foaming agent and stabilizer on the density of the resulting geopolymer foams is demonstrated in the data presented in Figure 8. It becomes evident that increasing the quantities of these additives correlates with a noticeable decrease in the foam density. With an increase in the content of additives, specifically, as the amount of H2O2 rises from 0.25 to 1.25 wt% and the stabilizer from 0 to 0.3 wt%, the density changes from 0.76 to 0.53 g/cm3. This notable variance can largely be attributed to the concurrent increase in porosity facilitated by the intensified presence of these agents. The foaming agent and stabilizer contribute to the formation of gas bubbles within the geopolymer mixture, thereby generating pores in the material as it sets or cures. With a greater volume of foaming agent and stabilizer, more stabilized gas bubbles are introduced into the mixture, leading to higher porosity and, consequently, lower foam density. This observed relationship indicates the significant role played by these additives in modulating the physical properties of geopolymer foams, with implications for various applications where foam density is a critical parameter.
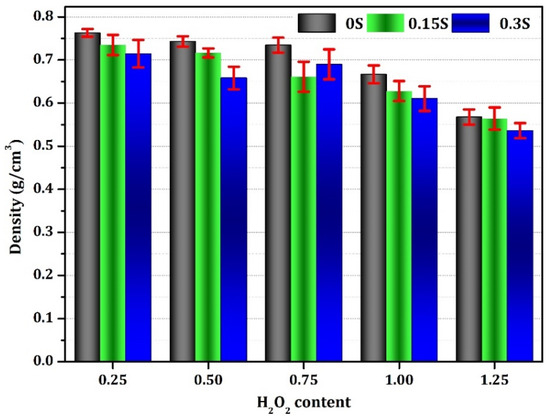
Figure 8.
Bulk density of the geopolymer foams generated with varying concentrations of stabilizer and foaming agent.
3.4.2. Porosity
The porosity data depicted in Figure 9 provide valuable insights into the characteristics of the generated geopolymer foams. Notably, a clear trend emerges wherein the porosity of the foams experiences a rapid increase, ranging from 66 to 82.6% with the rise of the H2O2 content from 0.25 to 1.20%. This significant increase in porosity suggests a direct correlation between H2O2 dosage and porosity level, indicating the essential role played by this additive in influencing the foam structure. Moreover, the introduction of calcium stearate into the samples also resulted in heightened porosity across all samples, attributed to the stabilizing effect it exerts on the foam. It is noteworthy that cracking was considered a contributing factor to the increased porosity observed in the produced foams. Additionally, while the porosity increased uniformly across all samples with escalating dosages of both H2O2 and calcium stearate, there was a noticeable enlargement in pore size evident in the microscopic analysis depicted in Figure 6. This implies that, while increased porosity is achieved with higher dosages of these additives, there may also be a trade-off in terms of pore size, which could impact the overall properties and performance of the geopolymer foams.
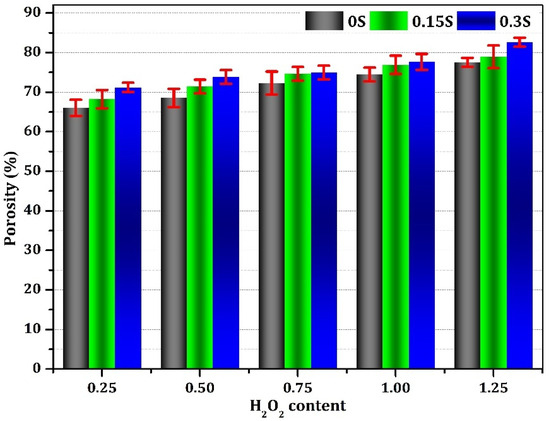
Figure 9.
Porosity of the geopolymer foams generated with varying concentrations of stabilizer and foaming agent.
3.4.3. Thermal Conductivity
Figure 10 presents the impact of both the H2O2 content and stabilizer concentration on the thermal conductivity of geopolymer foam. This test evaluates the foam’s ability to transfer heat under ambient conditions. A noteworthy observation was made regarding the impact of increasing H2O2 and the stabilizer amount on reducing the thermal conductivity values of the geopolymer specimens, resulting in a range of values from 0.193 to 0.062 W/m·K. The decrease in thermal conductivity values can be assigned to the presence of voids within the geopolymer matrix, which act as insulating barriers against heat transfer. Specifically, geopolymer samples containing 0.25% H2O2 and no calcium stearate demonstrated a maximum thermal conductivity of 0.193, whereas samples with 1.20% H2O2 and 0.30% calcium stearate exhibited a minimum thermal conductivity of 0.060 W/m·K, marking a significant reduction of 68.97%. This reduction in thermal conductivity holds significant implications for energy efficiency in building applications, as it helps minimize heat loss and thus lowers overall energy consumption.
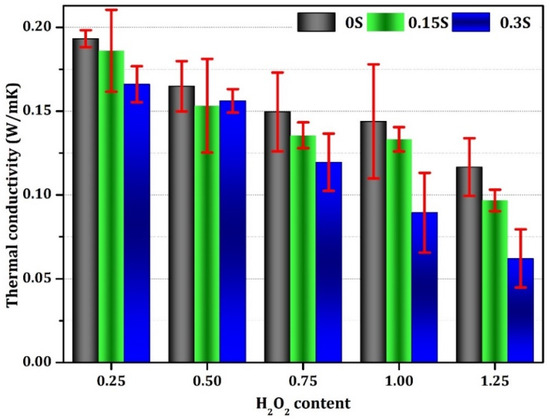
Figure 10.
Thermal conductivity of the geopolymer foams generated with varying concentrations of stabilizer and foaming agent.
3.4.4. Compressive Strength
The results of the compressive strength test, displayed in Figure 11, offer important information on the mechanical characteristics of the geopolymer foams. Within this dataset, the compressive strength values ranged from 1.05 to 3.30 MPa, indicating significant variability in the foam’s structural integrity. Notably, an inverse relationship was observed between the H2O2 content and compressive strength, with increasing H2O2 levels leading to a substantial decrease in compressive strength [70,71]. This decrease was found to be about a 68% reduction when the H2O2 content increased from 0.25 to 1.25. However, it is worth noting that, while an increase in stabilizer content resulted in heightened porosity within the foam, it assisted in raising the compressive strength. This seemingly contradictory effect can be ascribed to the creation of smaller and more uniformly distributed pore structures within the foam matrix, since evenly distributed pores help to prevent isolated areas of weakness by more uniformly distributing stress throughout the material and reducing the likelihood of structural failure. As a result, foams with smaller and evenly distributed pores tend to exhibit a higher compressive strength compared to foams with larger or irregularly distributed pores [72,73].
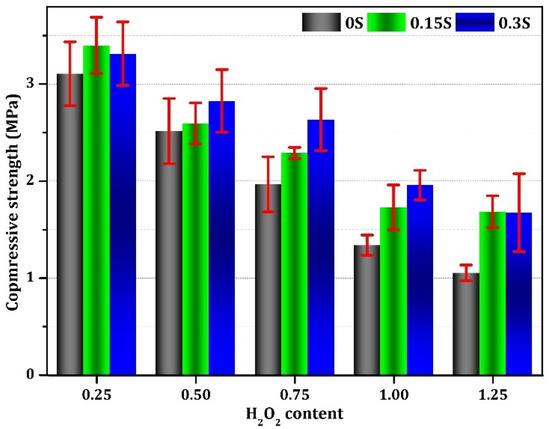
Figure 11.
Compressive strength of the geopolymer foams generated with varying concentrations of stabilizer and foaming agent.
3.4.5. The Connection Between Density, Thermal Conductivity, and Compressive Strength
Figure 12 illustrates the relationships between bulk density, thermal conductivity, and compressive strength of geopolymer foams with varying H2O2 contents and 0.3% stabilizer. Low-density, high-porosity foams effectively reduce heat transfer, lowering thermal conductivity. In contrast, higher-density foams contain more paste, which increases thermal conductivity. Increasing density also enhances the compressive strength due to a higher material volume, improved interparticle bonding, and smaller, more closely packed pores, which contribute to better load distribution and resistance to deformation.
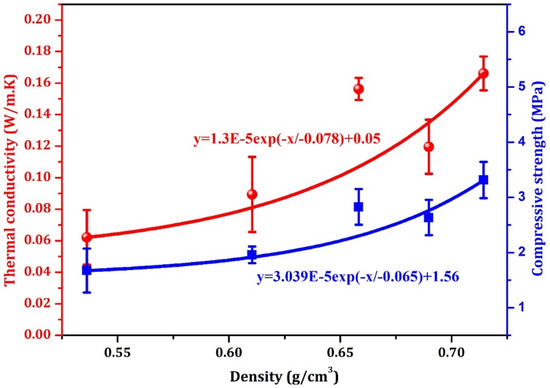
Figure 12.
The correlations between density thermal conductivity and compressive strength of geopolymer foam with different H2O2 contents and 0.3 stabilizer.
3.5. Fundamental Technical Features of the Created Geopolymer Foams Compared to Those Documented in the Literature
The geopolymer foams examined in this research demonstrate notable improvements in both thermal conductivity and compressive strength when compared to previously documented geopolymer foams generated through different foaming methods and employing diverse raw materials, as delineated in Table 4. This comparison underscores the progress achieved in the current study, suggesting enhanced performance and potential applications for the geopolymer foams produced in this work.

Table 4.
Properties of the prepared geopolymer foams compared to earlier research.
4. Conclusions
The investigation explores the green synthesis of high silica content geopolymer foams from zeolite tuffs and silica fume, with a focus on the influence of H2O2 and calcium stearate addition. The findings in this work lead to several clear conclusions:
- XRD analysis confirms the occurrence of dissolution and subsequent geopolymerization reactions, resulting in the formation of an amorphous structure. The observed peak shift towards lower wavelengths further validates the geopolymerization process.
- Compressive strength measurements of the samples falling within the range of 1.60 to 3.39 MPa, alongside thermal conductivity values spanning from 0.19 to 0.06 W/m·K, underscore the improved performance of the geopolymer foams synthesized in this investigation.
- The introduction of foaming agents and stabilizers significantly impacts porosity and pore size, thereby influencing the technological characteristics of the produced foams.
- The development of high strength is found to be highly affected by the size and uniformity of pores, emphasizing their crucial role in the overall strength characteristics.
- Zeolite’s high porosity and reactive sites improve the polymerization and structural integrity, while a high Si content strengthens the foam through Si–O–Si bonds. The result is a geopolymer foam with superior mechanical and thermal performance.
- The eco-friendly synthesis of these materials presents a sustainable approach to waste reduction while offering the potential for producing thermal insulation materials that contribute to energy conservation in building applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.I.Ş. and J.-E.F.M.I.; methodology, E.I.Ş. and J.-E.F.M.I.; software and formal analysis, J.-E.F.M.I.; resources, J.-E.F.M.I.; data curation, E.I.Ş. and J.-E.F.M.I.; writing—original draft preparation and writing—review, E.I.Ş. and J.-E.F.M.I.; visualization, E.I.Ş. and J.-E.F.M.I.; supervision, J.-E.F.M.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude for the collaboration and support we received from our colleagues in the Departments of Ceramics and Polymer Engineering, University of Miskolc and Adana Alparslan Türkeş Science and Technology University, throughout the duration of this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Voumik, L.C.; Sultana, T. Impact of urbanization, industrialization, electrification and renewable energy on the environment in BRICS: Fresh evidence from novel CS-ARDL model. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiller, G.; Roscher, J. Impact of urbanization on construction material consumption: A global analysis. J. Ind. Ecol. 2023, 27, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Hua, J.; Osman, A.I.; Farghali, M.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; et al. Green building practices to integrate renewable energy in the construction sector: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 751–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, J.E.F.; Gömze, L.A.; Koncz-Horvath, D.; Filep, Á.; Kocserha, I. Preparation, characterization, and physicomechanical properties of glass-ceramic foams based on alkali-activation and sintering of zeolite-poor rock and eggshell. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 25905–25917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Bakker, D.C.E.; Hauck, J.; Landschützer, P.; Le Quéré, C.; Luijkx, I.T.; Peters, G.P.; et al. Global Carbon Budget 2023. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 5301–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Farghali, M.; Dong, Y.; Kong, J.; Yousry, M.; Rashwan, A.K.; Chen, Z.; Al-Fatesh, A.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.-S. Reducing the carbon footprint of buildings using biochar-based bricks and insulating materials: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 71–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, J.E.F.; Tihtih, M.; Gömze, L.A. Environmentally-friendly ceramic bricks made from zeolite-poor rock and sawdust. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 297, 123715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.A.; Ahmad, M.I.; Yusup, Y. Issues, impacts, and mitigations of carbon dioxide emissions in the building sector. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Opoku, A.; Agyekum, K.; Oppon, J.A.; Ahmed, V.; Chen, C.; Lok, K.L. The critical role of the construction industry in achieving the sustainable development goals (SDGs): Delivering projects for the common good. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavoni, S.; D׳Alessandro, F.; Bianchi, F.; Asdrubali, F. Insulation materials for the building sector: A review and comparative analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 988–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, H.; Zhou, H.; Song, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Mechanical properties and energy absorption performance of foamed geopolymer under quasi-static and dynamic compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stochero, N.P.; Chami, J.O.R.d.S.; Souza, M.T.; de Moraes, E.G.; de Oliveira, A.P.N. Green Glass Foams from Wastes Designed for Thermal Insulation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.-L.; Zhao, M.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J. Recent trends of foaming in polymer processing: A review. Polymers 2019, 11, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, J.E.F.; Tihtih, M.; Kurovics, E.; Gömze, L.A.; Kocserha, I. Innovative glass-ceramic foams prepared by alkali activation and reactive sintering of clay containing zeolite (zeolite-poor rock) and sawdust for thermal insulation. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 59, 105160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggarini, U.; Pratapa, S.; Purnomo, V.; Sukmana, N.C. A comparative study of the utilization of synthetic foaming agent and aluminum powder as pore-forming agents in lightweight geopolymer synthesis. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gong, L.; Shi, L.; Cao, W.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, X. Experimental investigation on the influencing factors of preparing porous fly ash-based geopolymer for insulation material. Energy Build. 2018, 168, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Ni, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Colombo, P. Porosity, mechanical and insulating properties of geopolymer foams using vegetable oil as the stabilizing agent. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.S.; Abdel-Gawwad, H.; García, S.V.; Israde-Alcántara, I. Fabrication and characterization of thermally-insulating coconut ash-based geopolymer foam. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maged, A.; El-Fattah, H.A.; Kamel, R.M.; Kharbish, S.; Elgarahy, A.M. A comprehensive review on sustainable clay-based geopolymers for wastewater treatment: Circular economy and future outlook. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawan, S.A.; Zawrah, M.; Khattab, R.; Abdel-Shafi, A.A. In-situ formation of geopolymer foams through addition of silica fume: Preparation and sinterability. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 121998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalkah, F.; Ababneh, A.; Aqel, R. Synthesis of calcined kaolin-based geopolymer foam: Assessment of mechanical properties, thermal insulation, and elevated temperature stability. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 9967–9977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Xu, F.; Ruan, S.; Huang, X.; Zhu, J.; Peng, C. Influence of precast foam on the pore structure and properties of fly ash-based geopolymer foams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Gu, G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhu, J. Pore structure analysis and properties evaluations of fly ash-based geopolymer foams by chemical foaming method. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 19989–19997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Bai, C.; Zheng, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, G.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, X.; Colombo, P. Rapid fabrication of porous metakaolin-based geopolymer via microwave foaming. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 249, 107238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshghabadi, F.; Javanbakht, V. Preparation of porous metakaolin-based geopolymer foam as an efficient adsorbent for dye removal from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1295, 136639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candamano, S.; Coppola, G.; Mazza, A.; Caranqui, J.C.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Alexis, F.; Algieri, C. Batch and fixed bed adsorption of methylene blue onto foamed metakaolin-based geopolymer: A preliminary investigation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 197, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Fu, G.; Liang, B.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X. Mechanical properties and microstructure evaluation of fly ash—Slag geopolymer foaming materials. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18224–18237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, X. Slurry rheological behaviors and effects on the pore evolution of fly ash/metakaolin-based geopolymer foams in chemical foaming system with high foam content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 379, 131259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Ma, B.; Wang, J.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, J.; Qian, B.; Cheng, G.; Hu, Y.; Ma, F.; Sun, J.; et al. The influence of ZSM-5 waste on the properties of fly ash-based foamed geopolymer. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, C.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Colombo, P. Preparation, properties and applications of fly ash-based porous geopolymers: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 132043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.J.H.T.V.; Marques, M.d.F.V.; Aguiar, V.d.O.; Jorge, F.E. Performance of geopolymer foams of blast furnace slag covered with poly(lactic acid) for wastewater treatment. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.J.T.V.; Vieira, M.d.F.M.; Tienne, L.G.P.; Aguiar, V.d.O. Evaluation and characterization of geopolymer foams synthesized from blast furnace with sodium metasilicate. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12019–12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupathy, K.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Sanjayan, J. Formulating eco-friendly geopolymer foam concrete by alkali-activation of ground brick waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelikci, E.; Ozdogru, E.; Tugluca, M.S.; Ilcan, H.; Sahmaran, M. Comprehensive investigation of performance of construction and demolition waste based wood fiber reinforced geopolymer composites. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.J.; Raut, A.; Murmu, A.L.; Jameel, M. Influence of Glass Powder Incorporated Foamed Geopolymer Blocks on Thermal and Energy Analysis of Building Envelope. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, D.; Güden, M. Processing and characterization of geopolymer and sintered geopolymer foams of waste glass powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 124259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lu, J.-X.; Ou, G.; Yang, S.; Poon, C.S. Development of self-foaming cold-bonded lightweight aggregates from waste glass powder and incineration bottom ash for lightweight concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakouri, S.; Bayer, Ö.; Erdoğan, S.T. Development of silica fume-based geopolymer foams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 120442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Galiano, Y.; Leiva, C.; Arenas, C.; Fernández-Pereira, C. Fly ash based geopolymeric foams using silica fume as pore generation agent. Physical, mechanical and acoustic properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 500, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, E.; Medri, V.; Kpogbemabou, D.; Morinière, V.; Laumonier, J.; Vaccari, A.; Rossignol, S. Porosity and insulating properties of silica-fume based foams. Energy Build. 2016, 131, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciotti, L.; Occhicone, A.; Petrillo, A.; Ferone, C.; Cioffi, R.; Roviello, G. Geopolymer-based hybrid foams: Lightweight materials from a sustainable production process. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadia, N.F.J.; Gharzouni, A.; Nait-Ali, B.; Ouamara, L.; Ndassa, I.M.; Bebga, G.; Elie, K.; Rossignol, S. New laterite-based geopolymer foam resistance under drastic conditions: A comparative study with a metakaolin model. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 13050–13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozub, B.; Bazan, P.; Gailitis, R.; Korniejenko, K.; Mierzwiński, D. Foamed geopolymer composites with the addition of glass wool waste. Materials 2021, 14, 4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouin, J.; Fekoua, J.N.; Ouamara, L.; Piolet, E.; Gharzouni, A.; Rossignol, S. Insulating phosphoric acid-based geopolymer foams with water and high temperature resistance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 398, 132406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovářík, T.; Hájek, J.; Hervert, T.; Deshmukh, K.; Pola, M.; Jansa, Z.; Beneš, J.; Svoboda, M. Silica-based geopolymer spherical beads: Influence of viscosity on porosity architecture. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 124, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, J.F.M.; Kurovics, E.; Tihtih, M.; Somdee, P.; Gerezgiher, A.G.; Nuilek, K.; E Khine, E.; Sassi, M. Preparation and Investigation of Alumina-Zeolite Composite Materials. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1527, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, J.E.F.; Kotova, O.B.; Sun, S.; Kurovics, E.; Tihtih, M.; Gömze, L.A. Preparation of innovative eco-efficient composite bricks based on zeolite-poor rock and Hen’s eggshell. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.; Pecina, E.; Torres, R.; Gómez, L. Geopolymer synthesis using alkaline activation of natural zeolite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A. Geopolymers Based on Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite with Addition of Metakaolin. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-04176504 (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- Nikolov, A.; Rostovsky, I.; Nugteren, H. Geopolymer materials based on natural zeolite. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2017, 6, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan, P.; Figiela, B.; Kozub, B.; Łach, M.; Mróz, K.; Melnychuk, M.; Korniejenko, K. Geopolymer Foam with Low Thermal Conductivity Based on Industrial Waste. Materials 2024, 17, 6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, A.; Korim, T. Development of Geopolymer Foams for Multifunctional Applications. Crystals 2022, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, A.; Murmu, A.L. Building a Sustainable Future with Geopolymer Thermal Insulation: Availability and Opportunities. In Development of Sustainable Thermal Insulators from Waste Materials: A Circular Economy Approach; Verma, S., Khan, M.A., Srivastava, A.K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febriana, E.; Mayangsari, W.; Yudanto, S.D.; Sulistiyono, E.; Handayani, M.; Firdiyono, F.; Maksum, A.; Prasetyo, A.B.; Soedarsono, J. Novel method for minimizing reactant in the synthesis of sodium silicate solution from mixed-phase quartz-amorphous SIO2. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Sahajwalla, V. Alkali-activated foam: Understanding the relationship between rheology, activator-precursor interaction, and pore characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Contreras, S.; Bonet-Martínez, E.; Sánchez-Soto, P.J.; Gencel, O.; Eliche-Quesada, D. Synthesis and characterization of alkali-activated materials containing biomass fly ash and metakaolin: Effect of the soluble salt content of the residue. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2022, 22, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhametkaliyev, T.; Ali, H.; Kutugin, V.; Savinova, O.; Vereschagin, V. Influence of Mixing Order on the Synthesis of Geopolymer Concrete. Polymers 2022, 14, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fansuri, H.; Supriadi, W.; Ediati, R.; Utomo, W.P.; Hidayati, R.E.; Iqbal, R.M.; Sulistiono, D.O.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B. Subaer Immobilization and leaching behavior of Cd2+ and Pb2+ heavy metal ions in Indonesian fly ash-based geopolymers. Environ. Adv. 2024, 15, 100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggetto, G.D.; D’angelo, A.; Blanco, I.; Piccolella, S.; Leonelli, C.; Catauro, M. FT-IR study, thermal analysis, and evaluation of the antibacterial activity of a MK-Geopolymer mortar using glass waste as fine aggregate. Polymers 2021, 13, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, Z.; Abdullah, M.M.A.; Hussin, K.; Ismail, K.N.; Abd Razak, R.; Sandu, A.V. Effect of solids-to-liquids, Na2SiO3-to-NaOH and curing temperature on the palm oil boiler ash (Si + Ca) geopolymerisation system. Materials 2015, 8, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliche-Quesada, D.; Ruiz-Molina, S.; Pérez-Villarejo, L.; Castro, E.; Sánchez-Soto, P. Dust filter of secondary aluminium industry as raw material of geopolymer foams. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zang, J.; Tang, L.; Ma, F.; Qian, B.; Ma, B.; Wang, L. Investigation into the influence of calcium compounds on the properties of micropore-foamed geopolymer. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniolo, N.; Rincon, A.; Roether, J.; Ercole, P.; Bernardo, E.; Boccaccini, A.; Toniolo, N.; Rincon, A.; Roether, J.; Ercole, P.; et al. Extensive reuse of soda-lime waste glass in fly ash-based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, B.O.; Kinuthia, J.M.; Oti, J.; Ebailila, M. Physico-Mechanical Evaluation of Geopolymer Concrete Activated by Sodium Hydroxide and Silica Fume-Synthesised Sodium Silicate Solution. Materials 2023, 16, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwaida, Z.; Dulaimi, A.; Mashaan, N.; Mydin, A.O. Geopolymers: The Green Alternative to Traditional Materials for Engineering Applications. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer technology: The current state of the art. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, V.F.; MacKenzie, K.J.; Thaumaturgo, C. Synthesis and characterisation of materials based on inorganic polymers of alumina and silica: Sodium polysialate polymers. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2000, 2, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanasiriwech, D.; Yomthong, K.; Wattanasiriwech, S. Characterisation and properties of class C-fly ash based geopolymer foams: Effects of foaming agent content, aggregates, and surfactant. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D. Preparation and characterization of ultra-lightweight foamed geopolymer (UFG) based on fly ash-metakaolin blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Pelisser, F.; Labrincha, J.; Novais, R. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Lightweight Geopolymer Mortar Panels. Minerals 2023, 13, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.Z.; Norzeity, A.; Johari, I.; Kasim, S.R. Effect of Adding Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) and Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate (SDS) to the Properties of Fly Ash (FA)-Based Geopolymer Mortar. Key Eng. Mater. 2022, 908, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Li, X.; Bai, C.; Li, H.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, T.; Colombo, P. Effects of surfactants/stabilizing agents on the microstructure and properties of porous geopolymers by direct foaming. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2021, 9, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Xue, J. Characterization and Performance Evaluation of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Foams Obtained by Adding Palm Olein as the Foam Stabilizer. Materials 2022, 15, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmero, P.; Formia, A.; Antonaci, P.; Brini, S.; Tulliani, J.-M. Geopolymer technology for application-oriented dense and lightened materials. Elaboration and characterization. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 12967–12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, R.; Gong, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, W.; Cheng, X. Development of porous fly ash-based geopolymer with low thermal conductivity. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petlitckaia, S.; Poulesquen, A. Design of lightweight metakaolin based geopolymer foamed with hydrogen peroxide. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Ascensão, G.; Buruberri, L.; Senff, L.; Labrincha, J. Influence of blowing agent on the fresh- and hardened-state properties of lightweight geopolymers. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Ren, X.; Wang, W.; He, C.; Xing, P. Preparation of eco-friendly porous ceramic with low thermal conductivity by high-temperature treatment of foamed solid waste based geopolymer with cenospheres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 398, 131190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamseu, E.; Ngouloure, Z.N.; Ali, B.N.; Zekeng, S.; Melo, U.; Rossignol, S.; Leonelli, C. Cumulative pore volume, pore size distribution and phases percolation in porous inorganic polymer composites: Relation microstructure and effective thermal conductivity. Energy Build. 2015, 88, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimohammadi, A.; Ngo, T.; Mendis, P.; Sanjayan, J. Regulating the chemical foaming reaction to control the porosity of geopolymer foams. Mater. Des. 2017, 120, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Dong, C.; Wei, X.; Su, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Z. Quantitative characterization and control mechanism of pore structure in geopolymer foams with addition of various surfactants. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 149, 105522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Tian, D.; Ma, M.; Wang, T. Optimized pore structure and high permeability of metakaolin/fly-ash-based geopolymer foams from Al– and H2O2–sodium oleate foaming systems. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18348–18360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).