Exploring Factors Influencing Speech Intelligibility in Airport Terminal Pier-Style Departure Lounges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
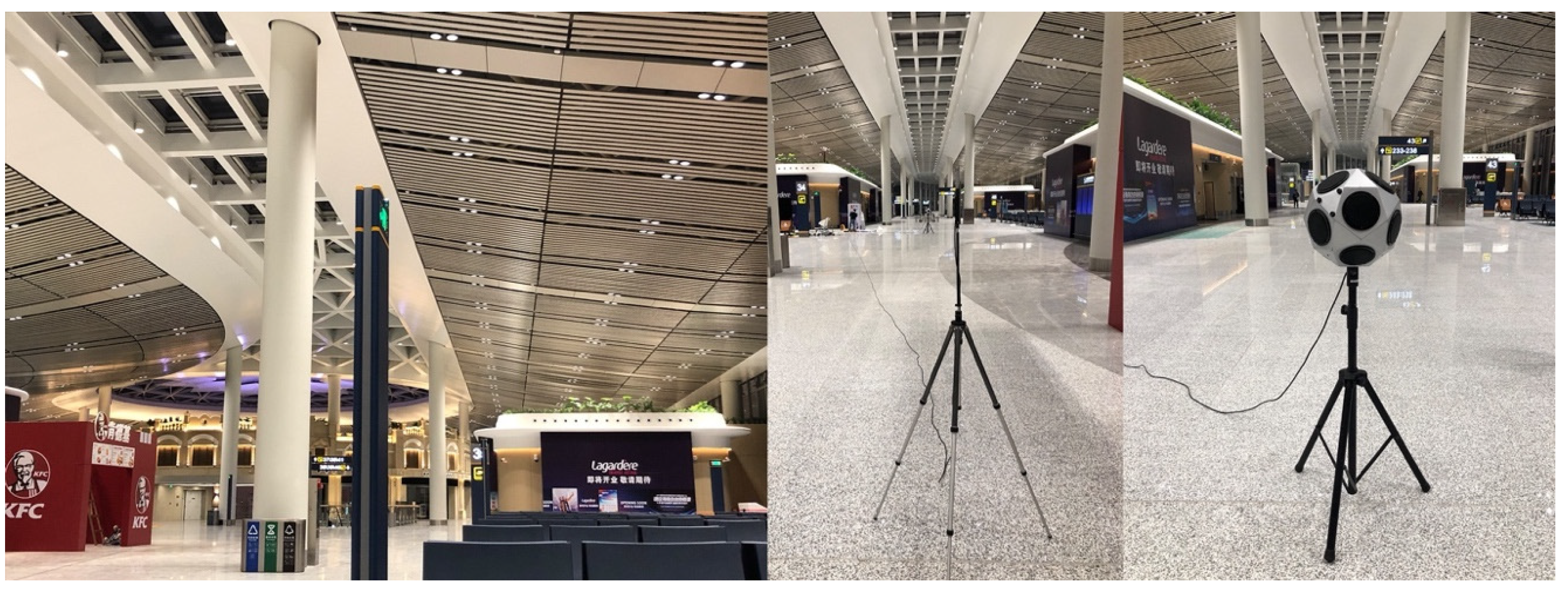
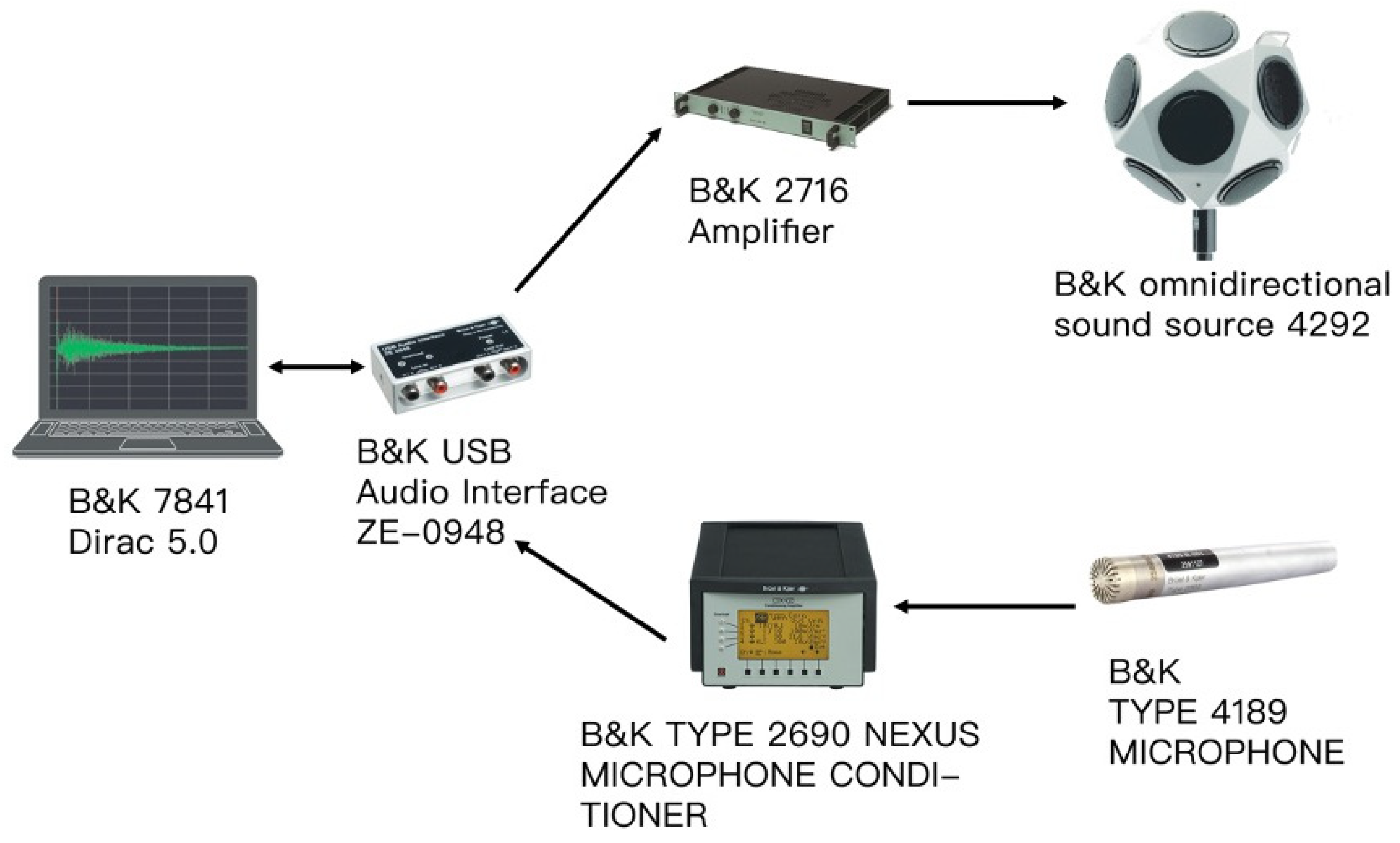
2.1. Field Impulse Response Measurements
2.2. Virtual Room Modelling
2.3. Multi-Source Simulation
2.4. Speech Intelligibility Test
2.4.1. Speech Materials
2.4.2. Subjects
3. Results
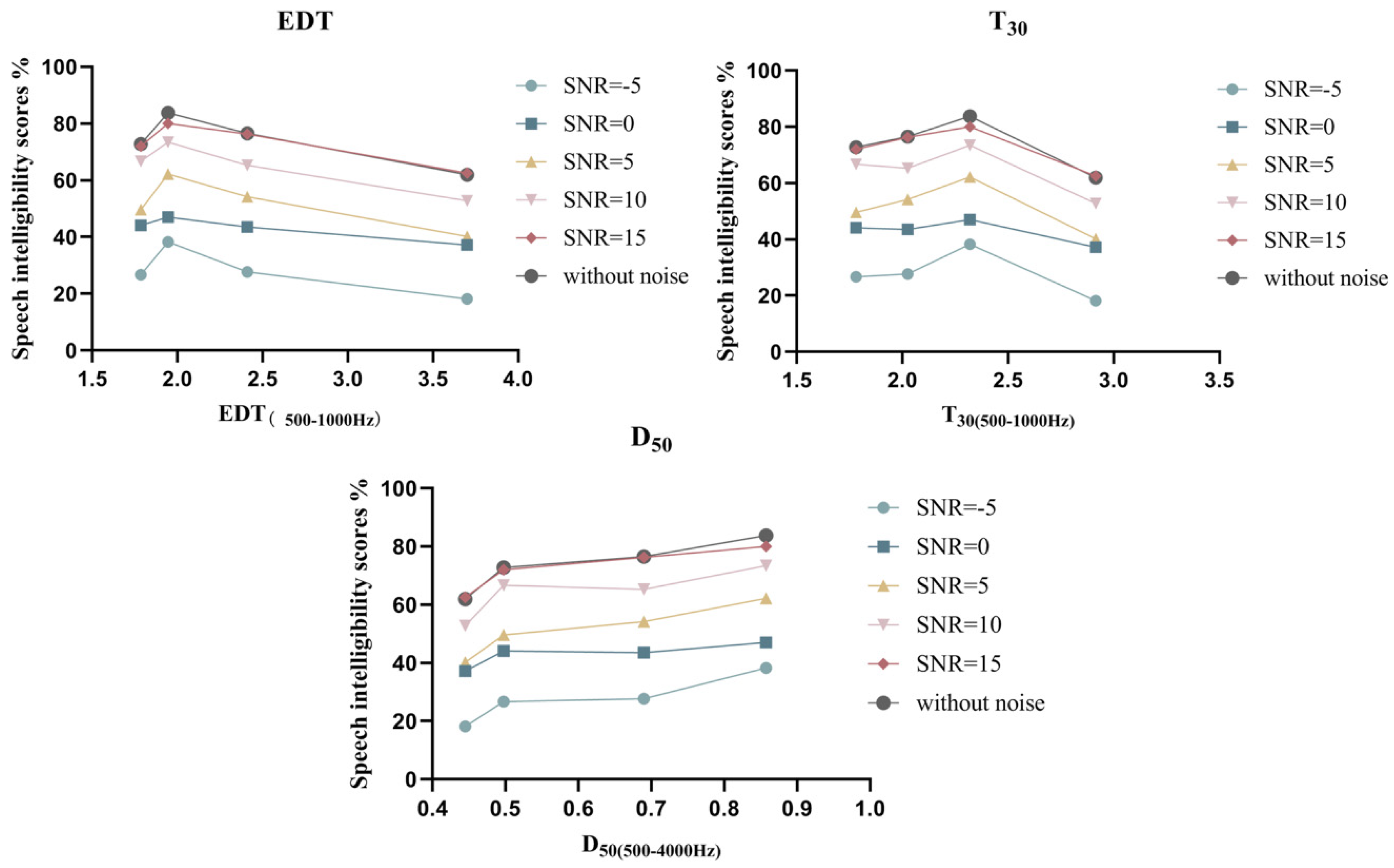
3.1. Effect of the SNR
3.2. Effect of the Room Acoustic Parameters
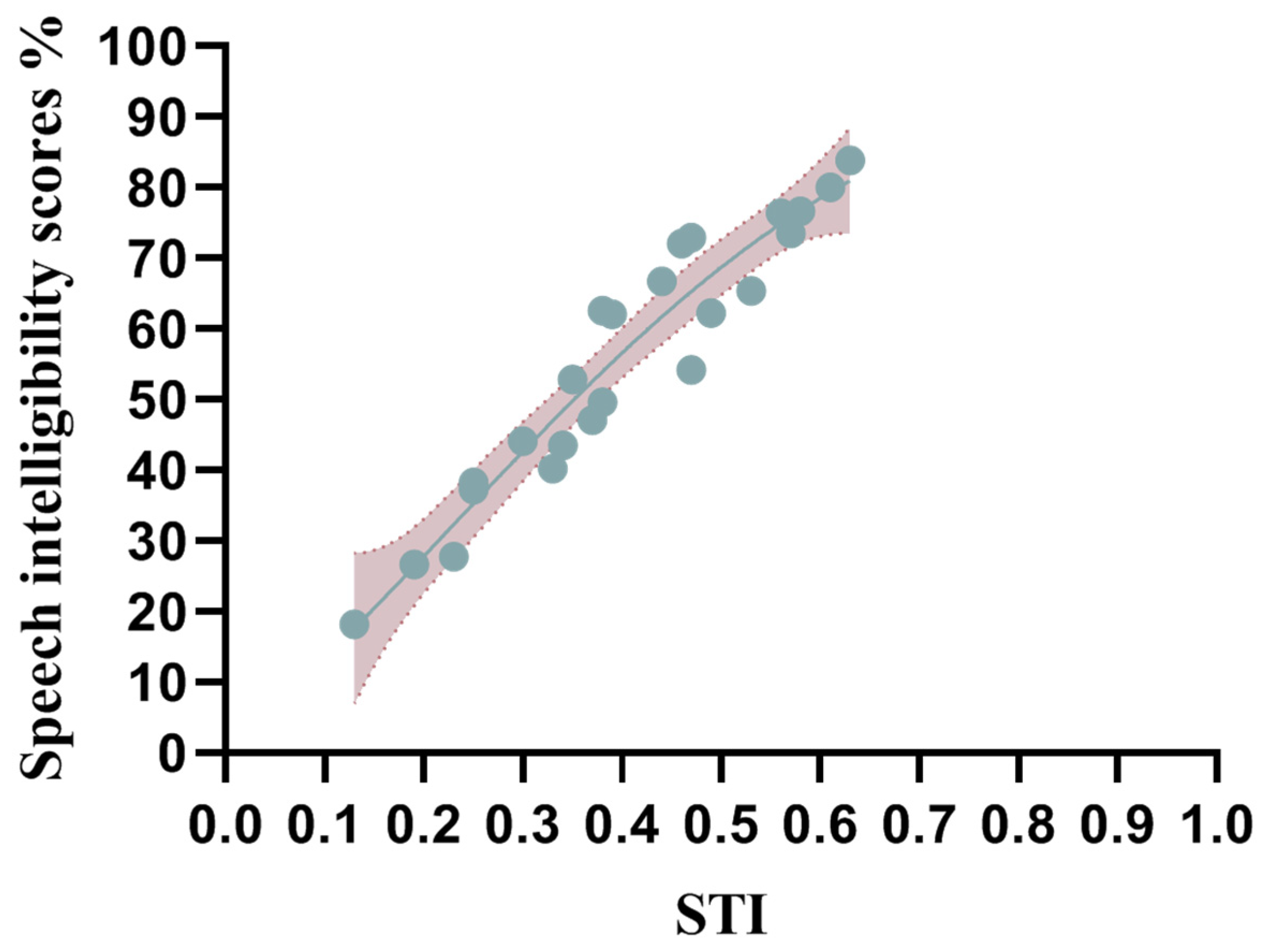
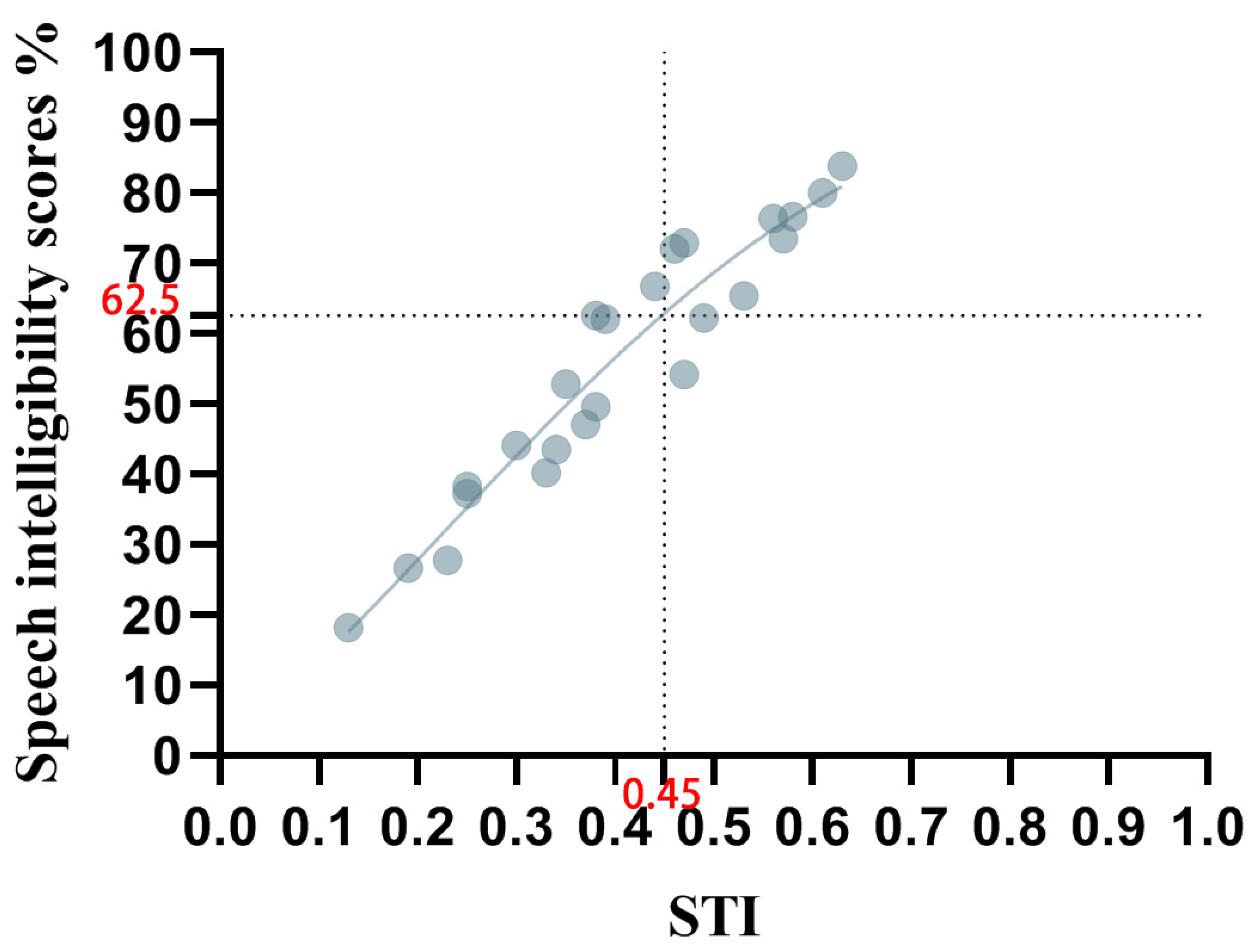
3.3. Relationship Between STI and Speech Intelligibility Score
4. Discussion
4.1. SNR for Public Announcements
4.2. Discussion on Required Speech Intelligibility Scores
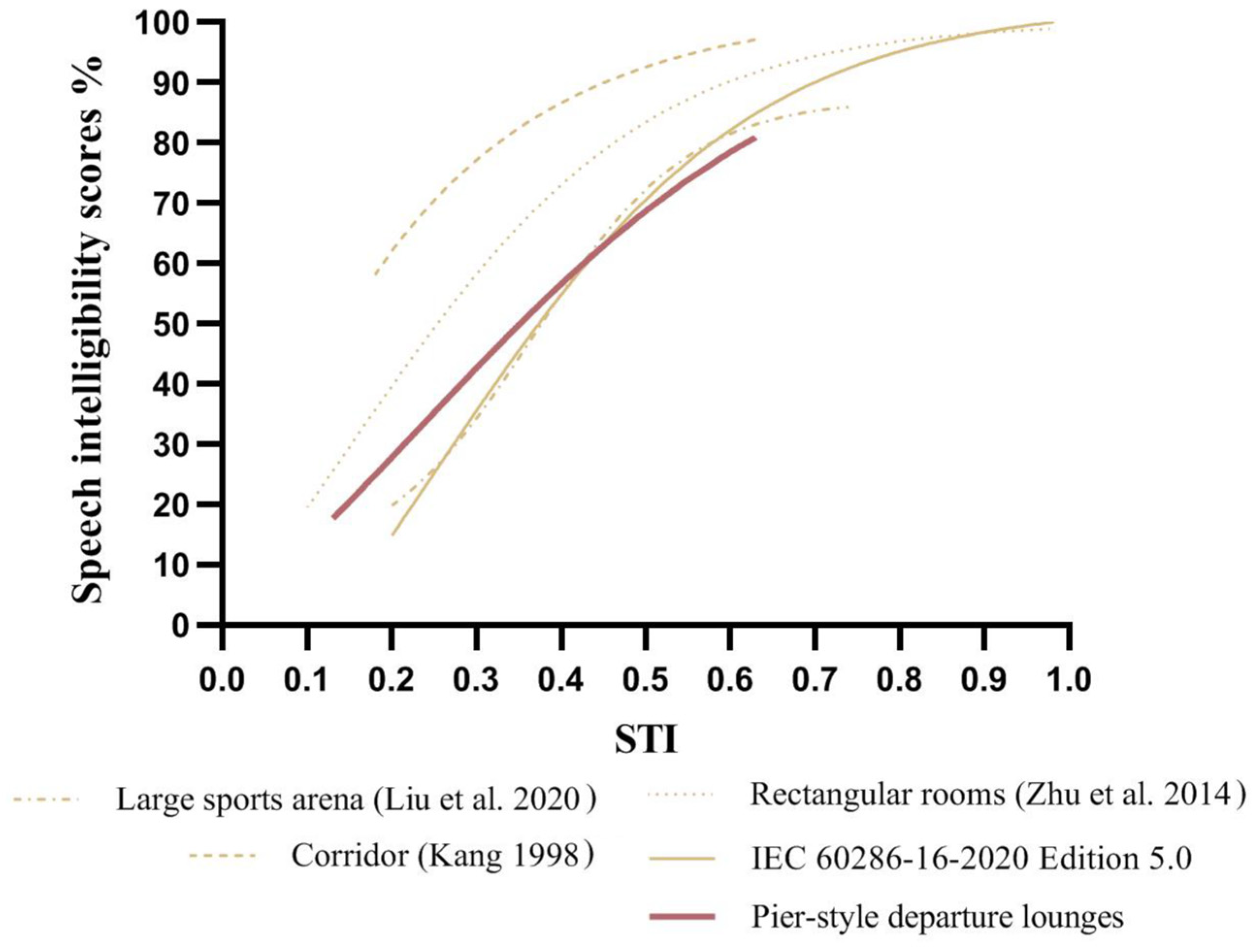
4.3. STI Rating for Terminal Pier-Style Departure Lounges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Departure Lounge | Length/Width/Height (m) | EDT (500–1 k) (s) | T30 (500–1 k)(s) | D50 (500–4 k) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier A | R1 | 220 m, 40 m, 8.2 m~12 m, | 0.11 | 2.63 | 3.93 | 0.42 |
| R2 | 3.26 | 3.89 | 0.35 | |||
| R3 | 2.99 | 3.80 | 0.27 | |||
| R4 | 3.98 | 3.90 | 0.18 | |||
| R5 | 3.46 | 4.23 | 0.23 | |||
| R6 | 3.95 | 3.49 | 0.13 | |||
| R7 | 4.41 | 3.76 | 0.30 | |||
| R8 | 4.52 | 4.34 | 0.23 | |||
| R9 | 4.91 | 4.59 | 0.06 | |||
| R10 | 4.58 | 3.68 | 0.08 | |||
| R11 | 2.28 | 3.82 | 0.39 | |||
| R12 | 3.06 | 3.66 | 0.38 | |||
| R13 | 3.03 | 3.80 | 0.24 | |||
| R14 | 3.50 | 3.85 | 0.24 | |||
| R15 | 3.27 | 3.87 | 0.21 | |||
| R16 | 3.84 | 3.78 | 0.19 | |||
| R17 | 4.31 | 3.97 | 0.09 | |||
| R18 | 4.71 | 4.06 | 0.05 | |||
| R19 | 4.92 | 4.40 | 0.02 | |||
| R20 | 4.06 | 3.89 | 0.19 | |||
| Pier B | R1 | 160 m, 32 m~40 m, 8.2 m~12 m, | 0.11 | 2.37 | 3.43 | 0.51 |
| R2 | 2.44 | 2.93 | 0.54 | |||
| R3 | 3.57 | 3.49 | 0.32 | |||
| R4 | 3.78 | 3.50 | 0.24 | |||
| R5 | 3.90 | 3.56 | 0.11 | |||
| R6 | 3.84 | 3.52 | 0.14 | |||
| R7 | 3.18 | 3.47 | 0.31 | |||
| R8 | 2.70 | 3.41 | 0.52 | |||
| R9 | 3.12 | 3.60 | 0.32 | |||
| R10 | 3.46 | 3.59 | 0.33 | |||
| R11 | 3.81 | 3.83 | 0.29 | |||
| R12 | 4.08 | 3.97 | 0.25 | |||
| R13 | 4.66 | 4.11 | 0.20 | |||
| R14 | 4.75 | 4.20 | 0.07 | |||
| R15 | 4.15 | 4.10 | 0.13 | |||
| R16 | 4.24 | 3.89 | 0.08 | |||
Appendix B
| Departure Lounge | Acoustic Parameters | Frequency Bands (Hz) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 4000 | |||
| Pier A | EDT | Measured | 2.04 | 2.88 | 3.79 | 3.78 | 3.82 | 2.98 |
| Simulated | 2.44 | 3.21 | 3.87 | 3.84 | 3.80 | 3.10 | ||
| Difference (JND) | 3.30 | 2.07 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.76 | ||
| T30 | Measured | 2.53 | 3.32 | 3.96 | 3.91 | 3.82 | 3.01 | |
| Simulated | 2.58 | 3.30 | 3.95 | 3.89 | 3.83 | 3.05 | ||
| Difference (JND) | 0.36 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.28 | ||
| D50 | Measured | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.26 | |
| Simulated | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.23 | ||
| Difference (JND) | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.60 | ||
| Pier B | EDT | Measured | 2.31 | 2.89 | 3.60 | 3.66 | 3.57 | 2.75 |
| Simulated | 2.71 | 3.08 | 3.78 | 3.82 | 3.76 | 2.89 | ||
| Difference (JND) | 2.99 | 1.23 | 0.96 | 0.86 | 1.03 | 0.99 | ||
| T30 | Measured | 2.56 | 3.15 | 3.70 | 3.63 | 3.56 | 2.86 | |
| Simulated | 2.45 | 3.13 | 3.66 | 3.66 | 3.61 | 2.88 | ||
| Difference (JND) | 0.90 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.14 | ||
| D50 | Measured | 0.41 | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.32 | |
| Simulated | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.27 | ||
| Difference (JND) | 1.80 | 0.80 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.20 | 1.00 | ||
References
- Edwards, B. The Modern Airport Terminal: New Approaches to Airport Architecture; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Hu, E. A new model predictive control scheme for energy and cost savings in commercial buildings: An airport terminal building case study. Build. Environ. 2015, 89, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, S.; Wirasinghe, S.C. Walking distance minimization for airport terminal configurations. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 1992, 26, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, S.; Saraswati, B. Low cost airport terminal locations and configurations. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2011, 17, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Lin, B.; Zhu, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Yu, J. Investigation of indoor environment quality of Chinese large-hub airport terminal buildings through longitudinal field measurement and subjective survey. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Yu, J.; Lin, B.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y. Impact of individual IEQ factors on passengers’ overall satisfaction in Chinese airport terminals. Build. Environ. 2017, 112, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y. Evaluation of sound environment in departure lounges of a large hub airport. Build. Environ. 2023, 232, 110046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffarzadeh, M.; Braaksma, J.P. Optimum design and operation of airport passenger terminal buildings. Transp. Res. Rec. 2000, 1703, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotopouleas, A.; Nikolopoulou, M. Evaluation of comfort conditions in airport terminal buildings. Build. Environ. 2018, 130, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijngaarden, S.J.; Atsma, R. Ambient noise inside airport terminals: A detailed survey of the background noise at Amsterdam Airport Schiphol. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 23–26 August 2020; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2020; pp. 1588–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Gao, Z.; Chang, F.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, C. Passengers’ Perception of Acoustic Environment in the Airport Terminal: A Case Study of Tianjin Binhai International Airport. Buildings 2023, 13, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhen, M. Effects of thermal-acoustic interaction on airport terminal’s indoor thermal comfort: A case study in cold region of China. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetjoki, N.; Kaarlela-Tuomaala, A.; Keskinen, E.; Hongisto, V. The effect of speech and speech intelligibility on task performance. Ergonomics 2006, 49, 1068–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbelboer, F.; Houtgast, T. A detailed study on the effects of noise on speech intelligibility. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 2865–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlittmeier, S.J.; Hellbrück, J.; Thaden, R.; Vorländer, M. The impact of background speech varying in intelligibility: Effects on cognitive performance and perceived disturbance. Ergonomics 2008, 51, 719–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borille, G.M.R.; da Silva, E.J.; Nascimento, M.V.D.; Bandeira, M.C.G.D.S.P.; Rendhol, A.L.M.; da Silva, L.M.; Ansélmo, C.S.; Gomes, R.D.A. Airport passenger building assessment of circulation facilities for smooth traffic and efficient design. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2022, 119, 102555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, G.; Majumdar, A. Characteristics of emergency evacuations in airport terminal buildings: A new event database. Saf. Sci. 2020, 130, 104897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, X. Simulation-based framework for evaluating the evacuation performance of the passenger terminal building in a Ro-Pax terminal. Autom. Constr. 2021, 121, 103445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bistafa, S.R.; Bradley, J.S. Reverberation time and maximum background-noise level for classrooms from a comparative study of speech intelligibility metrics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.S.; Sato, H. The intelligibility of speech in elementary school classrooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Mo, F.; Kang, J. Relationship between Chinese speech intelligibility and speech transmission index under reproduced general room conditions. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2014, 100, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. Speech intelligibility improvement for multiple loudspeakers by increasing loudspeaker directionality architecturally. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 1996, 17, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. Acoustics in long enclosures with multiple sources. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 99, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. Comparison of speech intelligibility between English and Chinese. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 103, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianxin, P. Chinese syllable and phoneme identification in noise and reverberation. Arch. Acoust. 2014, 39, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, H.; Wu, Y.; Kang, J. Characteristics and prediction of sound level in extra-large spaces. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 134, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, H.; Kang, J.; Wang, C. The speech intelligibility and applicability of the speech transmission index in large spaces. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 167, 107400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. The unsuitability of the classic room acoustical theory in long enclosures. Archit. Sci. Rev. 1996, 39, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. Sound attenuation in long enclosures. Build. Environ. 1996, 31, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianxin, P. Relationship between Chinese speech intelligibility and speech transmission index using diotic listening. Speech Commun. 2007, 49, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. A method for predicting acoustic indices in long enclosures. Appl. Acoust. 1997, 51, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.M.; Lam, P.M. Prediction of reverberation time and speech transmission index in long enclosures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 3716–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. Improvement of the STI of multiple loudspeakers in long enclosures by architectural treatments. Appl. Acoust. 1996, 47, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Soeta, Y. Architectural treatments for improving sound fields for public address announcements in underground station platforms. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 1205–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60286-16; Sound System Equipment-Part 16: Objective Rating of Speech Intelligibility by Speech Transmission Index. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Odeon-Room Acoustics Software. Available online: http://odeon.dk (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Zhu, P.; Mo, F.; Kang, J.; Zhu, G. Comparisons between simulated and in-situ measured speech intelligibility based on (binaural) room impulse responses. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 97, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Tao, W.; Mo, F.; Lu, X.; Zhang, H. Experimental comparisons of speech transmission index prediction methods. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 220, 109985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 3382-2; Acoustics—Measurement of Room Acoustic Parameters—Part 2 Reverberation Time in Ordinary Rooms. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Jianxin, P. Chinese speech intelligibility at different speech sound pressure levels and signal-to-noise ratios in simulated classrooms. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ODEON Room Acoustics Software User’s Manual. Available online: https://odeon.dk/downloads/user-manual/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Riener, K.R.; Warren, R.M.; Bashford, J.A., Jr. Novel findings concerning intelligibility of bandpass speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91 (Suppl. 4), 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickney, G.S.; Assmann, P.F. Intelligibility of bandpass-filtered speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 102 (Suppl. 5), 3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ge, J.; Meller, L.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, F.-G. Speech intelligibility and talker identification with non-telephone frequencies. JASA Express Lett. 2024, 4, 075202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, P.; Başkent, D. Effects of low-pass filtering on intelligibility of periodically interrupted speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, EL87–EL92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM SPSS Software. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/spss (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Yegnanarayana, B.; Ramakrishna, B. Intelligibility of speech under nonexponential decay conditions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1975, 58, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 15508-1995; Acoustics-Speech Articulation Testing Method. Standard of PR China. CAS (Chinese Academy of Sciences); State Bureau of Technical Supervision: Beijing, China, 1995.
- Brachmański, S. Effect of additive interference on speech transmission. Arch. Acoust. 2002, 27, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Richie, C.; Kewley-Port, D.; Coughlin, M. Vowel perception by noise masked normal-hearing young adultsa). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, M.; Kewley-Port, D.; Humes, L.E. The relation between identification and discrimination of vowels in young and elderly listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 3597–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.K. Speech related acoustical parameters in classrooms and their relationships. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 1318–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellotta, F. The just noticeable difference of center time and clarity index in large reverberant spaces. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.H.; Morgan, S.D. Acoustic and perceptual correlates of subjectively rated sentence clarity in clear and conversational speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138 (Suppl. 3), 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.S. Predictors of speech intelligibility in rooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 80, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, L.; Li, F.F. A new verification of the speech transmission index for the English language. Speech Commun. 2018, 105, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.S. Speech intelligibility studies in classrooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 80, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9921:2003; Ergonomics—Assessment of Speech Communication. Edition 1; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.





| Departure Lounge | Acoustic Parameters | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier A | EDT | Measured | 3.7985 | 0.8186 | 0.747 |
| Simulated | 3.8375 | 0.4402 | |||
| T30 | Measured | 3.9054 | 0.2695 | 0.791 | |
| Simulated | 3.8905 | 0.1050 | |||
| D50 | Measured | 0.1985 | 0.1337 | 0.618 | |
| Simulated | 0.2080 | 0.1258 | |||
| Pier B | EDT | Measured | 3.6547 | 0.8128 | 0.175 |
| Simulated | 3.8244 | 0.5377 | |||
| T30 | Measured | 3.6631 | 0.3369 | 0.659 | |
| Simulated | 3.6338 | 0.1301 | |||
| D50 | Measured | 0.2613 | 0.1863 | 0.261 | |
| Simulated | 0.2319 | 0.1317 | |||
| No. | Listening Positions | EDT (500–1000 Hz) | T30 (500–1000 Hz) | D50 (500–4000 Hz) | SNR | STI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 1.79 | 1.78 | 0.49 | −5 | 0.19 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.3 | ||||
| 3 | 5 | 0.38 | ||||
| 4 | 10 | 0.44 | ||||
| 5 | 15 | 0.46 | ||||
| 6 | without noise | 0.47 | ||||
| 7 | B | 1.95 | 2.32 | 0.86 | −5 | 0.25 |
| 8 | 0 | 0.37 | ||||
| 9 | 5 | 0.49 | ||||
| 10 | 10 | 0.57 | ||||
| 11 | 15 | 0.61 | ||||
| 12 | without noise | 0.63 | ||||
| 13 | C | 2.41 | 2.025 | 0.69 | −5 | 0.23 |
| 14 | 0 | 0.34 | ||||
| 15 | 5 | 0.47 | ||||
| 16 | 10 | 0.53 | ||||
| 17 | 15 | 0.56 | ||||
| 18 | without noise | 0.58 | ||||
| 19 | D | 3.70 | 2.915 | 0.45 | −5 | 0.13 |
| 20 | 0 | 0.25 | ||||
| 21 | 5 | 0.33 | ||||
| 22 | 10 | 0.35 | ||||
| 23 | 15 | 0.38 | ||||
| 24 | without noise | 0.39 |
| Formula Number | Acoustic Parameter Indicators | Expression | Determination Coefficient R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | SNR | 0.849 | |
| (2) | SNR, EDT | 0.950 | |
| (3) | SNR, T30 | 0.897 | |
| (4) | SNR, D50 | 0.957 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhao, Y. Exploring Factors Influencing Speech Intelligibility in Airport Terminal Pier-Style Departure Lounges. Buildings 2025, 15, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030426
Li X, Zhao Y. Exploring Factors Influencing Speech Intelligibility in Airport Terminal Pier-Style Departure Lounges. Buildings. 2025; 15(3):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030426
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xi, and Yuezhe Zhao. 2025. "Exploring Factors Influencing Speech Intelligibility in Airport Terminal Pier-Style Departure Lounges" Buildings 15, no. 3: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030426
APA StyleLi, X., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Exploring Factors Influencing Speech Intelligibility in Airport Terminal Pier-Style Departure Lounges. Buildings, 15(3), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15030426







