Life Cycle Environmental Evaluation Framework for Mining Waste Concrete: Insights from Molybdenum Tailings Concrete in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production of Molybdenum Tailings Concrete
2.2. Life Cycle Assessment Methodology
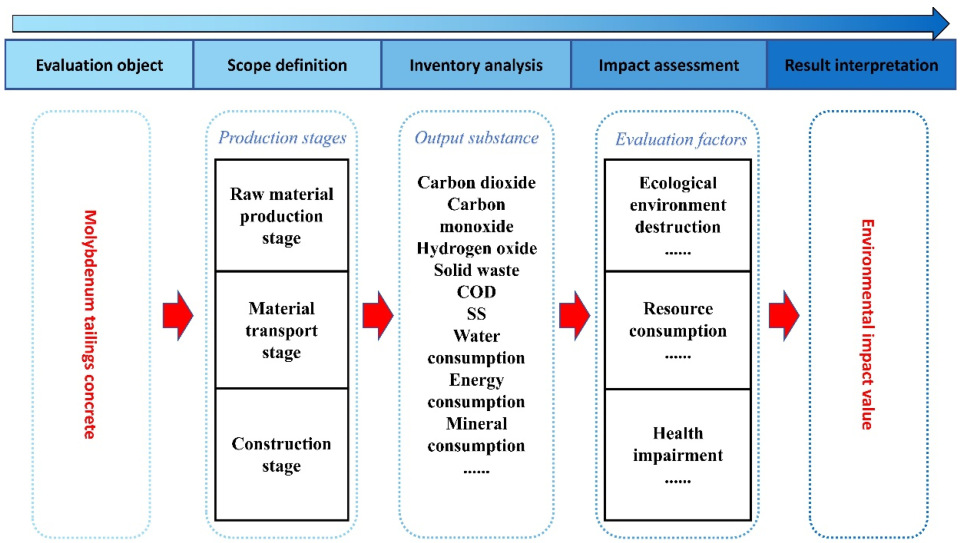
2.2.1. Theoretical Foundation of the Three-Dimensional LCA Framework
2.2.2. Resource–Environment–Economy LCA
2.2.3. LCA Framework
2.2.4. Evaluation Framework for BEPAS and BHIAS Based on Willingness to Pay
2.3. Life Cycle Inventory Analysis
- (1)
- Raw Material Production Stage: This stage accounts for the environmental burdens of each input. The core of our methodological approach here was the selection of specific, relevant data sources for each material to accurately represent the production processes defined in our study.
- (2)
- Raw Material Transportation Stage: A key part of our modeling was the dynamic calculation of transportation impacts. The distances, vehicle types, and efficiencies were not generic but were determined through GIS analysis and supplier interviews specifically for this study, making the transport assessment a defined part of our methodology.
- (3)
- Concrete Preparation Stage: The inventory for this stage was built by applying standardized energy consumption factors to the operational parameters of the mixing plant assumed in our experimental setup.
2.3.1. Raw Material Production Stage
Environmental Impact Inventory of Cement
Environmental Impact Inventory of Natural Coarse and Fine Aggregates
Environmental Impact Inventory of Molybdenum Tailings
Environmental Impact Inventory of High-Efficiency Water Reducers
Environmental Impact Inventory of Water, Electricity, Fossil Fuels, and Derived Energy Sources
2.3.2. Raw Material Transportation Stage
2.3.3. Concrete Preparation Stage
2.4. Model and Calculation
2.4.1. Environmental Cost List Model
Raw Material Production-Stage List Model
Raw Material Transportation Stage Inventory Model
Construction Stage List Model
2.4.2. Classification and Quantification of Environmental Impacts
2.5. Weighted Comprehensive Evaluation
2.6. Methodological Note on Global Applicability of WTP Model
2.7. Research Limitations
- (1)
- Incompleteness of the system boundary: This study adopts a “cradle-to-gate” system boundary, focusing on raw material production, transportation, and construction stages, but does not include the use, maintenance, and end-of-life recycling stages. This may lead to an underestimation of the full life cycle environmental impact and limits the generalizability of the conclusions across different regions or long-term scenarios.
- (2)
- Limitations of region-specific data and transportation networks: The evaluation framework is based on data specific to China, which means that the results need to be recalibrated according to local policies, economic preferences, and logistical conditions when applied to other regions to ensure accuracy.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Life Cycle Impact of Molybdenum Tailings Concrete Production Process
3.1.1. Production Stage
3.1.2. Transportation Stage
3.1.3. Construction Stage
3.1.4. Summary of Molybdenum Tailings Concrete Production Process
3.2. Mechanical Properties, Energy Consumption, Environmental Impact, and WTP of Molybdenum Tailings Concrete
3.2.1. Energy Consumption Impact
3.2.2. Environmental Implications
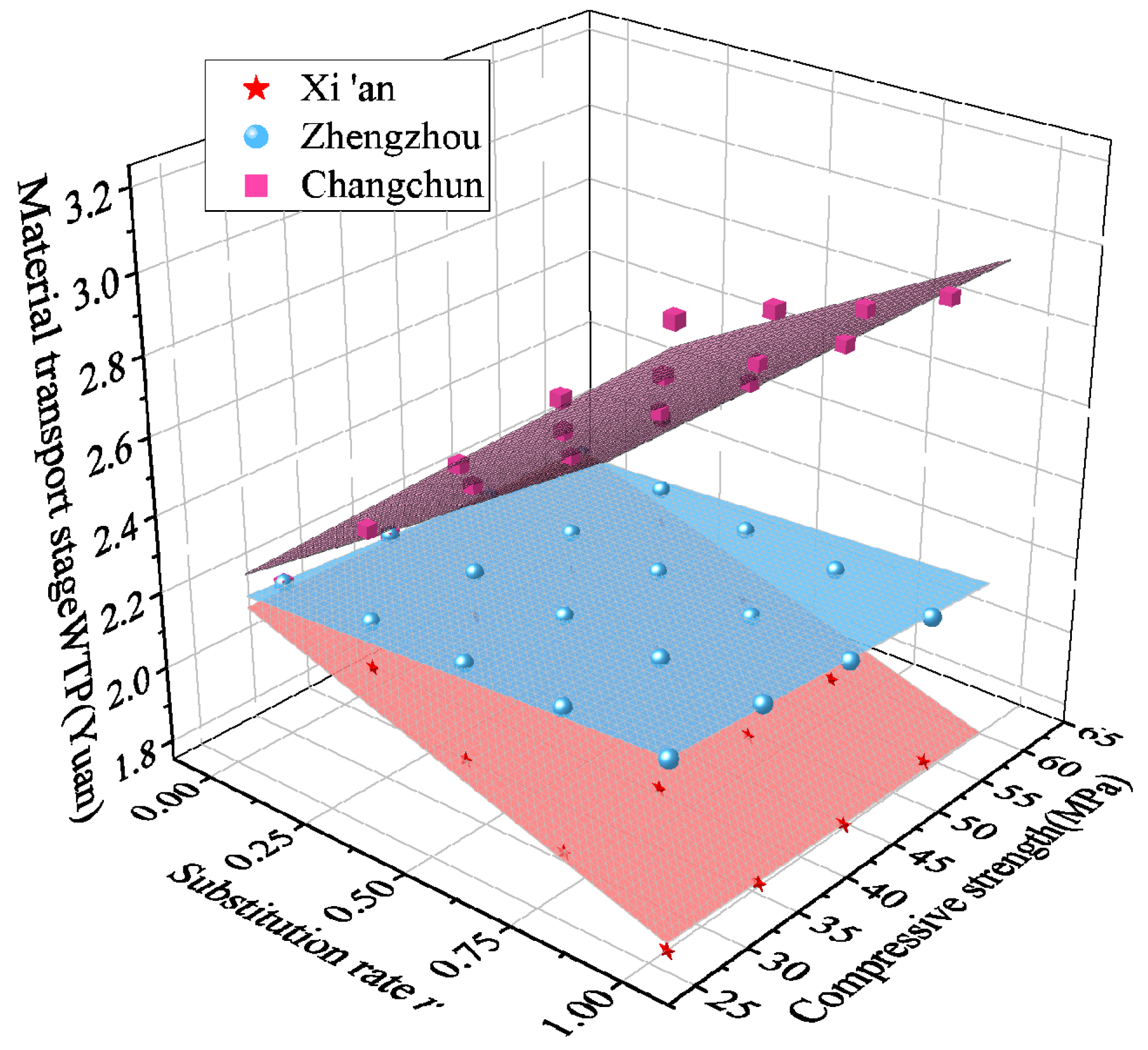
3.2.3. Environmental Cost Impact
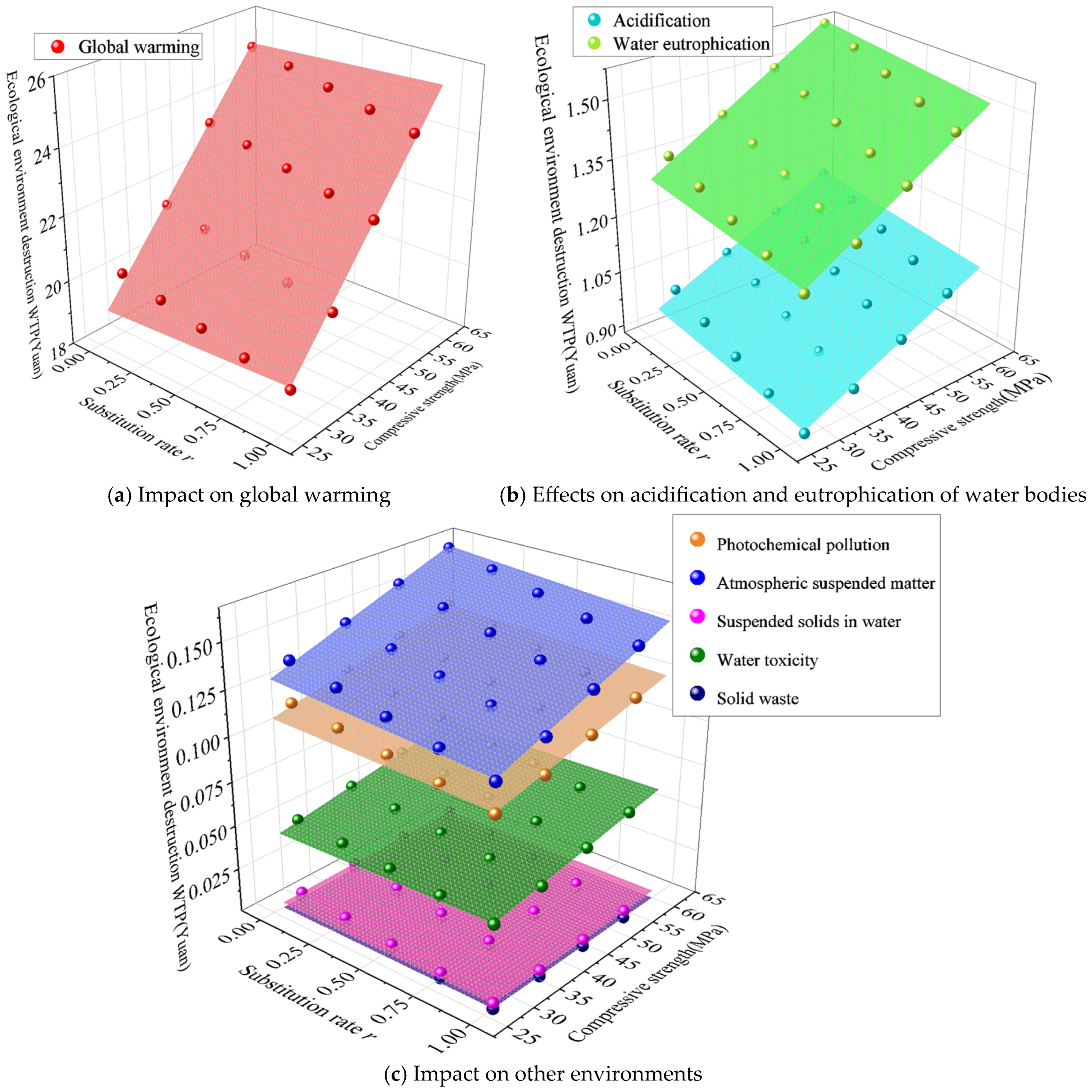
3.3. Environmental and Mechanical Analysis
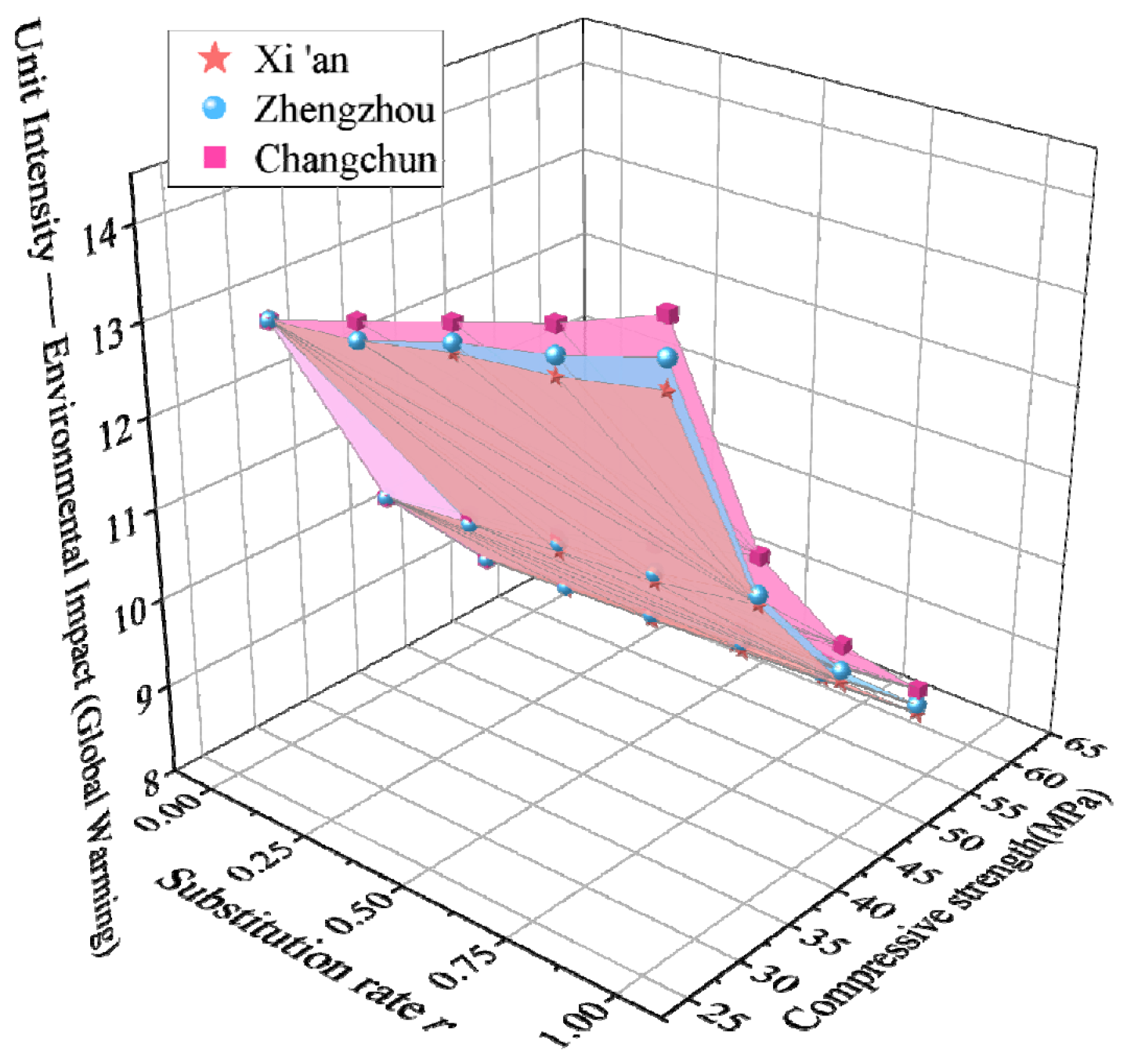
3.3.1. Unit Strength-Energy Consumption
3.3.2. Unit Strength Environmental Impact
- (1)
- Improvement of hydration efficiency, which reduces binder content by 22–28%, directly reducing carbon emissions from raw material production;
- (2)
- Process carbon reduction, due to a 30% shortening of the steam curing cycle;
- (3)
- Densified microstructure, which extends the service life and achieves carbon sharing optimization throughout the life cycle.
3.3.3. Unit Strength Environmental Cost
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Molybdenum tailings, as a substitute for river sand, demonstrate significant environmental advantages. Their use reduces resource consumption, alleviates ecological pressure, and improves energy efficiency, particularly in low- to medium-strength concrete. The incorporation of tailings also contributes to reduced greenhouse gas emissions through the “strength dilution effect,” especially in high-strength concrete grades.
- (2)
- A synergistic relationship between substitution rate and concrete strength was observed. Within the 10–60% replacement range, increasing strength consistently offsets the environmental cost rise associated with higher substitution rates. The optimal balance was found at 20–40% substitution with C40–C50 strength levels, providing a practical pathway for performance–sustainability optimization.
- (3)
- Regional analysis indicates that transportation distance significantly affects energy consumption and carbon emissions. Short-distance regions such as Xi’an exhibit lower marginal costs in the transportation stage, while longer distances in cities like Changchun amplify logistical burdens. These findings underscore the importance of localized supply chain strategies in sustainable construction.
- (4)
- The coupling of environmental cost and mechanical performance reveals a multidimensional optimization strategy. By improving compressive strength and controlling substitution rates, molybdenum tailings concrete can achieve high strength and low environmental cost simultaneously. This supports a viable path toward green, low-carbon material innovation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Material Flow | Resource Consumption and Material Emissions | Unit | Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enter | Limestone | kg | 1.10 × 103 |
| Sandstone | kg | 5.95 × 101 | |
| Iron powder | kg | 3.11 × 101 | |
| Fly ash | kg | 1.38 × 102 | |
| Plaster | kg | 5.68 × 101 | |
| Slag | kg | 1.31 × 102 | |
| Electricity | kWh | 9.53 × 101 | |
| Water | kg | 9.05 × 102 | |
| Output | CO2 | kg | 7.94 × 102 |
| SO2 | kg | 9.02 × 10−1 | |
| NOx | kg | 1.87 × 100 | |
| CO | kg | 4.72 × 10−1 | |
| COD | kg | 2.15 × 10−2 | |
| SS | kg | 4.56 × 10−2 | |
| Oil | kg | 1.30 × 10−3 | |
| Dust | kg | 1.03 × 100 |
| Material Flow | Resource Consumption and Environmental Impact | Unit | Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enter | Run-of-coal | kg | 5.62 × 10−1 |
| Crude | kg | 4.81 × 10−2 | |
| Natural gas | m3 | 2.67 × 10−1 | |
| Gravel | kg | 4.49 × 10−2 | |
| Iron ore | kg | 1.00 × 10−2 | |
| Barite | kg | 3.61 × 10−4 | |
| Sulfur | kg | 1.04 × 10−7 | |
| Output | CO2 | kg | 9.93 × 10−1 |
| CH4 | kg | 2.68 × 10−3 | |
| SO2 | kg | 1.04 × 10−2 | |
| NMVOC | kg | 3.41 × 10−4 | |
| COD | kg | 5.38 × 10−4 | |
| CO | kg | 3.95 × 10−3 | |
| NOx | kg | 5.15 × 10−3 | |
| N2O | kg | 6.98 × 10−6 | |
| Zn | kg | 3.52 × 10−6 | |
| Cr | kg | 2.61 × 10−6 | |
| Cd | kg | 4.91 × 10−8 | |
| Pb | kg | 6.54 × 10−7 | |
| As | kg | 1.96 × 10−7 | |
| Ni | kg | 4.05 × 10−6 | |
| V | kg | 9.96 × 10−7 | |
| Hg | kg | 2.26 × 10−8 | |
| Dust | kg | 5.08 × 10−3 |
| Serial Number | River Sand | Molybdenum Tailings | Water | P.O Cement | Stone | Water Reducing Agent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 775.00 | 0.00 | 180 | 390 | 1040 | 3.90 |
| M25-C30 | 581.25 | 193.75 | 180 | 390 | 1040 | 3.90 |
| M50-C30 | 387.50 | 387.50 | 180 | 390 | 1040 | 3.90 |
| M75-C30 | 193.75 | 581.25 | 180 | 390 | 1040 | 3.90 |
| M100-C30 | 0.00 | 775.00 | 180 | 390 | 1040 | 3.90 |
| M0-C40 | 730.00 | 0.00 | 174 | 425 | 1065 | 4.25 |
| M25-C40 | 547.50 | 182.50 | 174 | 425 | 1065 | 4.25 |
| M50-C40 | 365.00 | 365.00 | 174 | 425 | 1065 | 4.25 |
| M75-C40 | 182.50 | 547.50 | 174 | 425 | 1065 | 4.25 |
| M100-C40 | 0.00 | 730.00 | 174 | 425 | 1065 | 4.25 |
| M0-C50 | 675.00 | 0.00 | 170 | 472 | 1085 | 4.72 |
| M25-C50 | 506.25 | 168.75 | 170 | 472 | 1085 | 4.72 |
| M50-C50 | 337.50 | 337.50 | 170 | 472 | 1085 | 4.72 |
| M75-C50 | 168.75 | 506.25 | 170 | 472 | 1085 | 4.72 |
| M100-C50 | 0.00 | 675.00 | 170 | 472 | 1085 | 4.72 |
| M0-C60 | 628.00 | 0.00 | 165 | 516 | 1110 | 5.16 |
| M25-C60 | 471.00 | 157.00 | 165 | 516 | 1110 | 5.16 |
| M50-C60 | 314.00 | 314.00 | 165 | 516 | 1110 | 5.16 |
| M75-C60 | 157.00 | 471.00 | 165 | 516 | 1110 | 5.16 |
| M100-C60 | 0.00 | 628.00 | 165 | 516 | 1110 | 5.16 |
| Material Flow | Resource Consumption and Environmental Impact | Unit | Shaanxi | National |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enter | Run-of-coal | g | 3.28 × 10−2 | 4.59 × 102 |
| Clean coal | g | 0.00 × 100 | 1.50 × 10−1 | |
| Other coal washing | g | 1.20 × 102 | 6.74 × 100 | |
| Coke oven gas | m3 | 1.31 × 10−2 | 3.41 × 100 | |
| Blast furnace gas | m3 | 1.85 × 10−2 | 2.47 × 101 | |
| Converter gas | m3 | 0.00 × 100 | 2.46 × 100 | |
| Crude | g | 0.00 × 100 | 2.79 × 10−2 | |
| Diesel fuel | g | 3.55 × 10−2 | 9.15 × 10−2 | |
| Fuel oil | g | 0.00 × 100 | 1.11 × 10−1 | |
| Natural gas | m3 | 7.42 × 10−4 | 5.25 × 100 | |
| Heat | MJ | 5.13 × 10−1 | 9.61 × 100 | |
| Output | CO2 | g | 7.91 × 102 | 1.04 × 103 |
| CH4 | g | 1.19 × 10−2 | 1.56 × 10−2 | |
| N2O | g | 9.01 × 10−3 | 1.19 × 10−2 | |
| SO2 | g | 6.81 × 100 | 2.23 × 101 | |
| CO | g | 1.71 × 10−1 | 8.85 × 100 | |
| NOx | g | 3.13 × 100 | 4.08 × 100 | |
| Dust | g | 7.81 × 100 | 1.01 × 101 |
| Resource Consumption and Material Emissions | Raw Coal (g/MJ) | Crude (g/MJ) | Natural Gas (g/MJ) | Gasoline (g/kg) | Diesel Fuel (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw coal | 5.02 × 101 | 1.33 × 10−1 | 1.33 × 10−1 | 3.74 × 100 | 3.71 × 100 |
| Clean coal | 2.76 × 10−2 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 3.05 × 100 | 3.02 × 100 |
| Coke | 3.69 × 10−3 | 1.40 × 10−4 | 1.40 × 10−4 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 |
| Crude | 0.00 × 100 | 2.66 × 101 | 4.07 × 10−1 | 1.37 × 103 | 1.36 × 103 |
| Gasoline | 8.03 × 10−2 | 1.96 × 10−2 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 |
| Diesel fuel | 1.91 × 10−1 | 1.74 × 10−1 | 3.38 × 10−1 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 |
| Kerosene | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 8.70 × 10−2 | 8.60 × 10−2 |
| Fuel oil | 3.34 × 10−4 | 2.78 × 10−2 | 0.00 × 100 | 3.37 × 101 | 3.34 × 101 |
| LPG | 1.99 × 10−5 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 1.86 × 100 | 1.84 × 100 |
| Coke oven gas | 1.36 × 10−4 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 |
| Natural gas | 3.14 × 10−3 | 1.12 × 10−1 | 3.79 × 10−2 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 |
| Heat | 2.18 × 10−3 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 |
| Electricity | 1.55 × 10−1 | 3.69 × 10−2 | 4.09 × 10−2 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 |
| CO2 | 4.10 × 100 | 3.07 × 100 | 3.33 × 100 | 5.42 × 102 | 5.36 × 102 |
| CH4 | 4.53 × 10−4 | 1.74 × 10−4 | 1.89 × 10−4 | 1.91 × 10−2 | 1.89 × 10−2 |
| N2O | 8.74 × 10−5 | 6.18 × 10−5 | 4.89 × 10−5 | 6.34 × 10−3 | 6.24 × 10−3 |
| SO2 | 2.67 × 10−2 | 2.58 × 10−2 | 2.73 × 10−2 | 1.90 × 100 | 1.87 × 100 |
| CO | 6.96 × 10−2 | 3.71 × 10−2 | 4.05 × 10−2 | 2.50 × 100 | 2.43 × 100 |
| NOx | 1.56 × 10−2 | 7.31 × 10−3 | 6.85 × 10−3 | 1.28 × 100 | 1.26 × 100 |
| Dust | 2.97 × 10−2 | 8.91 × 10−3 | 8.38 × 10−2 | 6.97 × 10−1 | 6.10 × 10−3 |
| Type of Impact | Emissions (kg) | Equivalent Pollutants (kg) | Characterization Factors (kg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Warming | CO2 | CO2 | 1.00 × 100 |
| CO | CO2 | 3.00 × 100 | |
| CH4 | CO2 | 2.50 × 101 | |
| N2O | CO2 | 2.98 × 102 | |
| Acidification | SO2 | SO2 | 1.00 × 100 |
| NOx | SO2 | 7.00 × 10−1 | |
| Eutrophication of water | NOx | NO3- | 1.35 × 100 |
| N2O | NO3- | 1.41 × 100 | |
| COD | NO3- | 2.30 × 10−1 | |
| Photochemical pollution | CH4 | C2H4 | 3.03 × 10−4 |
| NOx | C2H4 | 3.00 × 10−2 | |
| N2O | C2H4 | 3.00 × 10−4 | |
| NMVOC | C2H4 | 3.00 × 10−2 | |
| Solid waste | Solid waste | Solid waste | 1.00 × 100 |
| Atmospheric suspension | Dust | Atmospheric suspension | 1.00 × 100 |
| Water suspension | SS | SS | 1.00 × 100 |
| Water toxicity | Pb | Pb | 1.00 × 100 |
| Zn | Pb | 3.48 × 102 | |
| Cr | Pb | 3.80 × 100 | |
| Cd | Pb | 2.77 × 101 | |
| As | Pb | 3.91 × 101 | |
| Ni | Pb | 7.59 × 101 | |
| V | Pb | 2.94 × 102 | |
| Hg | Pb | 8.22 × 101 |
| Serial Number | Global Warming | Acidification | Eutrophicate | Pollution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 2.63 × 101 | 2.89 × 10−1 | 4.86 × 10−1 | 1.08 × 10−2 |
| M25-C30 | 2.50 × 101 | 2.75 × 10−1 | 4.62 × 10−1 | 1.03 × 10−2 |
| M50-C30 | 2.38 × 101 | 2.61 × 10−1 | 4.39 × 10−1 | 9.79 × 10−2 |
| M75-C30 | 2.25 × 101 | 2.48 × 10−1 | 4.15 × 10−1 | 9.27 × 10−2 |
| M100-C30 | 2.13 × 101 | 2.34 × 10−1 | 3.92 × 10−1 | 8.75 × 10−2 |
| M0-C40 | 2.61 × 101 | 2.87 × 10−1 | 4.82 × 10−1 | 1.08 × 10−2 |
| M25-C40 | 2.50 × 101 | 2.74 × 10−1 | 4.60 × 10−1 | 1.03 × 10−2 |
| M50-C40 | 2.38 × 101 | 2.61 × 10−1 | 4.38 × 10−1 | 9.78 × 10−2 |
| M75-C40 | 2.26 × 101 | 2.48 × 10−1 | 4.16 × 10−1 | 9.29 × 10−2 |
| M100-C40 | 2.14 × 101 | 2.35 × 10−1 | 3.94 × 10−1 | 8.79 × 10−2 |
| M0-C50 | 2.58 × 101 | 2.84 × 10−1 | 4.76 × 10−1 | 1.06 × 10−2 |
| M25-C50 | 2.48 × 101 | 2.72 × 10−1 | 4.56 × 10−1 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M50-C50 | 2.37 × 101 | 2.59 × 10−1 | 4.35 × 10−1 | 9.71 × 10−2 |
| M75-C50 | 2.26 × 101 | 2.47 × 10−1 | 4.15 × 10−1 | 9.26 × 10−2 |
| M100-C50 | 2.15 × 101 | 2.35 × 10−1 | 3.95 × 10−1 | 8.80 × 10−2 |
| M0-C60 | 2.57 × 101 | 2.82 × 10−1 | 4.73 × 10−1 | 1.05 × 10−2 |
| M25-C60 | 2.47 × 101 | 2.71 × 10−1 | 4.54 × 10−1 | 1.01 × 10−2 |
| M50-C60 | 2.37 × 101 | 2.59 × 10−1 | 4.35 × 10−1 | 9.70 × 10−2 |
| M75-C60 | 2.27 × 101 | 2.48 × 10−1 | 4.16 × 10−1 | 9.28 × 10−2 |
| M100-C60 | 2.17 × 101 | 2.37 × 10−1 | 3.97 × 10−1 | 8.86 × 10−2 |
| Serial Number | Global Warming | Acidification | Eutrophicate | Pollution | Atmospheric Suspension | Water Suspension | Water Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 3.38 × 102 | 1.15 × 100 | 1.15 × 100 | 2.55 × 10−2 | 6.06 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M25-C30 | 3.36 × 102 | 1.13 × 100 | 1.13 × 100 | 2.52 × 10−2 | 5.88 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M50-C30 | 3.34 × 102 | 1.11 × 100 | 1.12 × 100 | 2.49 × 10−2 | 5.70 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M75-C30 | 3.32 × 102 | 1.08 × 100 | 1.11 × 100 | 2.46 × 10−2 | 5.52 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M100-C30 | 3.30 × 102 | 1.06 × 100 | 1.10 × 100 | 2.43 × 10−2 | 5.34 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M0-C40 | 3.66 × 102 | 1.23 × 100 | 1.24 × 100 | 2.75 × 10−2 | 6.43 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M25-C40 | 3.64 × 102 | 1.21 × 100 | 1.22 × 100 | 2.72 × 10−2 | 6.26 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M50-C40 | 3.62 × 102 | 1.19 × 100 | 1.21 × 100 | 2.69 × 10−2 | 6.09 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M75-C40 | 3.60 × 102 | 1.17 × 100 | 1.20 × 100 | 2.66 × 10−2 | 5.92 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M100-C40 | 3.58 × 102 | 1.15 × 100 | 1.19 × 100 | 2.64 × 10−2 | 5.75 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M0-C50 | 4.03 × 102 | 1.34 × 100 | 1.36 × 100 | 3.01 × 10−2 | 6.91 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M25-C50 | 4.02 × 102 | 1.32 × 100 | 1.35 × 100 | 2.99 × 10−2 | 6.75 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M50-C50 | 4.00 × 102 | 1.30 × 100 | 1.34 × 100 | 2.96 × 10−2 | 6.59 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M75-C50 | 3.98 × 102 | 1.28 × 100 | 1.32 × 100 | 2.94 × 10−2 | 6.44 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M100-C50 | 3.96 × 10−2 | 1.26 × 100 | 1.31 × 100 | 2.91 × 10−2 | 6.28 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M0-C60 | 4.39 × 102 | 1.44 × 100 | 1.47 × 10−0 | 3.26 × 10−2 | 7.37 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M25-C60 | 4.37 × 102 | 1.42 × 100 | 1.46 × 100 | 3.24 × 10−2 | 7.22 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M50-C60 | 4.35 × 102 | 1.41 × 100 | 1.45 × 100 | 3.22 × 10−2 | 7.07 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M75-C60 | 4.34 × 102 | 1.39 × 100 | 1.44 × 100 | 3.19 × 10−2 | 6.93 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M100-C60 | 4.32 × 102 | 1.37 × 100 | 1.43 × 100 | 3.17 × 10−2 | 6.78 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| Serial Number | Global Warming | Acidification | Eutrophicate | Pollution | Atmospheric Suspension | Water Suspension | Water Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 3.38 × 102 | 1.15 × 100 | 1.15 × 100 | 2.55 × 10−2 | 6.06 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M25-C30 | 3.36 × 102 | 1.13 × 100 | 1.14 × 100 | 2.52 × 10−2 | 5.91 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M50-C30 | 3.34 × 102 | 1.11 × 100 | 1.12 × 100 | 2.49 × 10−2 | 5.75 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M75-C30 | 3.32 × 102 | 1.09 × 100 | 1.11 × 100 | 2.47 × 10−2 | 5.60 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M100-C30 | 3.31 × 102 | 1.07 × 100 | 1.10 × 100 | 2.44 × 10−2 | 5.44 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−2 | 7.71 × 10−3 |
| M0-C40 | 3.66 × 102 | 1.23 × 100 | 1.24 × 100 | 2.75 × 10−2 | 6.43 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M25-C40 | 3.64 × 102 | 1.22 × 100 | 1.23 × 100 | 2.72 × 10−2 | 6.28 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M50-C40 | 3.62 × 102 | 1.20 × 100 | 1.22 × 100 | 2.70 × 10−2 | 6.14 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M75-C40 | 3.61 × 102 | 1.18 × 100 | 1.21 × 100 | 2.67 × 10−2 | 5.99 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M100-C40 | 3.59 × 102 | 1.16 × 100 | 1.20 × 100 | 2.65 × 10−2 | 5.84 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−2 | 8.40 × 10−3 |
| M0-C50 | 4.03 × 102 | 1.34 × 100 | 1.36 × 100 | 3.01 × 10−2 | 6.91 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M25-C50 | 4.02 × 102 | 1.32 × 100 | 1.35 × 100 | 2.99 × 10−2 | 6.77 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M50-C50 | 4.00 × 102 | 1.31 × 100 | 1.34 × 100 | 2.97 × 10−2 | 6.64 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M75-C50 | 3.99 × 102 | 1.29 × 100 | 1.33 × 100 | 2.95 × 10−2 | 6.50 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M100-C50 | 3.97 × 102 | 1.27 × 100 | 1.32 × 100 | 2.92 × 10−2 | 6.37 × 10−1 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−3 |
| M0-C60 | 4.39 × 102 | 1.44 × 100 | 1.47 × 100 | 3.26 × 10−2 | 7.37 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M25-C60 | 4.37 × 102 | 1.43 × 100 | 1.46 × 100 | 3.24 × 10−2 | 7.24 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M50-C60 | 4.36 × 102 | 1.41 × 100 | 1.45 × 100 | 3.22 × 10−2 | 7.11 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M75-C60 | 4.34 × 102 | 1.39 × 100 | 1.44 × 100 | 3.20 × 10−2 | 6.99 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M100-C60 | 4.33 × 102 | 1.38 × 100 | 1.43 × 100 | 3.18 × 10−2 | 6.86 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| Serial Number | Global Warming | Acidification | Eutrophicate | Pollution | Atmospheric Suspension | Solid Waste |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 1.84 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.10 × 10−1 | 4.67 × 10 | 7.91 × 10−3 | 7.20 × 10−4 |
| M25-C30 | 1.84 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.10 × 10−1 | 4.67 × 10 | 7.91 × 10−3 | 7.20 × 10−4 |
| M50-C30 | 1.84 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.10 × 10−1 | 4.67 × 10 | 7.91 × 10−3 | 7.20 × 10−4 |
| M75-C30 | 1.84 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.10 × 10−1 | 4.67 × 10 | 7.91 × 10−3 | 7.20 × 10−4 |
| M100-C30 | 1.84 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.10 × 10−1 | 4.67 × 10 | 7.91 × 10−3 | 7.20 × 10−4 |
| M0-C40 | 1.85 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.11 × 10−1 | 4.69 × 10 | 7.94 × 10−3 | 6.96 × 10−4 |
| M25-C40 | 1.85 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.11 × 10−1 | 4.69 × 10 | 7.94 × 10−3 | 6.96 × 10−4 |
| M50-C40 | 1.85 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.11 × 10−1 | 4.69 × 10 | 7.94 × 10−3 | 6.96 × 10−4 |
| M75-C40 | 1.85 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.11 × 10−1 | 4.69 × 10 | 7.94 × 10−3 | 6.96 × 10−4 |
| M100-C40 | 1.85 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.11 × 10−1 | 4.69 × 10 | 7.94 × 10−3 | 6.96 × 10−4 |
| M0-C50 | 1.86 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.12 × 10−1 | 4.71 × 10 | 7.97 × 10−3 | 6.80 × 10−4 |
| M25-C50 | 1.86 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.12 × 10−1 | 4.71 × 10 | 7.97 × 10−3 | 6.80 × 10−4 |
| M50-C50 | 1.86 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.12 × 10−1 | 4.71 × 10 | 7.97 × 10−3 | 6.80 × 10−4 |
| M75-C50 | 1.86 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.12 × 10−1 | 4.71 × 10 | 7.97 × 10−3 | 6.80 × 10−4 |
| M100-C50 | 1.86 × 101 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 2.12 × 10−1 | 4.71 × 10 | 7.97 × 10−3 | 6.80 × 10−4 |
| M0-C60 | 1.87 × 101 | 1.19 × 10−1 | 2.13 × 10−1 | 4.74 × 10 | 8.02 × 10−3 | 6.60 × 10−4 |
| M25-C60 | 1.87 × 101 | 1.19 × 10 | 2.13 × 10−1 | 4.74 × 10 | 8.02 × 10−3 | 6.60 × 10−4 |
| M50-C60 | 1.87 × 101 | 1.19 × 10−1 | 2.13 × 10−1 | 4.74 × 10 | 8.02 × 10−3 | 6.60 × 10−4 |
| M75-C60 | 1.87 × 101 | 1.19 × 10−1 | 2.13 × 10−1 | 4.74 × 10 | 8.02 × 10−3 | 6.60 × 10−4 |
| M100-C60 | 1.87 × 101 | 1.19 × 10−1 | 2.13 × 10−1 | 4.74 × 10 | 8.02 × 10−3 | 6.60 × 10−4 |
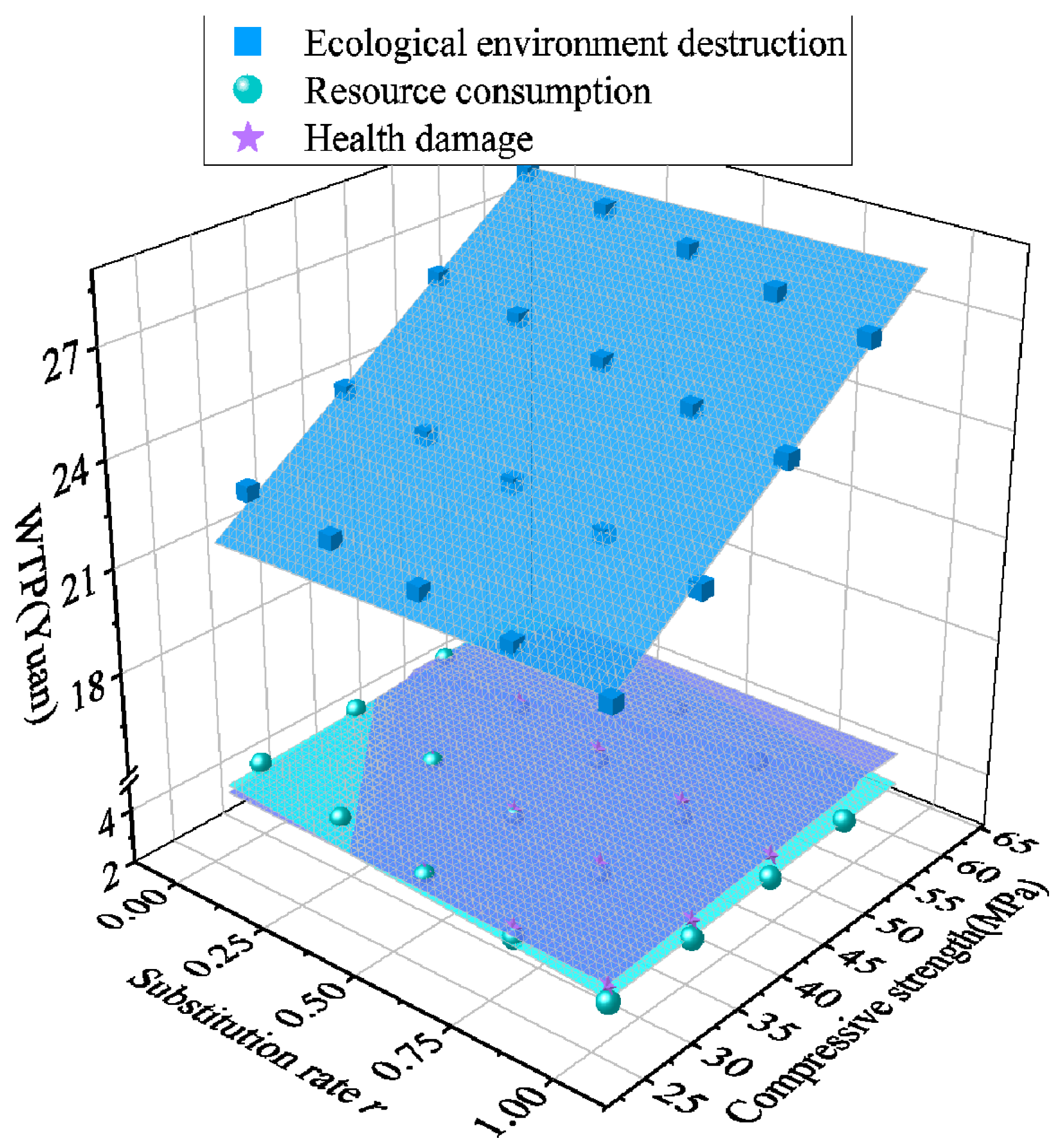
| Serial Number | Ecological Environment Damage WTP | Resource Consumption WTP | Health Damage WTP | Total WTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 1.94 × 101 | 4.38 × 100 | 4.26 × 100 | 2.80 × 101 |
| M25-C30 | 1.92 × 101 | 4.05 × 100 | 4.14 × 100 | 2.74 × 101 |
| M50-C30 | 1.91 × 101 | 3.72 × 100 | 4.02 × 100 | 2.68 × 101 |
| M75-C30 | 1.90 × 101 | 3.39 × 100 | 3.89 × 100 | 2.63 × 101 |
| M100-C30 | 1.88 × 101 | 3.06 × 100 | 3.77 × 100 | 2.57 × 101 |
| M0-C40 | 2.10 × 101 | 4.48 × 100 | 4.52 × 100 | 3.00 × 101 |
| M25-C40 | 2.08 × 101 | 4.17 × 100 | 4.40 × 100 | 2.94 × 101 |
| M50-C40 | 2.07 × 101 | 3.86 × 100 | 4.29 × 100 | 2.89 × 101 |
| M75-C40 | 2.06 × 101 | 3.55 × 100 | 4.17 × 100 | 2.83 × 101 |
| M100-C40 | 2.05 × 101 | 3.23 × 100 | 4.05 × 100 | 2.77 × 101 |
| M0-C50 | 2.31 × 101 | 4.61 × 100 | 4.86 × 100 | 3.26 × 101 |
| M25-C50 | 2.30 × 101 | 4.32 × 100 | 4.75 × 100 | 3.21 × 101 |
| M50-C50 | 2.29 × 101 | 4.03 × 100 | 4.64 × 100 | 3.15 × 101 |
| M75-C50 | 2.27 × 101 | 3.74 × 100 | 4.53 × 100 | 3.10 × 101 |
| M100-C50 | 2.26 × 101 | 3.45 × 100 | 4.43 × 100 | 3.05 × 101 |
| M0-C60 | 2.51 × 101 | 4.74 × 100 | 5.18 × 100 | 3.50 × 101 |
| M25-C60 | 2.50 × 101 | 4.47 × 100 | 5.08 × 100 | 3.46 × 101 |
| M50-C60 | 2.49 × 101 | 4.21 × 100 | 4.98 × 100 | 3.41 × 101 |
| M75-C60 | 2.48 × 101 | 3.94 × 100 | 4.88 × 100 | 3.36 × 101 |
| M100-C60 | 2.47 × 101 | 3.67 × 100 | 4.78 × 100 | 3.31 × 101 |
| Serial Number | Ecological Environment Damage WTP | Resource Consumption WTP | Health Damage WTP | Total WTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 1.94 × 101 | 4.38 × 100 | 4.26 × 100 | 2.80 × 101 |
| M25-C30 | 1.93 × 101 | 4.05 × 100 | 4.16 × 100 | 2.75 × 101 |
| M50-C30 | 1.91 × 101 | 3.72 × 100 | 4.05 × 100 | 2.69 × 101 |
| M75-C30 | 1.90 × 101 | 3.39 × 100 | 3.94 × 100 | 2.64 × 101 |
| M100-C30 | 1.89 × 101 | 3.06 × 100 | 3.84 × 100 | 2.58 × 101 |
| M0-C40 | 2.10 × 101 | 4.48 × 100 | 4.52 × 100 | 3.00 × 101 |
| M25-C40 | 2.09 × 101 | 4.17 × 100 | 4.42 × 100 | 2.95 × 101 |
| M50-C40 | 2.08 × 101 | 3.86 × 100 | 4.32 × 100 | 2.89 × 101 |
| M75-C40 | 2.06 × 101 | 3.55 × 100 | 4.22 × 100 | 2.84 × 101 |
| M100-C40 | 2.05 × 101 | 3.24 × 100 | 4.12 × 100 | 2.79 × 101 |
| M0-C50 | 2.31 × 101 | 4.61 × 100 | 4.86 × 100 | 3.26 × 101 |
| M25-C50 | 2.30 × 101 | 4.32 × 100 | 4.77 × 100 | 3.21 × 101 |
| M50-C50 | 2.29 × 101 | 4.03 × 100 | 4.67 × 100 | 3.16 × 101 |
| M75-C50 | 2.28 × 101 | 3.74 × 100 | 4.58 × 100 | 3.11 × 101 |
| M100-C50 | 2.27 × 101 | 3.46 × 100 | 4.49 × 100 | 3.06 × 101 |
| M0-C60 | 2.51 × 101 | 4.74 × 100 | 5.18 × 100 | 3.50 × 101 |
| M25-C60 | 2.50 × 101 | 4.47 × 100 | 5.10 × 100 | 3.46 × 101 |
| M50-C60 | 2.49 × 101 | 4.21 × 100 | 5.01 × 100 | 3.41 × 101 |
| M75-C60 | 2.48 × 101 | 3.94 × 100 | 4.92 × 100 | 3.37 × 101 |
| M100-C60 | 2.47 × 101 | 3.67 × 100 | 4.84 × 100 | 3.32 × 101 |
| Serial Number | Ecological Environment Damage WTP | Resource Consumption WTP | Health Damage WTP | Total WTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 2.63 × 101 | 2.89 × 10−1 | 4.86 × 10−1 | 1.08 × 10−2 |
| M25-C30 | 2.50 × 101 | 2.75 × 10−1 | 4.62 × 10−1 | 1.03 × 10−2 |
| M50-C30 | 2.38 × 101 | 2.61 × 10−1 | 4.39 × 10−1 | 9.79 × 10−3 |
| M75-C30 | 2.25 × 101 | 2.48 × 10−1 | 4.15 × 10−1 | 9.27 × 10−3 |
| M100-C30 | 2.13 × 101 | 2.34 × 10−1 | 3.92 × 10−1 | 8.75 × 10−3 |
| M0-C40 | 2.61 × 101 | 2.87 × 10−1 | 4.82 × 10−1 | 1.08 × 10−2 |
| M25-C40 | 2.50 × 101 | 2.74 × 10−1 | 4.60 × 10−1 | 1.03 × 10−2 |
| M50-C40 | 2.38 × 101 | 2.61 × 10−1 | 4.38 × 10−1 | 9.78 × 10−3 |
| M75-C40 | 2.26 × 101 | 2.48 × 10−1 | 4.16 × 10−1 | 9.29 × 10−3 |
| M100-C40 | 2.14 × 101 | 2.35 × 10−1 | 3.94 × 10−1 | 8.79 × 10−3 |
| M0-C50 | 2.58 × 101 | 2.84 × 10−1 | 4.76 × 10−1 | 1.06 × 10−2 |
| M25-C50 | 2.48 × 101 | 2.72 × 10−1 | 4.56 × 10−1 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| M50-C50 | 2.37 × 101 | 2.59 × 10−1 | 4.35 × 10−1 | 9.71 × 10−3 |
| M75-C50 | 2.26 × 101 | 2.47 × 10−1 | 4.15 × 10−1 | 9.26 × 10−3 |
| M100-C50 | 2.15 × 101 | 2.35 × 10−1 | 3.95 × 10−1 | 8.80 × 10−3 |
| M0-C60 | 2.57 × 101 | 2.82 × 10−1 | 4.73 × 10−1 | 1.05 × 10−2 |
| M25-C60 | 2.47 × 101 | 2.71 × 10−1 | 4.54 × 10−1 | 1.01 × 10−2 |
| M50-C60 | 2.37 × 101 | 2.59 × 10−1 | 4.35 × 10−1 | 9.70 × 10−3 |
| M75-C60 | 2.27 × 101 | 2.48 × 10−1 | 4.16 × 10−1 | 9.28 × 10−3 |
| M100-C60 | 2.17 × 101 | 2.37 × 10−1 | 3.97 × 10−1 | 8.86 × 10−3 |
| Serial Number | Ecological Environment Damage WTP | Resource Consumption WTP | Health Damage WTP | Total WTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 1.20 × 100 | 3.35 × 10−1 | 6.20 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
| M25-C30 | 1.20 × 100 | 3.35 × 10−1 | 6.20 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
| M50-C30 | 1.20 × 100 | 3.35 × 10−1 | 6.20 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
| M75-C30 | 1.20 × 100 | 3.35 × 10−1 | 6.20 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
| M100-C30 | 1.20 × 100 | 3.35 × 10−1 | 6.20 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
| M0-C40 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.27 × 10−1 | 6.22 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M25-C40 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.27 × 10−1 | 6.22 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M50-C40 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.27 × 10−1 | 6.22 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M75-C40 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.27 × 10−1 | 6.22 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M100-C40 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.27 × 10−1 | 6.22 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M0-C50 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.21 × 10−1 | 6.24 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M25-C50 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.21 × 10−1 | 6.24 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M50-C50 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.21 × 10−1 | 6.24 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M75-C50 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.21 × 10−1 | 6.24 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M100-C50 | 1.21 × 100 | 3.21 × 10−1 | 6.24 × 10−2 | 1.59 × 100 |
| M0-C60 | 1.22 × 100 | 3.15 × 10−1 | 6.28 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
| M25-C60 | 1.22 × 100 | 3.15 × 10−1 | 6.28 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
| M50-C60 | 1.22 × 100 | 3.15 × 10−1 | 6.28 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
| M75-C60 | 1.22 × 100 | 3.15 × 10−1 | 6.28 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
| M100-C60 | 1.22 × 100 | 3.15 × 10−1 | 6.28 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 100 |
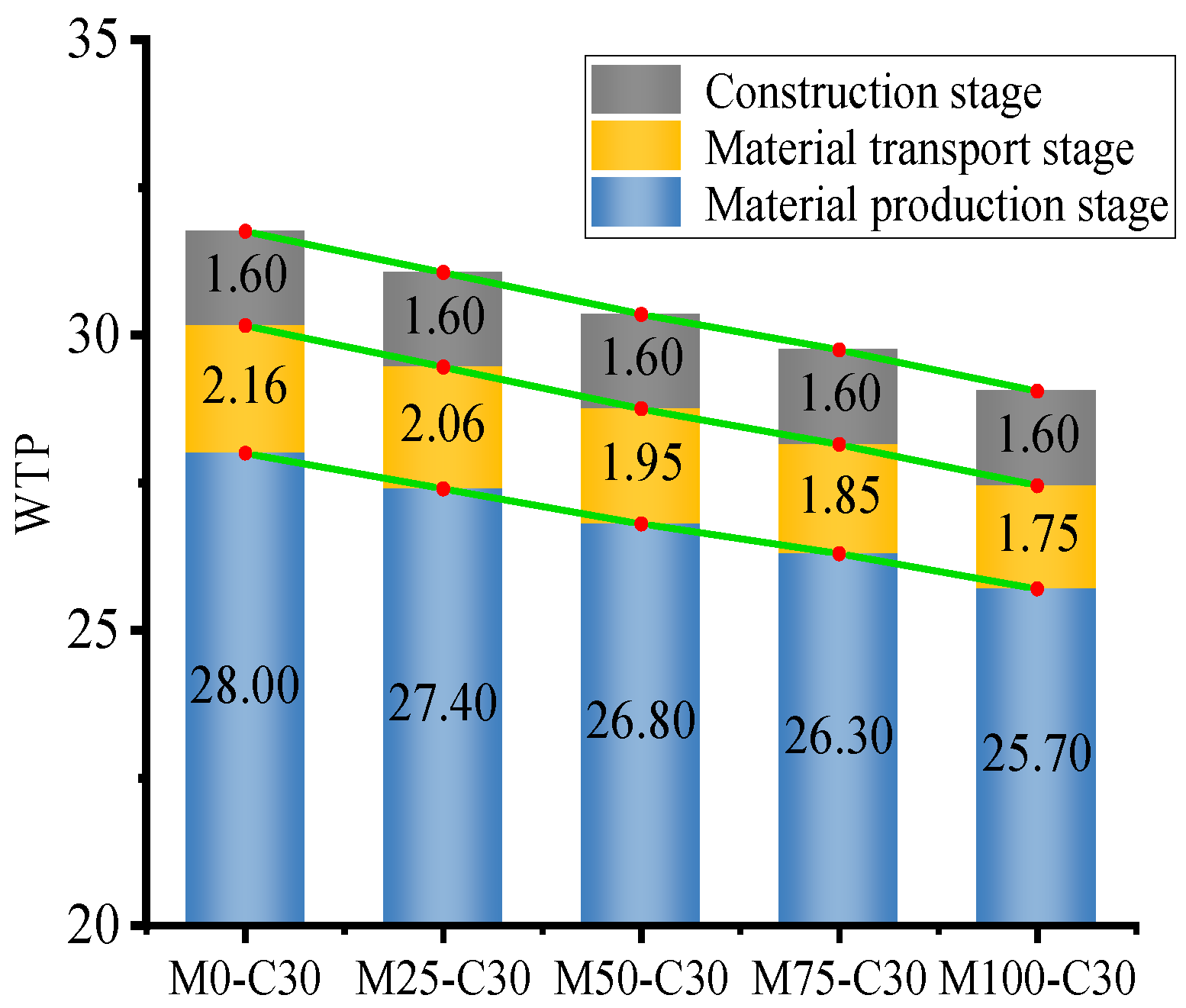
| Serial Number | Raw Material Production-Stage WTP | Raw Material Transportation Stage WTP | Construction Stage WTP | Total WTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 2.80 × 101 | 2.16 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.18 × 101 |
| M25-C30 | 2.74 × 101 | 2.06 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.11 × 101 |
| M50-C30 | 2.68 × 101 | 1.95 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.04 × 101 |
| M75-C30 | 2.63 × 101 | 1.85 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 2.97 × 101 |
| M100-C30 | 2.57 × 101 | 1.75 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 2.90 × 101 |
| M0-C40 | 3.00 × 101 | 2.15 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.37 × 101 |
| M25-C40 | 2.94 × 101 | 2.05 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.31 × 101 |
| M50-C40 | 2.89 × 101 | 1.95 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.24 × 101 |
| M75-C40 | 2.83 × 101 | 1.86 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.18 × 101 |
| M100-C40 | 2.77 × 101 | 1.76 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.11 × 101 |
| M0-C50 | 3.26 × 101 | 2.12 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.63 × 101 |
| M25-C50 | 3.21 × 101 | 2.03 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.57 × 101 |
| M50-C50 | 3.15 × 101 | 1.94 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.51 × 101 |
| M75-C50 | 3.10 × 101 | 1.85 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.45 × 101 |
| M100-C50 | 3.05 × 101 | 1.76 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.39 × 101 |
| M0-C60 | 3.50 × 101 | 2.11 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.87 × 101 |
| M25-C60 | 3.46 × 101 | 2.03 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.82 × 101 |
| M50-C60 | 3.41 × 101 | 1.94 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.76 × 101 |
| M75-C60 | 3.36 × 101 | 1.86 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.71 × 101 |
| M100-C60 | 3.31 × 101 | 1.78 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.65 × 101 |
| Serial Number | Raw Material Production-Stage WTP | Raw Material Transportation Stage WTP | Construction Stage WTP | Total WTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 2.80 × 101 | 2.16 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.18 × 101 |
| M25-C30 | 2.75 × 101 | 2.06 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.11 × 101 |
| M50-C30 | 2.69 × 101 | 1.95 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.05 × 101 |
| M75-C30 | 2.64 × 101 | 1.85 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 2.98 × 101 |
| M100-C30 | 2.58 × 101 | 1.75 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 2.92 × 101 |
| M0-C40 | 3.00 × 101 | 2.15 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.37 × 101 |
| M25-C40 | 2.95 × 101 | 2.05 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.31 × 101 |
| M50-C40 | 2.89 × 101 | 1.95 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.25 × 101 |
| M75-C40 | 2.84 × 101 | 1.86 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.19 × 101 |
| M100-C40 | 2.79 × 101 | 1.76 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.12 × 101 |
| M0-C50 | 3.26 × 101 | 2.12 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.63 × 101 |
| M25-C50 | 3.21 × 101 | 2.03 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.57 × 101 |
| M50-C50 | 3.16 × 101 | 1.94 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.51 × 101 |
| M75-C50 | 3.11 × 101 | 1.85 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.46 × 101 |
| M100-C50 | 3.06 × 101 | 1.76 × 100 | 1.59 × 100 | 3.40 × 101 |
| M0-C60 | 3.50 × 101 | 2.11 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.87 × 101 |
| M25-C60 | 3.46 × 101 | 2.03 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.82 × 101 |
| M50-C60 | 3.41 × 101 | 1.94 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.77 × 101 |
| M75-C60 | 3.37 × 101 | 1.86 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.71 × 101 |
| M100-C60 | 3.32 × 101 | 1.78 × 100 | 1.60 × 100 | 3.66 × 101 |
| Serial Number | No Allocation Method | Allocation Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption MJ | Energy Saving Ratio | Energy Consumption MJ | Energy Saving Ratio | |
| M0-C30 | 3.10 × 102 | / | 3.10 × 102 | / |
| M25-C30 | 3.02 × 102 | 2.63% | 3.04 × 102 | 1.98% |
| M50-C30 | 2.94 × 102 | 2.70% | 2.98 × 102 | 2.02% |
| M75-C30 | 2.86 × 102 | 2.77% | 2.92 × 102 | 2.06% |
| M100-C30 | 2.77 × 102 | 2.85% | 2.85 × 102 | 2.11% |
| M0-C40 | 3.29 × 102 | / | 3.29 × 102 | / |
| M25-C40 | 3.22 × 102 | 2.33% | 3.24 × 102 | 1.76% |
| M50-C40 | 3.14 × 102 | 2.38% | 3.18 × 102 | 1.79% |
| M75-C40 | 3.06 × 102 | 2.44% | 3.12 × 102 | 1.82% |
| M100-C40 | 2.99 × 102 | 2.50% | 3.06 × 102 | 1.85% |
| M0-C50 | 3.55 × 102 | / | 3.55 × 102 | / |
| M25-C50 | 3.48 × 102 | 2.00% | 3.50 × 102 | 1.51% |
| M50-C50 | 3.41 × 102 | 2.04% | 3.44 × 102 | 1.53% |
| M75-C50 | 3.34 × 102 | 2.08% | 3.39 × 102 | 1.55% |
| M100-C50 | 3.27 × 102 | 2.12% | 3.34 × 102 | 1.58% |
| M0-C60 | 3.80 × 102 | / | 3.80 × 102 | / |
| M25-C60 | 3.73 × 102 | 1.74% | 3.75 × 102 | 1.31% |
| M50-C60 | 3.67 × 102 | 1.77% | 3.70 × 102 | 1.33% |
| M75-C60 | 3.60 × 102 | 1.80% | 3.65 × 102 | 1.35% |
| M100-C60 | 3.53 × 102 | 1.83% | 3.60 × 102 | 1.36% |
References
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, J.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Ta, W.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics, source analysis, and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements pollution in soil of dense molybdenum tailing ponds area in central China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettima, A.; Hussin, M.; Ahmad, Y.; Mirza, J. Evaluation of iron ore tailings as replacement for fine aggregate in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 72, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshassi, M. Global warming potential implications of US waste LCA assumptions: A perturbation-based approach for decision support. Waste Manag. 2025, 204, 114953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yang, Y.; Ruan, K.; Wu, D.; Xu, Y.; Jacobs, D.F.; Zeng, S. Combined application of sewage sludge, bagasse, and molybdenum tailings ameliorates rare earth mining wasteland soil. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 1775–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.; Cui, X.; Ning, N.; Zhou, C. Hydration reaction of cementitious materials prepared with molybdenum tailings. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2018, 66, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, P.M.; Fraser, L.H.; Gardner, W.C.; Broersma, K.; Karakatsoulis, J.; Phillips, M.E. Long term carbon sequestration potential of biosolids-amended copper and molybdenum mine tailings following mine site reclamation. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 117, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordo, B.; Rathje, E.; Kumar, K. Runout of liquefaction-induced tailings dam failure: Influence of earthquake motions and residual strength. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2025, 194, 109371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onesorge Miranda Lopes, T.; Rodrigues da Silveira, C.; Araujo da Silva, J.; Guedes, T.; Adler Tavella, R.; Coimbra Rola, R.; Aparecida Marques, J.; Delfino Vieira, C.E.; Bianchini, A.; de Martinez Gaspar Martins, C. A six-year ecotoxicological assessment of the Doce River and coastal marine areas impacted by the Fundão tailings dam failure, Brazil. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 371, 125897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Chang, Z.; Leng, H.; Zhong, H.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Y. Experimental investigation on properties of gold tailings recycled brick-concrete aggregate concrete under microwave curing. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Xu, R.; Wang, L.; Tang, H. Research on resource comprehensive utilization of granite-type sulfide mine tailings. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2738, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; He, M.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Che, H.; Cheng, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Sun, B.; et al. Resource utilization of waste tailings: Simulated removal of nitrogen from secondary effluent by autotrophic denitrification based on pyrite tailings. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 949618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Basic research on the preparation of mineral admixtures with iron ore tailings. Non-Met. Mines 2020, 43, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Yang, A.; Zhang, Q. Pollution and Biotoxicity of Molybdenum-nickel Mine Tailing and Smelting Waste. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Su, R.X.; Yuan, J.; Ma, H.Y. Experimental study on the frost resistance of molybdenum tailings concrete. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 3313–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Bai, Q.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S. Uniaxial compressive stress-strain model of Molybdenum tailings concrete after high-temperature exposure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 428, 136343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, C.-J. Experimental study on the mechanical properties of C30 molybdenum tailings concrete after high-temperature and sulfate corrosion. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Comprehensive Assessment of Environmental Impact of Fly Ash Concrete Life Cycle. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. Research on the Life Cycle Evaluation of a Copper Tailings Resource Utilization Process in Jiangxi Province. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J. Research on the Life Cycle Evaluation of Copper and Tungsten Tailings Resource Utilization Process. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Kurda, R.; Silvestre, J.; de Brito, J. Life cycle assessment of concrete made with high volume of recycled concrete aggregates and fly ash. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 139, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziminezhad, M.; Habibi, A.; Jamhiri, B.; Bamshad, O.; Aziminezhad, M. Beyond carbon: An integrated LCA–MCDA framework for circularity measurement of ordinary and geopolymer concrete. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2026, 116, 108133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keykha, M.; Einollahipeer, F.; Abyar, H.; Erfani, M. Life cycle assessment of copper concentrate production and improvement potentials for tailing management. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2025, 21, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, H.; Rinne, M.; Elomaa, H.; Aromaa, J.; Lundström, M. Environmental impacts of lithium hydroxide monohydrate production from spodumene concentrate—Life Cycle Assessment Based on Simulation. Miner. Eng. 2024, 209, 108632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugas, R.A.; Luca, C.; Stephan, P.; Stefanie, H. Toward sustainable reprocessing and valorization of sulfidic copper tailings: Scenarios and prospective LCA. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporchia, F.; Bruno, M.; Neri, E.; Pulselli, F.M.; Patrizi, N.; Bastianoni, S. Complementing emergy evaluation and life cycle assessment for enlightening the environmental benefits of using engineered timber in the building sector. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 970, 179030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emily, G.S.; Kíra, L.; Henrikke, B.; Thomas, E. Transparent or hidden choices: Exploring perceptions and practices of LCA in building projects. Build. Environ. 2025, 285 Pt A, 113439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibalsadati, F.; Karimi, N.; Mim, S.J.; Ng, K.T.W. Thematic evolution of Life Cycle Assessment in construction and demolition waste management: Before and after ISO 14040 and the Paris Agreement. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 111, 113482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, B.; Aoife, H.W.; Jonathan, N.; Ellie, M.; Stephen, A. Hybrid life cycle assessment (H-LCA) for buildings and construction materials: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Build. Environ. 2025, 272, 112630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. Research on Environmental Impact Assessment System and Application of Construction Engineering. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X. Research on Human Health Damage Evaluation System During the Life Cycle of Construction Engineering. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Dandautiya, R.; Singh, P. Utilization potential of fly ash and copper tailings in concrete as partial replacement of cement along with life cycle assessment. Waste Manag. 2019, 99, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Zhang, Z. Research on the physical and chemical environment status in the life cycle of cement. J. Civ. Eng. 2004, 37, 86–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X. Life Cycle Evaluation of China’s Cement Industry. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K. Research on the Preparation of Recycled Concrete and Mortar Using Construction Waste. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Yang, C. Comparative life cycle assessment of conventional and dry stack tailings disposal schemes: A case study in northern China. Minerals 2022, 12, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Research on the High-Performance Concrete Properties of High-Titanium Slag and Its Slurry-Bone Interface Action Mechanism. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R. Environmental Coordination Evaluation of Naphthalene and Polycarboxylic Acid Water Reducing Agents. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Research on Environmental Impact Assessment of Life Cycle of Commercial Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Yang, J.; Lu, B. Analysis of the life cycle list of provincial thermal power supply in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7192–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Yang, J. Analysis of the life cycle list of fossil energy in China. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 1592–1600. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 2589-2020; General Rules for Calculation of the Comprehensive Energy Consumption. State Administration for Market Regulation; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Cao, X. Environmental Impact Assessment and Comparative Study on Industrialized Residential and Traditional Residential Construction. Ph.D. Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Cui, X.; Kang, S.; Ding, Y. Sustainable applications for utilizing molybdenum tailings in concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 122020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Cui, X.; Zhang, S. Utilization of molybdenum tailings in concrete manufacturing: A review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, W.; Yuan, K.K.; Rong, C.X. Properties and application of thixotropic cement paste backfill with molybdenum tailings. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 391, 136169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Damare, A.; Gupta, R. Strength and durability characteristics of copper tailing concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jabri, K.; Hisada, M.; Al-Saidy, A.; Al-Oraimi, S. Performance of high strength concrete made with copper slag as a fine aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Qu, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Huang, Z. A comparative study on mechanical and environmental performance of concrete-filled steel tubes using molybdenum tailing aggregate. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 186, 107100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




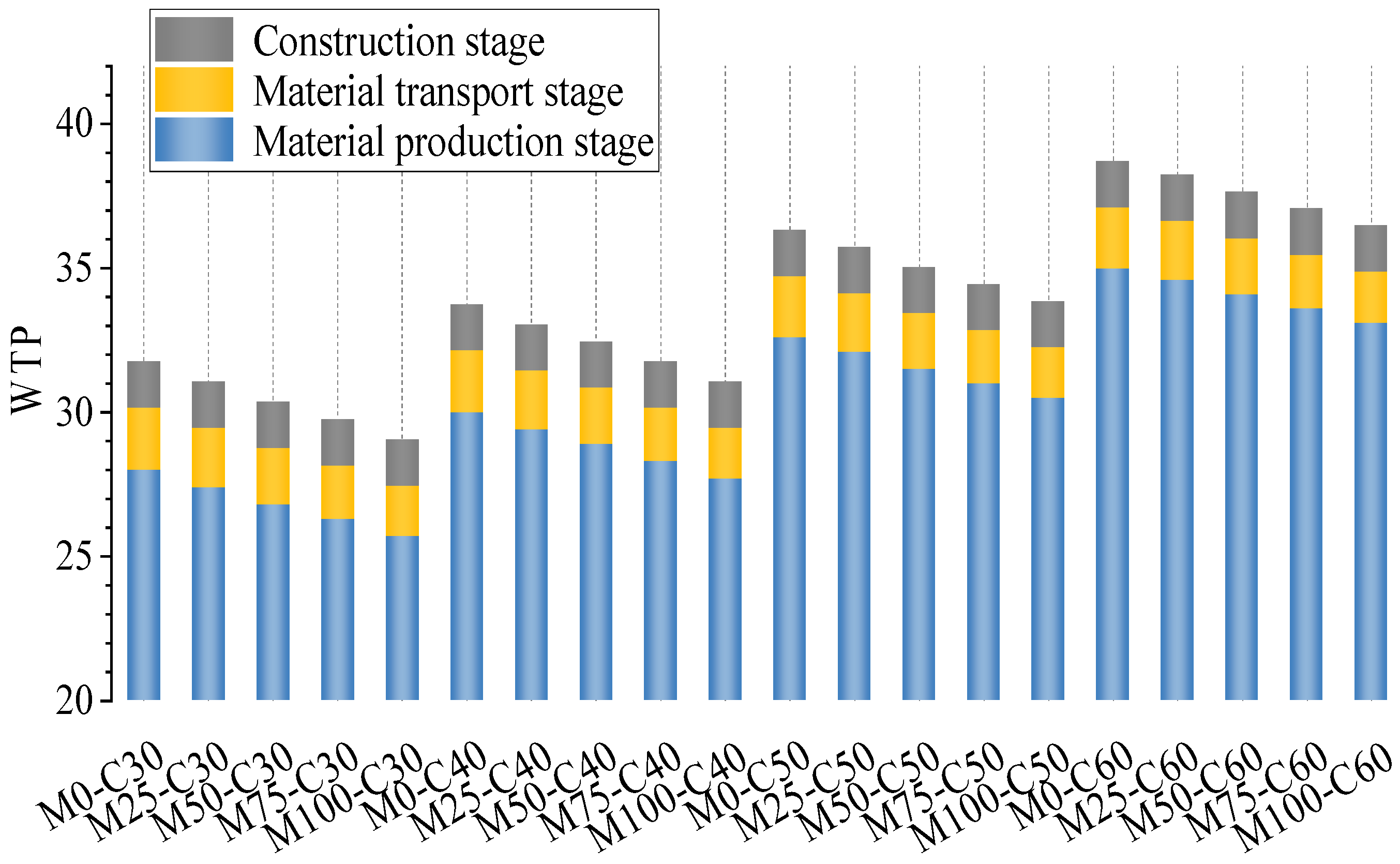







| Resource Consumption and Material Emissions | Measurement Unit | River Sand Quality | Aggregate Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical energy consumption | kWh | 1.19 × 10−2 | 1.39 × 10−2 |
| CO2 | kg | 1.12 × 10−6 | 2.01 × 10−6 |
| CO | kg | 5.63 × 10−4 | 6.74 × 10−4 |
| SO2 | kg | 3.10 × 10−6 | 4.62 × 10−6 |
| NOx | kg | 1.21 × 10−5 | 1.36 × 10−5 |
| Resource Consumption and Environmental Impact | Measurement Unit | Primary Production Processes | Secondary Production Processes | Absence of Economic Allocation | Economic Allocation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-grade ore | t | 1.10 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 1.10 × 100 |
| Energy consumption | MJ | 1.18 × 104 | 8.59 × 10−1 | 8.59 × 10−1 | 1.11 × 101 |
| CO2 | kg | 1.58 × 103 | 1.74 × 100 | 1.74 × 100 | 3.12 × 100 |
| SO2 | kg | 1.33 × 101 | 2.84 × 10−3 | 2.84 × 10−3 | 1.44× 10−2 |
| CO | kg | 3.29 × 101 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 2.87 × 10−2 |
| NOx | kg | 6.16 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 5.37 × 10−3 |
| Material Flow | Resource Consumption and Environmental Impact | Measurement Unit | Measured Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enter | Standard coal | kg | 8.20 × 10−2 |
| Water resources | m3 | 1.00 × 100 | |
| Output | CO2 | kg | 2.13 × 10−1 |
| NOx | kg | 1.00 × 10−3 | |
| SO2 | kg | 2.00 × 10−3 | |
| COD | kg | 5.40 × 10−5 | |
| Solid waste | kg | 4.00 × 10−3 |
| Energy Name | Average Low Calorific Value | Measurement Unit | Standard Coal Coefficient | Measurement Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard coal | 29,306.0 | kJ/kg | 1.0000 | kgce/kg |
| Raw coal | 20,934.0 | kJ/kg | 0.7143 | kgce/kg |
| Clean coal | 26,377.0 | kJ/kg | 0.9000 | kgce/kg |
| Coke charcoal | 28,470.0 | kJ/kg | 0.9714 | kgce/kg |
| Crude | 41,868.0 | kJ/kg | 1.4286 | kgce/kg |
| Gasoline | 43,124.0 | kJ/kg | 1.4714 | kgce/kg |
| Diesel fuel | 42,705.0 | kJ/kg | 1.4571 | kgce/kg |
| Kerosene | 43,124.0 | kJ/kg | 1.4714 | kgce/kg |
| Fuel oil | 41,868.0 | kJ/kg | 1.4286 | kgce/kg |
| LPG | 50,242.0 | kJ/kg | 1.7143 | kgce/kg |
| Coke oven gas | 17,375.0 | kJ/m3 | 0.5928 | kgce/m3 |
| Natural gas | 35,608.5 | kJ/m3 | 1.2150 | kgce/m3 |
| Heat | / | / | 0.0341 | kgce/MJ |
| Electricity | / | / | 0.1229 | kgce/kWh |
| Other coal washing | 8374.0 | kJ/kg | 0.2857 | kgce/kg |
| Converter gas | 5234.0 | kJ/m3 | 0.1786 | kgce/m3 |
| Blast furnace gas | 3768.0 | kJ/m3 | 0.1286 | kgce/m3 |
| Transportation (t·km) | Energy Consumption (MJ) | CO2 (kg) | CH4 (kg) | SO2 (kg) | NOx (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Highway | Diesel truck | 8.59 × 10−1 | 1.74 × 10−1 | 1.07 × 10−3 | 2.84 × 10−4 | 2.79 × 10−3 |
| Gasoline truck | 9.60 × 10−1 | 1.52 × 10−1 | 1.19 × 10−3 | 2.85 × 10−4 | 2.07 × 10−3 | |
| Railway | Electric locomotive | 3.39 × 10−1 | 1.00 × 10−2 | 2.86 × 10−5 | 3.52 × 10−5 | 2.90 × 10−5 |
| Diesel locomotive | 4.09 × 10−1 | 8.72 × 10−3 | 5.06 × 10−5 | 1.20 × 10−5 | 1.28 × 10−4 | |
| Waterway | Dry bulk carrier | 5.03 × 10−2 | 1.34 × 10−2 | 6.28 × 10−5 | 1.66 × 10−5 | 4.06 × 10−4 |
| Container ship | 4.05 × 10−2 | 1.07 × 10−2 | 5.05 × 10−5 | 1.33 × 10−5 | 3.26 × 10−4 | |
| Production Machinery/Method | Measurement Unit | Energy Consumption (MJ) | CO2 (kg) | SO2 (kg) | NOx (kg) | Dust (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ready-mixed concrete | Concrete mixing station | t | 1.15 × 102 | 7.70 × 100 | 3.42 × 10−3 | 6.51 × 10−2 | 3.31 × 10−3 |
| Concrete mixer | m3 | 1.51 × 101 | 6.50 × 10−1 | 2.17 × 10−4 | 2.67 × 10−4 | 5.01 × 10−5 | |
| Pouring | Concrete pump truck | m3 | 4.57 × 100 | 2.00 × 10−1 | 6.60 × 10−5 | 8.13 × 10−5 | 1.52 × 10−5 |
| Vibrate | Soft shaft vibration | h | 5.35 × 100 | 2.00 × 10−1 | 7.72 × 10−5 | 9.50 × 10−5 | 1.78 × 10−5 |
| Die shell vibrator | h | 4.86 × 10−1 | 0.00 × 100 | 7.02 × 10−6 | 8.64 × 10−6 | 1.62 × 10−6 | |
| Planar vibrator | h | 4.32 × 101 | 2.90 × 100 | 6.05 × 10−7 | 1.77 × 10−5 | 6.56 × 10−7 | |
| Maintenance | Standard maintenance | m3 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 |
| Steam maintenance | m3 | 5.93 × 102 | 3.85 × 101 | 2.41 × 10−2 | 3.17 × 10−2 | 3.48 × 10−2 | |
| Pressure steam maintenance | m3 | 7.12 × 102 | 4.62 × 101 | 2.89 × 10−2 | 3.81 × 10−2 | 4.17 × 10−2 | |
| Environmental Impact Type | Main List Substances | Equivalent Index Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological environment damage | Global Warming | CO2, CO, CH4… | kgCO2 eq |
| Acidification | SO2, NOx, NH3… | kgSO2 eq | |
| Eutrophication of water | NO3-, COD, NOx… | kgNO3− eq | |
| Photochemical pollution | NMVOC, NOx… | kgC2H4 eq | |
| Solid waste | Solid waste | kg | |
| Atmospheric suspension | Dust | kg | |
| Water suspension | SS | kg | |
| Water toxicity | Pb | kgPb eq | |
| Resource consumption | Water consumption | Water | m3 |
| Fossil energy consumption | Standard coal | MJ | |
| Mineral resource consumption | Limestone/Gravel/River sand… | kg | |
| Health damage | Health damage | Unit DALY | a.case-1 |
| Environmental Impact Factors | Weight W (Yuan/kg) |
|---|---|
| Global Warming (CO2 Equivalent) | 5.20 × 10−2 |
| Acidification (SO2 equivalent) | 6.30 × 10−1 |
| Eutrophication of water bodies (NO3-equivalent) | 7.30 × 10−1 |
| Photochemical pollution (C2H4 equivalent) | 2.74 × 100 |
| Solid Waste (kg) | 2.50 × 10−2 |
| Atmospheric suspension (kg) | 2.20 × 10−1 |
| Water suspension (kg) | 1.75 × 10−1 |
| Water toxicity (Pb equivalent) | 6.04 × 100 |
| Resource Impact Factor | Weight W (Yuan/kg) |
|---|---|
| Water Resources (Yuan·m−3) | 1.44 × 100 |
| Fossil Energy (Standard Coal) (Yuan·MJ−1) | 2.76 × 10−4 |
| Iron ore (kg) | 1.95 × 10−2 |
| Limestone (kg) | 3.00 × 10−3 |
| River sand (kg) | 1.70 × 10−3 |
| Gravel (kg) | 1.40 × 10−3 |
| Manganese ore (kg) | 7.90 × 10−3 |
| Coding | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength of Splitting (MPa) | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M0-C30 | 30.00 | 2.49 | 2.91 |
| M25-C30 | 29.18 | 2.44 | 2.89 |
| M50-C30 | 28.35 | 2.39 | 2.86 |
| M75-C30 | 27.53 | 2.34 | 2.83 |
| M100-C30 | 26.70 | 2.29 | 2.80 |
| M0-C40 | 40.00 | 3.04 | 3.20 |
| M25-C40 | 38.90 | 2.98 | 3.17 |
| M50-C40 | 37.80 | 2.92 | 3.14 |
| M75-C40 | 36.70 | 2.86 | 3.11 |
| M100-C40 | 35.60 | 2.80 | 3.08 |
| M0-C50 | 50.00 | 3.56 | 3.45 |
| M25-C50 | 48.63 | 3.49 | 3.42 |
| M50-C50 | 47.25 | 3.42 | 3.39 |
| M75-C50 | 45.88 | 3.35 | 3.35 |
| M100-C50 | 44.50 | 3.28 | 3.32 |
| M0-C60 | 60.00 | 4.04 | 3.66 |
| M25-C60 | 58.35 | 3.96 | 3.63 |
| M50-C60 | 56.70 | 3.88 | 3.60 |
| M75-C60 | 55.05 | 3.80 | 3.56 |
| M100-C60 | 53.40 | 3.72 | 3.53 |
| Primary Category | Table Reference | Concise Description |
|---|---|---|
| Material Production | Table 1 | Resource and environmental data for producing 1 kg of natural aggregates |
| Table 2 | Resource consumption and emissions for producing 1 ton of molybdenum tailings | |
| Table A1 | Resource and emission inventory for producing 1 ton of Portland cement | |
| Table A2 | Environmental impact list for producing 1 kg of a naphthalene-based water reducer | |
| Mechanical Properties | Table A3 | Mix proportions per m3 of concrete for different tailings replacement rates and strength grades |
| Table 10 | Mechanical properties | |
| Energy, Resource, Transportation Benchmarks | Table 3 | Resource use and emissions for producing 1 m3 of tap water |
| Table 4 | Standard coal conversion coefficients for various energy sources | |
| Table A4 | Life cycle inventory for producing 1 kWh of thermal power | |
| Table A5 | Life cycle inventory for various fossil fuels and derived energy sources | |
| Table 5 | Energy intensity and emission factors for different transport methods | |
| Impact Assessment Methodology | Table 7 | List of environmental impact type indicators |
| Table A6 | Characterization factors for converting emissions into impact equivalents | |
| Economic Valuation | Table 8 | Monetized weights for ecological and environmental damage categories |
| Table 9 | Monetized weights for resource consumption categories | |
| Process-Specific Environmental Impacts | Table 6 | Environmental impact data for construction machinery and methods |
| Table A7 | Environmental impact of the transportation stage for Xi’an | |
| Environmental Impact | Table A8 | Environmental impacts for the production stage |
| Table A9 | Environmental impacts for the production stage | |
| Table A10 | Environmental impacts of the construction stage | |
| Economic Cost (WTP) | Table A11 | WTP values for the production stage |
| Table A12 | WTP values for the production stage (Economic allocation) | |
| Table A13 | WTP values for the transportation stage (Xi’an) | |
| Table A14 | WTP values for the construction stage | |
| Table A15 | Total WTP results for full life cycle | |
| Table A16 | Total WTP results for full life cycle (Economic allocation) | |
| Energy Analysis | Table A17 | Energy consumption and saving ratios for different mixes and methods |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, S.; Xu, J.; Huang, Z.; Nishiwaki, T.; Rong, C. Life Cycle Environmental Evaluation Framework for Mining Waste Concrete: Insights from Molybdenum Tailings Concrete in China. Buildings 2025, 15, 3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203755
Gao S, Xu J, Huang Z, Nishiwaki T, Rong C. Life Cycle Environmental Evaluation Framework for Mining Waste Concrete: Insights from Molybdenum Tailings Concrete in China. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203755
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Shan, Jicheng Xu, Zhenhua Huang, Tomoya Nishiwaki, and Chuanxin Rong. 2025. "Life Cycle Environmental Evaluation Framework for Mining Waste Concrete: Insights from Molybdenum Tailings Concrete in China" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203755
APA StyleGao, S., Xu, J., Huang, Z., Nishiwaki, T., & Rong, C. (2025). Life Cycle Environmental Evaluation Framework for Mining Waste Concrete: Insights from Molybdenum Tailings Concrete in China. Buildings, 15(20), 3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203755