A Framework for Evaluating Cost Performance of Architectural Projects Using Unstructured Data and Random Forest Model Focusing on Korean Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Preliminary Review
2.1.1. Contract Statistics of Korean Construction
2.1.2. Construction Supervision System in Korea
2.1.3. The Need for an Advanced Framework from Conventional Evaluation Methods
2.2. Development Methods of a Proposed Framework
2.2.1. Overview
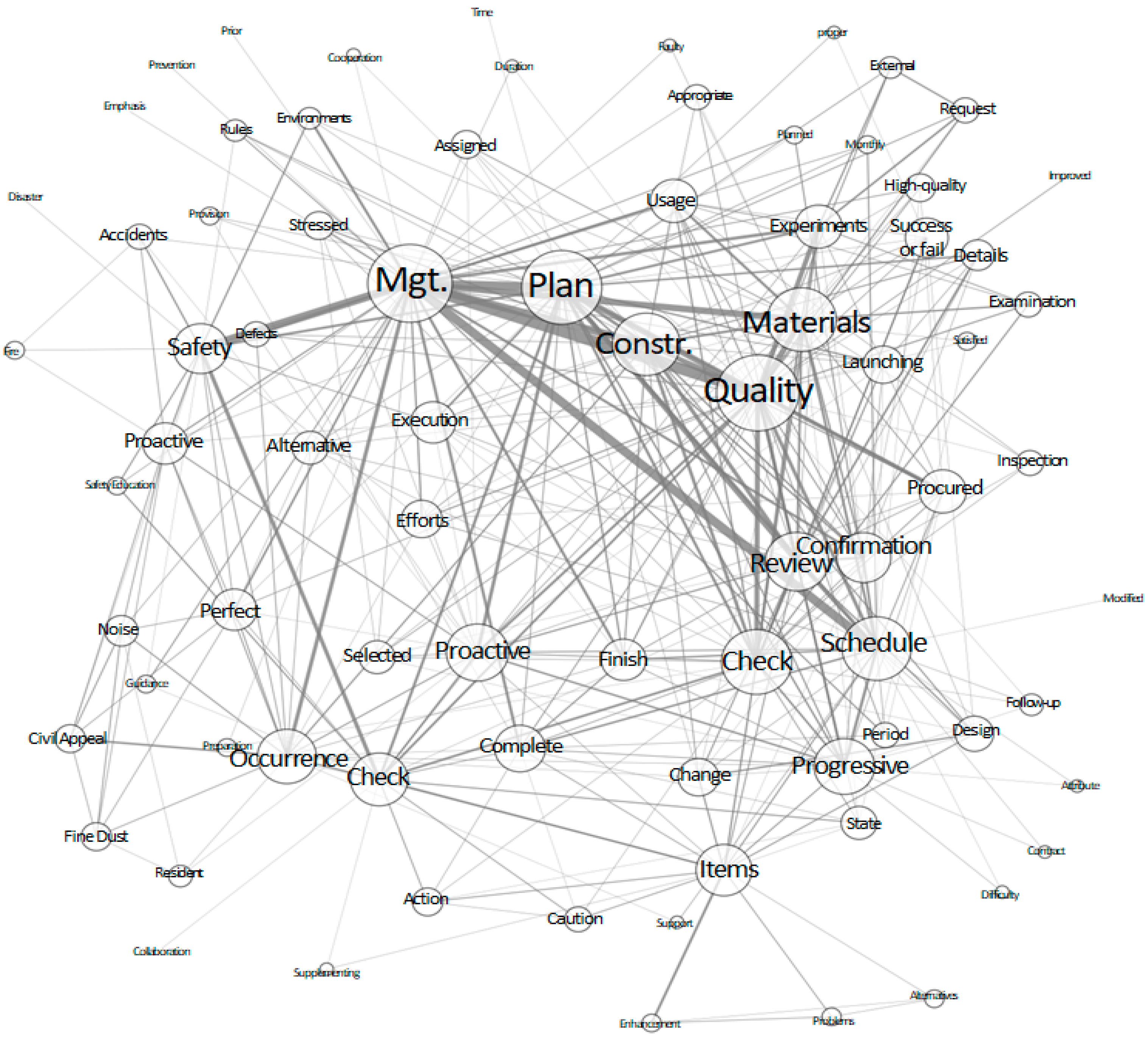
2.2.2. ARA and SNA
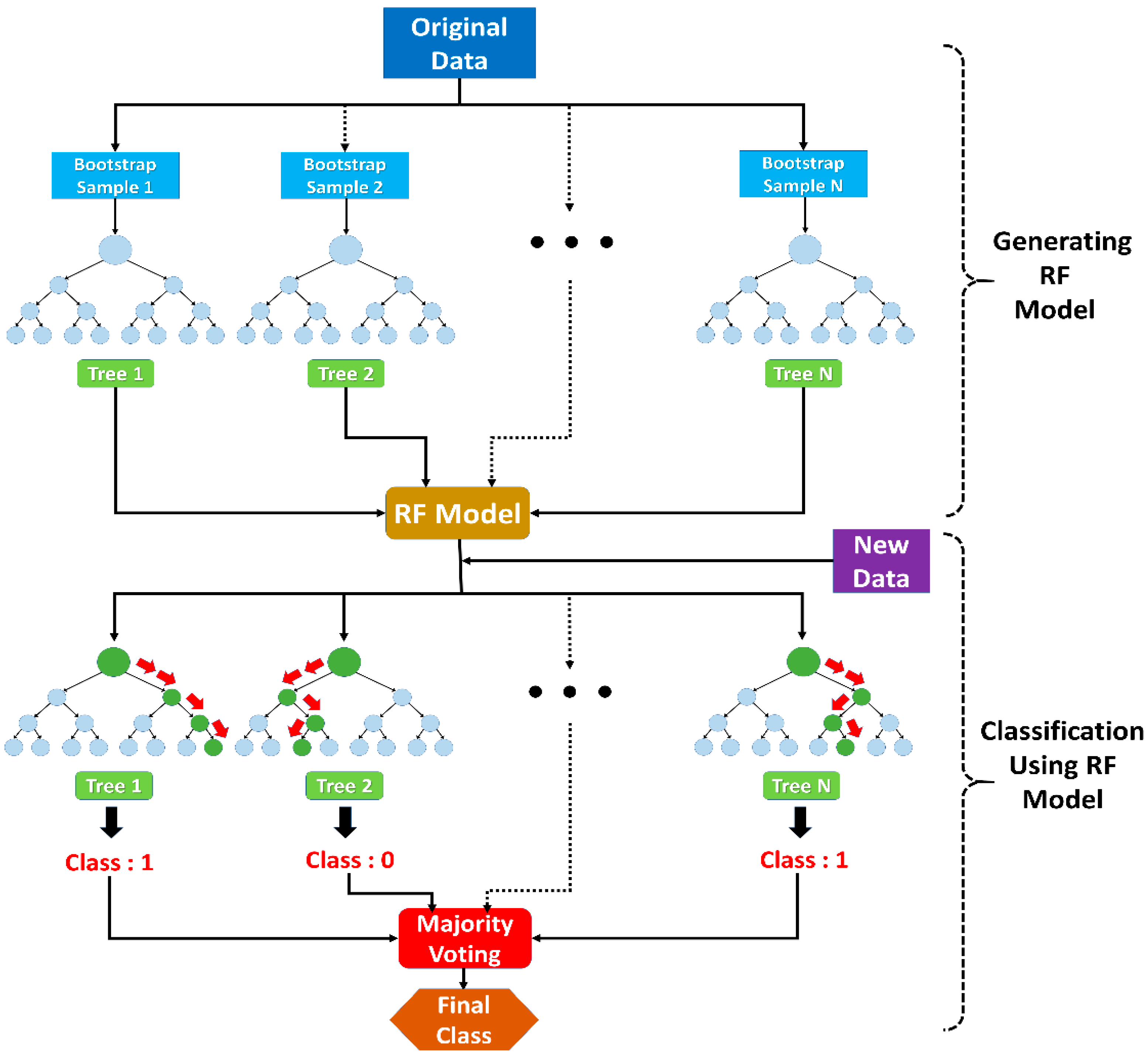
2.2.3. RF Model
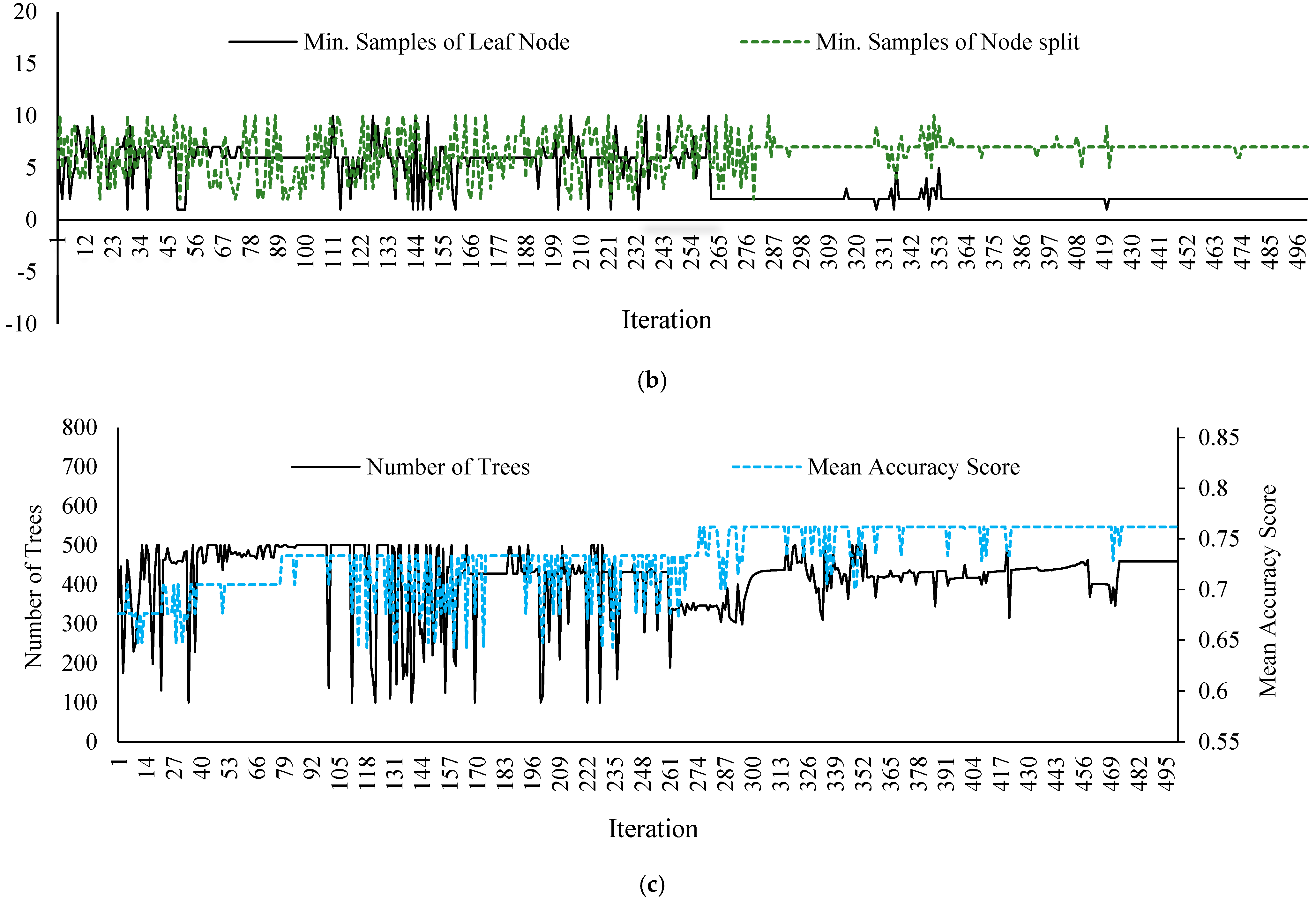
2.2.4. Dataset Augmentation for Stabilizing the RF Model
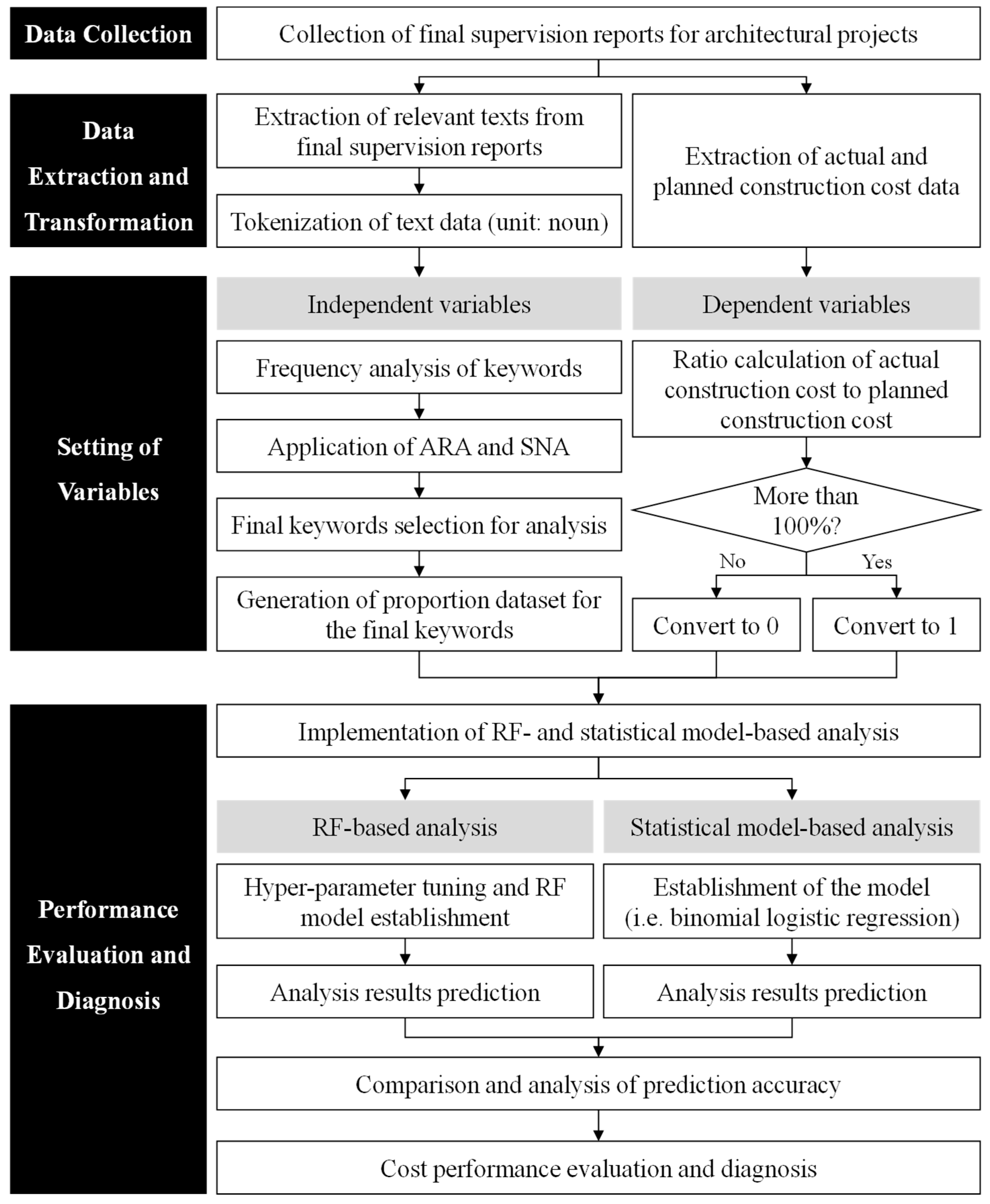
2.3. Development Process of a Proposed Framework
3. Results
3.1. Setting Independent and Dependent Variables
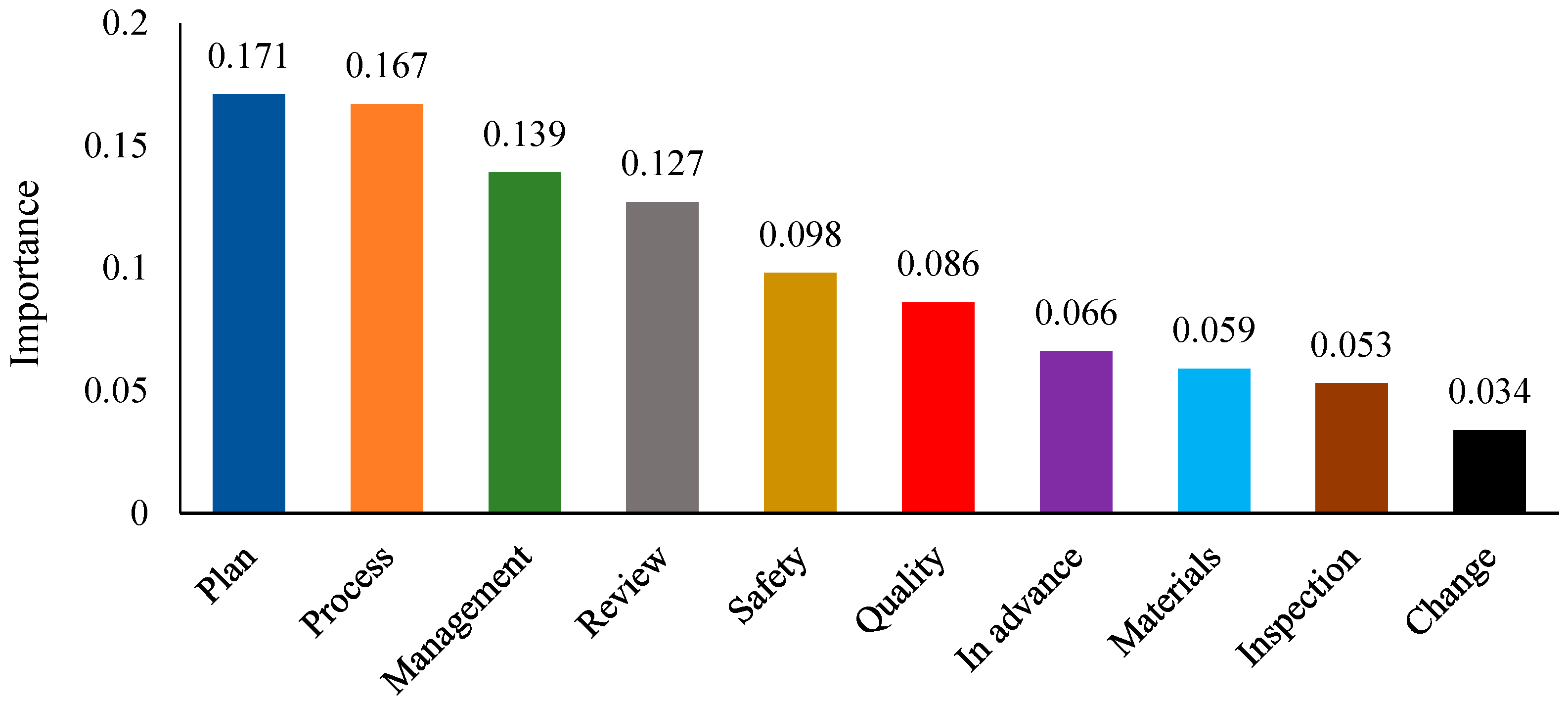
3.2. Analysis Results Based on RF
3.3. Operational Concept of a Proposed Cost Performance Evaluation Framework
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nan, J.; Choi, J.W.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.H. A Study on Estimating Construction Cost of Apartment Housing Projects using Genetic Algorithm-Support Vector Regression. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2014, 15, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.W.; Yoo, W.S.; Lim, H.; Yu, I.; Cho, H.; Kang, K.I. Early-warning performance monitoring system (EPMS) using the business information of a project. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2018, 36, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Seo, J.; Yoo, W.S.; Kim, C.W. Critical impact factors affecting the performance of domestic construction projects through megatrend analysis. J. Korean Inst. Build. Constr. 2022, 22, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.W.; Yoo, W.S.; Park, H.T. Development Direction of Performance Assessment System based on Building Supervision using Digital Technology. Build. Constr. 2022, 22, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.W.; Yoo, W.S.; Lim, H. Priority analysis for applying digital technology to improve the efficiency of building supervision work. J. Korean Inst. Build. Constr. 2023, 23, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.W. Development of Diagnostic Performance Index for Domestic Construction Projects. Ph.D. Thesis, Korea University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chandanshive, V.; Kambekar, A.R. Estimation of building construction cost using artificial neural networks. J. Soft Comput. Civ. Eng. 2019, 3, 91–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, D.; Elhegazy, H.; Elzarka, H.; Gutierrez, L. A novel construction cost prediction model using hybrid natural and light gradient boosting. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 46, 101201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; Yun, S.H. Analysis of the construction cost prediction performance according to feature scaling and long conversation of target variables. J. Korean Inst. Build. Constr. 2022, 22, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.-Y. Analysis on the characteristics of construction practice information using text mining: Focusing on information such as construction technology, cases, and cost Reduction. J. Korean Soc. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2022, 56, 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Leu, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.L. Project cost overrun risk prediction using Hidden Markov chain Analysis. Buildings 2023, 13, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Zayed, T.; Lafhaj, Z. Enhancing construction performance: A critical review of performance measurement practices at the project level. Buildings 2024, 14, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, G.; Bayram, S.; Çıtakoğlu, H. Evaluation of Earned Value Management-Based Cost Estimation via Machine Learning. Buildings 2024, 14, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateş, B.; Eirgash, M.A. Proactive and Data-Driven Decision-Making Using Earned Value Analysis in Infrastructure Projects. Buildings 2025, 15, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S. AI-powered forecasting of environmental impacts and construction costs to enhance project management in highway projects. Buildings 2025, 15, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Kim, B.; Yang, J.; Park, H.; Kim, C.W. An environmental performance estimation model for architectural projects using unstructured data from construction supervision documents. J. Korean Inst. Build. Constr. 2024, 24, 697–705. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.W.; Yoo, W.S.; Seo, J.; Kim, B.G.; Lim, H. A roadmap for applying digital technology to improve the efficiency of construction supervision in building projects: Focusing on Korean cases. Buildings 2023, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.W.; Song, T.; Lee, K.; Yoo, W.S. Cost performance evaluation framework through analysis of unstructured construction supervision documents using binomial logistic regression. J. Korean Inst. Build. Constr. 2024, 24, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. Building Act. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/법령/건축법 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. Housing Act. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/법령/주택법 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. Construction Technology Promotion Act. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/법령/건설기술진흥법 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. Electrical Construction Business Act. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/법령/전기공사업법 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- National Fire Agency. Firefighting System Installation Business Act. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/법령/소방시설공사업법 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Ministry of Science and ICT. Information and Communication Construction Business Act. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/법령/정보통신공사업법 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. Notice on Detailed Standards for Building Supervision. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/행정규칙/건축공사감리세부기준 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Aragao, R.; El-Diraby, T.E. Network analytics and social BIM for managing project unstructured data. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Stephan, T.; Deverajan, G.G.; Patan, R. Performance analysis of machine learning algorithms for big data classification: Ml and ai-based algorithms for big data analysis. Int. J. E-Health Med. Commum. 2021, 12, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Casasayas, O.; Wang, J.; Mao, P.; Cui, P. Stakeholder-associated impact factors of building energy performance gap and their intersections: A social network analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Surmi, A.; Bashiri, M.; Koliousis, I. AI based decision making: Combining strategies to improve operational performance. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 4464–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Integrating BIM and AI for smart construction management: Current status and future directions. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 1081–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Saad, S.; Rasheed, K.; Ammad, S. AI Future Perspectives and Trends in Construction. In *AI in Material Science: Revolutionizing Construction. In *AI in Material Science: Revolutionizing Construction in the Age of Industry 4.0*; Saad, S., Ammad, S., Rasheed, K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Construction Association of Korea. Annual Contract Amount by Ordering Agency, Construction Scales, and Construction Project Type in Korea (2013–2023). Available online: https://www.cak.or.kr/lay1/S1T39C246/contents.do (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Chung, H.M.; Gray, P. Special Section: Data Mining. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1999, 16, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J. Data mining; a conceptual overview. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2022, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Imieliński, T.; Swami, A. Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases. In Proceedings of the 1993 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Washington, DC, USA, 25–28 May 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.R.; Kim, H.S. Association rules analysis between the types and causes of disputes in construction projects. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 23, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Lee, M.; Hwang, S.; Oh, S. TF-IDF based association rule analysis system for medical data. KIPS Trans. Softw. Data Eng. 2016, 5, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.J. Cryptocurrency recommendation model using the similarity and association rule mining. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2022, 28, 287–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, J.H.; You, Y.Y. The Fourth Industrial Revolution core technology association analysis using text mining. J. Digit. Converg. 2018, 16, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Son, K.Y.; Ryu, H.G. Association rules analysis of safe accidents caused by falling objects. J. Korean Inst. Build. Constr. 2019, 19, 341–350. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, P.N.; Steinbach, M.; Kumar, V. Introduction to Data Mining; Pearson Addison-Wesley: New Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Lee, D.; Kim, J. A Study on the Task Variation and Social Network Analysis in the Construction Process. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 20, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, P.; Wright, M.N.; Boulesteix, A.L. Hyperparameters and tuning strategies for random forest. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. 2019, 9, e1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scikit-Optimize. Available online: https://scikit-optimize.github.io/stable/modules/generated/skopt.BayesSearchCV.html (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Díaz-Uriarte, R.; Alvarez de Andrés, S. Gene selection and classification of microarray data using random forest. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuer, R.; Poggi, J.M.; Tuleau-Malot, C. Variable selection using random forests. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daviran, M.; Maghsoudi, A.; Ghezelbash, R.; Pradhan, B. A new strategy for spatial predictive mapping of mineral prospectivity: Automated hyperparameter tuning of random forest approach. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 148, 104688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Yoon, D.; Choi, J.; Byun, J. Hyperparameter search for facies classification with bayesian optimization. Geophys. Geophys. Explor. 2020, 23, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Brochu, E.; Cora, V.M.; De Freitas, N. A tutorial on Bayesian optimization of expensive cost functions, with application to active user modeling and hierarchical reinforcement learning. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1012.2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.L.; Cho, S. KoNLPy: Korean natural language processing in Python. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Human & Cognitive Language Technology, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea, 10 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Estrepo, J.P.; Rivera, J.C.; Laniado, H.; Osorio, P.; Becerra, O.A. Nonparametric generation of synthetic data using copulas. Electronics 2023, 12, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, J.; Yu, J.Y.; Jung, K.; Yoon, J.; Cha, W.C. Computationally efficient and stable real-world synthetic emergency room electronic health record data generation: High similarity and privacy preserving diffusion model approach. Precis. Future Med. 2024, 8, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Cheng, G.; Guo, J.; Zhu, H. Test for high-dimensional correlation matrices. Ann. Stat. 2019, 47, 2887–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Project Type | Number of Contracts | Amount of Contracts | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Each | Ratio (%) | Billion USD | Ratio (%) | |
| Architectural | 50,321 | 64 | 77 | 72 |
| Civil infrastructure | 23,705 | 30 | 20 | 19 |
| Industrial facility | 1243 | 2 | 7 | 7 |
| Landscape | 3134 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 78,403 | 100 | 106 | 100 |
| Variables | KS Statistics | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cost performance | 0.1933 | 0.0980 |
| Review | 0.1562 | 0.2745 |
| Plan | 0.1435 | 0.3702 |
| Process | 0.1813 | 0.1404 |
| Management | 0.1204 | 0.1401 |
| Change | 0.1533 | 0.1115 |
| In advance | 0.1211 | 0.5823 |
| Safety | 0.1365 | 0.4316 |
| Materials | 0.1005 | 0.7947 |
| Inspection | 0.1803 | 0.1441 |
| Quality | 0.1205 | 0.5883 |
| Rule No. | Antecedent Event | Consequent Event | Support | Confidence | Lift |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quality | Management | 0.16 | 0.66 | 1.36 |
| 2 | Process | Management | 0.12 | 0.67 | 1.38 |
| 3 | Plan | Management | 0.12 | 0.58 | 1.20 |
| 4 | Safety | Management | 0.12 | 0.68 | 1.41 |
| 5 | Construction | Management | 0.11 | 0.56 | 1.15 |
| 6 | Materials | Management | 0.09 | 0.61 | 1.25 |
| 7 | Plan | Quality | 0.09 | 0.41 | 1.71 |
| 8 | Materials | Quality | 0.08 | 0.52 | 2.15 |
| 9 | Check | Plan | 0.07 | 0.49 | 2.38 |
| 10 | Test | Quality | 0.07 | 0.79 | 3.26 |
| 11 | Confirmation | Quality | 0.07 | 0.45 | 1.84 |
| 12 | Secure | Quality | 0.06 | 0.84 | 3.47 |
| 13 | Construction | Quality | 0.06 | 0.32 | 1.30 |
| 14 | Check | Construction | 0.06 | 0.39 | 2.03 |
| 15 | Inspection | Safety | 0.06 | 0.44 | 2.56 |
| 16 | Occurrence | Management | 0.05 | 0.53 | 1.10 |
| 17 | Advance | Plan | 0.05 | 0.48 | 2.30 |
| 18 | Process | Quality | 0.05 | 0.28 | 1.15 |
| 19 | Confirmation | Construction | 0.05 | 0.32 | 1.65 |
| 20 | Test | Management | 0.05 | 0.57 | 1.17 |
| 21 | Process | Plan | 0.05 | 0.26 | 1.28 |
| 22 | Construction | Plan | 0.05 | 0.24 | 1.18 |
| 23 | Check | Quality | 0.04 | 0.31 | 1.29 |
| 24 | Completion | Management | 0.04 | 0.53 | 1.10 |
| 25 | Progress | Process | 0.04 | 0.40 | 2.20 |
| 26 | Check | Confirmation | 0.04 | 0.29 | 1.94 |
| 27 | Confirmation | Plan | 0.04 | 0.28 | 1.34 |
| 28 | Finish | Management | 0.04 | 0.52 | 1.06 |
| 29 | Inspection | Plan | 0.04 | 0.33 | 1.61 |
| 30 | Operation | Materials | 0.04 | 0.56 | 3.76 |
| Variable | Average | 1st Quartile | Median | 3rd Quartile | Max | Standard Deviation | Kurtosis | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost performance | 101.5 | 95.8 | 103.3 | 108.5 | 137.9 | 16.5 | 11.8 | −2.3 |
| Review | 6.4 | 3 | 5.3 | 9.3 | 16.7 | 4.8 | −0.3 | 0.7 |
| Plan | 7.8 | 5.2 | 7.8 | 9.8 | 26.1 | 5 | 3.6 | 1.0 |
| Process | 9.4 | 5.6 | 8.1 | 10.8 | 30.2 | 6.1 | 4.5 | 1.9 |
| Management | 26.5 | 21.6 | 23.3 | 29.4 | 60.0 | 8.5 | 5.9 | 2.0 |
| Change | 4.2 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 5.2 | 48.0 | 8.3 | 21.4 | 4.2 |
| In advance | 3.4 | 1.4 | 3.2 | 5.7 | 7.2 | 2.6 | −1.4 | 0.1 |
| Safety | 8.4 | 5.4 | 9.3 | 10.5 | 20.6 | 4.1 | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| Materials | 7.6 | 4.9 | 7.4 | 10.8 | 22.4 | 5.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Inspection | 5.1 | 0.0 | 3.9 | 10.4 | 15.8 | 4.9 | −1.3 | 0.4 |
| Quality | 11.5 | 8.2 | 11.7 | 13.9 | 29.2 | 5.4 | 2.4 | 0.6 |
| Traditional LR | Constrain-Based BLR | RF | |
|---|---|---|---|
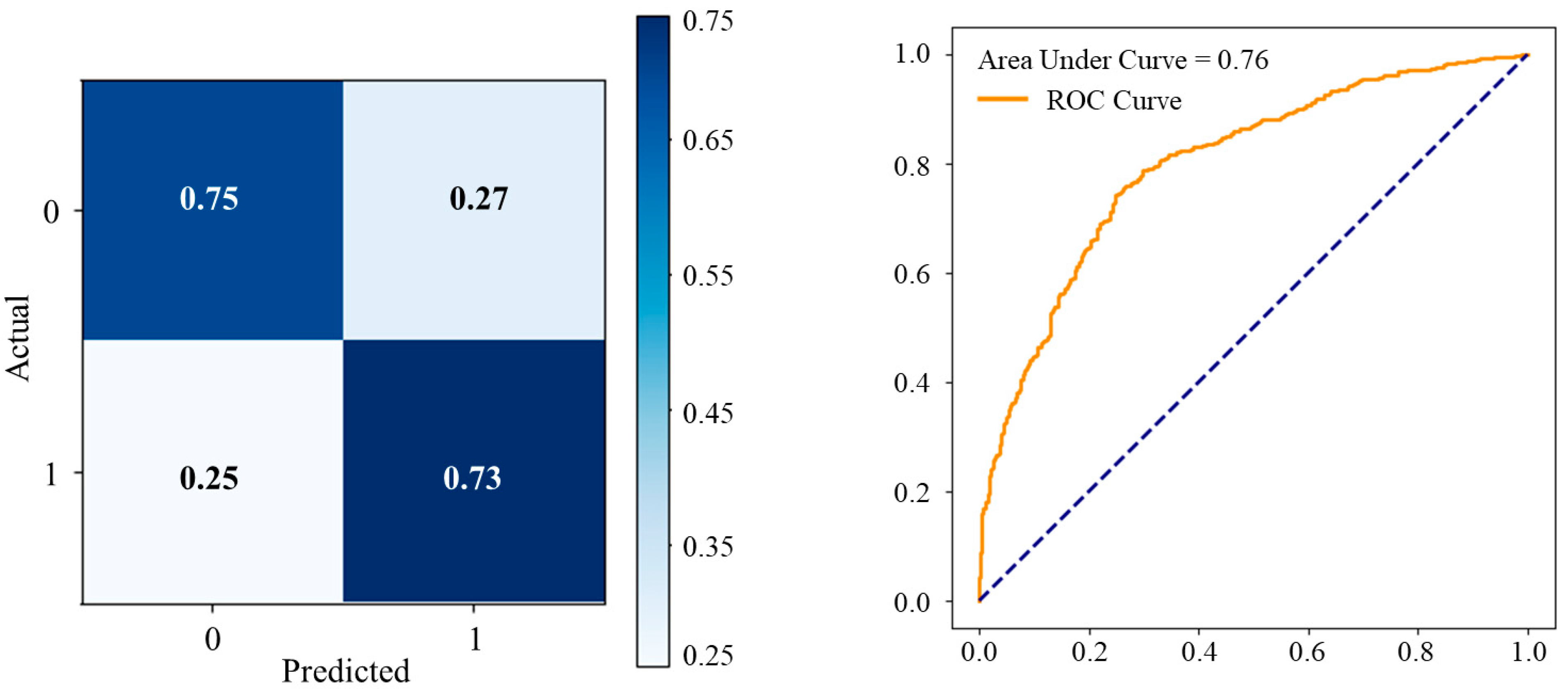
| Accuracy of Models | 0.59 | 0.74 | 0.76 |
| Project No. | Review | Plan | Process | Management | Change | In Advance | Safety | Materials | Inspection | Quality | Actual Cost Performance | Predicted Cost Performance | Vote Class 0 | Vote Class 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.7 | 7.4 | 11.1 | 37.0 | 0.0 | 3.7 | 14.8 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 11.1 | 1 | 1 | 0.42 | 0.58 |
| 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 27.8 | 27.8 | 16.7 | 0.0 | 5.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.6 | 0 | 0 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3 | 10.3 | 5.2 | 9.3 | 21.6 | 3.1 | 7.2 | 9.3 | 6.2 | 2.1 | 16.5 | 0 | 1 | 0.10 | 0.90 |
| 4 | 14.3 | 6.3 | 6.3 | 22.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 1.6 | 12.7 | 1 | 1 | 0.17 | 0.83 |
| 5 | 4.2 | 9.7 | 5.6 | 22.2 | 0.0 | 5.6 | 9.7 | 12.5 | 11.1 | 13.9 | 1 | 1 | 0.12 | 0.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, C.-W.; Song, T.; Lee, K.; Yoo, W.S. A Framework for Evaluating Cost Performance of Architectural Projects Using Unstructured Data and Random Forest Model Focusing on Korean Cases. Buildings 2025, 15, 3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203799
Kim C-W, Song T, Lee K, Yoo WS. A Framework for Evaluating Cost Performance of Architectural Projects Using Unstructured Data and Random Forest Model Focusing on Korean Cases. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203799
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Chang-Won, Taeguen Song, Kiseok Lee, and Wi Sung Yoo. 2025. "A Framework for Evaluating Cost Performance of Architectural Projects Using Unstructured Data and Random Forest Model Focusing on Korean Cases" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203799
APA StyleKim, C.-W., Song, T., Lee, K., & Yoo, W. S. (2025). A Framework for Evaluating Cost Performance of Architectural Projects Using Unstructured Data and Random Forest Model Focusing on Korean Cases. Buildings, 15(20), 3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203799





