Shear Strength of Double-Skin Truss-Reinforced Composite Shear Walls: Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Benchmark Tests for Finite Element Model
3. Finite Element Model (FEM)
3.1. Overview
3.2. Material Constitutive Model
3.2.1. Steel Material Constitutive Model
3.2.2. Concrete Material Constitutive Model
4. Result Comparison Between FEM and Experiment
4.1. Comparison of Deformation Results
4.2. Load–Displacement Curves
4.3. Quantitative Validation of Hysteretic Parameters
5. Finite Element Parametric Analysis
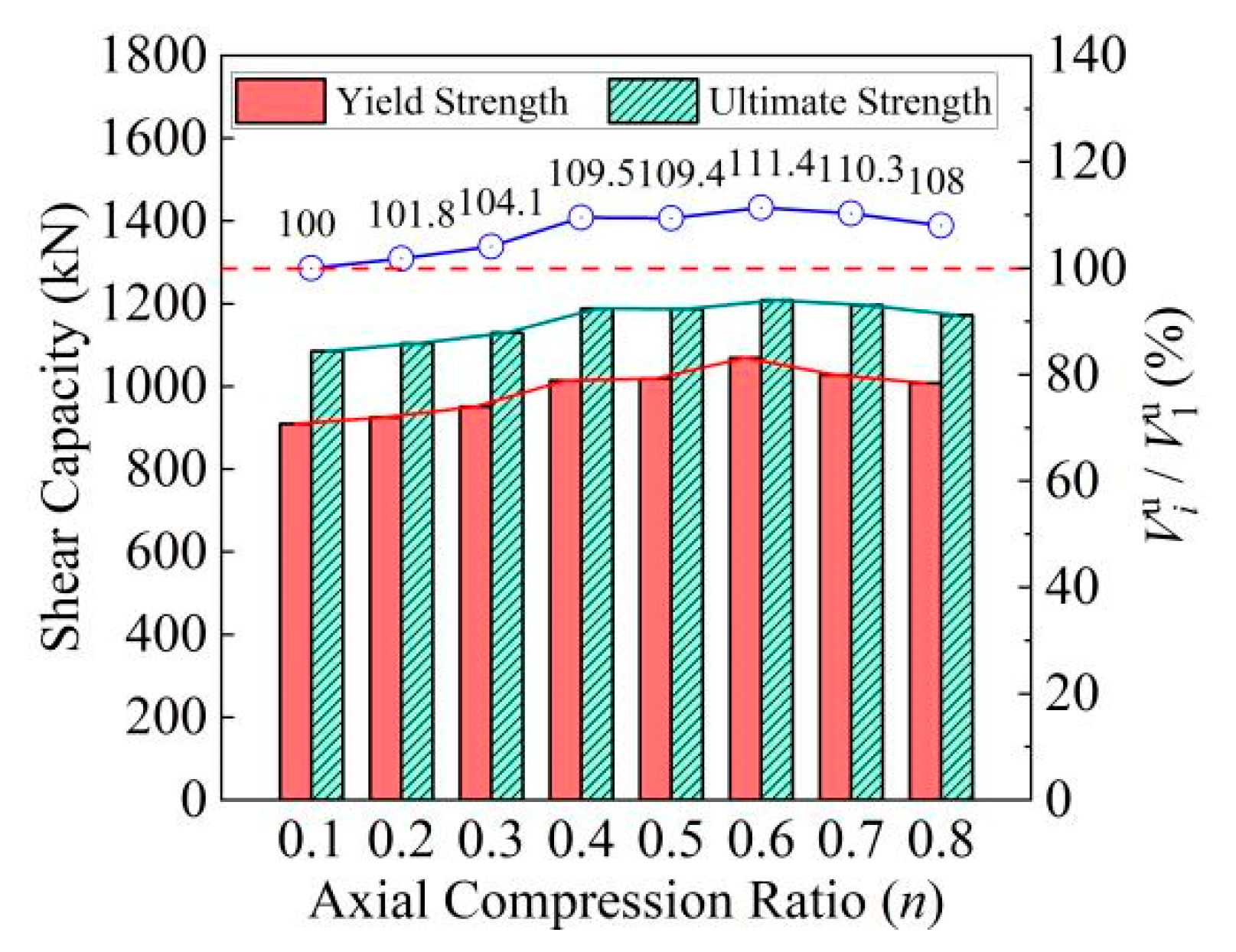
5.1. Impact of Axial Compression Ratio
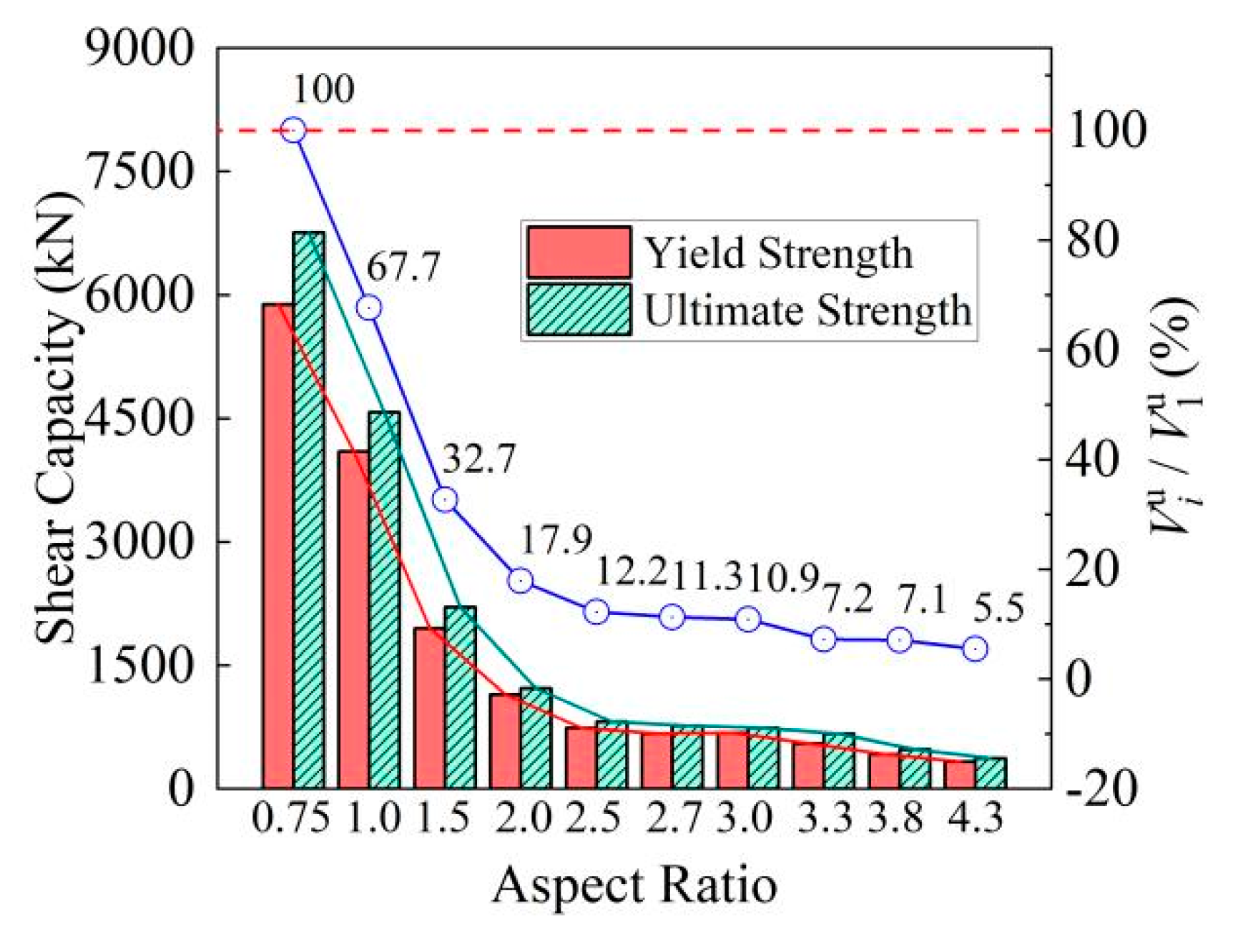
5.2. Impact of Aspect Ratio
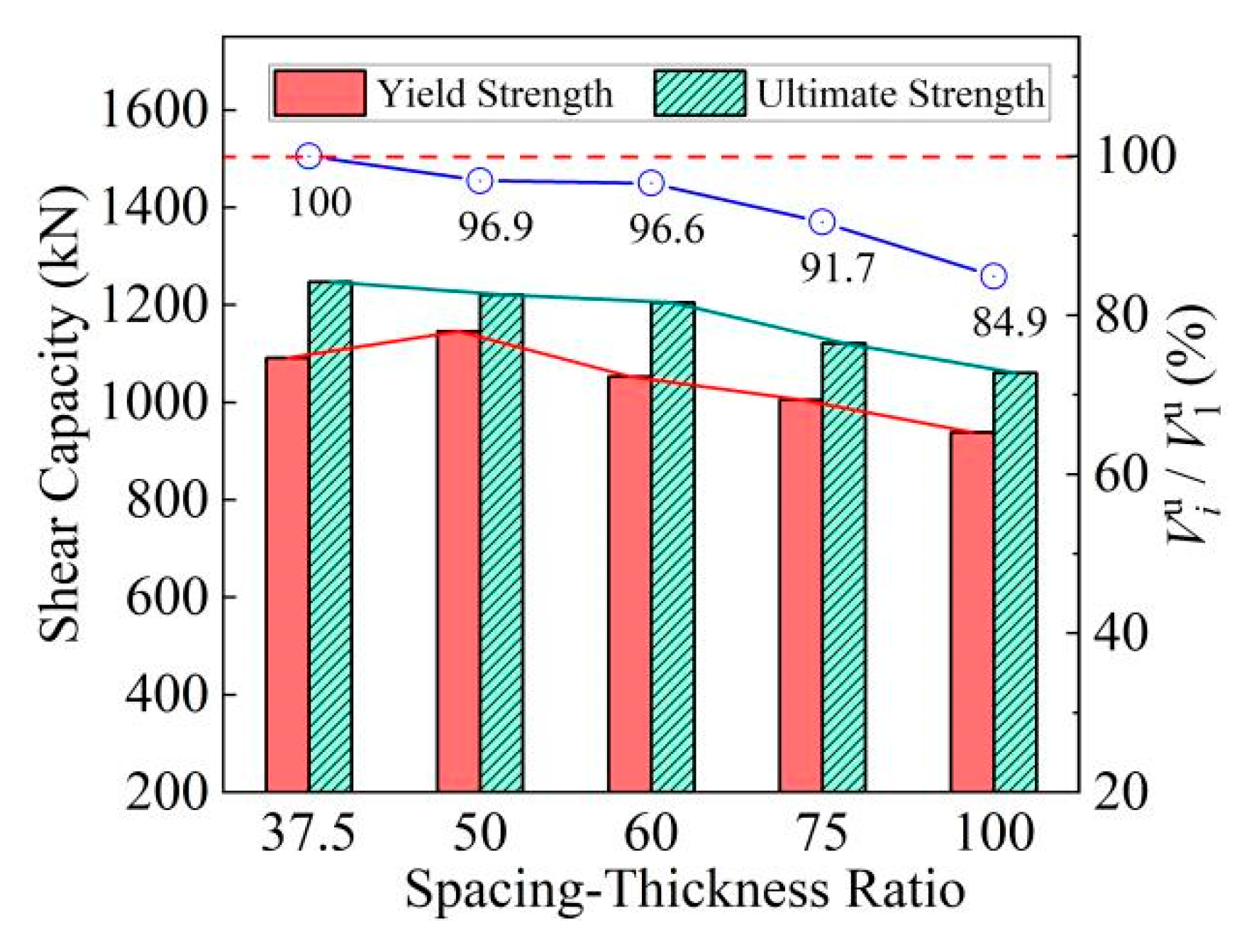
5.3. Impact of Spacing-Thickness Ratio
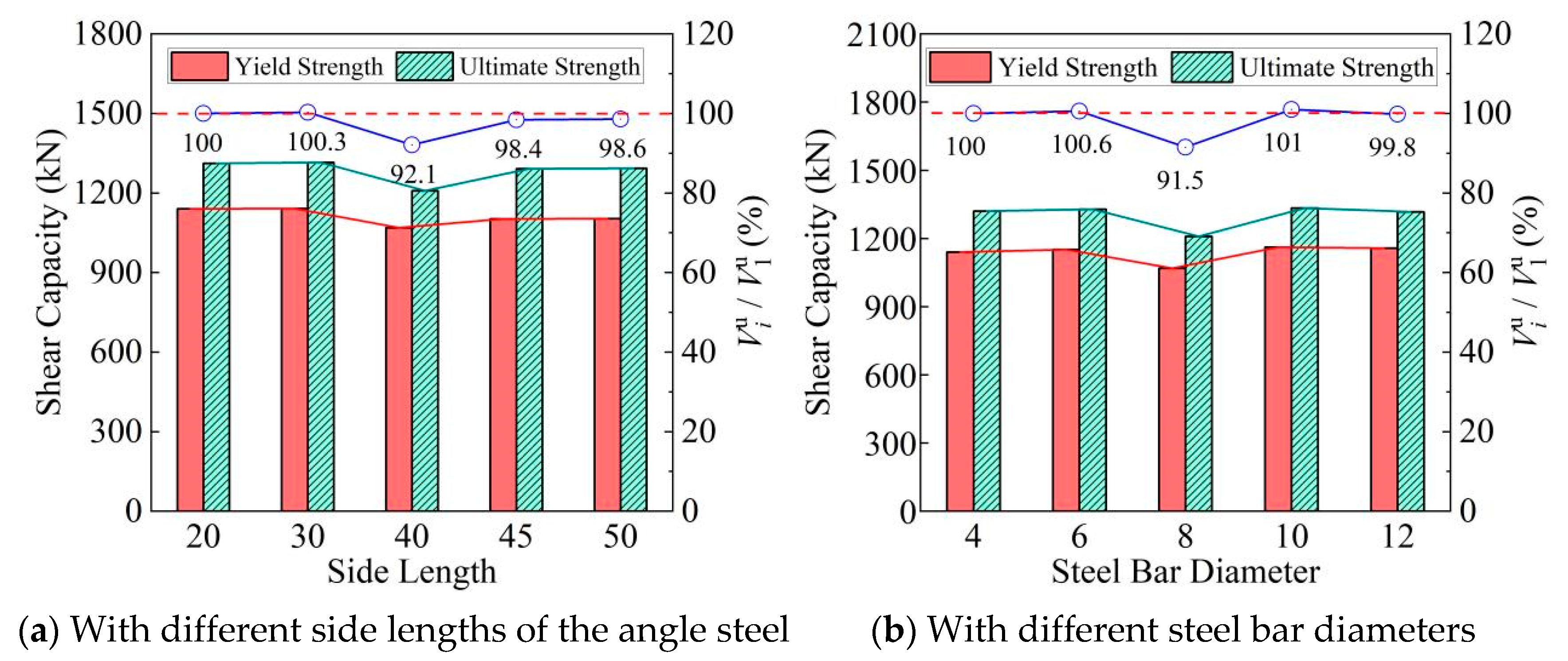
5.4. Impact of Truss Connector Specifications
6. Establishment of Ultimate Shear Strength Design Formulas
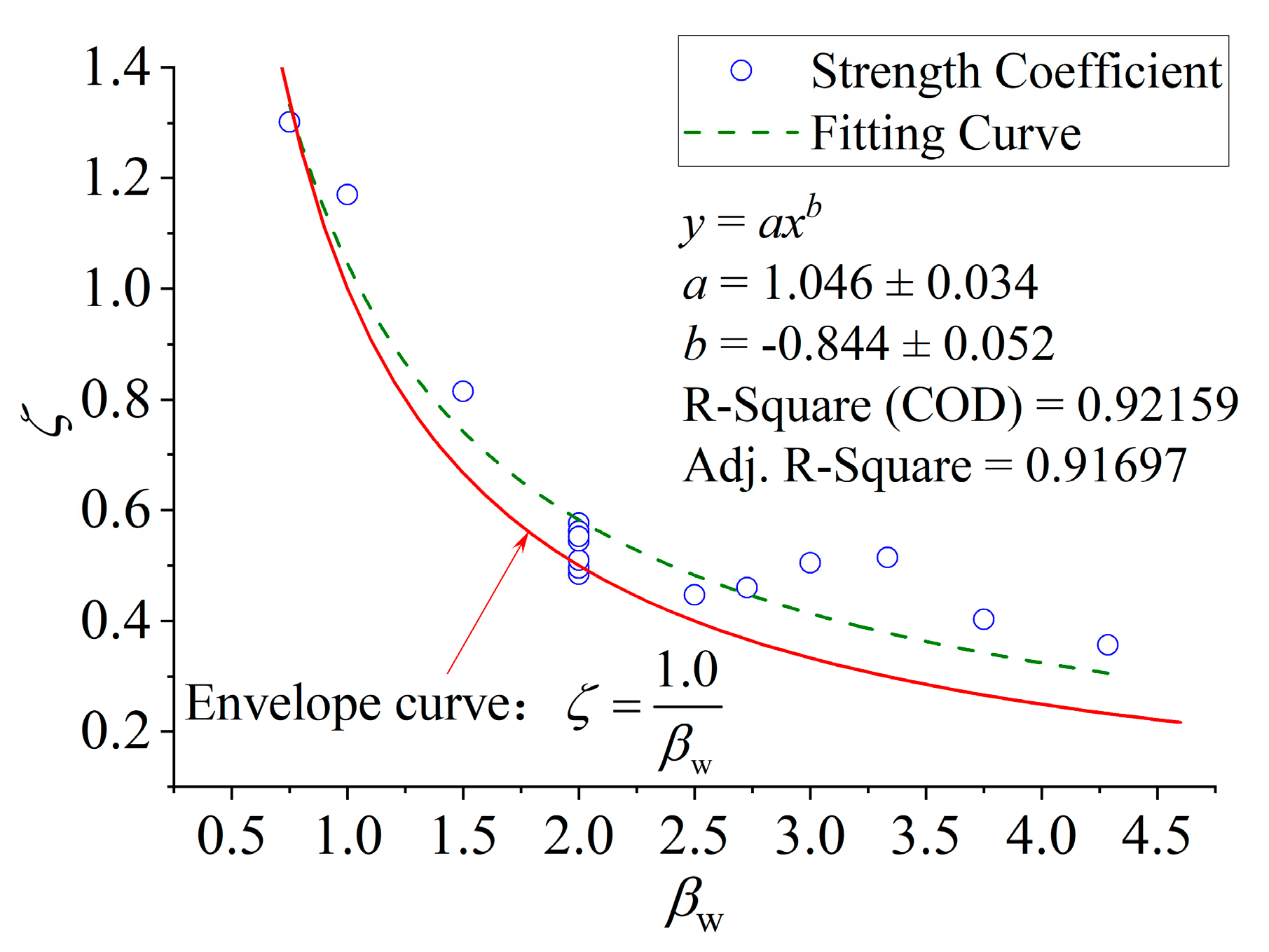
6.1. Formulation Establishment
6.2. Formula Verification
7. Conclusions and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, Y.; Shu, G.P.; Zhou, X.L.; Han, J.H.; He, Y.F. Height-thickness ratio on axial behavior of composite wall with truss connector. Steel Compos. Struct. 2019, 30, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Shu, G.-P.; Zhou, X.-L.; Han, J.-H.; Zhang, H.-K. Behavior of T-shaped sandwich composite walls with truss connectors under eccentric compression. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 169, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Shu, G.-P.; Luo, K.-R.; Qin, Y. Performance of double-skin truss-reinforced composite wall under axial compression. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 202, 107778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.R.; Shu, G.P.; Liu, Z.H. Research on the axial compressive behavior of double skin composite wall with steel truss. Structures 2024, 62, 106159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Shu, G.-P.; Zhang, H.-K.; Zhou, G.-G. Experimental cyclic behavior of connection to double-skin composite wall with truss connector. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 162, 105759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Shu, G.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, X. Experimental seismic behavior of double skin composite wall with steel truss. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 180, 106569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Shu, G.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, X. Experimental seismic behavior of T-shaped double skin composite wall with steel truss. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 184, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Shu, G.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, X. Sectional strength design of a double-skin truss-reinforced composite shear wall. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 195, 111377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharavi, A.; Asgarpoor, M.; Epackachi, S.; Mirghaderi, S.R.; Imanpour, A. Axial-flexural strength of steel-concrete composite shear walls. J. Build Eng. 2023, 76, 107122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Sun, G.; Yang, W. Axial compressive behavior of low steel–concrete composite walls with multi-partition steel tubes and concrete. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2023, 415, 112684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Xie, S.; Chen, Y. Behavior and design method of double skin composite wall under axial compression. J. Build Eng. 2023, 64, 105554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Ma, H. The seismic behaviors of steel-concrete-steel composite walls with dumbbell-shaped connectors. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 211, 108182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-Z.; Guo, Y.-L.; Zhu, J.-S.; Yang, X.; Tong, J.-Z. Sectional strength design of concrete-infilled double steel corrugated-plate walls with T-section. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 160, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, F.; Chen, H. Performance of concrete-filled double-skin shallow-corrugated steel plate composite walls under axial compression. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 196, 107374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-Z.; Guo, Y.-L.; Zhu, J.-S.; Yang, X. Flexural buckling of axially loaded concrete-infilled double steel corrugated-plate walls with T-section. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 166, 105940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, H.; Li, F. Performance of concrete-filled double-skin shallow-corrugated steel plate composite walls under compression-bending load. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 201, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-Z.; Guo, Y.-L.; Zhu, J.-S.; Yang, X. Flexural-torsional buckling and design recommendations of axially loaded concrete-infilled double steel corrugated-plate walls with T-section. Eng. Struct. 2020, 208, 110345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-B.; Guan, H.-N.; Yan, Y.-Y.; Wang, T. Numerical and parametric studies on SCS sandwich walls subjected to in-plane shear. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 169, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, P.N.; Bhardwaj, S.R.; Tseng, T.-C.; Seo, J.; Varma, A.H. Ultimate shear strength of steel-plate composite (SC) walls with boundary elements. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 165, 105810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Malidarreh, N.R.; Ghaseminejad, V.; Asgari, A. Seismic resilience assessment of RC superstructures on long–short combined piled raft foundations: 3D SSI modeling with pounding effects. Structures 2025, 81, 110176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Mohsen, B.; Mohammad, H. Advanced seismic analysis of soil-foundation-structure interaction for shallow and pile foundations in saturated and dry deposits: Insights from 3D parallel finite element modeling. Structures 2024, 69, 107503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.H. Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Structures—Theory and Practice; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- GB 50010-2010; Code for Design of Concrete Structures. Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Wang, J.C.; Chen, Y.K. Application of ABAQUS in Civil Engineering; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.Z. An Overview of Plastic Damage Model of ABAQUS Concrete. Chongqing Archit. 2014, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, B.; Mehdi, E.J.; Bijan, S. Effect of Seismic Soil–Pile–Structure Interaction on Mid- and High-Rise Steel Buildings Resting on a Group of Pile Foundations. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 04018103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ/T 380–2015; Technical Specification for Steel Plate Shear Wall. China Association for Engineering Construction Standardization: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Zhang, X.M.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Z.H. Experimental seismic behavior of innovative composite shear walls. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 116, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.B.; Yan, Y.Y.; Wang, T. Cyclic tests on novel steel-concrete-steel sandwich shear walls with boundary CFST columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 164, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Research on Seismic Behavior of High Strength Concrete Composite Shear Wall with Double Steel Plates. Master’s Thesis, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Yin, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. Experimental study on seismic behavior of double-skin composite wall with L-shaped connectors. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 174, 106312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. New L-Shaped Connector Double Steel Plate-Concrete Experimental Study on Hysteretic Performance of Composite Shear Wall. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.L. Study on Seismic Behavior of Composite Shear Wall with Double Steel Plates and Infill Concrete with Binding Bars. Ph.D. Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
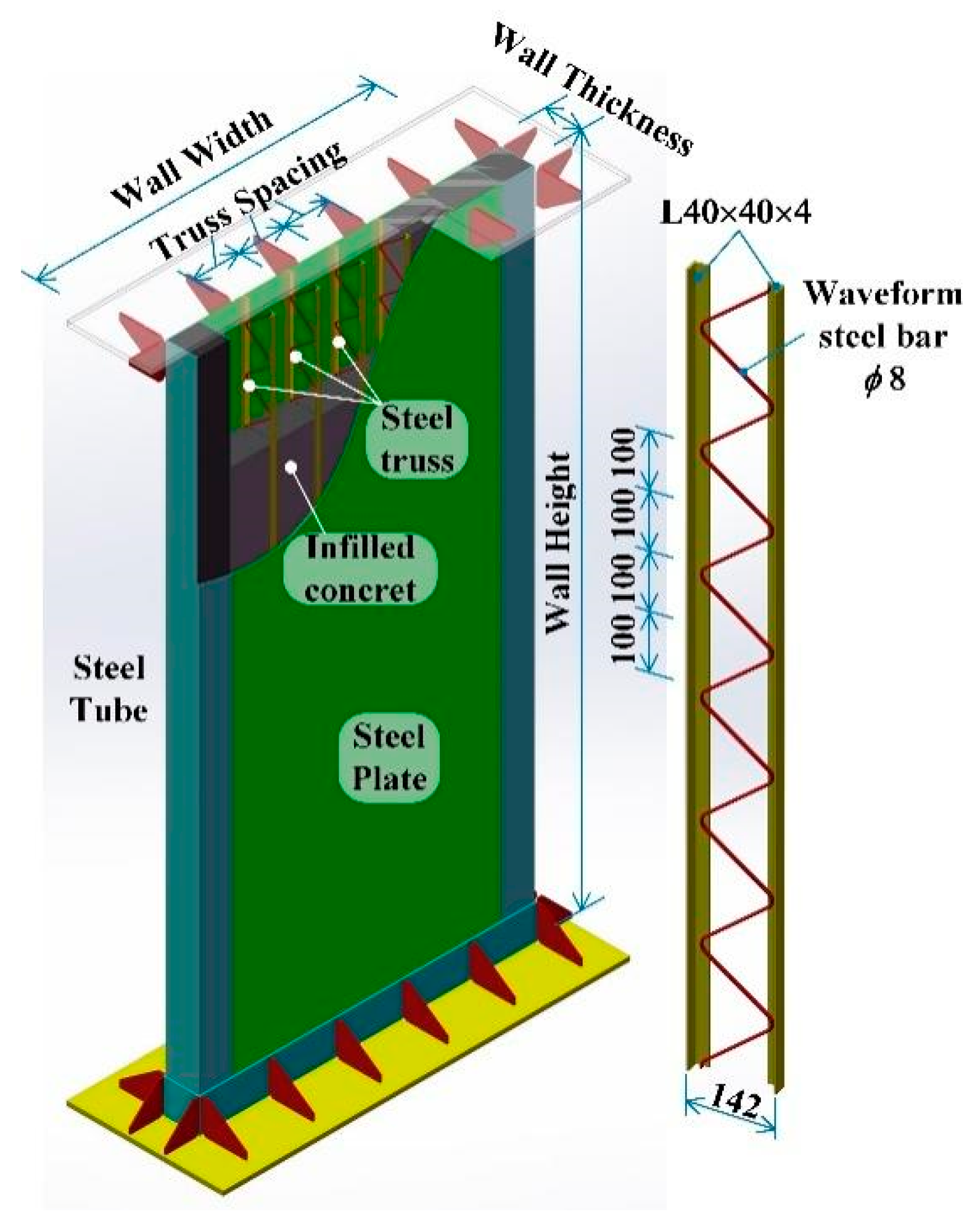

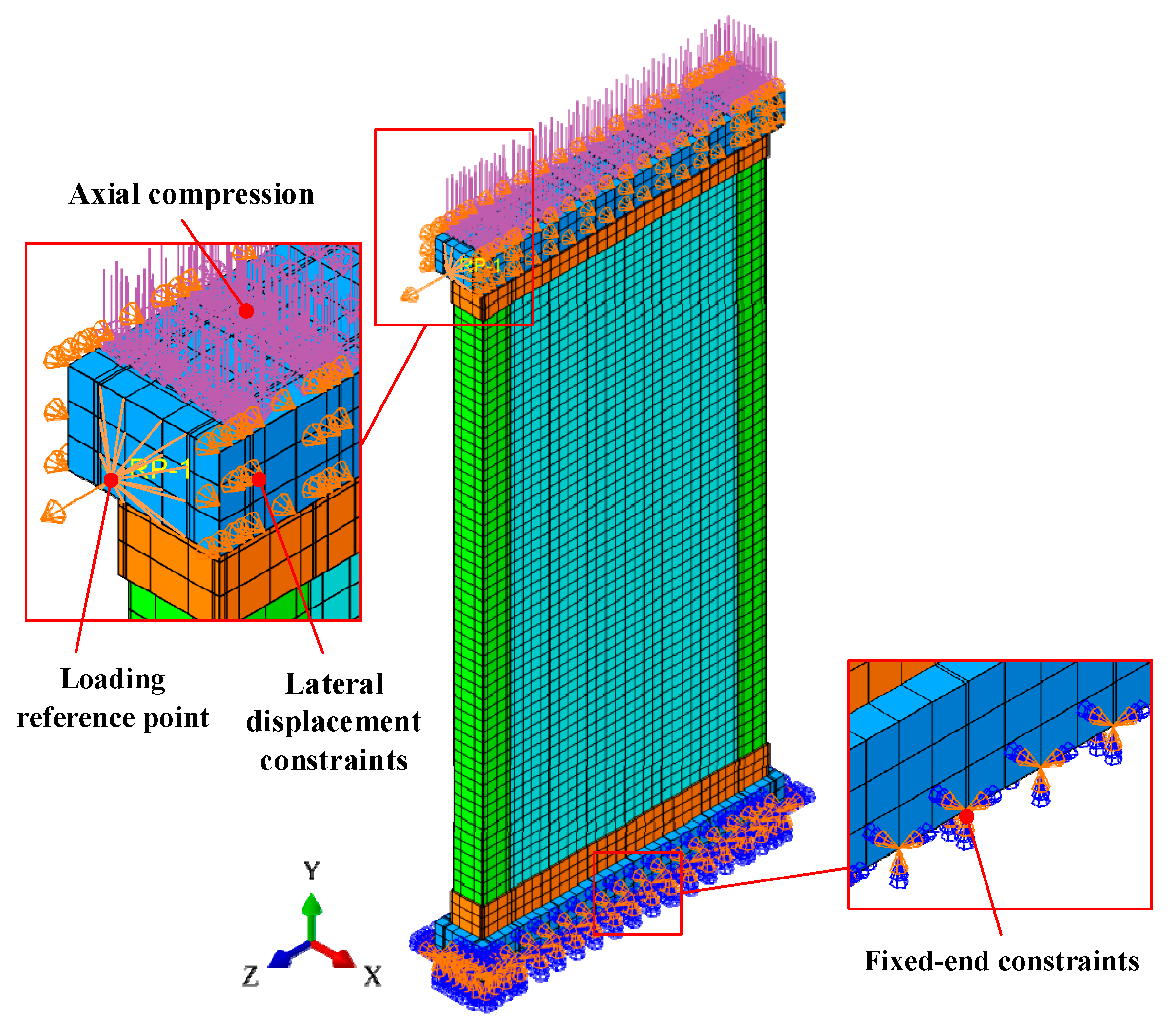
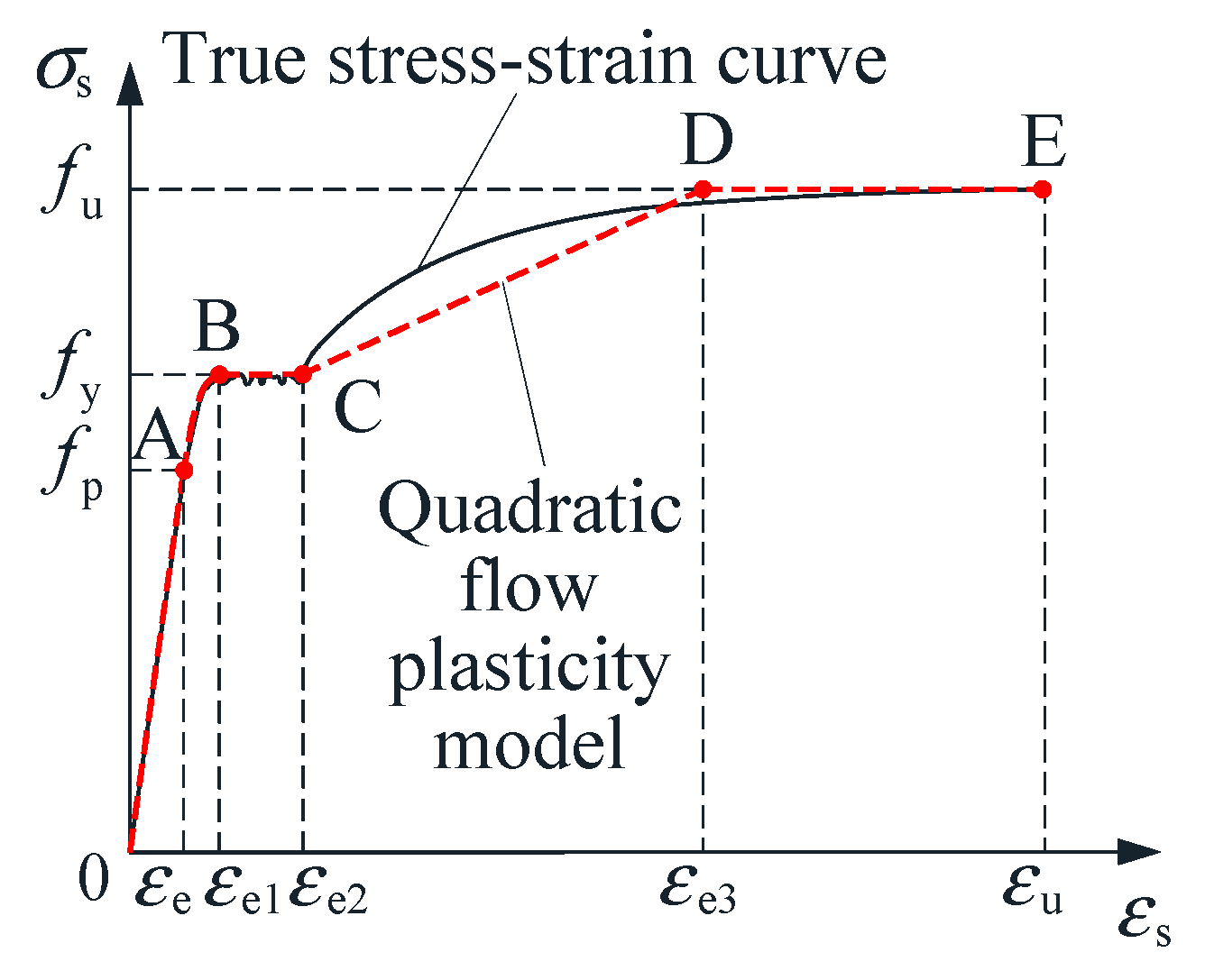
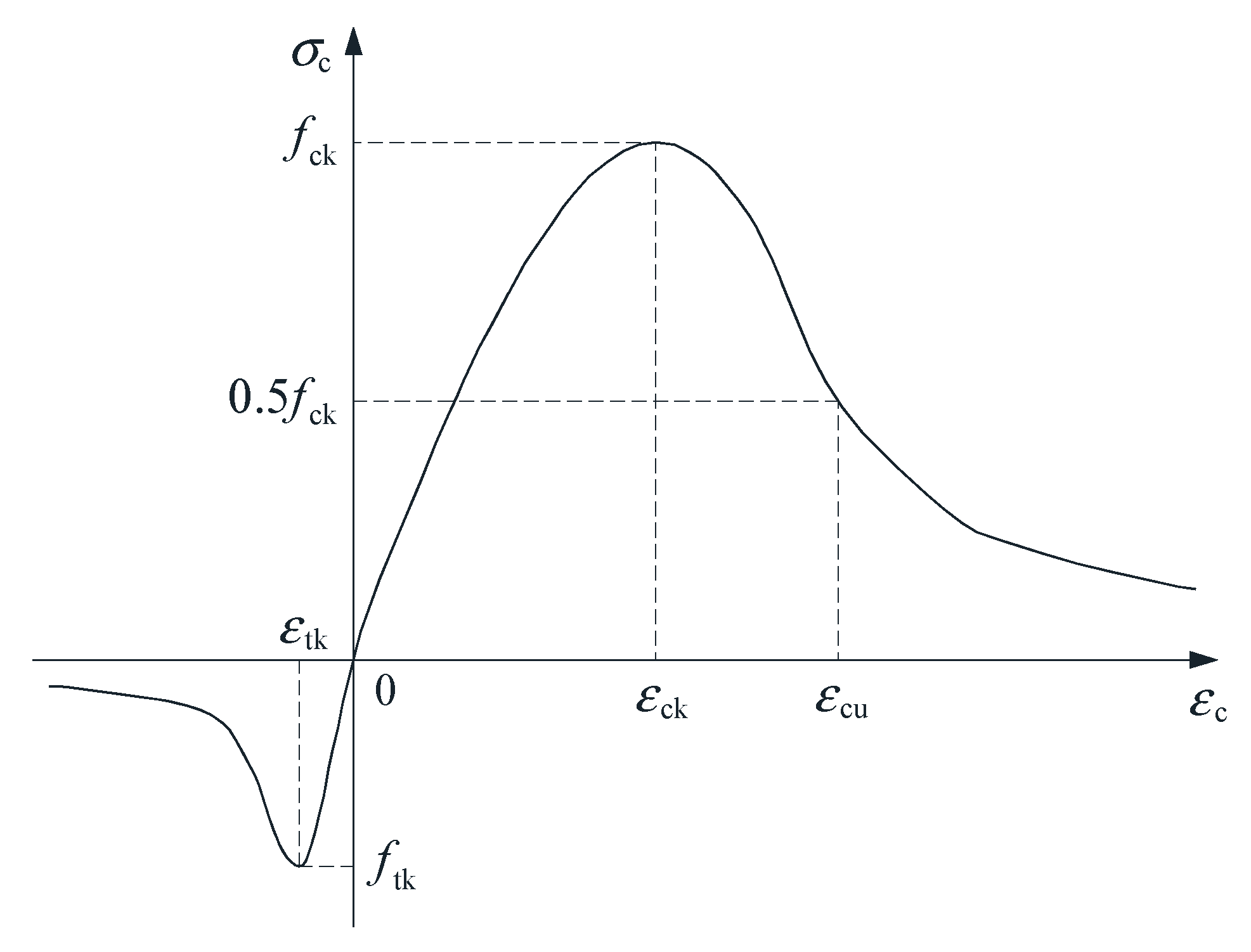
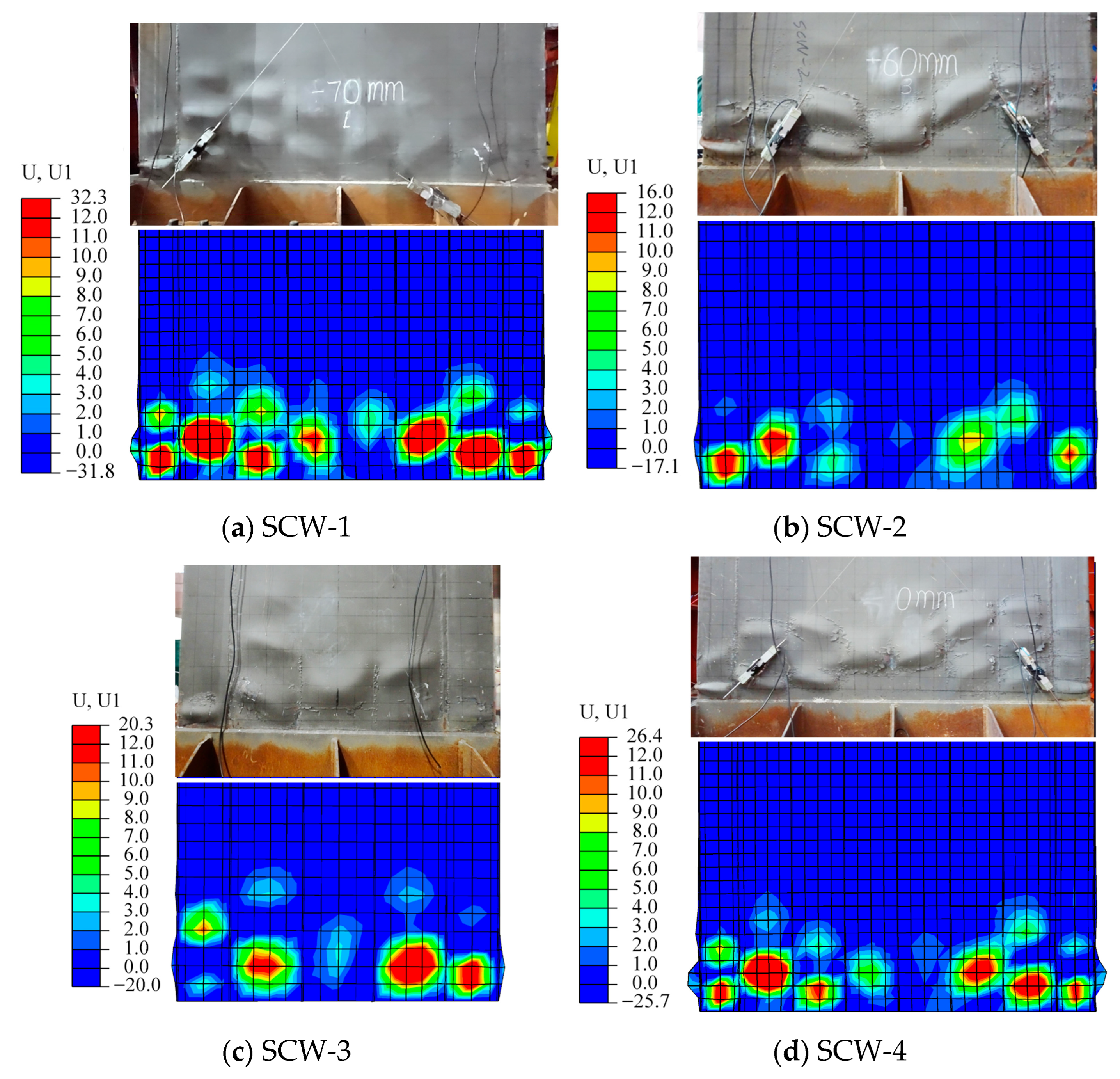


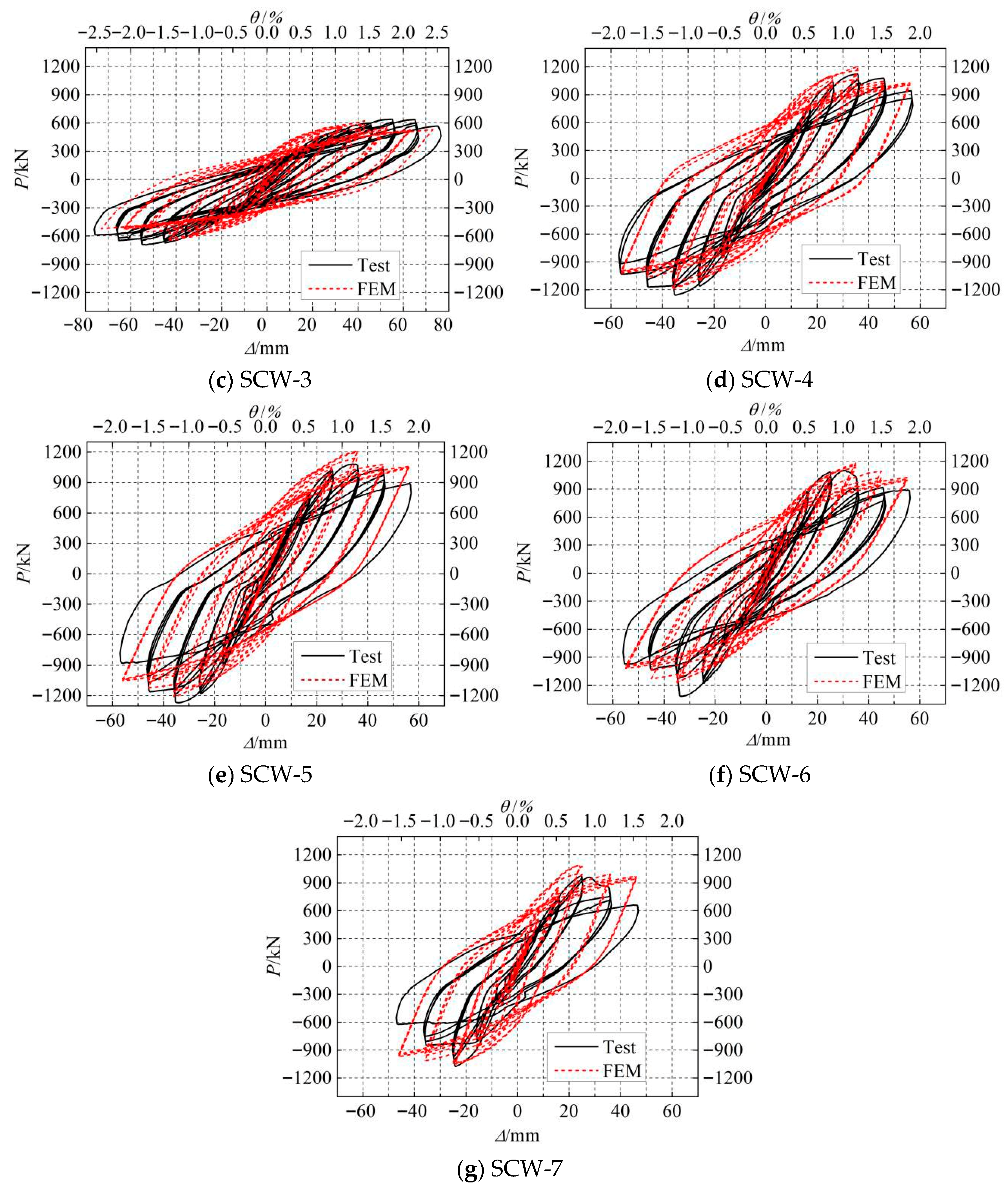



| Specimens No. | Steel Plate Thickness (mm) | Wall Height (mm) | Wall Width (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Truss Spacing (mm) | Aspect Ratios | Spacing-Thickness Ratio | Axial Compression Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCW-1 | 4 | 3000 | 1200 | 150 | 200 | 2.5 | 50 | 0.4 |
| SCW-2 | 4 | 3000 | 1200 | 150 | 200 | 2.5 | 50 | 0.6 |
| SCW-3 | 4 | 3000 | 900 | 150 | 200 | 3.3 | 50 | 0.6 |
| SCW-4 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 200 | 2.0 | 50 | 0.5 |
| SCW-5 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 200 | 2.0 | 50 | 0.6 |
| SCW-6 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 300 | 2.0 | 75 | 0.6 |
| SCW-7 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 400 | 2.0 | 100 | 0.6 |
| Specimen No. | Initial Shear Stiffness, K0 (kN/mm) | Max. Equivalent Viscous Damping Coeff., he, max (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEA | Test | Ratio | FEA | Test | Ratio | |
| SCW-1 | 63.8 | 60.3 | 1.06 | 22.5 | 23.9 | 0.94 |
| SCW-2 | 35.2 | 36.3 | 0.97 | 23.8 | 27.9 | 0.85 |
| SCW-3 | 20.7 | 21.7 | 0.95 | 24.6 | 23.8 | 1.03 |
| SCW-4 | 60.3 | 59.5 | 1.01 | 25 | 21.4 | 1.17 |
| SCW-5 | 59.2 | 54.5 | 1.09 | 24.2 | 20.6 | 1.17 |
| SCW-6 | 56.1 | 57.6 | 0.98 | 25.1 | 26.7 | 0.94 |
| SCW-7 | 56.5 | 54 | 1.05 | 26.5 | 32.8 | 0.81 |
| Models No. | Steel Plate Thickness (mm) | Wall Height (mm) | Wall Width (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Column Side Length (mm) | Truss Spacing (mm) | Axial Compression Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WN-0.1 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 0.1 |
| WN-0.2 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 0.2 |
| WN-0.3 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 0.3 |
| WN-0.4 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 0.4 |
| WN-0.5 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 0.5 |
| WN-0.6 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 0.6 |
| WN-0.7 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 0.7 |
| WN-0.8 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 0.8 |
| Model No. | Steel Plate Thickness (mm) | Wall Height (mm) | Wall Width (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Column Side Length (mm) | Truss Spacing (mm) | Aspect Ratio | Axial Compression Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WA-0.75 | 4 | 3000 | 4000 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 0.75 | 0.6 |
| WA-1.0 | 4 | 3000 | 3000 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| WA-1.5 | 4 | 3000 | 2000 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 1.5 | 0.6 |
| WA-2.0 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 2.0 | 0.6 |
| WA-2.5 | 4 | 3000 | 1200 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 2.5 | 0.6 |
| WA-3.0 | 4 | 3000 | 1000 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 3.0 | 0.6 |
| WA-3.3 | 4 | 3000 | 800 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 3.3 | 0.6 |
| WA-4.3 | 4 | 3000 | 700 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 4.3 | 0.6 |
| Model No. | Steel Plate Thickness (mm) | Wall Height (mm) | Wall Width (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Column Side Length (mm) | Truss Spacing (mm) | Spacing–Thickness Ratio | Axial Compression Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS-37.5 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 37.5 | 0.6 |
| WS-50 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 50 | 0.6 |
| WS-60 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 240 | 60 | 0.6 |
| WS-75 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 300 | 75 | 0.6 |
| WS-100 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 400 | 100 | 0.6 |
| Model No. | Steel Plate Thickness (mm) | Wall Height (mm) | Wall Width (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Column Side Length (mm) | Angle Steel Specification (mm) | Steel Bar Diameter (mm) | Axial Compression Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WST-20&8 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 20 × 20 × 4 * | 8 | 0.6 |
| WST-30&8 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 30 × 30 × 4 | 8 | 0.6 |
| WST-40&8 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 40 × 40 × 4 | 8 | 0.6 |
| WST-45&8 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 45 × 45 × 4 | 8 | 0.6 |
| WST-50&8 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 50 × 50 × 4 | 8 | 0.6 |
| WST-40&6 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 40 × 40 × 4 | 6 | 0.6 |
| WST-40&10 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 40 × 40 × 4 | 10 | 0.6 |
| WST-40&12 | 4 | 3000 | 1500 | 150 | 150 | 40 × 40 × 4 | 12 | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Tian, P.; Shan, Z.; Tang, D. Shear Strength of Double-Skin Truss-Reinforced Composite Shear Walls: Finite Element Analysis. Buildings 2025, 15, 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203788
Han J, Tian P, Shan Z, Tang D. Shear Strength of Double-Skin Truss-Reinforced Composite Shear Walls: Finite Element Analysis. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203788
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jianhong, Panpan Tian, Zhihan Shan, and Dingbo Tang. 2025. "Shear Strength of Double-Skin Truss-Reinforced Composite Shear Walls: Finite Element Analysis" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203788
APA StyleHan, J., Tian, P., Shan, Z., & Tang, D. (2025). Shear Strength of Double-Skin Truss-Reinforced Composite Shear Walls: Finite Element Analysis. Buildings, 15(20), 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203788





