Assessment of Damage Progression in Corner Buildings with Infill Walls During an Intraplate Earthquake in Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The 19 September 2017 Earthquake
3. Damage Statistics of Corner Buildings
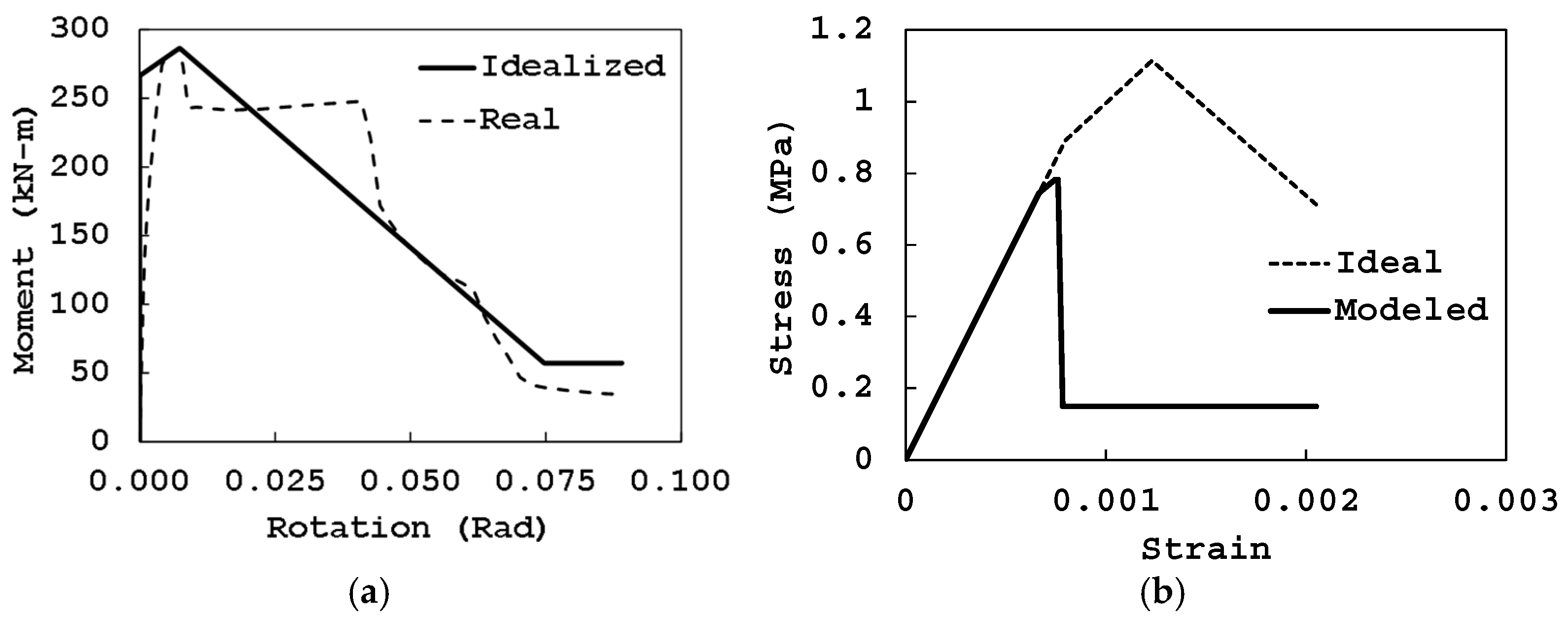
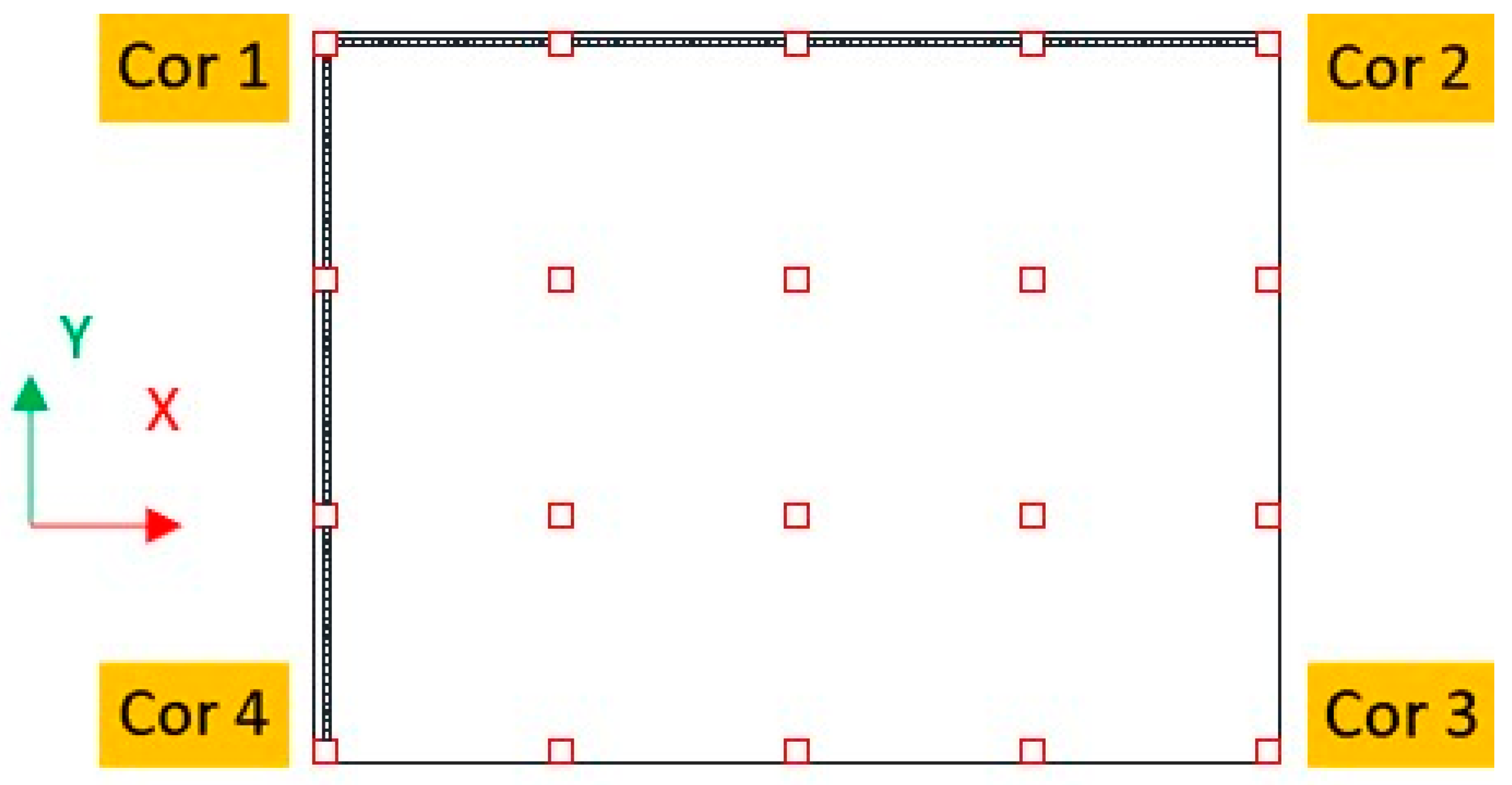
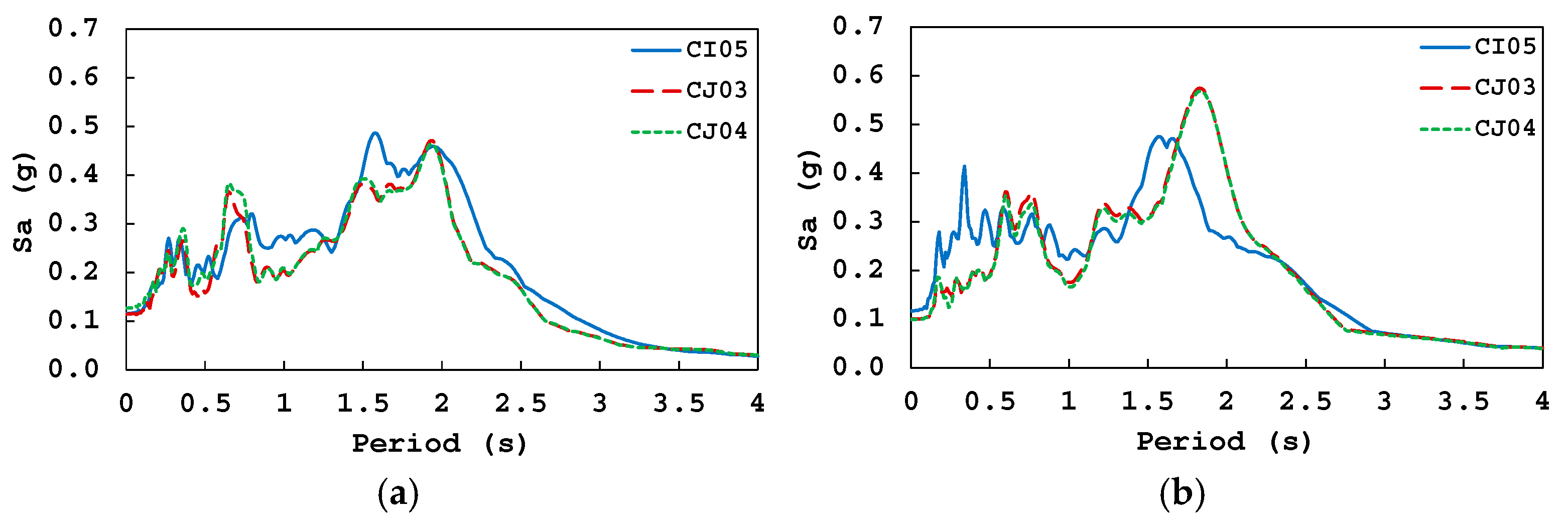
4. Numerical Models
5. Nonlinear Analysis
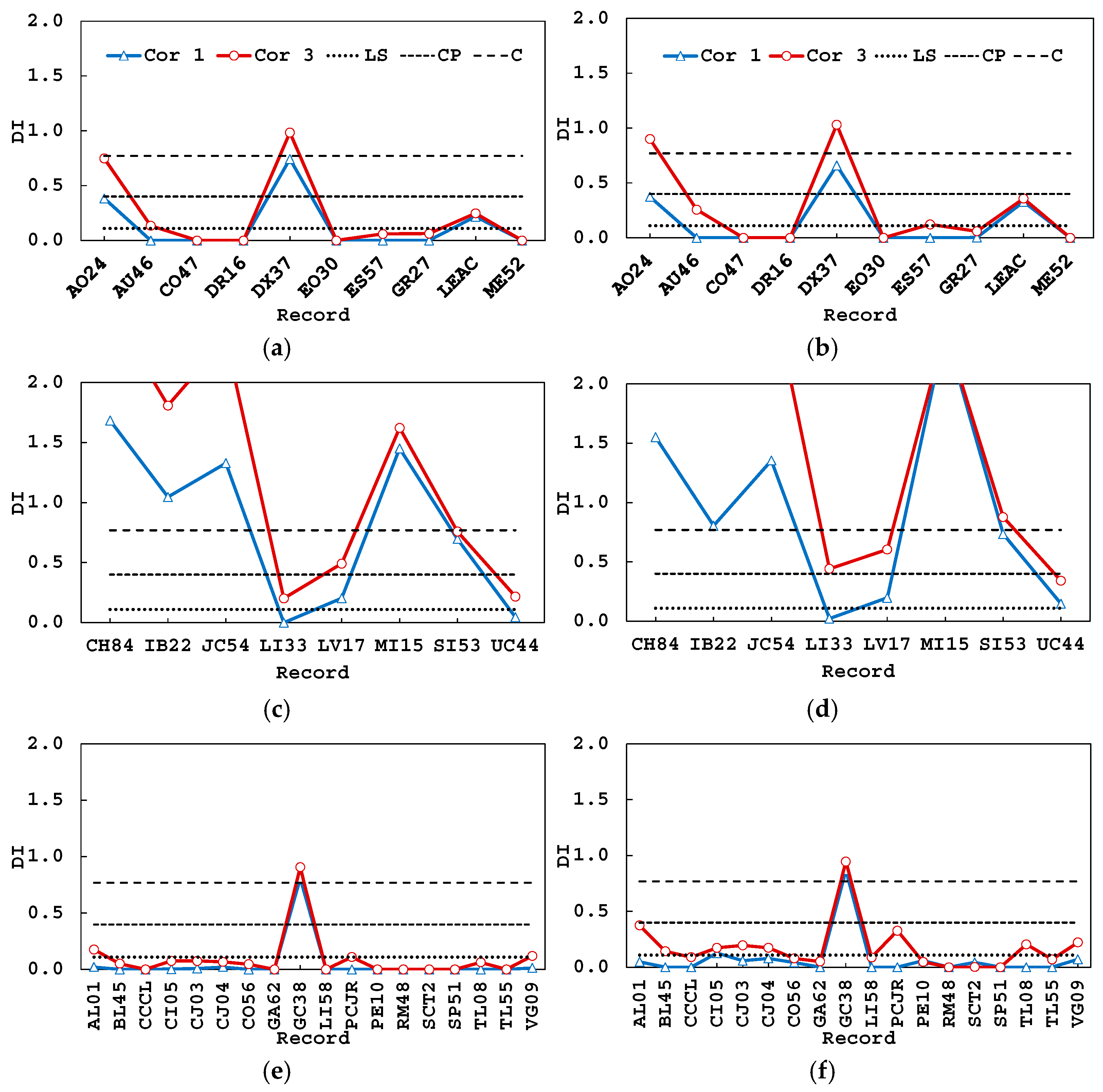
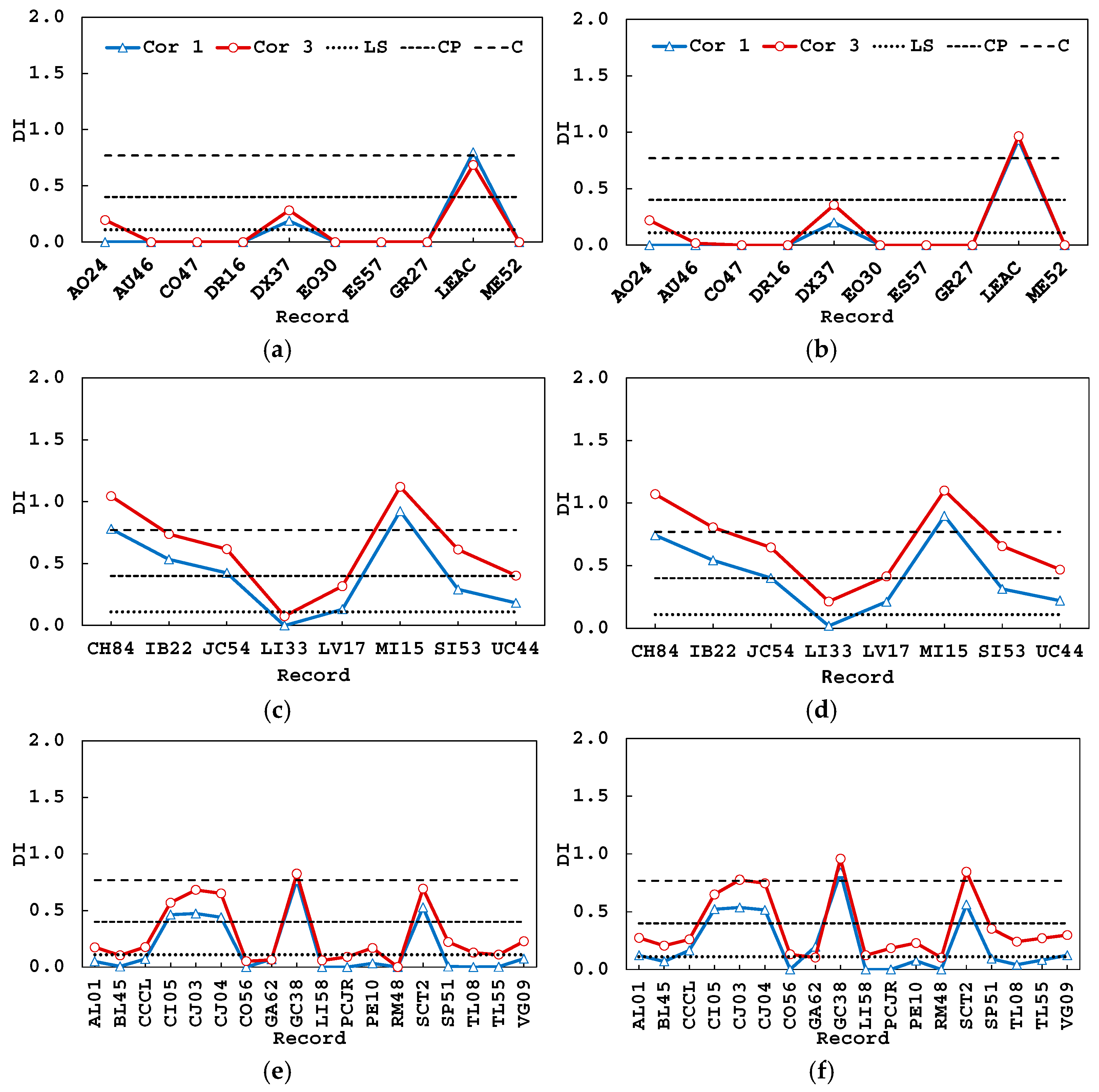
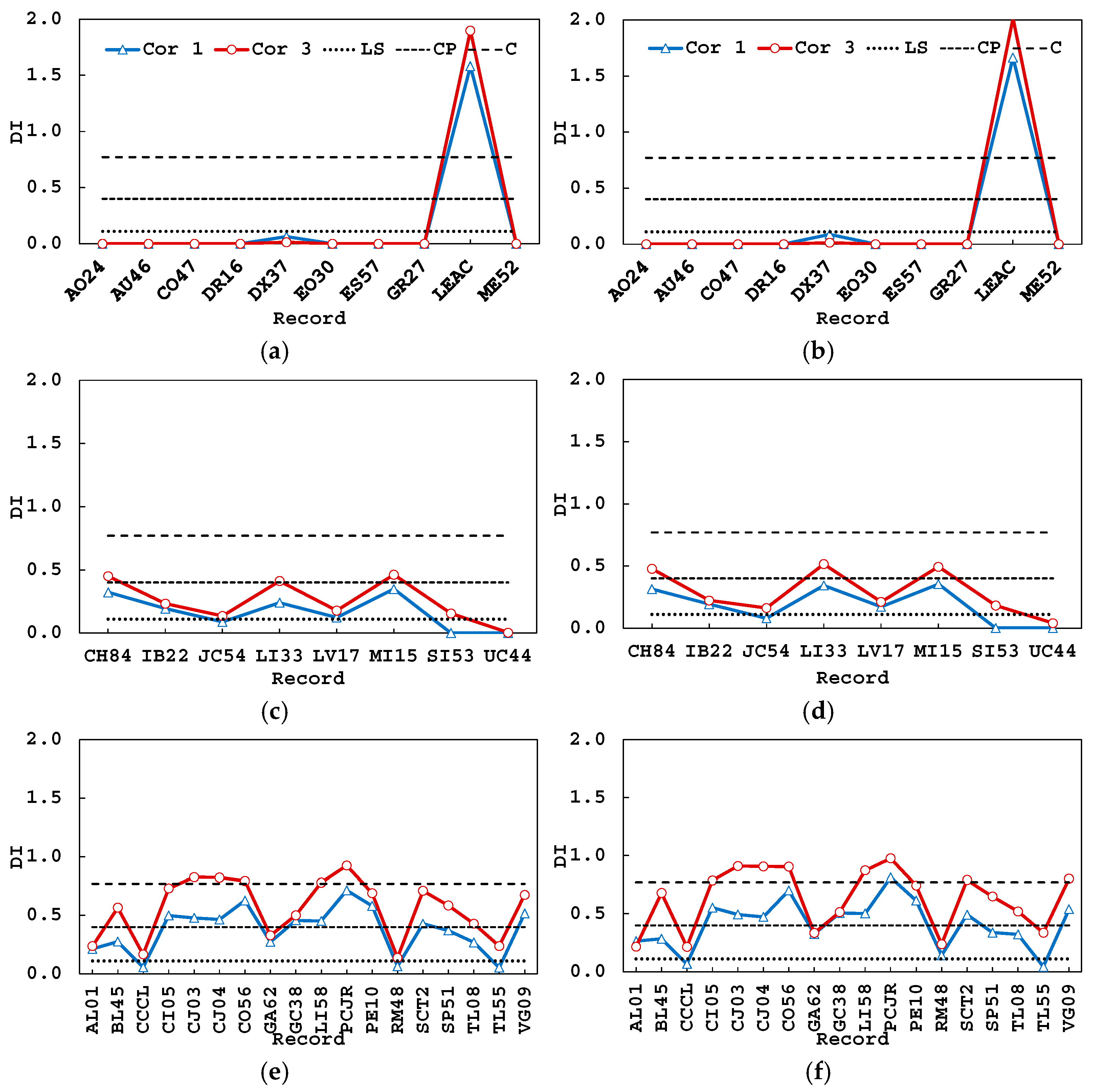
5.1. Damage Index
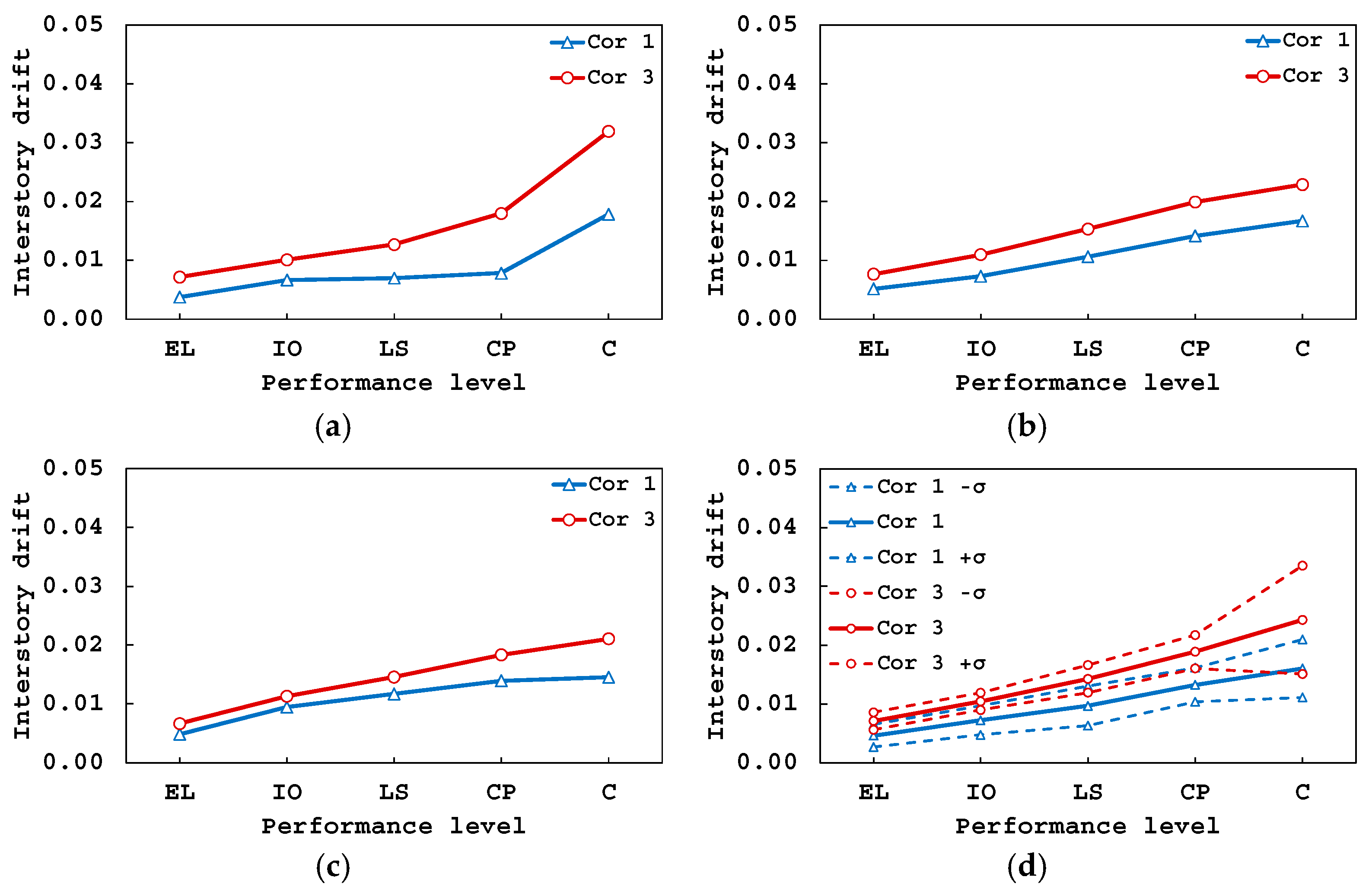
5.2. Inter-Story Drift Ratios and Performance Levels
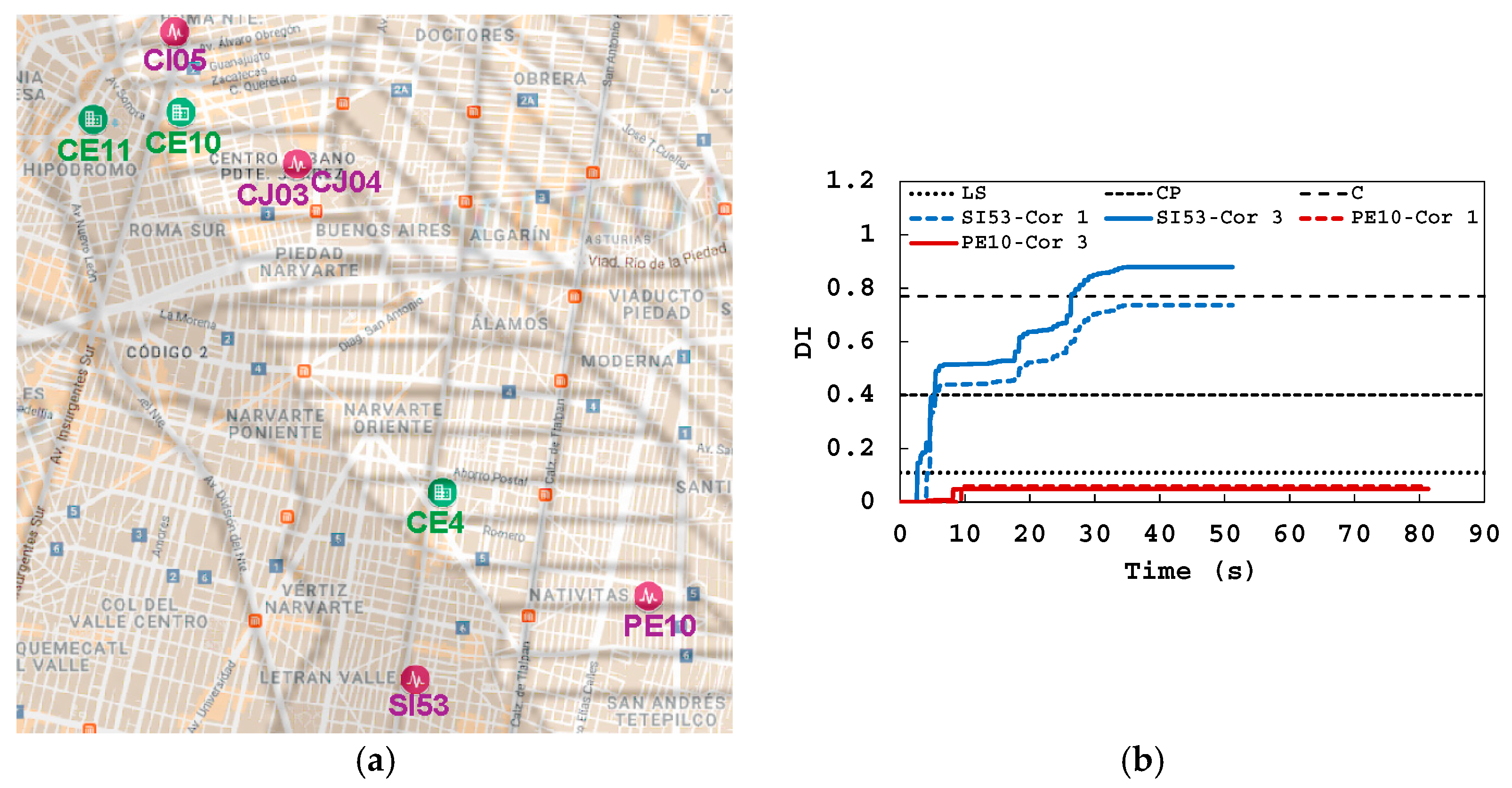
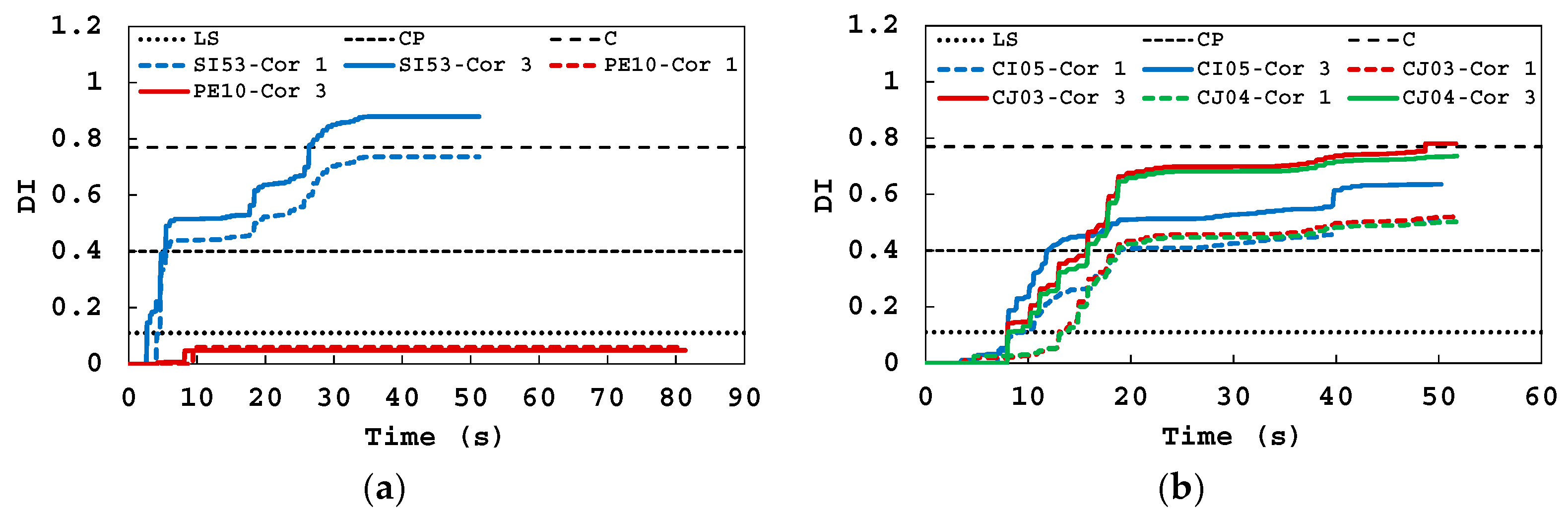
5.3. Damage Evolution
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Juárez, C. Otro Sismo el 19 de Septiembre. Ciencia UNAM. Available online: https://ciencia.unam.mx/leer/649/otro-sismo-el-19-de-septiembre- (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- NTC DF. Normas Técnicas Complementarias para Diseño por Sismo; Gaceta Oficial del Distrito Federal: Ciudad de México, México, 2004.
- Nikolaou, S.; Gazetas, G.; Garini, E.; Diaz-Fanas, G.; Ktenidou, O. Geoseismic Design Challenges in Mexico City, Part 1: A 32-year déjà vu. Structure Magazine, 14 December 2018; 10–13. Available online: https://www.structuremag.org/article/geoseismic-design-challenges-in-mexico-city/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Jara, J.M.; Hernández, E.J.; Olmos, B.A.; Martínez, G. Building damages during the 19 September 2017 earthquake in Mexico City and seismic retrofitting of existing first soft-story buildings. Eng. Struct. 2020, 209, 109977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gavilán, J.J.; Aguirre, J.; Ramírez, L. Sismicidad y seguridad estructural en las construcciones: Lecciones aprendidas en México. Salud Publica Mex. 2018, 60, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostopoulos, S.A.; Kyrkos, M.T.; Stathopoulos, K.G. Earthquake induced torsion in buildings: Critical review and state of the art. Earthq. Struct. 2015, 8, 305–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, W.K.; Dempsey, K.M. Seismic torsional provisions for dynamic eccentricity. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1980, 8, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.K.; Chopra, A.K. Inelastic seismic response of one-storey, asymmetric-plan systems: Effects of stiffness and strength distribution. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1990, 19, 949–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, A.M.; Duan, X.N. Performance of asymmetric code-designed buildings for serviceability and ultimate limit states. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1997, 26, 717–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, M.; Pintucchi, B. A review of research on seismic behaviour of irregular building structures since 2002. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2008, 6, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Dutta, S.C.; Datta, T.K. Seismic behavior of plan and vertically irregular structures: State of art and future challenges. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2021, 22, 04020062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroborty, S.; Roy, R. Role of ground motion characteristics on inelastic seismic response of irregular structures. J. Archit. Eng. 2016, 22, B4015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Colina, J.; Valdés-González, J. New proposal to incorporate seismic accidental torsion in the design. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, V.; Reinoso, E. Revisión a 50 años de los daños ocasionados en la Ciudad de México por el sismo del 28 de julio de 1957 con ayuda de investigaciones recientes y sistemas de información geográfica. Rev. De Ing. Sísmica 2007, 76, 61–87. [Google Scholar]
- Fundación ICA, A.C. El sismo del 19 de Septiembre de 1985. In Experiencias Derivadas de los Sismos de Septiembre de 1985, 1st ed.; Limusa: Ciudad de México, México, 1988; pp. 67–123. [Google Scholar]
- Dilsiz, A.; Gunay, S.; Mosalam, K.; Miranda, E.; Arteta, C.A.; Sezen, H.; Fischer, E.; Hakhamaneshi, M.; Hassan, W.M.; Alhawamdeh, B.; et al. Joint Preliminary Virtual Reconnaissance Report (PVRR); Report PRJ-3824; Earthquake Engineering Research Institute (EERI): Oakland, CA, USA, 2023; pp. 1–145. Available online: https://www.research-collection.ethz.ch/handle/20.500.11850/645478 (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Al-ahmar, R.; Al Kousa, M.A.; Wardeh, G. Some of recommendations and learned lessons from buildings’ performance during the recent Turkey-Syria earthquake. J. Univ. Duhok 2023, 26, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, S.; Vukobratović, V. The influence of torsion on acceleration demands in low-rise RC buildings. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 22, 2433–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Silva, A. Colapso por Torsión en Edificios en Esquina Durante el Temblor del 19 de Septiembre de 2017. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo, Morelia, Michoacán, México, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, F.; Astroza, R.; Ochoa, F.; Pasten, C. Razones Estructurales del Colapso de Edificios debido al Terremoto de Puebla-Morelos (Mw 7.1). In Proceedings of the XII Congreso Chileno de Sismología e Ingeniería Sísmica ACHISINA, Valdivia, Chile, 3 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jara, J.M.; Hernández, E.J.; Olmos, B.A.; Martínez, G.; Roa, M.I. Seismic Vulnerability and Retrofit Alternatives for Typical Soft-story Buildings in Earthquake Prone Areas. Struct. Eng. Int. 2020, 30, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvis, F.; Miranda, E.; Heresi, P.; Dávalos, H.; Ruiz, J. Overview of collapsed buildings in Mexico City after the 19 September 2017 (Mw7.1) earthquake. Earthq. Spectra 2020, 36, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redacción. En Imágenes: Todas las Zonas Colapsadas de la CDMX y su Impacto Económico. El Financiero. Available online: http://www.elfinanciero.com.mx/nacional/19s-asi-fue-el-impacto-economico-en-zonas-colapsadas-de-la-cdmx (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- Google (n.d.). Images of Google Earth. Available online: https://maps.app.goo.gl/N65EgZ3Nqke2G7NQ7 (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- NTC DF-Concreto. Normas Técnicas Complementarias para Elementos de Concreto; Departamento del Distrito Federal: Ciudad de México, México, 1977.
- Reinoso, E.; Quinde, P.; Buendía, L.; Ramos, S. Intensity and damage statistics of the September 19, 2017 Mexico earthquake: Influence of soft story and corner asymmetry on the damage reported during the earthquake. Earthq. Spectra 2021, 37, 1875–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena-Colunga, A.; Abrams, D.P. Seismic behavior of structures with flexible diaphragms. ASCE J. Struct. Eng. 1996, 122, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena-Colunga, A.; Chinchilla, K.L.; Juárez, G. Evaluación de la flexibilidad elástica de sistemas de piso utilizados en edificios urbanos. Rev. De Ing. Sísmica 2013, 89, 135–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ju, S.H.; Lin, M.C. Comparison of building analyses assuming rigid or flexible floors. J. Struct. Eng. 1999, 125, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecce, M.; Ceroni, F.; Maddaloni, G.; Iannuzzella, V. Assessment of the in-plane deformability of RC floors with traditional and innovative lightening elements in RC framed and wall structures. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 15, 3125–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTC DF-Sismo. Normas Técnicas Complementarias para Diseño por Sismo; Departamento del Distrito Federal: Ciudad de México, México, 1977.
- CSI SAP2000; CSI Analysis Reference Manual. Computers and Structures Inc.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2017.
- CSI PERFORM 3D; Nonlinear Analysis and Performance Assessment for 3D Structures. Computers and Structures Inc.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015.
- Arias, A. A Measure of Earthquake Intensity. In Seismic Design of Nuclear Power Plants; Hansen, R.J., Ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Priestley, M.J.N. Performance based seismic design. Bull. N. Z. Soc. Earthq. Eng. 2000, 33, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mander, J.B.; Priestley, M.J.; Park, R. Theoretical stress–strain model for confined concrete. J. Struct. Div. ASCE 1988, 144, 1804–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.; Paulay, T. Reinforced Concrete Structures, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Comité de Mampostería. Guide for the Analysis of Masonry Structures, 1st ed.; Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia (CONACYT) & Fondo Sectorial de la Comisión Nacional para el Fomento de la Vivienda (CONAFOVI): Ciudad de México, México, 2012.
- Deierlein, G.G.; Reinhorn, A.M.; Willford, M.R. Nonlinear Structural Analysis for Seismic Design; National Earthquake Hazards Reduction Program, NIST GCR 10-915-5; Applied Technology Council: Redwood City, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Structural Engineering Institute. ASCE Standard 41-17 Seismic Evaluation and Retrofit of Existing Buildings; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jara, J.M.; Florio, E.; Olmos, B.A. Seismic evaluation and reliability index of soft story buildings on flexible soils by using old and current seismic regulations in Mexico. Eng. Struct. 2023, 286, 116048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTCM-20; Normas Técnicas Complementarias para Diseño y Construcción de Estructuras de Mampostería. Gaceta Oficial de la Ciudad de México: Ciudad de México, México, 2020.
- Park, Y.J.; Ang, A.H.S.; Wen, Y.K. Seismic damage analysis of reinforced concrete buildings. J. Struct. Eng. 1985, 111, 722–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalateh-Ahani, M.; Amiri, S.A. Park-Ang damage index-based framework for post-mainshock structural safety assessment. Structures 2021, 33, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, R. Seismic fragility analysis of reinforced concrete continuous span bridges with irregular configuration. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2012, 8, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
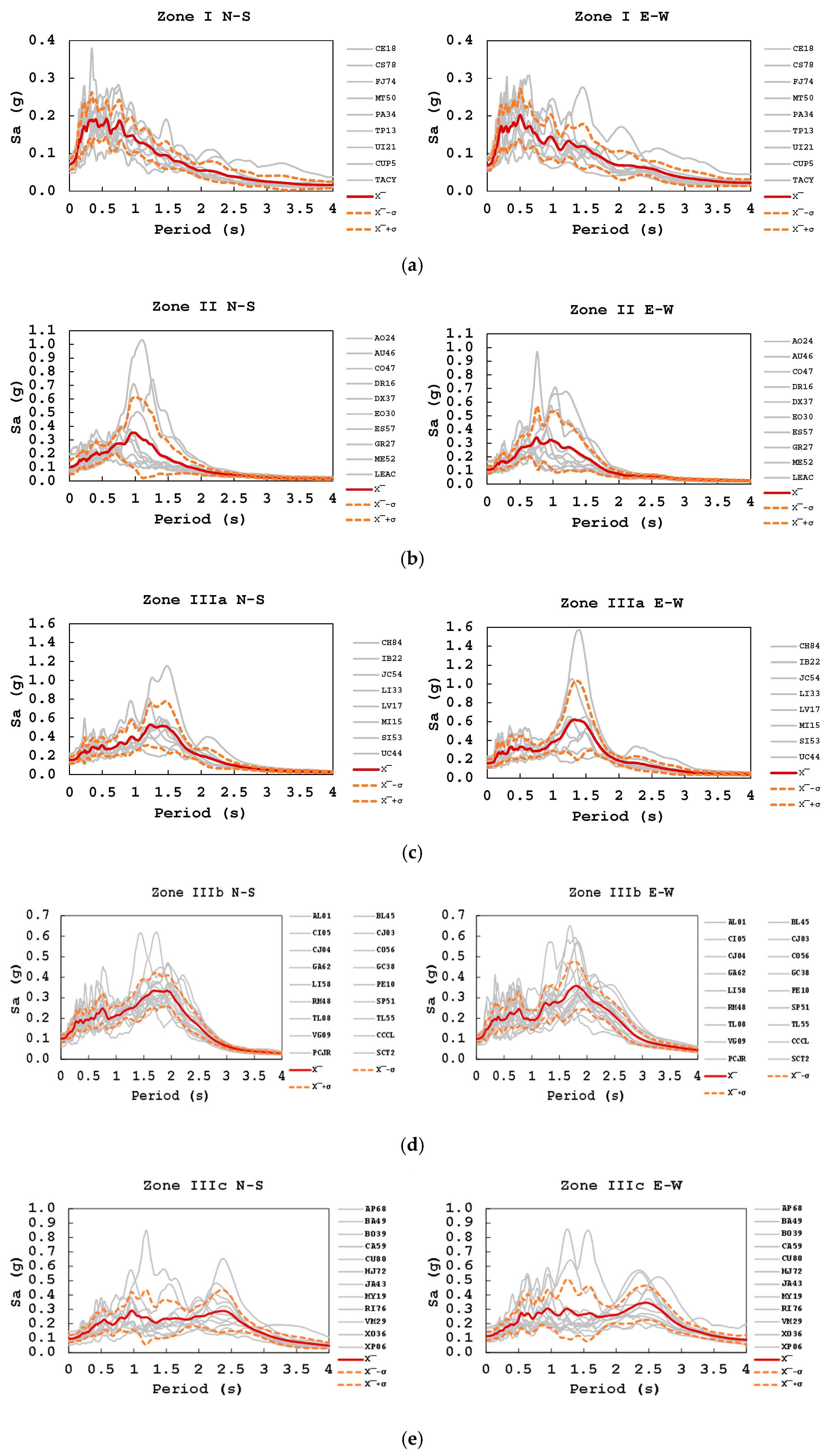



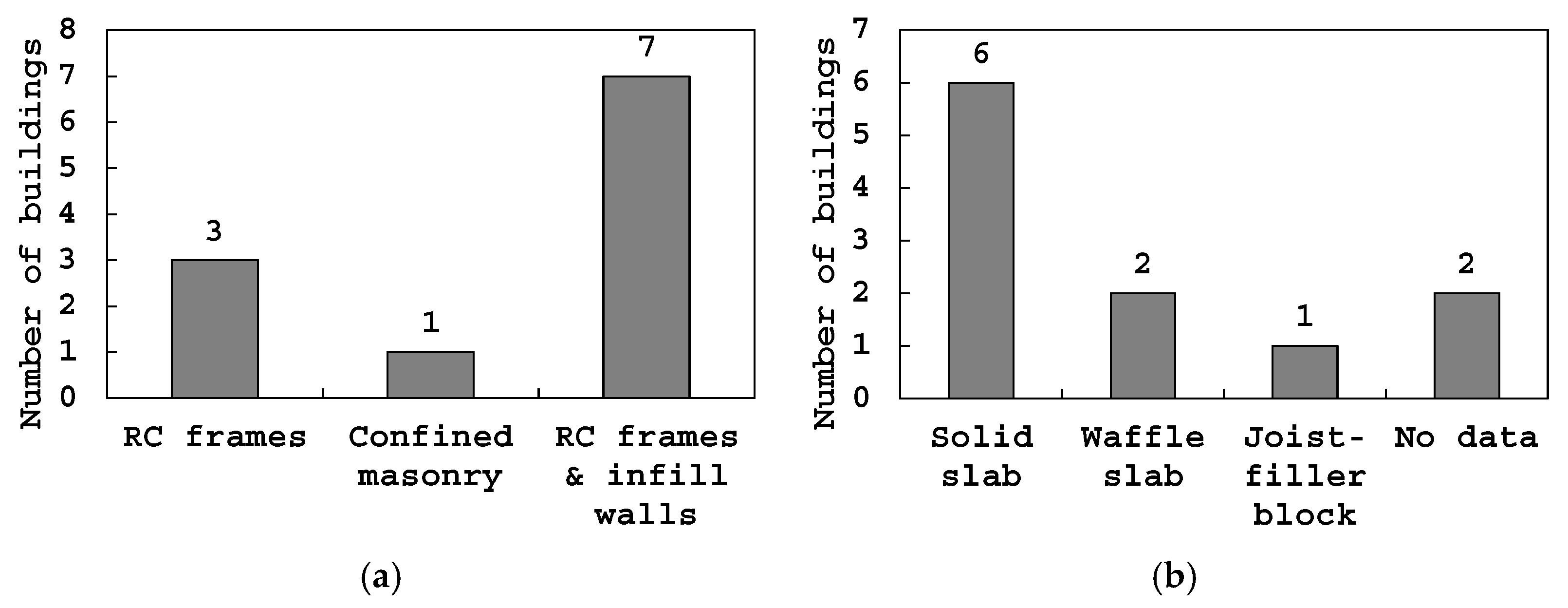
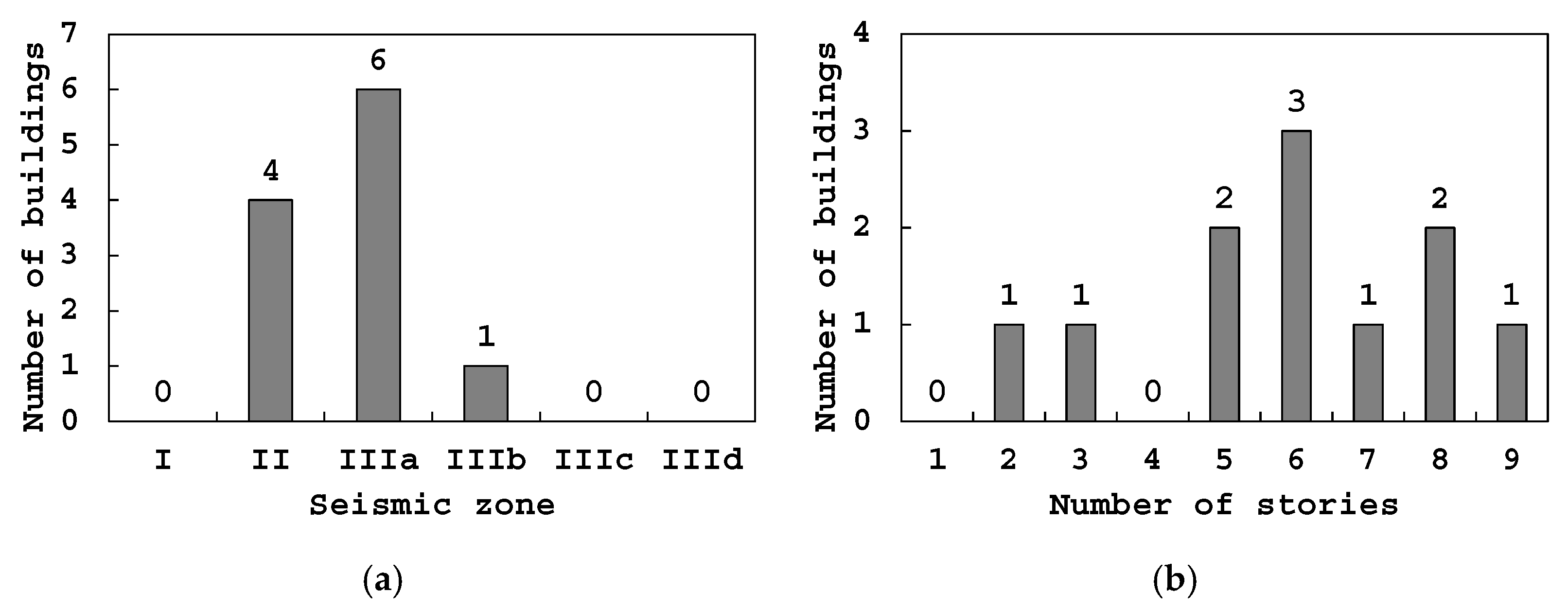
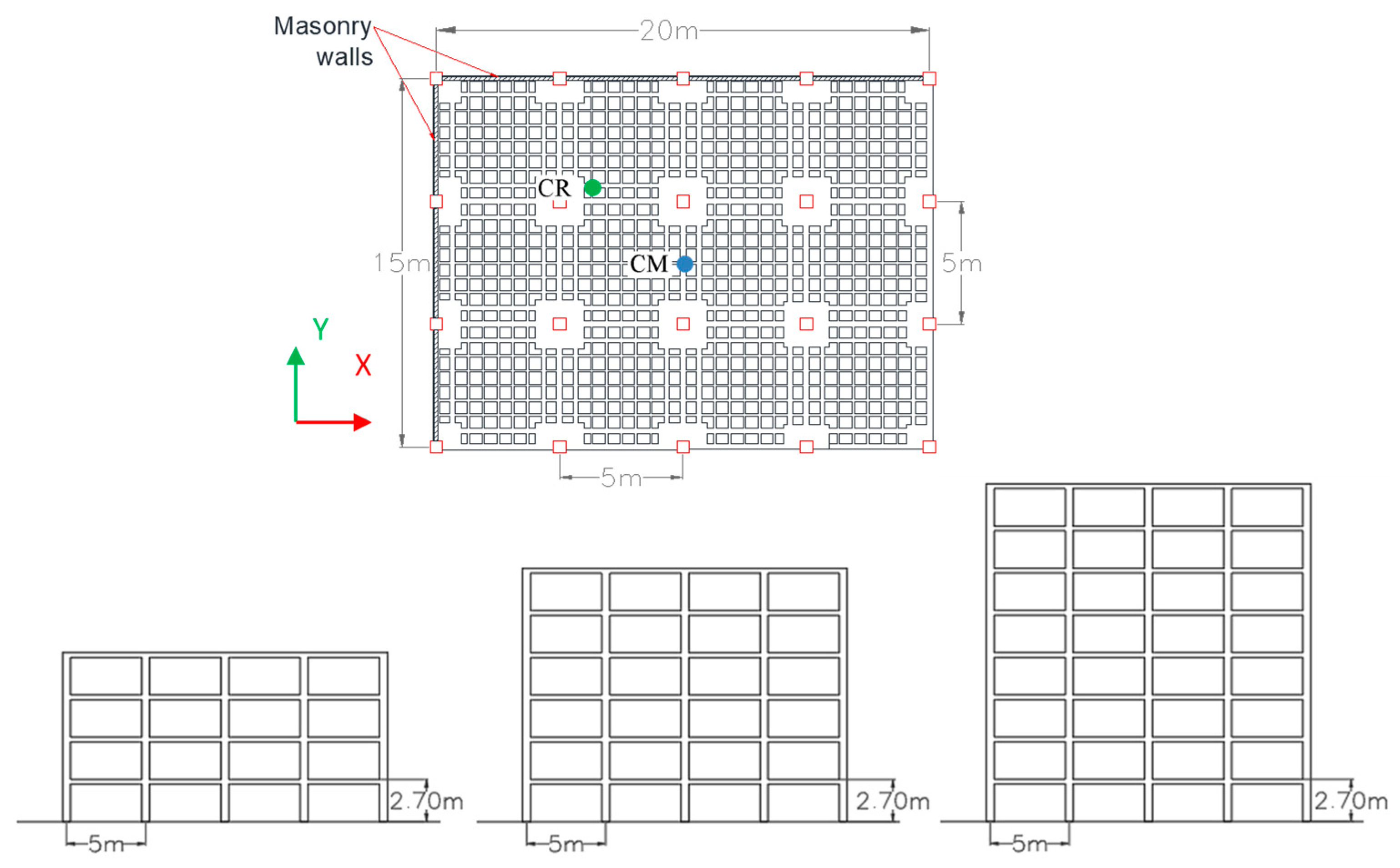
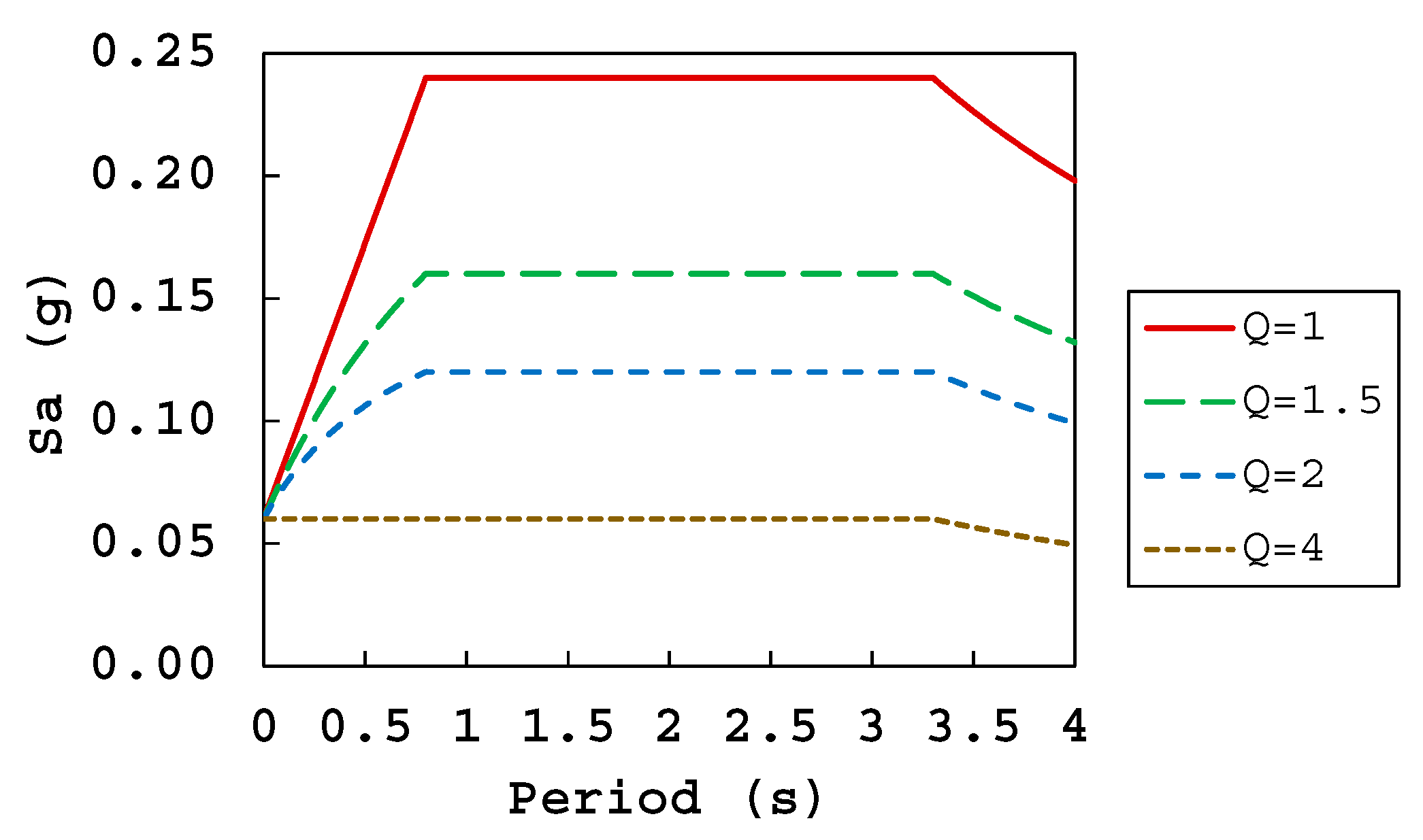

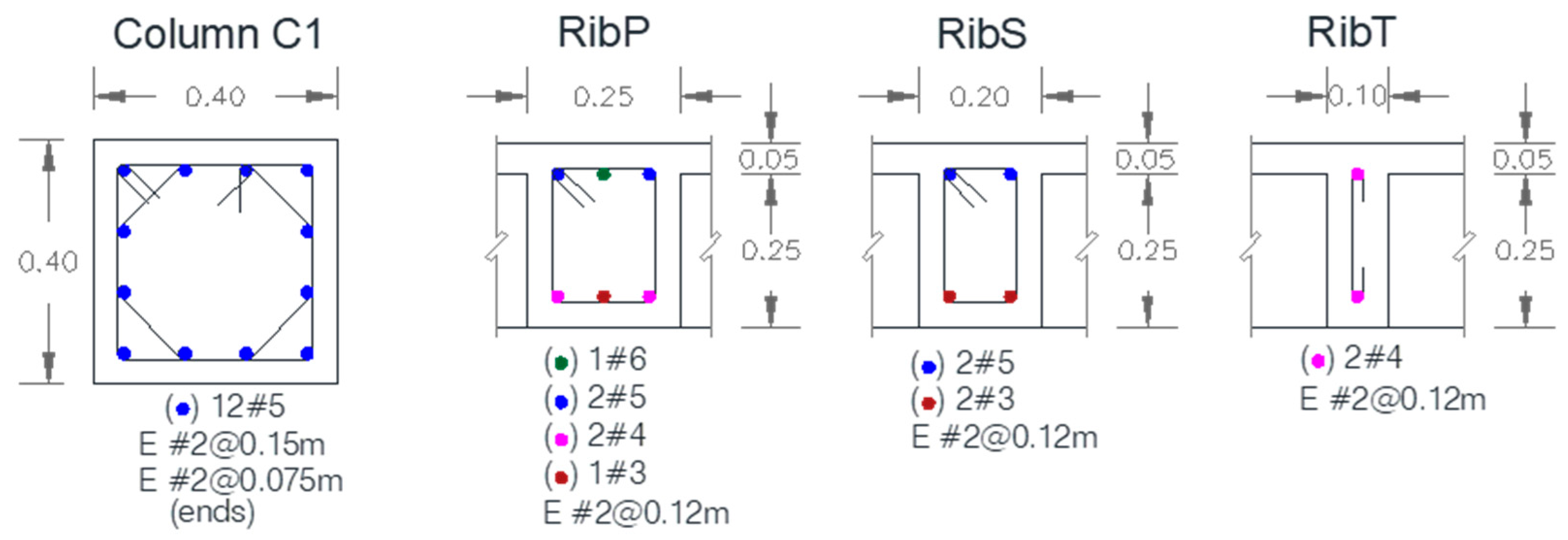
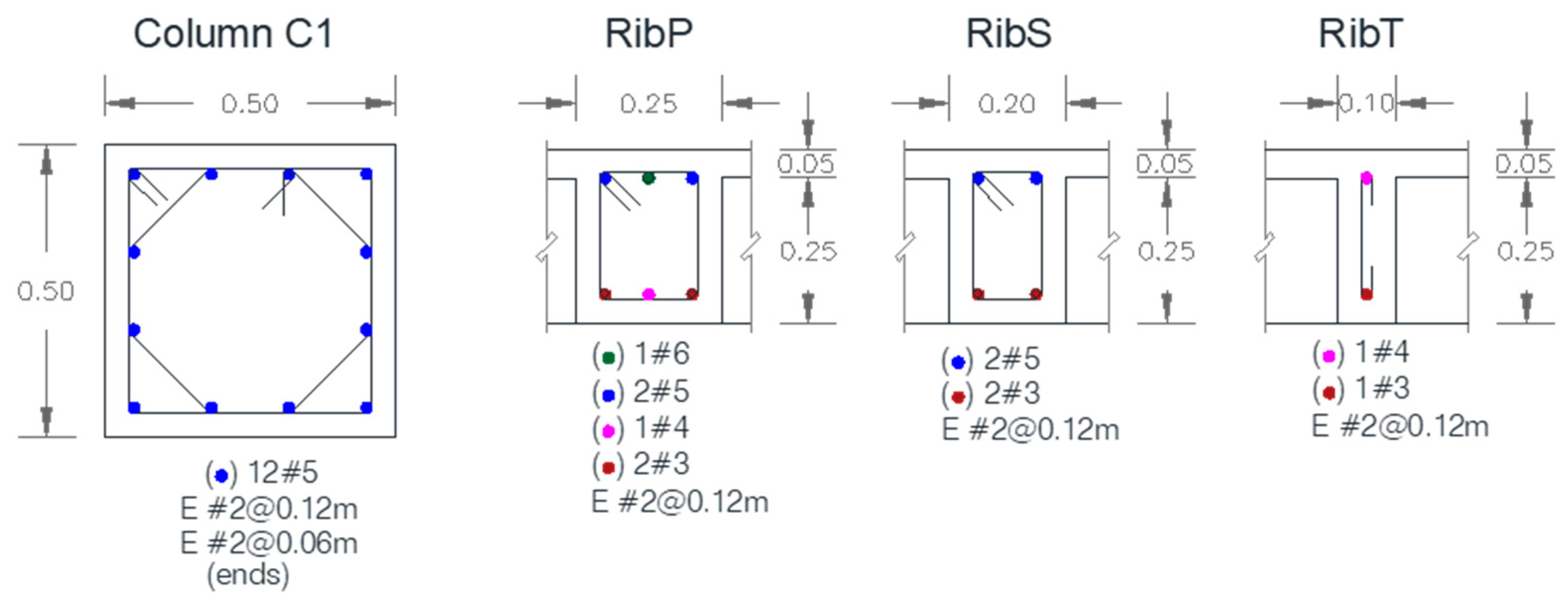
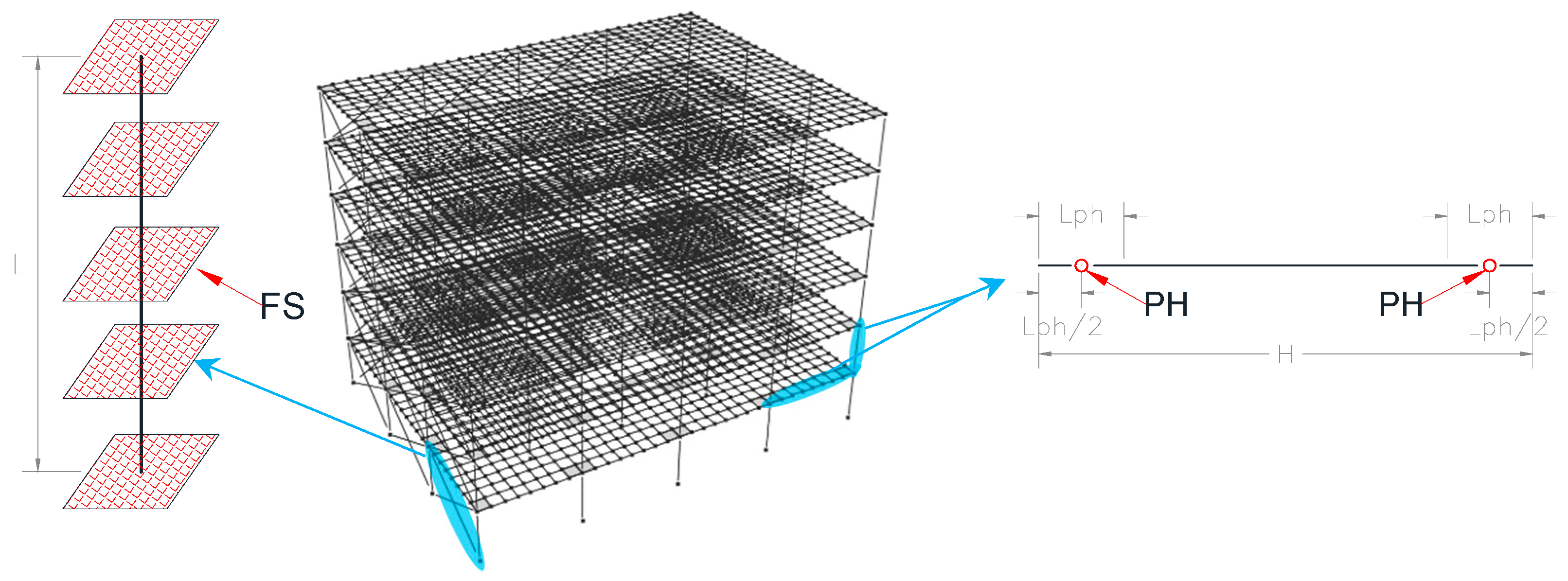

| Building Id | Address | Number of Stories | Seismic Zone |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE1 | 4 Edimburgo & Escocia, Colonia del Valle. | 8 | II |
| CE2 | 4 Escocia & Gabriel Mancera, colonia del Valle Centro. | 5 | II |
| CE3 | 1503 Concepción Beistegui, colonia Narvarte Poniente | 5 | II |
| CE4 | 173 Niños Héroes & Galicia, colonia Niños Héroes | 6 | IIIb |
| CE5 | 56 Emiliano Zapata, Colonia Portales | 7 | IIIa |
| CE6 | 915 Prolongación Petén, colonia emperadores | 6 | IIIa |
| CE7 | 106 Viaducto Presidente Miguel Alemán & Torreón, colonia Piedad Narvarte. | 2 | IIIa |
| CE8 | 480 Calzada del Hueso & Canal de Miramontes Ave., colonia Los Girasoles | 3 | IIIa |
| CE9 | México & Lázaro Cárdenas, colonia San Gregorio Atlapulco | 6 | II |
| CE10 | 176 Medellín & San Luis Potosí, colonia Roma Norte | 8 | IIIa |
| CE11 | 107 Ámsterdam & Laredo, colonia Hipódromo | 8 | IIIa |
| Building Model | Mode 1 | Mode 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period (s) | PF UX | PF UY | PF RZ | Period (s) | PF UX | PF UY | PF RZ | |
| N4 | 1.09 | 21.92% | 40.21% | 22.38% | 0.54 | 50.95% | 35.39% | 0.79% |
| N6 | 1.42 | 20.94% | 38.78% | 21.94% | 0.77 | 48.87% | 34.13% | 0.83% |
| N8 | 1.77 | 20.16% | 37.73% | 21.37% | 1.02 | 47.57% | 33.18% | 0.88% |
| Mode 3 | Mode 4 | |||||||
| N4 | 0.34 | 1.41% | 3.33% | 65.67% | 0.31 | 15.39% | 12.43% | 1.06% |
| N6 | 0.45 | 9.35% | 5.59% | 62.10% | 0.44 | 7.39% | 9.71% | 1.99% |
| N8 | 0.61 | 13.22% | 9.26% | 60.27% | 0.55 | 3.37% | 5.80% | 2.37% |
| Performance Level | Drift Ratio |
|---|---|
| Elastic (EL) | Δ < 0.0100 |
| Immediate operation (IO) | 0.0100 ≤ Δ < 0.0140 |
| Life safety (LS) | 0.0140 ≤ Δ < 0.0190 |
| Collapse prevention (CP) | 0.0190 ≤ Δ < 0.0240 |
| Collapse (C) | 0.0240 ≤ Δ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez, A.; Jara, J.M.; López, J.I.; Olmos, B.A.; Varum, H.; Lampropoulos, A. Assessment of Damage Progression in Corner Buildings with Infill Walls During an Intraplate Earthquake in Mexico. Buildings 2025, 15, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15050745
Martínez A, Jara JM, López JI, Olmos BA, Varum H, Lampropoulos A. Assessment of Damage Progression in Corner Buildings with Infill Walls During an Intraplate Earthquake in Mexico. Buildings. 2025; 15(5):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15050745
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez, Abel, José M. Jara, Juan I. López, Bertha A. Olmos, Humberto Varum, and Andreas Lampropoulos. 2025. "Assessment of Damage Progression in Corner Buildings with Infill Walls During an Intraplate Earthquake in Mexico" Buildings 15, no. 5: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15050745
APA StyleMartínez, A., Jara, J. M., López, J. I., Olmos, B. A., Varum, H., & Lampropoulos, A. (2025). Assessment of Damage Progression in Corner Buildings with Infill Walls During an Intraplate Earthquake in Mexico. Buildings, 15(5), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15050745










