Intelligent Defect Recognition of Glazed Components in Ancient Buildings Based on Binocular Vision
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Development of a Multi-Type Damage Dataset for Glazed Architectural Components. To address the diverse morphological characteristics and significant scale variations of surface damages, cracks and spalling on glazed architectural components, this study establishes a specialized dataset focusing on ancient glazed structures. In particular, it incorporates a full processing pipeline for detecting and analyzing the prevalent crack and spalling damages found on the Nine-Dragon Wall. This dataset provides a foundational resource for the digital monitoring and quantitative scale assessment of cultural heritage components.
- Proposal of a Deep Learning-Based Detection Algorithm for Glazed Surface Damage with Complex Textures. This study designs a deep neural network architecture tailored for detecting damages in the intricate textures of glazed surfaces. The CBAM is integrated into the backbone network and applied to the output of each feature processing stage, enabling the model to learn highly discriminative and semantically rich features at early stages of extraction. This attention-enhanced architecture significantly improves feature representation capabilities and provides more accurate and robust semantic support for downstream damage detection tasks, ultimately achieving higher precision in image-based defect recognition.
- Construction of a Depth Estimation and Scale Restoration Fusion Algorithm for Accurate 2D to 3D Mapping. Based on the depth information obtained from the detected damage regions, this study introduces a 3D coordinate back-projection method using pre-calibrated intrinsic camera parameters to transform the 2D pixel-based segmentation results into real-world physical space. This approach enhances the geometric accuracy of damage quantification and improves the spatial interpretability of the detection outcomes. It provides reliable and quantifiable 3D data support for subsequent tasks such as structural health analysis, restoration planning, and long-term monitoring of architectural heritage components.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Methods
2.2. Deep Learning Methods
3. Method
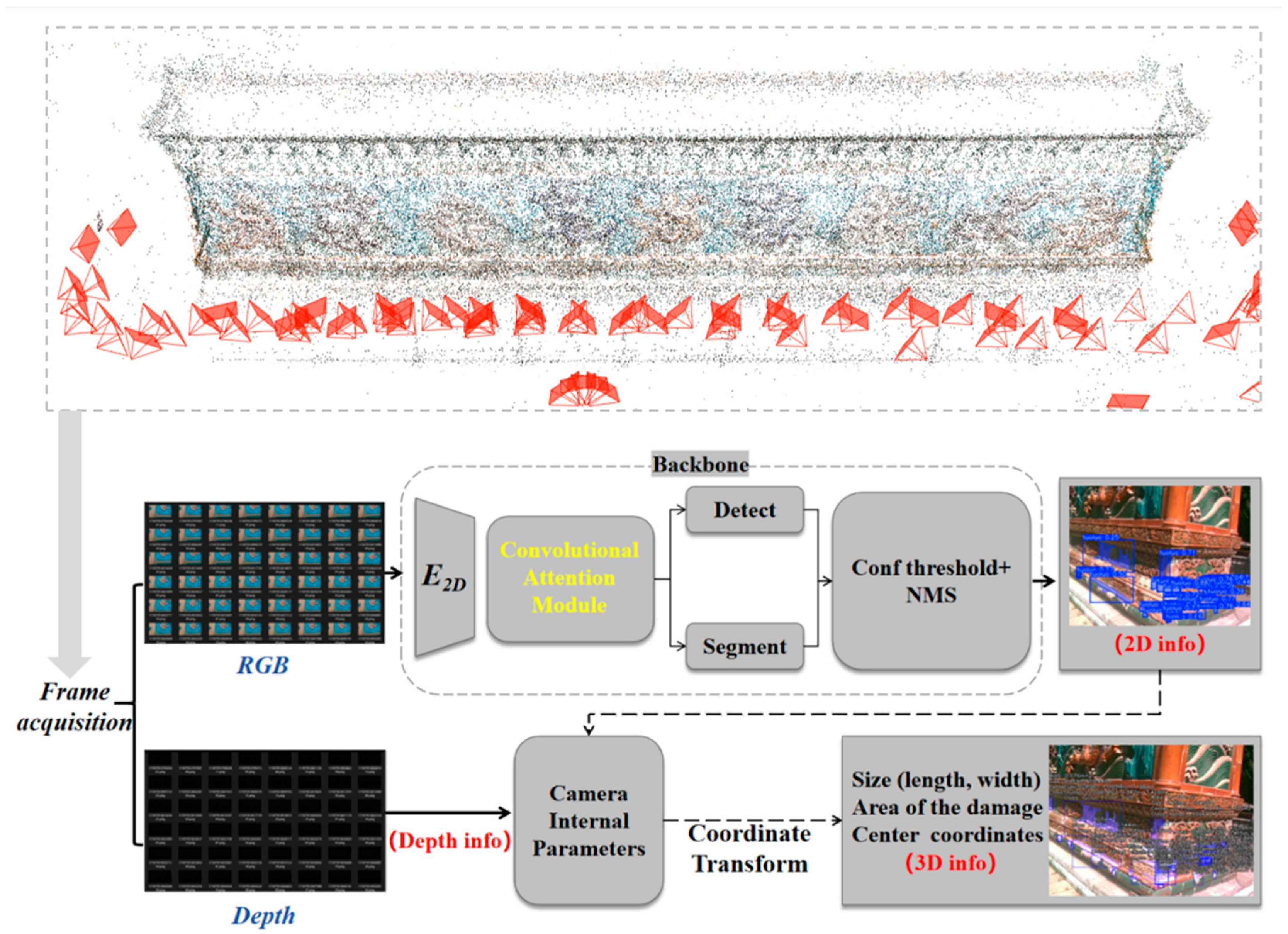
3.1. Technical Route for Automatic Damage Identification Method and Scale Restoration of Glazed Components
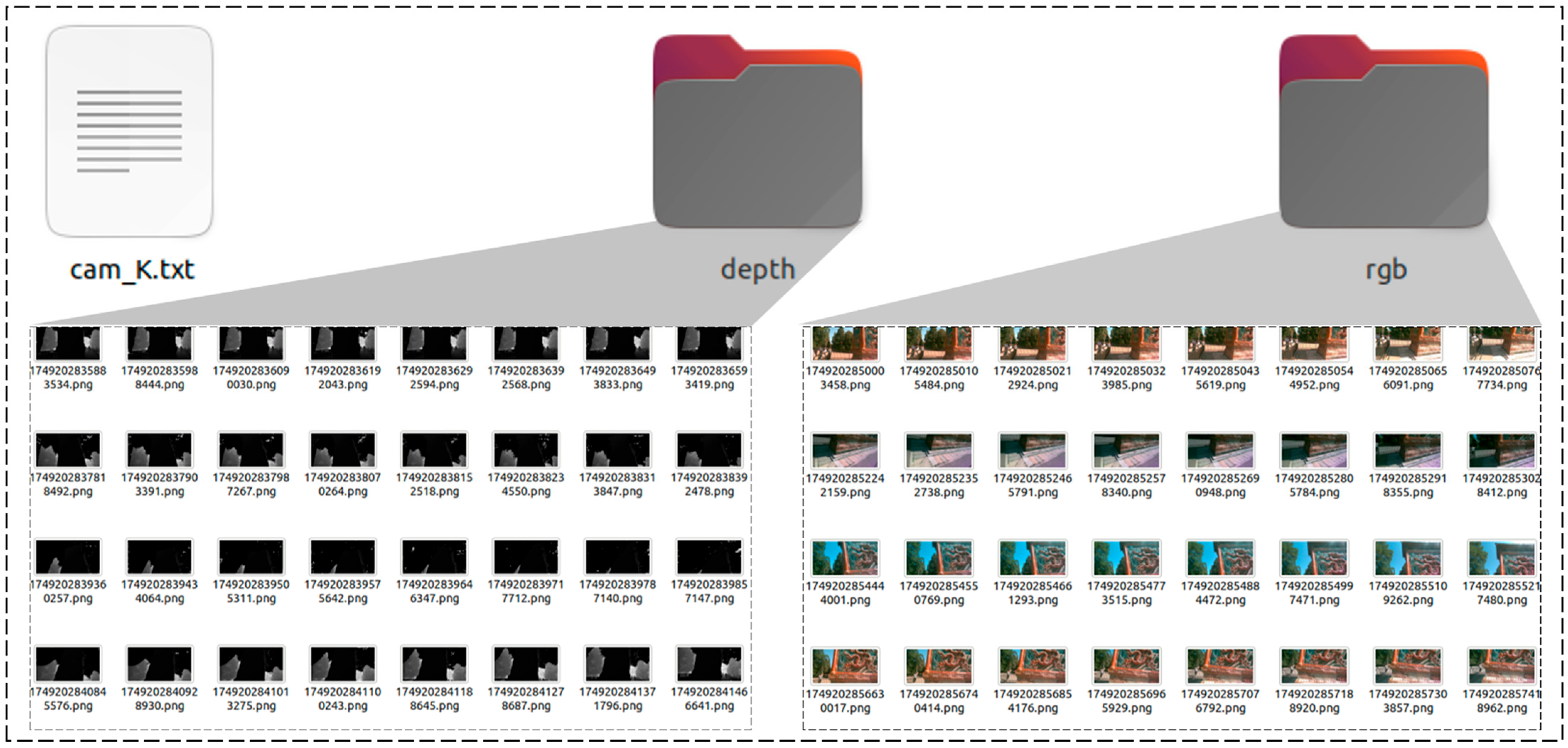
3.2. Binocular Vision System Data Acquisition and Enhancement
3.3. Scale Uncertainty Analysis
3.4. Design of Scale Restoration Algorithm
4. Result and Discussion
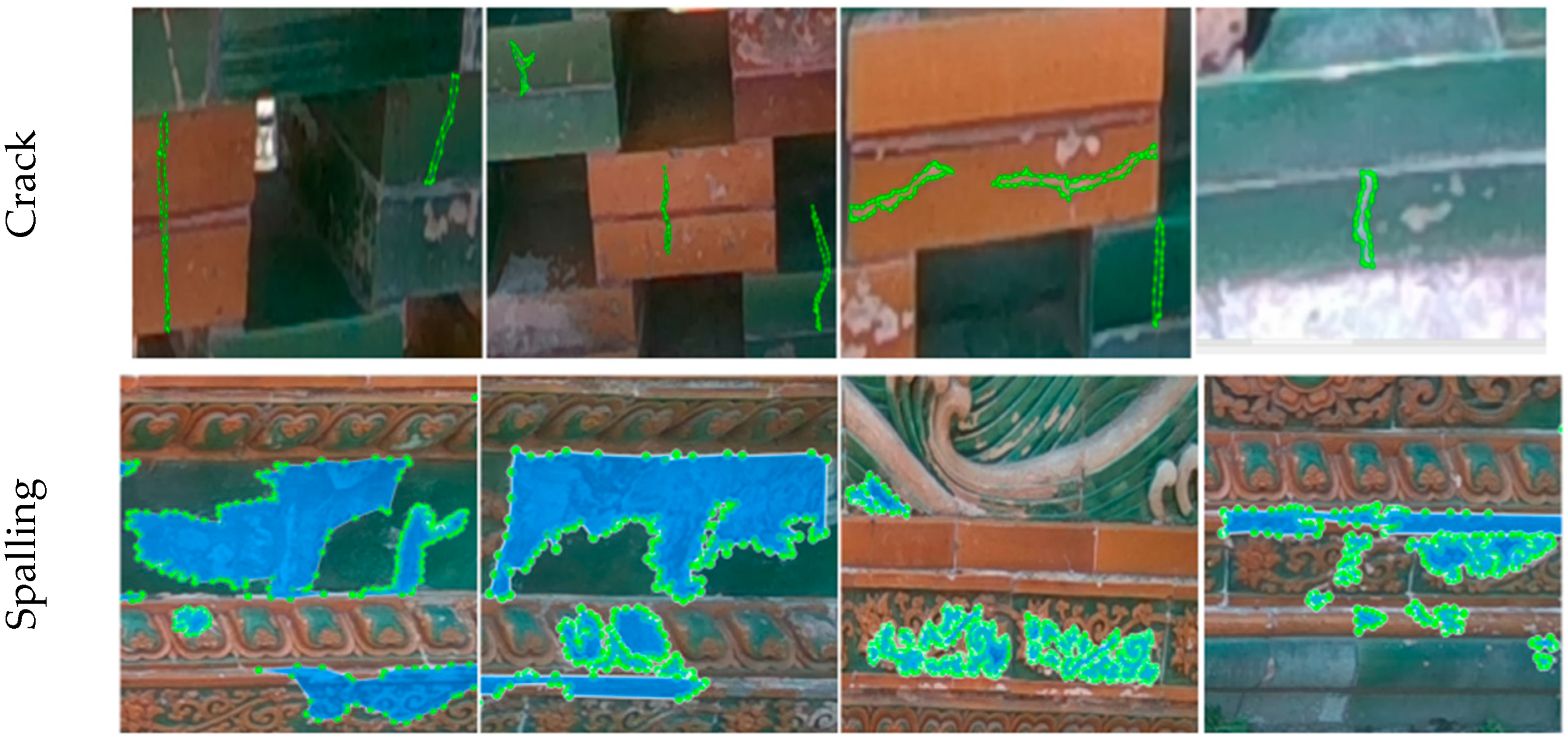
4.1. Dataset Creation
4.2. Dataset Train
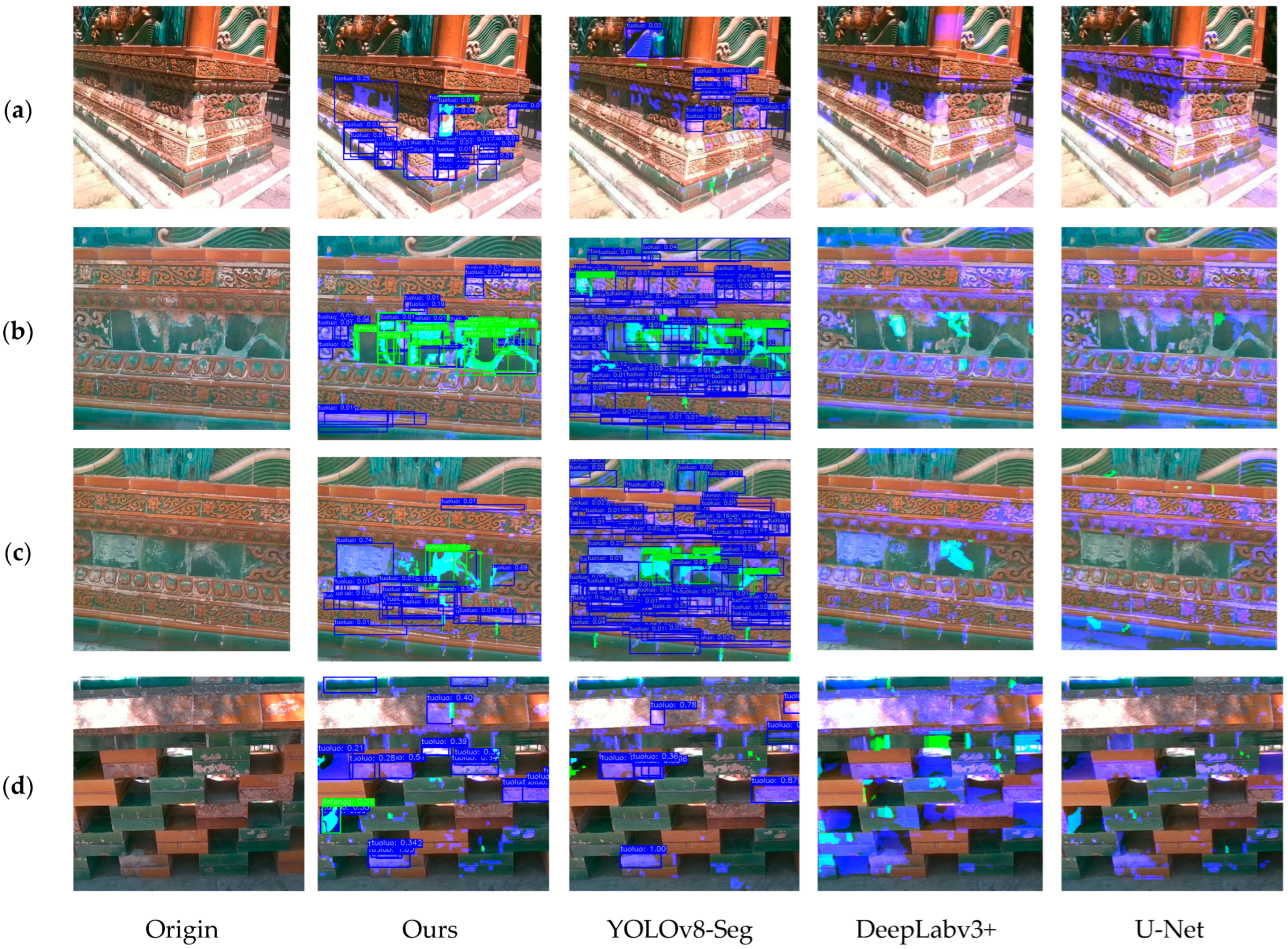
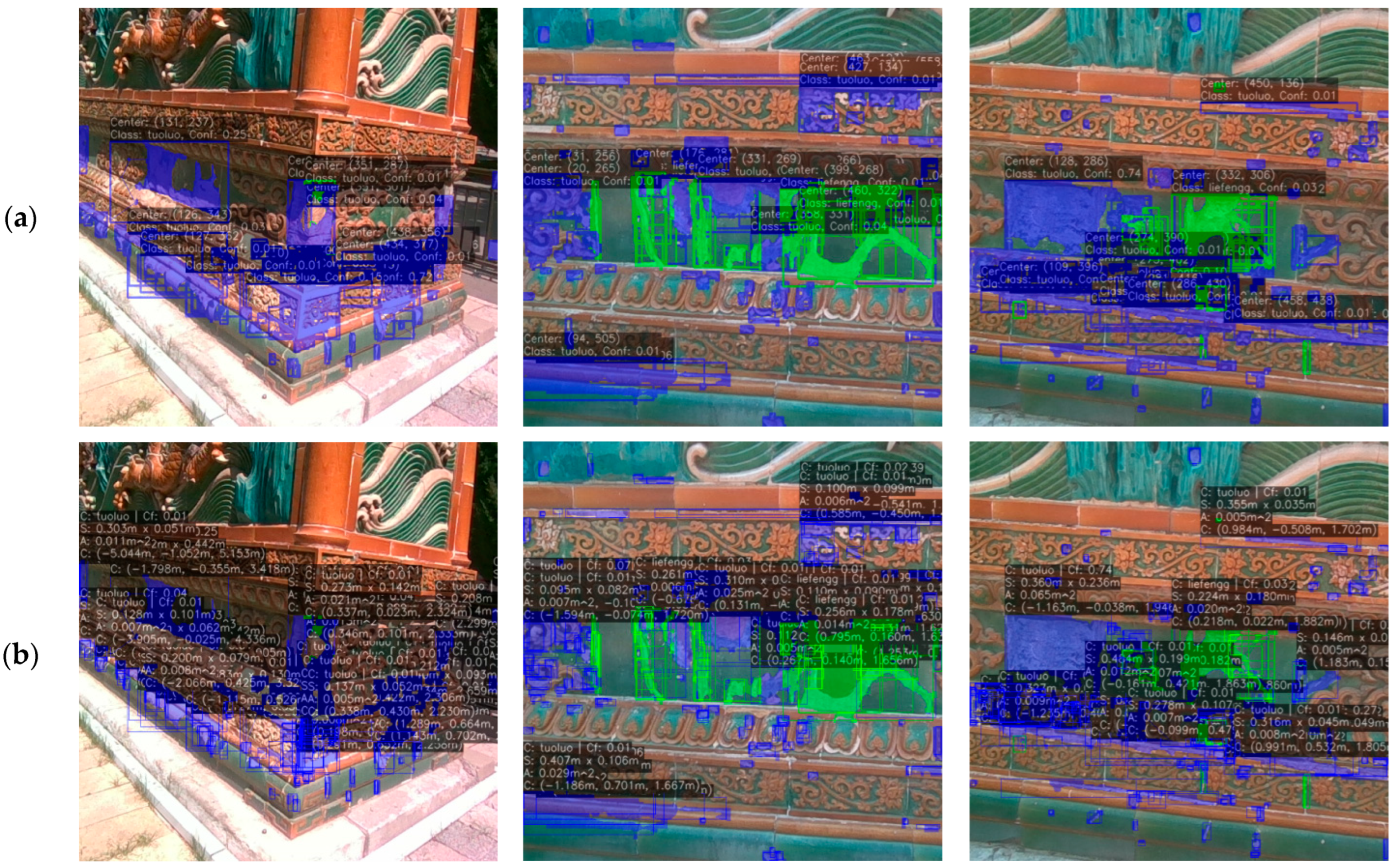
4.3. Damage Identification Results and Discussion
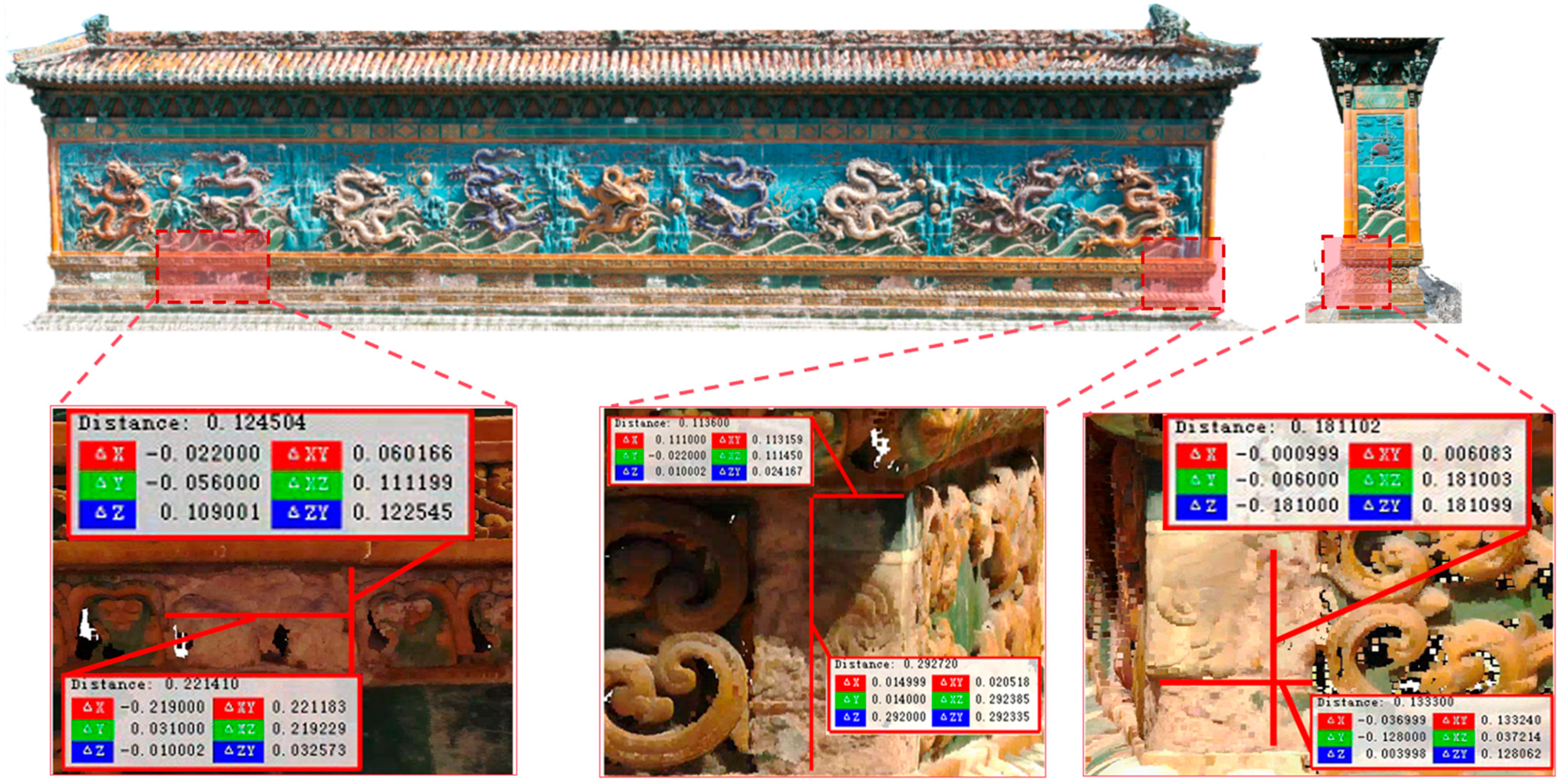
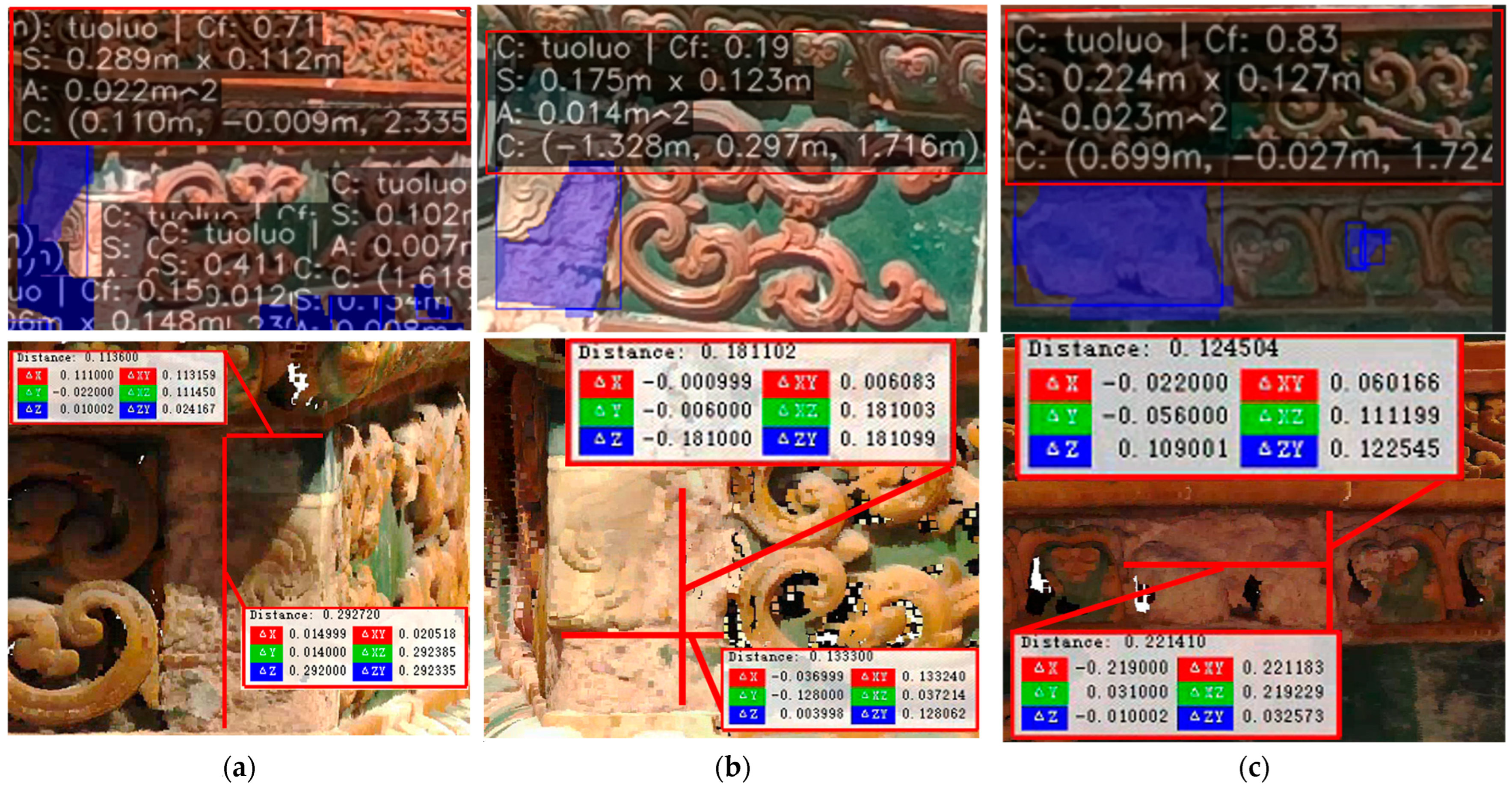
4.4. Scale Restoration Accuracy Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adili, D.; Zhao, J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, P.; Wang, C.; Luo, H. Protection of glazed tiles in ancient buildings of China. Herit. Sci. 2020, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Miao, J.; Li, Y.; Kang, B.; Li, H. Analysis and research on the diseases of green glazed components in ancient Chinese buildings. J. Palace Mus. 2013, 166, 114–124+161. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, D. The Regulation of Temperature Fluctuations and Energy Consumption in Buildings Using Phase Change Material-Gypsum Boards in Summer. Buildings 2024, 14, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Gong, Q.; Dai, Y.; Bian, F.; Shang, D. Application of thermal expansion series fireproof sealing products in building passive fireproofing projects. Fire Technol. Prod. Inf. 2004, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Yan, W.; Yang, R. Seismic isolation, vibration reduction and vibration control of building structures. J. Build. Struct. 2002, 2–12+26. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Wang, R.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Huang, F. Analysis and study of green glazed tile fragments from Liao Dynasty. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 3839–3843. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Gao, F.; Sun, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J. Study on the correlation between oxide composition of glazed tile matrix and matrix color, water absorption, apparent porosity and mechanical strength. J. Beijing Univ. Chem. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 48, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Huang, Y. Modern restoration and reconstruction of classical architecture and supervision. Build. Tech. 2009, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Tang, H. Evolution and development of the composition and formula of Chinese glazed tiles. Glass Enamel 2014, 42, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, R.; Wang, L.; Liang, J.; Wei, C.; Li, H. Preliminary study on the “powdery rust” disease of glazed tiles in ancient Chinese buildings. Cult. Herit. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 19, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, N. Analysis of the decorative art and pattern significance of glazed bricks in Xinjiang. Design 2023, 8, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, Y.; Duan, H.; Liang, G.; Miao, J. Non-destructive determination of the main and trace elements in glazed tile components by EDXRF. Cult. Herit. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 20, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Difficult issues and solutions in the roof maintenance of the Qin’an Hall. Anc. Archit. Gard. Technol. 2014, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Huang, L. Brief analysis of key points in the production process of traditional architectural glazed components. Chin. Foreign Archit. 2016, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Huang, X.; Luo, H. Preparation and performance study of bridge-type siloxane for the protection of glazed tiles in Qing Dynasty buildings in the Forbidden City. J. Inorg. Mater. 2014, 29, 657–660. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Miao, J.; Ding, Y. Study on the weather resistance evaluation of glazed tile replicas of Qing Dynasty official buildings. Bricks Tiles 2014, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, G. Protection of Urban Cultural Heritage and the Construction of Cultural Cities. Ph.D. Thesis, Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H. Exploration of the cultural nature of ancient Chinese architecture. Ind. Technol. Forum 2015, 105–106. [Google Scholar]
- López, F.J.; Lerones, P.M.; Llamas, J.; Gomez-Garcia-Bermejo, J.; Zalama, E. A review of heritage building information modeling (H-BIM). Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2018, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, P.; Herraez, J.; Lorenzo, H.; Ordoñez, C. Control of structural problems in cultural heritage monuments using close-range photogrammetry and computer methods. Comput. Struct. 2005, 83, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, B.; Yokoya, N.; Xia, J.; Miura, H.; Liu, W.; Matsuoka, M.; Koshimura, S. Learning from multimodal and multitemporal earth observation data for building damage mapping. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Gong, S. Structural system recognition based on computer vision. J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 51, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Kang, J.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Y. Surface damage detection for steel wire ropes using deep learning and computer vision techniques. Measurement 2020, 161, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Computer vision for SHM of civil infrastructure: From dynamic response measurement to damage detection—A review. Eng. Struct. 2018, 156, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiechefu, C.B.; Kromanis, R. Damage detection techniques for structural health monitoring of bridges from computer vision derived parameters. Struct. Monit. Maint. 2021, 8, 91–110. [Google Scholar]
- Khuc, T.; Catbas, F.N. Structural identification using computer vision-based bridge health monitoring. J. Struct. Eng. 2018, 144, 04017202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.Z.; Catbas, F.N. A review of computer vision-based structural health monitoring at local and global levels. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 20, 692–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C. Application of computer vision techniques to damage detection in underwater concrete structures. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 104, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crognale, M.; De Iuliis, M.; Rinaldi, C.; Gattulli, V. Damage detection with image processing: A comparative study. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2023, 22, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yin, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Guo, M. A graph convolution-based method for vehicle-mounted video object semantic segmentation. Surv. Mapp. Sci. 2023, 48, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, X.; Guo, K.; Shi, Y.; Han, L. Intelligent Extraction of Surface Cracks on LNG Outer Tanks Based on Close-Range Image Point Clouds and Infrared Imagery. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2024, 43, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Najmi, A.; Gray, R.M. Image classification by a two-dimensional hidden Markov model. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2000, 48, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhu, L.; Huang, M.; Ji, J.; Ren, X.; Wei, Y.; Gao, C. Intelligent extraction of road cracks based on vehicle laser point cloud and panoramic sequence images. J. Road Eng. 2024, 4, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, J.T.; Malik, J. Intrinsic scene properties from a single rgb-d image. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Janani, M.; Jebakumar, R. Detection and classification of groundnut leaf nutrient level extraction in RGB images. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2023, 175, 103320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Mian, A. Hyperspectral recovery from RGB images using Gaussian processes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 42, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.D.; Chen, D. A hybrid image segmentation method for building extraction from high-resolution RGB images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 192, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, J. A deep learning and stereo vision-based method for quantitative assessment of bridge surface damage severity. J. Civ. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2025, 17, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Qian, S. Research on concrete damage evolution based on machine vision and digital image correlation technology. J. Hunan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X. Road crack localization and quantification method based on UAV monocular video. Eng. Mech. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harika, A.; Sivanpillai, R.; Sajith Variyar, V.V.; Sowmya, V. Extracting water bodies in rgb images using deeplabv3+ algorithm. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 46, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Wen, Y.; Xu, X.; Song, H. Extracting cow point clouds from multi-view RGB images with an improved YOLACT++ instance segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 230, 120730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhao, J.; Liang, X.; Shang, X.; Huang, M.; Guo, S.; Zhao, Y. Optimization of structural reinforcement assessment for architectural heritage digital twins based on LiDAR and multi-source remote sensing. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhou, J.; Liang, X. Analysis of static stiffness properties of column-architrave structures of ancient buildings under long term load-natural aging coupling. Structures 2024, 59, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Shang, X.; Zhao, J.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, S. Synergy of LIDAR and hyperspectral remote sensing: Health status assessment of architectural heritage based on normal cloud theory and variable weight theory. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Guo, M.; Wang, G.; Guo, K.; Zhao, Y. 3D Change Detection Method for Exterior Wall of LNG Storage Tank Supported by Multi-Source Spatial Data. Adv. Theory Simul. 2024, 7, 2300941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhao, J.; Pan, D.; Sun, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, B. Normal cloud model theory-based comprehensive fuzzy assessment of wooden pagoda safety. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Guo, M.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Pan, D. Behavioral model construction of architectural heritage for digital twin. NPJ Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, B.B.; Kamsu-Foguem, B.; Tangara, F. Deep convolution neural network for image recognition. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 48, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Fu, Z.; Pan, D.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, M.; Guo, K. 3D Digital protection and representation of burial ruins based on LiDAR and UAV survey. Meas. Control 2022, 55, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, G.; Guo, M.; Zhou, T. Application of TLS in feature acquisition of complex steel structures. Surv. Bull. 2020, 151–154+159. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Sun, M.; Pan, D.; Huang, M.; Yan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, P.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y. High-precision detection method for large and complex steel structures based on global registration algorithm and automatic point cloud generation. Measurement 2021, 172, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serre, T.; Kreiman, G.; Kouh, M.; Cadieu, C.; Knoblich, U.; Poggio, T. A quantitative theory of immediate visual recognition. Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 165, 33–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, N. Application of artificial intelligence in cultural heritage conservation. Nat. J. 2024, 46, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, T.; Shen, T.; Yang, T. Research on high-precision crack width variation measurement technology. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2020, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janc, B.; Vižintin, G.; Pal, A. Investigation of disc cutter wear in tunnel-boring machines (tbms): Integration of photogrammetry, measurement with a caliper, weighing, and macroscopic visual inspection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Luo, X.; Xie, G.; Wang, K.; Peng, Y.; Rao, Y. Effects of the printing parameters on geometric accuracy and mechanical properties of digital light processing printed polymer. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 14807–14819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, X.; Guo, K.; Tang, K. Integration of Time-Series Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery and LiDAR Point Cloud for Monitoring and Analysis of Liquefied Natural Gas Storage Tank Exteriors. Sens. Mater. 2024, 36, 3713–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, N. Protective reuse of industrial heritage buildings in post-industrial era in China. J. Archit. 2006, 8, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, L.; Guo, K. Monitoring Scheme of Liquified Natural Gas External Tank Using Air—Space—Land Integration Multisource Remote Sensing. Sens. Mater. 2024, 36, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaria, J.A.; Fadhel, M.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Ergu, D.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Ma, B. A Review of Yolo algorithm developments. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 199, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, M.; Shi, P.; Ren, R.; He, X.; Wei, X.; Yang, H. Crack detection and comparison study based on faster R-CNN and mask R-CNN. Sensors 2022, 22, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Bashir, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Ekere, N.; Li, C. Multisensory collaborative damage diagnosis of a 10 MW floating offshore wind turbine tendons using multi-scale convolutional neural network with attention mechanism. Renew. Energy 2022, 199, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Wu, N.; Jiang, H. Reconstruction of environmental elements in cultural heritage protection using 3D surveying and mapping data. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 14, 3028. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, Z. Novel system for rapid investigation and damage detection in cultural heritage conservation based on deep learning. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2019, 25, 04019020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohan, M.; Sai Ram, T.; Rami Reddy, C.V. A review on yolov8 and its advancements. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics, Tirunelveli, India, 27–28 June 2023; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H.; Gao, L.; Yuan, Z.; Qu, H.; Sun, Q.; Cheng, H.; Wang, R. A novel transformer model for surface damage detection and cognition of concrete bridges. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Size | Batch Size | Optimizer | Number of Epoch | Initial Learning Rate | Learning Rate Decay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 640 | 16 | Adam | 300 | 0.001 | 0.75 |
| Class | IoU | P | R | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | tuoluo | 74.1 | 88.2 | 84.1 | 85.5 |
| liefengg | 70.5 | 82.4 | 80.4 | 81.4 | |
| DeepLabv3+ | tuoluo | 77.2 | 87.0 | 83.8 | 85.4 |
| liefengg | 72.7 | 85.3 | 78.8 | 82.2 | |
| YOLOv8-Seg | tuoluo | 80.6 | 93.5 | 90.4 | 92.4 |
| liefengg | 74.9 | 94.1 | 89.6 | 93.9 | |
| Ours | tuoluo | 92.2 | 97.1 | 94.1 | 96.5 |
| liefengg | 86.4 | 95.7 | 95.9 | 95.5 |
| (a) (Length × Width)/m | (b) | (c) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted value | 0.289 | 0.112 | 0.175 | 0.123 | 0.224 | 0.127 |
| Measured value | 0.292 | 0.113 | 0.181 | 0.133 | 0.221 | 0.124 |
| Difference | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.010 | −0.003 | −0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, M.; Han, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, M. Intelligent Defect Recognition of Glazed Components in Ancient Buildings Based on Binocular Vision. Buildings 2025, 15, 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203641
Zhao Y, Zhang X, Guo M, Han H, Wang J, Wang Y, Li X, Huang M. Intelligent Defect Recognition of Glazed Components in Ancient Buildings Based on Binocular Vision. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203641
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Youshan, Xiaolan Zhang, Ming Guo, Haoyu Han, Jiayi Wang, Yaofeng Wang, Xiaoxu Li, and Ming Huang. 2025. "Intelligent Defect Recognition of Glazed Components in Ancient Buildings Based on Binocular Vision" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203641
APA StyleZhao, Y., Zhang, X., Guo, M., Han, H., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Li, X., & Huang, M. (2025). Intelligent Defect Recognition of Glazed Components in Ancient Buildings Based on Binocular Vision. Buildings, 15(20), 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203641







