Decarbonizing the Building Sector: The Integrated Role of Environmental, Social, and Governance Indicators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
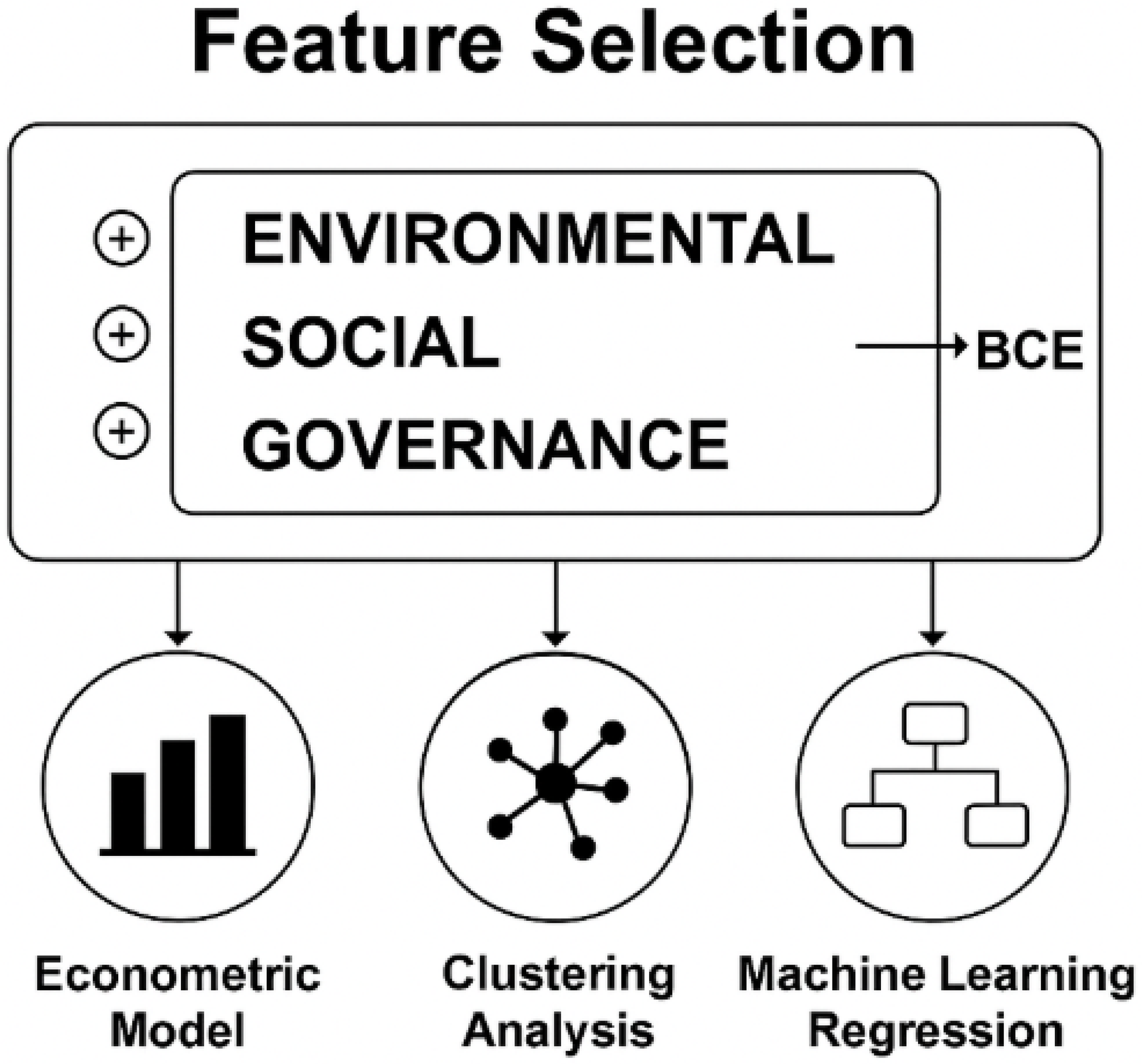
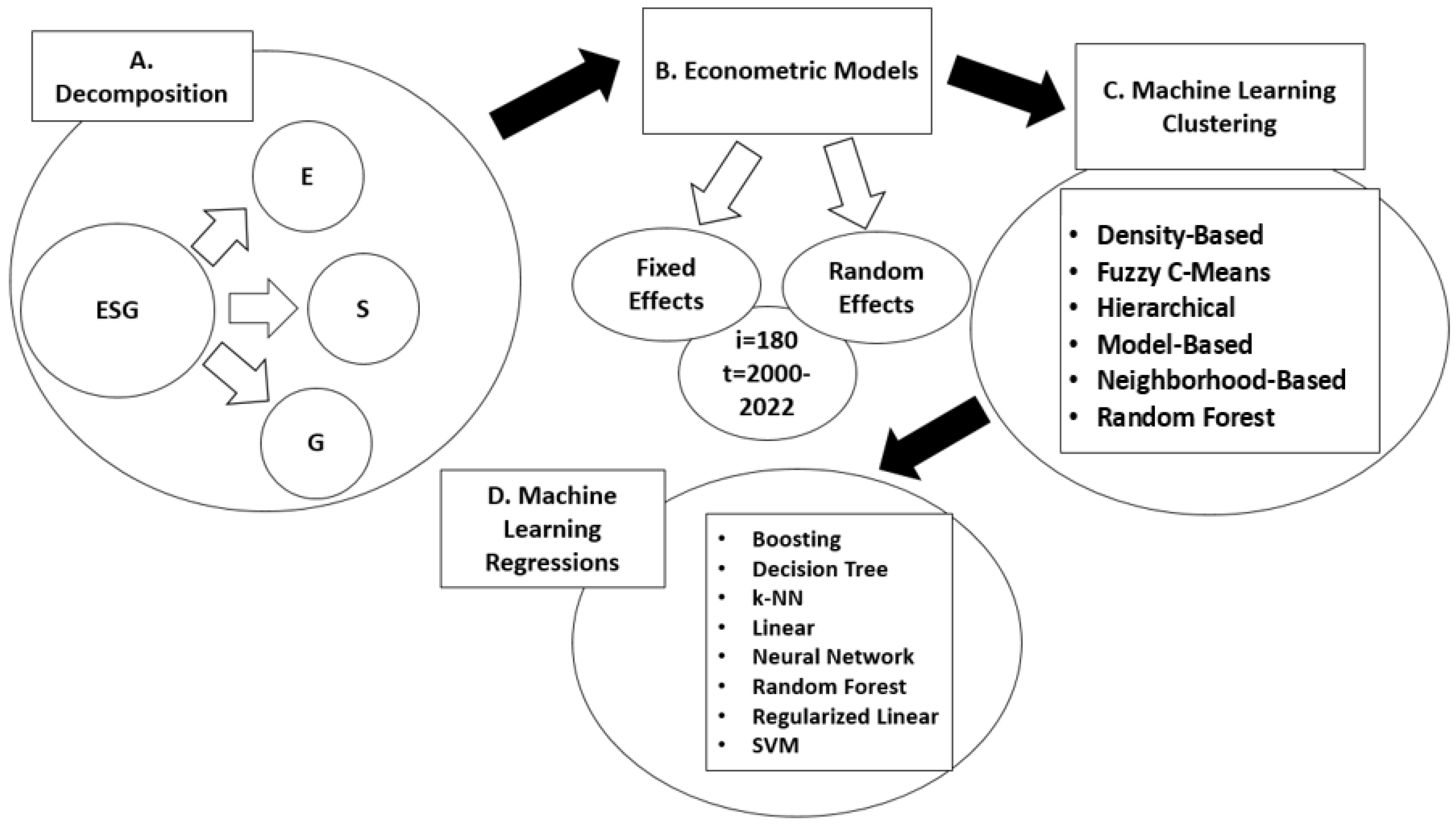
3. Modeling Building-Related Emissions Through ESG Dimensions: A Multi-Method Analysis Using Econometrics, Clustering, and Machine Learning
4. Decoding Building Emissions: Environmental Drivers in an ESG Framework (2000–2022)
4.1. Modeling the Environmental Determinants of Building Emissions: A Global ESG-Informed Econometric Analysis
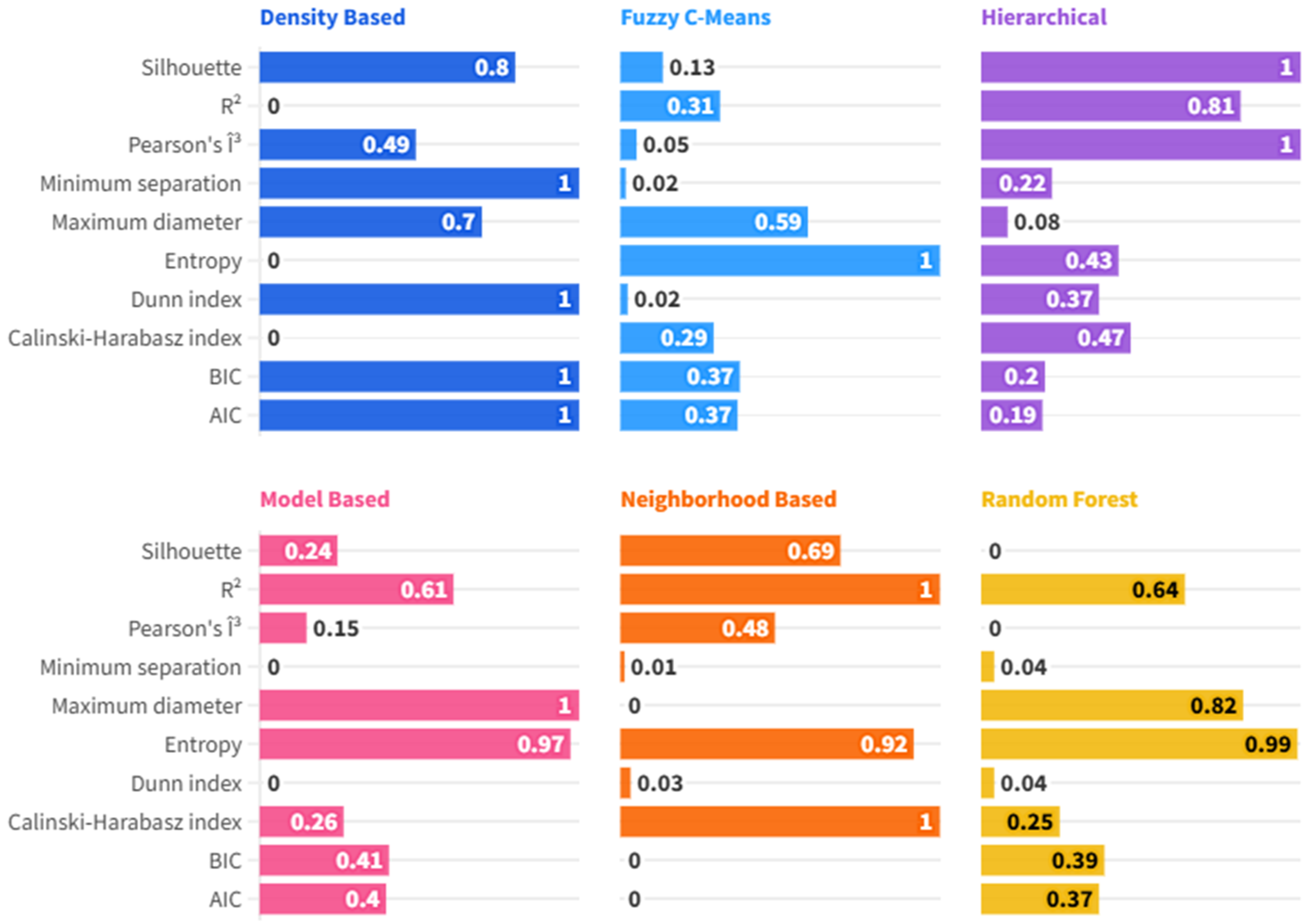
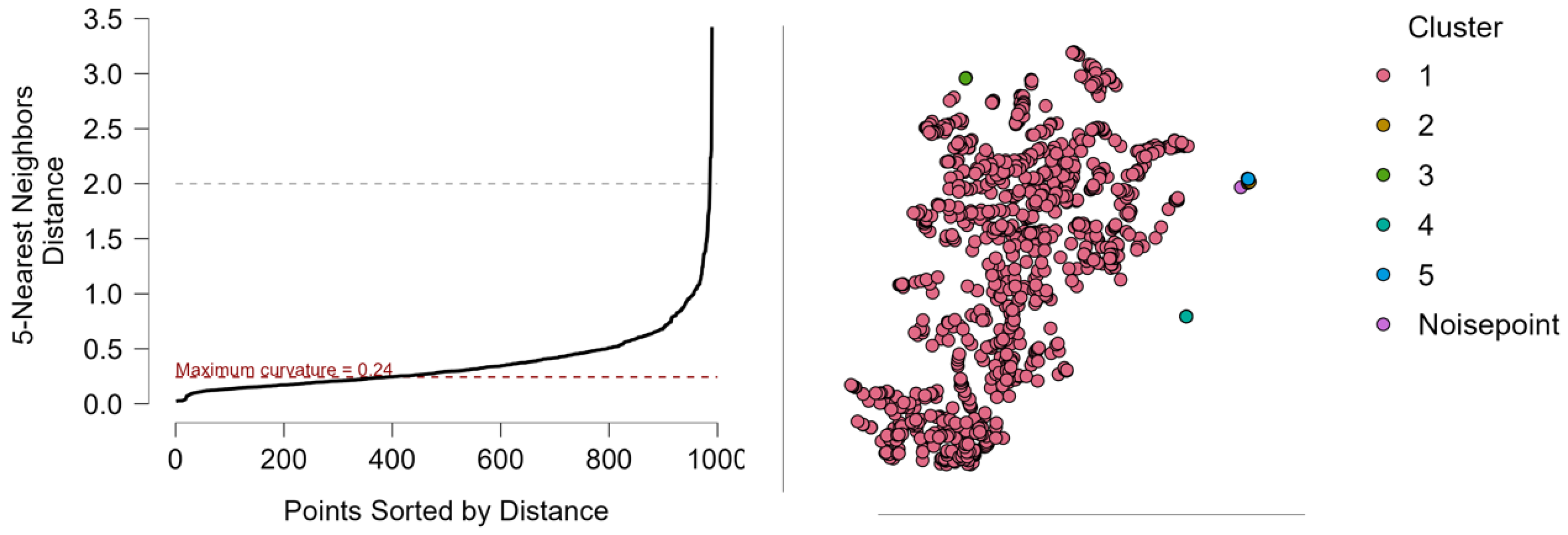
4.2. Evaluating Clustering Strategies for Building Emissions: A Multi-Metric Comparison
Evaluating Cluster Quality and Structure in ESG-Driven Density-Based Analysis
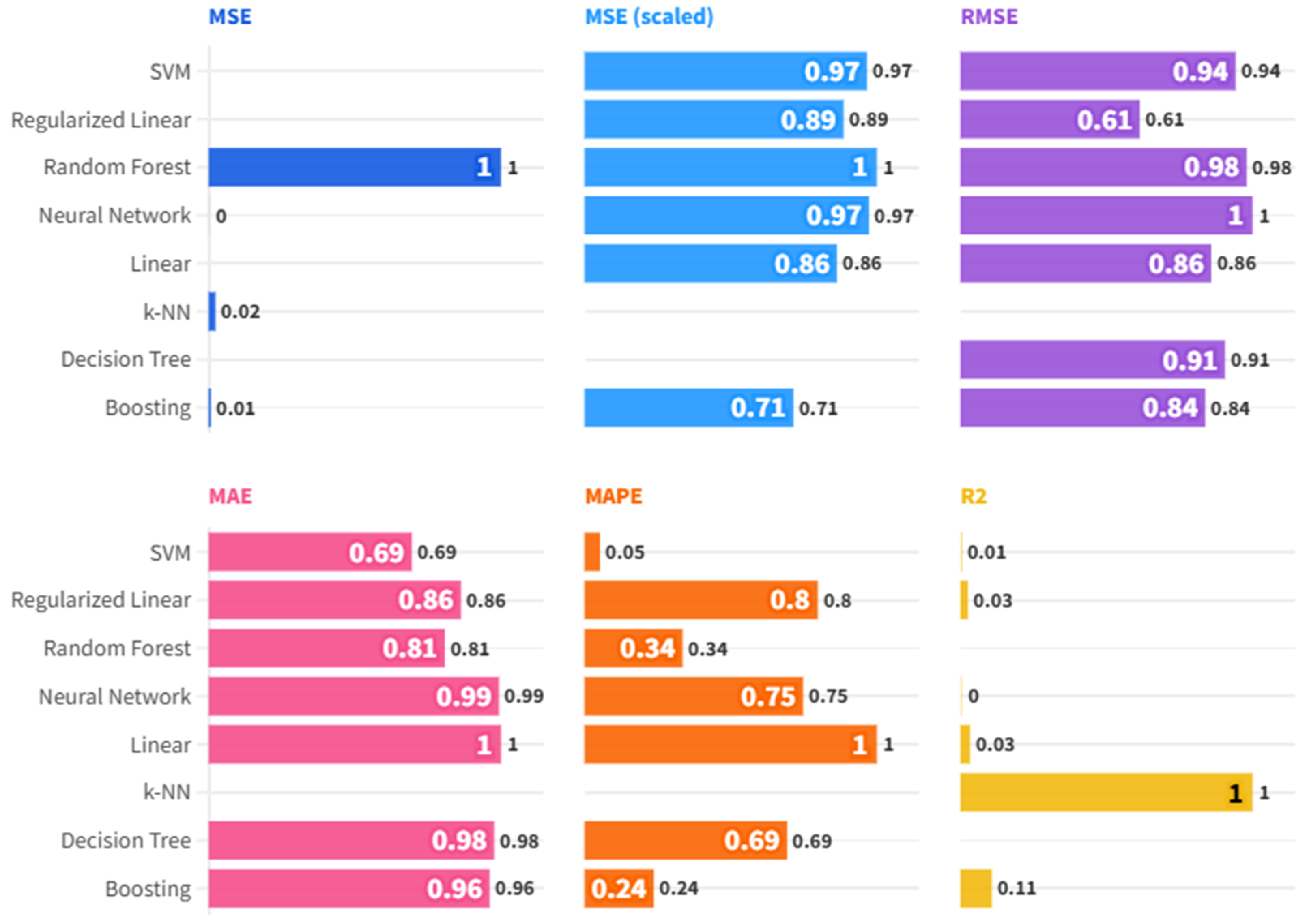
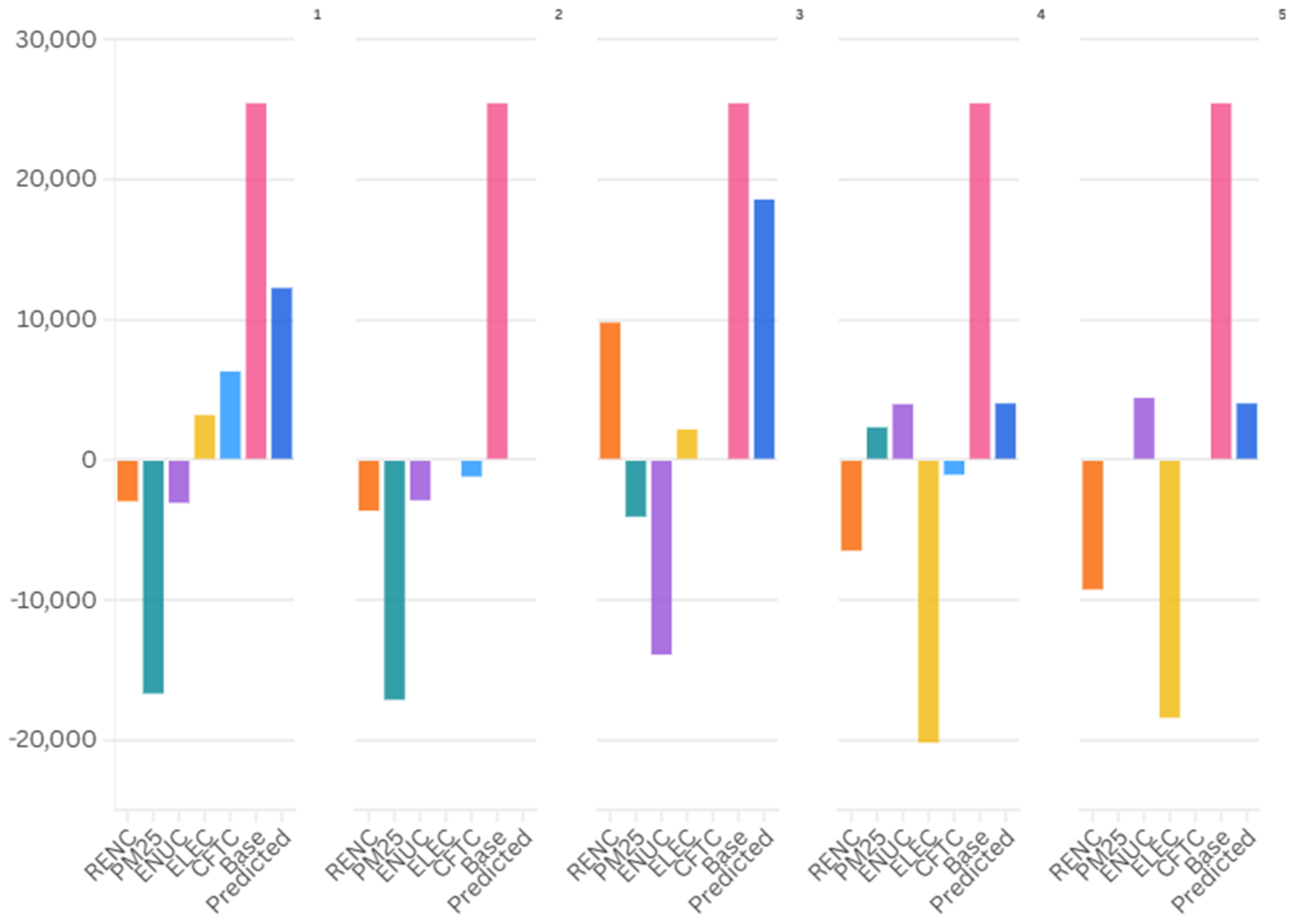
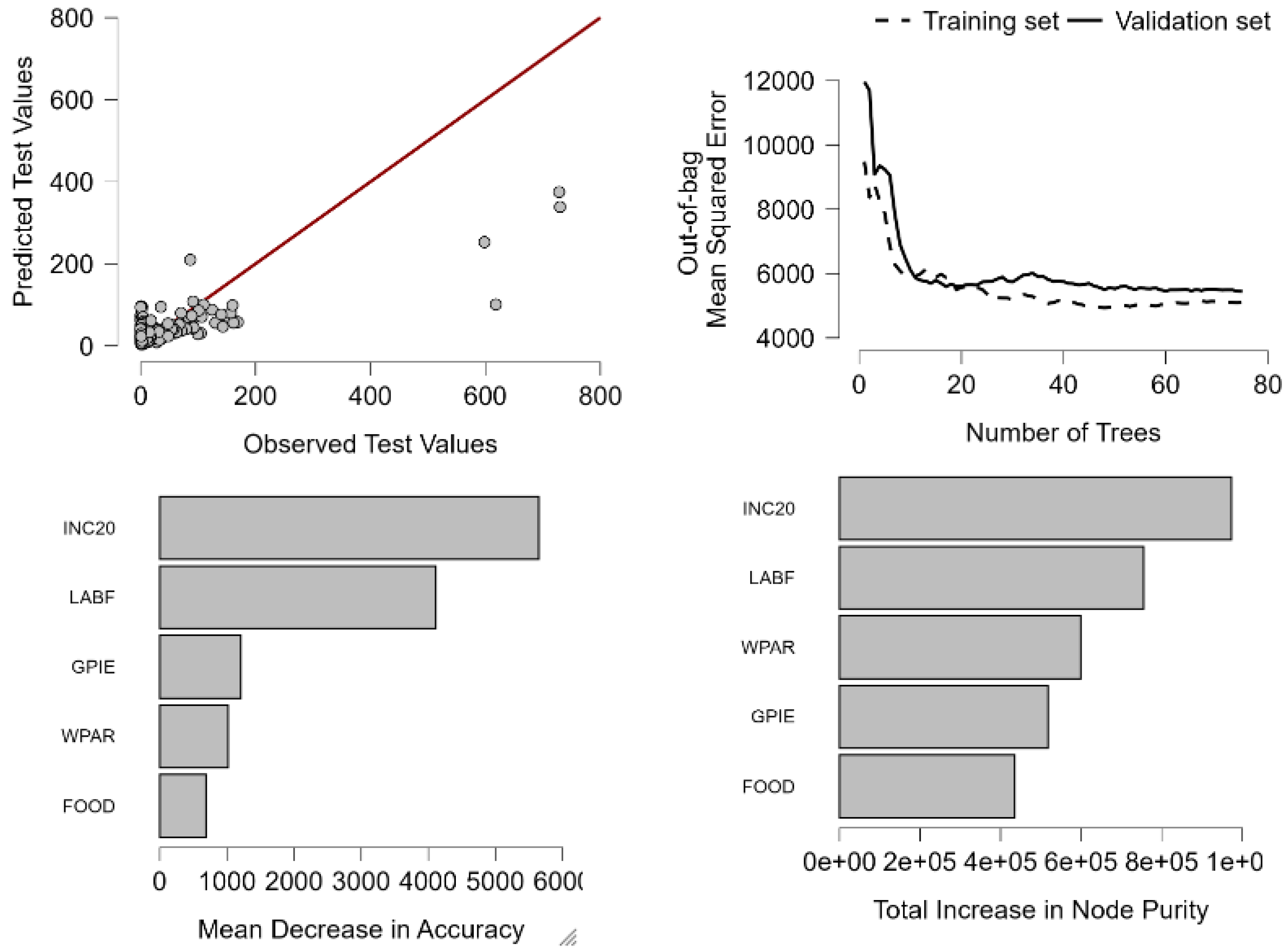
4.3. Explaining Carbon Emissions in the Built Environment: A Comparative Machine Learning Approach
5. Equity, Participation, and Emissions: Social Determinants of Building-Sector CO2
5.1. Social Dimensions of Carbon Emissions: A Panel Data Approach to the Building Sector
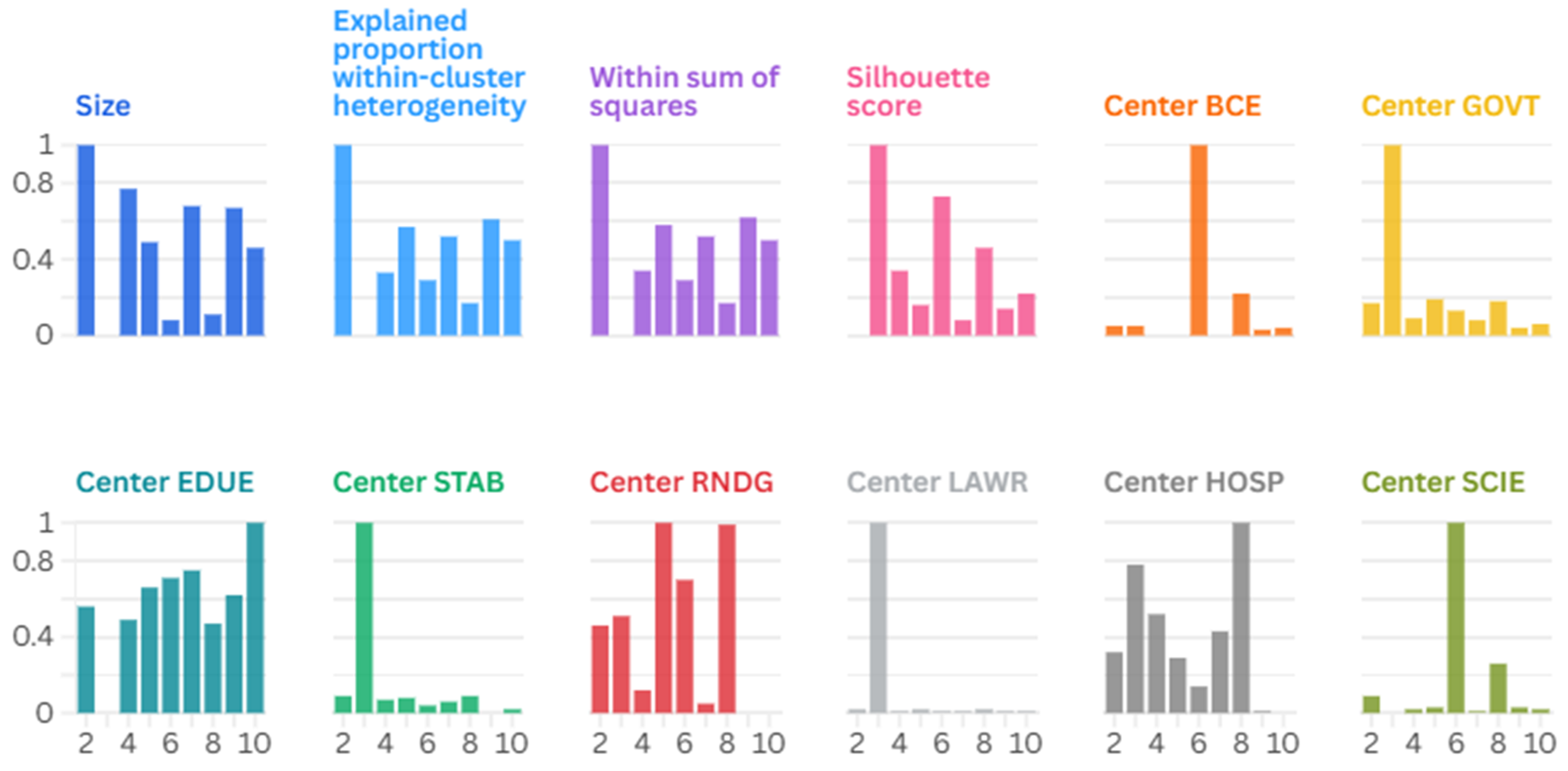
5.2. Clustering Social Determinants of Emissions: An Evaluation of Algorithmic Performance
Decoding Emissions and Equity: A Density-Based Clustering Approach to ESG Social Metrics
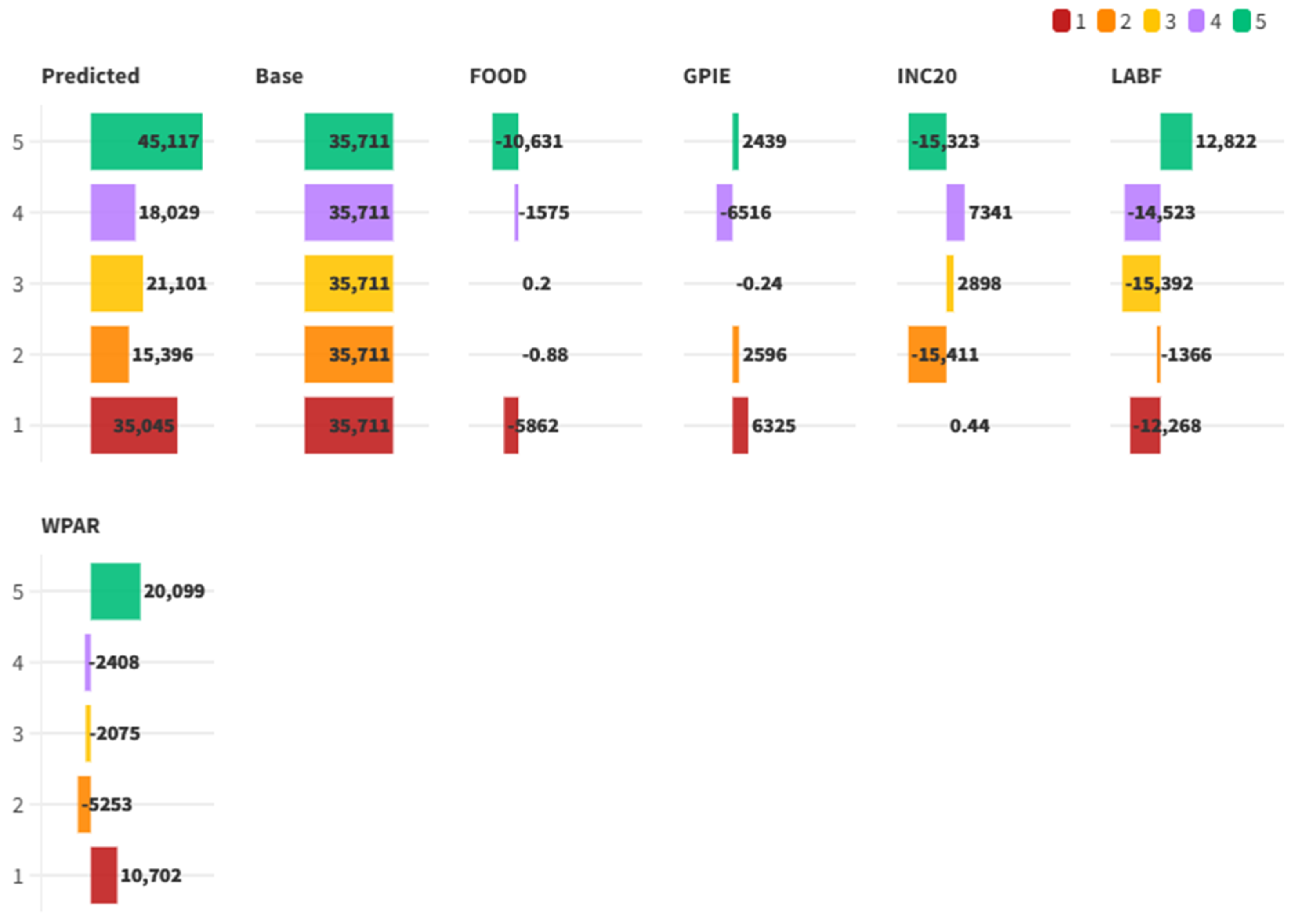
5.3. Finding the Best Fit: A Comparative Evaluation of Regression Models on ESG Data
Social Drivers of Emissions: Interpreting BCE Through Machine Learning and ESG Indicators
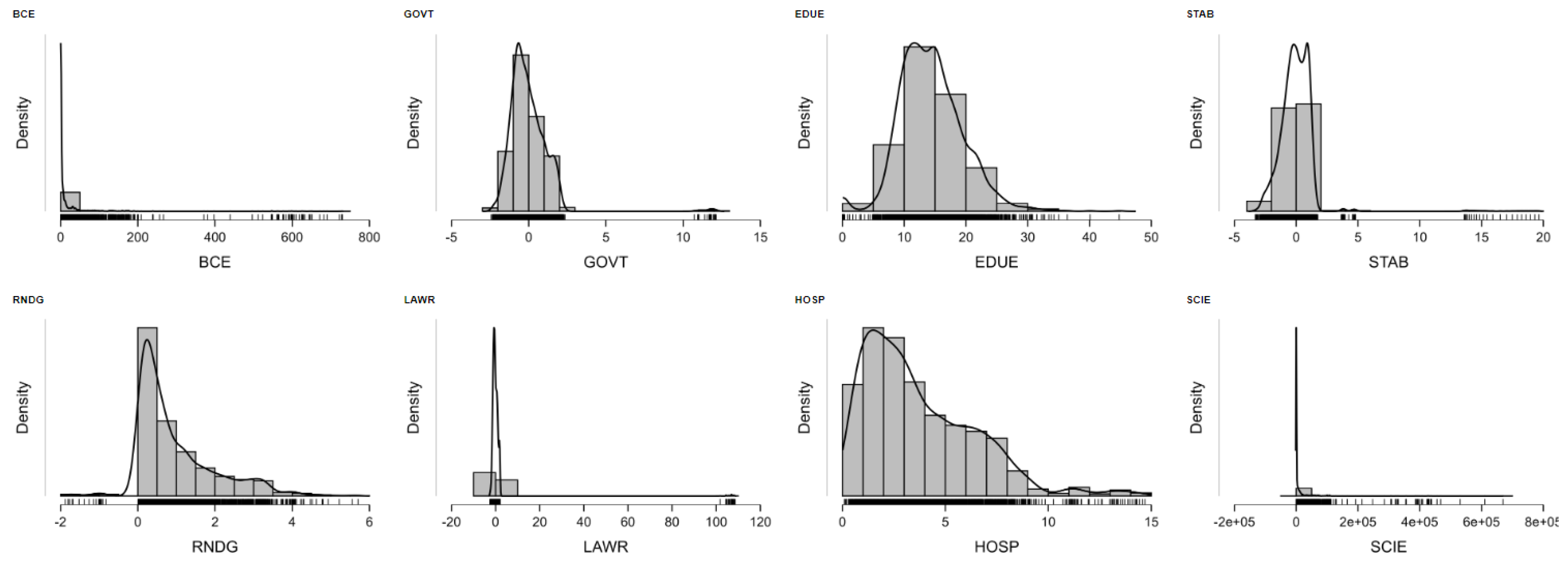
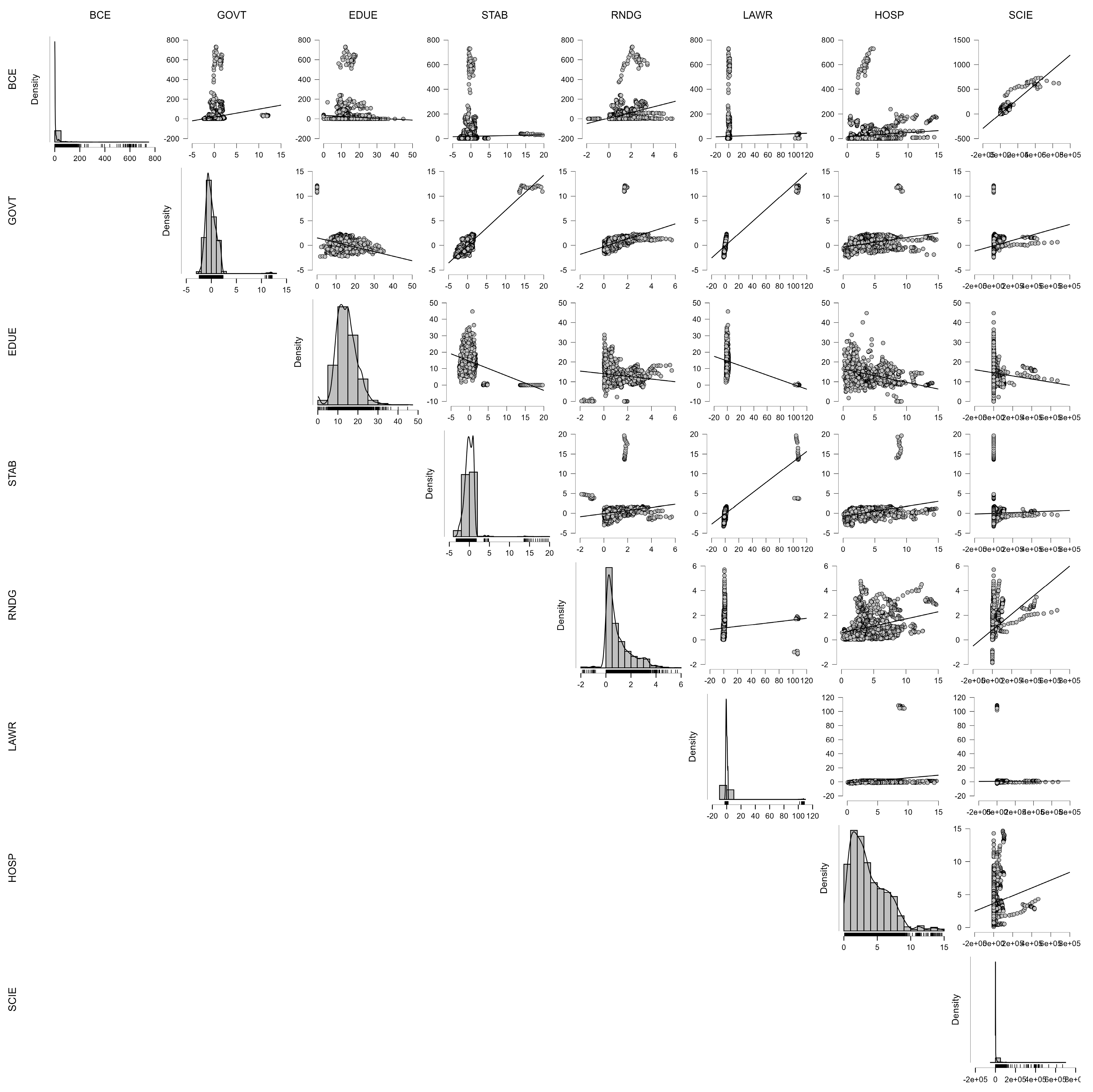
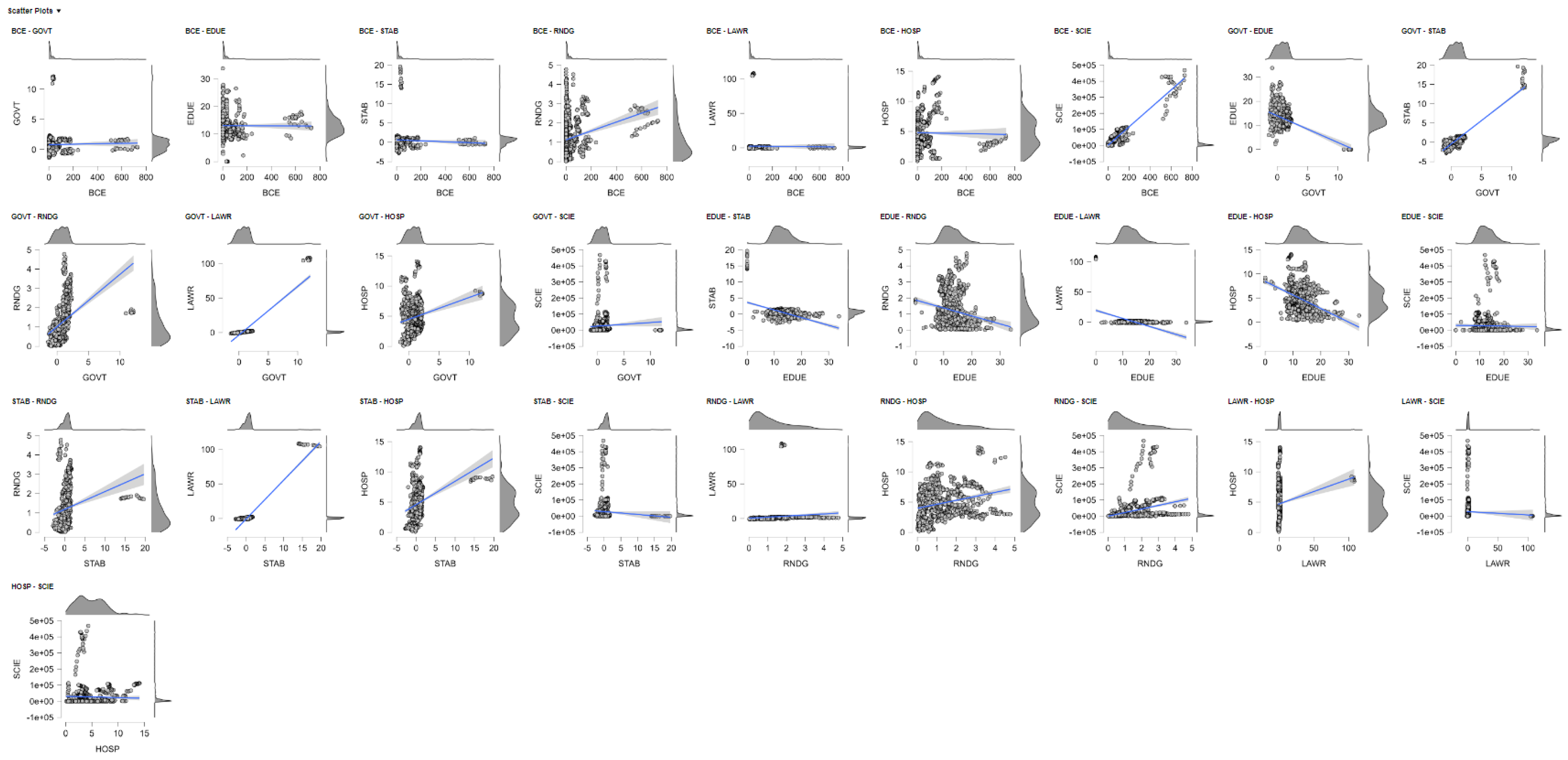
6. Governance and Carbon: Unpacking the Institutional Drivers of Building-Sector Emissions
6.1. Governance and the Carbon Cost of Development: A Panel Analysis of Building Emissions
6.2. Governance and Emissions: Clustering Insights from Neighborhood-Based Algorithms
Mapping Governance-Emission Profiles: Insights from Neighborhood-Based Clustering
6.3. Predicting Emissions with Precision: Machine Learning Models for Governance and BCE
What Drives Emissions? Feature Importance of Governance and Knowledge Indicators
7. Harnessing ESG Dimensions for Effective Building Sector Climate Action
8. Limitations
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
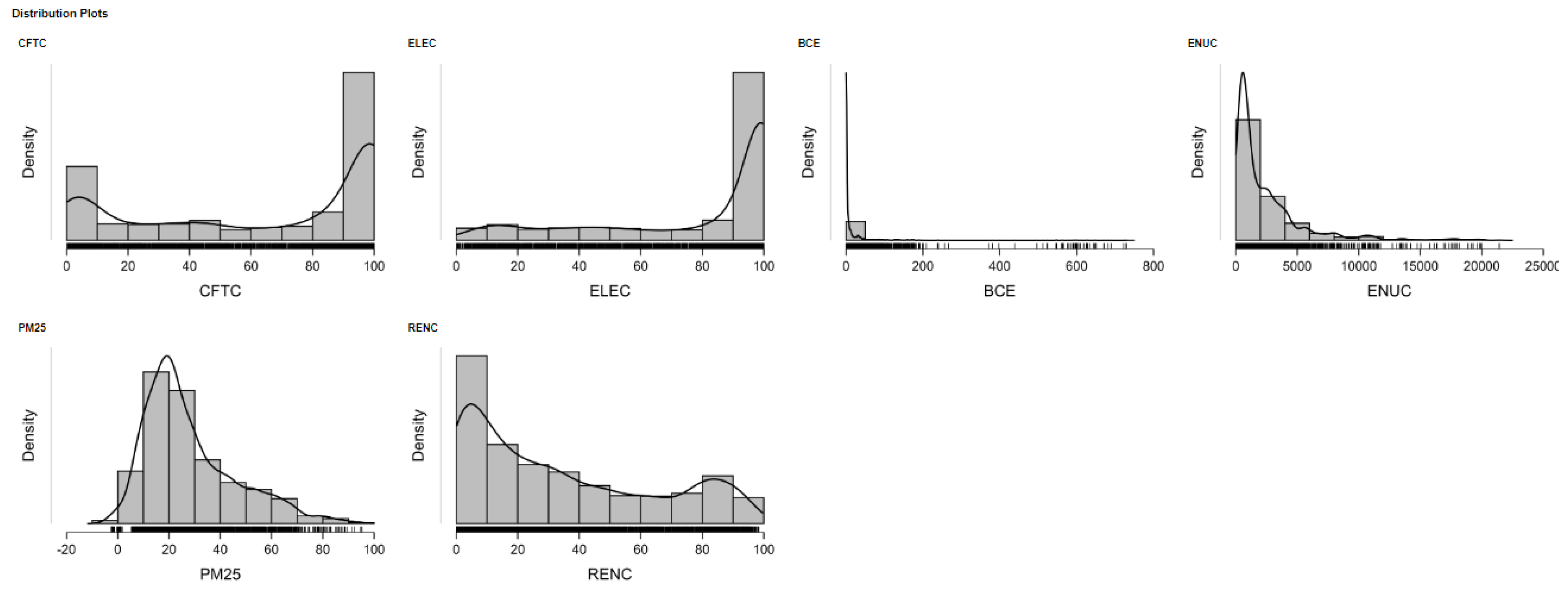
Appendix A. Data Description
| Acronym | Variables | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| BCE | Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions From Building (energy) (Mt CO2e) | Total annual carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) emissions from energy use in the buildings sector, covering IPCC 2006 categories 1.A.4 (Residential and other) and 1.A.5 (Unspecified), converted to CO2e using global warming potentials from the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report (AR5). Unit: Mt CO2e per year. |
| CFTC | Access to Clean Fuels and Technologies for Cooking | Access to clean cooking fuel and technology estimates come from the WHO Global Household Energy Database with national representative household surveys as the sole data source (e.g., DHS, MICS, LSMS, WHS, national censuses). A multivariate hierarchical model—split by urban and rural—estimates fuel-type trends by grouping them as ‘clean’ (e.g., gas, electricity, alcohol) and ‘polluting’ (e.g., biomass, charcoal, coal, kerosene). There are estimates for 191 countries. High-income countries (by World Bank 2022 classification) have universal clean fuel access assumed. |
| ELEC | Access to Electricity | Reliable and secure electricity is essential for economic growth, poverty reduction, and human development. As countries decarbonize, dependence on clean, efficient power will grow. Electricity access enables basic services (lighting, refrigeration, appliances) and is a key indicator of energy poverty. Especially in lower-income countries, governments are prioritizing electrification through rural programs and national agencies. While vital for raising living standards, electricity generation can harm the environment—its impact depends on the energy sources used, with fossil fuels like coal being especially carbon-intensive. |
| ENUC | Energy Use per Capita | Total energy consumption gauges final energy use after conversion into end-use fuels (e.g., electricity, processed oil). It encompasses energy from combustible renewables and waste—like biomass, biogas, and municipal waste. Biomass describes plant materials used as such or converted into fuel, heat, or power. Figures, as gathered by the IEA, use per capita estimates from the World Bank population. National non-OECD data are converted to IEA equivalence. Figures are imprecise and not completely comparable for countries because of limited data quality, particularly for waste and renewables. Energy values have been computed in terms of oil equivalents on the basis of 33% thermal conversion for nuclear and 100% for hydropower. |
| PM25 | PM2.5 Pollution | Population-weighted exposure to ambient PM2.5 refers to the average level of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) pollution that a country’s population is exposed to. PM2.5 particles, with a diameter smaller than 2.5 microns, can penetrate deep into the lungs and pose serious health risks. This measure is calculated by weighting the annual average PM2.5 concentrations by the population distribution across urban and rural areas. |
| RENC | Renewable Energy Consumption | The share of total final energy consumption derived from renewable sources, based on data from IEA, IRENA, UNSD, WHO, and the World Bank (Tracking SDG 7, 2023). |
| FOOD | Food Production Index | The Food Production Index reflects the output of edible crops that offer nutritional value. It excludes items like coffee and tea, which, despite being consumable, do not contribute meaningfully to nutrition. This metric emphasizes food sources that support dietary needs, aligning production data with human nutritional requirements rather than general edibility alone. |
| GPIE | Gender Parity in Enrollment | The Gender Parity Index (GPI) in primary education is calculated by dividing female gross enrollment by male gross enrollment. Data are collected by UNESCO from national education surveys and aligned with ISCED standards to ensure international comparability. The current methodology was adopted in 2011. Reference years reflect when the school year ends. A GPI below 1 indicates girls are disadvantaged; above 1 indicates boys are. Achieving gender parity enhances women’s opportunities and contributes to broader social and economic development. |
| INC20 | Income Share Lowest 20% | The percentage share of income or consumption reflects the portion received by population subgroups, typically divided into deciles or quintiles. Due to rounding, quintile shares may not total exactly 100%. Data come from household surveys via national statistics agencies and World Bank departments, with high-income country data largely from the Luxembourg Income Study. These measures support the World Bank’s goal of shared prosperity—focusing on income growth among the bottom 40%—and help assess inequality within and across countries. |
| LABF | Labor Force Participation | The labor force participation rate represents the share of the population aged 15 and older that is economically active, including all individuals engaged in the production of goods and services during a specific period. Data, sourced from the ILO’s modeled estimates, highlight persistent gender disparities: women’s labor force participation is generally lower than men’s due to social, legal, and cultural norms. In low-income countries, women often work unpaid in family enterprises, while, in high-income nations, higher education has expanded their access to better employment opportunities, though inequalities persist. |
| WPAR | Women in Parliament | Women in parliament refers to the percentage of seats held by women in a single or lower house of national parliaments. Although progress has been made, women remain significantly underrepresented in decision-making roles, especially in lower-income countries. Gender inequality in political participation limits women’s influence on policy and national priorities. Equal representation is essential for inclusive governance and sustainable development. True democracy requires full participation of women, whose perspectives and leadership are vital for shaping equitable and effective public policies. |
| GOVT | Government Effectiveness | Government effectiveness: Estimated measures of perceptions of public service quality, civil service independence, policy formulation and implementation, and government credibility. Scores range from −2.5 to 2.5, based on a standard normal distribution. |
| EDUE | Gov. Expenditure on Education | General government expenditure on education, including current spending, capital outlays, and transfers, is measured as a percentage of GDP. It accounts for education funding from all government levels—local, regional, and central—and includes international transfers to the government. This indicator reflects the government’s financial commitment to the education sector relative to the country’s economic output. |
| STAB | Political Stability | Political stability and absence of violence/terrorism reflect perceptions of the risk of political unrest, government instability, and politically motivated violence or terrorism. Countries are ranked by percentile, from 0 (least stable) to 100 (most stable), allowing global comparison. Percentile ranks are adjusted over time to ensure consistency despite changes in the number of countries included in the Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGIs). |
| RNDG | R&D Expenditure | Gross domestic expenditures on research and development (R&D), measured as a percentage of GDP, represent a country’s financial commitment to innovation and technological progress. This includes both capital and current spending across four key sectors: business enterprises, government institutions, higher education, and private non-profits. It encompasses all R&D activities—basic research, applied research, and experimental development—supporting economic and scientific advancement. |
| LAWR | Rule of Law | Rule of law reflects perceptions of how much confidence individuals and institutions have in societal rules, particularly regarding contract enforcement, property rights, police effectiveness, and judicial independence. It also considers the likelihood of crime and violence. Countries receive a score ranging from approximately −2.5 (weak rule of law) to 2.5 (strong), based on a standard normal distribution. |
| HOSP | Hospital Beds | Hospital beds refer to the total number of beds that are maintained, staffed, and immediately available for the admission of patients. These include inpatient beds in public and private hospitals, general and specialized institutions, and rehabilitation centers. The count typically covers beds used for both acute and chronic care, reflecting the overall healthcare system’s capacity for treatment and recovery. |
| SCIE | Scientific Articles | Scientific and technical journal articles represent the total number of peer-reviewed publications in key research areas, including physics, biology, chemistry, mathematics, clinical medicine, biomedical research, engineering and technology, and earth and space sciences. These articles reflect ongoing advancements, innovation, and collaboration within the global scientific community, contributing to knowledge expansion and technological development across multiple disciplines and industries. |
Appendix B. E-Environment
| CFTC | ELEC | BCE | ENUC | PM25 | RENC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valid | 3916 | 3940 | 4140 | 2173 | 2180 | 3805 |
| Missing | 224 | 200 | 0 | 1967 | 1960 | 335 |
| Mode | 100,000 | 100,000 | 0.006 | 1720 | 17,869 | 0.000 |
| Median | 83,450 | 97,000 | 1098 | 1190 | 22,748 | 24,690 |
| Mean | 63,312 | 77,349 | 18,177 | 2347 | 28,010 | 33,772 |
| Std. Error of Mean | 0.626 | 0.497 | 1052 | 62,281 | 0.383 | 0.488 |
| 95% CI Mean Upper | 64,540 | 78,323 | 20,239 | 2469 | 28,761 | 34,728 |
| 95% CI Mean Lower | 62,085 | 76,376 | 16,114 | 2225 | 27,260 | 32,816 |
| Std. Deviation | 39,179 | 31,169 | 67,687 | 2903 | 17,871 | 30,072 |
| 95% CI Std. Dev. Upper | 40,067 | 31,873 | 69,178 | 2992 | 18,418 | 30,764 |
| 95% CI Std. Dev. Lower | 38,330 | 30,496 | 66,260 | 2819 | 17,356 | 29,411 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.619 | 0.403 | 3724 | 1237 | 0.638 | 0.890 |
| MAD | 16,550 | 3000 | 1064 | 851,251 | 9497 | 20,700 |
| MAD Robust | 24,537 | 4448 | 1578 | 1,262,064 | 14,081 | 30,690 |
| IQR | 77,400 | 44,176 | 6976 | 2,531,125 | 21,584 | 49,260 |
| Variance | 1534 | 971,537 | 4581 | 8.429 × 106 | 319,361 | 904,338 |
| 95% CI Variance Upper | 1605 | 1015 | 4785 | 8.954 × 106 | 339,207 | 946,397 |
| 95% CI Variance Lower | 1469 | 930,018 | 4390 | 7.949 × 106 | 301,215 | 865,034 |
| Skewness | −0.509 | −1129 | 7251 | 2758 | 1059 | 0.649 |
| Std. Error of Skewness | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.038 | 0.053 | 0.052 | 0.040 |
| Kurtosis | −1431 | −0.236 | 59,218 | 9911 | 0.716 | −0.932 |
| Std. Error of Kurtosis | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.076 | 0.105 | 0.105 | 0.079 |
| Shapiro–Wilk | 0.797 | 0.737 | 0.265 | 0.699 | 0.917 | 0.885 |
| p-value of Shapiro–Wilk | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Range | 99,900 | 99,928 | 729,783 | 21,419 | 97,808 | 98,340 |
| Minimum | 0.100 | 0.072 | 0.000 | 1540 | −2566 | 0.000 |
| Maximum | 100,000 | 100,000 | 729,783 | 21,420 | 95,243 | 98,340 |
| 25th percentile | 22,600 | 55,824 | 0.168 | 536,617 | 15,575 | 7450 |
| 50th percentile | 83,450 | 97,000 | 1098 | 1190 | 22,748 | 24,690 |
| 75th percentile | 100,000 | 100,000 | 7144 | 3067 | 37,158 | 56,710 |
| 25th percentile | 22,600 | 55,824 | 0.168 | 536,617 | 15,575 | 7450 |
| 50th percentile | 83,450 | 97,000 | 1098 | 1190 | 22,748 | 24,690 |
| 75th percentile | 100,000 | 100,000 | 7144 | 3067 | 37,158 | 56,710 |
| Sum | 247,931 | 304,755 | 75,251 | 5.102 × 106 | 61,062 | 128,502 |
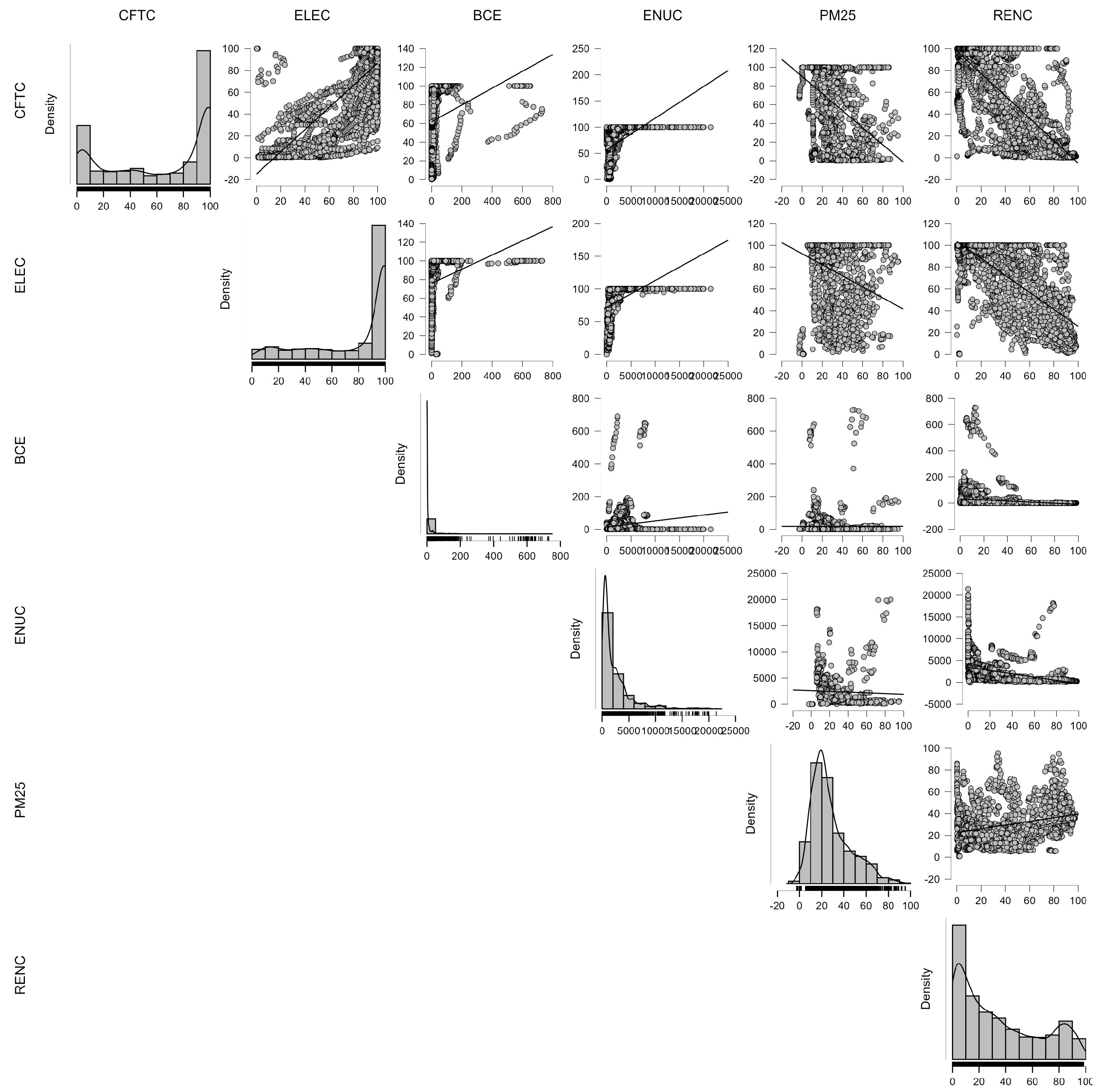
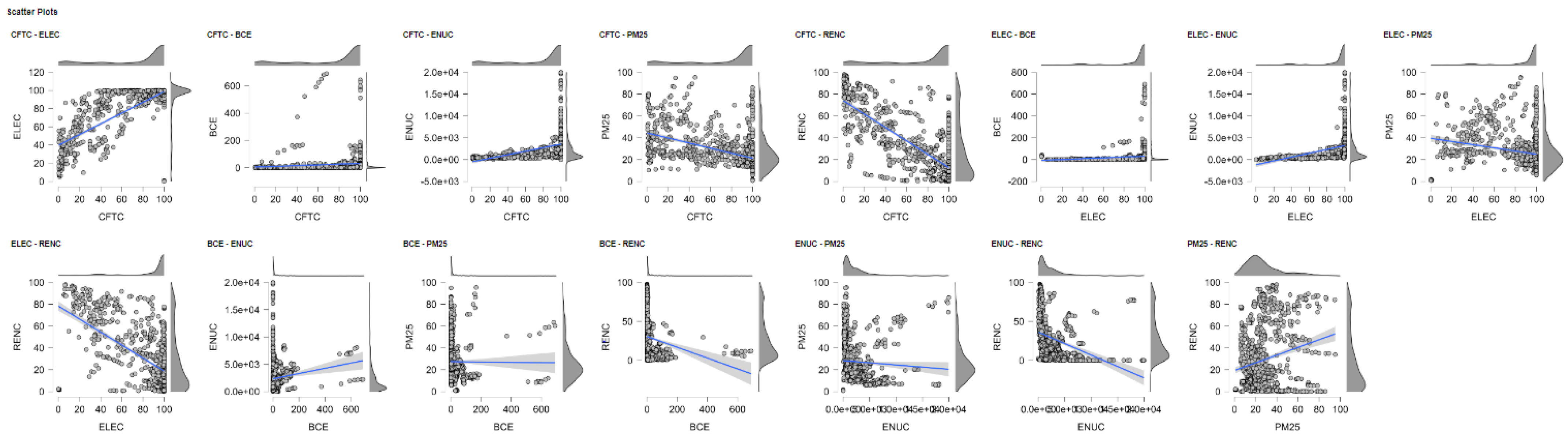
| CFTC | ELEC | BCE | ENUC | PM25 | RENC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFTC | 1.212 | 715.040 | 328.145 | 49.067 | −281.490 | −744.185 |
| ELEC | 715.040 | 771.991 | 294.482 | 33.913 | −112.064 | −458.817 |
| BCE | 328.145 | 294.482 | 6.011 | 28.989 | −8.701 | −416.588 |
| ENUC | 49.067 | 33.913 | 28.989 | 8.975 × 106 | −3.560 | −26.307 |
| PM25 | −281.490 | −112.064 | −8.701 | −3.560 | 310.835 | 109.470 |
| RENC | −744.185 | −458.817 | −416.588 | −26.307 | 109.470 | 746.022 |
| CFTC | ELEC | BCE | ENUC | PM25 | RENC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFTC | 1.000 | 0.739 | 0.122 | 0.470 | −0.459 | −0.783 |
| ELEC | 0.739 | 1.000 | 0.137 | 0.407 | −0.229 | −0.605 |
| BCE | 0.122 | 0.137 | 1.000 | 0.125 | −0.006 | −0.197 |
| ENUC | 0.470 | 0.407 | 0.125 | 1.000 | −0.067 | −0.321 |
| PM25 | −0.459 | −0.229 | −0.006 | −0.067 | 1.000 | 0.227 |
| RENC | −0.783 | −0.605 | −0.197 | −0.321 | 0.227 | 1.000 |
Appendix C. S-Social
| FOOD | GPIE | INC20 | LABF | WPAR | BCE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valid | 4102 | 2665 | 1607 | 3998 | 3963 | 4140 |
| Missing | 38 | 1475 | 2533 | 142 | 177 | 0 |
| Mode | 0.123 | 0.990 | 7100 | 55,146 | 0.000 | 0.006 |
| Median | 96,020 | 0.998 | 7100 | 67,324 | 17,302 | 1098 |
| Mean | 92,769 | 216,096 | 7879 | 65,663 | 19,263 | 18,177 |
| Std. Error of Mean | 0.383 | 47,245 | 0.236 | 0.186 | 0.204 | 1052 |
| 95% CI Mean Upper | 93,520 | 308,737 | 8341 | 66,029 | 19,663 | 20,239 |
| 95% CI Mean Lower | 92,017 | 123,454 | 7416 | 65,297 | 18,863 | 16,114 |
| Std. Deviation | 24,542 | 2438 | 9458 | 11,791 | 12,847 | 67,687 |
| 95% CI Std. Dev. Upper | 25,085 | 2506 | 9797 | 12,055 | 13,136 | 69,178 |
| 95% CI Std. Dev. Lower | 24,022 | 2375 | 9142 | 11,538 | 12,570 | 66,260 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.265 | 11,287 | 1200 | 0.180 | 0.667 | 3724 |
| MAD | 10,000 | 0.024 | 1500 | 6989 | 7927 | 1064 |
| MAD Robust | 14,826 | 0.035 | 2224 | 10,361 | 11,752 | 1578 |
| IQR | 21,758 | 0.049 | 3050 | 14,340 | 16,190 | 6976 |
| Variance | 602,295 | 5.949 × 106 | 89,448 | 139,028 | 165,038 | 4581 |
| 95% CI Variance Upper | 629,238 | 6.281 × 106 | 95,972 | 145,331 | 172,554 | 4785 |
| 95% CI Variance Lower | 577,053 | 5.642 × 106 | 83,570 | 133,129 | 158,005 | 4390 |
| Skewness | 2615 | 11,601 | 7932 | −0.916 | 1197 | 7251 |
| Std. Error of Skewness | 0.038 | 0.047 | 0.061 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.038 |
| Kurtosis | 43,986 | 135,463 | 65,260 | 1406 | 2689 | 59,218 |
| Std. Error of Kurtosis | 0.076 | 0.095 | 0.122 | 0.077 | 0.078 | 0.076 |
| Shapiro–Wilk | 0.816 | 0.060 | 0.250 | 0.954 | 0.930 | 0.265 |
| p-value of Shapiro–Wilk | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Range | 502,017 | 33,376 | 93,769 | 76,467 | 87,730 | 729,783 |
| Minimum | 0.123 | 0.000 | 0.187 | 13,156 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Maximum | 502,140 | 33,376 | 93,956 | 89,623 | 87,730 | 729,783 |
| 25th percentile | 81,757 | 0.971 | 5350 | 59,368 | 10,000 | 0.168 |
| 50th percentile | 96,020 | 0.998 | 7100 | 67,324 | 17,302 | 1098 |
| 75th percentile | 103,515 | 1020 | 8400 | 73,709 | 26,190 | 7144 |
| Sum | 380,537 | 575,894 | 12,660 | 262,520 | 76,338 | 75,251 |


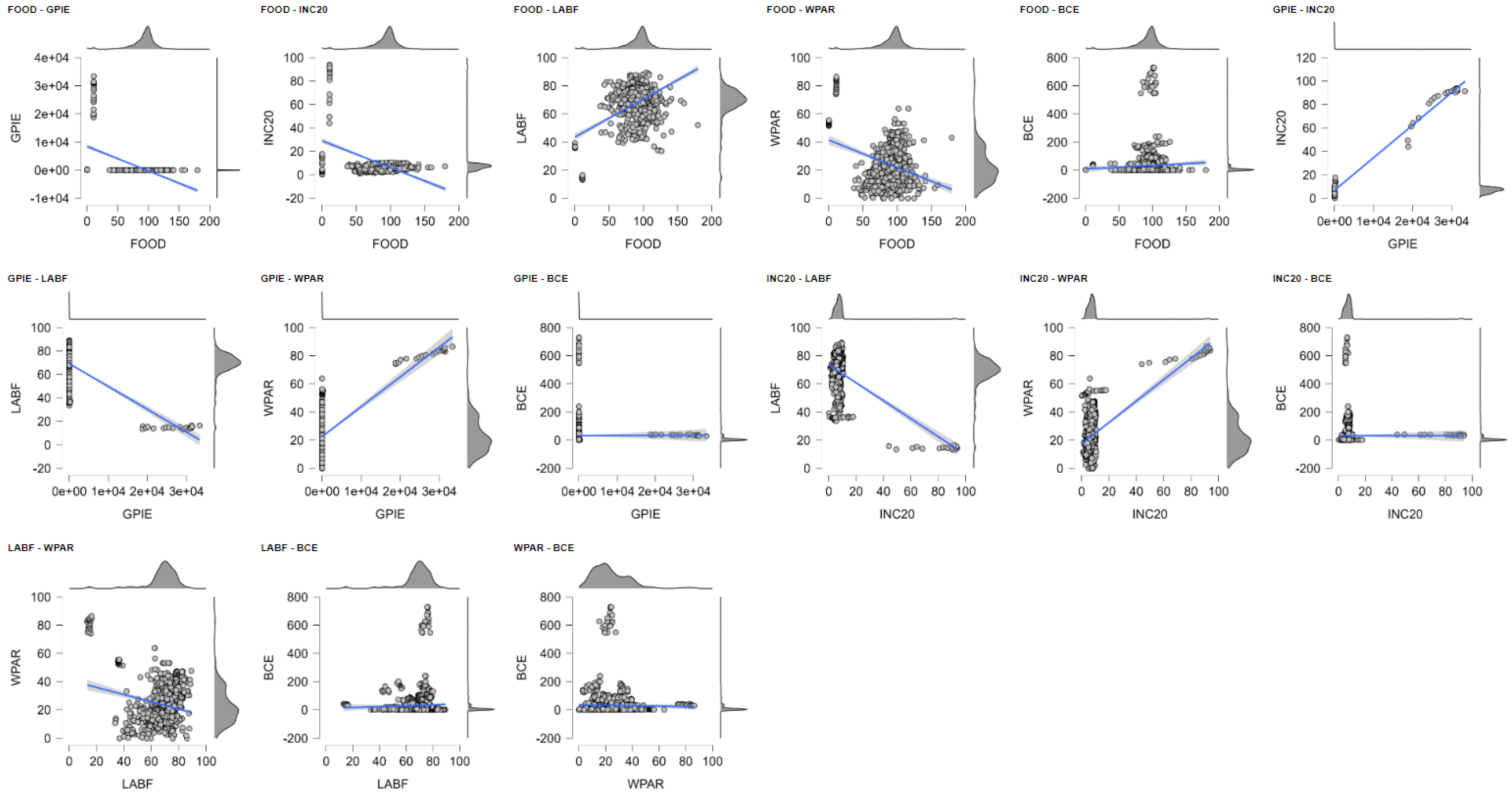
| FOOD | GPIE | INC20 | LABF | WPAR | BCE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOOD | 424.789 | −37.108 | −96.944 | 114.735 | −82.864 | 107.769 |
| GPIE | −37.108 | 1.262 × 107 | 35.079 | −24.538 | 26.719 | 1.483 |
| INC20 | −96.944 | 35.079 | 102.362 | −65.165 | 77.834 | −0.529 |
| LABF | 114.735 | −24.538 | −65.165 | 126.359 | −32.177 | 39.820 |
| WPAR | −82.864 | 26.719 | 77.834 | −32.177 | 191.207 | −29.946 |
| BCE | 107.769 | 1.483 | −0.529 | 39.820 | −29.946 | 7.518 |
| FOOD | GPIE | INC20 | LABF | WPAR | BCE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOOD | 1.000 | −0.507 | −0.465 | 0.495 | −0.291 | 0.060 |
| GPIE | −0.507 | 1.000 | 0.976 | −0.615 | 0.544 | 0.005 |
| INC20 | −0.465 | 0.976 | 1.000 | −0.573 | 0.556 | −6.033 × 10−4 |
| LABF | 0.495 | −0.615 | −0.573 | 1.000 | −0.207 | 0.041 |
| WPAR | −0.291 | 0.544 | 0.556 | −0.207 | 1.000 | −0.025 |
| BCE | 0.060 | 0.005 | −6.033 × 10−4 | 0.041 | −0.025 | 1.000 |
Appendix D. G-Governance
| BCE | GOVT | EDUE | STAB | RNDG | LAWR | HOSP | SCIE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valid | 4140 | 3907 | 2760 | 3949 | 1883 | 3941 | 2030 | 3782 |
| Missing | 0 | 233 | 1380 | 191 | 2257 | 199 | 2110 | 358 |
| Mode | 0.006 | −1.158 | 0.000 | 1.170 | 0.018 | 0.834 | 1.300 | 0.000 |
| Median | 1.098 | −0.215 | 14.031 | −0.019 | 0.577 | −0.270 | 3.015 | 226.270 |
| Mean | 18.177 | −0.029 | 14.370 | −0.009 | 0.948 | 0.583 | 3.733 | 10.180 |
| Std. Error of Mean | 1.052 | 0.021 | 0.097 | 0.025 | 0.023 | 0.138 | 0.060 | 688.649 |
| 95% CI Mean Upper | 20.239 | 0.012 | 14.561 | 0.040 | 0.994 | 0.854 | 3.850 | 11.530 |
| 95% CI Mean Lower | 16.114 | −0.069 | 14.180 | −0.058 | 0.902 | 0.312 | 3.616 | 8.830 |
| Std. Deviation | 67.687 | 1.300 | 5.102 | 1.558 | 1.017 | 8.682 | 2.683 | 42.350 |
| 95% CI Std. Dev. Upper | 69.178 | 1.329 | 5.240 | 1.594 | 1.051 | 8.878 | 2.769 | 43.327 |
| 95% CI Std. Dev. Lower | 66.260 | 1.272 | 4.971 | 1.525 | 0.986 | 8.494 | 2.603 | 41.417 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 3.724 | −45.259 | 0.355 | −171.768 | 1.073 | 14.889 | 0.719 | 4.160 |
| MAD | 1.064 | 0.660 | 3.235 | 0.711 | 0.430 | 0.700 | 1.715 | 222.835 |
| MAD Robust | 1.578 | 0.979 | 4.797 | 1.054 | 0.638 | 1.038 | 2.543 | 330.375 |
| IQR | 6.976 | 1.373 | 6.506 | 1.424 | 1.138 | 1.440 | 3.878 | 3.153 |
| Variance | 4.581 | 1.690 | 26.028 | 2.429 | 1.034 | 75.370 | 7.201 | 1.794 × 109 |
| 95% CI Variance Upper | 4.785 | 1.767 | 27.458 | 2.540 | 1.104 | 78.812 | 7.665 | 1.877 × 109 |
| 95% CI Variance Lower | 4.390 | 1.617 | 24.707 | 2.325 | 0.971 | 72.149 | 6.777 | 1.715 × 109 |
| Skewness | 7.251 | 4.152 | 0.454 | 6.009 | 1.273 | 11.968 | 1.111 | 8.482 |
| Std. Error of Skewness | 0.038 | 0.039 | 0.047 | 0.039 | 0.056 | 0.039 | 0.054 | 0.040 |
| Kurtosis | 59.218 | 34.610 | 1.477 | 63.863 | 1.633 | 143.174 | 1.259 | 85.379 |
| Std. Error of Kurtosis | 0.076 | 0.078 | 0.093 | 0.078 | 0.113 | 0.078 | 0.109 | 0.080 |
| Shapiro–Wilk | 0.265 | 0.734 | 0.977 | 0.615 | 0.858 | 0.112 | 0.911 | 0.235 |
| p-value of Shapiro–Wilk | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Range | 729.783 | 14.580 | 44.802 | 22.960 | 7.586 | 111.216 | 14.590 | 669.746 |
| Minimum | 0.000 | −2.439 | 0.000 | −3.313 | −1.880 | −2.591 | 0.100 | −2.283 |
| Maximum | 729.783 | 12.141 | 44.802 | 19.647 | 5.706 | 108.625 | 14.690 | 669.744 |
| 25th percentile | 0.168 | −0.796 | 10.877 | −0.722 | 0.230 | −0.854 | 1.603 | 25.813 |
| 50th percentile | 1.098 | −0.215 | 14.031 | −0.019 | 0.577 | −0.270 | 3.015 | 226.270 |
| 75th percentile | 7.144 | 0.577 | 17.383 | 0.702 | 1.368 | 0.586 | 5.480 | 3.179 |
| Sum | 75.251 | −112.215 | 39.661 | −35.830 | 1.785 | 2.297 | 7.577 | 3.850 × 107 |

| BCE | GOVT | EDUE | STAB | RNDG | LAWR | HOSP | SCIE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCE | 11.950 | 4.309 | −3.168 | −14.152 | 27.514 | −15.110 | −4.792 | 6.849 × 106 |
| GOVT | 4.309 | 2.653 | −2.943 | 3.235 | 0.722 | 18.655 | 0.966 | 5.898 |
| EDUE | −3.168 | −2.943 | 16.500 | −3.925 | −0.818 | −21.927 | −4.630 | −4.123 |
| STAB | −14.152 | 3.235 | −3.925 | 4.703 | 0.433 | 26.401 | 1.816 | −8.322 |
| RNDG | 27.514 | 0.722 | −0.818 | 0.433 | 1.011 | 1.560 | 0.665 | 22.538 |
| LAWR | −15.110 | 18.655 | −21.927 | 26.401 | 1.560 | 169.873 | 6.960 | −34.172 |
| HOSP | −4.792 | 0.966 | −4.630 | 1.816 | 0.665 | 6.960 | 7.315 | −5.751 |
| SCIE | 6.849 × 106 | 5.898 | −4.123 | −8.322 | 22.538 | −34.172 | −5.751 | 4.319 × 109 |
| BCE | GOVT | EDUE | STAB | RNDG | LAWR | HOSP | SCIE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCE | 1.000 | 0.024 | −0.007 | −0.060 | 0.250 | −0.011 | −0.016 | 0.953 |
| GOVT | 0.024 | 1.000 | −0.445 | 0.916 | 0.441 | 0.879 | 0.219 | 0.055 |
| EDUE | −0.007 | −0.445 | 1.000 | −0.446 | −0.200 | −0.414 | −0.421 | −0.015 |
| STAB | −0.060 | 0.916 | −0.446 | 1.000 | 0.199 | 0.934 | 0.310 | −0.058 |
| RNDG | 0.250 | 0.441 | −0.200 | 0.199 | 1.000 | 0.119 | 0.245 | 0.341 |
| LAWR | −0.011 | 0.879 | −0.414 | 0.934 | 0.119 | 1.000 | 0.197 | −0.040 |
| HOSP | −0.016 | 0.219 | −0.421 | 0.310 | 0.245 | 0.197 | 1.000 | −0.032 |
| SCIE | 0.953 | 0.055 | −0.015 | −0.058 | 0.341 | −0.040 | −0.032 | 1.000 |
Appendix E. Autocorrelation and Heteroscedasticity
Appendix E.1. Autocorrelation for E-Environment
| Source | SS | df | MS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 12,807.621 | 1 | 12,807.621 | |
| Residual | 18,995.4902 | 568 | 33.4427644 | |
| Total | 31,803.1112 | 569 | 55.8929898 | |
| Number of obs | 570 | |||
| F(1, 568) | 382.97 | |||
| Prob > F | 0.000 | |||
| R-Squared | 0.4027 | |||
| Adj R-Squared | 0.4017 | |||
| Root MSE | 5.783 | |||
| Uhat | Uhat_lag | _cons | ||
| Coefficient | 0.7561607 | −0.0021011 | ||
| Std. Err. | 0.0386394 | 0.2423395 | ||
| T | 19.57 | −0.01 | ||
| p > |t| | 0.680267 | −0.4780921 | ||
| [95% Con. Interval] | 0.8320543 | 0.4738899 | ||
| Model Statistics | Value | Model Statistics | Value | Model Statistics | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of observations | 990 | Observations per group (max) | 20 | ρ (rho) | 0.9784 | |
| Number of groups (N) | 159 | F(5, 158) | 1.56 | Observations per group (avg) | 6.2 | |
| R-squared (Within) | 0.1127 | Prob > F | 0.1740 | Observations per group (min) | 1 | |
| R-squared (Between) | 0.0337 | corr(ui Xb) | −0.1328 | σe (sigma_e) | 104.782 | |
| R-squared (Overall) | 0.0312 | σu (sigma_u) | 705.105 | |||
| CFTC | ELEC | ENUC | PM25 | RENC | _cons | |
| Coefficient | 0.3551 | −0.2731 | 0.0028 | 0.6920 | −0.5133 | 102.987 |
| Std. Err. | 0.3332 | 0.2572 | 0.0016 | 0.3869 | 0.2821 | 121.714 |
| t | 1.07 | −1.06 | 1.83 | 1.79 | −1.82 | 0.85 |
| ** p < 0.05 | 0.288 | 0.290 | 0.070 | 0.076 | 0.071 | 0.399 |
| 95% Conf. Interval | [−0.3029, 1.0132] | [−0.7810, 0.2349] | [−0.0002, 0.0059] | [−0.0722, 1.4562] | [−1.0705, 0.0438] | [−13.7409, 34.3383] |
| Description | Value | Description | Value | Description | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of observations | 990 | Number of groups (N) | 159 | R-squared (Within) | 0.1126 | |
| R-squared (Between) | 0.0341 | R-squared (Overall) | 0.0316 | Observations per group (min) | 1 | |
| Observations per group (avg) | 6.2 | Observations per group (max) | 20 | Wald chi2(5) | 10.33 | |
| Prob > chi2 | 0.0664 | corr(ui, X) (assumed) | 0 | σu (sigma_u) | 699.504 | |
| σe (sigma_e) | 104.782 | ρ (rho) | 0.9781 | |||
| CFTC | ELEC | ENUC | PM25 | RENC | _cons | |
| Coefficient | 0.3110 | −0.2399 | 0.0027 | 0.6584 | −0.4853 | 94.543 |
| Robust Std. Err. | 0.2739 | 0.2280 | 0.0014 | 0.4349 | 0.2393 | 105.143 |
| z | 1.14 | −1.05 | 1.86 | 1.51 | −2.03 | 0.90 |
| p > |z| | 0.256 | 0.293 | 0.063 | 0.130 | 0.043 | 0.369 |
| 95% Conf. Interval | [−0.2259, 0.8479] | [−0.6868, 0.2070] | [−0.0001, 0.0055] | [−0.1940, 1.5108] | [−0.9542, −0.0164] | [−11.1532, 30.0619] |
| Method | Number of Observations | Number of Groups | Group Variable (i) | F-Statistic (25, 20) | Maximum Lag | Prob > F | Within R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-effect regression | 990 | 159 | n | 3071.86 | 2 | 0.0000 | 0.1188 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Err. | t | p > |t| | CI Lower | CI Upper | Note |
| cftc | 0.3376 | 0.0550 | 6.14 | 0.000 | 0.2228 | 0.4523 | |
| elec | −0.2915 | 0.0967 | −3.01 | 0.007 | −0.4933 | −0.0897 | |
| enuc | 0.0028 | 0.0005 | 5.09 | 0.000 | 0.0016 | 0.0039 | |
| pm25 | 0.7560 | 0.2161 | 3.50 | 0.002 | 0.3052 | 12.067 | |
| renc | −0.5190 | 0.1812 | −2.86 | 0.010 | −0.8968 | −0.1411 | |
| t = 1 | empty | ||||||
| t = 2 | 0.2862 | 31.141 | 0.09 | 0.928 | −62.097 | 67.820 | |
| t = 3 | 28.584 | 14.427 | 1.98 | 0.061 | −0.1509 | 58.678 | |
| t = 4 | 39.223 | 14.521 | 2.70 | 0.014 | 0.8934 | 69.512 | |
| t = 5 | 39.634 | 14.640 | 2.71 | 0.014 | 0.9095 | 70.173 | |
| t = 6 | 13.700 | 0.3800 | 3.61 | 0.002 | 0.5773 | 21.627 | |
| t = 7 | 37.745 | 14.251 | 2.65 | 0.015 | 0.8018 | 67.473 | |
| t = 8 | −13.783 | 14.871 | −0.93 | 0.365 | −44.803 | 17.238 | |
| t = 9 | 17.018 | 14.956 | 1.14 | 0.269 | −14.181 | 48.216 | |
| t = 10 | 15.751 | 14.764 | 1.07 | 0.299 | −15.047 | 46.549 | |
| t = 11 | 11.696 | 0.5777 | 2.02 | 0.056 | −0.0354 | 23.746 | |
| t = 12 | 0.0126 | 0.4635 | 0.03 | 0.979 | −0.9541 | 0.9794 | |
| t = 13 | −0.3014 | 0.5163 | −0.58 | 0.566 | −13.785 | 0.7757 | |
| t = 14 | 13.368 | 0.7711 | 1.73 | 0.098 | −0.2717 | 29.453 | |
| t = 15 | 15.676 | 10.223 | 1.53 | 0.141 | −0.5648 | 37.000 | |
| t = 16 | 0.1722 | 10.759 | 0.16 | 0.874 | −20.720 | 24.164 | |
| t = 17 | −26.097 | 14.772 | −1.77 | 0.093 | −56.910 | 0.4716 | |
| t = 18 | −33.658 | 14.779 | −2.28 | 0.034 | −64.487 | −0.2828 | |
| t = 19 | −32.244 | 14.882 | −2.17 | 0.043 | −63.287 | −0.1201 | |
| t = 20 | −45.234 | 14.859 | −3.04 | 0.006 | −76.228 | −14.240 | |
| t = 21 | −60.561 | 14.831 | −4.08 | 0.001 | −91.498 | −29.625 | |
| t = 22 | omitted | ||||||
| t = 23 | omitted | ||||||
| _cons | 109.813 | 90.204 | 1.22 | 0.238 | −78.349 | 297.975 |
| Maximum Lag | corr(u_i, Xb) | Overall R-Squared | Sigma_u | Sigma_e | Rho |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 (assumed) | 0.0305 | 69.51 | 10.57 | 0.9774 |
| Number of observations | Number of groups | Group variable (i) | Method | Wald chi2(25) | Prob > chi2 |
| 990 | 159 | n | Random-effects GLS regression | 36,113.22 | 0.0000 |
| Variable | Coef. | Std. Err. | t | p > |t| | [95% Conf. Interval] |
| cftc | 0.2941 | 0.057 | 5.16 | 0.0 | (0.1753, 0.4129) |
| elec | −0.2602 | 0.0815 | −3.19 | 0.005 | (−0.4303, −0.0902) |
| enuc | 0.0026 | 0.001 | 2.65 | 0.016 | (0.0006, 0.0047) |
| pm25 | 0.705 | 0.163 | 4.32 | 0.0 | (0.3649, 1.045) |
| renc | −0.4967 | 0.1158 | −4.29 | 0.0 | (−0.7383, −0.255) |
| t2 | 0.114 | 17.325 | 0.07 | 0.948 | (−3.4999, 3.728) |
| t3 | 29.329 | 15.102 | 1.94 | 0.066 | (−0.2173, 6.083) |
| t4 | 39.908 | 15.132 | 2.64 | 0.016 | (0.8342, 7.1473) |
| t5 | 40.245 | 15.249 | 2.64 | 0.016 | (0.8437, 7.2054) |
| t6 | 13.775 | 0.2382 | 5.78 | 0.0 | (0.8807, 1.8743) |
| t7 | 36.424 | 15.469 | 2.35 | 0.029 | (0.4156, 6.8693) |
| t8 | −13.299 | 15.465 | −0.86 | 0.4 | (−4.5559, 1.8962) |
| t9 | 17.429 | 15.774 | 1.1 | 0.282 | (−1.5475, 5.0332) |
| t10 | 16.287 | 15.933 | 1.02 | 0.319 | (−1.6949, 4.9523) |
| t11 | 12.912 | 0.1402 | 9.21 | 0.0 | (0.9986, 1.5837) |
| t12 | 0.1817 | 0.2021 | 0.9 | 0.379 | (−0.24, 0.6034) |
| t13 | −0.1231 | 0.191 | −0.64 | 0.527 | (−0.5215, 0.2753) |
| t14 | 14.741 | 0.1939 | 7.6 | 0.0 | (1.0698, 1.8785) |
| t15 | 16.722 | 0.2935 | 5.7 | 0.0 | (1.06, 2.2845) |
| t16 | 0.1989 | 12.419 | 0.16 | 0.874 | (−2.3917, 2.7895) |
| t17 | −25.584 | 14.557 | −1.76 | 0.094 | (−5.5948, 0.4781) |
| t18 | −33.152 | 15.049 | −2.2 | 0.039 | (−6.4544, −0.176) |
| t19 | −31.796 | 15.339 | −2.07 | 0.051 | (−6.3793, 0.02) |
| t20 | −44.768 | 15.331 | −2.92 | 0.008 | (−7.6748, −1.2789) |
| t21 | −60.081 | 15.257 | −3.94 | 0.001 | (−9.1906, −2.8256) |
| _cons | 10.548 | 70.989 | 1.49 | 0.153 | (−4.26, 25.3559) |
Appendix E.2. Autocorrelation and Heteroscedasticity for S-Social
| Test | Null Hypothesis | F-Statistic | Degrees of Freedom | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wooldridge test for autocorrelation | No first-order autocorrelation | 8.892 | (1, 66) | 0.004 |
| Regression Method | Number of Observations | Number of Groups | Group Variable (i) | F-Statistic (df = 5, 21) | Maximum Lag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-effect regression DK | 1246 | 138 | n | 37.78 | 2 |
| Prob > F | Within R-squared | ||||
| 0.0 | 0.0325 | ||||
| Variable | Coefficient | DK Std. Err. | t | p > |t| | 95% Conf. Interval |
| wpar | −0.1692485 | 0.03145 | −5.38 | 0.0 | (−0.2346524, −0.1038446) |
| labf | −0.3234765 | 0.111633 | −2.9 | 0.009 | (−0.55563, −0.091323) |
| inc20 | 0.4546287 | 0.1480379 | 3.07 | 0.006 | (0.1467669, 0.7624904) |
| gpie | −0.0017332 | 0.0004127 | −4.2 | 0.0 | (−0.0025915, −0.0008749) |
| food | 0.0863615 | 0.0209798 | 4.12 | 0.0 | (0.0427317, 0.1299913) |
| _cons | 46.57 | 8.37 | 5.56 | 0.0 | (29.15322, 64.001) |
Appendix E.3. Autocorrelation and Heteroscedasticity for G-Governance
| Test | F-Statistic | Degrees of Freedom (df) | p-Value (Prob > F) | Decision on H0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wooldridge test for first-order autocorrelation | 19.200 | (1, 66) | 0.0000 | Reject H0: first-order autocorrelation is present |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t | p > |t| | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| govt | 12.843 | 2.421 | 5.31 | 0.000 | [8.092, 17.594] |
| edue | 0.452 | 0.245 | 1.84 | 0.065 | [−0.029, 0.933] |
| stab | −3.198 | 1.165 | −2.74 | 0.006 | [−5.485, −0.911] |
| rndg | −4.102 | 1.713 | −2.39 | 0.017 | [−7.464, −0.740] |
| lawr | −4.354 | 2.011 | −2.16 | 0.031 | [−8.302, −0.407] |
| hosp | 3.800 | 0.612 | 6.21 | 0.000 | [2.598, 5.002] |
| scie | 0.000433 | 0.000026 | 16.87 | 0.000 | [0.000383, 0.000484] |
| _cons | 14.801 | 6.118 | 2.42 | 0.016 | [2.793, 26.808] |
| Model Info | Value | F-statistic (7, 873) | 53.46 | F test (all ui = 0), F(101, 873) | 78.08 |
| Number of observations | 982 | Prob > F | 0.0000 | Prob > F | 0.0000 |
| Number of groups | 102 | corr(ui, Xb) | 0.0035 | Test | Value |
| Observations per group (min/avg/max) | 1/9.6/19 | Statistic | Value | Chi2 (df = 102) | 1,930,609.76 |
| R-squared (within) | 0.3000 | sigma_u (variance due to group effects) | 77.265 | Prob > Chi2 | 0.0000 |
| R-squared (between) | 0.2641 | sigma_e (variance due to idiosyncratic error) | 10.058 | Decision | Reject H0: Groupwise heteroskedasticity is present |
| R-squared (overall) | 0.2527 | rho (variance due to ui) | 0.983 |
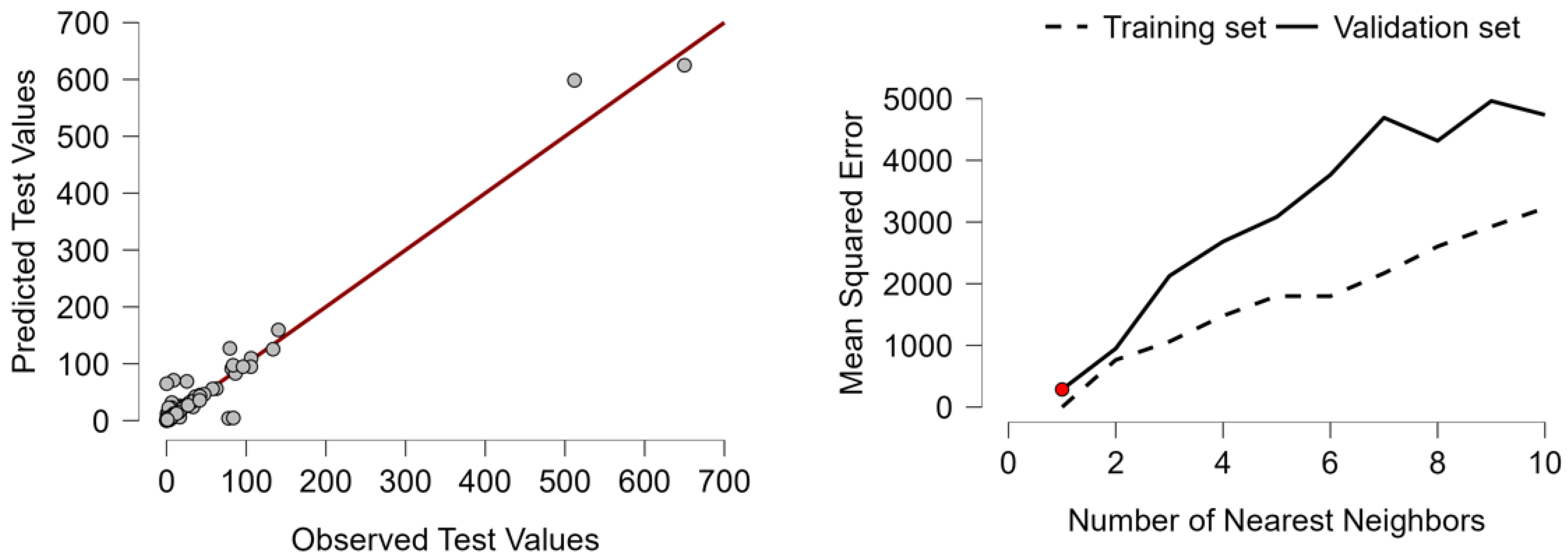
Appendix F. Hyperparameter Optimization of KNN Regression Algorithm
| Item | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Model type | k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) regression |
| Target variable | Building-related CO2 emissions (BCE) |
| Predictor variables (features) | PM2.5, RENC, ENUC, CFTC, ELEC (environmental indicators) |
| Feature scaling | Applied to all variables (standardization-enabled) |
| Distance metric | Euclidean |
| Weighting function | Rectangular (equal weights to neighbors) |
| Optimization method for k | Automated hyperparameter tuning based on validation MSE |
| Range of k tested | 1 to 10 |
| Optimal k selected | 2 |
| Data split | Training: 633 (64%), Validation: 159 (16%), Test: 198 (20%) |
| Validation MSE (used for tuning) | 6.353 |
| Test MSE | 2.264 |
| Test RMSE | 47.586 |
| Test R2 | 0.577 |
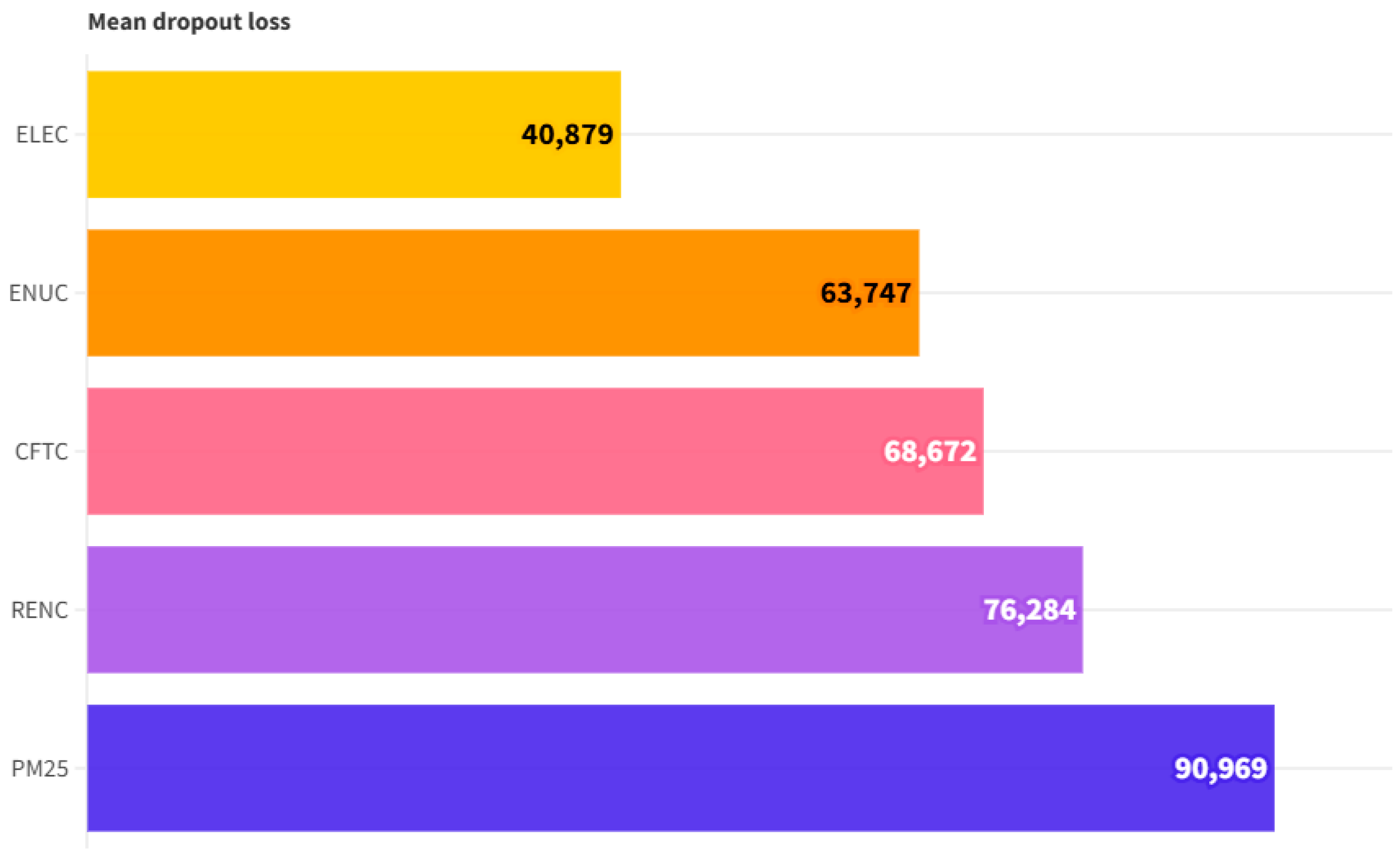
| Mean dropout loss (feature importance) | PM2.5: 83.622 RENC: 71.355 ENUC: 68.092 CFTC: 61.716 ELEC: 48.405 |
| Software settings used | Split: 20% test/20% validation, Scale features: Yes, Set seed: 1 |
| Item | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| ESG Component | S—social |
| Target Variable | Building-related CO2 emissions (BCE) |
| Model Type | k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) regression |
| Feature Set | Social indicators (e.g., income, labor force, education, representation) |
| Feature Scaling | Applied (standardization-enabled) |
| Distance Metric | Euclidean |
| Weighting Function | Rectangular (uniform weights) |
| k Values Tested | 1 to 10 |
| Optimization Method | Automated hyperparameter tuning on validation MSE |
| Optimal k Selected | 10 |
| Training Set Size | 797 observations (64%) |
| Validation Set Size | 200 observations (16%) |
| Test Set Size | 249 observations (20%) |
| Validation MSE | 5.830.302 |
| Test MSE | 7.185.254 |
| Test RMSE | 84.684 |
| Test R2 | 0.253 |
| Overfitting Evidence | No significant overfitting observed |
| Conclusion | k = 10 chosen based on best validation performance |
| Item | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| ESG Dimension | Governance (G) |
| Model Type | k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) regression |
| Training Set Size | 628 observations (≈64%) |
| Validation Set Size | 158 observations (≈16%) |
| Test Set Size | 196 observations (≈20%) |
| Hyperparameter Tuned | Number of Nearest Neighbors (k) |
| Range of k Tested | 1 to 10 |
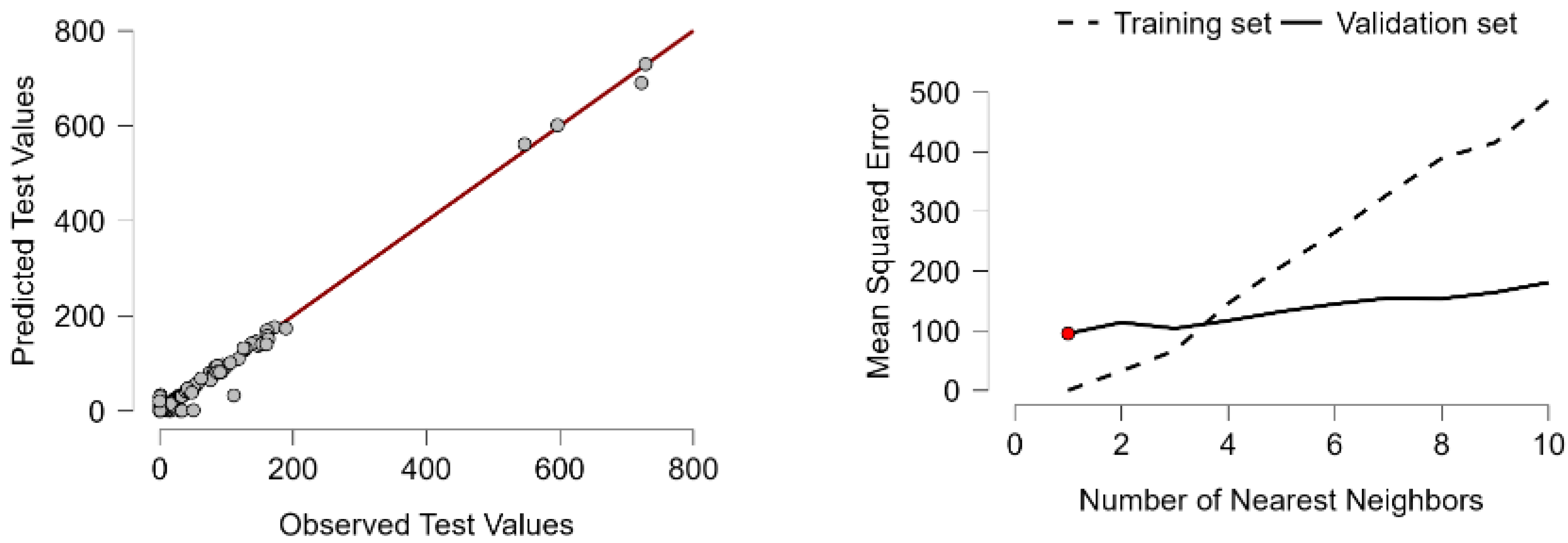
| Optimal k Selected | 2 (minimizes Validation MSE) |
| Validation MSE | 1.067 |
| Test MSE | 129.452 |
| Test RMSE | 11.378 |
| Test R2 | 0.975 |
| Distance Metric | Euclidean |
| Weighting Scheme | Rectangular (uniform weights) |
| Feature Scaling Applied | Yes (all features standardized) |
| Conclusion on k Selection | Optimized via validation MSE, k = 2 balances accuracy and complexity |
| Aspect | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Model type | k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) regression |
| Target variable (Y) | Building-related CO2 Emissions (BCE) |
| Predictors (X variables) | PM2.5, RENC (renewable energy consumption), ENUC (energy use per Capita), CFTC (clean fuel access), ELEC (electricity access) |
| Number of predictors | 5 environmental variables |
| Feature scaling applied | Yes—All variables standardized before training |
| Reason for scaling | To prevent any feature from dominating distance calculations due to scale differences |
| Multicollinearity test (formal) | Not performed—VIF not applicable to non-parametric models |
| Alternative control methods used | Feature scaling + feature importance (dropout loss) + manual selection |
| Feature importance method | Dropout-based permutation importance (50 permutations) |
| Dropout loss values | PM2.5: 83.62 RENC: 71.36 ENUC: 68.09 CFTC: 61.72 ELEC: 48.41 |
| Interpretation of dropout spread | Wide variation in loss suggests that predictors contribute uniquely → no dominance or redundancy |
| Conclusion on multicollinearity | No evidence of harmful multicollinearity affecting predictions in the E-component model |
| Item | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| ESG Component | S—Social |
| Model Type | k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) Regression |
| Target Variable | Building-related CO2 Emissions (BCE) |
| Predictor Variables | LABF, WPAR, FOOD, INC20, GPIE |
| Number of Predictors | 5 Social Indicators |
| Distance Metric | Euclidean |
| Weighting Scheme | Rectangular (equal weights) |
| Feature Scaling Applied | Yes (all variables standardized) |
| Multicollinearity Diagnostic Used | Not Applicable (k-NN is non-parametric; VIF not suitable) |
| Alternative Safeguards | Standardization + Permutation-based Feature Importance (Dropout Loss) |
| Feature Importance (Dropout Loss) | LABF: 84.697 WPAR: 81.206 FOOD: 77.663 INC20: 73.991 GPIE: 66.064 |
| Dropout Loss Method | Based on 50 Permutations Using RMSE Impact |
| Interpretation | High Variability In Dropout Loss Indicates Non-Redundant Predictors |
| Conclusion | No Harmful Multicollinearity Detected; Each Feature Contributes Uniquely |
| Item | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| ESG Dimension | Governance (G) |
| Model Type | k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) regression |
| Target Variable | Building-related CO2 Emissions (BCE) |
| Predictor Variables | SCIE, HOSP, EDUE, RNDG, GOVT, STAB, LAWR |
| Number of Predictors | 7 governance indicators |
| Feature Scaling | Applied (all variables standardized before modeling) |
| Distance Metric | Euclidean |
| Weighting Function | Rectangular (equal weights for neighbors) |
| Multicollinearity Test (VIF) | Not applied (not relevant to non-parametric k-NN) |
| Alternative Assessment | Permutation-based dropout loss (50 permutations) |
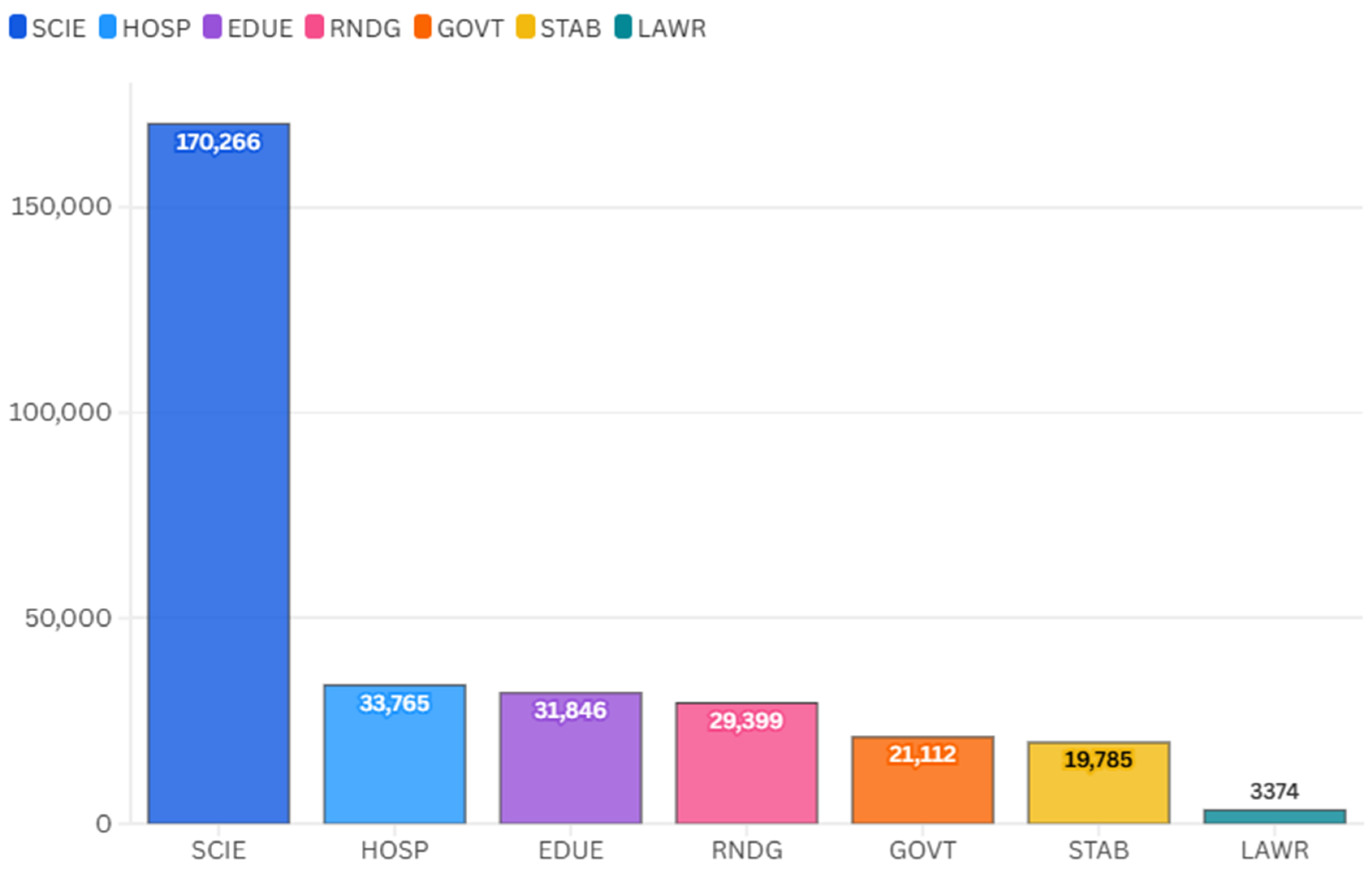
| Feature Importance (Dropout Loss) | SCIE: 165.690 HOSP: 30.104 EDUE: 28.272 RNDG: 28.038 GOVT: 20.035 STAB: 18.963 LAWR: 6.726 |
| Interpretation | Wide variability in dropout loss values indicates that predictors contribute uniquely |
| Conclusion | No evidence of harmful multicollinearity; predictors are complementary, not redundant |
| Aspect | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Model type | k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) regression |
| Target variable | Building-related CO2 Emissions (BCE) |
| Predictor variables (features) | PM2.5, RENC, ENUC, CFTC, ELEC (environmental indicators) |
| Training set size | 633 observations (64% of dataset) |
| Validation set size | 159 observations (16% of dataset) |
| Test set size | 198 observations (20% of dataset) |
| Hyperparameter tuning method | Automated optimization of k based on lowest validation MSE |
| Optimal k selected | 2 |
| Validation MSE | 6.353.665 |
| Test MSE | 2.264.407 |
| Test RMSE | 47.586 |
| Test R2 | 0.577 |
| Performance comparison | Test performance better than validation → no overfitting |
| Overfitting control techniques | Train-validation-test split + validation-based tuning + out-of-sample test evaluation |
| Interpretation | Model generalizes well with no signs of overfitting |
| Item | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| ESG Dimension | Social (S) |
| Model Type | k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) regression |
| Training Set Size | 797 observations (64%) |
| Validation Set Size | 200 observations (16%) |
| Test Set Size | 249 observations (20%) |
| Hyperparameter Tuned | Number of nearest neighbors (k) |
| Range of k Tested | 1 to 10 |
| Optimal k Selected | 10 |
| Validation MSE | 5.830.302 |
| Test MSE | 7.185.254 |
| Test RMSE | 84.766 |
| Test R2 | 0.253 |
| Distance Metric | Euclidean |
| Weighting Function | Rectangular (uniform weights) |
| Feature Scaling Applied | Yes (all features standardized) |
| Overfitting Evidence | No clear signs of overfitting; test performance remains stable |
| Safeguard Against Overfitting | Independent validation and test splits, validation-based k selection |
| Conclusion | The model generalizes well and retains predictive power on unseen data |
| Item | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| ESG Dimension | Governance (G) |
| Model Type | k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) regression |
| Training Set Size | 628 observations (≈64%) |
| Validation Set Size | 158 observations (≈16%) |
| Test Set Size | 196 observations (≈20%) |
| Hyperparameter Tuned | Number of neighbors (k) |
| Range of k Tested | 1 to 10 |
| Optimal k Selected | 2 |
| Validation MSE | 1.067.181 |
| Test MSE | 129.452 |
| Test RMSE | 11.378 |
| Test R2 | 0.975 |
| Distance Metric | Euclidean |
| Weighting Function | Rectangular (uniform weights) |
| Feature Scaling | Applied (all variables standardized before training) |
| Overfitting Evidence | No signs of overfitting: test error lower than validation error, stable high R2 |
| Conclusion | Model generalizes well, predictions are robust and not overfitted |
References
- Adewumi, A.S.; Opoku, A.; Dangana, Z. Sustainability assessment frameworks for delivering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) targets: A case of building research establishment environmental assessment method (BREEAM) UK new construction. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2024, 31, 3779–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantiello, A.; Laureti, L.; Quarto, A.; Leogrande, A. Methane Emissions in the ESG Framework at the World Level. Methane 2025, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amosh, H.; Khatib, S.F. Toward sustainable healthcare: Linking environmental governance, business innovation and carbon emission in Europe. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2024, 35, 1461–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, S.; Gao, J. Spatial Impacts of Green Finance Reform Pilot Zones on Renewable Energy Technology Innovation: Pathways for Accelerating Low-Altitude Economic Development. SSRN 2025, 5122716. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5122716 (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Salarin, T.; Staiano, J.; Bazzana, F.; Paterlini, S. Examining Intraday Stock Market Response to ESG News Classified by AI: An Event Study. SSRN 2024, 5040946. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5040946 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Valaskova, K.; Gajdosikova, D.; Lazaroiu, G. Has the COVID-19 pandemic affected the corporate financial performance? A case study of Slovak enterprises. Equilib. Q. J. Econ. Econ. Policy 2023, 18, 1133–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, F. SDGs and ESG Criteria in Housing: Defining Local Evaluation Criteria and Indicators for Verifying Project Sustainability Using Florence Metropolitan Area as a Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Das, P.; Fuerst, F. Are green and healthy building labels counterproductive in emerging markets? An examination of office rental contracts in India. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 455, 141838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Y.M.; Li, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Pu, R.; Song, L. Modularity clustering of economic development and ESG attributes in prefabricated building research. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 977887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A. The Impact of ESG Certifications on Class A Office Buildings in Madrid: A Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. Standards 2025, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronkov, A. Mechanisms for Attracting Investment into Green Building Projects. Am. J. Manag. Econ. Innov. 2025, 7, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimirova, I.; Dmitriev, A.; Kallaur, G.; Oleynikova, N.; Tsygankova, A. Trends in the application of “green” standards on the life cycle of capital housing construction objects. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 17–19 April 2023; p. 02018. [Google Scholar]
- Chungath, J. Modeling Architecture to manage Energy, Social, and Governance (ESG) Data of Commercial Buildings. Master’s Thesis, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, P.L.; Ávila, L.V.; Dinis, M.A.P.; Baggio, D.K. Environmental, social and governance (ESG) and innovation in the construction sector: Systematic Literature Review. Rev. Adm. UFSM 2023, 16, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, N.N.; Malaysia, U.T.H.O.; Omar, A.J.; Pakir, F.; Mohamad, M. Evaluating environmental, social and governance (ESG) practice among malaysian public listed construction companies using FTSE Russell rating model. Int. J. Sustain. Constr. Eng. Technol. 2024, 15, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.K.; Leow, C.S.; Goh, B. Sustainable construction materials under ESG: A literature review and synthesis. MOJ Biol. Med. 2024, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xue, F. Emerging trends of ESG in the construction sector: A promising pathway to sustainable and responsible development. In International Symposium on Advancement of Construction Management and Real Estate; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 2033–2044. [Google Scholar]
- Karerat, S.; Houghton, A.; Dickinson, G. Leveraging healthy buildings as a tool to apply a people-centric approach to ESG. Corp. Real Estate J. 2023, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagedal, M.T. Who’s Paying for Green?—Property Owners’ and Tenants’ Perspectives on ESG Investments. Master’s Thesis, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ifediora, C.O.; Igwenagu, C.L. Identifying Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Factors as Key Factors in Residential and Commercial Properties/Real Estate Investment Decision. Int. J. Energy Environ. Res. 2024, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masia, T.; Kajimo-Shakantu, K.; Opawole, A. A case study on the implementation of green building construction in Gauteng province, South Africa. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2020, 31, 602–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuradhi, M.; Wibowo, H.; Paulus; Fatimah, R.A. Beyond Green Building, How Giant Architecture Firm Contribute to Sustainable Development Goals. In International Conference on Sustainability in Creative Industries; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, S.; McIntosh, M.G. A literature review of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) in commercial real estate. J. Real Estate Lit. 2022, 30, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombati, P.M. Evaluating Awareness Levels and Barriers to Green Building Implementation. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kempeneer, S.; Peeters, M.; Compernolle, T. Bringing the user back in the building: An analysis of ESG in real estate and a behavioral framework to guide future research. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukoz, K.; Ersenkal, D. Environmental, Social and Governance-related Challenges in the Construction Industry (CIC 2023). In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Civil Infrastructure and Construction, Doha, Qatar, 5–8 February 2023; pp. 1238–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, T.J.; Soliva, E.; Haase, M.; Wrase, I. Corporate real estate and green building: Prevalence, transparency and drivers. J. Corp. Real Estate 2022, 24, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, O.T.N. Exploring the Mutual Reinforcement of ESG and Green Building Management for Long-Term Sustainability: A Case Study of Hong Kong; The University of Hong Kong: Pokfulam, Hong Kong, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, K.M.; Ghadas, Z.A.A. The Role of Contract in Advancing ESG in Construction: A Proposed Framework of ‘Green’ Standard Form of Contract for Use in Green Building Projects in Malaysia. In Artificial Intelligence and Transforming Digital Marketing; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 269–279. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wen, H. Research on Green Transformation of Real Estate Enterprises under ESG Concept. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Construction and Real Estate Management, Xi’an, China, 23–24 September 2023; pp. 500–505. [Google Scholar]
- Dugo, I. Finance Embraces Sustainability: An Empirical Analysis of the Financial Performances of ETFs Investing in Sustainable Real Estate and Green Building. Master’s Thesis, Università Ca’ Foscari, Venice, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, B.; Hutchison, N. Tenants’ ESG: Influence on preferences and rent premiums for green buildings in commercial real estate. J. Prop. Res. 2025, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudinova, Y.; Shushunova, N. Modern certification systems for green construction. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2791, 050034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, K.; Östling, M. Frameworks for Sustainable Construction: Comparing the EU Taxonomy, ESG Ratings and BREEAM-SE. Master’s Thesis, School of Industrial Engineering and Management Stockholm, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2024. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1874971&dswid=2548 (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Meshcheryakova, T. Development of “Green” Building Standards in the Context of Global ESG-transformation. In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference “Young Engineers of the Fuel and Energy Complex: Developing the Energy Agenda of the Future” (EAF 2021), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 10–11 December 2021; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2022; pp. 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Miklinska, J. Green buildings for greening supply chains—Selected Organisational and legal solutions on the polish commercial warehouse space market. Eur. Res. Stud. J. 2024, XXVII, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obushnyi, S.; Novikov, A. Influence of it solutions on ESG real estate development and investment attractiveness of the urban projects. Eur. Sci. J. Econ. Financ. Innov. 2024, 1, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Katz, S.; Wang, X.; Vasarhelyi, M.; Dai, J. Government ESG reporting in smart cities. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2024, 54, 100701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morri, G.; Yang, F.; Colantoni, F. Green investments, green returns: Exploring the link between ESG factors and financial performance in real estate. J. Prop. Invest. Financ. 2024, 42, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Pahi, D.; Dwibedi, P.; Mishra, A.P.; Mishra, B. Examining the role of ESG disclosure and firm characteristics in promoting global green building adoption: A panel probit approach. Socio-Ecol. Pract. Res. 2025, 7, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debrah, C.; Chan, A.P.C.; Darko, A. Green finance gap in green buildings: A scoping review and future research needs. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedchenko, E.; Gusarova, L.; Uskenbayeva, A. Green building in the ESG agenda for sustainable development of Russia: Conditions and trends. Constr. Mater. Prod. 2024, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrikin, P.; Andreeva, A. ESG-criteria for low-rise housing construction projects. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2560, 050003. [Google Scholar]
- Oloyede, B. ESG-LED Sustainable Finance: A Blueprint for Ending the Menace of Frequent Building Col-lapse in Nigeria. SSRN 2023, 5043885. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5043885 (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Zheng, J.; Khurram, M.U.; Chen, L. Can green innovation affect ESG ratings and financial performance? Evidence from Chinese GEM listed companies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantiello, A.; Leogrande, A. The determinants of CO2 emissions in the context of ESG models at world level. Acad. Account. Financ. Stud. J. 2023, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Shuai, Y.; Li, J. Identifying ESG types of Chinese solid waste disposal companies based on machine learning methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, D.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L. Exploring the key influencing factors of low-carbon innovation from urban characteristics in China using interpretable machine learning. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 107, 107573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulussever, T.; Depren, S.K.; Kartal, M.T.; Depren, Ö. Estimation performance comparison of machine learning approaches and time series econometric models: Evidence from the effect of sector-based energy consumption on CO2 emissions in the USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 52576–52592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelos, S.; Bellizio, F.; Strbac, G.; Zhang, T. Machine learning approaches for predictions of CO2 emissions in the building sector. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 235, 110735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. Complexity influence of societal development comprehensive indicators on building carbon emission: Empirical evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 117179–117200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Peng, B.; Arif, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, L.; Zhang, Z. Strategic Deployment of CCUS in China: Aiming for Carbon Neutrality in Key Industries. In Proceedings of the SPE Gas & Oil Technology Showcase and Conference, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 13–15 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.T.; Priya, J.C.; Le, H.C.; Le, N.V.L.; Duong, M.T.; Cao, D.N. Harnessing artificial intelligence for data-driven energy predictive analytics: A systematic survey towards enhancing sustainability. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2024, 13, 270–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Sun, H.; Alhussan, A.A.; Iqbal, A.; El-Kenawy, E.-S.M. Active learning-based machine learning approach for enhancing environmental sustainability in green building energy consumption. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Iqbal, S.; Shahzad, F. Role of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investment and natural capital stocks in achieving net-zero carbon emission. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 143919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Cai, X.; Zheng, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, X. Do electricity flows hamper regional economic–environmental equity? Appl. Energy 2022, 326, 120001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianghan, Z.; Zhengwei, L. Research on the Impact of Corporate Green Transformation on Organizational Performance under ESG Strategy Orientation. Risk Financ. Manag. 2025, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, J.; El Khoury, H.; Charr, J.C.; Guyeux, C.; Chrétien, S. Biological sequence clustering: Novel approaches and a comparative study. SN Comput. Sci. 2025, 6, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, D.; Cuc, L.D.; Lile, R.; Balas, V.E.; Barna, C.; Pantea, M.F.; Bâtcă-Dumitru, G.C.; Szentesi, S.G.; Rad, G. A cognitive systems engineering approach using unsupervised fuzzy c-means technique, exploratory factor analysis and network analysis—A preliminary statistical investigation of the bean counter profiling scale robustness. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Paleologos, E.K.; Mohamed, D.; Fayad, A.; Al Nahyan, M.T. Critical Minerals Mining: A Path Toward Sustainable Resource Extraction and Aquatic Conservation. 2025. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202501.2379/v1 (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Barua, S.; Adeleye, B.N.; Akam, D.; Ogunrinola, I.; Shafiq, M.M. Modeling mortality rates and environmental degradation in Asia and the Pacific: Does income group matter? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 30548–30567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, L. Effects of climate policy on urban carbon emissions—New insights from China’s low-carbon city pilot policy. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2025, 23, 3637–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciski, M.; Rząsa, K. The Environmental Dimension of Sustainable Development in Relation to the Transition from Brown to Green Energy—A Case Study of Poland from 2005 to 2023. Energies 2025, 18, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.-M.; Fernández-Avilés, G.; Laureti, T. A Local Spatial STIRPAT Model for Outdoor NOx Concentrations in the Community of Madrid, Spain. Mathematics 2021, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, Y.; Harrou, F.; Sun, Y. Unlocking the potential of wastewater treatment: Machine learning based energy consumption prediction. Water 2023, 15, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, M.K.; Ulku, I. Forecasting of Turkey’s Total Electricity Consumption in Sectoral Bases Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction, Optimization and Robotic Applications (HORA), Ankara, Turkey, 9–11 June 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sarro, F.; Petrozziello, A.; Harman, M. Multi-objective software effort estimation. In Proceedings of the ICSE ‘16: 38th International Conference on Software Engineering, Austin, TX, USA, 14–22 May 2016; pp. 619–630. [Google Scholar]
- Cakir, M.A.; Unlu, R.; Cakir, S.C. Future of Clean Cooking Energy Access in Emerging Economies by 2030. In Operations Research Forum; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; Volume 6, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Olmedo, D.; Ortiz-Yepez, P.; Faytong-Haro, M. Bridging the Gap: The Impact of Gender Equality on CO2 Emissions Across Countries. World 2025, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger, F.; Woodhouse, A.; Kuriakose, A.T.; Gren, A.; Liaqat, S. Placing Gender Equality at the Center of Climate Action; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Al Mamun, M.; Baghdadi, G.; Hossain, M.Z.; Rokonuzzaman, M. Towards Net-Zero: Legislative Gender Diversity and Cleaner Energy Transition. SSRN 2025, 5187015. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5187015 (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Achuo, E.D.; Nchofoung, T.N.; Zanfack, L.J.T.; Epoge, C.E. The nexus between labour force participation and environmental sustainability: Global comparative evidence. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ali, M.; Hashmi, S.H.; Jahanger, A. Do income inequality and institutional quality affect CO2 emissions in developing economies? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 42720–42741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragazou, K.; Garefalakis, A.; Samara, A. In the fight against climate change: The importance of environ-mental, social, and governance initiatives. In Environmental Sustainability and Global Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Parashar, M.; Jaiswal, R.; Sharma, M. A quantitative analysis of ESG disclosure and financial performance in renewable energy companies: A two-step approach using unsupervised machine learning. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2024, 19, 1186–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomadon, L.d.S.; Couto, E.V.D.; de Vries, W.T.; Moretto, Y. Smart city and sustainability indicators: A bibliometric literature review. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadi, S.M.A.; Barak, S.; Fereydooni, A. Online Portfolio Selection Using Macroeconomic Pattern Matching. SSRN 2024. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4960922 (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Sahu, R.T.; Verma, M.K.; Ahmad, I. Density-based spatial clustering of application with noise approach for regionalisation and its effect on hierarchical clustering. Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2023, 16, 240–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, E. SIMBA: Systematic clustering-based methodology to support built environment analysis. In Proceedings of the 30th Italian Symposium on Advanced Database Systems, Tirrenia, Italy, 19–22 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Järvenstrand, R.; Åström, L. Evaluating Thematic Exposures Using Natural Language processing: An Unsupervised Topic Modeling Approach to Improve Classification and Mitigate Risk. Master’s Thesis, Umeå Universitet, Umeå, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, L.; Salineeta; Poddar, P.N.; Singhal, P.B. Investing in Women, Investing in the Planet: Quantifying the Impact of Women’s Empowerment on Environmental Sustainability. Rev. Gest. Soc. Ambient. 2024, 18, e05345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Hou, F. The Impact of Socio-economic and environmental sustainability on CO2 emissions: A novel framework for thirty IEA countries. Soc. Indic. Res. 2021, 155, 1045–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, B.B.; Kumari, A.; Mohapatra, S.; Sahoo, B.K. Dynamic Relationship Between Carbon Dioxide Emissions and Gross Domestic Product for Low, Middle- and High-Income Countries. J. Quant. Econ. 2023, 21, 873–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimerenco, I.; Soare, B.E.L.; Panait, D.Z. Assessment of the Link between CO2 $emissions and Socio-Economic Indicators. Proc. Int. Conf. Bus. Excel. 2024, 18, 2594–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenifel, M.G.; Jasmine, R.A.; Umanandhini, D. Bitcoin Price Predictive Dynamics Using Machine Learning Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Sharma, A.; Anand, V.; Gupta, S. Automobile Price Prediction using Regression Models. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Lalitpur, Nepal, 20–22 July 2022; pp. 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.S.; Shak, M.S.; Devi, S.; Miah, M.R.; Al Mamun, A.; Ahmed, E.; Mozumder, M.S.A. Optimizing E-Commerce Pricing Strategies: A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Models for Predicting Customer Satisfaction. Am. J. Eng. Technol. 2024, 6, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, L.; Laio, F.; Mariani, M.S.; Ridolfi, L.; Sciarra, C. Forecasting national CO2 emissions world-wide. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22438. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Yuan, X. Forecasting CO2 emissions in Chinas commercial department, through BP neural network based on random forest and PSO. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y. Study on CO2 Emission Forecast of “Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers” Based on Time-Series Machine Learning. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriteanu, A.-A. The effect of good governance on CO2 emissions and FDI inflows. J. Public Adm. Financ. Law 2024, 30, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaoui, N.; Zabat, L.; Sekrafi, H.; Abid, M. The moderating role of natural resources between governance and CO2 emissions: Evidence from MENA countries. Energy Environ. 2024, 35, 1597–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Fannah, J.; Al Sabahi, S.; Al Harthi, H.; Al Bahrani, M.; Al Salmi, Q. Towards a green hospital approach in Oman: A case study of quantifying an environmental impact. Int. J. Health Plan. Manag. 2023, 38, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadrić, D.; Blažević, R.; Bajrić, H.; Peco, A.; Kadrić, E. Renovation Measures for Reduction of Primary Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions of Hospital Building. Teh. Glas. J. 2025, 19, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, F.; Lambertides, N. Exploring the role of ESG for the performance and risks of infrastructure investing: Evidence from the international funds’ market. Manag. Financ. 2024, 50, 92–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Preciado, A.L.; Cruz-Aké, S.; Venegas-Martínez, F. Identification of Patterns in CO2 Emissions among 208 Countries: K-Means Clustering Combined with PCA and Non-Linear t-SNE Visualization. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovancová, J.; Petruška, I.; Pata, U.K.; Adamišin, P. Diverse pathways to decarbonization: Cluster-specific impacts of energy sources on CO2 emissions in the European Union. Energy Nexus 2025, 17, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matviychuk, A.; Zhytkevych, O.; Osadcha, N. Modeling carbon dioxide emissions reduction. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 1876–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuradetchai, P.; Suksrikran, K. Random kernel k-nearest neighbors regression. Front. Big Data 2024, 7, 1402384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihzaniah, L.S.; Setiawan, A.; Wijaya, R.W.N. Perbandingan Kinerja Metode Regresi K-Nearest Neighbor dan Metode Regresi Linear Berganda pada Data Boston Housing. Jambura J. Probab. Stat. 2023, 4, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tatinati, S.; Khong, A.W.H. A Weighted feature extraction technique based on temporal accumulation of learner behavior features for early prediction of dropouts. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Teaching, Assessment, and Learning for Engineering (TALE), Takamatsu, Japan, 8–11 December 2020; pp. 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, W.; Servais, M. Nationwide ESG-Assessment of existing and new buildings at property level. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual European Real Estate Society Conference, London, UK, 12–15 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Samah, I.H.; Rashid, I.M.A.; Husain, W.A.F.W.; Ibrahim, S.; Hamzah, H.; Amlus, M.H. The impact of healthcare expenditure and healthcare sector growth on CO2 emission using dynamic panel data system GMM estimation model during COVID-19 crisis. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2020, 10, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, V. Estimating the European CO2 emissions change due to COVID-19 restrictions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, H.; Feng, G. Does national ESG performance curb greenhouse gas emissions? Innov. Green Dev. 2024, 3, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junsiri, C.; Sutthichaimethee, P.; Phong-A-Ran, N. Modeling CO2 Emission Forecasting in Energy Consumption of the Industrial Building Sector under Sustainability Policy in Thailand: Enhancing the LISREL-LGM Model. Forecasting 2024, 6, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, P.; Lobanov, M.M. The impact of R&D expenditures on CO2 emissions: Evidence from sixteen OECD countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J. The Impact of Regional Carbon Emission Reduction on Corporate ESG Performance in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqudah, M.Z.; Sierra-García, L.; Garcia-Benau, M.A. ESG sustainable technologies literature review using cluster-based methods. Pressacademia 2024, 18, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Gao, J.; Qiu, J.; Cui, Y.; Guo, M. The dynamic spatial effects of education investment on carbon emissions: Heterogeneous analysis based on north-south differences in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1432457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, C.; Arnone, M.; Leogrande, A. A Machine Learning and Panel Data Analysis of N2O Emissions in an ESG Framework. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagodiyenko, O.; Lagodiienko, V.; Ivanchenkova, L.; Romanashenko, I.; Laskaiev, O. Prospects for the development of the ESG concept in the face of new challenges. Collect. Pap. New Econ. 2023, 1, 179–195. [Google Scholar]
- Paolone, F.; Bitbol-Saba, N. Identifying thematic clusters of ESG in contemporary accounting studies through systematic literature review. Meas. Bus. Excel. 2025, 29, 368–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Liang, J. The effect of carbon regulation initiatives on corporate ESG performance in real estate sector: International evidence. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 453, 142188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Qin, Z.; Li, J. ESG performance and corporate carbon emission intensity: Based on panel data analysis of A-share listed companies. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1483237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, G.; Ma, X.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, S. Decarbonising residential building energy towards achieving the intended nationally determined contribution at subnational level under uncertainties. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelos, S.; Moreira, A.; Papadaskalopoulos, D.; Borozan, S.; Pudjianto, D.; Konstantelos, I.; Sun, M.; Strbac, G. A Machine learning approach for generating and evaluating forecasts on the environmental impact of the buildings sector. Energies 2023, 16, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Hei, Y. Research on the impact of enterprise ESG ratings on carbon emissions from a spatial perspective. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarboui, A.; Mnif, E.; Akrout, Z.; Chakroun, S. Unveiling the drivers behind carbon emissions disclosure: An ESG perspective. Soc. Bus. Rev. 2025, 20, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonna, F.R.; Mohaimin, M.R.; Ahmed, A.; Nayeem, M.B.; Akter, R.; Alam, S.; Nasiruddin, M.; Hossain, M.S. Machine Learning-Based Prediction of US CO2 Emissions: Developing Models for Forecasting and Sustainable Policy Formulation. J. Environ. Agric. Stud. 2023, 4, 85–99. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, X.; Liu, Z. Carbon Monitor Gridded Dataset (CMGD), a near-real-time high resolution gridded CO2 emission estimates dataset. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2021, Online, 19–30 April 2021. EGU21-4323. [Google Scholar]




| ESG Dimension | References | Main Results | Comparison with Our Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-Environmental | [1,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,20,28,30,31,32,35,36,37,38,39,40]. | ESG certifications and technologies are often disconnected from actual emission outcomes; operational routines are key but under-applied. | Our study directly quantifies the impact of environmental ESG indicators (e.g., renewable energy, air quality) on building emissions, validating their role with econometric models. |
| S—Social | [8,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,29]. | Social aspects are conceptually acknowledged but rarely implemented operationally; issues of equity, inclusion, and behavior are underdeveloped. | Our study empirically links social variables (e.g., gender equity, income equality, labor participation) to emission levels, revealing both mitigation and rebound effects. |
| G—Governance | [1,10,11,12,15,17,19,24,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,39,40,41,42,43,44]. | Governance is often fragmented; regulation and institutional routines are disconnected from long-term ESG outcomes. | Our study finds that governance indicators (e.g., government effectiveness, political stability) may paradoxically correlate with higher emissions, especially in higher-income countries, highlighting the complexity of governance–ESG links. |
| Random Effects (GLS), Using 990 Observations, Dependent Variable: BCE | Fixed Effects, Using 990 Observations Dependent Variable: BCE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Std. Error | z | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Ratio | |
| const | 9.3166 | 11.6274 | 0.8013 | 10.2987 | 10.6061 | 0.9710 |
| CFTC | 0.318025 *** | 0.0842985 | 3.773 | 0.355114 *** | 0.0893023 | 3.977 |
| ELEC | −0.245591 *** | 0.0923988 | −2.658 | −0.273064 *** | 0.0964139 | −2.832 |
| ENUC | 0.00269113 *** | 0.000691466 | 3.892 | 0.00284832 *** | 0.000735797 | 3.871 |
| PM25 | 0.664678 *** | 0.131472 | 5.056 | 0.691987 *** | 0.144470 | 4.790 |
| RENC | −0.489147 *** | 0.104604 | −4.676 | −0.513324 *** | 0.112617 | −4.558 |
| Statistics | Mean dependent var | 2.480 | 2.480 | |||
| Sum squared resid | 5,836,005 | 90,688 | ||||
| Log-likelihood | −5702 | −3640 | ||||
| Schwarz criterion | 11,445 | 8.413 | ||||
| Rho | 0.756174 | 0.756174 | ||||
| S.D. dependent var | 7.753 | |||||
| S.E. of regression | 7.697 | |||||
| Akaike criterion | 11,416 | |||||
| Hannan–Quinn | 11,427 | |||||
| Durbin–Watson | 0.324935 | |||||
| LSDV R-squared | 0.984747 | |||||
| LSDV F(163, 826) | 3.271 | |||||
| Test | ‘Between’ variance = 4971.73, ‘Within’ variance = 91.6047, mean theta = 0.935247, Joint test on named regressors—Asymptotic test statistic: chi-square(5) = 109.56 with p-value = | Joint test on named regressors— Test statistic: F(5, 826) = 20.981 with p-value = P(F(5, 826) > 20.981) = 8.85584 × 10−20 | ||||
| Breusch–Pagan test—Null hypothesis: Variance of the unit-specific error = 0, Asymptotic test statistic: chi-square(1) = 3155.73 with p-value = 0 | Test for differing group intercepts—Null hypothesis: The groups have a common intercept Test statistic: F(158, 826) = 319.607 with p-value = P(F(158, 826) > 319.607) = 0 | |||||
| Hausman test—Null hypothesis: GLS estimates are consistent, Asymptotic test statistic: chi-square(5) = 5.09644, with p-value = 0.404224 | ||||||
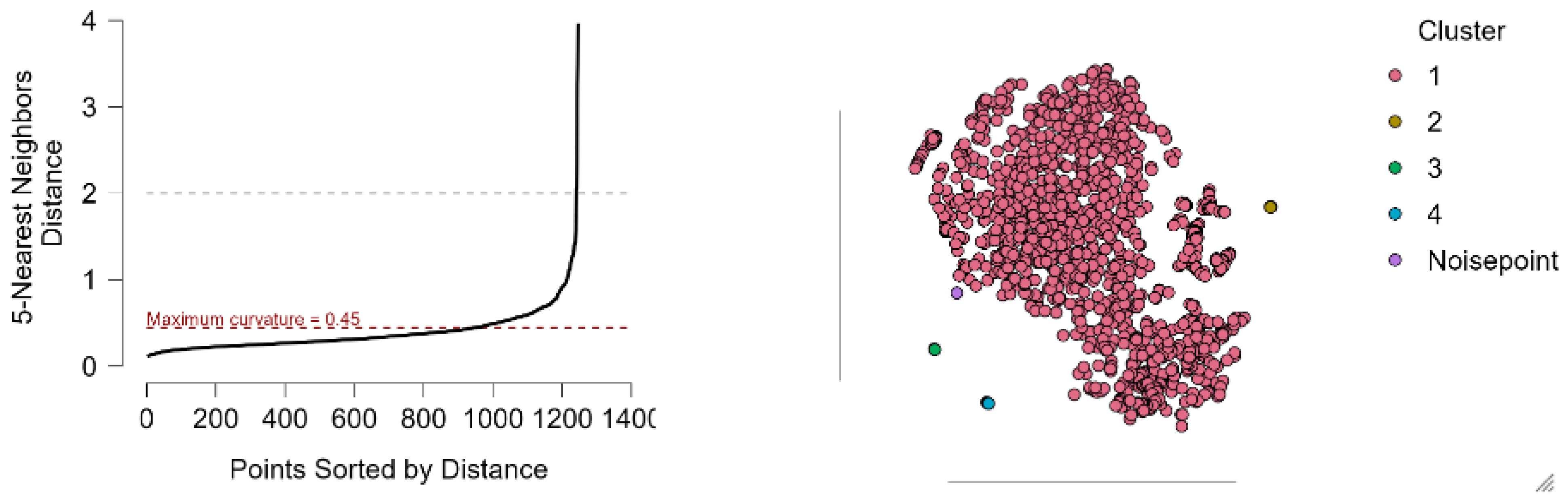
| Cluster | Noise Points | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | 1 | 949 | 6 | 6 | 20 | 8 |
| Explained proportion within-cluster heterogeneity | 0.000 | 0.999 | 8.471 × 10−4 | 2.529 × 10−5 | 1.102 × 10−5 | 4.580 × 10−4 |
| Within sum of squares | 0.000 | 4.584 | 3.888 | 0.116 | 0.051 | 2.103 |
| Silhouette score | 0.000 | 0.347 | 0.632 | 0.968 | 0.985 | 0.820 |
| Fixed Effects, Using 1246 Observations Dependent Variable: BCE | Random Effects (GLS), Using 1246 Observations Dependent Variable: BCE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Ratio | Coefficient | Std. Error | z | |
| const | 46.5798 *** | 8.08670 | 5.760 | 36.0405 | 10.5431 | 3.418 |
| FOOD | 0.0863615 *** | 0.0236010 | 3.659 | 0.0868547 | 0.0233877 | 3.714 |
| GPIE | −0.00173333 ** | 0.000727140 | −2.384 | −0.00171224 | 0.000720050 | −2.378 |
| INC20 | 0.454688 ** | 0.215227 | 2.113 | 0.451706 | 0.213527 | 2.115 |
| LABF | −0.323534 *** | 0.114301 | −2.831 | −0.299359 | 0.111774 | −2.678 |
| WPAR | −0.169214 *** | 0.0504386 | −3.355 | −0.169434 | 0.0499015 | −3.395 |
| Statistics | Mean dependent var | 31.32247 | Mean dependent var | 31.32247 | ||
| Sum squared resid | 73,866 | Sum squared resid | 9479 | |||
| LSDV R-squared | 0.992108 | Log-likelihood | −7335.684 | |||
| LSDV F(142, 1103) | 976.5221 | Schwarz criterion | 14,714 | |||
| Log-likelihood | −4311.281 | Rho | 0.727702 | |||
| Schwarz criterion | 9641.822 | S.D. dependent var | 86.70740 | |||
| Rho | 0.727702 | S.E. of regression | 87.39678 | |||
| S.D. dependent var | 86.70740 | Akaike criterion | 14,683 | |||
| S.E. of regression | 8.183426 | Hannan–Quinn | 14,694 | |||
| Within R-squared | 0.032513 | Durbin–Watson | 0.486805 | |||
| p-value (F) | 0.000000 | |||||
| Akaike criterion | 8908.562 | |||||
| Hannan–Quinn | 9184.263 | |||||
| Durbin–Watson | 0.486805 | |||||
| Tests | Joint test on named regressors— Test statistic: F(5, 1103) = 7.41335 with p-value = P(F(5, 1103) > 7.41335) = 7.51925 × 10−7 | ‘Between’ variance = 6423.31, ‘Within’ variance = 59.2827, mean theta = 0.953035, Joint test on named regressors—Asymptotic test statistic: chi-square(5) = 36.391 with p-value = 7.93233 × 10−7 | ||||
| Test for differing group intercepts— Null hypothesis: The groups have a common intercept Test statistic: F(137, 1103) = 1002.32 with p-value = P(F(137, 1103) > 1002.32) = 0 | Breusch–Pagan test—Null hypothesis: Variance of the unit-specific error = 0 Asymptotic test statistic: chi-square(1) = 5098.24, with p-value = 0 | |||||
| Hausman test—Null hypothesis: GLS estimates are consistent, Asymptotic test statistic: chi-square(5) = 2.65474 with p-value = 0.753031 | ||||||
| Cluster | Noise Points | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | 1 | 1188 | 21 | 15 | 21 |
| Explained proportion within-cluster heterogeneity | 0.000 | 0.956 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.036 |
| Within sum of squares | 0.000 | 2.288 | 13.632 | 5.502 | 84.952 |
| Silhouette score | 0.000 | 0.618 | 0.851 | 0.878 | 0.768 |
| Fixed Effects, Using 982 Observations Dependent Variable: BCE | Random Effects (GLS), Using 982 Observations Dependent Variable: BCE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Ratio | Coefficient | Std. Error | z | |
| const | 14.7556 ** | 6.12013 | 2.411 | 4.37823 | 9.08037 | 0.4822 |
| GOVT | 12.7921 *** | 2.42217 | 5.281 | 11.2943 *** | 2.15647 | 5.237 |
| EDUE | 0.450092 * | 0.245066 | 1.837 | 0.404457 * | 0.237995 | 1.699 |
| STAB | −3.19087 *** | 1.16516 | −2.739 | −2.29649 ** | 0.964108 | −2.382 |
| RNDG | −4.11812 ** | 1.71293 | −2.404 | −4.25068 ** | 1.65044 | −2.575 |
| LAWR | −4.29609 ** | 2.00928 | −2.138 | −1.36151 * | 0.755280 | −1.803 |
| HOSP | 3.80015 *** | 0.612354 | 6.206 | 3.75312 *** | 0.589134 | 6.371 |
| SCIE | 0.000433491 *** | 2.56973 × 10−5 | 16.87 | 0.000462643 *** | 2.50122 × 10−5 | 18.50 |
| Statistics | Mean dependent var | 44.83643 | Mean dependent var | 44.83643 | ||
| Sum squared resid | 88,339.25 | Sum squared resid | 6,648,511 | |||
| LSDV R-squared | 0.992464 | Log-likelihood | −5724.171 | |||
| LSDV F(108, 873) | 1064.614 | Schwarz criterion | 11,503.46 | |||
| Log-likelihood | −3602.578 | Rho | 0.766045 | |||
| Schwarz criterion | 7956.121 | S.D. dependent var | 109.3165 | |||
| Rho | 0.766045 | S.E. of regression | 82.57715 | |||
| S.D. dependent var | 109.3165 | Akaike criterion | 11,464.34 | |||
| S.E. of regression | 10.05935 | Hannan–Quinn | 11,479.22 | |||
| Within R-squared | 0.299880 | Durbin–Watson | 0.464047 | |||
| p-value (F) | 0.000000 | |||||
| Akaike criterion | 7423.156 | |||||
| Hannan–Quinn | 7625.898 | |||||
| Durbin–Watson | 0.464047 | |||||
| Tests | Joint test on named regressors- Test statistic: F(7, 873) = 53.4184 with p-value = P(F(7, 873) > 53.4184) = 1.58042 × 10−63 | ‘Between’ variance = 5929.08 ‘Within’ variance = 89.9585 Mean theta = 0.942699 Joint test on named regressors- Asymptotic test statistic: chi-square(7) = 437.883 with p-value = 1.77433 × 10−90 | ||||
| Test for differing group intercepts- Null hypothesis: The groups have a common intercept Test statistic: F(101, 873) = 78.0485 with p-value = P(F(101, 873) > 78.0485) = 0 | Breusch–Pagan test- Null hypothesis: Variance of the unit-specific error = 0 Asymptotic test statistic: chi-square(1) = 2207.29 with p-value = 0 | |||||
| Hausman test- Null hypothesis: GLS estimates are consistent Asymptotic test statistic: chi-square(7) = 73.1884 with p-value = 3.34305 × 10−13 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magaletti, N.; Notarnicola, V.; Di Molfetta, M.; Leogrande, A. Decarbonizing the Building Sector: The Integrated Role of Environmental, Social, and Governance Indicators. Buildings 2025, 15, 3601. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193601
Magaletti N, Notarnicola V, Di Molfetta M, Leogrande A. Decarbonizing the Building Sector: The Integrated Role of Environmental, Social, and Governance Indicators. Buildings. 2025; 15(19):3601. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193601
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagaletti, Nicola, Valeria Notarnicola, Mauro Di Molfetta, and Angelo Leogrande. 2025. "Decarbonizing the Building Sector: The Integrated Role of Environmental, Social, and Governance Indicators" Buildings 15, no. 19: 3601. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193601
APA StyleMagaletti, N., Notarnicola, V., Di Molfetta, M., & Leogrande, A. (2025). Decarbonizing the Building Sector: The Integrated Role of Environmental, Social, and Governance Indicators. Buildings, 15(19), 3601. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193601










